Deck 7: Crags, Cracks, and Crumples: Crustal Deformation and Mountain Building
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/59
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Crags, Cracks, and Crumples: Crustal Deformation and Mountain Building
1
Under which of the following conditions would a body of rock be more likely to exhibit plastic behavior?
A)low temperature
B)high temperature
C)low pressure
D)high rate of deformation
A)low temperature
B)high temperature
C)low pressure
D)high rate of deformation
B
2
A body of rock affected by compression will likely undergo
A)shortening.
B)stretching.
C)shear strain
D)rotation.
A)shortening.
B)stretching.
C)shear strain
D)rotation.
A
3
What kind of stress results in the lengthening of rock?
A)compressional
B)tensional
C)shear
D)brittle
A)compressional
B)tensional
C)shear
D)brittle
D
4
Under which condition would a body of rock be most likely to exhibit brittle behavior?
A)slow rate of deformation
B)low temperature
C)high temperature
D)high pressure
A)slow rate of deformation
B)low temperature
C)high temperature
D)high pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Normal, reverse, and thrust are all examples of _________ faults.
A)strike-slip
B)dip-slip
C)oblique-slip
D)lateral
A)strike-slip
B)dip-slip
C)oblique-slip
D)lateral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following occurs when rocks bend, break, or flow during mountain building?
A)deformation
B)orogeny
C)lengthening
D)stress
A)deformation
B)orogeny
C)lengthening
D)stress

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The formation of joints in a rock in response to tension is an example of
A)brittle deformation.
B)plastic deformation.
C)shear strain.
D)rotation.
A)brittle deformation.
B)plastic deformation.
C)shear strain.
D)rotation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following occurs when rocks are pulled apart?
A)compression
B)tension
C)shear
D)pressure
A)compression
B)tension
C)shear
D)pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Right-lateral and left-lateral are both examples of _________ faults.
A)strike-slip
B)dip-slip
C)oblique-slip
D)reverse
A)strike-slip
B)dip-slip
C)oblique-slip
D)reverse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A body of rock affected by tension will likely undergo
A)shortening.
B)stretching.
C)shear strain
D)rotation.
A)shortening.
B)stretching.
C)shear strain
D)rotation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which type of situation would be more likely to produce folds?
A)cold, brittle crust under tension
B)cold, brittle crust under compression
C)warm, ductile crust under tension
D)warm, ductile crust under compression
A)cold, brittle crust under tension
B)cold, brittle crust under compression
C)warm, ductile crust under tension
D)warm, ductile crust under compression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Folds are most often associated with _________ stress.
A)tensional
B)compressional
C)shear
D)straight
A)tensional
B)compressional
C)shear
D)straight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A fold shaped like an elongated arch is a(n)
A)anticline.
B)basin.
C)dome.
D)syncline
A)anticline.
B)basin.
C)dome.
D)syncline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Force-per-unit area is termed
A) stress.
B) strain.
C) power.
D) work.
A) stress.
B) strain.
C) power.
D) work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is a change in the shape of a rock induced by stress?
A)Elastic rebound
B)Pressure release
C)Strain
D)Metamorphosis
A)Elastic rebound
B)Pressure release
C)Strain
D)Metamorphosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How is stress different from strain?
A)Strain is a measure of the offset on a fault as a result of applied stress.
B)Stress is the change in shape of a rock as a result of applied strain.
C)Strain is the change in shape of a rock as a result of applied stress.
D)They are not different; stress and strain are synonymous.
A)Strain is a measure of the offset on a fault as a result of applied stress.
B)Stress is the change in shape of a rock as a result of applied strain.
C)Strain is the change in shape of a rock as a result of applied stress.
D)They are not different; stress and strain are synonymous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Tectonic foliation is most likely to occur as a result of
A)metamorphism.
B)faulting.
C)brittle deformation.
D)rotation.
A)metamorphism.
B)faulting.
C)brittle deformation.
D)rotation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How does the rate at which a body of rock is deformed affect its behavior?
A)A rock deformed quickly is likely to exhibit brittle behavior.
B)A rock deformed slowly is likely to exhibit brittle behavior.
C)The rate of deformation has no effect on a rock's behavior.
D)The rate of deformation is important only below the brittle/plastic transition.
A)A rock deformed quickly is likely to exhibit brittle behavior.
B)A rock deformed slowly is likely to exhibit brittle behavior.
C)The rate of deformation has no effect on a rock's behavior.
D)The rate of deformation is important only below the brittle/plastic transition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The fossil in the image below has been subjected to what type of stress? 
A)brittle
B)tensional
C)shear
D)compressional

