Deck 6: Air Pollution: Balancing Benefits and Costs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/85
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Air Pollution: Balancing Benefits and Costs
1
NAAQSs set lower limits for permissible concentrations of six common air pollutants.
False
2
The Coase theorem argues that government must correct market failures through the use of extensive regulations.
False
3
When external costs exist the market outcome will generally be inefficient.
True
4
Improved air quality results in improved health and visibility, reduced soiling and cleaning costs, and reduced damage to vegetation, materials, and structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The efficient level of pollution will generally be greater than zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If a resource is a common property resource, clear property rights exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If the market is producing where marginal social cost exceeds marginal social benefit, there will be a net loss to society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Global warming is caused by the accumulation of greenhouse gases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The provisions of the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990 that are designed to achieve ground-level ozone standards probably imposes a net loss on society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Measurements taken to date show no significant decrease in the ozone layer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
On a nationwide basis, many areas of the country still do not meet the NAAQS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When a marginal external cost exists, the market produces an amount that is greater than the efficient amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An offset is a regulation that allows a unit to contain several sources of pollution and be evaluated according to the total emissions it produces rather than by emissions produced by each source.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
While economists acknowledge that the use of an emissions tax can bring about the efficient level of pollution, they generally agree that regulation is a less costly method of achieving this goal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Reduction in stratospheric ozone could cause global warming to occur at a faster pace.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The Clean Air Act places restrictions on technologies that can be used to achieve air standards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Emissions reduction credits can be sold to firms seeking an offset for new sources of emission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Emissions taxes help to achieve the efficient level of production by forcing firms to bear the cost of pollution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
For a competitive industry, the marginal cost curve is also its demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Urban air quality is measured in terms of atmospheric concentrations of six common air pollutants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A common property resource is:
A) a resource that belongs exclusively to one individual.
B) a resource that has clearly identifiable property rights.
C) a resource that one individual allows another to use.
D) a resource that belongs to all.
A) a resource that belongs exclusively to one individual.
B) a resource that has clearly identifiable property rights.
C) a resource that one individual allows another to use.
D) a resource that belongs to all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
According to Ronald Coase:
A) pollution can be controlled by using the appropriate government regulations.
B) efficient levels of production could occur regardless of who receives property rights.
C) efficient levels of production will occur only if property rights are assigned to non-polluters.
D) regulations could be made more efficient by eliminating technology restrictions.
A) pollution can be controlled by using the appropriate government regulations.
B) efficient levels of production could occur regardless of who receives property rights.
C) efficient levels of production will occur only if property rights are assigned to non-polluters.
D) regulations could be made more efficient by eliminating technology restrictions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The costs of pollution are known as:
A) marginal social cost.
B) marginal cost.
C) marginal external cost.
D) marginal common property cost.
A) marginal social cost.
B) marginal cost.
C) marginal external cost.
D) marginal common property cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A marginal external cost is:
A) the cost associated with producing an additional unit of a product.
B) the cost of producing an additional unit of a product that accrues to a third party who is not involved in producing or consuming the product.
C) the cost imposed on society by the production of an additional unit of a product.
D) the cost imposed on consumers by the production of an additional unit of a product.
A) the cost associated with producing an additional unit of a product.
B) the cost of producing an additional unit of a product that accrues to a third party who is not involved in producing or consuming the product.
C) the cost imposed on society by the production of an additional unit of a product.
D) the cost imposed on consumers by the production of an additional unit of a product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The Clean Air Act has had an impact on:
A) visibility.
B) health.
C) damage to structures.
D) All of the above.
A) visibility.
B) health.
C) damage to structures.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Environmental regulation has likely caused:
A) the level of GDP to be greater than it would in the absence of such regulation.
B) the level of GDP to be less than it would in the absence of such regulation.
C) the level of GDP to be unaffected by such regulation.
D) air quality to fall relative to what would exist in the absence of such regulation.
A) the level of GDP to be greater than it would in the absence of such regulation.
B) the level of GDP to be less than it would in the absence of such regulation.
C) the level of GDP to be unaffected by such regulation.
D) air quality to fall relative to what would exist in the absence of such regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Under a system of marketable pollution permits, each firm would be issued a fixed number of permits. These could not be traded among firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) targeted 189 chemicals for regulation in the Clean Air Act of 1990. The primary impetus for these regulations:
A) is evidence that these chemicals impair domesticated animal health.
B) is evidence that these chemicals have detrimental impact on agriculture.
C) is evidence that these chemicals impair human health, especially in the form of central nervous system damage and cancer.
D) is evidence that these chemicals deplete the ozone.
A) is evidence that these chemicals impair domesticated animal health.
B) is evidence that these chemicals have detrimental impact on agriculture.
C) is evidence that these chemicals impair human health, especially in the form of central nervous system damage and cancer.
D) is evidence that these chemicals deplete the ozone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Electrical generating plants contribute to a sulfuric acid solution known as:
A) nitrogen oxide.
B) sulfur dioxide.
C) acid rain.
D) a volatile organic compound.
A) nitrogen oxide.
B) sulfur dioxide.
C) acid rain.
D) a volatile organic compound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The Environmental Protection Agency has authority to:
A) set emission limits.
B) specify the type of technology that can be used to achieve emissions standards.
C) regulate toxic pollutants.
D) All of the above.
A) set emission limits.
