Deck 3: Understanding Interests, interactions, and Institutions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Understanding Interests, interactions, and Institutions
1
What was the logic behind the United States' claim that the United Nations Security Council would become irrelevant if it did not endorse regime change in Iraq?
A)The United Nations is categorically opposed to dictatorships.
B)Regime change naturally follows a policy of economic sanctions.
C)The United States was the largest contributor to the United Nations and failure to listen to the United States was ill advised.
D)Failing to support regime change would be a failure to uphold its own resolutions on Iraq's weapon programs.
E)Iraq's continued refusal to vote on resolutions was undermining the United Nations.
A)The United Nations is categorically opposed to dictatorships.
B)Regime change naturally follows a policy of economic sanctions.
C)The United States was the largest contributor to the United Nations and failure to listen to the United States was ill advised.
D)Failing to support regime change would be a failure to uphold its own resolutions on Iraq's weapon programs.
E)Iraq's continued refusal to vote on resolutions was undermining the United Nations.
D
2
Which of the following is an example of cooperation?
A)A group of friends each contributing money to throw a party.
B)A single corporation lobbying Congress for trade protection from foreign imports.
C)A country cutting back on its emission of greenhouse gases.
D)Media companies dividing up the limited radio spectrum among themselves.
E)Two water districts agreeing that each should get half of a local river's water.
A)A group of friends each contributing money to throw a party.
B)A single corporation lobbying Congress for trade protection from foreign imports.
C)A country cutting back on its emission of greenhouse gases.
D)Media companies dividing up the limited radio spectrum among themselves.
E)Two water districts agreeing that each should get half of a local river's water.
A
3
A state wanting to promote democracy in developing countries would be pursuing which kind of goal?
A)Power.
B)Security.
C)Ideological.
D)Economic gain.
E)Material welfare.
A)Power.
B)Security.
C)Ideological.
D)Economic gain.
E)Material welfare.
C
4
What is NOT an assumption in studying interactions?
A)Actors can safely ignore the actions of others in pursuing their interests.
B)Actors are purposeful.
C)Actors behave with the intention of producing a desired result.
D)Actors are strategic.
E)Actors adopt strategies based on what they believe are the likely actions of others.
A)Actors can safely ignore the actions of others in pursuing their interests.
B)Actors are purposeful.
C)Actors behave with the intention of producing a desired result.
D)Actors are strategic.
E)Actors adopt strategies based on what they believe are the likely actions of others.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Why are some interactions considered to be strategic interactions?
A)In strategic interactions,an actor has to prepare an unconditional strategy.
B)In strategic interactions,different actors have different interests.
C)In strategic interactions,actors have a set of preferences that change,depending on what actions other actors have taken.
D)In strategic interactions,actors are unlikely to consider the future consequences of their choices.
E)In strategic interactions,each actor's plan of action depends on what the other actors are expected to do.
A)In strategic interactions,an actor has to prepare an unconditional strategy.
B)In strategic interactions,different actors have different interests.
C)In strategic interactions,actors have a set of preferences that change,depending on what actions other actors have taken.
D)In strategic interactions,actors are unlikely to consider the future consequences of their choices.
E)In strategic interactions,each actor's plan of action depends on what the other actors are expected to do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Why did the United Nations Security Council NOT endorse the preventive war against Iraq in 2003?
A)The members of the Security Council believed Iran was a bigger threat than Iraq,and the Council should direct its energy there instead.
B)The Security Council is unable to endorse military action against sovereign countries.
C)The United Nations General Assembly would veto any action by the Security Council.
D)Since the Security Council oversaw humanitarian programs in Iraq,it decided to remain neutral,rather than risk a conflict of interest.
E)Several permanent members of the Security Council opposed going to war against Iraq and could veto any endorsement of the war.
A)The members of the Security Council believed Iran was a bigger threat than Iraq,and the Council should direct its energy there instead.
B)The Security Council is unable to endorse military action against sovereign countries.
C)The United Nations General Assembly would veto any action by the Security Council.
D)Since the Security Council oversaw humanitarian programs in Iraq,it decided to remain neutral,rather than risk a conflict of interest.
E)Several permanent members of the Security Council opposed going to war against Iraq and could veto any endorsement of the war.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What does the triangle qba represent? 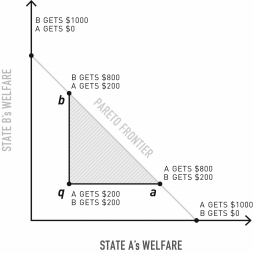
A)The set of all possible improvements for actor A.
B)The set of all possible improvements for actor B.
C)The set of all possible improvements for actors A and B.
D)The zone in which neither actor would agree to a bargain.