A)brittle
B)tensional
C)shear
D)compressional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Normal faults are generally the result of _________ stress.
A)tensional
B)compressional
C)shear
D)triaxial
A)tensional
B)compressional
C)shear
D)triaxial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Normal faulting is most often associated with mountain building along ___________ boundaries, whereas reverse faulting is generally observed at ___________ boundaries.
A) divergent; transform
B) transform; convergent
C)convergent; divergent
D)divergent; convergent
A) divergent; transform
B) transform; convergent
C)convergent; divergent
D)divergent; convergent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An episode of mountain building is termed a(n)
A)orogeny.
B)phylogeny.
C)aureole.
D)slickenside.
A)orogeny.
B)phylogeny.
C)aureole.
D)slickenside.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Mountains forming would be most likely found at the
A)eastern South American plate boundary.
B)western South American plate boundary.
C)eastern South American continental margin.
D)center of the South American continent.
A)eastern South American plate boundary.
B)western South American plate boundary.
C)eastern South American continental margin.
D)center of the South American continent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Regularly spaced joints in an outcrop may indicate that an area
A)is under intense shear stress.
B)has experienced compressional stress.
C)is underlain by a thrust fault.
D)is formed from rocks that were once at great depth.
A)is under intense shear stress.
B)has experienced compressional stress.
C)is underlain by a thrust fault.
D)is formed from rocks that were once at great depth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the following map, the vertical, north-south trending fault is a ________ fault. 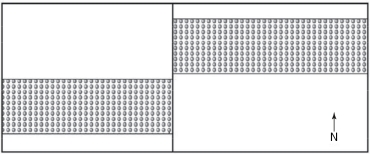
A)normal dip-slip
B)reverse dip-slip
C)right-lateral strike-slip
D)left-lateral strike-slip

A)normal dip-slip
B)reverse dip-slip
C)right-lateral strike-slip
D)left-lateral strike-slip

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
On a geologic map, if the contacts between sedimentary rock units form a series of parallel lines, with the youngest unit in the center, the underlying structure is a
A)horizontal anticline.
B)plunging anticline.
C)non-plunging syncline.
D)plunging syncline.
A)horizontal anticline.
B)plunging anticline.
C)non-plunging syncline.
D)plunging syncline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The Himalayan mountain range was formed at which tectonic setting?
A)a convergent plate boundary
B)a divergent plate boundary
C)a transform plate boundary
D)hotspots
A)a convergent plate boundary
B)a divergent plate boundary
C)a transform plate boundary
D)hotspots

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
During the formation of Pangea, Africa collided with North America and created the Appalachian Mountains. Which of the following mountain ranges is a modern analogue to the ancient Appalachian Mountains?
A)Andes Mountains
B)Sierra Nevada Mountains
C)Italian Alps
D)Cascade Mountains
A)Andes Mountains
B)Sierra Nevada Mountains
C)Italian Alps
D)Cascade Mountains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The formation of the Basin and Range Province, a fault-blocked mountain range in Utah, Nevada, and Arizona, is associated with which of the following processes?
A)continental rifting
B)continental collision
C)fold and thrust faulting
D)subduction zone volcanism
A)continental rifting
B)continental collision
C)fold and thrust faulting
D)subduction zone volcanism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The distinction between joints and faults is that
A)faults are joints that are greater than 1 square meter in areal extent.
B)faults are fractures along which displacement has occurred; displacement does not occur along joints.
C)joints are fractures along which displacement has occurred; displacement does not occur along faults.
D)There is no distinction; the two terms are synonymous.
A)faults are joints that are greater than 1 square meter in areal extent.
B)faults are fractures along which displacement has occurred; displacement does not occur along joints.
C)joints are fractures along which displacement has occurred; displacement does not occur along faults.
D)There is no distinction; the two terms are synonymous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The fold in the image below is a(n) 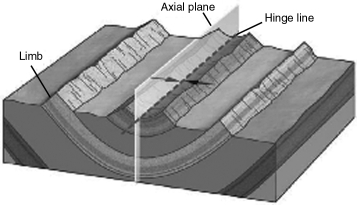
A)anticline.
B)basin.
C)dome.
D)syncline

