Deck 5: Market Power: Does It Help or Hurt the Economy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/93
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Market Power: Does It Help or Hurt the Economy
1
A monopolist's marginal revenue measures the marginal social benefit of selling an additional unit.
False
2
At the monopolist's profit maximizing level of output, price will exceed marginal revenue.
True
3
According to the marginal principle, profits are maximized when marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
False
4
Because the monopolist must lower price in order to sell more output, marginal revenue will be less than the demand price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A monopolist's profits will fall if output is increased when marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Economists object to monopoly because of the profits earned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Marginal revenue is the change in total revenue associated with a one-unit change in output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A monopolist will produce a greater level of output than a competitive industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
For a monopolist, price is greater than marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Technical conditions may create a natural monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
According to the marginal principle, a monopolist should increase output if marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Increased competition from foreign producers in the manufacturing sector has increased market power in the U. S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A monopolist is a price taker in the market place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A natural monopoly will exist if demand conditions are such that only one firm can survive in an industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The larger the number of firms, the easier it will be for an industry to form a cartel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Market power in the U. S. economy has decreased over the last 50 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A monopoly is an industry with only one seller of a good that has many close substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Market power in the U. S. has decreased as a result of increased foreign competition, deregulation, and the information revolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Most U.S. industries with market power are oligopolies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A monopolist's demand curve represents market demand for the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The desire to increase profits may cause firms to cheat on an agreement reached by a cartel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In a monopoly industry:
A) the firm is a price searcher.
B) the firm is a price taker.
C) markets are impersonal.
D) there are a large number of buyers and sellers.
A) the firm is a price searcher.
B) the firm is a price taker.
C) markets are impersonal.
D) there are a large number of buyers and sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The monopolist's demand curve:
A) slopes down and to the right.
B) is a horizontal line.
C) shows that the firm must increase price to sell more output.
D) slopes up and to the right.
A) slopes down and to the right.
B) is a horizontal line.
C) shows that the firm must increase price to sell more output.
D) slopes up and to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A monopoly is an industry composed of:
A) a few interdependent firms.
B) a large number of firms that produce a similar product.
C) a small number of firms that produce dissimilar products.
D) a single seller of a product that has no close substitutes.
A) a few interdependent firms.
B) a large number of firms that produce a similar product.
C) a small number of firms that produce dissimilar products.
D) a single seller of a product that has no close substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The benefit the monopolist receives when it produces and sells an additional unit of output is measured by:
A) the monopolist's demand price.
B) the monopolist's total revenue.
C) the monopolist's marginal revenue.
D) the monopolist's profit.
A) the monopolist's demand price.
B) the monopolist's total revenue.
C) the monopolist's marginal revenue.
D) the monopolist's profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose marginal cost currently exceeds marginal revenue. In order to maximize profits, the firm should:
A) decrease output.
B) increase output.
C) advertise more.
D) cease production.
A) decrease output.
B) increase output.
C) advertise more.
D) cease production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Relative to a competitive industry, a monopolist:
A) produces more output and charges a lower price.
B) produces less output and charges a higher price.
C) produces the same output and charges a higher price.
D) produces less output and charges a lower price.
A) produces more output and charges a lower price.
B) produces less output and charges a higher price.
C) produces the same output and charges a higher price.
D) produces less output and charges a lower price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose marginal revenue currently exceeds marginal cost. In order to maximize profits, the firm should:
A) decrease output.
B) increase output.
C) advertise less.
D) cease production.
A) decrease output.
B) increase output.
C) advertise less.
D) cease production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
According to the marginal principle, a monopoly firm maximizes profits as the point where:
A) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B) marginal revenue equals average cost.
C) marginal cost equals price.
D) demand price equals supply price.
A) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B) marginal revenue equals average cost.
C) marginal cost equals price.
D) demand price equals supply price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An oligopoly is an industry composed of:
A) a large number of firms that produce close substitutes.
B) a large number of firms that produce a no close substitutes.
C) a few producers or sellers of a good that recognize their interdependence.
D) a single seller of a product that has no close substitutes.
A) a large number of firms that produce close substitutes.
B) a large number of firms that produce a no close substitutes.
C) a few producers or sellers of a good that recognize their interdependence.
D) a single seller of a product that has no close substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Because the monopolist must lower price in order to sell additional units of output:
A) marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue.
B) demand price exceeds marginal revenue.
C) marginal cost exceeds demand price.
D) marginal revenue exceeds demand price.
A) marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue.
B) demand price exceeds marginal revenue.
C) marginal cost exceeds demand price.
D) marginal revenue exceeds demand price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Cartels are defined as:
A) a single seller of a product.
B) oil producers and exporters.
C) an organized group of firms that acts like a monopoly.
D) a large group of firms that exerts little influence in the market.
A) a single seller of a product.
B) oil producers and exporters.
C) an organized group of firms that acts like a monopoly.
D) a large group of firms that exerts little influence in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
To succeed, a cartel must restrict output and prevent entry of new firms. A successful cartel requires an ACE in the hole: agreement, cooperation, and enforcement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The less similar firms are, the easier it is to form a cartel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Many economists argue for the passage of additional antitrust laws because they believe that market power is a major problem in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) cartel had its biggest impact on oil prices in the 1970s and 1980s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Economists argue that government should not pass policies that would impede economic rent seeking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Marginal revenue is defined as:
A) the change in total revenue associated with a one-unit change in output.
B) total revenue minus total cost.
C) the profit associated with producing an additional unit of output.
D) the average revenue a firm receives per unit of output produced.
A) the change in total revenue associated with a one-unit change in output.
B) total revenue minus total cost.
C) the profit associated with producing an additional unit of output.
D) the average revenue a firm receives per unit of output produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When firms have high up-front costs, they can recover development costs only if they can price their successful products at monopoly levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A firm is said to have market power if:
A) it takes market price as given.
B) its actions affect market price.
C) its actions cause other firms to enter the industry.
D) it does not earn a loss.
A) it takes market price as given.
B) its actions affect market price.
C) its actions cause other firms to enter the industry.
D) it does not earn a loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Government may allow monopolies to exist in knowledge-based industries because:
A) of relatively low up-front costs.
B) of relatively high up-front costs.
C) of the fear of inferior products.
D) too much competition will result in allocative inefficiency.
A) of relatively low up-front costs.
B) of relatively high up-front costs.
C) of the fear of inferior products.
D) too much competition will result in allocative inefficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The existence of market power:
A) makes markets impersonal because the firms are so large.
B) gives consumers greater choice.
C) makes firms more responsive to consumer demand.
D) give consumers less choice.
A) makes markets impersonal because the firms are so large.
B) gives consumers greater choice.