E)The zone of potential losses for both actors.

A)The set of all possible improvements for actor A.
B)The set of all possible improvements for actor B.
C)The set of all possible improvements for actors A and B.
D)The zone in which neither actor would agree to a bargain.
E)The zone of potential losses for both actors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which entity is the most prominent actor in international relations?
A)States.
B)People.
C)Nongovernmental organizations.
D)Terrorist groups.
E)Leaders.
A)States.
B)People.
C)Nongovernmental organizations.
D)Terrorist groups.
E)Leaders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which category of interest is usually considered the most basic,a prerequisite for other goals?
A)Security.
B)Economic welfare.
C)Material welfare.
D)Ideological.
E)Geographic land.
A)Security.
B)Economic welfare.
C)Material welfare.
D)Ideological.
E)Geographic land.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is NOT a core element of sovereignty?
A)The sovereign possesses ultimate authority over the people and territory of a given realm.
B)External actors are excluded from exercising political authority over a sovereign people.
C)The sovereign does not share his or her authority of sovereignty with other actors.
D)Sovereign bodies must each have a military to defend themselves.
E)All sovereign units are formally equal or have the same legal status.
A)The sovereign possesses ultimate authority over the people and territory of a given realm.
B)External actors are excluded from exercising political authority over a sovereign people.
C)The sovereign does not share his or her authority of sovereignty with other actors.
D)Sovereign bodies must each have a military to defend themselves.
E)All sovereign units are formally equal or have the same legal status.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Cooperation is a type of:
A)institution that makes agreements easier for two actors.
B)institution that sets the rules for interactions between actors.
C)interaction in which one actor will receive more and the other actor less of the desired outcome.
D)interaction involving two or more actors working together to achieve some outcome they prefer.
E)interaction in which at least one party prefers the status quo.
A)institution that makes agreements easier for two actors.
B)institution that sets the rules for interactions between actors.
C)interaction in which one actor will receive more and the other actor less of the desired outcome.
D)interaction involving two or more actors working together to achieve some outcome they prefer.
E)interaction in which at least one party prefers the status quo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the figure,a point on the line segment ab represents what in relation to q? 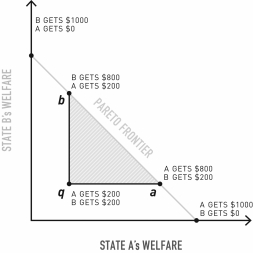
A)A gain only for actor A.
B)A gain only for actor B.
C)A loss for both actors.
D)A gain for both actors.
E)No improvement for either actor.

A)A gain only for actor A.
B)A gain only for actor B.
C)A loss for both actors.
D)A gain for both actors.
E)No improvement for either actor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is an example of a state?
A)The United Nations.
B)Iraq.
C)Saddam Hussein.
D)The Middle East.
E)The American Republican Party.
A)The United Nations.
B)Iraq.
C)Saddam Hussein.
D)The Middle East.
E)The American Republican Party.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In international relations,actors can be any of the following EXCEPT:
A)individuals.
B)international organizations.
C)groups.
D)rules.
E)states.
A)individuals.
B)international organizations.
C)groups.
D)rules.
E)states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What does line segment qb represent? 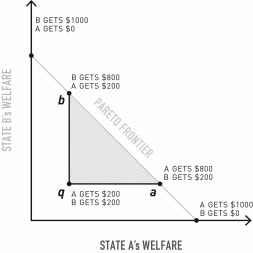
A)Possible improvements for actor A that do not affect the welfare of B.
B)Possible improvements for actor B that do not affect the welfare of A.
C)The set of all possible improvements for actors A and B.
D)The zone in which neither actor would agree to a bargain.
E)The zone of potential losses for both actors.

A)Possible improvements for actor A that do not affect the welfare of B.
B)Possible improvements for actor B that do not affect the welfare of A.
C)The set of all possible improvements for actors A and B.
D)The zone in which neither actor would agree to a bargain.
E)The zone of potential losses for both actors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A person goes to college with the hope of improving his or her earning power and future income upon graduation.This is an example of which type of goal that an actor might have?
A)Security.
B)Material welfare.
C)Ideological.
D)Power.
E)Geographic.
A)Security.
B)Material welfare.
C)Ideological.
D)Power.
E)Geographic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The following are all examples of nongovernmental organizations EXCEPT:
A)the Red Cross.
B)Amnesty International.
C)the United Nations.
D)Greenpeace.
E)Doctors without Borders.
A)the Red Cross.
B)Amnesty International.
C)the United Nations.
D)Greenpeace.
E)Doctors without Borders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is NOT considered a threat to the nature of sovereignty?
A)Supranational bodies.
B)Globalization.
C)Decolonization.
