Deck 25: Public Goods, the Consequences of Strategic Voting Behavior, and the Role of Government
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Public Goods, the Consequences of Strategic Voting Behavior, and the Role of Government
1
Rival consumption occurs when consumption of a good by one person ____________ the quantity of the good available for consumption by others.
A) has no effect on
B) decreases
C) increases
A) has no effect on
B) decreases
C) increases
decreases
2
The Gibbard-Satterthwaite theorem states that, when a single outcome is to be chosen from more than two alternatives, all possible voting rules can be manipulated.
False
3
In the Lindahl model, the government's role is as a(n)
A) coordinator or market aid
B) intervener or controller
C) hands-off observer
A) coordinator or market aid
B) intervener or controller
C) hands-off observer
coordinator or market aid
4
A competitive equilibrium for a market with both private and public goods is called a
A) Lindahl equilibrium
B) Pareto equilibrium
C) Nash equilibrium
A) Lindahl equilibrium
B) Pareto equilibrium
C) Nash equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The weakness of the Lindahl solution is the
A) free-rider problem
B) presence of public goods
C) competitive pricing system
A) free-rider problem
B) presence of public goods
C) competitive pricing system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A mechanism that creates the incentive for people to reveal their public goods preferences in a truthful manner is called a Lindahl-revealing mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The performance correspondence is a relationship between the environment and the set of desired outcomes, which tells us which outcomes will never satisfy our performance criteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Goods that have the properties of nonexcludability and nonrival consumption are called
A) private goods
B) public goods
C) Pigouvian goods
A) private goods
B) public goods
C) Pigouvian goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When members of a society have incentives to take advantage of a public good by not contributing to paying its costs, society experiences the
A) free-rider problem
B) Pareto problem
C) strategic-voting problem
A) free-rider problem
B) Pareto problem
C) strategic-voting problem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The free-rider problem occurs when members of a society have incentives to take advantage of a public good by contributing to paying its costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a Pareto-optimal condition for an economy with public goods and many private goods?
A) Private goods should be allocated until that point at which the marginal rate of substitution between any two goods equals their price ratio
B) The marginal rates of technical substitution of the inputs to production of only two goods must be equal
C) The marginal rates of substitution equal the marginal rates of transformation for any two goods
A) Private goods should be allocated until that point at which the marginal rate of substitution between any two goods equals their price ratio
B) The marginal rates of technical substitution of the inputs to production of only two goods must be equal
C) The marginal rates of substitution equal the marginal rates of transformation for any two goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A demand-revealing mechanism creates the incentive for people to reveal their public goods preferences in a
A) deceptive manner
B) truthful manner
C) probabilistic manner
A) deceptive manner
B) truthful manner
C) probabilistic manner

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Borda count method is used to choose between k alternatives where the voters allocate k votes to their first alternative, k - 1 votes to their second, k - 2 votes to their third, etc. The alternative receiving the largest total number of votes is the one chosen by the voting body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The behavior of interest groups in their attempt to extract rents from the government or other authorities is called strategic renting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Excludability occurs when consumption of a good is restricted to certain people, such as people who are willing to pay for the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Voting in a manner that does not reflect one's true preferences in an effort to affect the outcome of a vote is called strategic voting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Goods that have the properties of excludability and rival consumption are known as
A) public goods
B) competitive goods
C) private goods
A) public goods
B) competitive goods
C) private goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
As a general rule, society should provide a public good until that point at which the marginal benefit to society of having one more unit produced is __________________ the marginal cost of the good
A) less than
B) equal to
C) greater than
A) less than
B) equal to
C) greater than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Agenda manipulation is the process by which an individual who controls the agenda for a committee or voting body manipulates the order in which pairs of alternatives are voted on in an effort to influence the outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Arrow's impossibility theorem demonstrates that there is a voting mechanism that determines transitive social preferences and also satisfies the five conditions for a desirable voting mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the streetlight example of a demand-revealing mechanism, the "optimal" plan is the one that ____________ the difference between the total amount the members are willing to pay for a plan and its cost.