C) makes firms more responsive to consumer demand.
D) give consumers less choice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Market power can be beneficial to the economy if:
A) it decreases entrepreneurial activity.
B) it encourages political rent seeking.
C) it encourages economic rent seeking.
D) it discourages ruinous competition.
A) it decreases entrepreneurial activity.
B) it encourages political rent seeking.
C) it encourages economic rent seeking.
D) it discourages ruinous competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
One of the reasons OPEC has lost market power since the 1960s is
A) there were high barriers to entry.
B) there were not high barriers to entry.
C) the search for knowledge is costly.
D) refinery production in the United States has declined.
A) there were high barriers to entry.
B) there were not high barriers to entry.
C) the search for knowledge is costly.
D) refinery production in the United States has declined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The increased competitiveness of the U.S. economy can be explained by:
A) competition from imports.
B) government deregulation.
C) the information revolution.
D) All of the above.
A) competition from imports.
B) government deregulation.
C) the information revolution.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A monopoly may be able to earn profits greater than a competitive firm because:
A) entry by new firms may be prevented.
B) government policies often ensure that certain industries such as utilities earn a guaranteed rate of return on their investment.
C) consumers are unaware of the existence of such profits and unwittingly pay the higher price.
D) The above statement is False. In the long run a monopoly earns the same profit as a competitive firm.
A) entry by new firms may be prevented.
B) government policies often ensure that certain industries such as utilities earn a guaranteed rate of return on their investment.
C) consumers are unaware of the existence of such profits and unwittingly pay the higher price.
D) The above statement is False. In the long run a monopoly earns the same profit as a competitive firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A cartel would most likely form if:
A) there are a small number of firms that have similar production costs.
B) there are a large number of firms that have similar production costs.
C) there are a small number of firms that have different costs of production.
D) there are a large number of firms that have different costs of production.
A) there are a small number of firms that have similar production costs.
B) there are a large number of firms that have similar production costs.
C) there are a small number of firms that have different costs of production.
D) there are a large number of firms that have different costs of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The efficient level of output occurs when:
A) a monopolist is maximizing profits.
B) marginal social benefit exceeds marginal social cost.
C) marginal social cost exceeds marginal social benefit.
D) marginal social benefit equals marginal social cost.
A) a monopolist is maximizing profits.
B) marginal social benefit exceeds marginal social cost.
C) marginal social cost exceeds marginal social benefit.
D) marginal social benefit equals marginal social cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is not a source of market power in the United States?
A) low barriers to entry.
B) the cost advantages existing firms may have over potential new firms.
C) technical conditions of production.
D) a single firm having exclusive access to an essential input.
A) low barriers to entry.
B) the cost advantages existing firms may have over potential new firms.
C) technical conditions of production.
D) a single firm having exclusive access to an essential input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is a source of market power in the United States?
A) low barriers to entry.
B) competition from foreign firms.
C) technical conditions.
D) the existence of a large number of substitute goods.
A) low barriers to entry.
B) competition from foreign firms.
C) technical conditions.
D) the existence of a large number of substitute goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The problems encountered by the OPEC cartel can be explained by:
A) relatively high barriers to entry existing in the petroleum industry.
B) the fact that most OPEC producers had similar levels of reserves.
C) the small number of producers who made up the cartel having the same objectives.
D) the fact that OPEC did not have significant barriers to entry for new producers.
A) relatively high barriers to entry existing in the petroleum industry.
B) the fact that most OPEC producers had similar levels of reserves.
C) the small number of producers who made up the cartel having the same objectives.
D) the fact that OPEC did not have significant barriers to entry for new producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When a monopolist is maximizing profits:
A) marginal social benefit and marginal social cost are equal.
B) marginal social cost exceeds marginal social benefit.
C) output level is less than the efficient level of output.
D) no potential gains from trade exist.
A) marginal social benefit and marginal social cost are equal.
B) marginal social cost exceeds marginal social benefit.
C) output level is less than the efficient level of output.
D) no potential gains from trade exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The existence of market power in an industry implies that:
A) government should enact regulations to make the industry more competitive.
B) consumers should form consumer protection groups to offset the market power in the industry.
C) government should provide subsidies to encourage firms to enter the industry. As the number of firms increases market power will decline.
D) price is greater than marginal cost.
A) government should enact regulations to make the industry more competitive.
B) consumers should form consumer protection groups to offset the market power in the industry.
C) government should provide subsidies to encourage firms to enter the industry. As the number of firms increases market power will decline.
D) price is greater than marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Government encourages market power when it:
A) promotes international trade.
B) restricts imports.
C) enacts antitrust legislation.
D) eliminates licensing systems.
A) promotes international trade.
B) restricts imports.
C) enacts antitrust legislation.
D) eliminates licensing systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Cartel members have an incentive to cheat by:
A) lowering price and selling less output.
B) lowering price and selling more output.
C) raising price and selling less output.
D) raising price and selling more output.
A) lowering price and selling less output.
B) lowering price and selling more output.
C) raising price and selling less output.
D) raising price and selling more output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A likely source of market power in the United States is:
A) the explicit cooperation of firms on price and output decisions.
B) government licensing and regulations.
C) multiple firms having control over a vital input.
D) voluntary export restrictions.
A) the explicit cooperation of firms on price and output decisions.
B) government licensing and regulations.
C) multiple firms having control over a vital input.
D) voluntary export restrictions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When demand and cost conditions are such that only one firm can exist in an industry:
A) government must enact regulations to protect consumers and ensure competition.
B) production costs could be decreased if government were to divide the single firm into several smaller firms.
C) efficiency will be increased by dividing the single firm into several smaller firms.
D) a natural monopoly is said to exist.
A) government must enact regulations to protect consumers and ensure competition.
B) production costs could be decreased if government were to divide the single firm into several smaller firms.
C) efficiency will be increased by dividing the single firm into several smaller firms.
D) a natural monopoly is said to exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Government might grant patents in order to:
A) increase private-sector research.
B) enhance competition.
C) decrease market power.
D) ensure that politicians are re-elected to office.
A) increase private-sector research.
B) enhance competition.
C) decrease market power.
D) ensure that politicians are re-elected to office.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following would contribute to the break-up of a cartel?
A) There are a small number of firms.
B) The firms produce a similar product.
C) The firms' desire to increase their profits.
D) The firms have similar production costs.
A) There are a small number of firms.
B) The firms produce a similar product.
C) The firms' desire to increase their profits.
D) The firms have similar production costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Although cartels can increase the profits of their members, they are often difficult to maintain for extended periods of time because:
A) consumer pressure often forces cartels to disband.
B) managers realize that while the cartel increases profits in the short run, profits in the long run will be lower because of cartel activity.
C) there is an incentive for each member to further increase its profits by cheating on the cartel agreement.
D) producers may not understand the benefits of maintaining the cartel.
A) consumer pressure often forces cartels to disband.
B) managers realize that while the cartel increases profits in the short run, profits in the long run will be lower because of cartel activity.
C) there is an incentive for each member to further increase its profits by cheating on the cartel agreement.
D) producers may not understand the benefits of maintaining the cartel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.
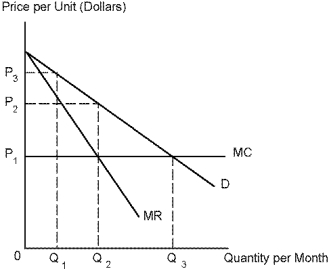
Refer to Diagram 5-1. If a competitive firm were currently producing output at Q₃, we know that:
A) profits are being maximized.
B) increasing output would increase profits.
C) decreasing output would increase profits.
D) there should be no change in output.