D)Civil conflict.
E)Centralization of power.
A)Supranational bodies.
B)Globalization.
C)Decolonization.
D)Civil conflict.
E)Centralization of power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is a failed state?
A)An area of the world that never became a consolidated state.
B)A state in which the central authority has broken down.
C)A state that initiates a war that it then loses.
D)A state that experiences a major debt crisis.
E)A state that is absorbed by another state.
A)An area of the world that never became a consolidated state.
B)A state in which the central authority has broken down.
C)A state that initiates a war that it then loses.
D)A state that experiences a major debt crisis.
E)A state that is absorbed by another state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Why did warfare play such an important role in the emergence of sovereign states?
A)Constant military struggle left voters wanting a more powerful central state.
B)The United Nations Security Council favors sovereign states to help prevent the outbreak of war.
C)The need for military success and protection forced smaller or less powerful states to merge.
D)Smaller,more agile states were better able to take advantage of technological advances in warfare.
E)Peace treaties often declared the boundaries of new states to help prevent future wars.
A)Constant military struggle left voters wanting a more powerful central state.
B)The United Nations Security Council favors sovereign states to help prevent the outbreak of war.
C)The need for military success and protection forced smaller or less powerful states to merge.
D)Smaller,more agile states were better able to take advantage of technological advances in warfare.
E)Peace treaties often declared the boundaries of new states to help prevent future wars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A state wanting to free ride with regard to ozone depletion would:
A)sign an agreement to reduce greenhouse gases but continue to produce such ozone-depleting emissions,while other states decreased their own emissions.
B)sign an agreement to reduce greenhouse gases but would reduce emissions only if all other signatories also reduced their emissions.
C)refuse to sign an agreement to reduce greenhouse gases,because it would not trust other states to reduce their own emissions.
D)sign an agreement to reduce greenhouse gases and then reduce its emissions only as much as the other signatories reduce their emissions.
E)freely reduce emissions without signing any entangling agreements.
A)sign an agreement to reduce greenhouse gases but continue to produce such ozone-depleting emissions,while other states decreased their own emissions.
B)sign an agreement to reduce greenhouse gases but would reduce emissions only if all other signatories also reduced their emissions.
C)refuse to sign an agreement to reduce greenhouse gases,because it would not trust other states to reduce their own emissions.
D)sign an agreement to reduce greenhouse gases and then reduce its emissions only as much as the other signatories reduce their emissions.
E)freely reduce emissions without signing any entangling agreements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
All of the following statements about power are true EXCEPT:
A)power is the ability to not have to make concessions when bargaining.
B)power is the ability to get another to do what that actor would not otherwise do.
C)power is the ability to get the other side to make concessions when bargaining.
D)the actor with more power always gets the outcome it prefers when bargaining with others.
E)the more power one has,the better the outcome one can expect from bargaining.
A)power is the ability to not have to make concessions when bargaining.
B)power is the ability to get another to do what that actor would not otherwise do.
C)power is the ability to get the other side to make concessions when bargaining.
D)the actor with more power always gets the outcome it prefers when bargaining with others.
E)the more power one has,the better the outcome one can expect from bargaining.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If the United Nations Security Council decides not to intervene to stop genocide,the reversion outcome would be:
A)the Security Council members would return for more negotiations.
B)the genocide would be ended.
C)the genocide would continue.
D)economic sanctions would automatically be enacted.
E)a 30-day cooling-off period would begin.
A)the Security Council members would return for more negotiations.
B)the genocide would be ended.
C)the genocide would continue.
D)economic sanctions would automatically be enacted.
E)a 30-day cooling-off period would begin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Successful cooperation depends upon all of the following EXCEPT:
A)the number of actors involved in an interaction.
B)how quickly the actors can interact.
C)the number of times actors interact.
D)how much the actors value the future.
E)the accuracy of the information they possess.
A)the number of actors involved in an interaction.
B)how quickly the actors can interact.
C)the number of times actors interact.
D)how much the actors value the future.
E)the accuracy of the information they possess.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is true if the status quo agreement is at point a? 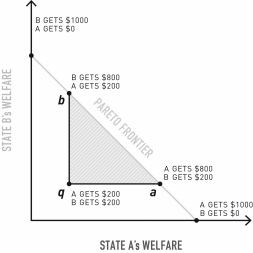
A)Any movement within the qba triangle is positive-sum.
B)Any movement along the line segment ab is zero-sum.
C)There are no possible agreements between the two actors.
D)Agreement within triangle qba is likely.
E)Actor A will improve its share by making an agreement that is closer to point b.

A)Any movement within the qba triangle is positive-sum.
B)Any movement along the line segment ab is zero-sum.
C)There are no possible agreements between the two actors.
