Deck 17: The Cosmic Web: the Large-Scale Structure of the Universe
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: The Cosmic Web: the Large-Scale Structure of the Universe
1
Imagine that Hubble discovered that the recession velocity of a galaxy increased proportionally to the square of the galaxy's distance from the Milky Way.Which of the following would NOT be true?
A) Astronomers could calculate a galaxy's distance from its redshift.
B) The density of the Universe would decrease with time.
C) Astronomers would observe more distance galaxies as they were farther back in time.
D) Astronomers in any other galaxy would measure the same relationship.
A) Astronomers could calculate a galaxy's distance from its redshift.
B) The density of the Universe would decrease with time.
C) Astronomers would observe more distance galaxies as they were farther back in time.
D) Astronomers in any other galaxy would measure the same relationship.
Astronomers in any other galaxy would measure the same relationship.
2
Which of the following objects will produce the strongest gravitational lensing,all other things being equal?
A) the hottest galaxy cluster
B) the most distant galaxy cluster
C) the most massive galaxy cluster
D) the galaxy cluster with the largest radius
A) the hottest galaxy cluster
B) the most distant galaxy cluster
C) the most massive galaxy cluster
D) the galaxy cluster with the largest radius
the most massive galaxy cluster
3
A region 1 Mpc across contains a total mass of 10¹³ MSᵤn.What kind of object is this most likely to be?
A) a spiral galaxy
B) an elliptical galaxy
C) a galaxy group
D) a galaxy cluster
A) a spiral galaxy
B) an elliptical galaxy
C) a galaxy group
D) a galaxy cluster
a galaxy group
4
Suppose Hubble's constant was equal to 300 km/s/Mpc.If you approximate 1 Mpc = 3 x 10¹⁹ km,and 1 year = 3 x 10⁷ s,how old would the Universe be?
A) 500 Myr
B) 3 Gyr
C) 13 Gyr
D) 50 Gyr
A) 500 Myr
B) 3 Gyr
C) 13 Gyr
D) 50 Gyr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Two galaxy clusters have identical radii,but the galaxies in cluster A have a typical orbital velocity of 700 km/s,while the galaxies in cluster B have a typical velocity of 1,400 km/s.How do the masses of these clusters compare to each other?
A) Cluster B is half as massive as cluster A.
B) Cluster B is twice as massive as cluster A.
C) Cluster B is four times as massive as cluster A.
D) Cluster B is eight times as massive as cluster A.
A) Cluster B is half as massive as cluster A.
B) Cluster B is twice as massive as cluster A.
C) Cluster B is four times as massive as cluster A.
D) Cluster B is eight times as massive as cluster A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Imagine that an astronomer in an alternate universe observes all galaxies to be blueshifted relative to the Milky Way.Which of the following would this imply?
A) The Big Bang happened in the recent past.
B) Space is contracting.
C) The Milky Way is the center of the universe.
D) Galaxies do not rotate
A) The Big Bang happened in the recent past.
B) Space is contracting.
C) The Milky Way is the center of the universe.
D) Galaxies do not rotate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The high temperature and pressure of gas in the intracluster medium of galaxy clusters implies that:
A) clusters are in the midst of expanding.
B) clusters host powerful active galactic nuclei.
C) many of the cluster galaxies are obscured by absorption from the intracluster medium.
D) clusters are dominated by dark matter.
A) clusters are in the midst of expanding.
B) clusters host powerful active galactic nuclei.
C) many of the cluster galaxies are obscured by absorption from the intracluster medium.
D) clusters are dominated by dark matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An astronomer observes three large spiral galaxies within a radius of 1 Mpc of each other.This is most likely a galaxy:
A) group.
B) cluster.
C) association.
D) merger.
A) group.
B) cluster.
C) association.
D) merger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which physical law allows astronomers to probe the Universe's past?
A) gravitational lensing
B) the Doppler effect
C) the finite speed of light
D) the inverse square law
A) gravitational lensing
B) the Doppler effect
C) the finite speed of light
D) the inverse square law

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the most likely source of the hot gas halos (with temperatures of 10 million K)within galaxy clusters?
A) ram pressure stripping of molecular clouds within galaxies
B) the individual halos of the constituent galaxies
C) by-products of stellar fusion
D) gas expelled from a central active galactic nucleus
A) ram pressure stripping of molecular clouds within galaxies
B) the individual halos of the constituent galaxies
C) by-products of stellar fusion
D) gas expelled from a central active galactic nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If an astronomer looked at the field shown in the image below with an X-ray telescope,what would he or she see? 
