Deck 36: Transport in Vascular Plants
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/84
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 36: Transport in Vascular Plants
1
All of the following has an effect on water potential (¬)in plants except
A)physical pressure.
B)water-attracting matrices.
C)dissolved solutes.
D)osmosis.
E)DNA structure.
A)physical pressure.
B)water-attracting matrices.
C)dissolved solutes.
D)osmosis.
E)DNA structure.
E
2
Which of the following is not a function of the plasma membrane proton pump?
A)hydrolyzes ATP
B)produces a proton gradient
C)generates a membrane potential
D)equalizes the charge on each side of a membrane
E)stores potential energy on one side of a membrane
A)hydrolyzes ATP
B)produces a proton gradient
C)generates a membrane potential
D)equalizes the charge on each side of a membrane
E)stores potential energy on one side of a membrane
D
3
A fellow student brought in a leaf to be examined. The leaf was dark green, thin, had stoma on the lower surface only, and had a surface area of 100 square meters. Where is the most likely environment where this leaf was growing?
A)a dry, sandy region
B)a large, still pond
C)a tropical rain forest
D)an oasis within a grassland
E)the floor of a deciduous forest
A)a dry, sandy region
B)a large, still pond
C)a tropical rain forest
D)an oasis within a grassland
E)the floor of a deciduous forest
C
4
Which of the following would be least likely to affect osmosis in plants?
A)proton pumps in the membrane
B)a difference in solute concentrations
C)receptor proteins in the membrane
D)aquaporins
E)a difference in water potential
A)proton pumps in the membrane
B)a difference in solute concentrations
C)receptor proteins in the membrane
D)aquaporins
E)a difference in water potential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The amount and direction of movement of water in plants can always be predicted by measuring which of the following?
A)pressure potential
B)number of aquaporins
C)proton gradients
D)dissolved solutes
E)water potential (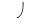 )
)
A)pressure potential
B)number of aquaporins
C)proton gradients
D)dissolved solutes
E)water potential (
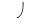 )
)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements about xylem is incorrect?
A)It conducts material upward.
B)It conducts materials within dead cells.
C)It transports mainly sugars and amino acids.
D)It has a lower water potential than soil does.
E)No energy input from the plant is required for xylem transport.
A)It conducts material upward.
B)It conducts materials within dead cells.
C)It transports mainly sugars and amino acids.
D)It has a lower water potential than soil does.
E)No energy input from the plant is required for xylem transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Compared to a cell with few aquaporins in its membrane, a cell containing many aquaporins will
A)have a faster rate of osmosis.
B)have a lower water potential.
C)have a higher water potential.
D)have a faster rate of active transport.
E)be flaccid.
A)have a faster rate of osmosis.
B)have a lower water potential.
C)have a higher water potential.
D)have a faster rate of active transport.
E)be flaccid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If you were to prune the shoot tips of a plant, what would be the effect on the plant and the leaf area index?
A)bushier plants lower leaf area index
B)tall plants lower leaf area index
C)tall plants higher leaf area index
D)short plants lower leaf area index
E)bushier plants higher leaf area indexes
A)bushier plants lower leaf area index
B)tall plants lower leaf area index
C)tall plants higher leaf area index
D)short plants lower leaf area index
E)bushier plants higher leaf area indexes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The value for ¬ in root tissue was found to be -0.15 MPa. If you take the root tissue and place it in a 0.1 M solution of sucrose (¬ = -0.23), net water flow would
A)be from the tissue into the sucrose solution.
B)be from the sucrose solution into the tissue.
C)be in both directions and the concentrations would remain equal.
D)occur only as ATP was hydrolyzed in the tissue.
E)be impossible to determine from the values given here.
A)be from the tissue into the sucrose solution.
B)be from the sucrose solution into the tissue.
C)be in both directions and the concentrations would remain equal.
D)occur only as ATP was hydrolyzed in the tissue.
E)be impossible to determine from the values given here.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Most angiosperms have alternate phyllotaxy. What allows each leaf to get the maximum exposure to light and reduces shading of lower leaves?
A)a leaf area index above 8
B)self pruning
C)one leaf only per node
D)leaf emergence at an angle of 137.5° from the site of previous leaves
E)A and D
A)a leaf area index above 8
B)self pruning
C)one leaf only per node
D)leaf emergence at an angle of 137.5° from the site of previous leaves
E)A and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If ¬P = 0.3 MPa and ¬S = -0.45 MPa, the resulting ¬ is
A)+0.75 MPa.
B)-0.75 MPa.
C)-0.15 MPa.
D)+0.15 MPa.
E)-0.42 MPa.
A)+0.75 MPa.
B)-0.75 MPa.
C)-0.15 MPa.
D)+0.15 MPa.
