Deck 2: Principles of Drug Action
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/39
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Principles of Drug Action
1
The process of incorporating a substance into a cell by engulfment and transport to the cell interior in vesicles is termed
A)aqueous diffusion.
B)lipid diffusion.
C)bioavailability.
D)pinocytosis.
A)aqueous diffusion.
B)lipid diffusion.
C)bioavailability.
D)pinocytosis.
pinocytosis.
2
Which of the following methods of drug administration requires a needle?
1)Transdermal
2)Inhalation
3)Subcutaneous
4)Intravenous
A)1 and 3 only
B)2 and 4 only
C)1 and 2 only
D)3 and 4 only
1)Transdermal
2)Inhalation
3)Subcutaneous
4)Intravenous
A)1 and 3 only
B)2 and 4 only
C)1 and 2 only
D)3 and 4 only
3 and 4 only
3
Approximately what percentage of an inhaled aerosol reaches the lower respiratory tract with current delivery devices?
A)0% to 10%
B)10% to 30%
C)50% to 60%
D)90% to 100%
A)0% to 10%
B)10% to 30%
C)50% to 60%
D)90% to 100%
10% to 30%
4
The drug albuterol binds to its corresponding receptor to initiate its intended response of bronchodilation.By definition,albuterol is known as a(n)
A)agonist.
B)antagonist.
C)both A and B.
D)neither A nor B.
A)agonist.
B)antagonist.
C)both A and B.
D)neither A nor B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The mechanism of drug action by which a drug molecule causes its effect in the body is known as the
A)pharmacodynamic phase.
B)elimination phase.
C)pharmacokinetic phase.
D)administration phase.
A)pharmacodynamic phase.
B)elimination phase.
C)pharmacokinetic phase.
D)administration phase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Given the following information,which drug is most potent? 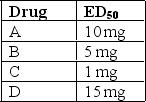
A)Drug A
B)Drug B
C)Drug C
D)Drug D

A)Drug A
B)Drug B
C)Drug C
D)Drug D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A drug's portal of entry into the body is known as the
A)formulation.
B)dosage.
C)route of administration.
D)additive.
A)formulation.
B)dosage.
C)route of administration.
D)additive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Out of the total systemically available drug,the proportion of drug available from the lung is known as the
A)TI
B)VD
C)L/T ratio
D)T1/2
A)TI
B)VD
C)L/T ratio
D)T1/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the four major body compartments contains the smallest average volume in liters?
A)Intracellular fluid
B)Vascular space
C)Interstitial fluid
D)Fat
A)Intracellular fluid
B)Vascular space
C)Interstitial fluid
D)Fat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following drugs has the greatest potential of crossing over from a therapeutic effect to a toxic effect? 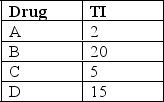
A)Drug A
B)Drug B
C)Drug C
D)Drug D

A)Drug A
B)Drug B
C)Drug C
D)Drug D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following routes of drug administration help to reduce the first-pass effect?
1)Oral administration
2)Injection
3)Sublingual tablets
4)Rectal administration
A)1 and 3 only
B)2 and 4 only
C)2,3,and 4 only
D)1,2,and 4 only
1)Oral administration
2)Injection
3)Sublingual tablets
4)Rectal administration
A)1 and 3 only
B)2 and 4 only
C)2,3,and 4 only
D)1,2,and 4 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is not a part of the pharmacokinetic phase of a drug?
A)Absorption
B)Receptor site
C)Metabolism
D)Elimination
A)Absorption
B)Receptor site
C)Metabolism
D)Elimination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Inhaled aerosols may have which types of intended effects on the body?
1)Enteral
2)Local
3)Systemic
4)Oral
A)1 and 3 only
B)2 and 4 only
C)2 and 3 only
D)1,2,3,and 4
1)Enteral
2)Local
3)Systemic
4)Oral
A)1 and 3 only
B)2 and 4 only
C)2 and 3 only
D)1,2,3,and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
During which phase of drug action is a drug made available to the body?
A)Administration
B)Pharmacokinetic
C)Pharmacodynamic
D)Pharmacogenetic
A)Administration
B)Pharmacokinetic
C)Pharmacodynamic
D)Pharmacogenetic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following organs is considered the primary site of drug excretion?
A)Kidney
B)Liver
C)Small intestine
D)Stomach
A)Kidney
B)Liver
C)Small intestine
D)Stomach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The principal organ for drug metabolism is the
A)brain.
