Deck 2: Consumers and Their Preferences
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Consumers and Their Preferences
1
A pychological assumption about consumer preferences that states that more of anything is always better is called satiation.
False
2
Rationality is the assumption that economic agents know what they like and behave accordingly.
True
3
An assumption on consumer preferences that states that any bundle is at least as good as itself is called
A) relexivity
B) transitivity
C) multiplicativity
A) relexivity
B) transitivity
C) multiplicativity
relexivity
4
Which of the following institutions exists in a primitive state of nature?
A) the state
B) banks
C) corporations
A) the state
B) banks
C) corporations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A utility function is a representation of an agent's preferences that tells the agent how good a bundle is by assigning a utility number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The assumption of complete binary ordering does not apply to
A) comparing a bag of two pounds of apples and one pound of raspberries to a bag of one pound of apples and three pounds of raspberries
B) asking if your economics or your marketing professor is your favorite
C) choosing between two slices of pizza plus one energy drink and three slices of pizza and two energy drinks
A) comparing a bag of two pounds of apples and one pound of raspberries to a bag of one pound of apples and three pounds of raspberries
B) asking if your economics or your marketing professor is your favorite
C) choosing between two slices of pizza plus one energy drink and three slices of pizza and two energy drinks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Transitivity is an assumption on consumer preferences that states that any bundle is at least as good as itself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The property of consumption sets that implies that it is possible to combine two bundles to produce a third by consuming fractions of them is called convexity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The assumption on consumption sets that states that it is possible to add consumption bundles is called
A) the divisibility assumption
B) the additivity assumption
C) convexity
A) the divisibility assumption
B) the additivity assumption
C) convexity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A consumption possibility set is the set of bundles feasible for a society's agents to consume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An additive utility function has the property that the marginal utility of one extra unit of any good consumed is independent of the amount of other goods consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An assumption on consumer preferences that implies that, if any two bundles in the consumption possibility set are chosen, then agents will be able to rank them is called
A) complete binary ordering
B) incomplete binary ordering
C) ordinal utility
A) complete binary ordering
B) incomplete binary ordering
C) ordinal utility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The reduced set of consumption bundles, each of which satisfies the budget constraint, is called the economically feasible consumption set.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In Experimental Teaser 1, what action can the divider choose?
A) Keep all the $10
B) Give some to the receiver
C) Both options are available
A) Keep all the $10
B) Give some to the receiver
C) Both options are available

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In a multiplicative utility function, utility is a function of the products of the various units of goods consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
One reason that agents cannot consume infinite amounts of goods is that
A) consumption takes time and time is finite in any given day
B) the agents' eyes are bigger than their stomachs
C) factories cannot produce that many goods over the long run
A) consumption takes time and time is finite in any given day
B) the agents' eyes are bigger than their stomachs
C) factories cannot produce that many goods over the long run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The divisibility assumption is the assumption on consumption sets that states that
A) goods are infinitely divisible
B) it is possible to add consumption bundles
C) it is possible to combine two bundles to produce a third by consuming fractions of them
A) goods are infinitely divisible
B) it is possible to add consumption bundles
C) it is possible to combine two bundles to produce a third by consuming fractions of them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is not a choice facing agents in the primitive state of nature?
A) how much money to earn
B) how much time to spend at leisure and how much to spend picking fruit
C) what mix of fruit they want to consume at any given point in time
A) how much money to earn
B) how much time to spend at leisure and how much to spend picking fruit
C) what mix of fruit they want to consume at any given point in time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Not included in the economic definition of rationality is the concept that
A) agents know what they like
B) economists evaluate or judge the preferences of agents
C) agents behave based on their knowledge of what they like
A) agents know what they like
B) economists evaluate or judge the preferences of agents
C) agents behave based on their knowledge of what they like

