Deck 36: Nursing Management: Dysrhythmias
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/28
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 36: Nursing Management: Dysrhythmias
1
A patient with dilated cardiomyopathy has an atrial fibrillation that has been unresponsive to drug therapy for several days. The nurse anticipates that further treatment of the patient will require
A) IV adenosine (Adenocard).
B) electrical cardioversion.
C) insertion of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD).
D) anticoagulant therapy with warfarin (Coumadin).
A) IV adenosine (Adenocard).
B) electrical cardioversion.
C) insertion of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD).
D) anticoagulant therapy with warfarin (Coumadin).
anticoagulant therapy with warfarin (Coumadin).
2
A patient who has been successfully resuscitated after developing ventricular fibrillation asks the nurse about what happened. The most appropriate response by the nurse is,
A) "You almost died, but we were able to save you with electrical therapy."
B) "You had an episode of some cardiac dysrhythmias that are common after a heart attack."
C) "You had a serious abnormal heart rhythm, which treatment was able to reverse."
D) "Your heart stopped beating, and we shocked you to get it started again."
A) "You almost died, but we were able to save you with electrical therapy."
B) "You had an episode of some cardiac dysrhythmias that are common after a heart attack."
C) "You had a serious abnormal heart rhythm, which treatment was able to reverse."
D) "Your heart stopped beating, and we shocked you to get it started again."
"You had a serious abnormal heart rhythm, which treatment was able to reverse."
3
The nurse hears the cardiac monitor alarm and notes that the patient has a cardiac pattern of undulations of varying contours and amplitude with no measurable ECG pattern. The patient is unconscious with no pulse or respirations. After calling for assistance, the nurse should
A) start basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
B) administer an IV bolus dose of epinephrine.
C) prepare the patient for endotracheal intubation.
D) wait for the defibrillator to arrive.
A) start basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
B) administer an IV bolus dose of epinephrine.
C) prepare the patient for endotracheal intubation.
D) wait for the defibrillator to arrive.
start basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
4
The nurse reviews data from the cardiac monitor indicating that a patient with a myocardial infarction experienced a 50-second episode of ventricular tachycardia before a sinus rhythm and a heart rate of 98 were re-established. The most appropriate initial action by the nurse is to
A) notify the health care provider.
B) administer IV antidysrhythmic drugs per protocol.
C) defibrillate the patient.
D) document the rhythm and continue to monitor the patient.
A) notify the health care provider.
B) administer IV antidysrhythmic drugs per protocol.
C) defibrillate the patient.
D) document the rhythm and continue to monitor the patient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The nurse obtains a monitor strip on a patient admitted to the coronary care unit with a myocardial infarction and makes the following analysis: P wave not apparent; ventricular rate 162, R-R interval regular; PR interval not measurable; and QRS complex wide and distorted, QRS duration 0.18 second. The nurse interprets the patient's cardiac rhythm as
A) sinus tachycardia.
B) atrial fibrillation.
C) ventricular tachycardia.
D) ventricular fibrillation.
A) sinus tachycardia.
B) atrial fibrillation.
C) ventricular tachycardia.
D) ventricular fibrillation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A patient with supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is hemodynamically stable and requires cardioversion. The nurse will plan to
A) turn the synchronizer switch to the "off" position.
B) set the level of joules to 300 to convert the SVT.
C) administer a sedative before the procedure is begun.
D) check the incision for bleeding after the procedure.
A) turn the synchronizer switch to the "off" position.
B) set the level of joules to 300 to convert the SVT.
C) administer a sedative before the procedure is begun.
D) check the incision for bleeding after the procedure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A patient has a permanent pacemaker inserted for treatment of chronic atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response. The nurse teaches the patient that the pacemaker will
A) prevent or minimize ventricular irritability.
B) discharge if ventricular fibrillation occurs and prevent cardiac arrest.
C) depolarize the atria and generate a P wave.
D) stimulate a heart beat if the patient's own heart rate drops too low.
A) prevent or minimize ventricular irritability.
