Deck 9: Government in the Economy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/136
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Government in the Economy
1
Which of the following is NOT a role that most people expect of the government?
A) providing public institutions
B) clearly defining property rights
C) protecting its citizens
D) supplying certain goods to the economy
E) maintaining a record of people's political activities
A) providing public institutions
B) clearly defining property rights
C) protecting its citizens
D) supplying certain goods to the economy
E) maintaining a record of people's political activities
maintaining a record of people's political activities
2
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The presence of property rights sometimes gives rise to market failure.
B) Property rights are only relevant in markets where they are well-defined.
C) The absence of property rights sometimes gives rise to market failure.
D) In the context of public goods, efficiency in most markets can be improved by the elimination of property rights.
E) Government regulation of private behavior, in response to market failure, rarely can improve social well-being.
A) The presence of property rights sometimes gives rise to market failure.
B) Property rights are only relevant in markets where they are well-defined.
C) The absence of property rights sometimes gives rise to market failure.
D) In the context of public goods, efficiency in most markets can be improved by the elimination of property rights.
E) Government regulation of private behavior, in response to market failure, rarely can improve social well-being.
The absence of property rights sometimes gives rise to market failure.
3
Which of the following characteristics best defines a private good?
A) rival and excludable
B) rival and non-excludable
C) non-rival and non-excludable
D) non-rival and excludable
E) a good that is never produced by the government
A) rival and excludable
B) rival and non-excludable
C) non-rival and non-excludable
D) non-rival and excludable
E) a good that is never produced by the government
rival and excludable
4
A good that is rival and excludable is defined as a ________ good.
A) private
B) public
C) common-resource
D) club
E) government
A) private
B) public
C) common-resource
D) club
E) government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Visiting the public beach during summer is an example of an activity that is:
A) excludable.
B) rival.
C) non-excludable and rival.
D) non-rival.
E) excludable and non-rival.
A) excludable.
B) rival.
C) non-excludable and rival.
D) non-rival.
E) excludable and non-rival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The term "market failure" refers to:
A) cutthroat competition among firms.
B) an unsuccessful advertising campaign that does not increase demand.
C) a firm that is forced out of business because of excess losses.
D) a product that fails to sell.
E) a market that fails to allocate resources efficiently.
A) cutthroat competition among firms.
B) an unsuccessful advertising campaign that does not increase demand.
C) a firm that is forced out of business because of excess losses.
D) a product that fails to sell.
E) a market that fails to allocate resources efficiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The market works efficiently in the absence of externalities if the good is:
A) rival and excludable.
B) non-rival and non-excludable.
C) rival and non-excludable.
D) non-rival and excludable.
E) rival and either excludable or non-excludable.
A) rival and excludable.
B) non-rival and non-excludable.
C) rival and non-excludable.
D) non-rival and excludable.
E) rival and either excludable or non-excludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Driving in the city is an example of a good that is:
A) excludable.
B) rival.
C) non-excludable and rival.
D) non-rival.
E) excludable and non-rival.
A) excludable.
B) rival.
C) non-excludable and rival.
D) non-rival.
E) excludable and non-rival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A free-rider problem exists when:
A) people receive a benefit for which they do not need to pay.
B) firms impose a cost on third parties.
C) negative externalities exist.
D) a private good is produced.
E) any market is in equilibrium.
A) people receive a benefit for which they do not need to pay.
B) firms impose a cost on third parties.
C) negative externalities exist.
D) a private good is produced.
E) any market is in equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which good has well-defined property rights?
A) wild animals
B) the ocean
C) a country club golf course
D) the air
E) a street performance
A) wild animals
B) the ocean
C) a country club golf course
D) the air
E) a street performance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In a market economy,government intervention:
A) may improve market outcomes if markets fail.
B) will always improve market outcomes.
C) reduces efficiency in the presence of externalities.
D) is necessary to control individual greed.
E) is what the people usually want to improve the economy.
A) may improve market outcomes if markets fail.
B) will always improve market outcomes.
C) reduces efficiency in the presence of externalities.
D) is necessary to control individual greed.
E) is what the people usually want to improve the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which goods are sold in markets?
