Deck 23: Finance, Saving, and Investment
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/141
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Finance, Saving, and Investment
1
The funds used to buy physical capital are
A)net investment.
B)financial capital.
C)saving.
D)wealth.
E)investment.
A)net investment.
B)financial capital.
C)saving.
D)wealth.
E)investment.
financial capital.
2
Capital is
A)the tools, instruments, machines, buildings, and other items that have been produced in the past and that are used today to produce goods and services.
B)financial wealth.
C)the sum of investment and government expenditure on goods.
D)net investment.
E)gross investment.
A)the tools, instruments, machines, buildings, and other items that have been produced in the past and that are used today to produce goods and services.
B)financial wealth.
C)the sum of investment and government expenditure on goods.
D)net investment.
E)gross investment.
the tools, instruments, machines, buildings, and other items that have been produced in the past and that are used today to produce goods and services.
3
At the beginning of the year, your wealth is $10,000. During the year, you have an income of $80,000 and you spend $90,000 on consumption goods and services. You pay no taxes. Your wealth at the end of the year is
A)$20,000.
B)$0.
C)$90,000.
D)$100,000.
E)$10,000.
A)$20,000.
B)$0.
C)$90,000.
D)$100,000.
E)$10,000.
$0.
4
In 2011, Tim's Gyms needs to finance the building of a new gym. Suppose Tim secures this financing from a bank, and the bank receives ownership if Tim fails to make payments. This type of funding is
A)a mortgage obtained in the loan market.
B)a stock issued in the bond market.
C)a bond issued in the bond market.
D)a mortgage obtained in the stock market.
E)a stock issued in the loan market.
A)a mortgage obtained in the loan market.
B)a stock issued in the bond market.
C)a bond issued in the bond market.
D)a mortgage obtained in the stock market.
E)a stock issued in the loan market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The Acme Stereo Company had capital of $24 million at the beginning of the year. At the end of the year, the firm had a capital stock of $20 million. Its
A)net investment was some amount but we need more information to determine the amount.
B)net investment was $4 million for the year.
C)gross investment was zero.
D)net investment was -$4 million for the year.
E)depreciation was $4 million.
A)net investment was some amount but we need more information to determine the amount.
B)net investment was $4 million for the year.
C)gross investment was zero.
D)net investment was -$4 million for the year.
E)depreciation was $4 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is FALSE?
A)Saving adds to wealth.
B)Income left after paying taxes can either be consumed or saved.
C)Saving equals wealth minus consumption expenditure.
D)Saving is the source of funds used to finance investment.
E)Saving supplies funds in loan markets, bond markets, and stock markets.
A)Saving adds to wealth.
B)Income left after paying taxes can either be consumed or saved.
C)Saving equals wealth minus consumption expenditure.
D)Saving is the source of funds used to finance investment.
E)Saving supplies funds in loan markets, bond markets, and stock markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Capital stock increases when
A)gross investment exceeds net investment.
B)net investment exceeds gross investment.
C)gross investment is negative.
D)net investment is positive.
E)net investment is zero.
A)gross investment exceeds net investment.
B)net investment exceeds gross investment.
C)gross investment is negative.
D)net investment is positive.
E)net investment is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
At the beginning of the year, Tom's Tubes had capital of 5 tube-inflating machines. During the year, Tom scrapped 2 old machines and purchased 3 new machines. Tom's gross investment for the year is
A)1 machine.
B)2 machines.
C)3 machines.
D)6 machines.
E)8 machines.
A)1 machine.
B)2 machines.
C)3 machines.
D)6 machines.
E)8 machines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
At the beginning of the year, Tom's Tubes had capital of 5 tube-inflating machines. During the year, Tom scrapped 2 old machines and purchased 3 new machines. Tom's net investment for the year is
A)1 machine.
B)2 machines.
C)3 machines.
D)6 machines.
E)5 machines
A)1 machine.
B)2 machines.
C)3 machines.
D)6 machines.
E)5 machines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Net investment equals
A)capital minus depreciation.
B)gross investment minus depreciation.
C)the total quantity of plant, equipment, and buildings.
D)gross investment divided by depreciation.
E)wealth minus saving.
A)capital minus depreciation.
B)gross investment minus depreciation.
C)the total quantity of plant, equipment, and buildings.
D)gross investment divided by depreciation.
E)wealth minus saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The total amount spent on new capital is
A)wealth.
B)gross investment.
C)depreciation.
D)net investment.
E)saving.
A)wealth.
B)gross investment.
C)depreciation.
D)net investment.