D)Agreement within triangle qba is likely.
E)Actor A will improve its share by making an agreement that is closer to point b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In 2003,why did Saddam Hussein keep it a secret that Iraq had destroyed its weapons of mass destruction?
A)Saddam Hussein thought Iran might attack if the Iranians knew he did not have any weapons of mass destruction.
B)Saddam Hussein thought that the United States would be deterred from invading if it thought Iraq still had weapons of mass destruction.
C)Saddam Hussein had been lied to by Iraqi scientists and thought that Iraq really did have weapons of mass destruction.
D)Saddam Hussein thought that Russia would approve of an invasion if it knew Iraq did not have weapons of mass destruction.
E)Saddam Hussein thought that inspectors from the United Nations would be able to find out for themselves that Iraq did not have weapons of mass destruction.
A)Saddam Hussein thought Iran might attack if the Iranians knew he did not have any weapons of mass destruction.
B)Saddam Hussein thought that the United States would be deterred from invading if it thought Iraq still had weapons of mass destruction.
C)Saddam Hussein had been lied to by Iraqi scientists and thought that Iraq really did have weapons of mass destruction.
D)Saddam Hussein thought that Russia would approve of an invasion if it knew Iraq did not have weapons of mass destruction.
E)Saddam Hussein thought that inspectors from the United Nations would be able to find out for themselves that Iraq did not have weapons of mass destruction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When bargaining with others,one actor will have an advantage if:
A)there are many other actors with whom to bargain.
B)the actor is more satisfied with the reversion outcome than the others.
C)it cares more about the outcome of the bargain.
D)the actor needs to end the bargaining process quickly.
E)the actor has no other options but to come to an agreement.
A)there are many other actors with whom to bargain.
B)the actor is more satisfied with the reversion outcome than the others.
C)it cares more about the outcome of the bargain.
D)the actor needs to end the bargaining process quickly.
E)the actor has no other options but to come to an agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Two actors facing a coordination problem are:
A)unlikely to find a mutually acceptable solution to the problem.
B)likely to find a mutually acceptable solution only if one actor has more power than the other.
C)likely to find an acceptable solution that is much more beneficial for one actor than for the other.
D)likely to find a mutually acceptable solution that is difficult to enforce.
E)likely to find a mutually acceptable solution that requires little enforcement.
A)unlikely to find a mutually acceptable solution to the problem.
B)likely to find a mutually acceptable solution only if one actor has more power than the other.
C)likely to find an acceptable solution that is much more beneficial for one actor than for the other.
D)likely to find a mutually acceptable solution that is difficult to enforce.
E)likely to find a mutually acceptable solution that requires little enforcement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Bargaining is a type of interaction:
A)that involves the distribution of a fixed value.
B)in which no one loses.
C)in which success is determined by institutions.
D)in which zero-sum calculations do not apply.
E)in which new value is created.
A)that involves the distribution of a fixed value.
B)in which no one loses.
C)in which success is determined by institutions.
D)in which zero-sum calculations do not apply.
E)in which new value is created.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
How does iteration differ from linkage?
A)In iteration,agreements are specifically enumerated,rather than being combined or linked to other agreements.
B)In iteration,all actors share all relevant information,rather than strategically withholding key information.
C)In iteration,an actor makes the first move in negotiations rather than waiting to use information from other sources to get a better outcome.
D)In iteration,an actor waits for others to set the agenda for bargaining,rather than promising cooperation in the future.
E)In iteration,an actor can punish another by withholding cooperation in the future,rather than withholding cooperation on other issues.
A)In iteration,agreements are specifically enumerated,rather than being combined or linked to other agreements.
B)In iteration,all actors share all relevant information,rather than strategically withholding key information.
C)In iteration,an actor makes the first move in negotiations rather than waiting to use information from other sources to get a better outcome.
D)In iteration,an actor waits for others to set the agenda for bargaining,rather than promising cooperation in the future.
E)In iteration,an actor can punish another by withholding cooperation in the future,rather than withholding cooperation on other issues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Imposing some cost on others to reduce the value of the reversion outcome is known as:
A)coercion.
B)reversion.
C)linkage.
D)enforcement.
E)collaboration.
A)coercion.
B)reversion.
C)linkage.
D)enforcement.
E)collaboration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What kind of problem does the Prisoner's Dilemma story illustrate?
A)Coordination.
B)Linkage.
C)Coercion.
D)Collaboration.
E)Zero-sum.
A)Coordination.
B)Linkage.
C)Coercion.
D)Collaboration.
E)Zero-sum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Why are countries more likely to cooperate when there is iteration?
A)Countries are better able to threaten reciprocal punishment and cooperation in the future.
B)Countries that are closer together are also more likely to cooperate.
