Deck 13: The Respiratory System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/150
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: The Respiratory System
1
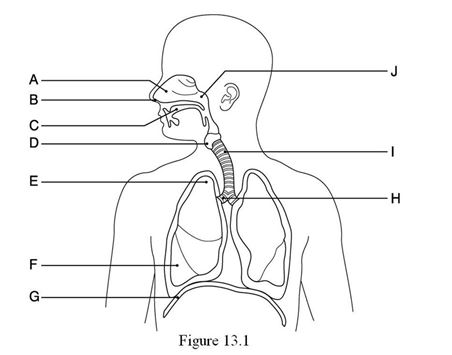
Using Figure 13.1, identify the following:
The diaphragm muscle is indicated by ________.
A) Label C
B) Label E
C) Label F
D) Label G
E) Label J
D
2
Which part of the larynx produces sounds when air passes by?
A) thyroid cartilage
B) epiglottis
C) glottis
D) vocal folds (True vocal cords)
A) thyroid cartilage
B) epiglottis
C) glottis
D) vocal folds (True vocal cords)
D
3
The three mucosa-covered projections into the nasal cavity that greatly increase surface area of mucosa exposed to air are called ________.
A) tonsils
B) adenoids
C) conchae
D) paranasal sinuses
A) tonsils
B) adenoids
C) conchae
D) paranasal sinuses
C
4
What protects the superior opening of the larynx?
A) trachea
B) epiglottis
C) glottis
D) thyroid cartilage
A) trachea
B) epiglottis
C) glottis
D) thyroid cartilage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The anterior portion of the palate that is supported by bone is called the ________.
A) soft palate
B) glottis
C) epiglottis
D) hard palate
A) soft palate
B) glottis
C) epiglottis
D) hard palate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What part of the respiratory system routes air and food into their proper channels and plays a role in speech?
A) tongue
B) pharynx
C) nasal conchae
D) larynx
A) tongue
B) pharynx
C) nasal conchae
D) larynx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
From superior to inferior, the three regions of the pharynx are the ________.
A) oropharynx, nasopharynx, laryngopharynx
B) nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
C) laryngopharynx, oropharynx, nasopharynx
D) nasopharynx, laryngopharynx, oropharynx
A) oropharynx, nasopharynx, laryngopharynx
B) nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
C) laryngopharynx, oropharynx, nasopharynx
D) nasopharynx, laryngopharynx, oropharynx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When breathing in, air enters the larynx through an opening called the ________.
A) glottis
B) epiglottis
C) esophagus
D) thyroid cartilage
A) glottis
B) epiglottis
C) esophagus
D) thyroid cartilage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9

Using Figure 13.1, identify the following:
The nostrils, or nares, are indicated by ________.
A) Label C
B) Label G
C) Label B
D) Label A
E) Label F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which tissue forms the epiglottis?
A) thyroid cartilage
B) elastic cartilage
C) hyaline cartilage
D) fibrous cartilage
A) thyroid cartilage
B) elastic cartilage
C) hyaline cartilage
D) fibrous cartilage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11

Using Figure 13.1, identify the following:
The inferior lobe of the right lung is indicated by ________.
A) Label E
B) Label J
C) Label I
D) Label G
E) Label F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

Using Figure 13.1, identify the following:
The right main (primary) bronchus is indicated by ________.
A) Label H
B) Label I
C) Label J
D) Label B
E) Label F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which tissue forms the C-shaped rings that reinforce the trachea?
A) fibrocartilage
B) elastic cartilage
C) hyaline cartilage
D) compact bone
A) fibrocartilage
B) elastic cartilage
C) hyaline cartilage
D) compact bone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which tonsils sit at the base of the tongue?
A) lingual
B) laryngeal
C) pharyngeal
D) palatine
A) lingual
B) laryngeal
C) pharyngeal
D) palatine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15

Using Figure 13.1, identify the following:
The apex of the right lung is indicated by ________.
A) Label E
B) Label F
C) Label H
D) Label G
E) Label J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16