E)saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
This year Pizza Hut spent $1.3 billion on new capital in its stores. Depreciation during the year was $300 million. Pizza Hut's gross investment was ________ and its net investment was ________.
A)$1.3 billion; $1.6 billion
B)$1.0 billion; $1.3 billion
C)$1.3 billion; $1.0 billion
D)$1.0 billion; $0.7 billion
E)$1.3 billion; $0.3 billion
A)$1.3 billion; $1.6 billion
B)$1.0 billion; $1.3 billion
C)$1.3 billion; $1.0 billion
D)$1.0 billion; $0.7 billion
E)$1.3 billion; $0.3 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The increase in the value of capital is
A)gross investment.
B)depreciation.
C)net investment.
D)private sector spending.
E)wealth.
A)gross investment.
B)depreciation.
C)net investment.
D)private sector spending.
E)wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Gross investment
A)is the total amount spent on new capital.
B)includes only replacement investment.
C)equals wealth minus saving.
D)equals saving minus wealth.
E)is the change in the value of capital
A)is the total amount spent on new capital.
B)includes only replacement investment.
C)equals wealth minus saving.
D)equals saving minus wealth.
E)is the change in the value of capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In January 2014, Tim's Gyms, Inc. owned machines valued at $1 million. During the year, the market value of the machines fell by 10 percent. During 2014, Tim spent $200,000 on new machines. During 2014, Tim's net investment was
A)$1 million.
B)$300,000.
C)$200,000.
D)$100,000.
E)$1.1 million.
A)$1 million.
B)$300,000.
C)$200,000.
D)$100,000.
E)$1.1 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In January 2014, Tim's Gyms, Inc. owned machines valued at $1 million. During the year, the market value of the machines fell by 30 percent. During 2011, Tim spent $200,000 on new machines. During 2014, Tim's gross investment was
A)$1 million.
B)$300,000.
C)$200,000
D)$900,000.
E)$100,000.
A)$1 million.
B)$300,000.
C)$200,000
D)$900,000.
E)$100,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
At the beginning of the year, Tom's Tubes had capital of 5 tube-inflating machines. During the year, Tom scrapped 2 old machines and purchased 3 new machines. Tom's capital at the end of year was
A)1 machine.
B)2 machines.
C)3 machines.
D)6 machines.
E)8 machines.
A)1 machine.
B)2 machines.
C)3 machines.
D)6 machines.
E)8 machines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
At the beginning of the year, your wealth is $10,000. During the year, you have an income of $90,000 and you spend $80,000 on consumption goods and services. You pay no taxes. Your wealth at the end of the year is
A)$20,000.
B)$0.
C)$90,000.
D)$100,000.
E)$10,000.
A)$20,000.
B)$0.
C)$90,000.
D)$100,000.
E)$10,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the economy's capital increases over time,
A)net investment is positive.
B)depreciation is less than zero.
C)depreciation exceeds gross investment.
D)gross investment equals depreciation.
E)gross investment is zero.
A)net investment is positive.
B)depreciation is less than zero.
C)depreciation exceeds gross investment.
D)gross investment equals depreciation.
E)gross investment is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If the economy's capital decreases over time,
A)net investment is positive.
B)depreciation is less than zero.
C)depreciation exceeds gross investment.
D)gross investment equals net investment.
E)gross investment is zero.
A)net investment is positive.
B)depreciation is less than zero.
C)depreciation exceeds gross investment.
D)gross investment equals net investment.
E)gross investment is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Investment is financed by which of the following?
I. Government spending
II. Household saving
III. Borrowing from the rest of the world
A)I, II, and III
B)I and II only
C)I and III only
D)II and III only
E)None of the above
I. Government spending
II. Household saving
III. Borrowing from the rest of the world
A)I, II, and III
B)I and II only
C)I and III only
D)II and III only
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Suppose that a bond promises to pay its holder $100 a year forever. If the price of the bond increases from $1,000 to $1,250, then the interest rate on the bond
A)rises from 8 percent a year to 10 percent a year.
B)falls from 10 percent a year to 6 percent a year.
C)falls from 10 percent a year to 8 percent a year.
D)rises because the bond becomes a better investment.
E)does not change because the purchaser buys the bond knowing that interest rates will be adjusted.
A)rises from 8 percent a year to 10 percent a year.
B)falls from 10 percent a year to 6 percent a year.
C)falls from 10 percent a year to 8 percent a year.
D)rises because the bond becomes a better investment.
E)does not change because the purchaser buys the bond knowing that interest rates will be adjusted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Choose the statement that is incorrect about trust and loan companies.
