Deck 34: Disorders of Secondary Hemostasis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/34
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 34: Disorders of Secondary Hemostasis
1
Predict results that will confirm the patient's diagnosis.
A)Abnormal aggregation with Ristocetin
B)An increased D-dimer
C)Decreased activity of either factors VIII or IX
D)The presence of an inhibitor pattern in a mixing study
A)Abnormal aggregation with Ristocetin
B)An increased D-dimer
C)Decreased activity of either factors VIII or IX
D)The presence of an inhibitor pattern in a mixing study
Decreased activity of either factors VIII or IX
2
What term describes hereditary or acquired disorders that relate to the absence of a coagulation protein or to a protein that is present in the plasma but is functionally defective?
A)Circulating anticoagulant
B)Lupus anticoagulant
C)Deficiency
D)Dysfunctional
A)Circulating anticoagulant
B)Lupus anticoagulant
C)Deficiency
D)Dysfunctional
Deficiency
3
Which of the following is used in the identification of a secondary hemostatic pathway anomaly?
A)Bleeding time
B)ACE activity
C)Platelet aggregation studies
D)Factor assays
A)Bleeding time
B)ACE activity
C)Platelet aggregation studies
D)Factor assays
Factor assays
4
A physician has confirmed von Willebrand's disease in a patient.Further testing is needed to determine which subtype the patient has.Multimer analysis is performed and comes back normal.What is the most probable explanation for this?
A)The patient is not suffering from von Willebrand's disease.
B)The patient is suffering from type I VWD.
C)The patient has BSS.
D)The wrong patient was drawn.
A)The patient is not suffering from von Willebrand's disease.
B)The patient is suffering from type I VWD.
C)The patient has BSS.
D)The wrong patient was drawn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following clinical symptoms correlates with a severe form of hemophilia A or B?
A)Bleeding at circumcision with a factor level of 1-5 U/dL
B)Excessive bleeding after surgery or trauma with a factor level of 6-30 U/dL
C)Frequent spontaneous hemarthroses
D)Infrequent spontaneous joint and tissue bleeds
A)Bleeding at circumcision with a factor level of 1-5 U/dL
B)Excessive bleeding after surgery or trauma with a factor level of 6-30 U/dL
C)Frequent spontaneous hemarthroses
D)Infrequent spontaneous joint and tissue bleeds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which congenital deficiency(ies)is(are)suspected with a normal platelet count,an abnormal PT and APTT,and normal PFA-100 and thrombin time?
A)Factor VII
B)Factors X,V,II (prothrombin)
C)Factor VIII
D)Fibrinogen
A)Factor VII
B)Factors X,V,II (prothrombin)
C)Factor VIII
D)Fibrinogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the inheritance pattern of hemophilia A?
A)Autosomal dominant
B)Autosomal recessive
C)Sex-linked
D)None of these
A)Autosomal dominant
B)Autosomal recessive
C)Sex-linked
D)None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A patient with a protein C deficiency is at risk for developing which of the following?
A)Thrombosis
B)Hemorrhage
C)Lupus anticoagulant inhibitor
D)Factor deficiency
A)Thrombosis
B)Hemorrhage
C)Lupus anticoagulant inhibitor
D)Factor deficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A patient might be suffering from a coagulopathy.Which of the following physical manifestations would suggest a primary hemostatic pathway problem?
A)Hematomas
B)Petechiae
C)Joint and muscle bleeding
D)Ecchymoses
A)Hematomas
B)Petechiae
C)Joint and muscle bleeding
D)Ecchymoses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
From what disorder is the patient suffering?
A)von Willebrand's disease
B)DIC
C)Hemophilia possibly
D)Lupus anticoagulant
A)von Willebrand's disease
B)DIC
C)Hemophilia possibly
D)Lupus anticoagulant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Use this case to answer the following questions: ? A 5-year-old boy visits his primary care physician after an accident on his bike.It was his first accident,and he fell on his knees.His mother noticed severe swelling in his knees and elbows but thought that it was from the accident.She placed an ice pack on the affected areas and put him to rest.After a few days,the swelling had not improved,so she made an appointment to see his physician who asks him a few questions about the accident and then proceeds to perform a physical examination.The physician notes small hematomas on his elbows,knees,and his upper torso.The results from the blood draw follow.