A) private goods
B) private goods and club goods
C) private goods, club goods, and common-resource goods
D) all types of goods
E) public goods
A) private goods
B) private goods and club goods
C) private goods, club goods, and common-resource goods
D) all types of goods
E) public goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which good is non-rival?
A) sharing a pizza with your family
B) swimming in a public pool
C) driving in a city
D) listening to public radio
E) visiting the post office
A) sharing a pizza with your family
B) swimming in a public pool
C) driving in a city
D) listening to public radio
E) visiting the post office

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Clean air becomes polluted because:
A) it is a private good.
B) no one owns the air.
C) it is a club good.
D) it is owned by private corporations.
E) it is owned by the government.
A) it is a private good.
B) no one owns the air.
C) it is a club good.
D) it is owned by private corporations.
E) it is owned by the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Markets fail to allocate resources efficiently when:
A) prices fluctuate.
B) people who have property rights abuse their privileges.
C) property rights are not well established.
D) the government privatizes an industry.
E) the government refuses to intervene in private markets.
A) prices fluctuate.
B) people who have property rights abuse their privileges.
C) property rights are not well established.
D) the government privatizes an industry.
E) the government refuses to intervene in private markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider the production of a private good such as a car,and a common-resource good such as fish.What do the markets for these two goods have in common?
A) The quantity of output produced is inefficiently low.
B) The quantity of output produced is inefficiently high.
C) Both create a positive externality.
D) Both markets are likely to arrive at the social optimum without government intervention.
E) The price of both goods is inefficiently high.
A) The quantity of output produced is inefficiently low.
B) The quantity of output produced is inefficiently high.
C) Both create a positive externality.
D) Both markets are likely to arrive at the social optimum without government intervention.
E) The price of both goods is inefficiently high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Copyright laws exist to:
A) eliminate negative externalities.
B) eliminate public goods.
C) limit free-riding.
D) solve the tragedy of the commons.
E) protect consumers.
A) eliminate negative externalities.
B) eliminate public goods.
C) limit free-riding.
D) solve the tragedy of the commons.
E) protect consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following characteristics best defines a public good?
A) rival and excludable
B) rival and non-excludable
C) non-rival and non-excludable
D) non-rival and excludable
E) a good that is never produced by the government
A) rival and excludable
B) rival and non-excludable
C) non-rival and non-excludable
D) non-rival and excludable
E) a good that is never produced by the government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Museum visits in a particular city are free.This good is:
A) excludable.
B) rival.
C) excludable and rival.
D) non-rival.
E) excludable and non-rival.
A) excludable.
B) rival.
C) excludable and rival.
D) non-rival.
E) excludable and non-rival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A major reason why the market for a manufactured good may fail is:
A) there is too much government regulation.
B) property rights are not well-defined.
C) there is likely to be a positive externality associated with production.
D) the industry is likely to be a monopoly.
E) the industry is producing too little output.
A) there is too much government regulation.
B) property rights are not well-defined.
C) there is likely to be a positive externality associated with production.
D) the industry is likely to be a monopoly.
E) the industry is producing too little output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Externalities are minimized if:
A) private property rights are well established.
B) the government owns all of the productive resources.
C) there are no private goods.
D) there are no public goods.
E) there are no free-riders.
A) private property rights are well established.
B) the government owns all of the productive resources.
C) there are no private goods.
D) there are no public goods.
E) there are no free-riders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A major reason why public goods are NOT supplied by the market is the:
A) free-rider problem.
B) existence of negative externalities.
C) fact that no one is willing to pay for them.
D) fact that public goods are rival.
E) fact that no firm would be able to earn a profit by producing them.
A) free-rider problem.
B) existence of negative externalities.
C) fact that no one is willing to pay for them.
D) fact that public goods are rival.
E) fact that no firm would be able to earn a profit by producing them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The air is a ________ good.
A) private
B) public
C) club
D) common-resource
E) government
A) private
B) public
C) club
D) common-resource
E) government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is the best example of a common-resource good?
