Deck 16: The Special Senses
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/117
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: The Special Senses
1
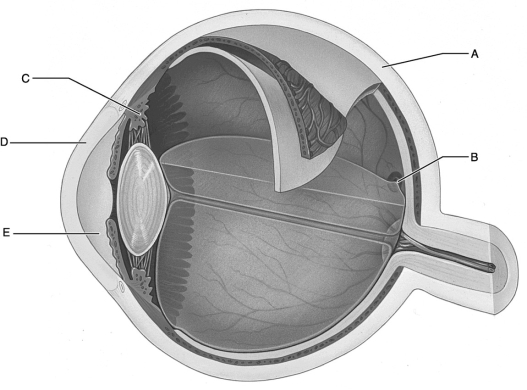
Figure 16.2
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the anterior segment, which is filled with aqueous humor.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
E
2
Transparent mucous membrane covering the inner surface of the eyelid.
A) palpebrae
B) tarsal glands
C) lacrimal apparatus
D) conjunctiva
E) lacrimal caruncle
A) palpebrae
B) tarsal glands
C) lacrimal apparatus
D) conjunctiva
E) lacrimal caruncle
D
3
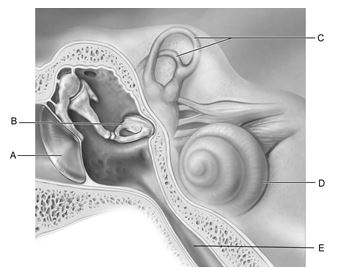
Figure 16.1
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the middle ear ossicle that is known as the stirrup.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
B
4
Fluid filling the posterior segment of the eye.
A) aqueous humor
B) vitreous humor
C) synovial fluid
D) serous fluid
E) endolymph
A) aqueous humor
B) vitreous humor
C) synovial fluid
D) serous fluid
E) endolymph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Bony labyrinth structure containing the utricle and saccule.
A) vestibule
B) macula lutea
C) macula densa
D) ora serrate
E) scala vestibule
A) vestibule
B) macula lutea
C) macula densa
D) ora serrate
E) scala vestibule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6

Figure 16.1
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the structure that contains receptors for rotational acceleration.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

Figure 16.2
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the ciliary body.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

Figure 16.2
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the region of the retina that contains only cones and provides maximal visual acuity.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9

Figure 16.2
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the portion of the fibrous layer known as the sclera.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Region of the forebrain overlying the cribriform plate of the ethmoid.
A) olfactory epithelium
B) temporal lobe
C) olfactory bulb
D) thalamus
E) insula
A) olfactory epithelium
B) temporal lobe
C) olfactory bulb
D) thalamus
E) insula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Melanin-containing layer of the eye's vascular tunic.
A) sclera
B) choroid
C) ciliary body
D) cornea
E) lens
A) sclera
B) choroid
C) ciliary body
D) cornea
E) lens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

Figure 16.1
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the structure that is important in equalizing air pressure on both sides of the eardrum.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Transparent structure of the eye containing regularly aligned collagen fibers.
A) sclera
B) choroid
C) ciliary body
D) cornea
E) lens
A) sclera
B) choroid
C) ciliary body
D) cornea
E) lens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14

Figure 16.1
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the structure that is called the cochlea.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15

Figure 16.1
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the structure that is the boundary between the external and middle ear.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Sensory receptor for taste.
A) taste bud
B) taste pore
C) tongue papilla
D) olfactory bulb
E) gustatory epithelial cells
A) taste bud
B) taste pore
C) tongue papilla
D) olfactory bulb
E) gustatory epithelial cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17

Figure 16.2
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the transparent portion of the fibrous layer.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Membrane attached to the stapes.
A) tympanic membrane
B) pharyngotympanic
C) oval window
D) round window
E) tectorial membrane
A) tympanic membrane
B) pharyngotympanic
C) oval window
D) round window
E) tectorial membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Filaments of the olfactory receptor cells synapse with these cells of the olfactory tract.
A) mitral cells
B) glomeruli
C) support epithelial cells
D) olfactory stem cells
E) cells in the lamina propria
A) mitral cells
B) glomeruli
C) support epithelial cells
D) olfactory stem cells
E) cells in the lamina propria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Microvilli from gustatory cells project through this structure.
A) taste bud
B) taste pore
C) tongue papilla
D) olfactory bulb
E) gustatory epithelial cells
A) taste bud
B) taste pore
C) tongue papilla
D) olfactory bulb
E) gustatory epithelial cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Calcium carbonate crystals of the macula.
A) stapedius
B) modiolus
C) otoliths
D) helicotrema
E) scala tympani
A) stapedius
B) modiolus
C) otoliths
D) helicotrema
E) scala tympani