PT: 12.2 sec (RR: 11.3-12.8 sec)
INR: 1.12
APTT: 72 sec (RR: 23-32 sec)
Platelet aggregation studies: normal aggregation with all agonists
The physician admits him to the area hospital.What should be the next course of action in investigating these results?
A)Repeat the aggregation studies
B)Start the patient on Coumadin
C)Order factor assays of the intrinsic pathway
D)Order factor assays of the intrinsic,extrinsic,and common pathways
PT: 12.2 sec (RR: 11.3-12.8 sec)
INR: 1.12
APTT: 72 sec (RR: 23-32 sec)
Platelet aggregation studies: normal aggregation with all agonists
The physician admits him to the area hospital.What should be the next course of action in investigating these results?
A)Repeat the aggregation studies
B)Start the patient on Coumadin
C)Order factor assays of the intrinsic pathway
D)Order factor assays of the intrinsic,extrinsic,and common pathways

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Hemophilia A is caused by a deficiency in which of the following proteins?
A)von Willebrand's factor
B)Factor VIII
C)Factor IX
D)Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa
A)von Willebrand's factor
B)Factor VIII
C)Factor IX
D)Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Screening tests for the evaluation of VWD include the platelet count,APTT,PT,bleeding time,and/or PFA-100.Which of the following results would be evident in most cases of VWD?
A)Low platelet count
B)Decreased ristocetin platelet aggregation
C)Normal ristocetin platelet aggregation
D)Normal Ag assay
A)Low platelet count
B)Decreased ristocetin platelet aggregation
C)Normal ristocetin platelet aggregation
D)Normal Ag assay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A patient has a prolonged PT.Which deficiency can you infer from this result?
A)Coagulation factors of the extrinsic pathway
B)Coagulation factors of the intrinsic pathway
C)Platelets
D)Coagulation factors of the common pathway
A)Coagulation factors of the extrinsic pathway
B)Coagulation factors of the intrinsic pathway
C)Platelets
D)Coagulation factors of the common pathway

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Deficiency of coagulation proteins is defined as a decrease in:
A)The concentration of the coagulation proteins
B)The concentration of the coagulation proteins and a subsequent decrease in the functionality of those proteins
C)The concentration of the coagulation proteins or impaired functionality of those proteins
D)Platelets that causes a decreased functionality of the coagulation proteins
A)The concentration of the coagulation proteins
B)The concentration of the coagulation proteins and a subsequent decrease in the functionality of those proteins
C)The concentration of the coagulation proteins or impaired functionality of those proteins
D)Platelets that causes a decreased functionality of the coagulation proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A 34-year-old woman has just given birth to a healthy baby boy.After the delivery of the baby,the physician proceeds to deliver the placenta.After it has been extracted from the mother's uterus,the resident examines it and notes that it appears incomplete.They try to deliver the remainder but are unsuccessful.A few moments later,the mother loses consciousness,and is bleeding profusely from her uterus.Blood is collected,and the results follow. PT: 17 sec (RR: 11.3-12.8 sec)
INR: 3.02
APTT: 67 sec (RR: 23-32 sec)
D-dimer: 540 ng/mL (RR: <400 ng/mL)
Fibrinogen: 82 mg/dL (RR: 200-400 mg/dL)
Factor V assay: 12%
Based on this information,from what is the patient most likely suffering?
A)Hemophilia A
B)von Willebrand's disease
C)Placenta previa
D)DIC
INR: 3.02
APTT: 67 sec (RR: 23-32 sec)
D-dimer: 540 ng/mL (RR: <400 ng/mL)
Fibrinogen: 82 mg/dL (RR: 200-400 mg/dL)
Factor V assay: 12%
Based on this information,from what is the patient most likely suffering?
A)Hemophilia A
B)von Willebrand's disease
C)Placenta previa
D)DIC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A 5-year-old boy has his blood drawn for platelet aggregation studies.Ristocetin aggregation (RIPA)comes back abnormal with all other agonists displaying normal aggregation.VWF antigen is within normal limits.What is the most likely reason for this discrepancy?