A) a fireworks display
B) a lighthouse
C) cable television
D) fish in a lake
E) the production of gasoline
A) a fireworks display
B) a lighthouse
C) cable television
D) fish in a lake
E) the production of gasoline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
________ goods can be jointly consumed by more than one person,and nonpayers are difficult to exclude.
A) Private
B) Foreign
C) Common-resource
D) Public
E) Government
A) Private
B) Foreign
C) Common-resource
D) Public
E) Government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The tragedy of the commons:
A) gives rise to a negative externality.
B) gives rise to a positive externality.
C) occurs when club goods are produced.
D) occurs when public goods are provided.
E) leads to underutilized resources.
A) gives rise to a negative externality.
B) gives rise to a positive externality.
C) occurs when club goods are produced.
D) occurs when public goods are provided.
E) leads to underutilized resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Common-resource goods tend to be offered at ________ market price and at ________ quantity than what society desires.
A) a lower; a lower
B) a higher; a higher
C) a higher; a lower
D) a lower; a higher
E) the same; the same
A) a lower; a lower
B) a higher; a higher
C) a higher; a lower
D) a lower; a higher
E) the same; the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following characteristics best defines a common-resource good?
A) rival and excludable
B) rival and non-excludable
C) non-rival and non-excludable
D) non-rival and excludable
E) a good that is never produced by the government
A) rival and excludable
B) rival and non-excludable
C) non-rival and non-excludable
D) non-rival and excludable
E) a good that is never produced by the government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The tragedy of the commons occurs because the good being produced is:
A) non-rival.
B) rival and excludable.
C) rival and non-excludable.
D) non-rival and non-excludable.
E) excludable.
A) non-rival.
B) rival and excludable.
C) rival and non-excludable.
D) non-rival and non-excludable.
E) excludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The ability to download music and movies from the Internet without paying is:
A) an example of a negative externality.
B) an example of a club good.
C) an illegal form of free-riding.
D) an illustration of the tragedy of the commons.
E) something that anyone who pays taxes should be allowed to do.
A) an example of a negative externality.
B) an example of a club good.
C) an illegal form of free-riding.
D) an illustration of the tragedy of the commons.
E) something that anyone who pays taxes should be allowed to do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A good that is non-rival and non-excludable is defined as a ________ good.
A) private
B) public
C) common-resource
D) club
E) government
A) private
B) public
C) common-resource
D) club
E) government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which good is excludable?
A) apples on a tree in a public park
B) a fireworks display
C) swimming in the ocean
D) a walk in a public park
E) education at a community college
A) apples on a tree in a public park
B) a fireworks display
C) swimming in the ocean
D) a walk in a public park
E) education at a community college

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The quantity produced of a common-resource good is likely to deviate from the socially optimal quantity because:
A) common-resource goods are non-rival.
B) common-resource goods cannot be traded.
C) there is an incentive to overproduce the good.
D) of the free-rider problem.
E) positive externalities are likely to exist.
A) common-resource goods are non-rival.
B) common-resource goods cannot be traded.
C) there is an incentive to overproduce the good.
D) of the free-rider problem.
E) positive externalities are likely to exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A good that is rival and non-excludable is defined as a ________ good.
A) private
B) public
C) common-resource
D) normal
E) government
A) private
B) public
C) common-resource
D) normal
E) government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The tragedy of the commons occurs for goods that are:
A) rival and excludable.
B) rival and non-excludable.
C) non-rival and non-excludable.
D) non-rival and excludable.
E) never produced by the government.
A) rival and excludable.
B) rival and non-excludable.
C) non-rival and non-excludable.
D) non-rival and excludable.
E) never produced by the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which rule would NOT protect fish populations?
A) limiting the length of the fishing season
B) limiting the number of fish that can be caught
C) not allowing female fish to be caught
D) not allowing young fish to be caught
E) catching any fish except males
A) limiting the length of the fishing season
B) limiting the number of fish that can be caught
C) not allowing female fish to be caught
D) not allowing young fish to be caught
E) catching any fish except males

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Global warming is an example of:
A) the tragedy of the commons.
B) a public good.
C) the government good problem.
D) a positive externality.
E) a problem that has an easy solution.
A) the tragedy of the commons.
B) a public good.
C) the government good problem.
D) a positive externality.
E) a problem that has an easy solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Common resources are:
A) overused.
B) underused.