E)-0.42 MPa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A plant developed a mineral deficiency after being treated with a fungicide. What is the most probable cause of the deficiency?
A)Mineral receptor proteins in the plant membrane were not functioning.
B)Mycorrhizal fungi were killed.
C)Active transport of minerals was inhibited.
D)The genes for the synthesis of transport proteins were destroyed.
E)Proton pumps reversed the membrane potential.
A)Mineral receptor proteins in the plant membrane were not functioning.
B)Mycorrhizal fungi were killed.
C)Active transport of minerals was inhibited.
D)The genes for the synthesis of transport proteins were destroyed.
E)Proton pumps reversed the membrane potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which structure or compartment is not part of the plant's apoplast?
A)the lumen of a xylem vessel
B)the lumen of a sieve tube
C)the cell wall of a mesophyll cell
D)the cell wall of a transfer cell
E)the cell wall of a root hair
A)the lumen of a xylem vessel
B)the lumen of a sieve tube
C)the cell wall of a mesophyll cell
D)the cell wall of a transfer cell
E)the cell wall of a root hair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The ancestors of land plants were aquatic algae. Which of the following is not an evolutionary adaptation to life on land?
A)C3 photosynthesis
B)a waxy cuticle
C)root hairs
D)xylem and phloem
E)guard cells
A)C3 photosynthesis
B)a waxy cuticle
C)root hairs
D)xylem and phloem
E)guard cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is False about bulk flow?
A)It is driven primarily by pressure potential.
B)It is more effective than diffusion over distances greater than 100 μm.
C)It depends on a difference in pressure potential at the source and sink.
D)It depends on the force of gravity on a column of water.
E)It may be the result of either positive or negative pressure potential.
A)It is driven primarily by pressure potential.
B)It is more effective than diffusion over distances greater than 100 μm.
C)It depends on a difference in pressure potential at the source and sink.
D)It depends on the force of gravity on a column of water.
E)It may be the result of either positive or negative pressure potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Active transport involves all of the following except the
A)diffusion of solute through the lipid bilayer of a membrane.
B)pumping of solutes across the membrane.
C)hydrolysis of ATP.
D)transport of solute against a concentration gradient.
E)a specific transport protein in the membrane.
A)diffusion of solute through the lipid bilayer of a membrane.
B)pumping of solutes across the membrane.
C)hydrolysis of ATP.
D)transport of solute against a concentration gradient.
E)a specific transport protein in the membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Active transport of various materials in plants at the cellular level requires all of the following except
A)a proton gradient.
B)ATP.
C)membrane potential.
D)transport proteins
E)xylem membranes.
A)a proton gradient.
B)ATP.
C)membrane potential.
D)transport proteins
E)xylem membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An open beaker of pure water has a water potential (¬)of
A)-0.23 MPa.
B)+0.23 MPa.
C)+0.07 MPa.
D)-0.0000001 MPa.
E)0)0 (zero).
A)-0.23 MPa.
B)+0.23 MPa.
C)+0.07 MPa.
D)-0.0000001 MPa.
E)0)0 (zero).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
All of the following involves active transport across membranes except
A)the movement of mineral nutrients from the apoplast to the symplast.
B)the movement of sugar from mesophyll cells into sieve-tube members in maize.
C)the movement of sugar from one sieve-tube member to the next.
D)K+ uptake by guard cells during stomatal opening.
E)the movement of mineral nutrients into cells of the root cortex.
A)the movement of mineral nutrients from the apoplast to the symplast.
B)the movement of sugar from mesophyll cells into sieve-tube members in maize.
C)the movement of sugar from one sieve-tube member to the next.
D)K+ uptake by guard cells during stomatal opening.
E)the movement of mineral nutrients into cells of the root cortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Some botanists argue that the entire plant should be considered as a single unit rather than a composite of many individual cells. Which of the following cellular structures cannot be used to support this view?
A)cell wall
B)cell membrane
C)cytosol
D)tonoplast
E)symplast
A)cell wall
B)cell membrane
C)cytosol
D)tonoplast
E)symplast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the role of proton pumps in root hair cells?
A)establish ATP gradients
B)acquire minerals from the soil
C)pressurize xylem transport
D)eliminate excess electrons
E)A and D only
A)establish ATP gradients
B)acquire minerals from the soil
C)pressurize xylem transport
D)eliminate excess electrons
E)A and D only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is not an important component of the long-distance transport process in plants?
A)The cohesion of water molecules.
B)A negative water potential.
C)The root parenchyma.
D)The active transport of solutes.
E)Bulk flow from source to sink.
A)The cohesion of water molecules.
B)A negative water potential.
C)The root parenchyma.
D)The active transport of solutes.
E)Bulk flow from source to sink.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
One is most likely to see guttation in small plants when the
A)transpiration rates are high.