A)anticline.
B)basin.
C)dome.
D)syncline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following faults could result from both strike-slip and dip-slip stresses? 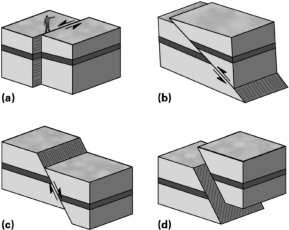
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Mountain ranges formed along subduction zones are formed, in part, by ___________ in the crust.
A)compression
B)stretching
C)extension
D)elongation
A)compression
B)stretching
C)extension
D)elongation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The balance between the weight of a mountain range and the buoyancy provided by the underlying mantle is termed
A) delamination.
B) suture.
C)isostasy.
D)orogen.
A) delamination.
B) suture.
C)isostasy.
D)orogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
As the mountains in a mountain range are slowly eroded, the crustal root
A)is eroded at the same rate.
B)remains stationary.
C)sinks deeper into the mantle.
D)rises out of the mantle.
A)is eroded at the same rate.
B)remains stationary.
C)sinks deeper into the mantle.
D)rises out of the mantle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Regions where Precambrian metamorphic rocks are exposed at the surface are termed
A)shields.
B)cratonic platforms.
C)convergent margins.
D)domes.
A)shields.
B)cratonic platforms.
C)convergent margins.
D)domes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Continental crust is typically 35 km thick but may be up to __________ thick under mountain ranges.
A)40 km
B)70 km
C)200
D)400
A)40 km
B)70 km
C)200
D)400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The outer portion of a craton, where deformed rocks are covered by sediments, is termed the
A)shield.
B)cratonic platform.
C)convergent margin.
D)exotic terrane.
A)shield.
B)cratonic platform.
C)convergent margin.
D)exotic terrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is the process whereby rocks from depth are exposed at the surface during mountain building?
A) subsidence
B) uplift
C)jointing
D)foliation
A) subsidence
B) uplift
C)jointing
D)foliation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of these properly illustrates the principle of isostasy?
A)High-density crust floats on top of low-density mantle.
B)Mountains stand high because they are gravitationally balanced by their deep crustal roots.
C)When weight is added to the crust, the crust responds by rebounding upward.
D)When material is removed from the crust, the crust maintains the new, lower elevation.
A)High-density crust floats on top of low-density mantle.
B)Mountains stand high because they are gravitationally balanced by their deep crustal roots.
C)When weight is added to the crust, the crust responds by rebounding upward.
D)When material is removed from the crust, the crust maintains the new, lower elevation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What can be said about a mountain range that is being uplifted at 2 cm/yr but is not growing any taller?
A)The crustal root is thinning at the same rate as the uplift.
B)The crustal root is thickening faster than the uplift.
C)The rate of erosion is the same as the rate of uplift.
D)The rate of erosion is higher than the rate of uplift.
A)The crustal root is thinning at the same rate as the uplift.
B)The crustal root is thickening faster than the uplift.
C)The rate of erosion is the same as the rate of uplift.
D)The rate of erosion is higher than the rate of uplift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The Appalachian Mountains were formed as a result of the collision of North America and Africa at the end of the Paleozoic era. Describe what the Appalachians looked like when formed and what has caused them to become a series of gently sloping hills today.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following shows a thrust fault? 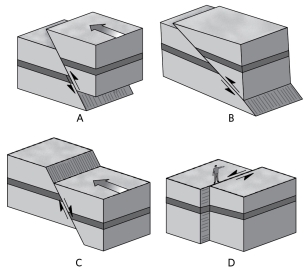
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Metamorphic rocks found in cratons are exposed during orogenesis by
A)faulting.
B)folding.
C)shields.
D)erosion.
A)faulting.
B)folding.
C)shields.
D)erosion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Describe the differences between brittle and ductile deformation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is the ultimate fate of all mountains on Earth?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How were the mountains in the Basin and Range Province formed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the difference between a dip-slip fault and a strike slip fault? Provide examples of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Draw a cross section of a normal and reverse fault. For each, list the stress involved and changes in the length of the crust, if any.
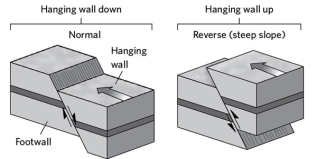


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What are the three components of deformation? Briefly explain each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Mount Marshak towers above the landscape at 5.3 km tall. The rate of uplift at Mount Marshak is 1.3 mm/yr and the rate of erosion is 1.5 mm/yr. How tall will Mount Marshak be after a million years, assuming everything remains constant?
A)5.5 km
B)7.3 km
C)5.1 km
D)3.3 km
A)5.5 km
B)7.3 km
C)5.1 km
D)3.3 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What types of geologic structures would you expect to find in an area that had undergone compression?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Compare and contrast domes and basins. If both are composed solely of sedimentary beds that have been eroded such that the ground surface is level, how would you identify each?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What do strike and dip describe?
A)orientation of planar features
B)degree of metamorphism
C)depth of faulting
D)location of a structure
A)orientation of planar features
B)degree of metamorphism
C)depth of faulting
D)location of a structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following shows a plunging fold? 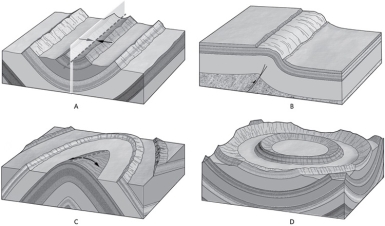
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which picture illustrates a likely outcome of compression in the crust? 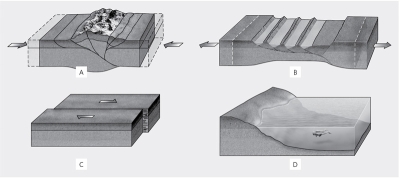
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What are joints? What might the presence of joints in a rock indicate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Regions of continents that have NOT been subjected to mountain-building events during the past 1 billion years are termed
A)exotic terranes.
B)accreted terranes.
C)cratons.
D)cratonic platforms.
A)exotic terranes.
B)accreted terranes.
C)cratons.
D)cratonic platforms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Erosional processes work to remove material from mountains; thus, over time the topography will become less
A)rugged.
B)weathered.
C)flat-lying
D)stretched.
A)rugged.
B)weathered.
C)flat-lying
D)stretched.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



