Deck 14: Thalassemia
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/32
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Thalassemia
1
What test could provide the diagnosis differential for β-thalassemia minor and iron deficiency?
A)PB smear
B)Iron studies
C)Hemoglobin electrophoresis
D)Bone marrow aspirate
A)PB smear
B)Iron studies
C)Hemoglobin electrophoresis
D)Bone marrow aspirate
Hemoglobin electrophoresis
2
Why are bone changes and deformities common findings in β-thalassemias?
A)The globin chain synthesis is increased.
B)The impaired globin chain synthesis causes erythroid hypoplasia.
C)The impaired globin chain synthesis causes increased erythropoiesis resulting in bone marrow expansion.
D)The impaired globin chain synthesis causes impaired oxygen delivery to the bone tissue,which causes bone deformities.
A)The globin chain synthesis is increased.
B)The impaired globin chain synthesis causes erythroid hypoplasia.
C)The impaired globin chain synthesis causes increased erythropoiesis resulting in bone marrow expansion.
D)The impaired globin chain synthesis causes impaired oxygen delivery to the bone tissue,which causes bone deformities.
The impaired globin chain synthesis causes increased erythropoiesis resulting in bone marrow expansion.
3
Which of the following statements is true regarding hemoglobinopathies but false in thalassemia?
A)Abnormal hemoglobin polymerizes inside erythrocytes,altering red cell shape.
B)Novel hemoglobins composed of abnormal combinations of normal globin chains can be detected on hemoglobin electrophoresis.
C)Elevations in embryonic and fetal hemoglobins can be observed.
D)The amino acid sequence of the globin chains of the abnormal hemoglobins is normal.
A)Abnormal hemoglobin polymerizes inside erythrocytes,altering red cell shape.
B)Novel hemoglobins composed of abnormal combinations of normal globin chains can be detected on hemoglobin electrophoresis.
C)Elevations in embryonic and fetal hemoglobins can be observed.
D)The amino acid sequence of the globin chains of the abnormal hemoglobins is normal.
Abnormal hemoglobin polymerizes inside erythrocytes,altering red cell shape.
4
Choose the thalassemia with the best prognosis from the following choices.
A)Hgb H disease
B)Silent carrier alpha thalassemia
C)Beta thalassemia minor
D)Beta thalassemia intermedia
A)Hgb H disease
B)Silent carrier alpha thalassemia
C)Beta thalassemia minor
D)Beta thalassemia intermedia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What can explain the imbalanced synthesis of either the alpha or beta chain in thalassemia?
A)Deletions of any of the gene clusters
B)Abnormal production of gamma chains
C)Presence of abnormal hemoglobin chains
D)Continued synthesis of epsilon and zeta production after birth
A)Deletions of any of the gene clusters
B)Abnormal production of gamma chains
C)Presence of abnormal hemoglobin chains
D)Continued synthesis of epsilon and zeta production after birth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the treatment of choice for thalassemias?
A)Supportive transfusions
B)Bone marrow transplant
C)Chemotherapy
D)Radiation
A)Supportive transfusions
B)Bone marrow transplant
C)Chemotherapy
D)Radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Thalassemia differs from hemoglobinopathies by what characteristic?
A)The production of abnormal globin chains
B)The point of genetic mutations
C)A decreased synthesis of normal hemoglobin
D)A qualitative defect in the globin structure
A)The production of abnormal globin chains
B)The point of genetic mutations
C)A decreased synthesis of normal hemoglobin
D)A qualitative defect in the globin structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
All of the following can lead to the development of thalassemias except:
A)Deletion mutation
B)Substitution mutation
C)Exposure to a mutagenic agent
D)Frameshift mutation
A)Deletion mutation
B)Substitution mutation
C)Exposure to a mutagenic agent
D)Frameshift mutation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The geographic prevalence of α-thalassemia is highest in which ancestry group?
A)Mediterranean,American Indian
B)Asian,Mediterranean,African
C)Canadian,African,Indian
D)South American,African,Asian
A)Mediterranean,American Indian
B)Asian,Mediterranean,African
C)Canadian,African,Indian
D)South American,African,Asian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Laboratory findings in thalassemia often include which of the following?
A)Microcytic hyperchromic anemia
B)Microcytic hypochromic anemia
C)Macrocytic hyperchromic anemia
D)Macrocytic hypochromic anemia
A)Microcytic hyperchromic anemia
B)Microcytic hypochromic anemia
C)Macrocytic hyperchromic anemia
D)Macrocytic hypochromic anemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When three of the four alpha genes are deleted,what is the disorder known as?
A)α-thalassemia
B)β-thalassemia
C)Hydrops fetalis
D)Hemoglobin H disease
A)α-thalassemia
B)β-thalassemia
C)Hydrops fetalis
D)Hemoglobin H disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Hemoglobin H disease can be detected by which of the following laboratory methods?
A)Complete blood count
B)PB smear for Heinz bodies
C)Bone marrow aspirate
D)Brilliant cresyl blue staining for Hb H inclusions
A)Complete blood count
B)PB smear for Heinz bodies
C)Bone marrow aspirate
D)Brilliant cresyl blue staining for Hb H inclusions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Impaired alpha chain production in alpha thalassemias causes:
A)Overproduction of hemoglobin F and A₂
B)Production of Hb Bart's and Hb H.
C)Normal hemoglobin distribution
D)Fusion of alpha and gamma chains
A)Overproduction of hemoglobin F and A₂
B)Production of Hb Bart's and Hb H.
C)Normal hemoglobin distribution
D)Fusion of alpha and gamma chains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
a-thalassemia major results from deletion in _____ alleles of the alpha chain gene.