B) discharge if ventricular fibrillation occurs and prevent cardiac arrest.
C) depolarize the atria and generate a P wave.
D) stimulate a heart beat if the patient's own heart rate drops too low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A patient who has a history of sudden cardiac death has an ICD inserted. When performing discharge teaching with the patient, it is important for the nurse to instruct the patient and family that
A) medications will no longer be needed to control dysrhythmias.
B) if the ICD fires and the patient loses consciousness, 911 should be called.
C) CPR may displace the ICD leads and should not be performed.
D) the ICD rarely triggers airport security alarms and travel without restrictions is allowed.
A) medications will no longer be needed to control dysrhythmias.
B) if the ICD fires and the patient loses consciousness, 911 should be called.
C) CPR may displace the ICD leads and should not be performed.
D) the ICD rarely triggers airport security alarms and travel without restrictions is allowed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In analyzing a patient's electrocardiographic (ECG) rhythm strip, the nurse uses the knowledge that the time of the conduction of an impulse through the Purkinje fibers is represented by the
A) P wave.
B) PR interval.
C) QRS complex.
D) QT interval.
A) P wave.
B) PR interval.
C) QRS complex.
D) QT interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
During change-of-shift report, the nurse learns that a patient with a large myocardial infarction has been having frequent PVCs. When monitoring the patient for the effects of PVCs, the nurse will check the patient's
A) medications.
B) recent electrolyte values.
C) apical radial heart rate.
D) oxygen saturation.
A) medications.
B) recent electrolyte values.
C) apical radial heart rate.
D) oxygen saturation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A patient has received instruction on the management of a new permanent pacemaker before discharge from the hospital. The nurse recognizes that teaching has been effective when the patient tells the nurse,
A) "I won't lift the arm on the pacemaker side up very high until I see the doctor."
B) "I will notify the airlines when I make a reservation that I have a pacemaker."
C) "I must avoid cooking with a microwave oven or being near a microwave in use."
D) "It will be 6 weeks before I can take a bath or return to my usual activities."
A) "I won't lift the arm on the pacemaker side up very high until I see the doctor."
B) "I will notify the airlines when I make a reservation that I have a pacemaker."
C) "I must avoid cooking with a microwave oven or being near a microwave in use."
D) "It will be 6 weeks before I can take a bath or return to my usual activities."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A patient experiences dizziness and shortness of breath for several days. During cardiac monitoring in the ED, the nurse obtains the following ECG tracing. 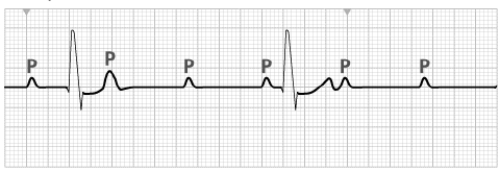
The nurse interprets this cardiac rhythm as
A) third-degree AV block.
B) sinus rhythm with premature atrial contractions (PACs).
C) sinus rhythm with PVCs.
D) junctional escape rhythm.

The nurse interprets this cardiac rhythm as
A) third-degree AV block.
B) sinus rhythm with premature atrial contractions (PACs).
C) sinus rhythm with PVCs.
D) junctional escape rhythm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A patient has a dysrhythmia that requires careful monitoring of atrial activity. Which lead will be best to use for continuous monitoring?
A) MCL1
B) AVF
C) V6
D) I
A) MCL1
B) AVF
C) V6
D) I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A patient has a normal cardiac rhythm strip except that the PR interval is 0.34 seconds. The appropriate intervention by the nurse is to
A) prepare the patient for temporary pacemaker insertion.
B) document the finding and continue to monitor the patient.
C) notify the health care provider immediately.
D) administer atropine per protocol.
A) prepare the patient for temporary pacemaker insertion.
B) document the finding and continue to monitor the patient.
C) notify the health care provider immediately.