A)Trust and loan companies hold more than 70 percent of the total assets of the Canadian financial services sector.
B)The largest trust and loan companies are owned by banks.
C)Trust and loan companies accept deposits and make personal loans and mortgage loans.
D)Trust and loan companies administer estates.
E)Trust and loan companies administer trusts and pension plans.
A)Trust and loan companies hold more than 70 percent of the total assets of the Canadian financial services sector.
B)The largest trust and loan companies are owned by banks.
C)Trust and loan companies accept deposits and make personal loans and mortgage loans.
D)Trust and loan companies administer estates.
E)Trust and loan companies administer trusts and pension plans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Approximately, the real interest rate ________ the inflation rate ________ the nominal interest rate.
A)plus; equals
B)equals; plus
C)equals; minus
D)minus; equals
E)times; divided by 100 equals
A)plus; equals
B)equals; plus
C)equals; minus
D)minus; equals
E)times; divided by 100 equals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
National saving equals
A)private saving + private wealth.
B)private saving + government saving.
C)private saving - net taxes.
D)government saving.
E)investment.
A)private saving + private wealth.
B)private saving + government saving.
C)private saving - net taxes.
D)government saving.
E)investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Elena owns a Canada Savings Bond with a a price of $5,000, which pays $500 per year. The price of the bond rises in the bond market to $7,500. What is the new interest rate on the bond?
A)5 percent
B)6.67 percent
C)10 percent
D)20 percent
E)500 percent
A)5 percent
B)6.67 percent
C)10 percent
D)20 percent
E)500 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose Canada spends more on foreign goods and services than foreigners spend on our goods and services. Then
A)Canada must borrow an amount equal to national saving.
B)Canada must borrow an amount equal to imports minus exports.
C)the rest of the world may or may not finance Canada's trade deficit.
D)Canada must borrow an amount equal to consumption expenditure plus investment.
E)the Bank of Canada will raise the foreign exchange rate of the Canadian dollar.
A)Canada must borrow an amount equal to national saving.
B)Canada must borrow an amount equal to imports minus exports.
C)the rest of the world may or may not finance Canada's trade deficit.
D)Canada must borrow an amount equal to consumption expenditure plus investment.
E)the Bank of Canada will raise the foreign exchange rate of the Canadian dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If a bank's net worth is negative, then the bank is
A)liquid.
B)insolvent.
C)illiquid.
D)solvent.
E)none of the above
A)liquid.
B)insolvent.
C)illiquid.
D)solvent.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In 2014, Country A has net taxes of $30 million and government expenditures of $35 million. Private saving in Country A is $5 million and consumption expenditure is $80 million. The government of Country A is running a budget ________ and national saving is ________.
A)surplus; $5 million
B)deficit; -$5 million
C)deficit; $5 million
D)surplus; $25 million
E)deficit; zero
A)surplus; $5 million
B)deficit; -$5 million
C)deficit; $5 million
D)surplus; $25 million
E)deficit; zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Choose the statement that is incorrect about Treasury bonds.
A)If the price of a Treasury bond rises, other things remaining the same, the interest rate falls because the interest payment is a smaller percentage of the Treasury bond price.
B)The price of a Treasury bond and the interest rate on a Treasury bond are determined simultaneously.
C)If the demand for Treasury bonds increases, the interest rate on the Treasury bond rises.
D)The interest rate is a percentage of the price of the Treasury bond.
E)When the interest rate on a Treasury bond rises, the supply of Treasury bonds increases.
A)If the price of a Treasury bond rises, other things remaining the same, the interest rate falls because the interest payment is a smaller percentage of the Treasury bond price.
B)The price of a Treasury bond and the interest rate on a Treasury bond are determined simultaneously.
C)If the demand for Treasury bonds increases, the interest rate on the Treasury bond rises.
D)The interest rate is a percentage of the price of the Treasury bond.
E)When the interest rate on a Treasury bond rises, the supply of Treasury bonds increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Table 23.2.1

Refer to Table 23.2.1. Government saving is
A)$15 million.
B)-$5 million.
C)$5 million.
D)$45 million.
E)$20 million.

Refer to Table 23.2.1. Government saving is
A)$15 million.
B)-$5 million.
C)$5 million.
D)$45 million.
E)$20 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In which market would you find mortgage-backed securities?
A)stock market
B)bond market
C)housing market
D)capital market
E)loan market
A)stock market
B)bond market
C)housing market
D)capital market
E)loan market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If national saving equals $100,000, net taxes equal $100,000 and government expenditure equals $25,000, what is private saving?