A) small blobs of high-temperature emission around each of the large galaxies
B) a few bright point-like emitters
C) a large, high-temperature-emitting region spanning all the galaxies
D) no significant emission

A) small blobs of high-temperature emission around each of the large galaxies
B) a few bright point-like emitters
C) a large, high-temperature-emitting region spanning all the galaxies
D) no significant emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Imagine that the expansion of the Universe proceeds at a constant rate at later times.How will the redshift of a particular galaxy change?
A) It will decrease.
B) It will remain the same, because the light will spend more time traveling.
C) It will remain the same, because all lengths expand by the same factor.
D) It will increase.
A) It will decrease.
B) It will remain the same, because the light will spend more time traveling.
C) It will remain the same, because all lengths expand by the same factor.
D) It will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the typical environment of a spiral galaxy?
A) isolated
B) inside a group of a few dozen members
C) inside a group with 100 members
D) inside a cluster with 1,000 or more members
A) isolated
B) inside a group of a few dozen members
C) inside a group with 100 members
D) inside a cluster with 1,000 or more members

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which nearby object has at least 1,300 galaxies in a region about 5 Mpc across?
A) the Virgo Cluster
B) the Great Wall
C) the Local Group
D) the Taurus cluster
A) the Virgo Cluster
B) the Great Wall
C) the Local Group
D) the Taurus cluster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An astronomer observes many galaxies in distant parts of the sky to have emission lines redshifted relative to the same lines seen in a laboratory.What is the most likely explanation?
A) Space is expanding.
B) The galaxy is experiencing gravitational lensing.
C) The galaxy has a strong wind.
D) The galaxy is moving through space away from the Milky Way.
A) Space is expanding.
B) The galaxy is experiencing gravitational lensing.
C) The galaxy has a strong wind.
D) The galaxy is moving through space away from the Milky Way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Imagine that astronomers in an alternate universe discover that galaxies at all distances from the Milky Way have similar luminosities,stellar properties,and structures.Which of the following is most likely to follow in this universe?
A) The Big Bang did not occur.
B) Galaxies cannot form new stars.
C) There is very little obscuring dust between galaxies.
D) The universe is shaped like a sphere.
A) The Big Bang did not occur.
B) Galaxies cannot form new stars.
C) There is very little obscuring dust between galaxies.
D) The universe is shaped like a sphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Collisions are important in forming:
A) elliptical galaxies.
B) galaxy groups.
C) galaxy clusters.
D) barred spiral galaxies.
A) elliptical galaxies.
B) galaxy groups.
C) galaxy clusters.
D) barred spiral galaxies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following astronomical objects has the largest look-back time?
A) a galaxy with z = 1
B) a supernova with z = 3
C) a quasar with z = 6
D) a gamma-ray burst with z = 8
A) a galaxy with z = 1
B) a supernova with z = 3
C) a quasar with z = 6
D) a gamma-ray burst with z = 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following discoveries disproved Aristotle's conception of an unchanging cosmos?
A) the existence of galaxies
B) the finite speed of light
C) Hubble's law
D) the cosmic microwave background
A) the existence of galaxies
B) the finite speed of light
C) Hubble's law
D) the cosmic microwave background

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following configurations is most likely to produce an Einstein ring?
A) a massive galaxy in the center of a spherical galaxy cluster
B) a massive galaxy in the center of a football-shaped galaxy cluster
C) a distant galaxy situated behind a football-shaped galaxy cluster
D) a distant galaxy situated behind a spherical galaxy cluster
A) a massive galaxy in the center of a spherical galaxy cluster
B) a massive galaxy in the center of a football-shaped galaxy cluster
C) a distant galaxy situated behind a football-shaped galaxy cluster
D) a distant galaxy situated behind a spherical galaxy cluster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following presents the most significant problem for mapping the positions of galaxies over the largest scales?
A) the motions of galaxies toward filaments and walls
B) the evolution of galaxies with time
C) gravitational lensing
D) all of the above
A) the motions of galaxies toward filaments and walls
B) the evolution of galaxies with time
C) gravitational lensing
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How is matter distributed on the largest scales in our Universe?
