Deck 14: Savings, Investment, and the Market for Loanable Funds
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/136
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Savings, Investment, and the Market for Loanable Funds
1
Savings represents:
A) the demand for loanable funds.
B) the supply of loanable funds.
C) the minimum interest rate people are willing to accept (i.e., the "reservation" interest rate).
D) only funds supplied by foreigners, because Americans do not save.
E) the willingness of firms to borrow.
A) the demand for loanable funds.
B) the supply of loanable funds.
C) the minimum interest rate people are willing to accept (i.e., the "reservation" interest rate).
D) only funds supplied by foreigners, because Americans do not save.
E) the willingness of firms to borrow.
the supply of loanable funds.
2
Refer to the following graph to answer the questions that follow.
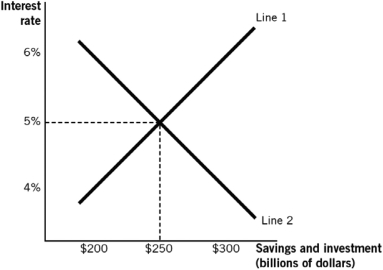
In the figure,line 2 represents the ________ loanable funds,and at an interest rate of 6%,a ________ of loanable funds exists.
A) supply of; shortage
B) quantity demanded of; surplus
C) demand for; shortage
D) quantity supplied of; surplus
E) demand of; surplus

In the figure,line 2 represents the ________ loanable funds,and at an interest rate of 6%,a ________ of loanable funds exists.
A) supply of; shortage
B) quantity demanded of; surplus
C) demand for; shortage
D) quantity supplied of; surplus
E) demand of; surplus
demand of; surplus
3
The correct production timeline is:
A) investment occurs, dollars are borrowed, and output is produced.
B) dollars are borrowed, investment occurs, and output is produced.
C) output is produced, dollars are borrowed, and investment occurs.
D) savings occurs, output is produced, and dollars are borrowed.
E) borrowing occurs, output is produced, and investment occurs.
A) investment occurs, dollars are borrowed, and output is produced.
B) dollars are borrowed, investment occurs, and output is produced.
C) output is produced, dollars are borrowed, and investment occurs.
D) savings occurs, output is produced, and dollars are borrowed.
E) borrowing occurs, output is produced, and investment occurs.
dollars are borrowed, investment occurs, and output is produced.
4
Typically,savers in the loanable funds market are the ________,and borrowers are ________.
A) government and households; foreign entities and firms
B) government and foreign entities; households and firms
C) foreign firms and households; foreign banks and domestic firms
D) households and foreign entities; firms and the (U.S.) government
E) large firms and households; small firms and micro-capital organizations
A) government and households; foreign entities and firms
B) government and foreign entities; households and firms
C) foreign firms and households; foreign banks and domestic firms
D) households and foreign entities; firms and the (U.S.) government
E) large firms and households; small firms and micro-capital organizations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Refer to the following graph to answer the questions that follow.

In the figure,at an interest rate of 5%,the:
A) quantity demanded of loanable funds equals the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and equilibrium is reached.
B) quantity demanded of loanable funds is greater than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a surplus of loanable funds.
C) demand for loanable funds is greater than the supply of loanable funds, and there is a shortage of loanable funds.
D) quantity demanded of loanable funds is greater than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a shortage of loanable funds.
E) quantity demanded of loanable funds is less than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a surplus of loanable funds.

In the figure,at an interest rate of 5%,the:
A) quantity demanded of loanable funds equals the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and equilibrium is reached.
B) quantity demanded of loanable funds is greater than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a surplus of loanable funds.
C) demand for loanable funds is greater than the supply of loanable funds, and there is a shortage of loanable funds.
D) quantity demanded of loanable funds is greater than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a shortage of loanable funds.
E) quantity demanded of loanable funds is less than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a surplus of loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Refer to the following graph to answer the questions that follow.

In the figure,line 1 represents ________,line 2 represents the ________ loanable funds,and 5% represents ________ of loanable funds.
A) savings; supply of; a surplus
B) savings; demand for; the equilibrium interest rate (price)
C) investment; supply of; a shortage
D) investment; demand for; the equilibrium interest rate (price)
E) foreign savings; supply of; a surplus

In the figure,line 1 represents ________,line 2 represents the ________ loanable funds,and 5% represents ________ of loanable funds.
A) savings; supply of; a surplus
B) savings; demand for; the equilibrium interest rate (price)
C) investment; supply of; a shortage
D) investment; demand for; the equilibrium interest rate (price)
E) foreign savings; supply of; a surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Savings is the ________ loanable funds and is ________.
A) demand for; downward-sloping
B) supply of; horizontal
C) supply of; vertical
D) supply of; upward-sloping
E) demand for; upward-sloping
A) demand for; downward-sloping
B) supply of; horizontal
C) supply of; vertical
D) supply of; upward-sloping
E) demand for; upward-sloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The supply of loanable funds comes from:
A) households and is downward-sloping.
B) firms and is upward-sloping.
C) households and is upward-sloping.
D) the government and is upward-sloping.
E) either foreign entities or firms and is upward-sloping.
A) households and is downward-sloping.
B) firms and is upward-sloping.
C) households and is upward-sloping.
D) the government and is upward-sloping.
E) either foreign entities or firms and is upward-sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Refer to the following graph to answer the questions that follow.