A)$25,000
B)$225,000
C)-$25,000
D)zero
E)$175,000
A)$25,000
B)$225,000
C)-$25,000
D)zero
E)$175,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The real interest rate
A)can never be negative.
B)is approximately equal to the nominal interest rate plus the inflation rate.
C)is approximately equal to the nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate.
D)increases when the inflation rate increases.
E)is determined in the market for money.
A)can never be negative.
B)is approximately equal to the nominal interest rate plus the inflation rate.
C)is approximately equal to the nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate.
D)increases when the inflation rate increases.
E)is determined in the market for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A stock is
A)a certificate of ownership and claim to the firm's profits.
B)a promise to make specified payments on specified dates.
C)a document which entitles its holder to the income from a package of mortgages.
D)a financial market.
E)available from a bank in the form of a loan.
A)a certificate of ownership and claim to the firm's profits.
B)a promise to make specified payments on specified dates.
C)a document which entitles its holder to the income from a package of mortgages.
D)a financial market.
E)available from a bank in the form of a loan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose a bond promises to pay its holder $100 a year forever. The interest rate on the bond rises from 4 percent to 5 percent. The price of the bond
A)falls from $2,500 to $2,000.
B)falls from $25,000 to $20,000.
C)rises from $2,000 to $2,500.
D)rises from $20,000 to $25,000.
E)does not change. Bond prices are constant.
A)falls from $2,500 to $2,000.
B)falls from $25,000 to $20,000.
C)rises from $2,000 to $2,500.
D)rises from $20,000 to $25,000.
E)does not change. Bond prices are constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Table 23.2.1

Refer to Table 23.2.1. Private saving is
A)-$15 million.
B)$40 million.
C)$25 million.
D)$20 million.
E)$80 million.

Refer to Table 23.2.1. Private saving is
A)-$15 million.
B)$40 million.
C)$25 million.
D)$20 million.
E)$80 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The key Canadian financial institutions include all of the following except
A)commercial banks.
B)trust and loan companies.
C)credit unions and caisses populaires.
D)pension funds.
E)ATMs.
A)commercial banks.
B)trust and loan companies.
C)credit unions and caisses populaires.
D)pension funds.
E)ATMs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Choose the statement that is incorrect.
A)A financial institution can be solvent but illiquid.
B)A firm is illiquid if it has made long-term loans with borrowed funds and is faced with a sudden demand to repay more of what is has borrowed than its available cash.
C)Insolvency and illiquidity were at the core of a global financial meltdown in 2007-2008.
D)A financial institution's net worth is the market value of what it has lent minus the market value of what it has borrowed.
E)If a financial institution's net worth is negative, the institution is solvent.
A)A financial institution can be solvent but illiquid.
B)A firm is illiquid if it has made long-term loans with borrowed funds and is faced with a sudden demand to repay more of what is has borrowed than its available cash.
C)Insolvency and illiquidity were at the core of a global financial meltdown in 2007-2008.
D)A financial institution's net worth is the market value of what it has lent minus the market value of what it has borrowed.
E)If a financial institution's net worth is negative, the institution is solvent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Choose the statement that is incorrect.
A)Stocks, bonds, short-term securities, and loans are financial assets.
B)The interest rate on a financial asset is the interest received expressed as a percentage of the price of the asset.
C)If the asset price rises, other things remaining the same, the interest rate falls.
D)Insolvency can arise from a previously unexpected large rise in the interest rate.
E)The price of an asset is determined first, then the interest rate is determined.
A)Stocks, bonds, short-term securities, and loans are financial assets.
B)The interest rate on a financial asset is the interest received expressed as a percentage of the price of the asset.
C)If the asset price rises, other things remaining the same, the interest rate falls.
D)Insolvency can arise from a previously unexpected large rise in the interest rate.
E)The price of an asset is determined first, then the interest rate is determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.
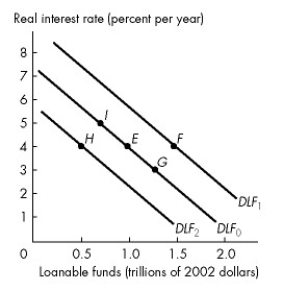
Figure 23.2.2
Refer to Figure 23.2.2. In Figure 23.2.2, an increase in expected profit will result in a movement from point E to
A)point F.
B)point G.
C)point H.
D)point I.
E)either point I or point F.

Figure 23.2.2
Refer to Figure 23.2.2. In Figure 23.2.2, an increase in expected profit will result in a movement from point E to
A)point F.
B)point G.
C)point H.
D)point I.
E)either point I or point F.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.