D) administer atropine per protocol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A patient with myocardial infarction develops symptomatic hypotension. The monitor shows a type 1, second-degree AV block with a heart rate of 30. The nurse administers IV atropine as prescribed. The nurse determines that the drug has been effective on finding a(n)
A) increase in the patient's heart rate.
B) increase in peripheral pulse volume.
C) decrease in ventricular response.
D) decrease in premature contractions.
A) increase in the patient's heart rate.
B) increase in peripheral pulse volume.
C) decrease in ventricular response.
D) decrease in premature contractions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The nurse determines that a patient has ventricular bigeminy when the rhythm strip indicates that
A) there are pairs of wide and distorted QRS complexes.
B) every other QRS complex is wide and starts prematurely.
C) all QRS complexes are wide and the rate is 150 to 250 beats/min.
D) there are premature QRS complexes with two different shapes.
A) there are pairs of wide and distorted QRS complexes.
B) every other QRS complex is wide and starts prematurely.
C) all QRS complexes are wide and the rate is 150 to 250 beats/min.
D) there are premature QRS complexes with two different shapes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A patient who is complaining of a "racing" heart and nervousness comes to the emergency department. The patient's blood pressure (BP) is 102/68. The nurse places the patient on a cardiac monitor and obtains the following ECG tracing. 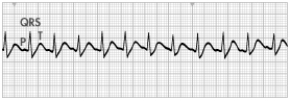
Which action should the nurse take next?
A) Have the patient perform the Valsalva maneuver.
B) Prepare to administer b-blocker medication to slow the heart rate.
C) Get ready to perform electrical cardioversion.
D) Obtain further information about possible causes for the heart rate.

Which action should the nurse take next?
A) Have the patient perform the Valsalva maneuver.
B) Prepare to administer b-blocker medication to slow the heart rate.
C) Get ready to perform electrical cardioversion.
D) Obtain further information about possible causes for the heart rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A patient with diabetes mellitus is admitted unresponsive to the emergency department (ED). Initial laboratory findings are serum potassium 2.8 mEq/L (2.8 mmol/L), serum sodium 138 mEq/L (138 mmol/L), serum chloride 90 mEq/L (90 mmol/L), and blood glucose 628 mg/dl (34.9 mmol/L). Cardiac monitoring shows multifocal PVCs. The nurse understands that the patient's PVCs are most likely caused by
A) hyperglycemia.
B) hypoxemia.
C) dehydration.
D) hypokalemia.
A) hyperglycemia.
B) hypoxemia.
C) dehydration.
D) hypokalemia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When needing to estimate the ventricular rate quickly for a patient with a regular heart rhythm using an ECG strip, the nurse will
A) print a 1-minute ECG strip and count the number of QRS complexes.
B) count the number of large squares in the R-R interval and divide by 300.
C) calculate the number of small squares between one QRS complex and the next and divide into 1500.
D) use the 3-second markers to count the number of QRS complexes in 6 seconds and multiply by 10.
A) print a 1-minute ECG strip and count the number of QRS complexes.
B) count the number of large squares in the R-R interval and divide by 300.
C) calculate the number of small squares between one QRS complex and the next and divide into 1500.
D) use the 3-second markers to count the number of QRS complexes in 6 seconds and multiply by 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A patient has a junctional escape rhythm on the monitor. The nurse would expect the patient to have a pulse rate of ____ beats/min.
A) 15-20
B) 20-40
C) 40-60
D) 60-100
A) 15-20
B) 20-40
C) 40-60
D) 60-100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A 21-year-old college student arrives at the student health center at the end of the quarter complaining, "My heart is skipping beats." The nurse obtains an ECG and notes the presence of occasional PVCs. What action should the nurse take first?
A) Ask the patient about any history of coronary artery disease.
B) Question the patient about current stress level and coffee use.
C) Have the patient transported to the hospital ED.
D) Administer O2 to the patient at 2 to 3 L/min using nasal prongs.
A) Ask the patient about any history of coronary artery disease.
B) Question the patient about current stress level and coffee use.
C) Have the patient transported to the hospital ED.