B)liver.
C)stomach.
D)lung.
A)brain.
B)liver.
C)stomach.
D)lung.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following methods of drug delivery are commonly considered parenteral?
1)Intravenous
2)Intramuscular
3)Paste
4)Aerosol
A)1 and 4 only
B)1 and 2 only
C)3 and 4 only
D)1,2,3,and 4
1)Intravenous
2)Intramuscular
3)Paste
4)Aerosol
A)1 and 4 only
B)1 and 2 only
C)3 and 4 only
D)1,2,3,and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The relationship between a drug's chemical structure and its clinical activity is known as
A)bioavailability.
B)biotransformation.
C)pharmacokinetics.
D)structure-activity relationship.
A)bioavailability.
B)biotransformation.
C)pharmacokinetics.
D)structure-activity relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following are routes of drug administration?
1)Enteral
2)Parenteral
3)Ointment
4)Inhalation
A)1 and 4 only
B)1,2,and 3 only
C)1,2,and 4 only
D)1,2,3,and 4
1)Enteral
2)Parenteral
3)Ointment
4)Inhalation
A)1 and 4 only
B)1,2,and 3 only
C)1,2,and 4 only
D)1,2,3,and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following factors may have an effect on drug absorption?
1)Route of administration
2)Metabolic degradation
3)Inactivation by stomach acids
4)Blood flow to absorption site
A)1 only
B)1 and 2 only
C)1 and 4 only
D)1,2,3,and 4
1)Route of administration
2)Metabolic degradation
3)Inactivation by stomach acids
4)Blood flow to absorption site
A)1 only
B)1 and 2 only
C)1 and 4 only
D)1,2,3,and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The time required for the plasma concentration of a drug to decrease by one-half is referred to as
A)bioavailability.
B)biotransformation.
C)drug distribution.
D)plasma half-life.
A)bioavailability.
B)biotransformation.
C)drug distribution.
D)plasma half-life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following factors can increase the lung availability/total systemic availability ratio of inhaled drugs?
1)Efficient delivery devices
2)Inhaled drugs with a high first-pass metabolism rate
3)Mouth washing
4)Use of a reservoir device
A)1 and 2 only
B)1 and 3 only
C)1,2,and 3 only
D)1,2,3,and 4
1)Efficient delivery devices
2)Inhaled drugs with a high first-pass metabolism rate
3)Mouth washing
4)Use of a reservoir device
A)1 and 2 only
B)1 and 3 only
C)1,2,and 3 only
D)1,2,3,and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The drug methacholine can stimulate parasympathetic receptors in the airways,causing bronchoconstriction.Epinephrine can stimulate 2 receptors in the airways,causing bronchodilation.These two opposing effects that cancel each other out are an example of
A)chemical antagonism.
B)functional antagonism.
C)competitive antagonism.
D)synergism.
A)chemical antagonism.
B)functional antagonism.
C)competitive antagonism.
D)synergism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An allergic or immune-mediated reaction to a drug,which can be serious,requiring airway maintenance or ventilatory assistance is called
A)potency.
B)hypersensitivity.
C)potentiation.
D)additivity.
A)potency.
B)hypersensitivity.
C)potentiation.
D)additivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The term used to indicate the proportion of a drug that reaches the systemic circulation is
A)bioavailability.
B)biotransformation.
C)pharmacokinetics.
D)structure-activity relationship.
A)bioavailability.
B)biotransformation.
C)pharmacokinetics.
D)structure-activity relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A perfectly efficient aerosol delivery device would theoretically have an L/T ratio of which of the following?
A)0
B)0.5
C)0.75
D)1.0
A)0
B)0.5
C)0.75
D)1.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The difference between the minimal therapeutic and toxic concentrations of a drug is known as the
A)TI.
B)VD.
C)L/T ratio.
D)T1/2.
A)TI.
B)VD.
C)L/T ratio.
D)T1/2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
After inhalation of an aerosol by a spontaneously breathing patient with no artificial airway,a proportion of the aerosol does which of the following?
1)Impacts in the oropharynx
2)Is swallowed
3)Is absorbed by the lungs
4)Is exhaled
A)1 and 2 only
B)1 and 3 only
C)1,2,and 3 only
D)1,2,3,and 4
1)Impacts in the oropharynx
2)Is swallowed
3)Is absorbed by the lungs
4)Is exhaled
A)1 and 2 only
B)1 and 3 only
C)1,2,and 3 only
D)1,2,3,and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Why is lipid diffusion an important mechanism for drug absorption?