C) optimally used.
D) always owned by the government.
E) never owned by anyone.
A) overused.
B) underused.
C) optimally used.
D) always owned by the government.
E) never owned by anyone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What type of good is often provided by the government because it is hard to get people to voluntarily contribute their fair share of the expense?
A) private goods
B) foreign goods
C) common-resource goods
D) public goods
E) government goods
A) private goods
B) foreign goods
C) common-resource goods
D) public goods
E) government goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The market over-produces common-resource goods because private decision-makers consider ________ costs,but society experiences ________ costs.
A) internal; external
B) internal; internal and external
C) external; internal
D) external; internal and external
E) internal and external; external
A) internal; external
B) internal; internal and external
C) external; internal
D) external; internal and external
E) internal and external; external

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The amount you pay for gasoline for your car is an example of a(n)________ cost.
A) internal
B) social
C) external
D) third-party
E) public-good
A) internal
B) social
C) external
D) third-party
E) public-good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The costs or benefits of a market activity that affect a third party are called:
A) externalities.
B) public goods.
C) club goods.
D) internal costs.
E) common-resource goods.
A) externalities.
B) public goods.
C) club goods.
D) internal costs.
E) common-resource goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is true?
A) social costs = internal costs - external costs
B) social costs = internal costs + external costs
C) internal costs = social costs + external costs
D) external costs = social costs + internal costs
E) internal costs - social costs = external costs
A) social costs = internal costs - external costs
B) social costs = internal costs + external costs
C) internal costs = social costs + external costs
D) external costs = social costs + internal costs
E) internal costs - social costs = external costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A carbon tax would be an efficient method of addressing the problem of global warming because:
A) carbon taxes are an external cost.
B) it forces firms to internalize the external cost of emissions.
C) it eliminates the positive externalities associated with global warming.
D) firms are likely to prefer the carbon tax over the cap-and-trade policy.
E) it is less likely than the cap-and-trade policy to result in rising prices.
A) carbon taxes are an external cost.
B) it forces firms to internalize the external cost of emissions.
C) it eliminates the positive externalities associated with global warming.
D) firms are likely to prefer the carbon tax over the cap-and-trade policy.
E) it is less likely than the cap-and-trade policy to result in rising prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If the government implements a cap-and-trade system to reduce pollution in a particular industry,then the:
A) supply curve shifts to the left.
B) supply curve shifts to the right.
C) demand curve shifts to the left.
D) demand curve shifts to the right.
E) supply curve and the demand curve shift to the left.
A) supply curve shifts to the left.
B) supply curve shifts to the right.
C) demand curve shifts to the left.
D) demand curve shifts to the right.
E) supply curve and the demand curve shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A negative externality exists whenever:
A) there are no internal costs.
B) production of a good creates an external cost.
C) production of a good creates an external benefit.
D) production of a good has no social cost.
E) production of a good has no social benefit.
A) there are no internal costs.
B) production of a good creates an external cost.
C) production of a good creates an external benefit.
D) production of a good has no social cost.
E) production of a good has no social benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The personal decisions of consumers and firms are based on ________ costs.
A) external
B) social
C) internal
D) third-party
E) public-good
A) external
B) social
C) internal
D) third-party
E) public-good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A cap-and-trade policy is an efficient method of reducing pollution because:
A) all firms will be forced to reduce pollution.
B) only high-cost firms will be forced to reduce pollution.
C) only low-cost firms will be forced to reduce pollution.
D) those who can reduce pollution relatively more cheaply will have an incentive to buy permits.
E) those who can reduce pollution relatively more cheaply will have an incentive to sell permits.
A) all firms will be forced to reduce pollution.
B) only high-cost firms will be forced to reduce pollution.
C) only low-cost firms will be forced to reduce pollution.
D) those who can reduce pollution relatively more cheaply will have an incentive to buy permits.
E) those who can reduce pollution relatively more cheaply will have an incentive to sell permits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An internal cost is best defined as the cost of an activity paid for by:
A) the individual who is engaged in the activity.
B) the government.
C) a third party.
D) a free-rider.
E) the individual and the third party.
A) the individual who is engaged in the activity.
B) the government.
C) a third party.