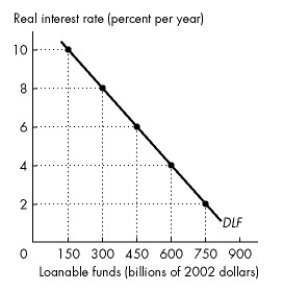
Figure 23.2.3
Refer to Figure 23.2.3. In Figure 23.2.3, if the real interest rate is 6 percent, the quantity of loanable funds demanded is
A)$150 billion.
B)$300 billion.
C)$450 billion.
D)$600 billion.
E)any amount less than $450 billion.

Figure 23.2.3
Refer to Figure 23.2.3. In Figure 23.2.3, if the real interest rate is 6 percent, the quantity of loanable funds demanded is
A)$150 billion.
B)$300 billion.
C)$450 billion.
D)$600 billion.
E)any amount less than $450 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The demand for loanable funds is the relationship between the quantity of loanable funds demanded and the ________, other things remaining the same.
A)real interest rate
B)nominal interest rate
C)inflation rate
D)price level
E)quantity of loanable funds supplied
A)real interest rate
B)nominal interest rate
C)inflation rate
D)price level
E)quantity of loanable funds supplied

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
As the ________ interest rate rises ________.
A)nominal; the demand for loanable funds curve shifts rightward
B)real; the demand for loanable funds curve shifts rightward
C)nominal; the demand for loanable funds curve shifts leftward
D)real; a movement occurs up along the demand for loanable funds curve
E)real; a movement occurs down along the demand for loanable funds curve
A)nominal; the demand for loanable funds curve shifts rightward
B)real; the demand for loanable funds curve shifts rightward
C)nominal; the demand for loanable funds curve shifts leftward
D)real; a movement occurs up along the demand for loanable funds curve
E)real; a movement occurs down along the demand for loanable funds curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Refer to the figure below to answer the following question.
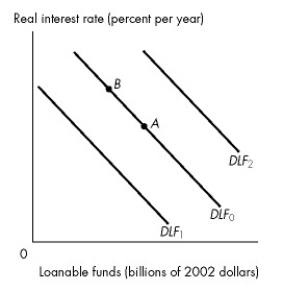
Figure 23.2.1
Refer to Figure 23.2.1. In Figure 23.2.1, the economy is at point A on the initial demand for loanable funds curve DLF₀. What happens if the real interest rate rises?
A)There is a movement to a point such as B on the demand for loanable funds curve DLF₀.
B)The demand for loanable funds curve shifts rightward to curve DLF₂.
C)The demand for loanable funds curve shifts leftward to curve DLF₁.
D)Either A or B can occur.
E)Either A or C can occur.

Figure 23.2.1
Refer to Figure 23.2.1. In Figure 23.2.1, the economy is at point A on the initial demand for loanable funds curve DLF₀. What happens if the real interest rate rises?
A)There is a movement to a point such as B on the demand for loanable funds curve DLF₀.
B)The demand for loanable funds curve shifts rightward to curve DLF₂.
C)The demand for loanable funds curve shifts leftward to curve DLF₁.
D)Either A or B can occur.
E)Either A or C can occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the nominal interest rate is 11 percent and the inflation rate is 9 percent, then the real interest rate is approximately
A)2 percent.
B)20 percent.
C)4 percent.
D)18 percent.
E)-2 percent.
A)2 percent.
B)20 percent.
C)4 percent.
D)18 percent.
E)-2 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Suppose that you took out a $1,000 loan in January and were required to pay $75 in annual interest. During the year, inflation was 6 percent. Which of the following statements is correct?
A)The nominal interest rate is 7.5 percent and the real interest rate is 1.5 percent.
B)The nominal interest rate is 7.5 percent and the real interest rate is 13.5 percent.
C)The real interest rate is 7.5 percent and the nominal interest rate is 1.5 percent.
D)The real interest rate is 6 percent and the nominal interest rate is 7.5 percent.
E)The real interest rate is 6 percent and the nominal interest rate is -1.5 percent.
A)The nominal interest rate is 7.5 percent and the real interest rate is 1.5 percent.
B)The nominal interest rate is 7.5 percent and the real interest rate is 13.5 percent.
C)The real interest rate is 7.5 percent and the nominal interest rate is 1.5 percent.
D)The real interest rate is 6 percent and the nominal interest rate is 7.5 percent.
E)The real interest rate is 6 percent and the nominal interest rate is -1.5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 23.2.2
Refer to Figure 23.2.2. In Figure 23.2.2, a decrease in the real interest rate will result in a movement from point E to
A)point F.