Using Figure 13.1, identify the following:
The oral cavity is indicated by ________.
A) Label C
B) Label A
C) Label E
D) label B
E) Label G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17

Using Figure 13.1, identify the following:
The pharynx is indicated by ________.
A) Label H
B) Label I
C) Label J
D) Label F
E) Label B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18

Using Figure 13.1, identify the following:
The trachea is indicated by ________.
A) Label D
B) Label I
C) Label B
D) Label F
E) Label G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19

Using Figure 13.1, identify the following:
The larynx is indicated by ________.
A) Label H
B) Label G
C) Label F
D) Label A
E) Label D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

Using Figure 13.1, identify the following:
The nasal cavity is indicated by ________.
A) Label D
B) Label C
C) Label B
D) Label H
E) Label A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The total amount of exchangeable air is known as ________.
A) residual volume
B) inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
C) tidal volume (TV)
D) vital capacity (VC)
A) residual volume
B) inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
C) tidal volume (TV)
D) vital capacity (VC)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which passageways branch off of the inferior end of the trachea?
A) bronchioles
B) bronchi
C) alveolar ducts
D) alveolar sacs
A) bronchioles
B) bronchi
C) alveolar ducts
D) alveolar sacs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the most common transport method for carbon dioxide?
A) oxyhemoglobin
B) deoxyhemoglobin
C) carbon monoxide
D) bicarbonate ions
A) oxyhemoglobin
B) deoxyhemoglobin
C) carbon monoxide
D) bicarbonate ions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What non-respiratory air movement is intended to ventilate all alveoli?
A) cough
B) hiccup
C) yawn
D) sneeze
A) cough
B) hiccup
C) yawn
D) sneeze

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which inspiratory muscles contract so we can inspire air?
A) rectus abdominis; external obliques
B) diaphragm; external intercostals
C) trapezius; latissimus dorsi
D) diaphragm; external obliques
A) rectus abdominis; external obliques
B) diaphragm; external intercostals
C) trapezius; latissimus dorsi
D) diaphragm; external obliques

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The normal respiratory rate of 12-15 breaths per minute is known as ________.
A) hyperpnea
B) eupnea
C) dyspnea
D) apnea
A) hyperpnea
B) eupnea
C) dyspnea
D) apnea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What portions of the brain contain respiratory centers and set the breathing rate?
A) medulla and pons
B) pons and cerebellum
C) cerebrum and cerebellum
D) thalamus and hypothalamus
A) medulla and pons
B) pons and cerebellum
C) cerebrum and cerebellum
D) thalamus and hypothalamus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Lung collapse, or ________, can occur if the intrapleural pressure equals atmospheric pressure when air enters the pleural space.
A) pleurisy
B) atelectasis
C) rales
D) wheezing
A) pleurisy
B) atelectasis
C) rales
D) wheezing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What are the smallest conducting passageways of the lungs?
A) main (primary) bronchi
B) alveoli
C) terminal bronchioles
D) alveolar ducts
A) main (primary) bronchi
B) alveoli
C) terminal bronchioles
D) alveolar ducts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The regulation of the activity of the breathing muscles, the diaphragm and external intercostals, is controlled by nerve impulses transmitted from the brain via the ________ and ________ nerves.
A) splanchnic; sacral
B) trochlear; trigeminal
C) phrenic; intercostal
D) cranial; spinal
A) splanchnic; sacral
B) trochlear; trigeminal
C) phrenic; intercostal
D) cranial; spinal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Gas exchange between the pulmonary blood and alveoli is called ________.
A) pulmonary ventilation
B) inhalation
C) external respiration
D) internal respiration
A) pulmonary ventilation
B) inhalation
C) external respiration
D) internal respiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The most important stimulus for breathing in a healthy person is the body's need to rid itself of the blood gas called ________.
A) carbon dioxide
B) oxygen
C) methane
D) nitrous oxide
A) carbon dioxide
B) oxygen
C) methane
D) nitrous oxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
During ________, oxygen binds to hemoglobin to form oxyhemoglobin.
A) internal respiration
B) external respiration
C) cellular respiration
D) expiration
A) internal respiration
B) external respiration
C) cellular respiration
D) expiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The serous membrane that surrounds each lung is created by a parietal and visceral ________.
A) pleura
B) pericardium
C) peritoneum
D) mediastinum
A) pleura
B) pericardium
C) peritoneum
D) mediastinum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The process of moving air into and out of the lungs is commonly called breathing or ________.
A) cellular respiration
B) internal respiration
C) respiratory gas transport
D) pulmonary ventilation
A) cellular respiration
B) internal respiration
C) respiratory gas transport
D) pulmonary ventilation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Air flowing out of the lungs is known as ________.
A) expiration
B) respiratory gas transport
C) inhalation
D) inspiration
A) expiration
B) respiratory gas transport
C) inhalation
D) inspiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
________ volume is the air moved into and out of the lungs during normal quiet breathing and is approximately 500 mL of air.
A) Tidal
B) Vital capacity
C) Residual
D) Inspiratory capacity
A) Tidal
B) Vital capacity
C) Residual
D) Inspiratory capacity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which zone includes the respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli and is where gas exchange occurs?
A) respiratory zone
B) conducting zone
C) terminal zone
D) filtering zone
A) respiratory zone
B) conducting zone
C) terminal zone
D) filtering zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Damage to the larynx can cause an inability to ________.
A) sneeze
B) cough
C) speak
D) hiccup
A) sneeze
B) cough
C) speak
D) hiccup

