Deck 18: International Trade Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/218
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: International Trade Policy
1
If the United States imports purses, then the quantity of purses produced in the United States will ________ and the quantity of purses purchased by consumers in the United States will ________.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
E) not change; increase
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
E) not change; increase
C
2
If the United States starts to import a good that had previously been produced in the United States, the market price of the good in the United States
A) rises.
B) falls.
C) remains constant.
D) either remains constant or rises, depending on how whether the supply of the good stays the same or increases.
E) There is not enough information to answer the question because we need to know if the market price in the United States had been above or below the world market price before trade began.
A) rises.
B) falls.
C) remains constant.
D) either remains constant or rises, depending on how whether the supply of the good stays the same or increases.
E) There is not enough information to answer the question because we need to know if the market price in the United States had been above or below the world market price before trade began.
B
3
A nation has a comparative advantage in a good when it has a
A) lower absolute cost of producing the good.
B) higher opportunity cost of producing the good.
C) lower opportunity cost of producing the good.
D) higher absolute cost of producing the good.
E) tariff in place protecting the producers of the good.
A) lower absolute cost of producing the good.
B) higher opportunity cost of producing the good.
C) lower opportunity cost of producing the good.
D) higher absolute cost of producing the good.
E) tariff in place protecting the producers of the good.
C
4
Most t-shirts bought by Americans are made in Asia.As a result of free trade, the production of t-shirts in America has
A) increased.
B) stayed the same.
C) decreased.
D) been taken over by the government.
E) might change, but more information about what else the United States imports is needed to determine if U.S.production increased, decreased, or did not change.
A) increased.
B) stayed the same.
C) decreased.
D) been taken over by the government.
E) might change, but more information about what else the United States imports is needed to determine if U.S.production increased, decreased, or did not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How can a domestic producer determine whether or not it has a comparative advantage in the production of a good or service?
A) It cannot.
B) by comparing the price it receives to the prices of other domestic producers
C) by comparing the price it receives to the world price
D) by comparing the quantity it produces to the quantity produced in the world
E) by comparing the total domestic quantity to the total world quantity
A) It cannot.
B) by comparing the price it receives to the prices of other domestic producers
C) by comparing the price it receives to the world price
D) by comparing the quantity it produces to the quantity produced in the world
E) by comparing the total domestic quantity to the total world quantity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The United States imports t-shirts from Asia.As a result, U.S.consumers pay ________ otherwise and Asian producers receive ________ otherwise.
A) a higher price than; a higher price than
B) a higher price than; a lower price than
C) a lower price than; a higher price than
D) a lower price than; a lower price than
E) the same price as; the same price as
A) a higher price than; a higher price than
B) a higher price than; a lower price than
C) a lower price than; a higher price than
D) a lower price than; a lower price than
E) the same price as; the same price as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Goods and services that the United States buys from other nations are called
A) exports.
B) imports.
C) bartered goods.
D) exchanges.
E) world goods.
A) exports.
B) imports.
C) bartered goods.
D) exchanges.
E) world goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Imports are defined as the goods and services that we
A) produce and consume in the United States.
B) sell to other countries.
C) buy from other countries.
D) partially produce in both the United States and another country.
E) produce abroad using U.S.owned factories and then consume in the United States.
A) produce and consume in the United States.
B) sell to other countries.
C) buy from other countries.
D) partially produce in both the United States and another country.
E) produce abroad using U.S.owned factories and then consume in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The fundamental force that generates international trade is
A) the need for more goods and services.
B) absolute advantage.
C) the sea rule.
D) comparative advantage.
E) the existence of tariffs.
A) the need for more goods and services.
B) absolute advantage.
C) the sea rule.
D) comparative advantage.
E) the existence of tariffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The United States imports t-shirts because
A) it is a dangerous job to produce them.
B) foreign nations have a lower opportunity cost of production.
C) the United States has a lower opportunity cost of production.
D) foreign economies have an absolute advantage in their production.
E) the United States must import goods and services from other countries so that they can develop economically.
A) it is a dangerous job to produce them.
B) foreign nations have a lower opportunity cost of production.
C) the United States has a lower opportunity cost of production.
D) foreign economies have an absolute advantage in their production.
E) the United States must import goods and services from other countries so that they can develop economically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Of the following, ________ accounts for the largest share of imports into the United States.
A) food and drinks
B) fuels
C) crude oil
D) semiconductors
E) chemicals
A) food and drinks
B) fuels
C) crude oil
D) semiconductors
E) chemicals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A country exports the goods
A) for which its domestic prices are very high compared to the world prices.
B) that the economy can produce the most of.
C) that the economy can produce at relatively lowest opportunity cost.
D) that it cannot sell domestically.
E) in which it has a comparative disadvantage.
A) for which its domestic prices are very high compared to the world prices.