B)root pressure exceeds transpiration pull.
C)preceding evening was hot, windy, and dry.
D)water potential in the stele of the root is high.
E)roots are not absorbing minerals from the soil.
A)transpiration rates are high.
B)root pressure exceeds transpiration pull.
C)preceding evening was hot, windy, and dry.
D)water potential in the stele of the root is high.
E)roots are not absorbing minerals from the soil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In plant roots, the Casparian strip is correctly described by which of the following?
A)It is located in the walls between endodermal cells and cortex cells.
B)It provides energy for the active transport of minerals into the stele from the cortex.
C)It ensures that all minerals are absorbed from the soil in equal amounts.
D)It ensures that all water and dissolved substances must pass through a cell membrane before entering the stele.
E)It provides increased surface area for the absorption of mineral nutrients.
A)It is located in the walls between endodermal cells and cortex cells.
B)It provides energy for the active transport of minerals into the stele from the cortex.
C)It ensures that all minerals are absorbed from the soil in equal amounts.
D)It ensures that all water and dissolved substances must pass through a cell membrane before entering the stele.
E)It provides increased surface area for the absorption of mineral nutrients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following statements is False concerning the xylem?
A)Xylem tracheids and vessels fulfill their vital function only after their death.
B)The cell walls of the tracheids are greatly strengthened with cellulose fibrils forming thickened rings or spirals.
C)Water molecules are transpired from the cells of the leaves, and replaced by water molecules in the xylem pulled up from the roots due to the cohesion of water molecules.
D)Movement of materials is by mass flow; materials move owing to a turgor pressure gradient from "source" to "sink."
E)In the morning, sap in the xylem begins to move first in the twigs of the upper portion of the tree, and later in the lower trunk.
A)Xylem tracheids and vessels fulfill their vital function only after their death.
B)The cell walls of the tracheids are greatly strengthened with cellulose fibrils forming thickened rings or spirals.
C)Water molecules are transpired from the cells of the leaves, and replaced by water molecules in the xylem pulled up from the roots due to the cohesion of water molecules.
D)Movement of materials is by mass flow; materials move owing to a turgor pressure gradient from "source" to "sink."
E)In the morning, sap in the xylem begins to move first in the twigs of the upper portion of the tree, and later in the lower trunk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following has the lowest (most negative)water potential?
A)soil
B)root xylem
C)trunk xylem
D)leaf cell walls
E)leaf air spaces
A)soil
B)root xylem
C)trunk xylem
D)leaf cell walls
E)leaf air spaces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The following factors may sometimes play a role in the movement of sap through xylem. Which one depends on the direct expenditure of ATP by the plant?
A)capillarity of water within the xylem
B)evaporation of water from leaves
C)cohesion among water molecules
D)concentration of ions in the symplast
E)bulk flow of water in the root apoplast
A)capillarity of water within the xylem
B)evaporation of water from leaves
C)cohesion among water molecules
D)concentration of ions in the symplast
E)bulk flow of water in the root apoplast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the main force by which most of the water within xylem vessels moves toward the top of a tree?
A)active transport of ions into the stele
B)atmospheric pressure on roots
C)evaporation of water through stoma
D)the force of root pressure
E)osmosis in the root
A)active transport of ions into the stele
B)atmospheric pressure on roots
C)evaporation of water through stoma
D)the force of root pressure
E)osmosis in the root

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What regulates the flow of water through the xylem?
A)passive transport by the endodermis
B)the number of companion cells in the phloem
C)the evaporation of water from the leaves
D)active transport by sieve-tube members
E)active transport by tracheid and vessel elements.
A)passive transport by the endodermis
B)the number of companion cells in the phloem
C)the evaporation of water from the leaves
D)active transport by sieve-tube members
E)active transport by tracheid and vessel elements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements about transport in plants is False?
A)Weak bonding between water molecules and the walls of xylem vessels or tracheids helps support the columns of water in the xylem.
B)Hydrogen bonding between water molecules, which results in the high cohesion of the water, is essential for the rise of water in tall trees.
C)Although some angiosperm plants develop considerable root pressure, this is not sufficient to raise water to the tops of tall trees.
D)Most plant physiologists now agree that the pull from the top of the plant resulting from transpiration is sufficient, when combined with the cohesion of water, to explain the rise of water in the xylem in even the tallest trees.
E)Gymnosperms can sometimes develop especially high root pressure, which may account for the rise of water in tall pine trees without transpiration pull.
A)Weak bonding between water molecules and the walls of xylem vessels or tracheids helps support the columns of water in the xylem.
B)Hydrogen bonding between water molecules, which results in the high cohesion of the water, is essential for the rise of water in tall trees.
C)Although some angiosperm plants develop considerable root pressure, this is not sufficient to raise water to the tops of tall trees.
