Deck 10: Brain Damage and Neuroplasticity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/185
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Brain Damage and Neuroplasticity
1
Which of the following is most likely to lead to an intracerebral hemorrhage?
A) an aneurysm
B) a hematoma
C) cerebral ischemia
D) thrombosis
E) embolism
A) an aneurysm
B) a hematoma
C) cerebral ischemia
D) thrombosis
E) embolism
an aneurysm
2
Cerebral ischemia is a disruption of the supply of __________ to the __________.
A) glutamate; brain
B) blood; heart
C) air; body
D) neurotransmitters; brain
E) blood; brain
A) glutamate; brain
B) blood; heart
C) air; body
D) neurotransmitters; brain
E) blood; brain
blood; brain
3
The 8th cranial nerve
A) is a sensory nerve that comes from the ear.
B) carries auditory information.
C) carries vestibular information.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
A) is a sensory nerve that comes from the ear.
B) carries auditory information.
C) carries vestibular information.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
all of the above
4
A tumor is
A) a neoplasm.
B) cluster of cells that grows independently of the rest of the body.
C) an aneurysm.
D) a thrombus.
E) both A and B
A) a neoplasm.
B) cluster of cells that grows independently of the rest of the body.
C) an aneurysm.
D) a thrombus.
E) both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Acoustic neuromas are
A) encapsulated.
B) benign.
C) located on the 8th cranial nerve.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) encapsulated.
B) benign.
C) located on the 8th cranial nerve.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Strokes are caused by
A) tardive dyskinesia.
B) cerebral hemorrhage.
C) cerebral ischemia.
D) all of the above
E) both B and C
A) tardive dyskinesia.
B) cerebral hemorrhage.
C) cerebral ischemia.
D) all of the above
E) both B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which type of tumor is likely to be benign?
A) encapsulated
B) metastatic
C) infiltrating
D) malignant
E) congenital
A) encapsulated
B) metastatic
C) infiltrating
D) malignant
E) congenital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Much of the brain damage caused by cerebral ischemia takes 1 or 2 __________ to fully develop.
A) seconds
B) minutes
C) hours
D) days
E) weeks
A) seconds
B) minutes
C) hours
D) days
E) weeks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Sites of arteriosclerosis are readily apparent in
A) a Nissl-stained brain section.
B) a CT scan.
C) an fMRI image.
D) an angiogram.
E) a PET scan.
A) a Nissl-stained brain section.
B) a CT scan.
C) an fMRI image.
D) an angiogram.
E) a PET scan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which type of tumor would be most easy to localize in a CT scan or a brain section?
A) an infiltrating tumor
B) a metastatic tumor
C) an encapsulated tumor
D) a malignant tumor
E) a congenital tumor
A) an infiltrating tumor
B) a metastatic tumor
C) an encapsulated tumor
D) a malignant tumor
E) a congenital tumor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If a person developed a brain tumor as a result of chronic cigarette smoking, the tumor would likely be
A) metastatic.
B) malignant.
C) encapsulated.
D) both A and B.
E) both B and C
A) metastatic.
B) malignant.
C) encapsulated.
D) both A and B.
E) both B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A disorder in which fat deposits cause the walls of blood vessels to thicken and reduce blood flow is
A) arteriosclerosis.
B) contusion.
C) embolism.
D) dementia.
E) encephalitis.
A) arteriosclerosis.
B) contusion.
C) embolism.
D) dementia.
E) encephalitis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Meningiomas are
A) encapsulated.
B) diffuse.
C) infiltrating.
D) metastatic.
E) malignant.
A) encapsulated.
B) diffuse.
C) infiltrating.
D) metastatic.
E) malignant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Metastasis refers
A) specifically to malignant tumors.
B) to tumors that have spread from the lungs to the brain.
C) to infiltrating tumors.
D) to the spread of disease from one organ to another.
E) to tumors and other growths that are attracted to neural tissue.
A) specifically to malignant tumors.
B) to tumors that have spread from the lungs to the brain.
C) to infiltrating tumors.
D) to the spread of disease from one organ to another.
E) to tumors and other growths that are attracted to neural tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is a cerebrovascular disorder?
A) cerebral arteriosclerosis
B) cerebral embolism
C) cerebral thrombosis
D) all of the above
E) both B and C
A) cerebral arteriosclerosis
B) cerebral embolism
C) cerebral thrombosis
D) all of the above
E) both B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When a thrombus moves to another site and becomes lodged there, the thrombus is called
A) a thrombosis.