B)point G.
C)point H.
D)point I.
E)either point G or point F.

Figure 23.2.2
Refer to Figure 23.2.2. In Figure 23.2.2, a decrease in the real interest rate will result in a movement from point E to
A)point F.
B)point G.
C)point H.
D)point I.
E)either point G or point F.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 23.2.2
Refer to Figure 23.2.2. In Figure 23.2.2, a decrease in expected profit will result in a movement from point E to
A)point F.
B)point G.
C)point H.
D)point I.
E)either point G or point H.

Figure 23.2.2
Refer to Figure 23.2.2. In Figure 23.2.2, a decrease in expected profit will result in a movement from point E to
A)point F.
B)point G.
C)point H.
D)point I.
E)either point G or point H.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the real interest rate rises from 3 percent to 5 percent,
A)the nominal interest rate falls.
B)the demand for loanable funds curve shifts rightward.
C)there is a movement up along the demand for loanable funds curve.
D)the supply of loanable funds curve shifts rightward.
E)there is a movement down along the supply of loanable funds curve.
A)the nominal interest rate falls.
B)the demand for loanable funds curve shifts rightward.
C)there is a movement up along the demand for loanable funds curve.
D)the supply of loanable funds curve shifts rightward.
E)there is a movement down along the supply of loanable funds curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
During a recession, firms decrease their profit expectations. As a result, there is a ________ shift of the ________ loanable funds curve.
A)rightward; supply of
B)leftward; demand for
C)rightward; demand for
D)rightward, supply of
E)leftward; demand for loanable funds curve and supply of
A)rightward; supply of
B)leftward; demand for
C)rightward; demand for
D)rightward, supply of
E)leftward; demand for loanable funds curve and supply of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
As the ________ interest rate increases, the quantity of loanable funds demanded ________.
A)real; increases
B)real; decreases
C)nominal; increases
D)nominal; decreases
E)none of the above. There is no relationship between interest rates and loanable funds.
A)real; increases
B)real; decreases
C)nominal; increases
D)nominal; decreases
E)none of the above. There is no relationship between interest rates and loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A fall in the real interest rate
A)shifts the demand for loanable funds curve rightward.
B)shifts the demand for loanable funds curve leftward.
C)creates a movement up along the demand for loanable funds curve.
D)creates a movement down along the demand for loanable funds curve.
E)decreases the inflation rate.
A)shifts the demand for loanable funds curve rightward.
B)shifts the demand for loanable funds curve leftward.
C)creates a movement up along the demand for loanable funds curve.
D)creates a movement down along the demand for loanable funds curve.
E)decreases the inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A decrease in the demand for loanable funds occurs when
A)the real interest rate rises.
B)government expenditure increases.
C)the government cuts taxes.
D)expected profit decreases.
E)expected profit increases.
A)the real interest rate rises.
B)government expenditure increases.
C)the government cuts taxes.
D)expected profit decreases.
E)expected profit increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A decrease in the real interest rate leads to a ________ the demand for loanable funds curve, and a decrease in expected profit leads to a ________ the demand for loanable funds curve.
A)rightward shift of; leftward shift of
B)movement down along; movement up along
C)rightward shift of; movement up along
D)movement down along; leftward shift of
E)movement down along; rightward shift of
A)rightward shift of; leftward shift of
B)movement down along; movement up along
C)rightward shift of; movement up along
D)movement down along; leftward shift of
E)movement down along; rightward shift of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A firm's decision to invest in a project is based on the
A)real interest rate and expected total revenue.
B)nominal interest rate and expected total revenue.
C)nominal interest rate and the expected profit.
D)real interest rate and the expected profit.
E)expected future income, wealth, and default risk.
A)real interest rate and expected total revenue.
B)nominal interest rate and expected total revenue.
C)nominal interest rate and the expected profit.
D)real interest rate and the expected profit.
E)expected future income, wealth, and default risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The quantity of loanable funds demanded increases when
A)expected profit decreases.
B)the real interest rate rises.
C)the real interest rate falls.
D)the supply of loanable funds decreases.
E)wealth increases.
A)expected profit decreases.
B)the real interest rate rises.
C)the real interest rate falls.
D)the supply of loanable funds decreases.
E)wealth increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Suppose a firm has an investment project which will cost $200,000 and result in $30,000 profit. The firm will not undertake the project if the interest rate is
A)greater than 15 percent.
B)greater than 10 percent.
C)greater than 5 percent.
D)positive.
E)greater than 7.5 percent.
A)greater than 15 percent.
B)greater than 10 percent.