D)Most plant physiologists now agree that the pull from the top of the plant resulting from transpiration is sufficient, when combined with the cohesion of water, to explain the rise of water in the xylem in even the tallest trees.
E)Gymnosperms can sometimes develop especially high root pressure, which may account for the rise of water in tall pine trees without transpiration pull.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the main cause of guttation in plants?
A)root pressure
B)transpiration
C)pressure flow in phloem
D)plant injury
E)condensation of atmospheric water
A)root pressure
B)transpiration
C)pressure flow in phloem
D)plant injury
E)condensation of atmospheric water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Pine seedlings grown in sterile potting soil grow much slower than seedlings grown in soil from the area where the seeds were collected. This is most likely because
A)the sterilization process kills the root hairs as they emerge from the seedling.
B)the normal symbiotic fungi are not present in the sterilized soil.
C)sterilization removes essential nutrients from the soil.
D)water and mineral uptake is faster when mycorrhizae are present.
E)B and D
A)the sterilization process kills the root hairs as they emerge from the seedling.
B)the normal symbiotic fungi are not present in the sterilized soil.
C)sterilization removes essential nutrients from the soil.
D)water and mineral uptake is faster when mycorrhizae are present.
E)B and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Water potential is generally most negative in which of the following parts of a plant?
A)mesophyll cells of the leaf
B)xylem vessels in leaves
C)xylem vessels in roots
D)cells of the root cortex
E)root hairs
A)mesophyll cells of the leaf
B)xylem vessels in leaves
C)xylem vessels in roots
D)cells of the root cortex
E)root hairs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In which plant cell or tissue would the pressure component of water potential most often be negative?
A)leaf mesophyll cell
B)stem xylem
C)stem phloem
D)root cortex cell
E)root epidermis
A)leaf mesophyll cell
B)stem xylem
C)stem phloem
D)root cortex cell
E)root epidermis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A water molecule could move all the way through a plant from soil to root to leaf to air and pass through a living cell only once. This living cell would be a part of which structure?
A)the Casparian strip
B)a guard cell
C)the root epidermis
D)the endodermis
E)the root cortex
A)the Casparian strip
B)a guard cell
C)the root epidermis
D)the endodermis
E)the root cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Root hairs are most important to a plant because they
A)anchor a plant in the soil.
B)store starches.
C)increase the surface area for absorption.
D)provide a habitat for nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
E)contain xylem tissue.
A)anchor a plant in the soil.
B)store starches.
C)increase the surface area for absorption.
D)provide a habitat for nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
E)contain xylem tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following would likely not contribute to the surface area available for water absorption from the soil by a plant root system?
A)root hairs
B)endodermis
C)mycorrhizae
D)fungi associated with the roots
E)fibrous arrangement of the roots
A)root hairs
B)endodermis
C)mycorrhizae
D)fungi associated with the roots
E)fibrous arrangement of the roots

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Transpiration in plants requires all of the following except
A)adhesion of water molecules to cellulose.
B)cohesion between water molecules.
C)evaporation of water molecules.
D)active transport through xylem cells.
E)transport through tracheids.
A)adhesion of water molecules to cellulose.
B)cohesion between water molecules.
C)evaporation of water molecules.
D)active transport through xylem cells.
E)transport through tracheids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is responsible for the cohesion of water molecules?
A)hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atoms of a water molecule and cellulose in a vessel cell
B)covalent bonds between the hydrogen atoms of two adjacent water molecules
C)hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and a hydrogen atom of another water molecule
D)covalent bonds between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and a hydrogen atom of another water molecule
E)Cohesion has nothing to do with the bonding but is the result of the tight packing of the water molecules in the xylem column.
A)hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atoms of a water molecule and cellulose in a vessel cell
B)covalent bonds between the hydrogen atoms of two adjacent water molecules
C)hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and a hydrogen atom of another water molecule
D)covalent bonds between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and a hydrogen atom of another water molecule
E)Cohesion has nothing to do with the bonding but is the result of the tight packing of the water molecules in the xylem column.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Active transport would be least important in the normal functioning of which of the following plant tissue types?
A)leaf transfer cells
B)stem xylem
C)root endodermis
D)leaf mesophyll
E)root phloem
A)leaf transfer cells
B)stem xylem
C)root endodermis
D)leaf mesophyll
E)root phloem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Ignoring all other factors, what kind of day would result in the fastest delivery of water and minerals to the leaves of a tree?
A)cool, dry day
B)warm, dry day
C)warm, humid day
D)cool, humid day
E)very hot, dry, windy day
A)cool, dry day
B)warm, dry day
C)warm, humid day
D)cool, humid day
E)very hot, dry, windy day

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Assume that a particular chemical interferes with the establishment and maintenance of proton gradients across the membranes of plant cells. All of the following processes would be directly affected by this chemical except
A)photosynthesis.