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What odorless, colorless gas binds preferentially with the same binding site on hemoglobin as oxygen?
A) hydrogen sulfide
B) carbon monoxide
C) nitrous oxide
D) methane
A) hydrogen sulfide
B) carbon monoxide
C) nitrous oxide
D) methane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Air from the nasal cavity enters the superior portion of the pharynx called the ________.
A) nasopharynx
B) oropharynx
C) palatopharynx
D) laryngopharynx
E) tracheopharynx
A) nasopharynx
B) oropharynx
C) palatopharynx
D) laryngopharynx
E) tracheopharynx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The correct pathway air flows through the respiratory system is ________.
A) nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, main (primary) bronchi
B) nose, larynx, pharynx, trachea, main (primary) bronchi
C) nose, pharynx, trachea, larynx, main (primary) bronchi
D) nose, larynx, trachea, pharynx, main (primary) bronchi
E) nose, pharynx, larynx, main (primary) bronchi, trachea
A) nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, main (primary) bronchi
B) nose, larynx, pharynx, trachea, main (primary) bronchi
C) nose, pharynx, trachea, larynx, main (primary) bronchi
D) nose, larynx, trachea, pharynx, main (primary) bronchi
E) nose, pharynx, larynx, main (primary) bronchi, trachea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the function of an alveolar macrophage?
A) secrete mucus
B) facilitate gas exchange
C) produce surfactant
D) engulf bacteria, carbon particles, and debris
E) sweep contaminated mucus and debris from the alveoli
A) secrete mucus
B) facilitate gas exchange
C) produce surfactant
D) engulf bacteria, carbon particles, and debris
E) sweep contaminated mucus and debris from the alveoli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What role do the tonsils play in the respiratory system?
A) Tonsils produce mucus which drains into the nasal cavities.
B) Tonsils humidify and warm incoming air.
C) Tonsils moisten the air entering the respiratory passageways.
D) Tonsils protect the body from infection.
E) Tonsils sweep contaminated mucus toward the throat.
A) Tonsils produce mucus which drains into the nasal cavities.
B) Tonsils humidify and warm incoming air.
C) Tonsils moisten the air entering the respiratory passageways.
D) Tonsils protect the body from infection.
E) Tonsils sweep contaminated mucus toward the throat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the role of mucus in the nasal cavity?
A) increase the air turbulence in the nasal cavity
B) separate the oral cavity from the nasal cavity
C) lighten the skull
D) act as a resonance chamber for speech
E) trap incoming bacteria and other foreign debris
A) increase the air turbulence in the nasal cavity
B) separate the oral cavity from the nasal cavity
C) lighten the skull
D) act as a resonance chamber for speech
E) trap incoming bacteria and other foreign debris