Refer to Diagram 5-1. If a competitive firm were currently producing output at Q₃, we know that:
A) profits are being maximized.
B) increasing output would increase profits.
C) decreasing output would increase profits.
D) there should be no change in output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Suppose a monopolist is currently producing at a point where marginal revenue is $20 and marginal cost is $25. This monopolist should:
A) decrease output in order to increase profits.
B) increase output in order to increase profits.
C) make no change in output. It is maximizing profits at its current level of production.
D) advertise less. This would cut its costs and bring it to a profit maximizing position.
A) decrease output in order to increase profits.
B) increase output in order to increase profits.
C) make no change in output. It is maximizing profits at its current level of production.
D) advertise less. This would cut its costs and bring it to a profit maximizing position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
For a monopolist, marginal revenue is less than demand price because:
A) the firm must take the market price as given.
B) the firm must raise price in order to sell additional units of output.
C) the firm must lower price in order to sell additional units of output.
D) the firm cannot raise price too much or additional firms will be attracted to the industry.
A) the firm must take the market price as given.
B) the firm must raise price in order to sell additional units of output.
C) the firm must lower price in order to sell additional units of output.
D) the firm cannot raise price too much or additional firms will be attracted to the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Diagram 5-1. If the firm were currently producing output level Q₁, we know that:
A) marginal revenue would exceed marginal cost.
B) marginal cost would exceed marginal revenue.
C) marginal revenue and marginal cost would be equal.
D) demand price and marginal revenue would be equal.