B) that the economy can produce the most of.
C) that the economy can produce at relatively lowest opportunity cost.
D) that it cannot sell domestically.
E) in which it has a comparative disadvantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a nation can produce a good or service at the lowest opportunity cost, then it
A) can sell the product at a lower price than other nations.
B) does not want to export the good because the low cost means it makes only a low profit.
C) is best for the nation to not trade the good internationally.
D) will definitely import the good because it can beat other countries' prices.
E) might export or import the good, depending on whether or not it has a comparative advantage in the production of the good.
A) can sell the product at a lower price than other nations.
B) does not want to export the good because the low cost means it makes only a low profit.
C) is best for the nation to not trade the good internationally.
D) will definitely import the good because it can beat other countries' prices.
E) might export or import the good, depending on whether or not it has a comparative advantage in the production of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
One of the major reasons why the United States exports jet airplanes is because Boeing faces ________ opportunity cost than firms in other nations in the production of such aircraft.
A) a higher
B) an unrelated
C) a lower
D) a nonexistent
E) an identical
A) a higher
B) an unrelated
C) a lower
D) a nonexistent
E) an identical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The country with a comparative advantage in the production of a good has a
A) lower opportunity cost of production.
B) higher opportunity cost of production.
C) horizontal production possibilities frontier.
D) vertical production possibilities frontier.
E) linear production possibilities frontier.
A) lower opportunity cost of production.
B) higher opportunity cost of production.
C) horizontal production possibilities frontier.
D) vertical production possibilities frontier.
E) linear production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The United States exports
A) goods only.
B) services only.
C) manufactured goods only.
D) goods and services.
E) only agricultural products and high-tech goods.
A) goods only.
B) services only.
C) manufactured goods only.
D) goods and services.
E) only agricultural products and high-tech goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The fundamental force that drives trade between nations is
A) the government.
B) NAFTA.
C) absolute advantage.
D) comparative advantage.
E) legal treaties.
A) the government.
B) NAFTA.
C) absolute advantage.
D) comparative advantage.
E) legal treaties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Goods and services that the United States sells to other nations are called
A) exports.
B) imports.
C) bartered goods.
D) exchanges.
E) world goods.
A) exports.
B) imports.
C) bartered goods.
D) exchanges.
E) world goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the world price of a good is below the no-trade domestic price, a country
A) will benefit from exporting the good.
B) will benefit from importing the good.
C) cannot benefit from trade.
D) has a comparative advantage in the production of that good.
E) will not engage in trade for that good.
A) will benefit from exporting the good.
B) will benefit from importing the good.
C) cannot benefit from trade.
D) has a comparative advantage in the production of that good.
E) will not engage in trade for that good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If you buy a DVD player produced in Japan, a
A) good was exported by Japan and imported by the United States.
B) good was imported by Japan and by the United States.
C) service was imported by Japan and exported by the United States.
D) service was exported by Japan and imported by the United States.
E) good was exported by Japan and by the United States.
A) good was exported by Japan and imported by the United States.
B) good was imported by Japan and by the United States.
C) service was imported by Japan and exported by the United States.
D) service was exported by Japan and imported by the United States.
E) good was exported by Japan and by the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A country exports a good if
A) it has a high opportunity cost of production.
B) the world price of the good is below the country's no-trade equilibrium price.
C) the world price of the good is above the country's no-trade equilibrium price.
D) the quantity demanded of the good in the country is greater than the quantity supplied at the world price.
E) it cannot import the good.
A) it has a high opportunity cost of production.
B) the world price of the good is below the country's no-trade equilibrium price.
C) the world price of the good is above the country's no-trade equilibrium price.
D) the quantity demanded of the good in the country is greater than the quantity supplied at the world price.
E) it cannot import the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
-The table above has the domestic demand and domestic supply schedules for a good.If the world price of the good is $10, then according to the table
A) domestic production is higher before trade than after trade.
B) the country imports 16 units a day.
C) the country imports 6 units a day.
D) the country exports 6 units a day.
E) the country exports 22 units a day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A nation will export a good if its
A) no-trade, domestic price is equal to the world price.
B) no-trade, domestic price is less than the world price
C) no-trade, domestic price is greater than the world price.
D) no-trade, domestic quantity is less than the world quantity.
E) no-trade, domestic quantity is greater than the world quantity.
A) no-trade, domestic price is equal to the world price.
B) no-trade, domestic price is less than the world price
C) no-trade, domestic price is greater than the world price.
D) no-trade, domestic quantity is less than the world quantity.
E) no-trade, domestic quantity is greater than the world quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
With no international trade, the U.S.price of wheat is lower than the world price of wheat.This indicates that the United States ________ a comparative advantage in the production of wheat and with international trade, the United States will ________ wheat.
A) has; export
B) has; not trade
C) has; import
D) does not have; export
E) might have; export
A) has; export
B) has; not trade
C) has; import
D) does not have; export
E) might have; export