B)phloem loading.
C)xylem transport.
D)cellular respiration.
E)stomatal opening.
A)photosynthesis.
B)phloem loading.
C)xylem transport.
D)cellular respiration.
E)stomatal opening.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Phloem transport of sucrose can be described as going from "source to sink." Which of the following would not normally function as a sink?
A)growing leaf
B)growing root
C)storage organ in summer
D)mature leaf
E)shoot tip
A)growing leaf
B)growing root
C)storage organ in summer
D)mature leaf
E)shoot tip

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Phloem transport is described as being from source to sink. Which of the following would most accurately complete this statement about phloem transport as applied to most plants in the late spring? Phloem transports __________ from the __________ source to the __________ sink.
A)amino acids; root; mycorrhizae
B)sugars; leaf; apical meristem
C)nucleic acids; flower; root
D)proteins; root; leaf
E)sugars; stem; root
A)amino acids; root; mycorrhizae
B)sugars; leaf; apical meristem
C)nucleic acids; flower; root
D)proteins; root; leaf
E)sugars; stem; root

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
As a biologist, it is your job to look for plants that have evolved structures with a selective advantage in dry, hot conditions. Which of the following adaptations would be least likely to meet your objective?
A)CAM plants that grow rapidly
B)small, thick leaves with stomata on the lower surface
C)a thick cuticle on fleshy leaves
D)large, fleshy stems with the ability to carry out photosynthesis
E)plants that do not produce abscisic acid and have a short, thick taproot
A)CAM plants that grow rapidly
B)small, thick leaves with stomata on the lower surface
C)a thick cuticle on fleshy leaves
D)large, fleshy stems with the ability to carry out photosynthesis
E)plants that do not produce abscisic acid and have a short, thick taproot

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is a correct statement about sugar movement in phloem?
A)Diffusion can account for the observed rates of transport.
B)Movement can occur both upward and downward in the plant.
C)Sugar is translocated from sinks to sources.
D)Only phloem cells with nuclei can perform sugar movement.
E)Sugar transport does not require energy.
A)Diffusion can account for the observed rates of transport.
B)Movement can occur both upward and downward in the plant.
C)Sugar is translocated from sinks to sources.
D)Only phloem cells with nuclei can perform sugar movement.
E)Sugar transport does not require energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
All of the following normally enter the plant through the roots except
A)carbon dioxide.
B)nitrogen.
C)potassium.
D)water.
E)calcium.
A)carbon dioxide.
B)nitrogen.
C)potassium.
D)water.
E)calcium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The water lost during transpiration is an unfortunate side effect of the plant's exchange of gases. However, the plant derives some benefit from this water loss in the form of
A)evaporative cooling.
B)mineral transport.
C)increased turgor.
D)A and B only
E)A, B, and C
A)evaporative cooling.
B)mineral transport.
C)increased turgor.
D)A and B only
E)A, B, and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Arrange the following five events in an order that explains the mass flow of materials in the phloem. 1. Water diffuses into the sieve tubes.
2) Leaf cells produce sugar by photosynthesis.
3) Solutes are actively transported into sieve tubes.
4) Sugar is transported from cell to cell in the leaf.
5) Sugar moves down the stem.
A)2, 1, 4, 3, 5
B)1, 2, 3, 4, 5
C)2, 4, 3, 1, 5
D)4, 2, 1, 3, 5
E)2, 4, 1, 3, 5
2) Leaf cells produce sugar by photosynthesis.
3) Solutes are actively transported into sieve tubes.
4) Sugar is transported from cell to cell in the leaf.
5) Sugar moves down the stem.
A)2, 1, 4, 3, 5
B)1, 2, 3, 4, 5
C)2, 4, 3, 1, 5
D)4, 2, 1, 3, 5
E)2, 4, 1, 3, 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Guard cells do which of the following?
A)protect the endodermis
B)accumulate K+ and close the stomata
C)contain chloroplasts that import K+ directly into the cells
D)guard against mineral loss through the stomata
E)help balance the photosynthesis-transpiration compromise
A)protect the endodermis
B)accumulate K+ and close the stomata
C)contain chloroplasts that import K+ directly into the cells
D)guard against mineral loss through the stomata
E)help balance the photosynthesis-transpiration compromise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is the driving force for the movement of materials in the phloem of plants?
A)gravity
B)a difference in osmotic water potential between the source and the sink.
C)root pressure
D)transpiration of water through the stomates
E)adhesion of water to phloem sieve tubes
A)gravity
B)a difference in osmotic water potential between the source and the sink.
C)root pressure
D)transpiration of water through the stomates
E)adhesion of water to phloem sieve tubes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Photosynthesis begins to decline when leaves wilt because
A)chloroplasts within wilted cells are incapable of photosynthesis.