C)Countries are more likely to comply with treaties when their commitments are clearly specified.
D)Countries are more likely to cooperate when no country is more powerful than the other.
E)Multiple interactions make the threat of force less credible.
A)Countries are better able to threaten reciprocal punishment and cooperation in the future.
B)Countries that are closer together are also more likely to cooperate.
C)Countries are more likely to comply with treaties when their commitments are clearly specified.
D)Countries are more likely to cooperate when no country is more powerful than the other.
E)Multiple interactions make the threat of force less credible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
One means with which a country can coerce other countries is:
A)walking away from negotiations.
B)setting the agenda for negotiations.
C)threatening or using military force against the other countries.
D)withholding information from the other countries.
E)having an international organization mediate the dispute.
A)walking away from negotiations.
B)setting the agenda for negotiations.
C)threatening or using military force against the other countries.
D)withholding information from the other countries.
E)having an international organization mediate the dispute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How was the nuclear arms race between the United States and the Soviet Union analogous to the Prisoner's Dilemma?
A)Both sides ended up with fewer weapons than they wanted but still had enough to defend themselves from the other.
B)Each side kept quiet about the number of nuclear weapons it had,so that it could more easily defect.
C)Both sides provided evidence of nuclear weapons and cooperated in creating an arms agreement.
D)The United States provided evidence of nuclear weapons,while the Soviet Union remained quiet and thus defected instead of cooperating.
E)Collectively each side would have been better off if both had fewer weapons,but each side had an incentive to defect.
A)Both sides ended up with fewer weapons than they wanted but still had enough to defend themselves from the other.
B)Each side kept quiet about the number of nuclear weapons it had,so that it could more easily defect.
C)Both sides provided evidence of nuclear weapons and cooperated in creating an arms agreement.
D)The United States provided evidence of nuclear weapons,while the Soviet Union remained quiet and thus defected instead of cooperating.
E)Collectively each side would have been better off if both had fewer weapons,but each side had an incentive to defect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which is the best definition of a public good?
A)A benefit that is paid for by the government out of tax dollars collected from the general public.
B)A product created by public agencies for the use of all citizens of a country.
C)A product that cannot be withheld from anyone and whose use does not prohibit anyone else from enjoying it.
D)The supplies that governments provide for infrastructure projects.
E)A good universally demanded by the public.
A)A benefit that is paid for by the government out of tax dollars collected from the general public.
B)A product created by public agencies for the use of all citizens of a country.
C)A product that cannot be withheld from anyone and whose use does not prohibit anyone else from enjoying it.
D)The supplies that governments provide for infrastructure projects.
E)A good universally demanded by the public.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
All of the following are examples of solutions to coordination problems EXCEPT:
A)drivers in the United Kingdom drive on the left side of the road.
B)international airline pilots all speak English to make international communication easier.
C)peacekeepers separate two armies in a civil war to stop the conflict.
D)all firms producing compact discs use a single compatible format.
E)countries allocate international flight paths to avoid midair collisions.
A)drivers in the United Kingdom drive on the left side of the road.
B)international airline pilots all speak English to make international communication easier.
C)peacekeepers separate two armies in a civil war to stop the conflict.
D)all firms producing compact discs use a single compatible format.
E)countries allocate international flight paths to avoid midair collisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
________ interactions are the simplest kind of cooperation between actors.
A)Competitive
B)Zero-sum
C)Coordination
D)Positive-sum
E)Collaborative
A)Competitive
B)Zero-sum
C)Coordination
D)Positive-sum
E)Collaborative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The most likely outcome for both participants in the Prisoner's Dilemma is:
A)both keep quiet,so that both prisoners go free.
B)both provide evidence against each other and go to jail.
C)both provide evidence against each other but avoid jail due to bargaining.
D)one prisoner keeps quiet,while the other provides evidence and avoids jail.
E)both keep quiet and spend time in jail.
A)both keep quiet,so that both prisoners go free.
B)both provide evidence against each other and go to jail.
C)both provide evidence against each other but avoid jail due to bargaining.
D)one prisoner keeps quiet,while the other provides evidence and avoids jail.
E)both keep quiet and spend time in jail.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is an example of a public good?
A)A free lunch provided by a soup kitchen.
B)The clean air resulting from laws reducing pollution.
C)A tariff protecting an important national industry.
D)Electric cars that reduce smog for everyone.
E)Government tax credits for companies that make safer cars.
A)A free lunch provided by a soup kitchen.
B)The clean air resulting from laws reducing pollution.
C)A tariff protecting an important national industry.
D)Electric cars that reduce smog for everyone.
E)Government tax credits for companies that make safer cars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Why do powerful countries NOT ignore World Trade Organization (WTO)rules that hurt their own economic interests?