C)greater than 5 percent.
D)positive.
E)greater than 7.5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The demand for loanable funds curve
A)is horizontal.
B)has a negative slope.
C)is vertical.
D)has a positive slope.
E)slopes downward at high real interest rates and slopes upward at low real interest rates.
A)is horizontal.
B)has a negative slope.
C)is vertical.
D)has a positive slope.
E)slopes downward at high real interest rates and slopes upward at low real interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A rise in the real interest rate
A)shifts the demand for loanable funds curve rightward.
B)shifts the demand for loanable funds curve leftward.
C)creates a movement up along the demand for loanable funds curve.
D)creates a movement down along the demand for loanable funds curve.
E)increases the inflation rate.
A)shifts the demand for loanable funds curve rightward.
B)shifts the demand for loanable funds curve leftward.
C)creates a movement up along the demand for loanable funds curve.
D)creates a movement down along the demand for loanable funds curve.
E)increases the inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Households will choose to save more if
A)expected future income decreases.
B)current disposable income increases.
C)current disposable income decreases.
D)Both A and B are correct.
E)Both A and C are correct.
A)expected future income decreases.
B)current disposable income increases.
C)current disposable income decreases.
D)Both A and B are correct.
E)Both A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Changes in all of the following shift the supply curve of loanable funds EXCEPT
A)the real interest rate.
B)wealth.
C)disposable income.
D)expected future income.
E)default risk.
A)the real interest rate.
B)wealth.
C)disposable income.
D)expected future income.
E)default risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following influences household saving?
I. The real interest rate
II. Disposable income
III. Expected future income
A)I only
B)I and II only
C)I and III only
D)I, II, and III only
E)II and III only
I. The real interest rate
II. Disposable income
III. Expected future income
A)I only
B)I and II only
C)I and III only
D)I, II, and III only
E)II and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
As the ________ rises, the quantity of loanable funds supplied ________, other things remaining the same.
A)nominal interest rate; increases
B)real interest rate; increases
C)inflation rate; increases
D)real interest rate; decreases
E)inflation rate; decreases
A)nominal interest rate; increases
B)real interest rate; increases
C)inflation rate; increases
D)real interest rate; decreases
E)inflation rate; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
All of the following are sources of loanable funds EXCEPT
A)business investment.
B)private saving.
C)government budget surplus.
D)international borrowing.
E)none of the above
A)business investment.
B)private saving.
C)government budget surplus.
D)international borrowing.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following will shift the supply of loanable funds curve leftward?
A)a decrease in the real interest rate
B)a decrease in real wealth
C)a decrease in disposable income
D)a decrease in expected future income
E)a decrease in default risk
A)a decrease in the real interest rate
B)a decrease in real wealth
C)a decrease in disposable income
D)a decrease in expected future income
E)a decrease in default risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A decrease in disposable income
A)has no effect on the supply of loanable funds curve.
B)shifts the supply of loanable funds curve rightward.
C)shifts the supply of loanable funds curve leftward.
D)creates a movement up along the supply of loanable funds curve.
E)creates a movement down along the supply of loanable funds curve.
A)has no effect on the supply of loanable funds curve.
B)shifts the supply of loanable funds curve rightward.
C)shifts the supply of loanable funds curve leftward.
D)creates a movement up along the supply of loanable funds curve.
E)creates a movement down along the supply of loanable funds curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
An increase in ________ will shift the supply of loanable funds curve ________.
A)expected future income; rightward
B)wealth; leftward
C)disposable income; leftward
D)default risk; rightward
E)the real interest rate; rightward
A)expected future income; rightward
B)wealth; leftward
C)disposable income; leftward
D)default risk; rightward
E)the real interest rate; rightward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is true?
I. As the real interest rate increases, people increase the quantity they save.
II. The supply of loanable funds curve is downward sloping.
III. As disposable income increases, the supply of loanable funds curve becomes steeper.
A)I and III only
B)II and III only
C)I only
D)III only
E)I, II, and III
I. As the real interest rate increases, people increase the quantity they save.
II. The supply of loanable funds curve is downward sloping.
III. As disposable income increases, the supply of loanable funds curve becomes steeper.
A)I and III only
B)II and III only
C)I only
D)III only
E)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 23.2.3
In Figure 23.2.3, if the real interest rate is constant at 6 percent and and expected profit rises, the amount of loanable funds demanded will be
A)less than $450 billion.
B)$450 billion.
C)between $300 billion and $450 billion.
D)greater than $450 billion.
E)zero.