A)The VWF antigen test was performed incorrectly and should be repeated.
B)The patient might be suffering from a qualitative platelet defect disorder.
C)The RIPA exam was performed incorrectly and should be repeated.
D)Multimer analysis should be performed to confirm these findings.
A)The VWF antigen test was performed incorrectly and should be repeated.
B)The patient might be suffering from a qualitative platelet defect disorder.
C)The RIPA exam was performed incorrectly and should be repeated.
D)Multimer analysis should be performed to confirm these findings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A preterm infant (29 weeks old)has a platelet count of 85 × 10⁹/L.Is this a normal or abnormal finding?
A)Abnormal because infants have normal adult amounts of platelets after 27 weeks' gestation
B)Normal because preterm infants have decreased platelet counts as a result of abnormal birthing circumstances
C)Normal because platelet development is similar to lung development in an infant;levels depend on the age of gestation
D)Abnormal because preterm infants are subject to DIC,and that results in a decreased platelet count
A)Abnormal because infants have normal adult amounts of platelets after 27 weeks' gestation
B)Normal because preterm infants have decreased platelet counts as a result of abnormal birthing circumstances
C)Normal because platelet development is similar to lung development in an infant;levels depend on the age of gestation
D)Abnormal because preterm infants are subject to DIC,and that results in a decreased platelet count

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
F-VIII deficiency and F-IX deficiency are classified as what category of disorder?
A)Autosomal dominant
B)X-linked recessive
C)Autosomal recessive
D)X-linked dominant
A)Autosomal dominant
B)X-linked recessive
C)Autosomal recessive
D)X-linked dominant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Interpret the following results: PT: 11.8 sec (RR: 11.2-13.8 sec)
INR: 1.07
APTT: 57 sec (RR: 23-32 sec)
BT: 12 min
Ristocetin aggregation: decreased aggregation
Based on this information,from what is the patient most likely suffering?
A)Hemophilia A
B)Bernard-Soulier syndrome
C)DIC
D)von Willebrand's disease
INR: 1.07
APTT: 57 sec (RR: 23-32 sec)
BT: 12 min
Ristocetin aggregation: decreased aggregation
Based on this information,from what is the patient most likely suffering?
A)Hemophilia A
B)Bernard-Soulier syndrome
C)DIC
D)von Willebrand's disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following laboratory assays would be useful in identifying the presence of primary fibrinolysis?
A)Fibrinogen and FDP
B)FDP and D-dimer
C)D-dimer and plasmin
D)Fibrinogen and platelet count
A)Fibrinogen and FDP
B)FDP and D-dimer
C)D-dimer and plasmin
D)Fibrinogen and platelet count

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
George Jones is admitted to the hospital with abdominal pain.Upon physical examination,the attending physician notices a yellow ring around his green eyes.George has a significant swelling in his abdomen and has been suffering from swollen joints for the last month.The physician runs a battery of labs.The results follow: 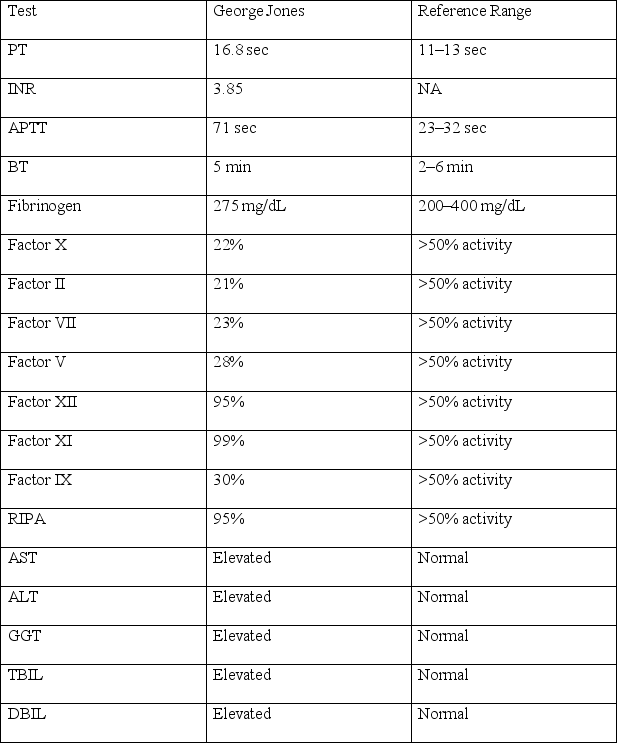
Based on this information,from what is George most likely suffering?