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A country will export a good if it
A) can sell the good to a foreigner at a higher price than the no-trade price.
B) can sell the good to a foreigner at a lower price than the no-trade price.
C) can dump the good on the world market.
D) has a high opportunity cost of production.
E) is impossible to import the good.
A) can sell the good to a foreigner at a higher price than the no-trade price.
B) can sell the good to a foreigner at a lower price than the no-trade price.
C) can dump the good on the world market.
D) has a high opportunity cost of production.
E) is impossible to import the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If a nation imports a good that can be domestically produced, what happens to the quantity consumed of the good and why?
A) The quantity consumed increases because the market price decreases.
B) The quantity consumed decreases because the market price increases.
C) The quantity consumed remains constant because the price is unchanged.
D) The quantity consumed increases because the market price increases.
E) The quantity consumed decreases because the market price decreases.
A) The quantity consumed increases because the market price decreases.
B) The quantity consumed decreases because the market price increases.
C) The quantity consumed remains constant because the price is unchanged.
D) The quantity consumed increases because the market price increases.
E) The quantity consumed decreases because the market price decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Airlines in other countries buy airplanes from Boeing because
A) it is illegal to produce airplanes in many other countries.
B) Boeing's prices are less than what the airlines would pay for planes built in their own country.
C) trade treaties require such purchases.
D) these nations must buy something from the United States.
E) None of the above answers is correct.
A) it is illegal to produce airplanes in many other countries.
B) Boeing's prices are less than what the airlines would pay for planes built in their own country.
C) trade treaties require such purchases.
D) these nations must buy something from the United States.
E) None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
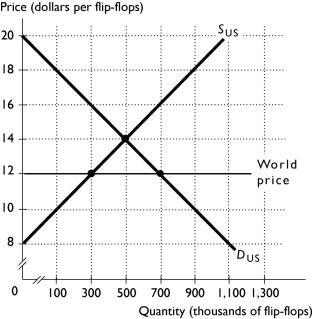
The above figure shows the U.S.market for flip-flops. When there is no international trade, the U.S.price is ________ per flip-flop and the U.S.quantity is ________ flip-flops.
A) $12; 300,000
B) $14; 500,000
C) $12; 700,000
D) $14; 300,000
E) $14; 700,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