B) specify the type of technology that can be used to achieve emissions standards.
C) regulate toxic pollutants.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Offset requirements refer to the requirements that:
A) gasoline stations in non-attainment carbon monoxide zones must offset pollutants by using oxygenated gasoline.
B) areas that have not attained ozone and carbon monoxide standards can permit new pollution sources only by reducing pollutants from existing sources.
C) areas that have not attained ozone and carbon monoxide standards must offset pollutants by using state-of-the-art technologies for new emissions sources.
D) the Environmental Protection Agency set national ambient air quality standards (NAAQSs) in order to offset pollutants.
A) gasoline stations in non-attainment carbon monoxide zones must offset pollutants by using oxygenated gasoline.
B) areas that have not attained ozone and carbon monoxide standards can permit new pollution sources only by reducing pollutants from existing sources.
C) areas that have not attained ozone and carbon monoxide standards must offset pollutants by using state-of-the-art technologies for new emissions sources.
D) the Environmental Protection Agency set national ambient air quality standards (NAAQSs) in order to offset pollutants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is the most important problem related to air pollution?
A) ozone depletion.
B) the manner in which nuclear wastes are being disposed of.
C) poor quality of air in non-urban areas.
D) non-hazardous air pollutants.
A) ozone depletion.
B) the manner in which nuclear wastes are being disposed of.
C) poor quality of air in non-urban areas.
D) non-hazardous air pollutants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The efficient level of pollution:
A) is usually zero.
B) will usually be some amount greater than zero.
C) occurs when marginal cost and marginal benefit are equal.
D) occurs when marginal social cost is less than marginal social benefit.
A) is usually zero.
B) will usually be some amount greater than zero.
C) occurs when marginal cost and marginal benefit are equal.
D) occurs when marginal social cost is less than marginal social benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Instead of controlling pollutants through the use of regulation, government could use taxes or create marketable pollution permits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The main culprit in global warming is:
A) ozone.
B) sulfuric acid.
C) sulfur dioxide.
D) carbon dioxide.
A) ozone.
B) sulfuric acid.
C) sulfur dioxide.
D) carbon dioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following would most likely lead to excessively high costs of pollution regulation?
A) excise taxes.
B) the use of regulations.
C) the use of marketable pollution permits.
D) the use of emissions taxes.
A) excise taxes.
B) the use of regulations.
C) the use of marketable pollution permits.
D) the use of emissions taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
As a result of pollution:
A) marginal social cost exceeds marginal cost.
B) marginal cost exceeds marginal social cost.
C) marginal external cost exceeds marginal social cost.
D) marginal social cost exceeds marginal external cost.
A) marginal social cost exceeds marginal cost.
B) marginal cost exceeds marginal social cost.
C) marginal external cost exceeds marginal social cost.
D) marginal social cost exceeds marginal external cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The warming of the Earth's surface caused by burning fossil fuels and clearing land is known as:
A) ozone depletion.
B) global warming.
C) a greenhouse gas.
D) a volatile organic chain reaction.
A) ozone depletion.
B) global warming.
C) a greenhouse gas.
D) a volatile organic chain reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In a market economy the amount of pollution is:
A) likely to be greater than the efficient amount because polluters do not bear the full costs of pollution.
B) likely to be the efficient amount because in general the price system causes production to be carried out to the point where quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal.
C) likely to be less than the efficient amount because the government regulations designed to reduce pollution increase firms' production costs causing them to decrease output.
D) is likely to be the efficient amount due to the regulatory powers of agencies like the Environmental Protection Agency.
A) likely to be greater than the efficient amount because polluters do not bear the full costs of pollution.
B) likely to be the efficient amount because in general the price system causes production to be carried out to the point where quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal.
C) likely to be less than the efficient amount because the government regulations designed to reduce pollution increase firms' production costs causing them to decrease output.
D) is likely to be the efficient amount due to the regulatory powers of agencies like the Environmental Protection Agency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) believes that the Clean Air Act:
A) imposes costs on society that are greater than the benefits receive.
B) gives society benefits that are greater than the costs imposed.
C) imposes equal costs and benefits on society.
D) has not provided any benefit to society.
A) imposes costs on society that are greater than the benefits receive.
B) gives society benefits that are greater than the costs imposed.
C) imposes equal costs and benefits on society.
D) has not provided any benefit to society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
First Rate Corporation emits airborne pollutants in connection with the production of its product. If there is no government regulation, it is likely that the amount of pollutants emitted by the corporation will be:
A) the efficient amount.
B) less than the efficient amount.
C) greater than the efficient amount.
D) this judgment cannot be made without further information.
A) the efficient amount.
B) less than the efficient amount.
C) greater than the efficient amount.
D) this judgment cannot be made without further information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Pig Pen Industries is currently producing 5000 tons of paper per day. At this level of production, marginal social costs are $10 per ton while marginal social benefits are $12 per ton. We know that Pig Pen:
A) is producing efficiently.
B) is producing an amount less than the efficient amount.
C) is producing an amount greater than the efficient amount.
D) could increase net benefits for society by increasing production.
A) is producing efficiently.
B) is producing an amount less than the efficient amount.
C) is producing an amount greater than the efficient amount.
D) could increase net benefits for society by increasing production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which statement is true?
A) The Kyoto Protocol will force less-developed countries to reduce emissions.
B) The Kyoto Protocol will not be financially difficult for developed countries like the United States.
C) An international agreement on emission permit trading would have no noticeable impact on the cost associated with the Kyoto Protocol.
D) Some estimates show that GDP in 2010 in the United States could be as much as 5% lower as a result of the changes required to achieve the Kyoto target.
A) The Kyoto Protocol will force less-developed countries to reduce emissions.
B) The Kyoto Protocol will not be financially difficult for developed countries like the United States.
C) An international agreement on emission permit trading would have no noticeable impact on the cost associated with the Kyoto Protocol.
D) Some estimates show that GDP in 2010 in the United States could be as much as 5% lower as a result of the changes required to achieve the Kyoto target.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.
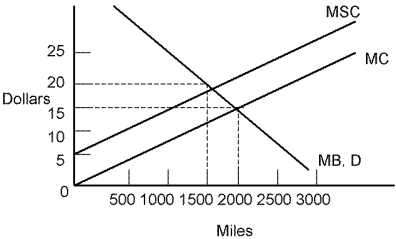
Refer to Miles. Suppose individuals are currently traveling 2,000 miles. The marginal external cost is:
A) $20
B) $15
C) $10
D) $5