A)Liver disease
B)Vitamin K deficiency
C)Disseminated intravascular coagulation
D)Massive cerebral hemorrhage

Based on this information,from what is George most likely suffering?
A)Liver disease
B)Vitamin K deficiency
C)Disseminated intravascular coagulation
D)Massive cerebral hemorrhage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which assay would assess for the presence of a circulating nonspecific inhibitor?
A)Bethesda titer
B)Factor-specific inhibitor
C)Lupus anticoagulant
D)D-dimer
A)Bethesda titer
B)Factor-specific inhibitor
C)Lupus anticoagulant
D)D-dimer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Explain how liver disease can be differentiated from DIC through laboratory test analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A known hemophiliac has developed an inhibitor.The physician in charge of his care wants to know how much inhibitor is present to properly treat him.What two lab tests would be ordered to assess this?
A)APTT;factor assay
B)Factor VIII: C level;Bethesda titer
C)VWF antigen;Bethesda titer
D)Type and screen;factor assay
A)APTT;factor assay
B)Factor VIII: C level;Bethesda titer
C)VWF antigen;Bethesda titer
D)Type and screen;factor assay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Explain why disseminated intravascular coagulation is not a primary disease state.Correlate etiology,pathophysiology,and laboratory analysis in your response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Deficiencies of the fibrin-forming proteins often have a delayed bleeding symptom that results from which of the following?
A)Excessive bleeding from a traumatic injury
B)Bleeding from rupture of small arterioles
C)Formation of hematomas
D)Absence of hemostatic plug stabilization with fibrin
A)Excessive bleeding from a traumatic injury
B)Bleeding from rupture of small arterioles
C)Formation of hematomas
D)Absence of hemostatic plug stabilization with fibrin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What type of VWD is the only type to have a decreased platelet count?
A)Type 1
B)Type 3
C)Type 2B
D)Type 2N
A)Type 1
B)Type 3
C)Type 2B
D)Type 2N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An advantage of prenatal diagnosis by genotypic analysis for hemophilia over phenotypic analysis is:
A)ABO blood type does not affect the analysis.
B)A chorionic villus biopsy can be tested at 4 weeks gestation.
C)Direct DNA diagnosis is available for all families.
D)It can be done as a point-of-care test.
A)ABO blood type does not affect the analysis.
B)A chorionic villus biopsy can be tested at 4 weeks gestation.
C)Direct DNA diagnosis is available for all families.
D)It can be done as a point-of-care test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What laboratory tests typically are utilized to detect lupus anticoagulants?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What plasma factor levels of the deficient factor can be expected in a female carrier of FVIII or FIX deficiency?
A)25% of the normal plasma levels
B)12.5% of the normal plasma levels
C)50% of the normal plasma levels
D)5% of the normal plasma levels
A)25% of the normal plasma levels
B)12.5% of the normal plasma levels
C)50% of the normal plasma levels
D)5% of the normal plasma levels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which is the most common FVIII mutation in patients with a severe phenotype (occurring in almost 50% of patients)?
A)Gross deletion of entire gene locus
B)Point mutation involving the thrombin cleavage site
C)Inversion mutation of intron 22
D)Point mutation involving the site of VWF attachment
A)Gross deletion of entire gene locus
B)Point mutation involving the thrombin cleavage site
C)Inversion mutation of intron 22
D)Point mutation involving the site of VWF attachment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Explain the inheritance pattern of the following disorder and how it contributes to the clinical manifestations of each of the following disorders:a.Hemophilia A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How does von Willebrand's disease (VWD)differ from Bernard-Soulier syndrome?
Correlate the pathophysiology of both disorders in your response.Name at least two laboratory tests that differentiate each.
Correlate the pathophysiology of both disorders in your response.Name at least two laboratory tests that differentiate each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