The above figure shows the U.S.market for flip-flops. With no international trade, the price in the United States for flip-flops is ________. With international trade, the price in the United States for flip-flops is ________.
A) $12; $14
B) $500; $300
C) $14; $12
D) $700; $300
E) $500; $700

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A country with a comparative advantage in the production of a good will ________ production of the good and ________.
A) decrease; import the good
B) increase; export the good
C) not change; import the good
D) increase; import the good
E) decrease; export the good
A) decrease; import the good
B) increase; export the good
C) not change; import the good
D) increase; import the good
E) decrease; export the good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31

The above figure shows the U.S.market for flip-flops. With international trade, U.S.consumers buy ________ flip-flops and U.S.producers produce ________ flip-flops.
A) 500,000; 500,000
B) 300,000; 700,000
C) 500,000; 300,000
D) 700,000; 300,000
E) 700,000; 500,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suevania opens its doors to trade with Barvania.Barvania has a comparative advantage in the production of machinery.Hence, once trade occurs Suevania's consumers will buy ________ machinery and pay ________ before.
A) more; a higher price than
B) more; a lower price than
C) less; a higher price than
D) less; a lower price than
E) the same amount of; the same price as
A) more; a higher price than
B) more; a lower price than
C) less; a higher price than
D) less; a lower price than
E) the same amount of; the same price as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33

The above figure shows the U.S.market for flip-flops. With international trade, the United States imports ________ flip-flops.
A) 300,000
B) 500,000
C) 700,000
D) 0 because the United States exports flip-flops
E) 400,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
As a result of importing a good, domestic producers ________ the quantity produced and the price of the good ________.
A) increase; rises
B) increase; falls
C) decrease; rises
D) decrease; falls
E) decrease; does not change
A) increase; rises
B) increase; falls
C) decrease; rises
D) decrease; falls
E) decrease; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When a country exports a good because the world price is higher than the no-trade domestic price, domestic purchases of the good ________ and domestic production of the good ________.
A) increase; increases
B) increase; decreases
C) decrease; increases
D) decrease; decreases
E) do not change; increases
A) increase; increases
B) increase; decreases
C) decrease; increases
D) decrease; decreases
E) do not change; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
-The table above has the domestic demand and domestic supply schedules for a good.According to the table, the no-trade price of the good is
A) $4.
B) $6.
C) $8.
D) $10.
E) $2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
As a result of importing a good, domestic consumers ________ the quantity consumed and the price of the good ________.
A) increase; rises
B) increase; falls
C) decrease; rises
D) decrease; falls
E) increase; does not change
A) increase; rises
B) increase; falls
C) decrease; rises
D) decrease; falls
E) increase; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
According to the above table, the country will import the good if the world price is less than ________ and will export the good if the world price is more than ________.
A) $4; $4
B) $6; $6
C) $8; $4
D) $10; $10
E) $4; $8
A) $4; $4
B) $6; $6
C) $8; $4
D) $10; $10
E) $4; $8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
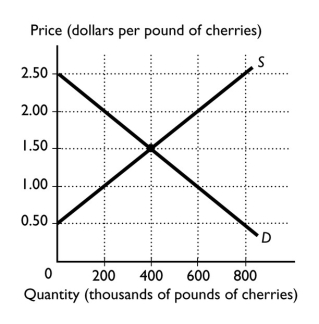
The figure above shows the U.S.demand and U.S.supply curves for cherries.In the absence of international trade, cherry farmers would receive ________ per pound of cherries.
A) $0.50
B) $1.50
C) $2.50
D) $2.00
E) $1.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