D) a free-rider.
E) the individual and the third party.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is true?
A) social benefits = internal benefits - external benefits
B) social benefits = internal benefits + external benefits
C) internal benefits = social benefits + external benefits
D) external benefits = social benefits + internal benefits
E) internal benefits - social benefits = external benefits
A) social benefits = internal benefits - external benefits
B) social benefits = internal benefits + external benefits
C) internal benefits = social benefits + external benefits
D) external benefits = social benefits + internal benefits
E) internal benefits - social benefits = external benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Negative externalities have ________ for third parties.
A) internal costs
B) internal benefits
C) external costs
D) external benefits
E) social costs
A) internal costs
B) internal benefits
C) external costs
D) external benefits
E) social costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A cap-and-trade policy is most often used to solve problems associated with:
A) making free-riders pay for the goods they consume.
B) the production of public goods.
C) the production of goods that generate a negative externality.
D) the production of goods that generate a positive externality.
E) the production of club goods.
A) making free-riders pay for the goods they consume.
B) the production of public goods.
C) the production of goods that generate a negative externality.
D) the production of goods that generate a positive externality.
E) the production of club goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is the best definition of a cap-and-trade policy for pollution?
A) The government sets a cap on emissions.Firms are given permits by the government to emit pollutants and have the right to trade the permits with each other.
B) Emissions of a pollutant are capped by the government at the current level, and the good being produced can still be traded in the market.
C) Production of the good is capped by the government at the current level, but the good can still be traded in the market.
D) The number of firms producing a good is capped by the government at the current level, but the good can still be traded in the market.
E) Consumption of the good being produced is capped by the government at the current level, but the good can still be traded in the market.
A) The government sets a cap on emissions.Firms are given permits by the government to emit pollutants and have the right to trade the permits with each other.
B) Emissions of a pollutant are capped by the government at the current level, and the good being produced can still be traded in the market.
C) Production of the good is capped by the government at the current level, but the good can still be traded in the market.
D) The number of firms producing a good is capped by the government at the current level, but the good can still be traded in the market.
E) Consumption of the good being produced is capped by the government at the current level, but the good can still be traded in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An external cost is best defined as the cost of an activity paid for by:
A) the individual who is engaged in the activity.
B) the government.
C) a third party.
D) a free-rider.
E) the individual and the third party.
A) the individual who is engaged in the activity.
B) the government.
C) a third party.
D) a free-rider.
E) the individual and the third party.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The costs of a market activity paid for by an individual NOT engaged in the market activity are ________ costs.
A) external
B) internal
C) free-rider
D) social
E) common
A) external
B) internal
C) free-rider
D) social
E) common

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The amount you pay for insurance on your car is an example of a(n)________ cost.
A) internal
B) social
C) external
D) third-party
E) public-good
A) internal
B) social
C) external
D) third-party
E) public-good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The pollution emitted by your car is an example of a(n)________ cost.
A) internal
B) social
C) external
D) production
E) public-good
A) internal
B) social
C) external
D) production
E) public-good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The costs of a market activity paid for by an individual engaged in the market activity are ________ costs.
A) external
B) internal
C) free-rider
D) social
E) common
A) external
B) internal
C) free-rider
D) social
E) common

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The cost of an activity paid for by the individual and the third party is defined as a(n)________ cost.
A) internal
B) social
C) external
D) third-party
E) public-good
A) internal
B) social
C) external
D) third-party
E) public-good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
To maximize social welfare,the optimal quantity of a public good to provide should be determined through the use of:
A) private markets.
B) the judicial system.
C) public survey.
D) cost-benefit analysis.
E) the political process.
A) private markets.
B) the judicial system.
C) public survey.
D) cost-benefit analysis.
E) the political process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Consider a market where production of a good generates a negative externality.In the market equilibrium:
A) too much of the good is being produced.
B) too little of the good is being produced.
C) there is usually little that can be done to correct the externality.
D) the external costs have been internalized.
E) firms are not maximizing profit.
A) too much of the good is being produced.
B) too little of the good is being produced.
C) there is usually little that can be done to correct the externality.
D) the external costs have been internalized.