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Endolymph is made
A) from perilymph.
B) from the dura mater.
C) in the scala vestibuli.
D) in the stria vascularis.
A) from perilymph.
B) from the dura mater.
C) in the scala vestibuli.
D) in the stria vascularis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In Chapter 12 on the CNS, we learned that the inferior olivary nucleus and medial lemniscus are a relay nucleus and a fiber tract in general somatic sensory pathways in the brain. The superior olivary nucleus and the lateral lemniscus are entirely different structures belonging to what sensory pathway?
A) taste
B) olfactory
C) visual
D) auditory
A) taste
B) olfactory
C) visual
D) auditory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Hair cells are receptor cells for
A) fine touch.
B) both hearing and equilibrium.
C) taste.
D) smell.
A) fine touch.
B) both hearing and equilibrium.
C) taste.
D) smell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Endolymph-filled structure containing receptors for hearing.
A) vestibule
B) saccule
C) utricle
D) cochlear duct
E) semicircular canals
A) vestibule
B) saccule
C) utricle
D) cochlear duct
E) semicircular canals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Along with the saccule, this structure senses linear acceleration.
A) vestibule
B) spiral organ
C) utricle
D) cochlear duct
E) semicircular canals
A) vestibule
B) spiral organ
C) utricle
D) cochlear duct
E) semicircular canals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements does not correctly describe the spiral organ of Corti?
A) High-frequency sounds stimulate hair cells at the basal end of the basilar membrane.
B) The "hairs" of the receptor cells are embedded in the tectorial membrane.
C) The spiral organ is part of the cochlear duct, which equals the scala media.
D) The tectorial membrane bends with vibrations, whereas the basilar membrane is rigid and fixed.
A) High-frequency sounds stimulate hair cells at the basal end of the basilar membrane.
B) The "hairs" of the receptor cells are embedded in the tectorial membrane.
C) The spiral organ is part of the cochlear duct, which equals the scala media.
D) The tectorial membrane bends with vibrations, whereas the basilar membrane is rigid and fixed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following structures in the eye are pigmented?
A) the cornea
B) sclera
C) the retina
D) lens
A) the cornea
B) sclera
C) the retina
D) lens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Gel-like structure embedded with the tips of cochlear hair cells.
A) basilar membrane
B) tectorial membrane
C) tympanic membrane
D) scala tympani
E) scala vestibule
A) basilar membrane
B) tectorial membrane
C) tympanic membrane
D) scala tympani
E) scala vestibule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Clouding of which of the following structures would lead to a clinical condition known as a cataract?
A) lens
B) cornea
C) aqueous humor
D) vitreous humor
A) lens
B) cornea
C) aqueous humor
D) vitreous humor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following areas has the highest concentration of cones?
A) the optic disc
B) the macula lutea
C) the fovea centralis
D) the ora serrata retinae
A) the optic disc
B) the macula lutea
C) the fovea centralis
D) the ora serrata retinae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
"Uncinate fits" are characterized by
A) auditory hallucinations.
B) photo sensitivity.
C) imaginary odors.
D) vertigo.
A) auditory hallucinations.
B) photo sensitivity.
C) imaginary odors.
D) vertigo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Of the following glands, which does not help keep the anterior part of the eye from drying out?
A) lacrimal caruncle
B) tarsal glands
C) goblet cells in the conjunctiva
D) lacrimal gland
A) lacrimal caruncle
B) tarsal glands
C) goblet cells in the conjunctiva
D) lacrimal gland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The ora serrata is a
A) type of papilla that houses taste buds.
B) part of the modiolus.
C) part of the choroid layer.
D) part of the retina.
A) type of papilla that houses taste buds.
B) part of the modiolus.
C) part of the choroid layer.
D) part of the retina.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The basilar membrane supports the
A) spiral lamina.
B) modiolus.
C) spiral ganglion.
D) bony labyrinth.
E) spiral organ.
A) spiral lamina.
B) modiolus.
C) spiral ganglion.
D) bony labyrinth.
E) spiral organ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What axons decussate in the optic chiasma?
A) the fibers in the optic radiation of white matter
B) all fibers from both eyes
C) those from the lateral half of each retina
D) axons from the medial half of each eye
A) the fibers in the optic radiation of white matter
B) all fibers from both eyes
C) those from the lateral half of each retina
D) axons from the medial half of each eye