The above figure shows the U.S.market for flip-flops. With international trade, the equilibrium price in the United States is ________ and the United States ________ flip-flops.
A) $12; imports
B) $12; exports
C) $12; exports
D) $14; imports
E) $14; does not trade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
After a nation starts importing a good from overseas, the domestic price of the good
A) falls.
B) stays the same.
C) rises.
D) might change, but more information about what the country exports is needed to determine if the price rises, falls, or does not change.
E) might change, but more information about what else the country imports is needed to determine if the price rises, falls, or does not change.
A) falls.
B) stays the same.
C) rises.
D) might change, but more information about what the country exports is needed to determine if the price rises, falls, or does not change.
E) might change, but more information about what else the country imports is needed to determine if the price rises, falls, or does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
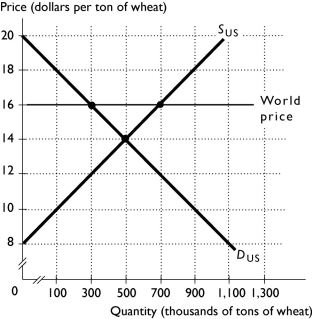
The above figure shows the U.S.market for wheat. With international trade, U.S.consumers buy ________ tons of wheat and U.S.producers produce ________ tons of wheat.
A) 700,000; 300,000
B) 500,000; 500,000
C) 300,000; 500,000
D) 300,000; 700,000
E) 500,000; 700,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43

The figure above shows the U.S.demand and U.S.supply curves for cherries.Suppose the world price of cherries is $2 per pound.At this price, U.S.consumption of cherries will equal
A) 200,000 pounds.
B) 400,000 pounds.
C) 600,000 pounds.
D) 800,000 pounds.
E) 0 pounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When a nation starts importing a good or service, the domestic production of the good or service
A) decreases.
B) stays the same.
C) increases.
D) might change, but more information about what the country exports is needed to determine if production increases, decreases, or does not change.
E) might change, but more information about what else the country imports is needed to determine if production increases, decreases, or does not change.
A) decreases.
B) stays the same.
C) increases.
D) might change, but more information about what the country exports is needed to determine if production increases, decreases, or does not change.
E) might change, but more information about what else the country imports is needed to determine if production increases, decreases, or does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When a nation exports a good or service, employment in that industry
A) decreases.
B) stays the same.
C) increases.
D) might change, but more information about what else the country exports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.
E) might change, but more information about what the country imports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.
A) decreases.
B) stays the same.
C) increases.
D) might change, but more information about what else the country exports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.
E) might change, but more information about what the country imports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When a nation exports a good or service in which it has a comparative advantage, production of the good or service
A) decreases.
B) stays the same.
C) increases.
D) might change, but more information about what the country imports is needed to determine if production increases, decreases, or does not change.
E) might change, but more information about what else the country exports is needed to determine if production increases, decreases, or does not change.
A) decreases.
B) stays the same.
C) increases.
D) might change, but more information about what the country imports is needed to determine if production increases, decreases, or does not change.
E) might change, but more information about what else the country exports is needed to determine if production increases, decreases, or does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Most t-shirts bought by Americans are made in Asia.Producers in Asia making t-shirts trade with America because they
A) receive a lower price than they would receive from another buyer.
B) receive a higher price than they would receive from another buyer.
C) must export something to the United States.
D) cannot produce enough t-shirts for their own domestic consumption.
E) cannot lower their price any lower and still make a profit.
A) receive a lower price than they would receive from another buyer.
B) receive a higher price than they would receive from another buyer.
C) must export something to the United States.
D) cannot produce enough t-shirts for their own domestic consumption.
E) cannot lower their price any lower and still make a profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48

The above figure shows the U.S.market for wheat. With international trade, the United States exports ________ of wheat.
A) 300,000 tons
B) 500,000 tons
C) 700,000 tons
D) 400,000 tons
E) None of the above answers are correct because the United States imports wheat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49

The figure above shows the U.S.demand and U.S.supply curves for cherries.At a world price of $2 per pound, the total exports of cherries from the United States to other nations equals
A) 200,000 pounds.
B) 400,000 pounds.
C) 600,000 pounds.
D) 800,000 pounds.
E) 0 pounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50

The above figure shows the U.S.market for wheat. With no international trade, the price of wheat in the United States is ________ per ton. With international trade, the price of wheat in the United States is ________ per ton.
A) $16; $14
B) $500; $300
C) $14; $16
D) $700; $300
E) $500; $700