Figure 23.2.3
In Figure 23.2.3, if the real interest rate is constant at 6 percent and and expected profit rises, the amount of loanable funds demanded will be
A)less than $450 billion.
B)$450 billion.
C)between $300 billion and $450 billion.
D)greater than $450 billion.
E)zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The supply of loanable funds is the relationship between the quantity of loanable funds supplied and ________, other things remaining the same.
A)real GDP
B)the price level
C)the real interest rate
D)the inflation rate
E)the nominal interest rate
A)real GDP
B)the price level
C)the real interest rate
D)the inflation rate
E)the nominal interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions.

Figure 23.2.3
In Figure 23.2.3, if the real interest rate is constant at 6 percent and expected profit falls, the quantity of loanable funds demanded will be
A)less than $450 billion.
B)$450 billion.
C)between $450 billion and $600 billion.
D)greater than $600 billion.
E)zero.

Figure 23.2.3
In Figure 23.2.3, if the real interest rate is constant at 6 percent and expected profit falls, the quantity of loanable funds demanded will be
A)less than $450 billion.
B)$450 billion.
C)between $450 billion and $600 billion.
D)greater than $600 billion.
E)zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When the real interest rate increases,
A)the supply of loanable funds curve shifts rightward.
B)the supply of loanable funds curve shifts leftward.
C)there is a movement up along the supply of loanable funds curve.
D)there is a movement down along the supply of loanable funds curve.
E)the demand for loanable funds curve shifts leftward.
A)the supply of loanable funds curve shifts rightward.
B)the supply of loanable funds curve shifts leftward.
C)there is a movement up along the supply of loanable funds curve.
D)there is a movement down along the supply of loanable funds curve.
E)the demand for loanable funds curve shifts leftward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The greater a household's ________ the less is its saving.
A)return from saving
B)wealth
C)disposable income
D)expected future profit
E)all of the above
A)return from saving
B)wealth
C)disposable income
D)expected future profit
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If households' disposable income decreases, then
A)households' saving will decrease.
B)households' saving will increase.
C)the supply of loanable funds decreases.
D)a movement occurs down along the supply of loanable funds curve.
E)Both A and C are correct.
A)households' saving will decrease.
B)households' saving will increase.
C)the supply of loanable funds decreases.
D)a movement occurs down along the supply of loanable funds curve.
E)Both A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
As a result of a recession, the default risk increases. How does this change affect the loanable funds market?
A)There is a movement up along the supply of loanable funds curve.
B)There is a leftward shift of the supply of loanable funds curve.
C)There is a movement down along the demand for loanable funds curve.
D)There is a rightward shift of the supply of loanable funds curve.
E)There is a rightward shift of the demand for loanable funds curve.
A)There is a movement up along the supply of loanable funds curve.
B)There is a leftward shift of the supply of loanable funds curve.
C)There is a movement down along the demand for loanable funds curve.
D)There is a rightward shift of the supply of loanable funds curve.
E)There is a rightward shift of the demand for loanable funds curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is correct?
A)As disposable income increases, the real interest rate rises.
B)As disposable income decreases, saving decreases.
C)The higher a household's wealth the greater is its saving.
D)Both B and C are correct.
E)Both A and C are correct.
A)As disposable income increases, the real interest rate rises.
B)As disposable income decreases, saving decreases.
C)The higher a household's wealth the greater is its saving.
D)Both B and C are correct.
E)Both A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If households believe they will experience higher income in the near future, there is a
A)rightward shift of the supply of loanable funds curve.
B)leftward shift of the supply of loanable funds curve.
C)movement up along the supply of loanable funds curve.
D)movement down along the demand for loanable funds curve.
E)rightward shift of the demand for loanable funds curve.
A)rightward shift of the supply of loanable funds curve.
B)leftward shift of the supply of loanable funds curve.
C)movement up along the supply of loanable funds curve.
D)movement down along the demand for loanable funds curve.
E)rightward shift of the demand for loanable funds curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
________ increases households' saving.
A)A decrease in the real interest rate
B)A tax cut that increases disposable income
C)Higher expected future income
D)An increase in wealth
E)An increase in default risk
A)A decrease in the real interest rate
B)A tax cut that increases disposable income
C)Higher expected future income
D)An increase in wealth
E)An increase in default risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The supply of loanable funds curve
A)has a positive slope.
B)is vertical.
C)is horizontal.
D)has a negative slope.
E)is upward sloping at low real interest rates and downward sloping at high real interest rates.
A)has a positive slope.
B)is vertical.
C)is horizontal.
D)has a negative slope.
E)is upward sloping at low real interest rates and downward sloping at high real interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