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A psychological assumption about agents that states that they are interested only in their own utility is called selfishness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
According to Fehr and Schmidt, if xⱼ > xᵢ, then an inequality-averse person i would have a utility function like
A) Ui(x) = xi
B) Ui(x) = xi - b(xi - xj)
C) Ui(x) = xi - a(xj - xi)
A) Ui(x) = xi
B) Ui(x) = xi - b(xi - xj)
C) Ui(x) = xi - a(xj - xi)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Beyond the three rationality assumptions--completeness, reflexivity, and transitivity--what assumption is required for the use of utility functions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The results of the Dictator game seem to violate which of the following assumptions?
A) both selfishness and nonsatiation
B) only selfishness
C) only nonsatiation
A) both selfishness and nonsatiation
B) only selfishness
C) only nonsatiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the Dictator game, subjects were most selfish when
A) the experiment is done using a double-blind protocol (no one is looking)
B) the right to be the divider is allocated randomly
C) subjects have to compete for the right to be the divider (excuse to justify selfishness)
A) the experiment is done using a double-blind protocol (no one is looking)
B) the right to be the divider is allocated randomly
C) subjects have to compete for the right to be the divider (excuse to justify selfishness)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Because it takes a fixed amount of time to consume each of two goods and the amounts differ, one good is more ____________ than the other
A) expensive
B) delicious
C) nutritious
A) expensive
B) delicious
C) nutritious

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If you believe that the amount of utility an agent receives from raspberries directly depends on how many units of apples the agent consumes, what type of utility function should you use?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The ________ bundle to choose from a set of available bundles is be the one that is assigned the _________ utility number by the agent's utility function.
A) best, biggest
B) best, smallest
C) worst, biggest
A) best, biggest
B) best, smallest
C) worst, biggest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The assumption on utility functions that states that, if two bundles are close to each other in the feasible set, then they will be assigned utility numbers that are close to each other as well is called
A) convexity
B) continuity
C) ordinality
A) convexity
B) continuity
C) ordinality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
According to Fehr and Schmidt, if people get _______ than others, the receivers feel __________, and if they get _______, they feel __________.
A) less, envious, more, guilty
B) less, guilty, more, envious
C) more, neutral, less, guilty
A) less, envious, more, guilty
B) less, guilty, more, envious
C) more, neutral, less, guilty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Imagine that you are a member of a team working on an economics group project. You have to choose between doing your share of the work to increase the group grade or sliding by on the work of the other team members. This example could be a case study for
A) nonsatiation
B) convexity of preferences
C) ambiguous selfishness
A) nonsatiation
B) convexity of preferences
C) ambiguous selfishness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Figure 2-1
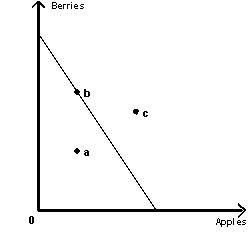
Refer to Figure 2-1. Which point is not contained in the economically feasible consumption set?
A) a
B) b
C) c

Refer to Figure 2-1. Which point is not contained in the economically feasible consumption set?
A) a
B) b
C) c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A place where agents can go and exchange one good for another at a fixed price is called a
A) market
B) trading pit
C) fair
A) market
B) trading pit
C) fair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is not a psychological assumption made about economic agents?
A) continuity
B) selfishness
C) nonsatiation
A) continuity
B) selfishness
C) nonsatiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Michelle Wu's favorite 16-ounce drinks are iced tea, lemonade, and an "Arnold Palmer," which is a mixture of iced tea and lemonade. Explain how these three drinks form a convex set.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Reflexivity is an example of a
A) psychological assumption
B) rationality assumption
C) psychiatric assumption
A) psychological assumption
B) rationality assumption
C) psychiatric assumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the utility numbers we assign to objects have no meaning other than to represent the ranking of these goods in terms of a person's preferences, then utility is measurable in the
A) ordinal sense
B) cardinal sense
C) rational sense
A) ordinal sense
B) cardinal sense
C) rational sense

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Why are economically feasible sets bounded?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The function U = xy is an example of a(n)
A) multiplicative utility function
B) additive utility function
C) cardinal utility function
A) multiplicative utility function
B) additive utility function
C) cardinal utility function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Robert Rubate's utility function assigns the number 100 to a piece of cheesecake and the number 250 to a book about Thomas Jefferson. These numbers imply that the Jefferson book is two-and-a-half times as good as a piece of cheesecake. What type of utility is Robert using?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which assumption or assumptions permits the derivation of the existence of a continuous utility function?
A) both rationality and continuity assumptions
B) only rationality assumptions
C) only continuity assumptions
A) both rationality and continuity assumptions
B) only rationality assumptions
C) only continuity assumptions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