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
When a nation exports a good or service in which it has a comparative advantage, employment in that industry
A) decreases.
B) stays the same.
C) increases.
D) might change, but more information about what else the country exports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.
E) might change, but more information about what the country imports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.
A) decreases.
B) stays the same.
C) increases.
D) might change, but more information about what else the country exports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.
E) might change, but more information about what the country imports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When a nation starts importing a good or service, domestic employment in that industry
A) decreases.
B) stays the same.
C) increases.
D) might change, but more information about what else the country imports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.
E) might change, but more information about what the country exports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.
A) decreases.
B) stays the same.
C) increases.
D) might change, but more information about what else the country imports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.
E) might change, but more information about what the country exports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Most t-shirts bought by Americans are made in Asia.U.S.consumers of t-shirts buy these t-shirts because
A) they pay a higher price for t-shirts made in Asia than they would for similar shirts made in the United States.
B) they pay a lower price for t-shirts made in Asia than they would for similar shirts made in the United States.
C) they must buy some goods or services produced in Asia.
D) by so doing they are helping preserve U.S.jobs producing t-shirts.
E) they know that the United States has a comparative advantage in wearing t-shirts.
A) they pay a higher price for t-shirts made in Asia than they would for similar shirts made in the United States.
B) they pay a lower price for t-shirts made in Asia than they would for similar shirts made in the United States.
C) they must buy some goods or services produced in Asia.
D) by so doing they are helping preserve U.S.jobs producing t-shirts.
E) they know that the United States has a comparative advantage in wearing t-shirts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54

The figure above shows the U.S.demand and U.S.supply curves for cherries.At a world price of $2 per pound, the production of cherries in the United States will equal
A) 200,000 pounds.
B) 400,000 pounds.
C) 600,000 pounds.
D) 800,000 pounds.
E) 0 pounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55

The above figure shows the U.S.market for wheat. With international trade, the price of wheat in the United States is ________ per ton and the United States ________ wheat.
A) $16; exports
B) $14; exports
C) $14; imports
D) $16; imports
E) $14; does not trade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56

The above figure shows the U.S.market for wheat. When there no international trade, the U.S.price of wheat is ________ per ton and the U.S.equilibrium quantity is ________ tons.
A) $14; 300,000
B) $14; 500,000
C) $16; 500,000
D) $16; 300,000
E) $16; 700,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Who gains from international trade?
A) only the exporting nation
B) only the importing nation
C) both the importing and the exporting nations
D) neither the importing nor the exporting nations
E) The gains depends on which nation gets to keep the total revenue from the sale
A) only the exporting nation
B) only the importing nation
C) both the importing and the exporting nations
D) neither the importing nor the exporting nations
E) The gains depends on which nation gets to keep the total revenue from the sale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58

The figure above shows the U.S.demand and U.S.supply curves for cherries.In the absence of international trade, how many pounds of cherries would U.S.farmers produce?
A) 200,000 pounds
B) 400,000 pounds
C) 600,000 pounds
D) 800,000 pounds
E) 0 pounds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
International trade benefits
A) only the exporter.
B) only the importer.
C) both the exporter and the importer.
D) neither the exporter nor the importer.
E) the exporter at all times and sometimes also the importer.
A) only the exporter.
B) only the importer.
C) both the exporter and the importer.
D) neither the exporter nor the importer.
E) the exporter at all times and sometimes also the importer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60