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Where does exchange occur?
A) nose
B) pharynx
C) larynx
D) trachea
E) alveoli
A) nose
B) pharynx
C) larynx
D) trachea
E) alveoli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In order to return acidic blood pH to normal, breathing becomes deeper and more rapid, a phenomenon known as ________.
A) hypoventilation
B) hyperventilation
C) apnea
D) dyspnea
A) hypoventilation
B) hyperventilation
C) apnea
D) dyspnea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which one of the following is NOT True of the lungs?
A) The narrower portion of each lung is called the apex.
B) The bases rest on the diaphragm.
C) The left lung has two lobes.
D) The right lung has three lobes.
E) Both lungs have two lobes.
A) The narrower portion of each lung is called the apex.
B) The bases rest on the diaphragm.
C) The left lung has two lobes.
D) The right lung has three lobes.
E) Both lungs have two lobes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which one of the following bones does NOT contain paranasal sinuses?
A) frontal
B) sphenoid
C) mandible
D) ethmoid
E) maxilla
A) frontal
B) sphenoid
C) mandible
D) ethmoid
E) maxilla

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The superior portion of each lung is the ________.
A) pleura
B) base
C) apex
D) mediastinum
E) fissure
A) pleura
B) base
C) apex
D) mediastinum
E) fissure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The respiratory conducting passageways perform all of the following functions EXCEPT ________.
A) allow air to reach the lungs
B) purify air
C) humidify air
D) exchange gases
E) warm incoming air
A) allow air to reach the lungs
B) purify air
C) humidify air
D) exchange gases
E) warm incoming air