A) maximizes
B) minimizes
C) equalizes
A) maximizes
B) minimizes
C) equalizes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A relationship between the environment and the set of desired outcomes, which tells us which outcomes will never satisfy our performance criteria is known as
A) rent-seeking behavior
B) the performance correspondence
C) the Borda count method
A) rent-seeking behavior
B) the performance correspondence
C) the Borda count method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the key assumption on which the Lindahl solution depends?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Summarize the reasons that some people feel that there is a legitimate role for government intervention.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Give some examples that support the Gibbard-Satterthwaite theorem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In voting for one-dimensional issues, if a person has a uniquely best alternative she or he prefers and her or his preferences decline as the distance between this best alternative and the alternative under consideration increases, then preferences are single
A) utility
B) peaked
C) optimal
A) utility
B) peaked
C) optimal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
According to the Gibbard-Satterthwaite theorem, when a single outcome is to be chosen from more than two alternatives, the only voting rule that cannot be manipulated is
A) the Borda count method
B) a dictatorial one
C) majority rules
A) the Borda count method
B) a dictatorial one
C) majority rules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
You like to play loud music at your house. One day you notice your neighbors dancing to your music. What type of good is your music?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Under the conditions that lead to strategic voting, truth-telling __________ a Nash equilibrium strategy.
A) must be
B) is
C) is not
A) must be
B) is
C) is not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A theorem that demonstrates that there is no voting mechanism that determines transitive social preferences and also satisfies the five conditions for a desirable voting mechanism is called
A) Arrow's impossibility theorem
B) Arrow's possibility theorem
C) Arrow's straight-shot theorem
A) Arrow's impossibility theorem
B) Arrow's possibility theorem
C) Arrow's straight-shot theorem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
To break the cycling of social preferences that results from the voting paradox, society might have to rely on
A) Coasian bargaining
B) some external authority
C) the Lindahl solution
A) Coasian bargaining
B) some external authority
C) the Lindahl solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The voting paradox holds that, even if all the people in a society have transitive preferences, the preferences of society taken as a whole
A) need not be transitive
B) must be transitive
C) will never be transitive
A) need not be transitive
B) must be transitive
C) will never be transitive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is a reason for some type of government mediation in a market?
A) social conflict over appropriate levels of public goods
B) need to aggregate the preferences of individuals to reach a socially desirable outcome
C) Both answers are correct
A) social conflict over appropriate levels of public goods
B) need to aggregate the preferences of individuals to reach a socially desirable outcome
C) Both answers are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Rent seeking implies that the loss to society from monopolies established by the government is much greater than the deadweight loss because of all the money wasted on
A) production
B) lobbying
C) living in apartments
A) production
B) lobbying
C) living in apartments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The moral of the agenda manipulation story is to beware of
A) the agenda
B) double-peaked preferences
C) Both answers are correct
A) the agenda
B) double-peaked preferences
C) Both answers are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
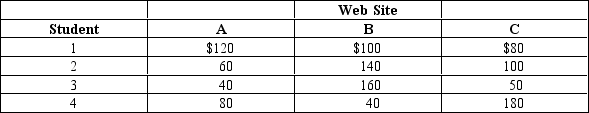
A professor is trying to decide which tutorial Web site to post for an economics course. Exhibit 25-1 is a demand-revealing mechanism representing students' truthful answers about their preferences for three different sites. Which site has the highest total willingness to pay?
A) A
B) B
C) C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
One condition for an ideal voting mechanism is
A) group selfishness
B) nondictatorship
C) Stackelberg optimality
A) group selfishness
B) nondictatorship
C) Stackelberg optimality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The behavior of interest groups in their attempt to extract rents from the government or other authorities is called
A) the performance correspondence
B) rent-seeking behavior
C) the Borda count method
A) the performance correspondence
B) rent-seeking behavior
C) the Borda count method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The auction election mechanism differs from the demand-revealing mechanism because the former requires that decisions be made
A) unanimously
B) by simple majority
C) based on total willingness to pay
A) unanimously
B) by simple majority
C) based on total willingness to pay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is so bad about rent seeking behavior?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