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Hyperopia and presbyopia may have some features in common, but a key difference between these two conditions is that
A) one is farsightedness, and the other is nearsightedness.
B) nearsighted people never develop presbyopia, but they can develop hyperopia.
C) in hyperopia the lens can accommodate, but in presbyopia it cannot.
D) people with astigmatism never develop presbyopia, but they can develop hyperopia.
A) one is farsightedness, and the other is nearsightedness.
B) nearsighted people never develop presbyopia, but they can develop hyperopia.
C) in hyperopia the lens can accommodate, but in presbyopia it cannot.
D) people with astigmatism never develop presbyopia, but they can develop hyperopia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which is true about a retinal detachment?
A) It can result from a blow to the eye.
B) It is a detachment of the complete thickness of the retina from the choroid.
C) It causes blindness immediately.
D) The detached portion contains no capillaries.
A) It can result from a blow to the eye.
B) It is a detachment of the complete thickness of the retina from the choroid.
C) It causes blindness immediately.
D) The detached portion contains no capillaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Of the following structures, which is the only one that contains perilymph (instead of endolymph)?
A) scala media
B) saccule
C) scala tympani
D) semicircular ducts
A) scala media
B) saccule
C) scala tympani
D) semicircular ducts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Where do tears drain?
A) into the Eustachian tube
B) into the nasal cavity
C) into the lacrimal gland
D) into the pharynx
A) into the Eustachian tube
B) into the nasal cavity
C) into the lacrimal gland
D) into the pharynx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The first "way station" (relay nucleus) in the visual pathway from the eye, after there has been partial crossover of the fibers in the optic chiasma, is the
A) superior colliculi.
B) lateral geniculate nucleus.
C) primary visual cortex.
D) temporal lobe.
A) superior colliculi.
B) lateral geniculate nucleus.
C) primary visual cortex.
D) temporal lobe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The cristae in the inner ear contain the receptors for
A) rotational equilibrium.
B) all aspects of hearing.
C) all aspects of equilibrium.
D) static equilibrium.
A) rotational equilibrium.
B) all aspects of hearing.
C) all aspects of equilibrium.
D) static equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Receptors for hearing are located in the
A) cochlear duct.
B) middle ear.
C) semicircular canals.
D) tympanic membrane.
A) cochlear duct.
B) middle ear.
C) semicircular canals.
D) tympanic membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which cranial nerve does not innervate the extrinsic eye muscles?
A) abducens
B) facial
C) oculomotor
D) trochlear
A) abducens
B) facial
C) oculomotor
D) trochlear

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The oil component found in tears is produced by the
A) lacrimal glands.
B) tarsal glands.
C) conjunctiva.
D) endocrine glands.
A) lacrimal glands.
B) tarsal glands.
C) conjunctiva.
D) endocrine glands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Ringing in the ears, vertigo, and gradual loss of hearing typify the disorder called
A) conjunctivitis.
B) Ménière's syndrome.
C) strabismus.
D) glaucoma.
A) conjunctivitis.
B) Ménière's syndrome.
C) strabismus.
D) glaucoma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following would not be associated with strabismus?
A) damage to the oculomotor nerve
B) paralysis of the extrinsic muscles of the eye
C) damage to the optic nerve
D) lesions of the midbrain
A) damage to the oculomotor nerve
B) paralysis of the extrinsic muscles of the eye
C) damage to the optic nerve
D) lesions of the midbrain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The oval window of the ear is connected directly to which passageway?
A) pharyngotympanic tube
B) external auditory canal
C) scala vestibuli
D) scala tympani
A) pharyngotympanic tube
B) external auditory canal
C) scala vestibuli
D) scala tympani