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Molecular analysis on a 4-month-old Chinese patient revealed three alpha genes deleted on chromosome 16.The physician ordered a hemoglobin electrophoresis on this patient.What is the expected finding?
A)80% F;15% A1;5% A₂
B)95% Hgb H
C)95% Hgb Bart's
D)80% A1;10% F;10% A₂
A)80% F;15% A1;5% A₂
B)95% Hgb H
C)95% Hgb Bart's
D)80% A1;10% F;10% A₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
All of the following morphology are typically seen in beta thalassemia patients except:
A)Codocytes
B)Polychromasia
C)Microcytes
D)Drepanocytes
A)Codocytes
B)Polychromasia
C)Microcytes
D)Drepanocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Thalassemias are defined as:
A)Qualitative defects in globin chain synthesis
B)Quantitative defects in globin chain synthesis
C)Kinetic defects of iron in heme synthesis
D)Structural defects in heme synthesis
A)Qualitative defects in globin chain synthesis
B)Quantitative defects in globin chain synthesis
C)Kinetic defects of iron in heme synthesis
D)Structural defects in heme synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Most defects in beta thalassemia are a result of what genetic defect?
A)Loss of gene expression because of promoter region methylation
B)Point mutations in regions of the DNA controlling gene expression
C)Deletion of the structural globin gene
D)Omission of the alpha globin chain
A)Loss of gene expression because of promoter region methylation
B)Point mutations in regions of the DNA controlling gene expression
C)Deletion of the structural globin gene
D)Omission of the alpha globin chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A fatigued 15-year-old Italian girl visits her general practitioner for a yearly physical.Her RBC count is elevated with a low H & H.The PB smear shows moderate microcytosis and hypochromia.Moderate poikilocytosis with moderate target cells is also noted.Hemoglobin electrophoresis is performed.The results indicate elevated levels of F and A₂.Based on these findings,what is the most probable thalassemia genotype of this patient?
A)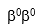
B)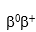
C)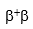
D)
A)
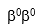
B)
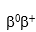
C)
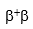
D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Impaired beta chain production translates to what on hemoglobin electrophoresis?
A)An increase in Hb H
B)An increase in Hb A1
C)An increase in Hb F and Hb A₂
D)A decrease in Hb S
A)An increase in Hb H
B)An increase in Hb A1
C)An increase in Hb F and Hb A₂
D)A decrease in Hb S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A physician diagnoses a patient with iron-deficiency anemia and begins treatment with iron supplementation.He scheduled a repeat appointment in six months that included routine blood work.Her blood work at this repeat appointment indicates a microcytic normochromic picture with elevated iron levels.Based on these findings,what should the doctor do next?
A)Order a bone marrow aspirate
B)Order a hemoglobin electrophoresis
C)Order a repeat CBC
D)Repeat the iron studies
A)Order a bone marrow aspirate
B)Order a hemoglobin electrophoresis
C)Order a repeat CBC
D)Repeat the iron studies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A promoter mutation of a globin chain gene in thalassemia has which effect on the globin chain?
A)Amino acid change
B)Change to a longer globin chain
C)Change to a shorter globin chain
D)Reduced or absent production
A)Amino acid change
B)Change to a longer globin chain
C)Change to a shorter globin chain
D)Reduced or absent production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When a diagnosis of thalassemia is suspected,which test should always be done?
A)Hemoglobin electrophoresis
B)Bone marrow aspiration
C)Iron studies
D)Vitamin B₁₂ assay
A)Hemoglobin electrophoresis
B)Bone marrow aspiration
C)Iron studies
D)Vitamin B₁₂ assay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A fusion of delta and beta globin chains produces which of the following hemoglobins?
A)Hemoglobin F
B)Hemoglobin Lepore
C)Hemoglobin Bart's
D)Hemoglobin Portland
A)Hemoglobin F
B)Hemoglobin Lepore
C)Hemoglobin Bart's
D)Hemoglobin Portland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the typical electrophoresis pattern in each of the following disorders?
a.α-thalassemia minor
b.Hgb H disease
c.β-thalassemia major
d.β-thalassemia minor
a.α-thalassemia minor
b.Hgb H disease
c.β-thalassemia major
d.β-thalassemia minor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
List the predominating hemoglobins in each of the following disorders:
a.Hgb H disease
b.α-thalassemia minor
c.β-thalassemia major
d.β-thalassemia intermedia
a.Hgb H disease
b.α-thalassemia minor
c.β-thalassemia major
d.β-thalassemia intermedia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Why are thalassemias considered a separate entity from hemoglobinopathies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Correlate the mutation type to each of the following disorders:
a.α-thalassemia major
b.β-thalassemia major
c.α- thalassemia silent carrier
a.α-thalassemia major
b.β-thalassemia major
c.α- thalassemia silent carrier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is another name for the phenotype of α-thalassemia major?
A)Hemoglobin H disease
B)Hydrops fetalis
C)Silent carrier
D)β-thalassemia major
A)Hemoglobin H disease
B)Hydrops fetalis
C)Silent carrier
D)β-thalassemia major

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Nucleated red blood cells in the peripheral blood are a common finding in beta thalassemia patients.Explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What red cell morphology marks most types of thalassemia?
A)Target cells
B)Basophilic stippling
C)Polychromasia
D)Normal findings
A)Target cells
B)Basophilic stippling
C)Polychromasia
D)Normal findings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The hemoglobin Constant Spring variant of alpha thalassemia is caused by:
A)A gamma chain fused to an existing beta chain
B)A beta chain fused to an existing alpha chain
C)An elongated alpha chain
D)An elongated beta chain
A)A gamma chain fused to an existing beta chain
B)A beta chain fused to an existing alpha chain
C)An elongated alpha chain
D)An elongated beta chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