Refer to Diagram 5-1. If the firm were currently producing output level Q₁, we know that:
A) marginal revenue would exceed marginal cost.
B) marginal cost would exceed marginal revenue.
C) marginal revenue and marginal cost would be equal.
D) demand price and marginal revenue would be equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.
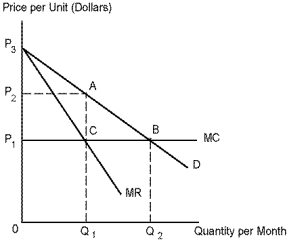
Refer to Diagram 5-2. The price and output that maximize the monopolist's profits are:
A) P₁ and Q₁, respectively.
B) P₁ and Q₂, respectively.
C) P₂ and Q₁, respectively.
D) P₂ and Q₂, respectively.

Refer to Diagram 5-2. The price and output that maximize the monopolist's profits are:
A) P₁ and Q₁, respectively.
B) P₁ and Q₂, respectively.
C) P₂ and Q₁, respectively.
D) P₂ and Q₂, respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose a monopolist is currently producing at a point where marginal revenue is $25 and marginal cost is $18. This monopolist should:
A) decrease output in order to increase profits.
B) increase output in order to increase profits.
C) advertise more to encourage consumers to buy more of the product.
D) cease production to cut its losses.
A) decrease output in order to increase profits.
B) increase output in order to increase profits.
C) advertise more to encourage consumers to buy more of the product.
D) cease production to cut its losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the 1980s Japanese automakers were successful in U.S. markets because:
A) U.S. management and production methods had become obsolete.
B) U.S. consumers were unwilling to buy foreign autos.
C) The U.S. government placed high tariffs on all foreign imports.
D) U.S cars were higher quality.
A) U.S. management and production methods had become obsolete.
B) U.S. consumers were unwilling to buy foreign autos.
C) The U.S. government placed high tariffs on all foreign imports.
D) U.S cars were higher quality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Diagram 5-2. The monopolist's profits are given by area:
A) P₁P₂AC.
B) OP₁CQ₁.
C) P₁P3AC.
D) P₁P3B.