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An essential part of the maculae involved in static equilibrium is/are the
A) spiral organ (of Corti).
B) cupula.
C) scala media.
D) otoliths.
A) spiral organ (of Corti).
B) cupula.
C) scala media.
D) otoliths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The eyelids house all of the following except the
A) tarsal glands.
B) superior tarsal muscle.
C) orbicularis oculi muscles.
D) lacrimal sac.
A) tarsal glands.
B) superior tarsal muscle.
C) orbicularis oculi muscles.
D) lacrimal sac.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The sensation of taste involves
A) bending of cilia.
B) chemicals binding to microvilli.
C) movement of crystals embedded in gelatinous masses.
D) photons altering pigment molecules.
A) bending of cilia.
B) chemicals binding to microvilli.
C) movement of crystals embedded in gelatinous masses.
D) photons altering pigment molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Farsightedness is more properly called
A) myopia.
B) presbyopia.
C) hyperopia.
D) emmetropia.
A) myopia.
B) presbyopia.
C) hyperopia.
D) emmetropia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study the body's few mitotic neurons. These neurons are the
A) photoreceptors.
B) olfactory stem cells.
C) basal cells in the taste buds.
D) auditory hair cells.
A) photoreceptors.
B) olfactory stem cells.
C) basal cells in the taste buds.
D) auditory hair cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The muscle that opens the eye is the
A) superior rectus.
B) orbicularis oculi.
C) frontalis on forehead.
D) levator palpebrae superioris.
A) superior rectus.
B) orbicularis oculi.
C) frontalis on forehead.
D) levator palpebrae superioris.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Nearsightedness is more properly called
A) myopia.
B) hyperopia.
C) presbyopia.
D) emmetropia.
A) myopia.
B) hyperopia.
C) presbyopia.
D) emmetropia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following lies closest to the anterior pole of the eye?
A) center of the lens
B) center of the cornea
C) tip of an eyelash
D) sclera
A) center of the lens
B) center of the cornea
C) tip of an eyelash
D) sclera

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What structure is handled by an "eye bank"?
A) whole eyes for eye transplants
B) just the lens
C) just the cornea
D) just the retina
A) whole eyes for eye transplants
B) just the lens
C) just the cornea
D) just the retina