B)CO2 accumulates in the leaves and inhibits the enzymes needed for photosynthesis.
C)there is insufficient water for photolysis during the light reactions.
D)stomata close, preventing CO2 entry into the leaf.
E)Wilted cells cannot absorb the red and blue wavelengths of light.
A)chloroplasts within wilted cells are incapable of photosynthesis.
B)CO2 accumulates in the leaves and inhibits the enzymes needed for photosynthesis.
C)there is insufficient water for photolysis during the light reactions.
D)stomata close, preventing CO2 entry into the leaf.
E)Wilted cells cannot absorb the red and blue wavelengths of light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Guard cells are the only cells in the epidermis that contain chloroplasts and can undergo photosynthesis. This is important because
A)chloroplasts sense when light is available so that guard cells will open.
B)photosynthesis provides the energy necessary for contractile proteins to flex and open the guard cells.
C)guard cells will produce the O2 necessary to power active transport.
D)ATP is required to power proton pumps in the guard cell membranes.
E)A and C
A)chloroplasts sense when light is available so that guard cells will open.
B)photosynthesis provides the energy necessary for contractile proteins to flex and open the guard cells.
C)guard cells will produce the O2 necessary to power active transport.
D)ATP is required to power proton pumps in the guard cell membranes.
E)A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following best explains why CAM plants are not tall?
A)They would be unable to move water and minerals to the top of the plant during the day.
B)They would be unable to supply sufficient sucrose for active transport of minerals into the roots during the day or night.
C)Transpiration occurs only at night, and this would cause a highly negative ¬ in the roots of a tall plant during the day.
D)Since the stomata are closed in the leaves, the Casparian strip is closed in the endodermis of the root.
E)With the stomata open at night, the transpiration rate would limit plant height.
A)They would be unable to move water and minerals to the top of the plant during the day.
B)They would be unable to supply sufficient sucrose for active transport of minerals into the roots during the day or night.
C)Transpiration occurs only at night, and this would cause a highly negative ¬ in the roots of a tall plant during the day.
D)Since the stomata are closed in the leaves, the Casparian strip is closed in the endodermis of the root.
E)With the stomata open at night, the transpiration rate would limit plant height.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Xylem vessels, found in angiosperms, have a much greater internal diameter than tracheids, the only xylem conducting cells found in gymnosperms. The tallest living trees, redwoods, are gymnosperms. Which of the following is an advantage of tracheids over vessels for long-distance transport to great heights?
A)Adhesive forces are proportionally greater in narrower cylinders than in wider cylinders.
B)The smaller the diameter of the xylem, the more likely cavitation will occur.
C)Cohesive forces are greater in narrow tubes than in wide tubes of the same height.
D)Only A and C are correct.
E)A, B, and C are correct.
A)Adhesive forces are proportionally greater in narrower cylinders than in wider cylinders.
B)The smaller the diameter of the xylem, the more likely cavitation will occur.
C)Cohesive forces are greater in narrow tubes than in wide tubes of the same height.
D)Only A and C are correct.
E)A, B, and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The opening of stomata is thought to involve
A)an increase in the osmotic concentration of the guard cells.
B)a decrease in the osmotic concentration of the stoma.
C)active transport of water out of the guard cells.
D)decreased turgor pressure in guard cells.
E)movement of K+ from the guard cells.
A)an increase in the osmotic concentration of the guard cells.
B)a decrease in the osmotic concentration of the stoma.
C)active transport of water out of the guard cells.
D)decreased turgor pressure in guard cells.
E)movement of K+ from the guard cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Water rises in plants primarily by the cohesion-tension model. Which of the following is not True about this model?
A)Water loss (transpiration)is the driving force for water movement.
B)The "tension" of this model represents the excitability of the xylem cells.
C)Cohesion represents the tendency for water molecules to stick together by hydrogen bonds.
D)The physical forces in the capillary-sized xylem cells make it easier to overcome gravity.
E)The water potential of the air is more negative than the xylem.
A)Water loss (transpiration)is the driving force for water movement.
B)The "tension" of this model represents the excitability of the xylem cells.
C)Cohesion represents the tendency for water molecules to stick together by hydrogen bonds.
D)The physical forces in the capillary-sized xylem cells make it easier to overcome gravity.
E)The water potential of the air is more negative than the xylem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
All of the following are adaptations that help reduce water loss from a plant except
A)transpiration.
B)sunken stomata.
C)C4 photosynthesis.
D)small, thick leaves.
E)crassulacean acid metabolism.
A)transpiration.
B)sunken stomata.
C)C4 photosynthesis.
D)small, thick leaves.
E)crassulacean acid metabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If the guard cells and surrounding epidermal cells in a plant are deficient in potassium ions, all of the following would occur except
A)photosynthesis would decrease.