In the figure,at an interest rate of 4%,the:
A) quantity demanded of loanable funds equals the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and equilibrium is reached.
B) quantity demanded of loanable funds is greater than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a surplus of loanable funds.
C) demand for loanable funds is greater than the supply of loanable funds, and there is a shortage of loanable funds.
D) quantity demanded of loanable funds is greater than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a shortage of loanable funds.
E) quantity demanded of loanable funds is less than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a shortage of loanable funds.

In the figure,at an interest rate of 4%,the:
A) quantity demanded of loanable funds equals the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and equilibrium is reached.
B) quantity demanded of loanable funds is greater than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a surplus of loanable funds.
C) demand for loanable funds is greater than the supply of loanable funds, and there is a shortage of loanable funds.
D) quantity demanded of loanable funds is greater than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a shortage of loanable funds.
E) quantity demanded of loanable funds is less than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a shortage of loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Every dollar borrowed:
A) represents a dollar leaving the circular flow.
B) requires a dollar to be saved.
C) represents a piece of capital.
D) requires the supply of loanable funds to increase.
E) causes inflation.
A) represents a dollar leaving the circular flow.
B) requires a dollar to be saved.
C) represents a piece of capital.
D) requires the supply of loanable funds to increase.
E) causes inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The demand for loanable funds is:
A) savings, because households borrow more than firms.
B) horizontal, because firms are infinitely sensitive to interest rates.
C) vertical, because it is non-responsive to interest rates.
D) upward-sloping, because at higher interest rates the opportunity cost of holding money increases.
E) investment, because firms are (on the aggregate) net borrowers.
A) savings, because households borrow more than firms.
B) horizontal, because firms are infinitely sensitive to interest rates.
C) vertical, because it is non-responsive to interest rates.
D) upward-sloping, because at higher interest rates the opportunity cost of holding money increases.
E) investment, because firms are (on the aggregate) net borrowers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The government:
A) sets most interest rates.
B) is a net lender (or supplier of loanable funds).
C) is a net borrower (or demander of loanable funds).
D) determines the "federal risk premium" portion of commercial interest rates.
E) earns more interest on treasury bills and other securities when interest rates rise.
A) sets most interest rates.
B) is a net lender (or supplier of loanable funds).
C) is a net borrower (or demander of loanable funds).
D) determines the "federal risk premium" portion of commercial interest rates.
E) earns more interest on treasury bills and other securities when interest rates rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The timeline of production would indicate:
A) supply creates its own investment.
B) first production occurs, then profit represents a residual, and this residual is saved.
C) firms first invest (which is borrowing), then they produce, and then the revenue they receive is used to pay resource suppliers and lenders.
D) firms first save (which is lending), then they produce, and then the revenue they receive is used to lend even more.
E) real interest rates rise faster than nominal interest rates because production occurs before income is received by the firm.
A) supply creates its own investment.
B) first production occurs, then profit represents a residual, and this residual is saved.
C) firms first invest (which is borrowing), then they produce, and then the revenue they receive is used to pay resource suppliers and lenders.
D) firms first save (which is lending), then they produce, and then the revenue they receive is used to lend even more.
E) real interest rates rise faster than nominal interest rates because production occurs before income is received by the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The notion of the loanable funds market is the method by which:
A) consumers get payday loans and auto-title loans.
B) savers (typically households and individuals) supply funds to borrowers (typically firms).
C) savers (typically firms) supply funds to borrowers (typically the government).
D) borrowers are exploited by loan sharks.
E) the government lends money to big corporations.
A) consumers get payday loans and auto-title loans.
B) savers (typically households and individuals) supply funds to borrowers (typically firms).
C) savers (typically firms) supply funds to borrowers (typically the government).
D) borrowers are exploited by loan sharks.
E) the government lends money to big corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Borrowers in the loanable funds market consist of:
A) governments and firms.
B) banks, foreign governments, and bonds.
C) mutual fund firms, stock exchanges, and banks.
D) households and foreign entities.
E) arbitrage companies, banks, and firms.
A) governments and firms.
B) banks, foreign governments, and bonds.
C) mutual fund firms, stock exchanges, and banks.
D) households and foreign entities.
E) arbitrage companies, banks, and firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The concept of the loanable funds market is:
A) similar to that of the grocery store-goods are sold and money is borrowed to pay for them.
B) the market by which lenders (savers) and borrowers exchange funds for earlier availability at a premium, which is represented by the interest rate.
C) similar to the notion of consumer and producer surplus, where the interest rate represents either consumer or producer surplus depending on who is doing the borrowing.
D) the market by which borrowers (suppliers) and lenders (demanders) exchange funds for earlier availability at a premium, which is represented by the interest rate.
E) that the interest rate is determined by multiplying the risk premium by the coefficient of pure interest.
A) similar to that of the grocery store-goods are sold and money is borrowed to pay for them.
B) the market by which lenders (savers) and borrowers exchange funds for earlier availability at a premium, which is represented by the interest rate.
C) similar to the notion of consumer and producer surplus, where the interest rate represents either consumer or producer surplus depending on who is doing the borrowing.
D) the market by which borrowers (suppliers) and lenders (demanders) exchange funds for earlier availability at a premium, which is represented by the interest rate.
E) that the interest rate is determined by multiplying the risk premium by the coefficient of pure interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The interest rate is:
A) the price of labor.
B) the price of land.
C) both the price of capital and the price of labor.
D) the price of loanable funds.
E) the marginal rate of investment supply.
A) the price of labor.
B) the price of land.
C) both the price of capital and the price of labor.
D) the price of loanable funds.
E) the marginal rate of investment supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Gross domestic product requires:
A) inflation equal to the nominal rate of interest, which means lending equals borrowing.
B) investment, which requires borrowing, which requires a functioning loanable funds market.
C) borrowing, which requires the real rate of interest to be equal to inflation, which requires a functioning loanable funds market.
D) borrowing, which requires sufficiently high interest rates to prevent free-riders.
E) investment, which requires borrowing, which requires sufficiently low interest rates to prevent free-riders.
A) inflation equal to the nominal rate of interest, which means lending equals borrowing.
B) investment, which requires borrowing, which requires a functioning loanable funds market.
C) borrowing, which requires the real rate of interest to be equal to inflation, which requires a functioning loanable funds market.
D) borrowing, which requires sufficiently high interest rates to prevent free-riders.
E) investment, which requires borrowing, which requires sufficiently low interest rates to prevent free-riders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Lenders in the loanable funds market consist of:
A) foreign governments, the domestic government, and households.
B) households and foreign entities.
C) mutual fund firms, stock exchanges, and banks.
D) firms and governments.
E) arbitrage companies, banks, and firms.
A) foreign governments, the domestic government, and households.
B) households and foreign entities.
C) mutual fund firms, stock exchanges, and banks.
D) firms and governments.
E) arbitrage companies, banks, and firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Refer to the following graph to answer the questions that follow.