E) firms are not maximizing profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Your neighbor likes to mow his grass each Saturday at 7 A.M.and the noise invariably wakes you up.This is an example of:
A) a negative externality.
B) the tragedy of the commons.
C) an internal cost.
D) the free-rider problem.
E) a positive externality.
A) a negative externality.
B) the tragedy of the commons.
C) an internal cost.
D) the free-rider problem.
E) a positive externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the questions that follow.
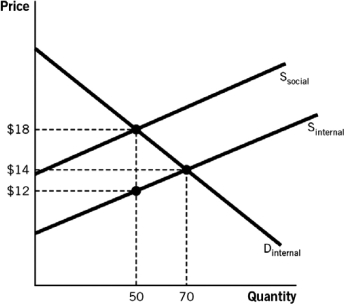
The figure best illustrates what type of market?
A) The good produced creates a positive externality.
B) The good produced creates a negative externality.
C) The good produced is a governmental good.
D) The good produced is a public good.
E) Firms in this industry have been given a subsidy to encourage more production.

The figure best illustrates what type of market?
A) The good produced creates a positive externality.
B) The good produced creates a negative externality.
C) The good produced is a governmental good.
D) The good produced is a public good.
E) Firms in this industry have been given a subsidy to encourage more production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Market activities that affect third-parties:
A) occur when a market activity leads to a negative externality.
B) occur when a market activity leads to a positive externality.
C) occur when a market activity leads to a negative or a positive externality.
D) are the same as the free-rider problem.
E) are associated with the production of private goods but not public goods.
A) occur when a market activity leads to a negative externality.
B) occur when a market activity leads to a positive externality.
C) occur when a market activity leads to a negative or a positive externality.
D) are the same as the free-rider problem.
E) are associated with the production of private goods but not public goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
You drive to work each day.The best example of an internal cost is the:
A) amount of pollution emitted by your car.
B) congestion created by your car being on the road.
C) amount the government paid to build the road.
D) amount you pay to maintain your car.
E) amount of money you save each day by avoiding the toll roads.
A) amount of pollution emitted by your car.
B) congestion created by your car being on the road.
C) amount the government paid to build the road.
D) amount you pay to maintain your car.
E) amount of money you save each day by avoiding the toll roads.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
External costs are the result of the actions of:
A) firms.
B) consumers.
C) firms and consumers.
D) the government.
E) firms, consumers, and the government.
A) firms.
B) consumers.
C) firms and consumers.
D) the government.
E) firms, consumers, and the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
It is best to reduce the level of pollution:
A) until all negative externalities are internalized.
B) to zero.
C) as long as the benefit exceeds the cost of doing so.
D) only in non-essential industries.
E) until all external costs have been eliminated.
A) until all negative externalities are internalized.
B) to zero.
C) as long as the benefit exceeds the cost of doing so.
D) only in non-essential industries.
E) until all external costs have been eliminated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A government decision to impose a tax on the sale of plastic disposable water bottles is an example of:
A) a positive externality.
B) internalizing the externality.
C) the third-party problem.
D) an external cost.
E) industry discrimination.
A) a positive externality.
B) internalizing the externality.
C) the third-party problem.
D) an external cost.
E) industry discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is true of a negative externality?
A) Some costs are borne by a third party.
B) The government can use subsidies to encourage firms to internalize the externality.
C) The government must take over the production of this good so that the externality can be internalized.
D) Some benefits accrue to a third party.
E) Its existence always requires corrective measures by the government.
A) Some costs are borne by a third party.
B) The government can use subsidies to encourage firms to internalize the externality.
C) The government must take over the production of this good so that the externality can be internalized.
D) Some benefits accrue to a third party.
E) Its existence always requires corrective measures by the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Your neighbor is an avid gardener who changes his flower displays four times per year and who was given the "best yard on the block" award last year.While you personally enjoy these changing flower displays,some of your neighbors have said they do not like some of the flowers your neighbor chooses to plant.For you,this is an example of:
A) a positive externality.
B) the tragedy of the commons.
C) an internal cost.
D) internalizing the external cost.
E) a negative externality.
A) a positive externality.
B) the tragedy of the commons.
C) an internal cost.
D) internalizing the external cost.