A)The World Trade Organization dispute arbitration panel can effectively enforce punishment of rule violators.
B)The World Trade Organization can take powerful countries to court in their own country.
C)Powerful countries would rather follow the rules than cause harm to poorer countries.
D)Powerful countries fear that they will have to pay fines if they violate the rules.
E)Powerful countries benefit from the whole system of trading rules and do not want others to also violate the rules.
A)The World Trade Organization dispute arbitration panel can effectively enforce punishment of rule violators.
B)The World Trade Organization can take powerful countries to court in their own country.
C)Powerful countries would rather follow the rules than cause harm to poorer countries.
D)Powerful countries fear that they will have to pay fines if they violate the rules.
E)Powerful countries benefit from the whole system of trading rules and do not want others to also violate the rules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Below is an example of which game? 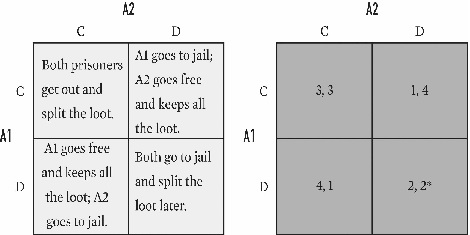
A)Chicken.
B)The Prisoner's Dilemma.
C)Stag Hunt.
D)Coordination.
E)Cooperation.

A)Chicken.
B)The Prisoner's Dilemma.
C)Stag Hunt.
D)Coordination.
E)Cooperation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Some organizations,like the World Trade Organization,have created dispute-settlement procedures that:
A)include a policing agency that can force states to comply with any court rulings.
B)help resolve disputes by interpreting ambiguous rules.
C)write new rules when the members of the organization disagree with the old rules.
D)create a court with the power to subpoena and fine members who violate the rules.
E)have not helped resolve disputes between members.
A)include a policing agency that can force states to comply with any court rulings.
B)help resolve disputes by interpreting ambiguous rules.
C)write new rules when the members of the organization disagree with the old rules.
D)create a court with the power to subpoena and fine members who violate the rules.
E)have not helped resolve disputes between members.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Institutions facilitate cooperation by doing all of the following EXCEPT:
A)forcing actors to collaborate.
B)setting standards of behavior.
C)verifying compliance.
D)reducing costs of joint decision making.
E)resolving disputes.
A)forcing actors to collaborate.
B)setting standards of behavior.
C)verifying compliance.
D)reducing costs of joint decision making.
E)resolving disputes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Below is an example of which game? 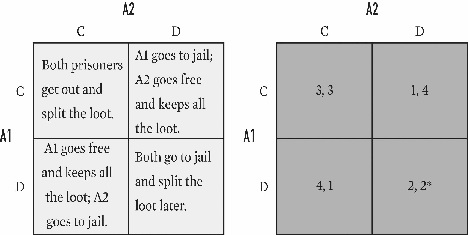
A)Chicken.
B)The Prisoner's Dilemma.
C)Stag Hunt.
D)Coordination.
E)Cooperation.

A)Chicken.
B)The Prisoner's Dilemma.
C)Stag Hunt.
D)Coordination.
E)Cooperation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
For the game below,what is A2's payoff in cell CD? 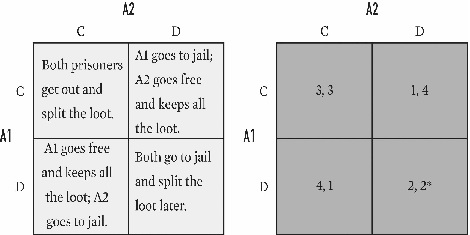
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)4.
E)Undefined.

A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)4.
E)Undefined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
For the game below,what is the equilibrium (or equilibria)for A1 and A2? 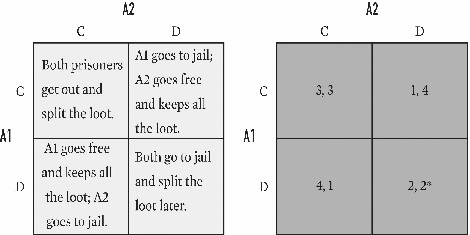
A)C,C.
B)C,D.
C)C,C and D,D.
D)C,D and D,C.
E)C,C;D,D;and C,D.

A)C,C.
B)C,D.
C)C,C and D,D.
D)C,D and D,C.
E)C,C;D,D;and C,D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is an example of a game of Chicken?
A)A trade agreement in which each side wants more concessions from the other country.
B)A nuclear crisis in which each side wants to take a tough stance.
C)A peacekeeping mission for which countries are reluctant to send their troops.
D)A conference in which countries negotiate over setting international standards for encoding CDs.