A) homogeneously
B) in the cosmic web
C) in superclusters and voids
D) in galaxy groups and clusters
A) homogeneously
B) in the cosmic web
C) in superclusters and voids
D) in galaxy groups and clusters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Each point in the image below represents a galaxy on the sky,with the Earth at the bottom point of the "pie piece" and distance away from that point representing distance from Earth.This map was made using: 
A) parallax.
B) spectroscopic parallax.
C) Hubble's law.
D) Cepheid variables.

A) parallax.
B) spectroscopic parallax.
C) Hubble's law.
D) Cepheid variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following discoveries would prove that the Universe is NOT isotropic,assuming all are made on very large scales?
A) a higher cosmic microwave background toward the South Celestial Pole than elsewhere
B) that most galaxies have a peculiar motion toward the Great Attractor
C) a larger galaxy density toward the North Celestial Pole than toward the South Celestial Pole
D) all of the above
A) a higher cosmic microwave background toward the South Celestial Pole than elsewhere
B) that most galaxies have a peculiar motion toward the Great Attractor
C) a larger galaxy density toward the North Celestial Pole than toward the South Celestial Pole
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Each point in the image below represents a galaxy on the sky,with the Earth at the bottom point of the "pie piece" and distance away from that point representing distance from Earth.What is the prominent set of galaxies in a straight line away from the observer most likely to be? 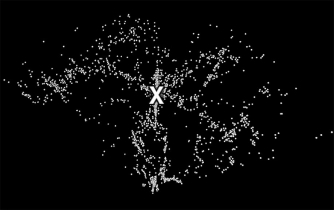
A) a filament
B) a galaxy cluster
C) a void
D) an active galactic nucleus

A) a filament
B) a galaxy cluster
C) a void
D) an active galactic nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the minimum scale on which the Universe becomes homogeneous?
A) 1 Mpc
B) 10 Mpc
C) 100 Mpc
D) The Universe is not homogeneous on any scale.
A) 1 Mpc
B) 10 Mpc
C) 100 Mpc
D) The Universe is not homogeneous on any scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the relative abundance of mass in stars,gas,and dark matter within galaxy clusters?
A) 10 percent stars, 1 percent gas, 89 percent dark matter
B) 10 percent stars, 10 percent gas, 80 percent dark matter
C) 1 percent stars, 1 percent gas, 98 percent dark matter
D) 1 percent stars, 10 percent gas, 89 percent dark matter
A) 10 percent stars, 1 percent gas, 89 percent dark matter
B) 10 percent stars, 10 percent gas, 80 percent dark matter
C) 1 percent stars, 1 percent gas, 98 percent dark matter
D) 1 percent stars, 10 percent gas, 89 percent dark matter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Why do many galaxies that are gravitationally lensed by galaxy clusters look like arcs of a circle?
A) Arc-like galaxies are more likely to be lensed.
B) asymmetries in the cluster
C) They are close behind the cluster.
D) They are the most luminous galaxies behind the cluster.
A) Arc-like galaxies are more likely to be lensed.
B) asymmetries in the cluster
C) They are close behind the cluster.
D) They are the most luminous galaxies behind the cluster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following accurately characterizes the state of most of the hydrogen in the Universe from the time of Big Bang nucleosynthesis to the present day?
A) neutral, then ionized, then neutral
B) neutral, then ionized
C) ionized, then neutral, then ionized
D) ionized, then neutral
A) neutral, then ionized, then neutral
B) neutral, then ionized
C) ionized, then neutral, then ionized
D) ionized, then neutral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A galaxy cluster consists of 1,000 galaxies within a radius of 2.5 Mpc,traveling at a typical velocity of 1,000 km/s.If the average stellar mass of a cluster galaxy is 10¹¹ MSun,what fraction of the cluster's mass is NOT stellar?
A) 5/6
B) 9/10
C) 1/2
D) 1/10
A) 5/6
B) 9/10
C) 1/2
D) 1/10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The Hubble Deep Field has revealed that:
A) galaxy clusters assembled early in the Universe's history.
B) starbursts were more common in the early Universe.
C) quasars were more common in the early Universe.
D) all of the above
A) galaxy clusters assembled early in the Universe's history.
B) starbursts were more common in the early Universe.
C) quasars were more common in the early Universe.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The figure below shows how the space density of a particular astronomical object depends on cosmic time.What kind of object does it show? 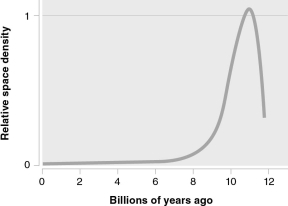
A) spiral galaxies
B) heavy elements
C) quasars
D) stars

A) spiral galaxies
B) heavy elements
C) quasars
D) stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements is typically true of galaxy clusters?