Refer to Diagram 5-2. The monopolist's profits are given by area:
A) P₁P₂AC.
B) OP₁CQ₁.
C) P₁P3AC.
D) P₁P3B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Diagram 5-2. The price and output that would emerge under a competitive industry are:
A) P₁ and Q₁, respectively.
B) P₁ and Q₂, respectively.
C) P₂ and Q₁, respectively.
D) P₂ and Q₂, respectively.

Refer to Diagram 5-2. The price and output that would emerge under a competitive industry are:
A) P₁ and Q₁, respectively.
B) P₁ and Q₂, respectively.
C) P₂ and Q₁, respectively.
D) P₂ and Q₂, respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose Kris Kraf, a monopolist is producing the profit-maximizing level of output. At this level of output we know that:
A) marginal revenue and marginal social benefit are equal.
B) marginal revenue exceeds marginal social benefit.
C) marginal social benefit exceeds marginal revenue.
D) marginal revenue exceeds price.
A) marginal revenue and marginal social benefit are equal.
B) marginal revenue exceeds marginal social benefit.
C) marginal social benefit exceeds marginal revenue.
D) marginal revenue exceeds price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Diagram 5-1. A competitive industry would charge what price and produce what level of output?
A) P₁ and Q₁, respectively.
B) P₂ and Q₂, respectively.
C) P₁ and Q₂, respectively.
D) P₁ and Q3, respectively.