E) a negative externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Refer to the accompanying table,where Q represents the quantity produced,internal cost and social cost are given for various quantities,and P represents the price consumers are willing to pay for various quantities.
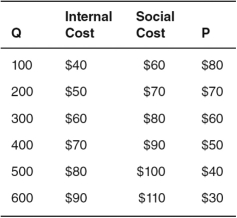
The external cost is equal to ________ per unit.
A) $60
B) $70
C) $20
D) $50
E) $30

The external cost is equal to ________ per unit.
A) $60
B) $70
C) $20
D) $50
E) $30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
You share a house with two other people.You are a concert pianist and often practice at home.One roommate enjoys listening to you practice,but the other does not.For the roommate who enjoys listening to you play,this is an example of ________; for the other roommate,it is an example of ________.
A) the tragedy of the commons; the third-party problem
B) a positive externality; a negative externality
C) a positive externality; the free-rider problem
D) the free-rider problem; the tragedy of the commons
E) a negative externality; the tragedy of the commons
A) the tragedy of the commons; the third-party problem
B) a positive externality; a negative externality
C) a positive externality; the free-rider problem
D) the free-rider problem; the tragedy of the commons
E) a negative externality; the tragedy of the commons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
External benefits arise from the actions of:
A) firms.
B) consumers.
C) firms and consumers.
D) the government.
E) firms, consumers, and the government.
A) firms.
B) consumers.
C) firms and consumers.
D) the government.
E) firms, consumers, and the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
For a market to work efficiently:
A) the external costs must be paid.
B) all external costs must be eliminated.
C) all internal costs must be eliminated.
D) the social costs must be equal to the internal costs.
E) all pollution must be eliminated.
A) the external costs must be paid.
B) all external costs must be eliminated.
C) all internal costs must be eliminated.
D) the social costs must be equal to the internal costs.
E) all pollution must be eliminated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Externalities exist because:
A) owners of private property have an incentive to maintain their property.
B) owners of private property have little incentive to protect their property.
C) owners of private property are not able to trade with others.
D) property rights are not clearly defined.
E) there is too much private ownership of property.
A) owners of private property have an incentive to maintain their property.
B) owners of private property have little incentive to protect their property.
C) owners of private property are not able to trade with others.
D) property rights are not clearly defined.
E) there is too much private ownership of property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the questions that follow.

To achieve the social optimum,the government could set a tax equal to ________ per unit sold.
A) $6
B) $4
C) $2
D) $3
E) $5

To achieve the social optimum,the government could set a tax equal to ________ per unit sold.
A) $6
B) $4
C) $2
D) $3
E) $5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A positive externality exists whenever:
A) there are no internal costs.
B) production of a good creates an external cost.
C) production of a good creates an external benefit.
D) production of a good has no social cost.
E) production of a good has no social benefit.
A) there are no internal costs.
B) production of a good creates an external cost.
C) production of a good creates an external benefit.
D) production of a good has no social cost.
E) production of a good has no social benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Refer to the accompanying figure to answer the questions that follow.

At the market equilibrium,price is equal to ________ units of the good are produced.
A) $18, and 70
B) $14, and 70
C) $12, and 50
D) $14, and 50
E) $18, and 50

At the market equilibrium,price is equal to ________ units of the good are produced.
A) $18, and 70
B) $14, and 70
C) $12, and 50
D) $14, and 50
E) $18, and 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
When production of a good creates an external benefit:
A) there is a negative externality.
B) too much of the good is being produced.
C) there is a positive externality.
D) it results in the tragedy of the commons.
E) a governmental good is being produced.
A) there is a negative externality.
B) too much of the good is being produced.
C) there is a positive externality.
D) it results in the tragedy of the commons.
E) a governmental good is being produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Your roommate is studying to be a drummer in a rock band.She practices in your apartment every evening for three hours and the noise makes it difficult for you to concentrate.This is an example of:
A) a negative externality.
B) the tragedy of the commons.
C) an internal cost.
D) the free-rider problem.
E) a positive externality.
A) a negative externality.
B) the tragedy of the commons.
C) an internal cost.
D) the free-rider problem.
E) a positive externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