A) Most of their galaxies are large and bright.
B) The fraction of spiral galaxies increases toward the outskirts of clusters.
C) The pressure of their hot intracluster medium supports the galaxies against falling toward the center.
D) Most of their galaxies have ongoing star formation.
A) Most of their galaxies are large and bright.
B) The fraction of spiral galaxies increases toward the outskirts of clusters.
C) The pressure of their hot intracluster medium supports the galaxies against falling toward the center.
D) Most of their galaxies have ongoing star formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The Hubble Deep Field was important for understanding:
A) supernovas.
B) galaxies.
C) stellar evolution.
D) the cosmic web.
A) supernovas.
B) galaxies.
C) stellar evolution.
D) the cosmic web.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An astronomer discovers a region of space in which all the galaxies have peculiar motions away from a central point.This region is:
A) a void.
B) a filament.
C) a supercluster.
D) fully explained by the Hubble flow.
A) a void.
B) a filament.
C) a supercluster.
D) fully explained by the Hubble flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An astronomer observes a set of galaxies that are exceptionally blue and have a large fraction of interactions.These galaxies are most likely:
A) at high redshifts.
B) inside galaxy clusters.
C) ellipticals.
D) gravitationally lensed.
A) at high redshifts.
B) inside galaxy clusters.
C) ellipticals.
D) gravitationally lensed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Why are quasars rare today?
A) The Universe's expansion has spread out the quasars.
B) The black holes are too massive to be classified as quasars.
C) There is so much dust today that it obscures quasar emission.
D) Little gas is left to accrete onto supermassive black holes.
A) The Universe's expansion has spread out the quasars.
B) The black holes are too massive to be classified as quasars.
C) There is so much dust today that it obscures quasar emission.
D) Little gas is left to accrete onto supermassive black holes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following techniques could allow astronomers to observe the structures in the Universe during the Dark Ages?
A) blackbody emission
B) the H-alpha line
C) the 21-cm-line
D) molecular lines
A) blackbody emission
B) the H-alpha line
C) the 21-cm-line
D) molecular lines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey is most famous for:
A) mapping the stars in the Milky Way galaxy.
B) mapping galaxies over a wide area of the sky.
C) measuring the properties of the first galaxies.
D) measuring the abundance of dark matter in galaxy clusters.
A) mapping the stars in the Milky Way galaxy.
B) mapping galaxies over a wide area of the sky.
C) measuring the properties of the first galaxies.
D) measuring the abundance of dark matter in galaxy clusters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following describes a void?
A) a gap between spiral arms in a spiral galaxy
B) a gap in a protoplanetary disk
C) a region of the interstellar medium cleared of material by supernovas
D) a region 10-100 Mpc across where the galaxy density is very low
A) a gap between spiral arms in a spiral galaxy
B) a gap in a protoplanetary disk
C) a region of the interstellar medium cleared of material by supernovas
D) a region 10-100 Mpc across where the galaxy density is very low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What physical principle is most responsible for galaxies forming disks?
A) the inverse square law
B) hydrostatic equilibrium
C) conservation of angular momentum
D) universal gravity
A) the inverse square law
B) hydrostatic equilibrium
C) conservation of angular momentum
D) universal gravity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
How large,in terms of number of galaxies,radius,and mass,is a typical galaxy group?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following would increase the density of quasars at the present day?
A) if more galaxies were ellipticals
B) if more galaxies were barred spirals
C) if more galaxies were isolated
D) if more galaxies were inside clusters
A) if more galaxies were ellipticals
B) if more galaxies were barred spirals
C) if more galaxies were isolated
D) if more galaxies were inside clusters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An astronomer observes 1,000 galaxies positioned within 5 Mpc of each other in a galaxy cluster.What other quantity or quantities should he or she measure to determine the mass of this cluster?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An astronomer observes a galaxy that is currently 1 billion light years away from us.Does he or she see the galaxy as it was 1 billion years ago,or is the look-back time greater than or less than that number? Explain your reasoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Why are distant galaxies' spectra redshifted?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is NOT a likely consequence of the merger of two spiral galaxies?
A) an elliptical galaxy
B) a starburst
C) an active galactic nucleus
D) star-star collisions
A) an elliptical galaxy
B) a starburst
C) an active galactic nucleus
D) star-star collisions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What drives structure formation in our Universe?