E)An invasion of a small country by a large coalition of countries that did not want to attack alone.
A)A trade agreement in which each side wants more concessions from the other country.
B)A nuclear crisis in which each side wants to take a tough stance.
C)A peacekeeping mission for which countries are reluctant to send their troops.
D)A conference in which countries negotiate over setting international standards for encoding CDs.
E)An invasion of a small country by a large coalition of countries that did not want to attack alone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For the game below,what is the equilibrium (or equilibria)for A1 and A2? 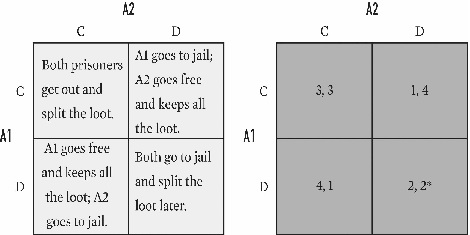
A)C,C.
B)C,D.
C)D,C.
D)D,D.
E)C,C and D,D.

A)C,C.
B)C,D.
C)D,C.
D)D,D.
E)C,C and D,D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Even though currently powerful countries like Germany,Brazil,and Japan would like a permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council,they have not started their own competing international organization but have kept their protests within the United Nations' system.This is best an example of what?
A)Often it is cheaper and easier to use existing institutions even if they do not exactly match an actor's preferences.
B)Institutions with self-enforcement are more likely to last.
C)Institutions are created to reflect the biases of those who have the most power at that time.
D)Institutions lower the costs of joint decision making by providing a forum for actors to have repeated interactions.
E)Institutions are most effective when they serve multiple roles,such as assisting in verifying compliance and reducing costs of joint decision making.
A)Often it is cheaper and easier to use existing institutions even if they do not exactly match an actor's preferences.
B)Institutions with self-enforcement are more likely to last.
C)Institutions are created to reflect the biases of those who have the most power at that time.
D)Institutions lower the costs of joint decision making by providing a forum for actors to have repeated interactions.
E)Institutions are most effective when they serve multiple roles,such as assisting in verifying compliance and reducing costs of joint decision making.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If not resolved,all of the following can hinder cooperation EXCEPT:
A)incentives to defect.
B)large numbers of actors.
C)nonrepeated interactions.
D)coalition building.
E)imperfect information.
A)incentives to defect.
B)large numbers of actors.
C)nonrepeated interactions.
D)coalition building.
E)imperfect information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is true about national elections prior to 1962?
A)More people turned out for elections than after 1962.
B)Elections were rarely or never monitored.
C)There were more elections held internationally.
D)Most elections were monitored by other states.
E)Some elections were monitored by other states.
A)More people turned out for elections than after 1962.
B)Elections were rarely or never monitored.
C)There were more elections held internationally.
D)Most elections were monitored by other states.
E)Some elections were monitored by other states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Why is enforcement by institutions actually "self-enforcement"?
A)Institutions can force their own members to comply with their agreements without outside help.
B)There is no central international authority capable of forcing actors to cooperate.
C)To force members to cooperate,actors pay dues to their institutions to create their own enforcement agency.
D)Each institution is defined as a sovereign entity or "self."
E)Conflicts are resolved by a rotating panel of members who punish those who violate the rules.
A)Institutions can force their own members to comply with their agreements without outside help.
B)There is no central international authority capable of forcing actors to cooperate.
C)To force members to cooperate,actors pay dues to their institutions to create their own enforcement agency.
D)Each institution is defined as a sovereign entity or "self."
E)Conflicts are resolved by a rotating panel of members who punish those who violate the rules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The best example of institutional bias reflecting the history of its creation is the:
A)one country-one vote procedure in the United Nations General Assembly.
B)unanimous consent of the Council of Ministers of the European Economic Community before 1986.
C)veto power of the five permanent members on the United Nations Security Council.
D)qualified majority voting rule of the European Union.
E)consensus procedure in the World Trade Organization (WTO).
A)one country-one vote procedure in the United Nations General Assembly.
B)unanimous consent of the Council of Ministers of the European Economic Community before 1986.
C)veto power of the five permanent members on the United Nations Security Council.
D)qualified majority voting rule of the European Union.
E)consensus procedure in the World Trade Organization (WTO).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is an example of an institution helping to verify compliance?
A)The United Nations banning the use of satellites and planes to spy on other countries.
B)United Nations resolutions clearly banning Iraq from possessing weapons of mass destruction.
C)The North American Free Trade Agreement having 22 chapters of detailed rules on trade and investment between the member countries.
D)International Atomic Energy Agency inspectors searching for nuclear weapons that would violate the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty.
E)The United Nations Security Council approving the use of military force to remove Iraqi troops from Kuwait in 1990.