B) a bolus.
C) an embolus.
D) an infarct.
E) an aneurysm.
A) a thrombosis.
B) a bolus.
C) an embolus.
D) an infarct.
E) an aneurysm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Both thrombuses and emboluses are
A) plugs that block blood flow.
B) tumors.
C) causes of arteriosclerosis.
D) infarcts.
E) hematomas.
A) plugs that block blood flow.
B) tumors.
C) causes of arteriosclerosis.
D) infarcts.
E) hematomas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The 8th cranial nerve is the
A) auditory-vestibular nerve.
B) vagus nerve.
C) trigeminal nerve.
D) olfactory nerve.
E) facial nerve.
A) auditory-vestibular nerve.
B) vagus nerve.
C) trigeminal nerve.
D) olfactory nerve.
E) facial nerve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Aneurysms are often
A) congenital.
B) caused by vascular poisons.
C) caused by infection.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) congenital.
B) caused by vascular poisons.
C) caused by infection.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
"Stroke" commonly refers to
A) closed-head injuries of sudden onset.
B) cancerous brain tumors of sudden onset.
C) cerebrovascular disorders of sudden onset.
D) brain infarcts.
E) cerebral attacks.
A) closed-head injuries of sudden onset.
B) cancerous brain tumors of sudden onset.
C) cerebrovascular disorders of sudden onset.
D) brain infarcts.
E) cerebral attacks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In a car accident, a woman banged the front of her head on the steering wheel.A subsequent CT scan revealed a subdural hematoma over the left occipital lobe.The woman clearly had suffered a
A) contrecoup injury.
B) contusion.
C) concussion.
D) both A and B
E) both A and C
A) contrecoup injury.
B) contusion.
C) concussion.
D) both A and B
E) both A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Rabies is caused by
A) a bacterial infection usually transmitted in the saliva of a rabid animal.
B) a bacteria infection usually transmitted in the saliva of a rabbit animal.
C) a virus.
D) an embolism.
E) an infarct.
A) a bacterial infection usually transmitted in the saliva of a rabid animal.
B) a bacteria infection usually transmitted in the saliva of a rabbit animal.
C) a virus.
D) an embolism.
E) an infarct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Involuntary smacking and sucking movements of the lips, thrusting and rolling of the tongue, lateral jaw movements, and puffing of the cheeks are all symptoms of
A) tardive dyskinesia.
B) general paresis.
C) dementia.
D) mercury poisoning.
E) lead poisoning.
A) tardive dyskinesia.
B) general paresis.
C) dementia.
D) mercury poisoning.
E) lead poisoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Tardive dyskinesia is caused by
A) the chronic use of some kinds of antipsychotic drugs.
B) lead poisoning.
C) toxic psychosis.
D) mercury poisoning.
E) viral infection.
A) the chronic use of some kinds of antipsychotic drugs.
B) lead poisoning.
C) toxic psychosis.
D) mercury poisoning.
E) viral infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When the brain slams against the inside of the skull, blood from the resulting contusion often accumulates in the
A) subdural space.
B) ventricles.
C) internal canal.
D) fissures.
E) sulci.
A) subdural space.
B) ventricles.
C) internal canal.
D) fissures.
E) sulci.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Brain damage following ischemic strokes seems to be caused by
A) NMDA buildup.
B) excessive serotonin release.
C) an imbalance of GABA.
D) excessive norepinephrine release.
E) excessive glutamate release.
A) NMDA buildup.
B) excessive serotonin release.
C) an imbalance of GABA.
D) excessive norepinephrine release.
E) excessive glutamate release.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Contusions
A) occur only when the brain is punctured by a sharp object.
B) involve hemorrhage and hematoma.
C) are often produced by the brain slamming against the inside of the skull.
D) all of the above
E) both B and C
A) occur only when the brain is punctured by a sharp object.
B) involve hemorrhage and hematoma.
C) are often produced by the brain slamming against the inside of the skull.
D) all of the above
E) both B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Following cerebral ischemia,
A) glutamate is released in excessive quantities.
B) excessive activity is induced at NMDA receptors.
C) excessive numbers of calcium and sodium ions enter postsynaptic neurons.
D) postsynaptic neurons slowly die.
E) all of the above
A) glutamate is released in excessive quantities.
