Deck 22: Carbohydrate Metabolism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/9
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Carbohydrate Metabolism
1
The activation of glucagon receptors turns the liver into a net producer of glucose.Glucagon stimulates a signal transduction pathway in liver involving:
A)SMAD protein phosphorylation.
B)Protein kinase A activation.
C)Calcium pumping into the endoplasmic reticulum.
D)Receptor tyrosine protein kinase activation.
E)Activation of G protein guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) activity.
A)SMAD protein phosphorylation.
B)Protein kinase A activation.
C)Calcium pumping into the endoplasmic reticulum.
D)Receptor tyrosine protein kinase activation.
E)Activation of G protein guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) activity.
Protein kinase A activation.
2
A 10-year-old boy has suffered from slowly progressing ataxia (poor motor coordination) since the age of 5.A blood test shows abnormal elevations of alanine and lactic acid levels after an oral glucose load.Partial deficiency of which of the following enzymes or transporters is the most likely cause of the boy's condition?
A)Carnitine-palmitoyl transferase 1.
B)Glucose transporter 4.
C)Pyruvate dehydrogenase.
D)Aldolase B.
E)Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
A)Carnitine-palmitoyl transferase 1.
B)Glucose transporter 4.
C)Pyruvate dehydrogenase.
D)Aldolase B.
E)Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase.
3
As shown in Figure 22.4, a patient has low blood glucose levels (dashed line) after a 24-hour fast.Normal values are indicated by the solid line. 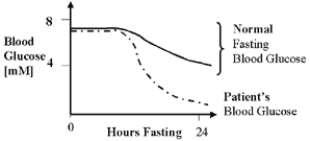 A partial deficiency of which of the following enzymes could possibly be a cause of the fasting hypoglycemia?
A partial deficiency of which of the following enzymes could possibly be a cause of the fasting hypoglycemia?
A)Pyruvate dehydrogenase.
B)Glucokinase.
C)Phosphofructokinase-1.
D)Aldolase A.
E)Pyruvate kinase.
 A partial deficiency of which of the following enzymes could possibly be a cause of the fasting hypoglycemia?
A partial deficiency of which of the following enzymes could possibly be a cause of the fasting hypoglycemia?A)Pyruvate dehydrogenase.
B)Glucokinase.
C)Phosphofructokinase-1.
D)Aldolase A.
E)Pyruvate kinase.
Aldolase A.
4
A 3-month-old infant is found to have fasting hypoglycemia.In order to test for possible enzyme deficiencies, you conduct a liver biopsy and test for several metabolic enzymes.Fasting hypoglycemia can be caused by deficiencies of all the following enzymes except:
A)Glucose-6-phosphatase.
B)Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
C)Glycogen phosphorylase.
D)Phosphorylase kinase.
E)Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase.
A)Glucose-6-phosphatase.
B)Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
C)Glycogen phosphorylase.
D)Phosphorylase kinase.
E)Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate is an allosteric inhibitor of which enzyme of carbohydrate metabolism?
A)Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
B)Phosphofructokinase-1.
C)Aldolase B.
D)Glycogen phosphorylase.
E)Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase.
A)Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
B)Phosphofructokinase-1.
C)Aldolase B.
D)Glycogen phosphorylase.
E)Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A 25-year-old man is found in a semicomatose state and is taken to the emergency room by friends, who say that the man has not eaten for the past 5 days.Which of the following substances is this patient's primary source of glucose?
A)Amino acids from liver proteins.
B)Amino acids from muscle proteins.
C)Liver glycogen.
D)Muscle glycogen.
E)Fatty acids from adipose tissue.
A)Amino acids from liver proteins.
B)Amino acids from muscle proteins.
C)Liver glycogen.
D)Muscle glycogen.
E)Fatty acids from adipose tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which liver enzyme is activated by insulin to stimulate glycogen deposition by glycogen synthase?
A)Phosphofructokinase-2.
B)Protein phosphatase-1.
C)Protein kinase A.
D)Protein kinase C.
E)Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase.
A)Phosphofructokinase-2.
B)Protein phosphatase-1.
C)Protein kinase A.
D)Protein kinase C.
E)Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A 30-year-old man of Italian ancestry is treated with high doses of a combination antibiotic for his chronic sinusitis.After 1 week of drug treatment, a dark brown discoloration of the urine is noted, and the hematocrit is found to be 32%.Haptoglobin is virtually undetectable.What is a likely mechanism for the patient's drug-induced anemia?
A)Galactose metabolism is inhibited.
B)There is not enough ribose to support DNA replication.
C)Red blood cells produce too much apo-hemoglobin.
D)Glutathione reduction by the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) is impaired.
E)The reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) oxidase overproduces oxygen radicals.
A)Galactose metabolism is inhibited.
B)There is not enough ribose to support DNA replication.
C)Red blood cells produce too much apo-hemoglobin.
D)Glutathione reduction by the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) is impaired.
E)The reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) oxidase overproduces oxygen radicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Glucokinase is used by liver and pancreatic b cells to adjust glucose metabolism to changing levels of blood glucose.This is possible because there is an important difference between glucokinase and the other isoforms of hexokinase:
A)Glucokinase uses ATP as a substrate, but hexokinase does not.
B)Glucokinase has a higher Km value for glucose than does hexokinase.
C)Glucokinase has a maximal reaction rate (Vmax) that changes with the blood glucose concentration.
D)Glucokinase uses both glucose and fructose as substrates, whereas the other forms of hexokinase can use only glucose.
E)Glucokinase is located on the cell surface, whereas the other forms of hexokinase are cytoplasmic.
A)Glucokinase uses ATP as a substrate, but hexokinase does not.
B)Glucokinase has a higher Km value for glucose than does hexokinase.
C)Glucokinase has a maximal reaction rate (Vmax) that changes with the blood glucose concentration.
D)Glucokinase uses both glucose and fructose as substrates, whereas the other forms of hexokinase can use only glucose.
E)Glucokinase is located on the cell surface, whereas the other forms of hexokinase are cytoplasmic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