A) turbulence
B) gravity
C) radiation
D) expansion
A) turbulence
B) gravity
C) radiation
D) expansion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Hubble originally measured the value of Hubble's constant to be about 500 km/s/Mpc.The currently accepted value is about 70 km/s/Mpc,while the currently accepted age of the Universe is about 14 Gyr.What would Hubble have estimated the Universe's age to be?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the galaxy cluster in the figure below is perfectly spherical,how will the object appear to the observer?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
How did the first galaxies in the Universe differ from those around us today?
A) They were all elliptical.
B) They produced more red light.
C) They had more heavy elements.
D) They were much less massive.
A) They were all elliptical.
B) They produced more red light.
C) They had more heavy elements.
D) They were much less massive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A group of galaxies with a diameter of 2 Mpc has 40 galaxies with typical velocities of 200 km/s.If the group is just a chance coincidence,how long will it last?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What does it mean when astronomers say that dark matter is "cold"?
A) It moves slowly.
B) It clumps.
C) It cannot undergo nuclear reactions.
D) It does not emit visible light.
A) It moves slowly.
B) It clumps.
C) It cannot undergo nuclear reactions.
D) It does not emit visible light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An astronomer detects a starburst galaxy with an irregular shape.She might reasonably conclude that it:
A) is the collision of two spiral galaxies.
B) has primarily red stars.
C) has very little interstellar gas.
D) will eventually form a spiral galaxy.
A) is the collision of two spiral galaxies.
B) has primarily red stars.
C) has very little interstellar gas.
D) will eventually form a spiral galaxy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The Local Group has about 50 galaxies in a region 2 Mpc across,while the Virgo Cluster has about 1,500 galaxies in a region 5 Mpc across.How do the densities of these systems compare?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Why are neutrinos NOT a good candidate for cold dark matter?
A) They move too fast.
B) They interact with matter too strongly.
C) They are formed in normal nuclear reactions.
D) They oscillate between different types.
A) They move too fast.
B) They interact with matter too strongly.
C) They are formed in normal nuclear reactions.
D) They oscillate between different types.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The figure below shows a schematic view of several galaxies in today's Universe,with an imaginary grid overlaid on top of them.If an astronomer drew a picture of this same system in 10 billion years,how would the picture differ?
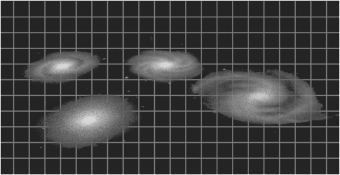


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Suppose that heavy elements were common in the clouds that would form the first stars during the Dark Ages.How would the history of our Universe be different?
A) The Dark Ages would have ended later, all other things being equal.
B) The first stars would have been more massive.
C) Black holes would have formed instead of stars.
D) Stars would not have formed until much later.
A) The Dark Ages would have ended later, all other things being equal.
B) The first stars would have been more massive.
C) Black holes would have formed instead of stars.
D) Stars would not have formed until much later.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
How do astronomers know that dark matter is "cold"?
A) laboratory measurements of its properties
B) computer simulations of structure formation
C) measurements of its annihilation radiation
D) gravitational lensing
A) laboratory measurements of its properties
B) computer simulations of structure formation
C) measurements of its annihilation radiation
D) gravitational lensing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Why are most galaxies inside clusters ellipticals or lenticular galaxies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How has the rate at which galaxies interact with each other changed with time?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Why do astronomers refer to the Dark Ages as "dark"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Why were quasars most common 10 billion years ago?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Why did the first generation of stars to form in the Universe differ from those in the Milky Way?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In what sense is the Universe homogeneous?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Two spiral galaxies collide with each other in the outskirts of a galaxy cluster.After a long time,what will the combined system look like?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How would the history of structure formation in our Universe have been different if dark matter were not cold,but moved at a moderately fast velocity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
An astronomer would like to study a region of the Universe 100 Mpc across and 1 Gpc away from Earth,situated behind an obscuring cloud of dust,so he or she cannot directly measure light from the region.How could he or she measure the mass contained in this region?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose a star produces an ultraviolet photon during the Dark Ages.The photon is emitted from a continuum source with a wavelength between the absorption lines of neutral hydrogen,but it is absorbed as it travels a long distance through the neutral hydrogen.Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Why do redshift surveys require so much telescope time?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