Refer to Miles. Suppose individuals are currently traveling 2,000 miles. The marginal external cost is:
A) $20
B) $15
C) $10
D) $5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose that at current production levels, Big Dog Inc. estimates its marginal cost to be $25, its marginal external cost to be $10, and its marginal social benefit to be $35. In this case, the corporation:
A) is imposing too much harm on the environment and should cut back production.
B) is producing the efficient amount.
C) is producing an amount less than the efficient amount.
D) could make society better off by decreasing production.
A) is imposing too much harm on the environment and should cut back production.
B) is producing the efficient amount.
C) is producing an amount less than the efficient amount.
D) could make society better off by decreasing production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The costs of environmental regulation could be reduced without reducing environmental quality by:
A) increasing the use of marketable emissions permits.
B) relying less on pollution taxes.
C) enacting stricter environmental regulations.
D) using technology forcing.
A) increasing the use of marketable emissions permits.
B) relying less on pollution taxes.
C) enacting stricter environmental regulations.
D) using technology forcing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An emissions tax can bring about an efficient solution to the pollution problem because it:
A) forces firms to bear the full cost of the tax.
B) forces both firms and households to bear the full cost of their decisions.
C) eliminates the external cost associated with pollution.
D) allows government agencies to use benefit-cost analysis to determine the efficient level of pollution.
A) forces firms to bear the full cost of the tax.
B) forces both firms and households to bear the full cost of their decisions.
C) eliminates the external cost associated with pollution.
D) allows government agencies to use benefit-cost analysis to determine the efficient level of pollution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Suppose that at current production levels, A Major Corporation's marginal cost is $15, its marginal external cost is $5, and the marginal social benefit of production is $25. In this case, the corporation:
A) is imposing too much harm on the environment and should cut back production.
B) is producing the efficient amount.
C) is producing an amount less than the efficient amount.
D) could make society better off by decreasing production.
A) is imposing too much harm on the environment and should cut back production.
B) is producing the efficient amount.
C) is producing an amount less than the efficient amount.
D) could make society better off by decreasing production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following have economists suggested as alternatives to regulating pollution?
A) the assignment of property rights.
B) an emissions tax.
C) the creation of a market for pollution permits.
D) All of the above.
A) the assignment of property rights.
B) an emissions tax.
C) the creation of a market for pollution permits.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The Kyoto Protocol is an agreement designed to reduce international emissions of:
A) carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas.
B) sulfate, the source of acid rain.
C) chlorofluorocarbons, which damage ozone in the earth's stratosphere.
D) all hazardous air pollutants.
A) carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas.
B) sulfate, the source of acid rain.
C) chlorofluorocarbons, which damage ozone in the earth's stratosphere.
D) all hazardous air pollutants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Miles. Suppose individuals are currently traveling at the efficient level of 1,500 miles. The level of pollution would be:
A) greater than zero.
B) zero.
C) less than zero.
D) inefficient.