B) excessive activity is induced at NMDA receptors.
C) excessive numbers of calcium and sodium ions enter postsynaptic neurons.
D) postsynaptic neurons slowly die.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A "crackpot," in the original sense of the word, was a person who was suffering from
A) the effects of lead poisoning.
B) a type of toxic psychosis.
C) general paresis.
D) tardive dyskinesia.
E) both A and B
A) the effects of lead poisoning.
B) a type of toxic psychosis.
C) general paresis.
D) tardive dyskinesia.
E) both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The word "crackpot" originally referred to people suffering from
A) caffeine poisoning.
B) tea poisoning.
C) syphilis.
D) lead poisoning.
E) mercury poisoning.
A) caffeine poisoning.
B) tea poisoning.
C) syphilis.
D) lead poisoning.
E) mercury poisoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When there is a disturbance of consciousness following a blow to the head and there is no evidence of physical damage, the diagnosis is
A) contusion.
B) laceration.
C) concussion.
D) hematoma.
E) aneurysm.
A) contusion.
B) laceration.
C) concussion.
D) hematoma.
E) aneurysm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The punch-drunk syndrome suggests that each individual concussion is associated with
A) some lasting damage.
B) dementia.
C) scarring.
D) a contusion.
E) meningitis.
A) some lasting damage.
B) dementia.
C) scarring.
D) a contusion.
E) meningitis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Meningitis is
A) the result of a bacterial infection.
B) a type of encephalitis.
C) an inflammation of the meninges of the brain.
D) all of the above
E) both a and B
A) the result of a bacterial infection.
B) a type of encephalitis.
C) an inflammation of the meninges of the brain.
D) all of the above
E) both a and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Given the cascade of events leading to ischemia-produced brain damage, __________ administered immediately after a stroke might reduce the development of brain damage.
A) NMDA receptor blockers
B) calcium-channel blockers
C) acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
A) NMDA receptor blockers
B) calcium-channel blockers
C) acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
D) all of the above
E) both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
General paresis is
A) an officer in the Spanish army.
B) a mild general paralysis.
C) the insanity and intellectual impairment associated with advanced cases of syphilis.
D) a bacterial infection that attacks a large group of people.
E) a viral infection that attacks a large group of people.
A) an officer in the Spanish army.
B) a mild general paralysis.
C) the insanity and intellectual impairment associated with advanced cases of syphilis.
D) a bacterial infection that attacks a large group of people.
E) a viral infection that attacks a large group of people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The brain inflammation resulting from an infection is
A) general paresis.
B) dementia.
C) encephalitis.
D) meningitis.
E) tardive dyskinesia.
A) general paresis.
B) dementia.
C) encephalitis.
D) meningitis.
E) tardive dyskinesia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Brain injuries produced by blows that do not penetrate the skull are called
A) closed-head injuries.
B) contrecoup injuries.
C) hematomas.
D) contusions.
E) lacerations.
A) closed-head injuries.
B) contrecoup injuries.
C) hematomas.
D) contusions.
E) lacerations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A hematoma is a
A) type of dementia.
B) localized collection of clotted blood.
C) bruise.
D) all of the above
E) both B and C
A) type of dementia.
B) localized collection of clotted blood.
C) bruise.
D) all of the above
E) both B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The mumps and herpes simplex viruses are common examples of
A) cerebral tumors.
B) viruses that can attack the brain but do not have a particular affinity for brain tissue.
C) diseases that usually cause brain abscesses.
D) viruses that have a particular affinity for brain tissue.
E) bacterial infections.
A) cerebral tumors.
B) viruses that can attack the brain but do not have a particular affinity for brain tissue.
C) diseases that usually cause brain abscesses.
D) viruses that have a particular affinity for brain tissue.
E) bacterial infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The punch-drunk syndrome typically results from the cumulative effects of many minor
A) contusions.
B) concussions.
C) infarcts.
D) aneurysms.
E) embolisms.
A) contusions.
B) concussions.
C) infarcts.
D) aneurysms.
E) embolisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In epileptic patients who do not experience convulsions, the diagnosis of epilepsy rests heavily on
A) postmortem evidence.
B) the analysis of blood samples.
C) electroencephalographic evidence.
D) angiograms.
E) CT scans.
A) postmortem evidence.
B) the analysis of blood samples.
C) electroencephalographic evidence.