A)The United Nations banning the use of satellites and planes to spy on other countries.
B)United Nations resolutions clearly banning Iraq from possessing weapons of mass destruction.
C)The North American Free Trade Agreement having 22 chapters of detailed rules on trade and investment between the member countries.
D)International Atomic Energy Agency inspectors searching for nuclear weapons that would violate the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty.
E)The United Nations Security Council approving the use of military force to remove Iraqi troops from Kuwait in 1990.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
For the game below,what is A2's payoff in cell CC? 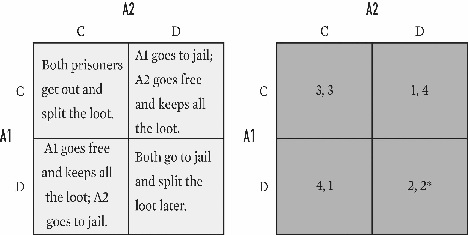
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)4.
E)Undefined.

A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)4.
E)Undefined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An actor using agenda-setting power during bargaining:
A)makes the last (and decisive)move.
B)uses knowledge of the agenda to create coalitions with other actors.
C)links items on the agenda to other issues,in order to coerce other actors.
D)acts first and therefore changes what choices are available to the other actors.
E)keeps the official record of the proceedings and uses this to promote its own description of the agreement or treaty.
A)makes the last (and decisive)move.
B)uses knowledge of the agenda to create coalitions with other actors.
C)links items on the agenda to other issues,in order to coerce other actors.
D)acts first and therefore changes what choices are available to the other actors.
E)keeps the official record of the proceedings and uses this to promote its own description of the agreement or treaty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Below is an example of which game? 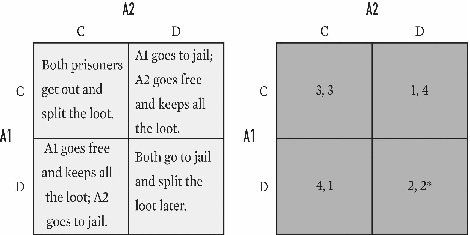
A)Chicken.
B)The Prisoner's Dilemma.
C)Stag Hunt.
D)Coordination.
E)Cooperation.

A)Chicken.
B)The Prisoner's Dilemma.
C)Stag Hunt.
D)Coordination.
E)Cooperation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
For the game below,what is the equilibrium (or equilibria)for A1 and A2? 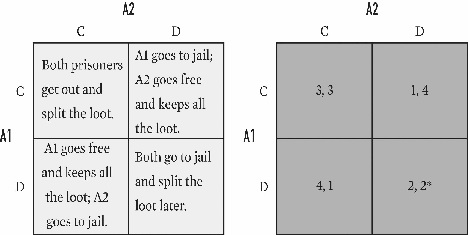
A)C,C.
B)D,D.
C)C,C and D,D.
D)C,D and D,C.
E)C,C;D,D;and C,D.

A)C,C.
B)D,D.
C)C,C and D,D.
D)C,D and D,C.
E)C,C;D,D;and C,D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
For the game below,what is A2's payoff in cell DD? 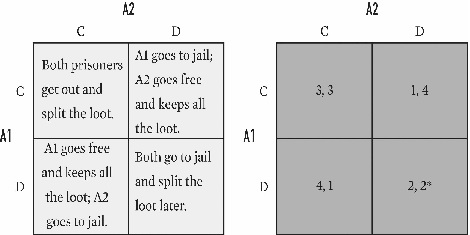
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)4.
E)Undefined.

A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)4.
E)Undefined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What do we mean when we refer to a "state" in world politics? Why must states have sovereignty? How has the notion of sovereignty changed over time?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
How does bargaining differ from cooperation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Under what conditions are both hunters likely to cooperate in the Stag Hunt game?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Why would the leader of a state want to invite outside monitors during an election?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Who can be considered an actor in international relations? Which actors are the most important for an analysis of world politics and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is the Prisoner's Dilemma game,and why is mutual defection the expected outcome of the game?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How can institutions enforce cooperation between states,given that the world is anarchic?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Explain how the number of actors,iteration,the importance of the future,and information contribute to successful cooperation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Explain how access to information affects the probability of successful cooperation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Why would it be in the interest of sovereign states to comply with institutions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
How can institutions be used to overcome the Prisoner's Dilemma?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What are public goods and why are public goods often provided by governments,rather than private individuals or groups?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What is the difference between a national interest and an interest of a politician acting as a head of state? Give an example of each to illustrate your point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
How might states use coercion,outside options,and agenda-setting to exercise power when bargaining with other actors?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Why did the interests and interactions of the United States and Iraq lead to the 2003 Iraq War?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