In the figure,at an interest rate of 6%,the:
A) quantity demanded of loanable funds equals the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and equilibrium is reached.
B) quantity demanded of loanable funds is greater than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a surplus of loanable funds.
C) demand for loanable funds is greater than the supply of loanable funds, and there is a shortage of loanable funds.
D) quantity demanded of loanable funds is greater than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a shortage of loanable funds.
E) quantity demanded of loanable funds is less than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a surplus of loanable funds.

In the figure,at an interest rate of 6%,the:
A) quantity demanded of loanable funds equals the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and equilibrium is reached.
B) quantity demanded of loanable funds is greater than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a surplus of loanable funds.
C) demand for loanable funds is greater than the supply of loanable funds, and there is a shortage of loanable funds.
D) quantity demanded of loanable funds is greater than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a shortage of loanable funds.
E) quantity demanded of loanable funds is less than the quantity supplied of loanable funds, and there is a surplus of loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The government engages in more deficit spending.Ceteris paribus (all else equal),this would cause:
A) the demand for loanable funds to increase.
B) the supply of loanable funds to increase.
C) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to increase.
D) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to decrease.
E) economic institutions to collapse.
A) the demand for loanable funds to increase.
B) the supply of loanable funds to increase.
C) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to increase.
D) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to decrease.
E) economic institutions to collapse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If interest rates fell between 1981 and 2012,then:
A) demand for loanable funds shifted right.
B) quantity demanded of loanable funds increased.
C) quantity demanded of loanable funds decreased.
D) quantity supplied of loanable funds increased.
E) supply of loanable funds shifted left.
A) demand for loanable funds shifted right.
B) quantity demanded of loanable funds increased.
C) quantity demanded of loanable funds decreased.
D) quantity supplied of loanable funds increased.
E) supply of loanable funds shifted left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Refer to the following graph to answer the questions that follow.
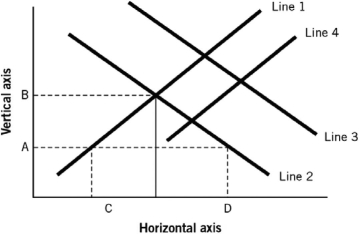
Assuming the figure represents the market for loanable funds,which of the following would represent a decrease in time preferences (i.e.,people are more patient)?
A) a shift from line 1 to line 4
B) a shift from line 4 to line 1
C) a shift from line 2 to line 3
D) movement from A to B
E) a new shortage of loanable funds represented by the distance from C to D