D) angiograms.
E) CT scans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Down syndrome is
A) a toxic psychosis.
B) a toxic dementia.
C) the result of a single abnormal dominant gene.
D) is associated with a lack of acetylcholine.
E) the result of a genetic accident.
A) a toxic psychosis.
B) a toxic dementia.
C) the result of a single abnormal dominant gene.
D) is associated with a lack of acetylcholine.
E) the result of a genetic accident.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An epileptic focus is a site in the brain of an epileptic patient.
A) into which epileptic discharges tend to spread from other sites.
B) at which discharges originating at other sites tend to be synchronized.
C) at which epileptic discharges can be elicited by drugs.
D) at which epileptic discharges spontaneously arise and spread to other sites.
E) that attracts epileptic discharges.
A) into which epileptic discharges tend to spread from other sites.
B) at which discharges originating at other sites tend to be synchronized.
C) at which epileptic discharges can be elicited by drugs.
D) at which epileptic discharges spontaneously arise and spread to other sites.
E) that attracts epileptic discharges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following disorders results from a mutation that produces an extra chromosome 21?
A) Down syndrome
B) meningitis
C) tardive dyskinesia
D) general paresis
E) multiple sclerosis
A) Down syndrome
B) meningitis
C) tardive dyskinesia
D) general paresis
E) multiple sclerosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The process by which neurons passively die as the result of injury is
A) apoptosis.
B) necrosis.
C) dementia pugilistic.
D) fasciculation.
E) general paresis.
A) apoptosis.
B) necrosis.
C) dementia pugilistic.
D) fasciculation.
E) general paresis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Neural apoptosis usually begins with
A) inflammation of the area.
B) ischemia.
C) shrinkage of the cell body.
D) swelling of the axon.
E) retrograde degeneration.
A) inflammation of the area.
B) ischemia.
C) shrinkage of the cell body.
D) swelling of the axon.
E) retrograde degeneration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following establishes with complete certainty that a patient is not epileptic?
A) The patient has no convulsions.
B) An EEG examination reveals no epileptic abnormalities.
C) There is no aura.
D) The patient has no psychomotor attacks.
E) none of the above
A) The patient has no convulsions.
B) An EEG examination reveals no epileptic abnormalities.
C) There is no aura.
D) The patient has no psychomotor attacks.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Neuropsychological disorders with genetic causes are not usually related to dominant genes because
A) those who possess them are less likely to produce fit offspring.
B) dominant genes are usually singular.
C) recessive genes are far more potent.
D) recessive genes are far more common.
E) humans are not evolving.
A) those who possess them are less likely to produce fit offspring.
B) dominant genes are usually singular.
C) recessive genes are far more potent.
D) recessive genes are far more common.
E) humans are not evolving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An epileptic aura is a psychological experience that
A) precedes the onset of epilepsy.
B) precedes a convulsion.
C) follows a convulsion.
D) occurs during a convulsion.
E) replaces a convulsion.
A) precedes the onset of epilepsy.
B) precedes a convulsion.
C) follows a convulsion.
D) occurs during a convulsion.
E) replaces a convulsion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
With respect to epilepsy, clonus is to tonus as
A) rigidity is to tremor.
B) rigidity is to loss of balance.
C) loss of balance is to rigidity.
D) tremor is to rigidity.
E) tonus is to loss of balance.
A) rigidity is to tremor.
B) rigidity is to loss of balance.
C) loss of balance is to rigidity.
D) tremor is to rigidity.
E) tonus is to loss of balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Cell death produced by activation of a cell's genetic program for suicide is called
A) apoptosis.
B) necrosis.
C) an infarct.
D) gliosis.
E) a shame.
A) apoptosis.
B) necrosis.
C) an infarct.
D) gliosis.
E) a shame.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The diagnosis of epilepsy is applied to all people who have
A) convulsions.
B) seizures.
C) scalp electroencephalography.
D) spontaneously recurring seizures.
E) clonus.
A) convulsions.
B) seizures.
C) scalp electroencephalography.
D) spontaneously recurring seizures.
E) clonus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The two major categories of seizures are
A) generalized and simple.
B) generalized and partial.
C) petit mal and grand mal.
D) cortical and subcortical.
E) complex and simple.
A) generalized and simple.
B) generalized and partial.
C) petit mal and grand mal.
D) cortical and subcortical.
