Deck 9: Pointers
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Pointers
1
Look at the following statement:
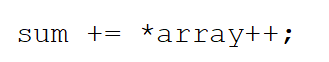
This statement ________.
A)is illegal in C++
B)will always result in a compiler error
C)assigns the dereferenced pointer's value, then increments the pointer's address
D)increments the dereferenced pointer's value by one, then assigns that value
E)None of these
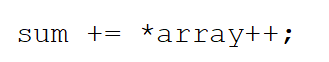
This statement ________.
A)is illegal in C++
B)will always result in a compiler error
C)assigns the dereferenced pointer's value, then increments the pointer's address
D)increments the dereferenced pointer's value by one, then assigns that value
E)None of these
assigns the dereferenced pointer's value, then increments the pointer's address
2
When this is placed in front of a variable name, it returns the address of that variable.
A)asterisk ( * )
B)conditional operator
C)ampersand ( & )
D)semicolon ( ; )
E)None of these
A)asterisk ( * )
B)conditional operator
C)ampersand ( & )
D)semicolon ( ; )
E)None of these
ampersand ( & )
3
A pointer variable is designed to store ________.
A)any legal C++ value
B)only floating-point values
C)a memory address
D)an integer
E)None of these
A)any legal C++ value
B)only floating-point values
C)a memory address
D)an integer
E)None of these
a memory address
4
The statement: 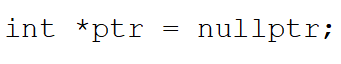
Has the same meaning as ________.
A)int ptr = nullptr;
B)*int ptr = nullptr;
C)int ptr* = nullptr;
D)int* ptr = nullptr;
E)None of these
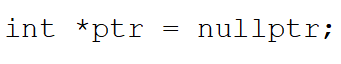
Has the same meaning as ________.
A)int ptr = nullptr;
B)*int ptr = nullptr;
C)int ptr* = nullptr;
D)int* ptr = nullptr;
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
With pointer variables, you can ________ manipulate data stored in other variables.
A)never
B)seldom
C)indirectly
D)All of these
E)None of these
A)never
B)seldom
C)indirectly
D)All of these
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In C++ 11, the ________ key word was introduced to represent the address 0.
A)nullptr
B)NULL
C)weak_ptr
D)All of these
E)None of these
A)nullptr
B)NULL
C)weak_ptr
D)All of these
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Assuming ptr is a pointer variable, what will the following statement output?
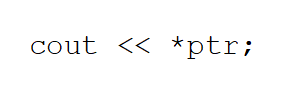
A)The value stored in the variable whose address is contained in ptr.
B)The string "*ptr".
C)The address of the variable stored in ptr.
D)The address of the variable whose address is stored in ptr.
E)None of these
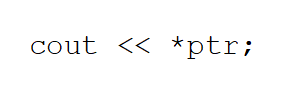
A)The value stored in the variable whose address is contained in ptr.
B)The string "*ptr".
C)The address of the variable stored in ptr.
D)The address of the variable whose address is stored in ptr.
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The contents of pointer variables may be changed with mathematical statements that perform ________.
A)all mathematical operations that are legal in C++
B)multiplication and division
C)addition and subtraction
D)B and C
E)None of these
A)all mathematical operations that are legal in C++
B)multiplication and division
C)addition and subtraction
D)B and C
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What will the following statement output?
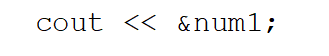
A)The value stored in the variable called num1
B)The memory address of the variable called num1
C)The number 1
D)The string "&num1"
E)None of these
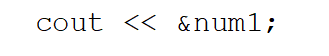
A)The value stored in the variable called num1
B)The memory address of the variable called num1
C)The number 1
D)The string "&num1"
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A function may return a pointer, but the programmer must ensure that the pointer ________.