A)Many epithelial membranes must be crossed if a drug is to distribute in the body and reach its target organ.
B)Epithelial cells do not have lipid membranes,so a drug must be water-soluble to diffuse across such a membrane.
C)It is directly related to the proportion of a drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
D)Lipid diffusion has no importance in drug absorption because the body has very few epithelial membranes drugs must cross.
A)Many epithelial membranes must be crossed if a drug is to distribute in the body and reach its target organ.
B)Epithelial cells do not have lipid membranes,so a drug must be water-soluble to diffuse across such a membrane.
C)It is directly related to the proportion of a drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
D)Lipid diffusion has no importance in drug absorption because the body has very few epithelial membranes drugs must cross.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Two different drugs (each with its own mechanism of action)are administered to a patient in an attempt to relieve bronchoconstriction.The ordering physician hopes that the effect of the drug pair will be greater than the sum of the separate effects of each individual drug.If successful,this would be an example of
A)potentiation.
B)synergism.
C)additivity.
D)tolerance.
A)potentiation.
B)synergism.
C)additivity.
D)tolerance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
This term is used to describe when two drugs act on the same receptors and the combined effect is the simple linear sum of the effects of the two drugs,up to a maximal effect.
A)Potency
B)Hypersensitivity
C)Potentiation
D)Additivity
A)Potency
B)Hypersensitivity
C)Potentiation
D)Additivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A special case of synergism in which one drug has no effect but can increase the activity of another drug is known as
A)potency.
B)hypersensitivity.
C)potentiation.
D)additivity.
A)potency.
B)hypersensitivity.
C)potentiation.
D)additivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A measure of how quickly a drug is eliminated from the body is known as the
A)TI.
B)VD.
C)L/T ratio.
D)T1/2.
A)TI.
B)VD.
C)L/T ratio.
D)T1/2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The study of genetic factors and their influence on drug response is termed
A)pharmacogenetics.
B)functional antagonism.
C)competitive antagonism.
D)pharmacokinetics.
A)pharmacogenetics.
B)functional antagonism.
C)competitive antagonism.
D)pharmacokinetics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The lining of the lower respiratory tract presents barriers to drug absorption and includes which of the following elements?
1)Airway surface liquid
2)Capillary vascular network
3)Epithelial cells
4)Interstitium
A)1 and 2 only
B)1 and 3 only
C)1,2,and 3 only
D)1,2,3,and 4
1)Airway surface liquid
2)Capillary vascular network
3)Epithelial cells
4)Interstitium
A)1 and 2 only
B)1 and 3 only
C)1,2,and 3 only
D)1,2,3,and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Mrs.Johnson is a 37-year-old woman who has been taking medication for lower back pain for the last 18 months.She reports to her physician that although the medication initially rendered her pain-free,she now receives very little relief from her daily dose.This situation is described by which of the following terms used to refer to drug responsiveness (assuming that her condition has not actually worsened)?
A)Hypersensitivity
B)Idiosyncratic effect
C)Tolerance
D)Tachyphylaxis
A)Hypersensitivity
B)Idiosyncratic effect
C)Tolerance
D)Tachyphylaxis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Mr.Ashoor is a 29-year-old asthmatic patient who takes MDI albuterol for wheezing and typically gets quick relief following two puffs.After he mowed the lawn today,he realized he was having a rapid decrease in responsiveness to his albuterol.He tried taking it again but still had no relief.This situation is described by which of the following terms used to refer to drug responsiveness?
A)Hypersensitivity
B)Idiosyncratic effect
C)Tolerance
D)Tachyphylaxis
A)Hypersensitivity
B)Idiosyncratic effect
C)Tolerance
D)Tachyphylaxis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which is the term that refers to the concentration (EC50)or dose (ED50)of a drug producing 50% of the maximal response of the drug?
A)Potency
B)Hypersensitivity
C)Potentiation
D)Additivity
A)Potency
B)Hypersensitivity
C)Potentiation
D)Additivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The process by which a drug is transported to its sites of action,eliminated,or stored is referred to as
A)bioavailability.
B)biotransformation.
C)drug distribution.
D)plasma half-life.
A)bioavailability.
B)biotransformation.
C)drug distribution.
D)plasma half-life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