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The external ear consists of each of the following structures except the
A) auricle.
B) helix.
C) lobule.
D) vestibule.
A) auricle.
B) helix.
C) lobule.
D) vestibule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Another name for the ciliary zonule is
A) olfactory glomerulus.
B) cochlear duct.
C) the bitter taste zone on the tongue.
D) the suspensory ligament of the lens.
A) olfactory glomerulus.
B) cochlear duct.
C) the bitter taste zone on the tongue.
D) the suspensory ligament of the lens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The middle ear cavity is normally filled with
A) perilymph.
B) endolymph.
C) air.
D) mucus.
A) perilymph.
B) endolymph.
C) air.
D) mucus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The ossicle that is shaped like the stirrup of a saddle is the
A) tympanic membrane.
B) incus.
C) malleus.
D) stapes.
A) tympanic membrane.
B) incus.
C) malleus.
D) stapes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The transmission of sound vibrations through the external acoustic meatus occurs chiefly through
A) nerve fibers.
B) air.
C) fluid.
D) bone.
A) nerve fibers.
B) air.
C) fluid.
D) bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following membranes is not part of the cochlea?
A) basilar
B) tectorial
C) tympanic
D) vestibular
A) basilar
B) tectorial
C) tympanic
D) vestibular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Abraham spoke so softly that Jason rolled a piece of paper into a funnel shape and put one end into his external auditory canal to signal Abraham to speak up. Abraham then shouted that a certain anatomical structure serves exactly the same function as Jason's paper funnel. That structure is the
A) round window.
B) pinna.
C) pharyngotympanic tube.
D) mastoid antrum.
A) round window.
B) pinna.
C) pharyngotympanic tube.
D) mastoid antrum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following is not part of the flow of taste sensation along the gustatory pathway to the cerebral cortex?
A) hypothalamic appetite centers
B) solitary nucleus of the medulla oblongata
C) thalamic nuclei
D) vagus nerve
A) hypothalamic appetite centers
B) solitary nucleus of the medulla oblongata
C) thalamic nuclei
D) vagus nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The sclera of the eye develops from
A) the lens placode.
B) head mesenchyme.
C) the optic cup.
D) the optic stalk.
A) the lens placode.
B) head mesenchyme.
C) the optic cup.
D) the optic stalk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Each of the following structures participates in bending of light entering the eye except the
A) cornea.
B) iris.
C) lens.
D) vitreous humor.
A) cornea.
B) iris.
C) lens.
D) vitreous humor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The superior oblique muscle turns the eye both laterally and
A) medially.
B) superiorly.
C) inferiorly.
D) laterally.
A) medially.
B) superiorly.
C) inferiorly.
D) laterally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following controls the amount of light entering the eye?
A) ciliary muscle
B) dilator/sphincter pupillae muscles
C) levator palpebrae
D) medial rectus
A) ciliary muscle
B) dilator/sphincter pupillae muscles
C) levator palpebrae
D) medial rectus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
There are three layers of neurons in the retina. Which of the following neurons have axons that form the optic nerves?
A) bipolar cells
B) ganglion cells
C) cone cells
D) rod cells
A) bipolar cells
B) ganglion cells
C) cone cells
D) rod cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
During embryonic development, the retina of the eye develops from
A) the surface ectoderm.
B) an outpocketing of the diencephalon.
C) the mesoderm.
D) the mesoderm and the endoderm.
A) the surface ectoderm.
B) an outpocketing of the diencephalon.
C) the mesoderm.
D) the mesoderm and the endoderm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What structure regulates the amount of light passing to the visual receptors of the eye?
A) aqueous humor
B) vitreous humor
C) lens
D) pupil
A) aqueous humor
B) vitreous humor
C) lens
D) pupil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The center for vision in the cerebral cortex is located in the
A) temporal lobe.
B) frontal lobe.
C) occipital lobe.
D) parietal lobe.
A) temporal lobe.
B) frontal lobe.
C) occipital lobe.
D) parietal lobe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Nerve axons from the lateral portion of each retina
A) cross over to the opposite side of the retina.
B) pass posteriorly without crossing over at the chiasma.
C) branch at the chiasma, some branches crossing and some not crossing.
D) carry information from the lateral half of the visual field.
A) cross over to the opposite side of the retina.
B) pass posteriorly without crossing over at the chiasma.
C) branch at the chiasma, some branches crossing and some not crossing.
D) carry information from the lateral half of the visual field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following could not be seen as one looks into the eye with an ophthalmoscope?
A) macula lutea
B) optic chiasma
C) fovea centralis
D) optic disc
A) macula lutea
B) optic chiasma
C) fovea centralis
D) optic disc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Filaments that pass through the olfactory foramina of the cribriform plate belong to
A) axons of the olfactory receptor cells.
B) dendrites of the olfactory receptor cells.
C) axons of the olfactory bulb mitral cells.
D) dendrites of the olfactory bulb mitral cells.
A) axons of the olfactory receptor cells.
B) dendrites of the olfactory receptor cells.
C) axons of the olfactory bulb mitral cells.
D) dendrites of the olfactory bulb mitral cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Ordinarily, it is not possible to transplant tissues from one person to another without rejection, yet corneas can be transplanted with impunity. This is because the cornea
A) is not a human structure.
B) has no nerve supply.
C) has no blood supply, except around the periphery.
D) is exposed and easily accessible.
A) is not a human structure.
B) has no nerve supply.
C) has no blood supply, except around the periphery.
D) is exposed and easily accessible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The bony labyrinth is located in which portion of the temporal bone?
A) mastoid
B) petrous
C) squamous
D) tympanic
A) mastoid
B) petrous
C) squamous
D) tympanic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The cristae ampullares in the inner ear are located in the
A) saccule.
B) utricle.
C) semicircular ducts.
D) cochlear duct.
A) saccule.
B) utricle.
C) semicircular ducts.
D) cochlear duct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The nerve carrying taste information from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue is the
A) hypoglossal.
B) glossopharyngeal.
C) olfactory.
D) facial.
A) hypoglossal.
B) glossopharyngeal.
C) olfactory.
D) facial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