A)still points to a valid object after the function ends
B)has not been assigned an address
C)was received as a parameter by the function
D)has not previously been returned by another function
E)None of these
A)still points to a valid object after the function ends
B)has not been assigned an address
C)was received as a parameter by the function
D)has not previously been returned by another function
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The ________, also known as the address operator, returns the memory address of a variable.
A)asterisk ( * )
B)ampersand ( & )
C)percent sign (%)
D)exclamation point ( ! )
E)None of these
A)asterisk ( * )
B)ampersand ( & )
C)percent sign (%)
D)exclamation point ( ! )
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Use the delete operator only on pointers that were ________.
A)never used
B)not correctly initialized
C)created with the new operator
D)dereferenced inappropriately
E)None of these
A)never used
B)not correctly initialized
C)created with the new operator
D)dereferenced inappropriately
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
________ can be used as pointers.
A)Array names
B)Numeric constants
C)Punctuation marks
D)All of these
E)None of these
A)Array names
B)Numeric constants
C)Punctuation marks
D)All of these
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Look at the following statement: 
In this statement, what does the word int mean?
A)The variable named *ptr will store an integer value.
B)The variable named *ptr will store an asterisk and an integer value.
C)ptr is a pointer variable that will store the address of an integer variable.
D)All of these
E)None of these

In this statement, what does the word int mean?
A)The variable named *ptr will store an integer value.
B)The variable named *ptr will store an asterisk and an integer value.
C)ptr is a pointer variable that will store the address of an integer variable.
D)All of these
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements deletes memory that has been dynamically allocated for an array?
A)int array = delete memory;
B)int delete[ ];
C)delete [] array;
D)new array = delete;
E)None of these
A)int array = delete memory;
B)int delete[ ];
C)delete [] array;
D)new array = delete;
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The ________ and ________ operators can be used to increment or decrement a pointer variable.
A)addition, subtraction
B)modulus, division
C)++, --
D)All of these
E)None of these
A)addition, subtraction
B)modulus, division
C)++, --
D)All of these
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When the less than ( < )operator is used between two pointer variables, the expression is testing whether ________.
A)the value pointed to by the first is less than the value pointed to by the second
B)the value pointed to by the first is greater than the value pointed to by the second
C)the address of the first variable comes before the address of the second variable in the computer's memory
D)the first variable was declared before the second variable
E)None of these
A)the value pointed to by the first is less than the value pointed to by the second
B)the value pointed to by the first is greater than the value pointed to by the second
C)the address of the first variable comes before the address of the second variable in the computer's memory
D)the first variable was declared before the second variable
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is not valid C++ code?
A)int ptr = &num1;
B)int ptr = int *num1;
C)float num1 = &ptr2;
D)All of these are valid.
E)All of these are invalid.
A)int ptr = &num1;
B)int ptr = int *num1;
C)float num1 = &ptr2;
D)All of these are valid.
E)All of these are invalid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What does the following statement do?
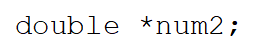
A)Declares a double variable named num2.
B)Declares and initializes an pointer variable named num2.
C)Initializes a variable named *num2.
D)Declares a pointer variable named num2.
E)None of these
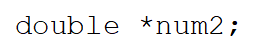
A)Declares a double variable named num2.
B)Declares and initializes an pointer variable named num2.
C)Initializes a variable named *num2.
D)Declares a pointer variable named num2.
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When you work with a dereferenced pointer, you are actually working with ________.
A)a variable whose memory has been allocated
B)a copy of the value pointed to by the pointer variable
C)the actual value of the variable whose address is stored in the pointer variable
D)All of these
E)None of these
A)a variable whose memory has been allocated
B)a copy of the value pointed to by the pointer variable
C)the actual value of the variable whose address is stored in the pointer variable
D)All of these
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The following statement: 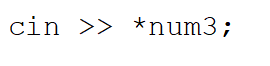
A)stores the keyboard input into the variable num3
B)stores the keyboard input into the pointer called num3
C)is illegal in C++
D)stores the keyboard input into the variable pointed to by num3
E)None of these
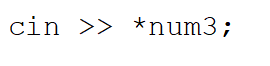
A)stores the keyboard input into the variable num3
B)stores the keyboard input into the pointer called num3
C)is illegal in C++
D)stores the keyboard input into the variable pointed to by num3
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Every byte in the computer's memory is assigned a unique ________.