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The pharynogotympanic tubes, which drain the middle ear, open into the ________.
A) nasopharynx
B) oropharynx
C) palatopharynx
D) laryngopharynx
E) tracheopharynx
A) nasopharynx
B) oropharynx
C) palatopharynx
D) laryngopharynx
E) tracheopharynx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What part of the larynx is commonly called the Adam's apple?
A) glottis
B) thyroid cartilage
C) vocal folds (True vocal cords)
D) trachea
E) epiglottis
A) glottis
B) thyroid cartilage
C) vocal folds (True vocal cords)
D) trachea
E) epiglottis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
How do goblet cells, present in the lining of the trachea, contribute to the protection of the respiratory system?
A) Goblet cells create a sweeping motion that propels mucus toward the throat.
B) Goblet cells create a patent airway.
C) Goblet cells protect the superior opening of the larynx by preventing the entry of food and fluids into the larynx.
D) Goblet cells produce mucus that traps dust particles and other debris.
E) Goblet cells vibrate to allow us to speak.
A) Goblet cells create a sweeping motion that propels mucus toward the throat.
B) Goblet cells create a patent airway.
C) Goblet cells protect the superior opening of the larynx by preventing the entry of food and fluids into the larynx.
D) Goblet cells produce mucus that traps dust particles and other debris.
E) Goblet cells vibrate to allow us to speak.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The serous membrane covering the surface of the lungs is called the ________.
A) mediastinum
B) visceral pleura
C) parietal pleura
D) main (primary) bronchi
E) pleurisy
A) mediastinum
B) visceral pleura
C) parietal pleura
D) main (primary) bronchi
E) pleurisy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Smoking destroys cilia in the respiratory passageways, such as the trachea. Which of the following is a likely consequence of damaged cilia?
A) inflammation and swelling of the tonsils
B) air is not moistened, warmed, or filtered before reaching the lungs
C) inability to propel mucus from the lungs to the throat
D) nasal congestion and postnasal drip
E) inability to produce mucus
A) inflammation and swelling of the tonsils
B) air is not moistened, warmed, or filtered before reaching the lungs
C) inability to propel mucus from the lungs to the throat
D) nasal congestion and postnasal drip
E) inability to produce mucus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What fatty molecule is made by alveolar cells to reduce surface tension and prevent alveolar collapse between breaths?
A) sebum
B) surfactant
C) nicotine
D) mucus
A) sebum
B) surfactant
C) nicotine
D) mucus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Vibration due to exhaled air that results in speech is a function of the ________.
A) trachea
B) larynx
C) pharynx
D) glottis
E) epiglottis
A) trachea
B) larynx
C) pharynx
D) glottis
E) epiglottis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What sweeps contaminated mucus from the nasal cavity to the throat?
A) tonsils
B) flagella
C) cilia
D) coarse hairs
E) air turbulence
A) tonsils
B) flagella
C) cilia
D) coarse hairs
E) air turbulence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity by ________.
A) the pharynx
B) the nasal conchae
C) the larynx
D) both the hard and soft palate
E) both the nasal conchae and hard palate
A) the pharynx
B) the nasal conchae
C) the larynx
D) both the hard and soft palate
E) both the nasal conchae and hard palate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Oxygen is transported in the blood as ________.
A) bicarbonate ion
B) oxyhemoglobin
C) carbonic acid
D) deoxyhemoglobin
E) carbonic anhydrase
A) bicarbonate ion
B) oxyhemoglobin
C) carbonic acid
D) deoxyhemoglobin
E) carbonic anhydrase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following events of respiration involves the flow of air out of the lungs?
A) internal respiration
B) inspiration
C) external respiration
D) expiration
E) cellular respiration
A) internal respiration
B) inspiration
C) external respiration
D) expiration
E) cellular respiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Hyperventilation is the body's response to ________.
A) increased carbon dioxide levels in the blood
B) increased oxygen levels in the blood
C) decreased carbon dioxide levels in the blood
D) alkalosis
E) increased blood pH
A) increased carbon dioxide levels in the blood
B) increased oxygen levels in the blood
C) decreased carbon dioxide levels in the blood
D) alkalosis
E) increased blood pH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Expiration (exhalation) occurs when ________.
A) the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract
B) air moves into the lungs
C) intrapulmonary volume increases
D) the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax
E) intrapulmonary pressure decreases
A) the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract
B) air moves into the lungs
C) intrapulmonary volume increases
D) the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax
E) intrapulmonary pressure decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What forms the respiratory membrane (air-blood barrier)?
A) respiratory bronchioles and alveoli
B) terminal bronchioles and respiratory bronchioles
C) systemic capillaries and cells of the body
D) the visceral and parietal pleura
E) the fused basement membranes of alveolar and pulmonary capillary walls
A) respiratory bronchioles and alveoli
B) terminal bronchioles and respiratory bronchioles
C) systemic capillaries and cells of the body
D) the visceral and parietal pleura
E) the fused basement membranes of alveolar and pulmonary capillary walls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The respiratory movement representing the total amount of exchangeable air is the ________.
A) tidal volume
B) inspiratory reserve volume
C) expiratory reserve volume
D) vital capacity
E) dead space volume
A) tidal volume
B) inspiratory reserve volume
C) expiratory reserve volume
D) vital capacity
E) dead space volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which one of the following structures is NOT part of the respiratory zone?
A) respiratory bronchioles
B) alveolar ducts
C) alveolar sacs
D) alveoli
E) primary bronchus
A) respiratory bronchioles
B) alveolar ducts
C) alveolar sacs
D) alveoli
E) primary bronchus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is NOT one of the four main events of respiration?
A) pulmonary ventilation
B) respiratory gas transport
C) residual volume
D) external respiration
E) internal respiration
A) pulmonary ventilation
B) respiratory gas transport
C) residual volume
D) external respiration
E) internal respiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of these terms is an abnormal bronchial sound that occurs when mucus is present in the lung passages?
A) sneeze
B) cough
C) pleural friction rub
D) wheezing
E) rales
A) sneeze
B) cough
C) pleural friction rub
D) wheezing
E) rales