Refer to Miles. Suppose individuals are currently traveling at the efficient level of 1,500 miles. The level of pollution would be:
A) greater than zero.
B) zero.
C) less than zero.
D) inefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is not an external cost attributed to the automobile?
A) air pollution
B) congestion
C) noise
D) purchase price of gasoline
A) air pollution
B) congestion
C) noise
D) purchase price of gasoline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Miles. In the absence of any government regulation individuals will travel:
A) 1,000 miles.
B) 1,500 miles.
C) 2,000 miles.
D) between 1,500 and 2,000 miles.

Refer to Miles. In the absence of any government regulation individuals will travel:
A) 1,000 miles.
B) 1,500 miles.
C) 2,000 miles.
D) between 1,500 and 2,000 miles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
ZAPCO Refinery is currently producing 100,000 barrels of refined oil per day. The marginal cost of this production is $40 per barrel and the marginal external cost is $30 per barrel. Suppose the marginal social benefit is $65 per barrel. In this case, ZAPCO is:
A) imposing too much harm on the environment and should cut back production.
B) is producing an efficient amount.
C) is producing an amount less than the efficient amount.
D) could make society better off by increasing production.
A) imposing too much harm on the environment and should cut back production.
B) is producing an efficient amount.
C) is producing an amount less than the efficient amount.
D) could make society better off by increasing production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Higher energy prices:
A) could trigger rising GDP and falling unemployment.
B) could trigger falling GDP and rising unemployment.
C) could leave the GDP unaffected.
D) could trigger higher consumption of energy.
A) could trigger rising GDP and falling unemployment.
B) could trigger falling GDP and rising unemployment.
C) could leave the GDP unaffected.
D) could trigger higher consumption of energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Miles. The efficient number of miles for individuals to travel is:
A) 1,000 miles.
B) 1,500 miles.
C) 2,000 miles.
D) anything over 500 miles.