E) complex and simple.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following can act as an endogenous neurotoxin?
A) mercury
B) lead
C) an antibody
D) tardive dyskinesia
E) an infarct
A) mercury
B) lead
C) an antibody
D) tardive dyskinesia
E) an infarct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Simple partial seizures are
A) Jacksonian.
B) partial seizures whose symptoms are primarily sensory or motor.
C) often characterized by the systematic spread of motor symptoms through the body.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) Jacksonian.
B) partial seizures whose symptoms are primarily sensory or motor.
C) often characterized by the systematic spread of motor symptoms through the body.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Automatisms are often components of
A) complex partial seizures.
B) simple partial seizures.
C) generalized seizures.
D) petit mal seizures.
E) grand mal seizures.
A) complex partial seizures.
B) simple partial seizures.
C) generalized seizures.
D) petit mal seizures.
E) grand mal seizures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following causes epilepsy?
A) neurotoxins
B) cerebrovascular diseases
C) head injuries
D) all of the above
E) both A and C
A) neurotoxins
B) cerebrovascular diseases
C) head injuries
D) all of the above
E) both A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Simple and complex are the two major categories of
A) epilepsy.
B) partial seizures.
C) generalized seizures.
D) convulsions.
E) automatisms.
A) epilepsy.
B) partial seizures.
C) generalized seizures.
D) convulsions.
E) automatisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Neurological disorders are rarely caused by dominant genes
A) because all individuals carrying them would be at a major disadvantage in terms of survival and reproduction.
B) unless the dominant genes do not express themselves until after the peak reproductive years.
C) unless their expression is uninfluenced by environmental factors.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
A) because all individuals carrying them would be at a major disadvantage in terms of survival and reproduction.
B) unless the dominant genes do not express themselves until after the peak reproductive years.
C) unless their expression is uninfluenced by environmental factors.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Necrotic cell death
A) usually involves inflammation.
B) is usually much slower than apoptotic cell death.
C) usually requires several days.
D) is the result of a genetic program for self-destruction.
E) is apoptotic.
A) usually involves inflammation.
B) is usually much slower than apoptotic cell death.
C) usually requires several days.
D) is the result of a genetic program for self-destruction.
E) is apoptotic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following is a generalized seizure?
A) complex partial seizure
B) petit mal
C) grand mal
D) all of the above
E) both B and C
A) complex partial seizure
B) petit mal
C) grand mal
D) all of the above
E) both B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The 3-per-second spike and wave is
A) an effective play in volleyball.
B) characteristic of tonic-clonic convulsions.
C) a correlate of petit mal seizures.
D) a correlate of simple partial seizures.
E) a correlate of complex partial seizures.
A) an effective play in volleyball.
B) characteristic of tonic-clonic convulsions.
C) a correlate of petit mal seizures.
D) a correlate of simple partial seizures.
E) a correlate of complex partial seizures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
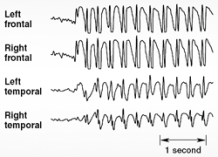
Illustrated here are EEG discharges characteristic of
A) petit mal seizures.
B) grand mal seizures.
C) simple partial seizures.
D) complex partial seizures.
E) myoclonic seizures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In cases of Parkinson's disease, the following are degenerated:
A) terminals in the striatum.
B) cell bodies in the substantia nigra.
C) axons in the nigrostriatal pathway.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
A) terminals in the striatum.
B) cell bodies in the substantia nigra.
C) axons in the nigrostriatal pathway.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which general class of drugs is useful in treating Parkinson's disease?
A) dopamine agonists
B) dopamine antagonists
C) MAO inhibitors
D) tricyclics
E) phenothiazines
A) dopamine agonists
B) dopamine antagonists
C) MAO inhibitors
D) tricyclics
E) phenothiazines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The symptoms of Parkinson's disease are temporarily alleviated in some patients by injections of
A) L-DOPA.
B) tyrosine.
C) dopamine.
D) serotonin.
E) adrenaline.
A) L-DOPA.
B) tyrosine.
C) dopamine.
D) serotonin.
E) adrenaline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is likely to lead to the label of daydreamer?
A) petit mal epilepsy
B) grand mal epilepsy
C) temporal lobe epilepsy
D) tonic-clonic epilepsy
E) Jacksonian epilepsy
A) petit mal epilepsy
B) grand mal epilepsy
C) temporal lobe epilepsy
D) tonic-clonic epilepsy
E) Jacksonian epilepsy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Parkinson's disease typically strikes in
A) infancy.