A)pointer
B)address
C)dynamic allocation
D)name
E)None of these
A)pointer
B)address
C)dynamic allocation
D)name
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When you pass a pointer as an argument to a function, you must ________.
A)declare the pointer variable again in the function call
B)dereference the pointer variable in the function prototype
C)use the #include statement
D)not dereference the pointer in the function's body
E)None of these
A)declare the pointer variable again in the function call
B)dereference the pointer variable in the function prototype
C)use the #include
D)not dereference the pointer in the function's body
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
C++ does not perform array bounds checking, making it possible for you to assign a pointer the address of an element out of the boundaries of an array.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Not all arithmetic operations may be performed on pointers. For example, you cannot ________ or ________ a pointer.
A)multiply, divide
B)add, subtract
C)+=, -=
D)increment, decrement
E)None of these
A)multiply, divide
B)add, subtract
C)+=, -=
D)increment, decrement
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
With pointer variables you can access, but you cannot modify, data in other variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a variable uses more than one byte of memory, for pointer purposes its address is ________.
A)the address of the last byte of storage
B)the average of the addresses used to store the variable
C)the address of the first byte of storage
D)general delivery
E)None of these
A)the address of the last byte of storage
B)the average of the addresses used to store the variable
C)the address of the first byte of storage
D)general delivery
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Look at the following code: ![<strong>Look at the following code: After this code executes, which of the following statements is true?</strong> A)ptr will hold the address of numbers[0]. B)ptr will hold the address of the 2nd byte within the element numbers[0]. C)ptr will hold the address of numbers[1]. D)This code will not compile.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2965/11ecab60_cc66_76ea_909e_cd6e768a920c_TB2965_00.jpg)
After this code executes, which of the following statements is true?
A)ptr will hold the address of numbers[0].
B)ptr will hold the address of the 2nd byte within the element numbers[0].
C)ptr will hold the address of numbers[1].
D)This code will not compile.
![<strong>Look at the following code: After this code executes, which of the following statements is true?</strong> A)ptr will hold the address of numbers[0]. B)ptr will hold the address of the 2nd byte within the element numbers[0]. C)ptr will hold the address of numbers[1]. D)This code will not compile.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2965/11ecab60_cc66_76ea_909e_cd6e768a920c_TB2965_00.jpg)
After this code executes, which of the following statements is true?
A)ptr will hold the address of numbers[0].
B)ptr will hold the address of the 2nd byte within the element numbers[0].
C)ptr will hold the address of numbers[1].
D)This code will not compile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In C++ 11, the nullptr key word was introduced to represent the address 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
It is legal to subtract a pointer variable from another pointer variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A pointer variable may be initialized with ________.
A)any non-zero integer value
B)a valid address in the computer's memory
C)an address less than 0
D)A and C only
E)None of these
A)any non-zero integer value
B)a valid address in the computer's memory
C)an address less than 0
D)A and C only
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
To help prevent memory leaks from occurring in C++ 11, a ________ automatically deletes a chunk of dynamically allocated memory when the memory is no longer being used.
A)null pointer
B)smart pointer
C)dereferenced pointer
D)A and C only
E)None of these
A)null pointer
B)smart pointer
C)dereferenced pointer
D)A and C only
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The following statement: 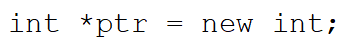
A)results in a compiler error
B)assigns an integer less than 32767 to the variable named ptr
C)assigns an address to the variable named ptr
D)creates a new pointer named int
E)None of these
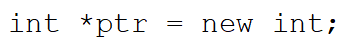
A)results in a compiler error
B)assigns an integer less than 32767 to the variable named ptr
C)assigns an address to the variable named ptr
D)creates a new pointer named int
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If you are using an older compiler that does not support the C++ 11 standard, you should initialize pointers with ________.