D) Administer O2 to the patient at 2 to 3 L/min using nasal prongs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A 19-year-old student has a mandatory ECG before participating on a college swim team and is found to have sinus bradycardia, rate 52. BP is 114/54, and the student denies any health problems. What action by the nurse is appropriate?
A) Refer the student to a cardiologist for further assessment.
B) Allow the student to participate on the swim team.
C) Obtain more detailed information about the student's health history.
D) Tell the student to stop swimming immediately if any dyspnea occurs.
A) Refer the student to a cardiologist for further assessment.
B) Allow the student to participate on the swim team.
C) Obtain more detailed information about the student's health history.
D) Tell the student to stop swimming immediately if any dyspnea occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A patient's sinus rhythm rate is 62. The PR interval is 0.18 seconds at 1:00 AM, 0.20 seconds at 12:30 PM, and 0.23 seconds at 4:00 PM. Which action should the nurse take?
A) Document the patient's rhythm and continue to monitor.
B) Prepare for possible pacemaker insertion.
C) Hold the ordered metoprolol (Lopressor) and call the health care provider.
D) Give the PRN dose of lidocaine (Xylocaine).
A) Document the patient's rhythm and continue to monitor.
B) Prepare for possible pacemaker insertion.
C) Hold the ordered metoprolol (Lopressor) and call the health care provider.
D) Give the PRN dose of lidocaine (Xylocaine).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When a patient requires defibrillation, in which order will the nurse accomplish the following steps?
A) Place the paddles on the patient's chest.
B) Turn the defibrillator on.
C) Check the location of other personnel and call out "all clear."
D) Select the appropriate energy level.
E) Deliver the electrical charge.
Correct
A) Place the paddles on the patient's chest.
B) Turn the defibrillator on.
C) Check the location of other personnel and call out "all clear."
D) Select the appropriate energy level.
E) Deliver the electrical charge.
Correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The nurse has received change-of-shift report about all of these patients on the telemetry unit. Which patient should the nurse see first?
A) A patient with atrial fibrillation, rate 88, who has a new warfarin (Coumadin) order
B) A patient with type 1 second-degree AV block, rate 60, who is dizzy when ambulating
C) A patient who is in a sinus rhythm, rate 98, after having electrical cardioversion 2 hours ago
D) A patient whose ICD fired three times today who is scheduled for a dose of amiodarone (Cordarone)
A) A patient with atrial fibrillation, rate 88, who has a new warfarin (Coumadin) order
B) A patient with type 1 second-degree AV block, rate 60, who is dizzy when ambulating
C) A patient who is in a sinus rhythm, rate 98, after having electrical cardioversion 2 hours ago
D) A patient whose ICD fired three times today who is scheduled for a dose of amiodarone (Cordarone)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When analyzing the waveforms of a patient's ECG, the nurse will need to investigate further upon finding a
A) PR interval of 0.18 second.
B) QRS interval of 0.14 second.
C) T wave of 0.16 second.
D) QT interval of 0.34 second.
A) PR interval of 0.18 second.
B) QRS interval of 0.14 second.
C) T wave of 0.16 second.
D) QT interval of 0.34 second.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A patient develops sinus bradycardia at a rate of 32 beats/min, has a BP of 80/36 mm Hg, and is complaining of feeling faint. Which action should the nurse take?
A) Continue to monitor the rhythm and BP.
B) Obtain and apply the transcutaneous pacemaker (TCP).
C) Give the scheduled dose of diltiazem (Cardizem).
D) Have the patient perform the Valsalva maneuver.
A) Continue to monitor the rhythm and BP.
B) Obtain and apply the transcutaneous pacemaker (TCP).
C) Give the scheduled dose of diltiazem (Cardizem).
D) Have the patient perform the Valsalva maneuver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When analyzing an ECG rhythm strip of a patient with a regular cardiac rhythm, the nurse finds there are 25 small blocks from one R wave to the next. The nurse calculates the patient's heart rate as ______.
Correct
Correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