Refer to Miles. The efficient number of miles for individuals to travel is:
A) 1,000 miles.
B) 1,500 miles.
C) 2,000 miles.
D) anything over 500 miles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose that in the process of production, Energy Incorporated emits large amounts of sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere. This is an example of:
A) a marginal social cost.
B) a marginal cost.
C) a marginal external cost.
D) a private external cost.
A) a marginal social cost.
B) a marginal cost.
C) a marginal external cost.
D) a private external cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A common property resource is a resource that:
A) is owned by the government in a command economy.
B) is owned by taxpayers in a market economy, but administered by government.
C) is the property of all individuals.
D) crosses the boundary of two or more landowners.
A) is owned by the government in a command economy.
B) is owned by taxpayers in a market economy, but administered by government.
C) is the property of all individuals.
D) crosses the boundary of two or more landowners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is not a way economists have suggested for imposing the external costs of driving on consumers?
A) higher gasoline taxes
B) uniform mileage limitations
C) congestion pricing
D) parking cash-outs
A) higher gasoline taxes
B) uniform mileage limitations
C) congestion pricing
D) parking cash-outs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is an example of a marginal external cost?
A) A patron of McDonald's is burned when coffee is spilled on their lap.
B) A firm's production costs increase because government regulations force it to provide more employee health benefits.
C) The people who fish in a river find their catch decreasing because pollution from a factory is killing the fish.
D) The price a corporation must pay for pollution control devices such as scrubbers.
A) A patron of McDonald's is burned when coffee is spilled on their lap.
B) A firm's production costs increase because government regulations force it to provide more employee health benefits.
C) The people who fish in a river find their catch decreasing because pollution from a factory is killing the fish.
D) The price a corporation must pay for pollution control devices such as scrubbers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.
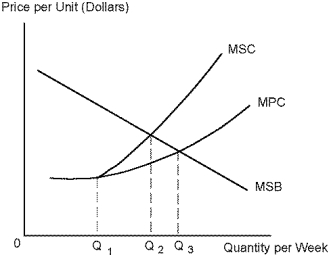
Refer to Diagram 6-1. The efficient output occurs at:
A) Q₁.
B) Q₂.
C) Q3.
D) between Q₁ and Q₂.

Refer to Diagram 6-1. The efficient output occurs at:
A) Q₁.
B) Q₂.
C) Q3.
D) between Q₁ and Q₂.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Suppose that at current consumption levels, the marginal social cost of using the Los Angeles freeway system is $25 while the marginal social benefit is $15. In this instance, government officials should:
A) take actions to decrease use of the freeway system.
B) take actions to increase use of the freeway system.
C) take no actions to change use of the freeway system.
D) build more freeways.
A) take actions to decrease use of the freeway system.
B) take actions to increase use of the freeway system.
C) take no actions to change use of the freeway system.
D) build more freeways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Evaluate the following statement. "Instead of controlling pollutants through regulation, the government should simply assign property rights."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.
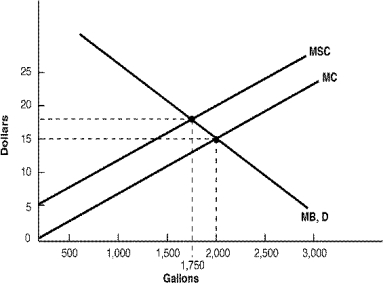
Refer to Gallons. Suppose that the production level was at 2,000 gallons where MC=MB. What would be the maximum amount that consumers would pay producers to reduce production (and pollution)?
A) $2 per gallon.
B) $12.50 per gallon.
C) $1.50 per gallon.
D) $5 per gallon.

Refer to Gallons. Suppose that the production level was at 2,000 gallons where MC=MB. What would be the maximum amount that consumers would pay producers to reduce production (and pollution)?
A) $2 per gallon.
B) $12.50 per gallon.
C) $1.50 per gallon.
D) $5 per gallon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Gallons. The external cost associated with the production of each gallon of output is:
A) $5.
B) $15.
C) $2.
D) $3.

Refer to Gallons. The external cost associated with the production of each gallon of output is:
A) $5.
B) $15.
C) $2.
D) $3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose two firms have different marginal costs of emission control. Would a governmental policy that allotted marketable pollution permits be more cost effective than a governmental policy that required all firms to reduce emissions by the same amount?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following statements is true about the marketable pollution permits?
A) All parties engaged in trading of marketable pollution permits become as well off or better off from trade, except the government.
B) All parties engaged in trading of marketable pollution permits become as well off or better off from trade, including the government.
C) Sellers engaged in trading of marketable pollution permits become worse off from trade.
D) Buyers engaged in trading of marketable pollution permits become worse off from trade.
A) All parties engaged in trading of marketable pollution permits become as well off or better off from trade, except the government.
B) All parties engaged in trading of marketable pollution permits become as well off or better off from trade, including the government.
C) Sellers engaged in trading of marketable pollution permits become worse off from trade.
D) Buyers engaged in trading of marketable pollution permits become worse off from trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The I Don't Care Corporation dumps pollution into the river that Mike uses for his fishing operation. The efficient level of pollution could prevail if government:
A) assigns the property right to I Don't Care.
B) assigns the property right to Mike.
C) assigns the river property rights to itself in the interest of all taxpayers.
D) Either a and b
A) assigns the property right to I Don't Care.
B) assigns the property right to Mike.
C) assigns the river property rights to itself in the interest of all taxpayers.
D) Either a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Recent reports of the adverse effects of second-hand smoke have led some cities to place a ban on smoking in public facilities. Discuss the efficiency of such a policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
"Because of market failure, it is necessary to have government regulations in order to deal with the problem of pollution."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

An emissions tax can bring about an efficient solution to the pollution problem because it:
A) shifts the supply curve to the left.
B) shifts the supply curve to the right.
C) shifts the demand curve to the left.
D) shifts the demand curve to the right.