B)roots would take up less water.
C)phloem transport rates would decrease.
D)leaf temperatures would decrease.
E)stomata would be closed.
A)photosynthesis would decrease.
B)roots would take up less water.
C)phloem transport rates would decrease.
D)leaf temperatures would decrease.
E)stomata would be closed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following experimental procedures would most likely reduce transpiration while allowing the normal growth of a plant?
A)subjecting the leaves of the plant to a partial vacuum
B)increasing the level of carbon dioxide around the plant
C)putting the plant in drier soil
D)decreasing the relative humidity around the plant
E)injecting potassium ions into the guard cells of the plant
A)subjecting the leaves of the plant to a partial vacuum
B)increasing the level of carbon dioxide around the plant
C)putting the plant in drier soil
D)decreasing the relative humidity around the plant
E)injecting potassium ions into the guard cells of the plant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Water can cross the cortex via the symplast or apoplast, but minerals moving via the apoplast must finally cross the selective membranes of endodermal cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A plant cell with a 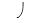 S of -0.65 MPa maintains a constant volume when bathed in a solution that has a
S of -0.65 MPa maintains a constant volume when bathed in a solution that has a 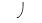 S of -0.30 MPa and is in an open container. The cell has a
S of -0.30 MPa and is in an open container. The cell has a
A)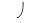 P of +0.65 MPa.
P of +0.65 MPa.
B)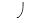 of -0.65 MPa.
of -0.65 MPa.
C)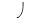 P of +0.35 MPa.
P of +0.35 MPa.
D)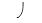 P of +0.30 MPa.
P of +0.30 MPa.
E)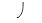 of 0 MPa.
of 0 MPa.
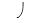 S of -0.65 MPa maintains a constant volume when bathed in a solution that has a
S of -0.65 MPa maintains a constant volume when bathed in a solution that has a 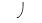 S of -0.30 MPa and is in an open container. The cell has a
S of -0.30 MPa and is in an open container. The cell has aA)
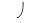 P of +0.65 MPa.
P of +0.65 MPa.B)
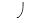 of -0.65 MPa.
of -0.65 MPa.C)
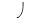 P of +0.35 MPa.
P of +0.35 MPa.D)
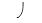 P of +0.30 MPa.
P of +0.30 MPa.E)
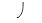 of 0 MPa.
of 0 MPa.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Photosynthesis ceases when leaves wilt, mainly because
A)the chlorophyll of wilting leaves breaks down.
B)flaccid mesophyll cells are incapable of photosynthesis.
C)stomata close, preventing CO2 from entering the leaf.
D)photolysis, the water-splitting step of photosynthesis, cannot occur when there is a water deficiency.
E)accumulation of CO2 in the leaf inhibits enzymes.
A)the chlorophyll of wilting leaves breaks down.
B)flaccid mesophyll cells are incapable of photosynthesis.
C)stomata close, preventing CO2 from entering the leaf.
D)photolysis, the water-splitting step of photosynthesis, cannot occur when there is a water deficiency.
E)accumulation of CO2 in the leaf inhibits enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following does not affect self-shading?
A)leaf area index
B)phyllotaxy
C)self-pruning
D)stem thickness
E)leaf orientation
A)leaf area index
B)phyllotaxy
C)self-pruning
D)stem thickness
E)leaf orientation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Plants do not have a circulatory system like that of some animals. If a given water molecule did "circulate" (that is, go from one point in a plant to another and back), it would require the activity of
A)only the xylem.
B)only the phloem.
C)only the endodermis.
D)both the xylem and the endodermis.
E)both the xylem and the phloem.
A)only the xylem.
B)only the phloem.
C)only the endodermis.
D)both the xylem and the endodermis.
E)both the xylem and the phloem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Water flows into the source end of a sieve tube because
A)sucrose has diffused into the sieve tube, making it hypertonic.
B)sucrose has been actively transported into the sieve tube, making it hypertonic.
C)water pressure outside the sieve tube forces in water.
D)the companion cell of a sieve tube actively pumps in water.
E)sucrose has been dumped from the sieve tube by active transport.
A)sucrose has diffused into the sieve tube, making it hypertonic.
B)sucrose has been actively transported into the sieve tube, making it hypertonic.
C)water pressure outside the sieve tube forces in water.
D)the companion cell of a sieve tube actively pumps in water.
E)sucrose has been dumped from the sieve tube by active transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When guard cells take up K+, they bow outward, widening the stomatal pore. Stomates close when K+ is actively transported out of the guard cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What would enhance water uptake by a plant cell?