Refer to Diagram 5-1. A competitive industry would charge what price and produce what level of output?
A) P₁ and Q₁, respectively.
B) P₂ and Q₂, respectively.
C) P₁ and Q₂, respectively.
D) P₁ and Q3, respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following methods does the U.S. government use to reduce market power?
A) The provision of patents
B) Anti-trust law
C) The requirement of licensing in various occupational areas
D) The provision of monopoly grants
A) The provision of patents
B) Anti-trust law
C) The requirement of licensing in various occupational areas
D) The provision of monopoly grants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
We should not tax windfall profits of U.S. oil refineries because
A) taxes would discourage future investment in capacity.
B) monopoly profits are necessary to motivate continued adaptation in production to an ever changing industry.
C) political decisions on taxation are driven by political benefits rather than market outcomes.
D) All of the above are possible explanations.
A) taxes would discourage future investment in capacity.
B) monopoly profits are necessary to motivate continued adaptation in production to an ever changing industry.
C) political decisions on taxation are driven by political benefits rather than market outcomes.
D) All of the above are possible explanations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Use the following information to answer the following questions.

Refer to Pharmaceuticals. The total revenue associated with selling 3 units of pharmaceuticals is:
A) $120.
B) $90.
C) $50.
D) $45.

Refer to Pharmaceuticals. The total revenue associated with selling 3 units of pharmaceuticals is:
A) $120.
B) $90.
C) $50.
D) $45.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the following information to answer the following questions.

Refer to Pharmaceuticals. The marginal revenue associated with the second unit of pharmaceuticals is:
A) $120.
B) $90.
C) $50.
D) $45.

Refer to Pharmaceuticals. The marginal revenue associated with the second unit of pharmaceuticals is:
A) $120.
B) $90.
C) $50.
D) $45.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Suppose the Ding-Dong Doorbell Co., a monopoly, finds that at current production levels marginal revenue is $15 while marginal cost is $10. This company should:
A) make no change in present production level.
B) without further information on average production cost there is no way to determine what actions the company should take.
C) decrease production, as this will allow price and marginal revenue to increase, thereby increasing profits.
D) increase output as this will result in higher profits.
A) make no change in present production level.
B) without further information on average production cost there is no way to determine what actions the company should take.
C) decrease production, as this will allow price and marginal revenue to increase, thereby increasing profits.
D) increase output as this will result in higher profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Suppose We Are Unique Corporation, a monopoly, finds that at its current production levels marginal revenue is $18 while marginal cost if $20. This company should:
A) make no change in present production level.
B) without further information on average production cost there is no way to determine what actions the company should take.
C) decrease production, as this will allow price and marginal revenue to increase, thereby increasing profits.
D) increase output as this will result in higher profits.
A) make no change in present production level.
B) without further information on average production cost there is no way to determine what actions the company should take.
C) decrease production, as this will allow price and marginal revenue to increase, thereby increasing profits.
D) increase output as this will result in higher profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Stuff-It Corporation is the sole producer of Trindles, a new toy. Stuff-It would be an example of:
A) a cartel.
B) a monopoly.
C) an oligopoly.
D) a competitive firm.
A) a cartel.
B) a monopoly.
C) an oligopoly.
D) a competitive firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Diagram 5-1. What level of output should the monopolist produce?
A) Q₁.
B) Q₂.
C) Q3.
D) Output should be between Q₂ and Q3, depending upon the level of market power the firm has.

Refer to Diagram 5-1. What level of output should the monopolist produce?
A) Q₁.
B) Q₂.
C) Q3.
D) Output should be between Q₂ and Q3, depending upon the level of market power the firm has.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Diagram 5-1. What price should the monopolist charge?
A) P₁.
B) P₂.
C) P3.
D) a price between P₁ and P₂.

Refer to Diagram 5-1. What price should the monopolist charge?
A) P₁.
B) P₂.
C) P3.
D) a price between P₁ and P₂.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