An emissions tax can bring about an efficient solution to the pollution problem because it:
A) shifts the supply curve to the left.
B) shifts the supply curve to the right.
C) shifts the demand curve to the left.
D) shifts the demand curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Gallons. In the absence of governmental policies the level of output will be:
A) 2,000 gallons.
B) 1,000 gallons.
C) 2,500 gallons.
D) between 1,500 and 2,000 gallons.

Refer to Gallons. In the absence of governmental policies the level of output will be:
A) 2,000 gallons.
B) 1,000 gallons.
C) 2,500 gallons.
D) between 1,500 and 2,000 gallons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Diagram 6-1. In the absence of governmental policies the level of output will be:
A) Q₁.
B) Q₂.
C) Q3.
D) between Q₂ and Q3.

Refer to Diagram 6-1. In the absence of governmental policies the level of output will be:
A) Q₁.
B) Q₂.
C) Q3.
D) between Q₂ and Q3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
At Big Dog Inc., the marginal cost of production is $32, the marginal external cost of production is $5, and the marginal benefit of production is $35. The marginal social cost of production is:
A) $2.
B) $27.
C) $37.
D) $40.
A) $2.
B) $27.
C) $37.
D) $40.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Gallons. The quantity produced if oil refiners (producers) were given property rights to the environment that would be:
A) 2,000 gallons.
B) 1,500 gallons.
C) 0 gallons.
D) 1,750 gallons.

Refer to Gallons. The quantity produced if oil refiners (producers) were given property rights to the environment that would be:
A) 2,000 gallons.
B) 1,500 gallons.
C) 0 gallons.
D) 1,750 gallons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the following table. Suppose Plant A and Plant B are currently emitting 4 tons of pollution each. Government requires each plant to reduce emissions by two tons and issues two one-ton marketable pollution permits to each plant. Will any permits be traded? 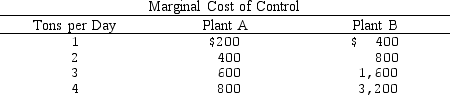
A) Yes, Plant A would be willing to buy one permit from Plant B.
B) Yes, Plant B would be willing to buy one permit from Plant A.
C) Yes, Plant B would be willing to buy two permits from Plant A.
D) Both firms' costs of control are so high that no trading will occur.
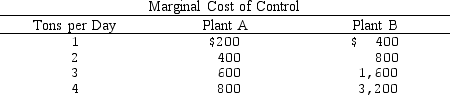
A) Yes, Plant A would be willing to buy one permit from Plant B.
B) Yes, Plant B would be willing to buy one permit from Plant A.
C) Yes, Plant B would be willing to buy two permits from Plant A.
D) Both firms' costs of control are so high that no trading will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions.

Refer to Gallons. The efficient output occurs at:
A) 2,500 gallons.
B) 5,000 gallons.
C) 1,000 gallons.
D) 1,750 gallons.

Refer to Gallons. The efficient output occurs at:
A) 2,500 gallons.
B) 5,000 gallons.
C) 1,000 gallons.
D) 1,750 gallons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Suppose that at current production levels, Bad Boy & Sons finds its marginal cost to be $12, its marginal external cost to be $2, and its marginal social benefit to be $15. In this case the company:
A) should be encouraged to expand production.
B) should be encouraged to decrease production.
C) should not change production levels.
D) is producing more than the efficient level of output.
A) should be encouraged to expand production.
B) should be encouraged to decrease production.
C) should not change production levels.
D) is producing more than the efficient level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Suppose that at current consumption levels, the marginal social cost of using the Kansas City freeway system is $15 while the marginal social benefit is $18. In this instance, government officials should:
A) take actions to decrease use of the freeway system.
B) take actions to increase use of the freeway system.
C) take no actions to change use of the freeway system.
D) build more freeways.
A) take actions to decrease use of the freeway system.
B) take actions to increase use of the freeway system.
C) take no actions to change use of the freeway system.
D) build more freeways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Evaluate the following statement. "The market will tend to overproduce when external costs are associated with production."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