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Hyperventilation leads to all of the following EXCEPT ________.
A) brief periods of apnea
B) cyanosis
C) dizziness
D) fainting
E) buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood
A) brief periods of apnea
B) cyanosis
C) dizziness
D) fainting
E) buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Hypoventilation dramatically increases carbonic acid concentration and involves ________.
A) extremely deep breathing
B) extremely fast breathing
C) extremely slow breathing
D) intermittent breathing
E) irregular breathing
A) extremely deep breathing
B) extremely fast breathing
C) extremely slow breathing
D) intermittent breathing
E) irregular breathing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The presence of air in the intrapleural space is known as ________.
A) pneumothorax
B) atelectasis
C) pneumonia
D) pleurisy
E) wheezing
A) pneumothorax
B) atelectasis
C) pneumonia
D) pleurisy
E) wheezing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The amount of air exchanged during normal quiet breathing is about ________.
A) 500 mL
B) 1200 mL
C) 2100 mL
D) 4800 mL
E) 6000 mL
A) 500 mL
B) 1200 mL
C) 2100 mL
D) 4800 mL
E) 6000 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Even after a forceful expiration, air still remains in the lungs for gas exchange to continue. This volume is about ________.
A) 500 mL
B) 1200 mL
C) 2100 mL
D) 4800 mL
E) 6000 mL
A) 500 mL
B) 1200 mL
C) 2100 mL
D) 4800 mL
E) 6000 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which nonrespiratory air movement clears the upper respiratory passageways?
A) coughing
B) yawning
C) laughing
D) hiccupping
E) sneezing
A) coughing
B) yawning
C) laughing
D) hiccupping
E) sneezing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which nerves stimulate the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles to contract?
A) splanchnic nerves
B) somatic nerves
C) phrenic and intercostal nerves
D) vagus nerves
E) myenteric nerves
A) splanchnic nerves
B) somatic nerves
C) phrenic and intercostal nerves
D) vagus nerves
E) myenteric nerves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Laura's lung collapsed during a skiing accident when a rib punctured her lung. The condition of a collapsed lung is known as ________.
A) atelectasis
B) asthma
C) eupnea
D) pleurisy
E) pneumothorax
A) atelectasis
B) asthma
C) eupnea
D) pleurisy
E) pneumothorax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Exchange of both oxygen and carbon dioxide through the respiratory membrane occurs by ________.
A) osmosis
B) simple diffusion
C) facilitated diffusion
D) active transport
E) endocytosis
A) osmosis
B) simple diffusion
C) facilitated diffusion
D) active transport
E) endocytosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which one of the following is NOT True of inspiration?
A) Contraction of the diaphragm muscle helps increase the size of the thoracic cavity.
B) Relaxation of the external intercostal muscles helps increase the size of the thoracic cavity.
C) Increased intrapulmonary volume causes inhaled gases to spread out.
D) The decreased gas pressure produces a partial vacuum that forcibly sucks air in.
E) Air continues to move into the lungs until intrapulmonary pressure equals atmospheric pressure.
A) Contraction of the diaphragm muscle helps increase the size of the thoracic cavity.
B) Relaxation of the external intercostal muscles helps increase the size of the thoracic cavity.
C) Increased intrapulmonary volume causes inhaled gases to spread out.
D) The decreased gas pressure produces a partial vacuum that forcibly sucks air in.
E) Air continues to move into the lungs until intrapulmonary pressure equals atmospheric pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Oxygen is unloaded from the blood stream and diffuses into surrounding cells and tissues during ________.
A) internal respiration
B) pulmonary ventilation
C) external respiration
D) respiratory gas transport
E) tidal volume
A) internal respiration
B) pulmonary ventilation
C) external respiration
D) respiratory gas transport
E) tidal volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