The figure above shows the U.S.demand and U.S.supply curves for cherries.At a world price of $2 per pound, the total imports of cherries to the United States from other nations equals
A) 200,000 pounds.
B) 400,000 pounds.
C) 600,000 pounds.
D) 800,000 pounds.
E) 0 pounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Since the mid-1970s, the average U.S.tariff rate is
A) less than 5 percent.
B) between 6 percent and 15 percent.
C) between 16 percent and 25 percent.
D) between 26 percent and 35 percent.
E) larger than 36 percent.
A) less than 5 percent.
B) between 6 percent and 15 percent.
C) between 16 percent and 25 percent.
D) between 26 percent and 35 percent.
E) larger than 36 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Looking at the average tariff rate in the United States since 1930, we see that
A) at first tariffs declined, but have recently risen.
B) tariffs have trended downward for most of the period.
C) tariff levels have remained high, at over 50 percent throughout the period.
D) while we talk about free trade, tariff levels have risen over the last 30 years.
E) tariffs were made illegal in the United States in 1955.
A) at first tariffs declined, but have recently risen.
B) tariffs have trended downward for most of the period.
C) tariff levels have remained high, at over 50 percent throughout the period.
D) while we talk about free trade, tariff levels have risen over the last 30 years.
E) tariffs were made illegal in the United States in 1955.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following chain of events occurs when a tariff is imposed on a good?
A) Domestic prices rise, shifting the domestic supply curve rightward.
B) Domestic prices fall, shifting the demand curve rightward, and consumers buy more of the good.
C) Domestic prices fall, decreasing the domestic quantity supplied and increasing the quantity demanded.
D) Domestic prices rise, decreasing the quantity demanded and increasing the domestic quantity supplied.
E) Domestic prices rise, shifting the demand curve leftward and the domestic supply curve rightward.
A) Domestic prices rise, shifting the domestic supply curve rightward.
B) Domestic prices fall, shifting the demand curve rightward, and consumers buy more of the good.
C) Domestic prices fall, decreasing the domestic quantity supplied and increasing the quantity demanded.
D) Domestic prices rise, decreasing the quantity demanded and increasing the domestic quantity supplied.
E) Domestic prices rise, shifting the demand curve leftward and the domestic supply curve rightward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A nation will import a good if its no-trade, domestic
A) price is equal to the world price.
B) price is less than the world price.
C) price is greater than the world price.
D) quantity is less than the world quantity.
E) quantity is greater than the world quantity.
A) price is equal to the world price.
B) price is less than the world price.
C) price is greater than the world price.
D) quantity is less than the world quantity.
E) quantity is greater than the world quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
After a tariff is imposed on a good, the price of the good
A) does not change.
B) falls.
C) rises.
D) rises only if the domestic demand for the good does not change.
E) might rise, fall, or not change depending on whether the government did or did not simultaneously impose a quota.
A) does not change.
B) falls.
C) rises.
D) rises only if the domestic demand for the good does not change.
E) might rise, fall, or not change depending on whether the government did or did not simultaneously impose a quota.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose the world price of widgets is $5 each.If a widget-importing country imposed a $2 per widget tariff, what price would that country's consumers pay for widgets?
A) $10
B) $7
C) $5
D) $3
E) A price that is greater than $5 and less than $7
A) $10
B) $7
C) $5
D) $3
E) A price that is greater than $5 and less than $7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The agreement between the United States, Mexico, and Canada that sought to lower trade barriers is known as
A) the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade.
B) the North American Free Trade Agreement.
C) the World Trade Organization.
D) the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act.
E) the New World Free Trade Agreement.
A) the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade.
B) the North American Free Trade Agreement.
C) the World Trade Organization.
D) the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act.
E) the New World Free Trade Agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When a country imports a good, the ________ to consumers is ________ the ________ to producers.
A) loss; larger than; gain
B) loss; smaller than; gain
C) gain; smaller than; loss
D) gain; equal to; loss
E) gain; larger than; loss
A) loss; larger than; gain
B) loss; smaller than; gain
C) gain; smaller than; loss
D) gain; equal to; loss
E) gain; larger than; loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
After a tariff is imposed, consumers must pay a price equal to the
A) world market price.
B) domestic equilibrium price when there is no trade.
C) world market price plus the tariff.
D) world market price less the tariff.