B) childhood.
C) adolescence.
D) early adulthood.
E) middle or late adulthood.
A) infancy.
B) childhood.
C) adolescence.
D) early adulthood.
E) middle or late adulthood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Complex partial seizures
A) often result from temporal lobe pathology.
B) are often characterized by automatisms.
C) often include petit mal attacks.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
A) often result from temporal lobe pathology.
B) are often characterized by automatisms.
C) often include petit mal attacks.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A professor in the middle of a lecture unbuttoned his shirt and rebuttoned it several times in rapid succession, started to sing, and then ran out of the room.He was discovered several hours later sleeping in the rain on a bench in front of the university library.He could not remember his classroom behavior, and he had no idea how he had fallen asleep in the rain.The professor may have experienced
A) a grand mal attack.
B) a generalized seizure.
C) a complex partial seizure.
D) a spike-and-wave discharge.
E) a petit mal absence attack.
A) a grand mal attack.
B) a generalized seizure.
C) a complex partial seizure.
D) a spike-and-wave discharge.
E) a petit mal absence attack.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is a controversial treatment for Parkinson's disease?
A) electroconvulsive shock
B) deep brain stimulation
C) prefrontal lobotomy
D) split-brain operations
E) dopamine antagonists
A) electroconvulsive shock
B) deep brain stimulation
C) prefrontal lobotomy
D) split-brain operations
E) dopamine antagonists

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Grand mal convulsions produce __________, which itself can cause brain damage.
A) petit mal absences
B) incontinence
C) cerebral hypoxia
D) auras
E) clonus
A) petit mal absences
B) incontinence
C) cerebral hypoxia
D) auras
E) clonus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Tremor at rest, muscular rigidity, slowness of movement, and a masklike face are symptoms of
A) Down syndrome.
B) Parkinson's disease.
C) epilepsy.
D) Huntington's disease.
E) multiple sclerosis.
A) Down syndrome.
B) Parkinson's disease.
C) epilepsy.
D) Huntington's disease.
E) multiple sclerosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In about 90% of patients with Parkinson's disease, there is clear evidence that the disease was caused by
A) genetic factors.
B) a stroke.
C) a tumor.
D) a neurotoxin.
E) none of the above
A) genetic factors.
B) a stroke.
C) a tumor.
D) a neurotoxin.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The most common type of epilepsy is
A) simple partial.
B) complex partial.
C) grand mal.
D) petit mal.
E) myoclonic.
A) simple partial.
B) complex partial.
C) grand mal.
D) petit mal.
E) myoclonic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Parkinson's disease is associated with degeneration of the
A) thalamus.
B) substantia nigra.
C) cerebellum.
D) cortex.
E) hippocampus.
A) thalamus.
B) substantia nigra.
C) cerebellum.
D) cortex.
E) hippocampus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Generalized seizures always involve
A) the entire brain.
B) tonus.
C) clonus.
D) cyanosis.
E) all of the above
A) the entire brain.
B) tonus.
C) clonus.
D) cyanosis.
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which type of convulsion is associated with petit mal epilepsy?
A) tonic
B) clonic
C) tonic-clonic
D) automatism
E) absence
A) tonic
B) clonic
C) tonic-clonic
D) automatism
E) absence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The major neurochemical correlate of Parkinson's disease is a reduction of
A) cortical acetylcholine.
B) dopamine in the substantia nigra and striatum.
C) acetylcholine in the striatum.
D) serotonin in the cortex.
E) the ratio of acetylcholine to dopamine in the cortex.
A) cortical acetylcholine.
B) dopamine in the substantia nigra and striatum.
C) acetylcholine in the striatum.
D) serotonin in the cortex.
E) the ratio of acetylcholine to dopamine in the cortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Although L-DOPA does have some beneficial effects, it is not a solution to the problem of Parkinson's disease because it
A) typically becomes less and less therapeutically effective with use.
B) is too expensive.
C) can be safely administered to only a small proportion of patients.
D) is unstable at room temperature.
E) does not pass through the blood-brain barrier.
A) typically becomes less and less therapeutically effective with use.
B) is too expensive.
C) can be safely administered to only a small proportion of patients.
D) is unstable at room temperature.
E) does not pass through the blood-brain barrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 185 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