A)the integer 0, or the value NULL
B)the null terminator '\0'
C)a nonzero value
D)All of these
E)None of these
A)the integer 0, or the value NULL
B)the null terminator '\0'
C)a nonzero value
D)All of these
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Dynamic memory allocation occurs ________.
A)when a new variable is created by the compiler
B)when a new variable is created at runtime
C)when a pointer fails to dereference the right variable
D)when a pointer is assigned an incorrect address
E)None of these
A)when a new variable is created by the compiler
B)when a new variable is created at runtime
C)when a pointer fails to dereference the right variable
D)when a pointer is assigned an incorrect address
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What will the following code output?
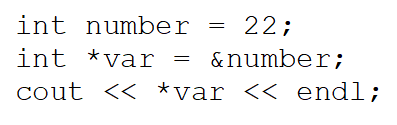
A)The address of the number variable
B)22
C)An asterisk followed by 22
D)An asterisk followed by the address of the number variable
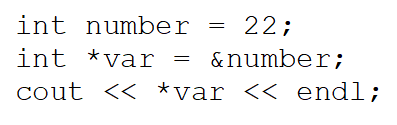
A)The address of the number variable
B)22
C)An asterisk followed by 22
D)An asterisk followed by the address of the number variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An array name is a pointer constant because the address stored in it cannot be changed during runtime.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What will the following code output?
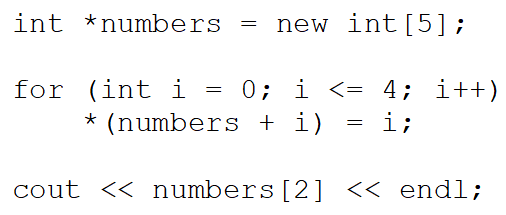
A)Five memory addresses
B)0
C)3
D)2
E)1
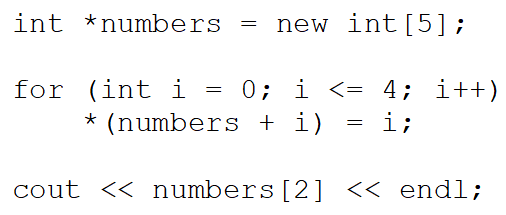
A)Five memory addresses
B)0
C)3
D)2
E)1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which statement displays the address of the variable num1?
A)cout << num1;
B)cout << *num1;
C)cin >> &num1;
D)cout << &num1;
E)None of these
A)cout << num1;
B)cout << *num1;
C)cin >> &num1;
D)cout << &num1;
E)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What will the following code output?
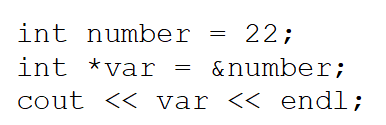
A)The address of the number variable
B)22
C)An asterisk followed by 22
D)An asterisk followed by the address of the number variable
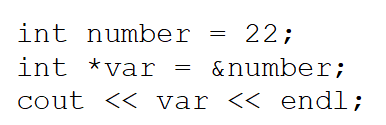
A)The address of the number variable
B)22
C)An asterisk followed by 22
D)An asterisk followed by the address of the number variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
To use any of the smart pointers in C++ 11, you must #include the memory header file with the following directive:
#include
#include

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The ampersand (&)is used to dereference a pointer variable in C++.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In C++ 11, you can use smart pointers to dynamically allocate memory and not worry about deleting the memory when you are finished using it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A pointer can be used as a function argument, giving the function access to the original argument.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Assuming myValues is an array of int values, and index is an int variable, both of the following statements do the same thing.
cout << myValues[index] << endl;
cout << *(myValues + index)<< endl;
cout << myValues[index] << endl;
cout << *(myValues + index)<< endl;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