E) domestic equilibrium price when there is no trade plus the tariff.
A) world market price.
B) domestic equilibrium price when there is no trade.
C) world market price plus the tariff.
D) world market price less the tariff.
E) domestic equilibrium price when there is no trade plus the tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In the wake of worsening relations with China, some Americans called for an increase in tariffs on Chinese products coming into America.If higher tariffs are imposed on clothing produced in China, the price of clothing in America would
A) decrease.
B) increase.
C) not change.
D) first increase then decrease.
E) first decrease then increase.
A) decrease.
B) increase.
C) not change.
D) first increase then decrease.
E) first decrease then increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A tariff is a tax
A) on an exported good.
B) on an imported good.
C) imposed on all traded goods.
D) imposed on people's income.
E) imposed on the difference between the value of the goods a firm imports and the value of the goods it exports.
A) on an exported good.
B) on an imported good.
C) imposed on all traded goods.
D) imposed on people's income.
E) imposed on the difference between the value of the goods a firm imports and the value of the goods it exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The United States exports a good if its no-trade U.S.price is ________ its world price.With international trade, U.S.production of the good ________ compared to the level of no-trade production.
A) higher than; does not change
B) higher than; increases
C) lower than; increases
D) the same as; increases
E) the same as; does not change
A) higher than; does not change
B) higher than; increases
C) lower than; increases
D) the same as; increases
E) the same as; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
During the past 70 years, the peak average tariff rate in the United States stemmed from the
A) creation of GATT in the middle of the 1940s.
B) Kennedy Administration in the early 1960s.
C) Uruguay round of GATT in the 1980s.
D) Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act in the early 1930s.
E) Clinton-Bush tariff of 2000-2001.
A) creation of GATT in the middle of the 1940s.
B) Kennedy Administration in the early 1960s.
C) Uruguay round of GATT in the 1980s.
D) Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act in the early 1930s.
E) Clinton-Bush tariff of 2000-2001.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Goods and services that we buy from firms in other countries are called our
A) imports.
B) exports.
C) inputs.
D) raw materials.
E) obligations.
A) imports.
B) exports.
C) inputs.
D) raw materials.
E) obligations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A tariff is
A) a tax imposed on imports.
B) any non-tax action used to restrict trade.
C) a tax imposed on exports.
D) any non-subsidy used to increase trade.
E) a subsidy granted to imports.
A) a tax imposed on imports.
B) any non-tax action used to restrict trade.
C) a tax imposed on exports.
D) any non-subsidy used to increase trade.
E) a subsidy granted to imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
When a good is imported, the domestic production of it ________ and the domestic consumption of it ________.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases
E) increases; does not change
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases
E) increases; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When Italy buys Boeing jets, the price Italy pays is ________ if it produced its own jets and the price Boeing receives is ________ than it could receive from an additional U.S.buyer.
A) lower than; lower
B) higher than; higher
C) lower than; higher
D) higher than; lower
E) the same as; higher
A) lower than; lower
B) higher than; higher
C) lower than; higher
D) higher than; lower
E) the same as; higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If the United States exports planes to Brazil and imports ethanol from Brazil, the price received by U.S.producers of planes ________ and the price received by Brazilian producers of ethanol ________.
A) does not change; does not change
B) rises; rises
C) rises; falls
D) falls; rises
E) falls; falls
A) does not change; does not change
B) rises; rises
C) rises; falls
D) falls; rises
E) falls; falls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A tariff is
A) the domestic price charged by an exporting firm.
B) a tax on an imported good imposed by the importing country.
C) a licensing regulation that limits imports.
D) price dumping by a firm engaging in international trade.
E) the world price of a good or service.
A) the domestic price charged by an exporting firm.
B) a tax on an imported good imposed by the importing country.
C) a licensing regulation that limits imports.
D) price dumping by a firm engaging in international trade.
E) the world price of a good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A tax on a good that is imposed by the importing country is called a
A) tariff.
B) nontariff barrier.
C) quantitative restriction.
D) licensing regulation.
E) trade constraint.
A) tariff.
B) nontariff barrier.
C) quantitative restriction.
D) licensing regulation.
E) trade constraint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