A)decreased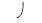 of the surrounding solution
of the surrounding solution
B)an increase in pressure exerted by the cell wall
C)the loss of solutes by the cell
D)an increase in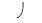 of the cytoplasm
of the cytoplasm
E)positive pressure on the surrounding solution
A)decreased
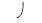 of the surrounding solution
of the surrounding solutionB)an increase in pressure exerted by the cell wall
C)the loss of solutes by the cell
D)an increase in
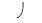 of the cytoplasm
of the cytoplasmE)positive pressure on the surrounding solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The apoplast is the cytoplasmic continuum linked by plasmodesmata. The symplast is the continuum of cell walls and extracellular spaces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
According to the pressure flow hypothesis of phloem transport,
A)solute moves from a high concentration in the "source" to a lower concentration in the "sink."
B)water is actively transported into the "source" region of the phloem to create the turgor pressure needed.
C)the combination of a high turgor pressure in the "source" and transpiration water loss from the "sink" moves solutes through phloem conduits.
D)the formation of starch from sugar in the "sink" increases the osmotic concentration.
E)the pressure in the phloem of a root is normally greater than the pressure in the phloem of a leaf.
A)solute moves from a high concentration in the "source" to a lower concentration in the "sink."
B)water is actively transported into the "source" region of the phloem to create the turgor pressure needed.
C)the combination of a high turgor pressure in the "source" and transpiration water loss from the "sink" moves solutes through phloem conduits.
D)the formation of starch from sugar in the "sink" increases the osmotic concentration.
E)the pressure in the phloem of a root is normally greater than the pressure in the phloem of a leaf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The xylem conducts nerve-like electrical signals that propagate through the apoplast and help to integrate whole plant function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The earliest land plants were nonvascular plants that grew leafless photosynthetic shoots above the shallow freshwater in which they lived.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Plasmodesmata can change in number, and when dilated can provide a passageway for macromolecules such as RNA and proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which structure or compartment is not part of the apoplast?
A)the lumen of a xylem vessel
B)the lumen of a sieve tube
C)the cell wall of a mesophyll cell
D)an extracellular air space
E)the cell wall of a root hair
A)the lumen of a xylem vessel
B)the lumen of a sieve tube
C)the cell wall of a mesophyll cell
D)an extracellular air space
E)the cell wall of a root hair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Transpiration raises water potential in the leaf by producing a positive pressure potential. This higher water potential draws water from the xylem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Long-distance electrical signaling in the phloem has been shown to elicit a change in all of the following except
A)rapid leaf movement
B)gene transcription
C)a switch from C4 to C3 photosynthesis
D)gene transcription
E)phloem unloading
A)rapid leaf movement
B)gene transcription
C)a switch from C4 to C3 photosynthesis
D)gene transcription
E)phloem unloading

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is an adaptation that enhances the uptake of water and minerals by roots?
A)mycorrhizae
B)cavitation
C)active uptake
D)rhythmic contraction by cortical cells
E)pumping through plasmodesmata
A)mycorrhizae
B)cavitation
C)active uptake
D)rhythmic contraction by cortical cells
E)pumping through plasmodesmata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Loading of sucrose at the source and unloading at the sink in angiosperms maintains a pressure difference that keeps sap flowing through the sieve tubes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following is not part of the transpiration-cohesion-tension mechanism for the ascent of xylem sap?
A)loss of water from the mesophyll cells, which initiates a pull of water molecules from neighboring cells
B)transfer of transpirational pull from one water molecule to the next, owing to cohesion by hydrogen bonds
C)hydrophilic walls of tracheids and vessels that help maintain the column of water against gravity
D)active pumping of water into the xylem of roots
E)lowering of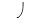 in the surface film of mesophyll cells due to transpiration
in the surface film of mesophyll cells due to transpiration
A)loss of water from the mesophyll cells, which initiates a pull of water molecules from neighboring cells
B)transfer of transpirational pull from one water molecule to the next, owing to cohesion by hydrogen bonds
C)hydrophilic walls of tracheids and vessels that help maintain the column of water against gravity
D)active pumping of water into the xylem of roots
E)lowering of
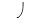 in the surface film of mesophyll cells due to transpiration
in the surface film of mesophyll cells due to transpiration
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which one of the following statements about transport of nutrients in phloem is False?
A)Solute particles can be actively transported into phloem at the source.
B)Companion cells control the rate and direction of movement of phloem sap.
C)Differences in osmotic concentration at the source and sink cause a hydrostatic pressure gradient to be formed.
D)A sink is that part of the plant where a particular solute is consumed or stored.
E)A sink may be located anywhere in the plant.
A)Solute particles can be actively transported into phloem at the source.
B)Companion cells control the rate and direction of movement of phloem sap.
C)Differences in osmotic concentration at the source and sink cause a hydrostatic pressure gradient to be formed.
D)A sink is that part of the plant where a particular solute is consumed or stored.
E)A sink may be located anywhere in the plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