Assuming the figure represents the market for loanable funds,which of the following would represent a decrease in time preferences (i.e.,people are more patient)?
A) a shift from line 1 to line 4
B) a shift from line 4 to line 1
C) a shift from line 2 to line 3
D) movement from A to B
E) a new shortage of loanable funds represented by the distance from C to D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An interest rate best represents ________ to borrowers and ________ to savers.
A) cost; return
B) return; cost
C) rate of change; static value
D) static value; rate of change
E) nominal return; real return
A) cost; return
B) return; cost
C) rate of change; static value
D) static value; rate of change
E) nominal return; real return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Refer to the following graph to answer the questions that follow.

Assuming the figure represents the market for loanable funds,which of the following would represent a general economic collapse in the United States,causing foreigners to become fearful about the U.S.economy?
A) a shift from line 1 to line 4
B) a shift from line 3 to line 2
C) a shift from line 2 to line 3
D) a shift from line 4 to line 1
E) a new shortage of loanable funds represented by the distance from C to D

Assuming the figure represents the market for loanable funds,which of the following would represent a general economic collapse in the United States,causing foreigners to become fearful about the U.S.economy?
A) a shift from line 1 to line 4
B) a shift from line 3 to line 2
C) a shift from line 2 to line 3
D) a shift from line 4 to line 1
E) a new shortage of loanable funds represented by the distance from C to D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the following graph to answer the questions that follow.

Assuming the figure represents the market for loanable funds,which of the following would represent an increase in household income?
A) a shift from line 1 to line 4
B) a shift from line 4 to line 1
C) a shift from line 2 to line 3
D) movement from A to B
E) a new shortage of loanable funds represented by the distance from C to D

Assuming the figure represents the market for loanable funds,which of the following would represent an increase in household income?
A) a shift from line 1 to line 4
B) a shift from line 4 to line 1
C) a shift from line 2 to line 3
D) movement from A to B
E) a new shortage of loanable funds represented by the distance from C to D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Smiley Myrus owns a large corporation that is building a new shopping mall in Winston-Salem,North Carolina.In all likelihood,Smiley's firm:
A) is a supplier of loanable funds.
B) pays a higher rate of interest than most borrowers, based on the Fisher equation.
C) is a borrower of loanable funds.
D) pays a lower rate of interest than most borrowers, based on the Fisher equation.
E) would loan its profits to foreign entities.
A) is a supplier of loanable funds.
B) pays a higher rate of interest than most borrowers, based on the Fisher equation.
C) is a borrower of loanable funds.
D) pays a lower rate of interest than most borrowers, based on the Fisher equation.
E) would loan its profits to foreign entities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
By 2014:
A) most interest rates were about 5%.
B) many interest rates were below 1%.
C) almost every interest rate was above 10%.
D) federal law required that the interest rate ceiling on all loans be capped at 11.5%.
E) the real interest rate was positive, but the nominal interest rate was less than the real rate.
A) most interest rates were about 5%.
B) many interest rates were below 1%.
C) almost every interest rate was above 10%.
D) federal law required that the interest rate ceiling on all loans be capped at 11.5%.
E) the real interest rate was positive, but the nominal interest rate was less than the real rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the federal government taxes the interest rate that savers receive:
A) the rate of return to savers increases because of transfer payments and people save more.
B) the demand for loanable funds increases.
C) the supply of loanable funds increases.
D) the supply of loanable funds decreases.
E) corporations are more willing to borrow.
A) the rate of return to savers increases because of transfer payments and people save more.
B) the demand for loanable funds increases.
C) the supply of loanable funds increases.
D) the supply of loanable funds decreases.
E) corporations are more willing to borrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
You are an entrepreneur about to start your first business.Based on this statement,you:
A) are most likely to be a borrower concerned mostly about the real interest rate you will earn.
B) are most likely to be a lender concerned mostly about the real interest rate you will earn.
C) are most likely to be a borrower concerned mostly about the nominal interest rate you will earn.
D) are most likely to be a lender concerned mostly about the nominal interest rate you will earn.
E) would only be concerned with whether inflation was greater or less than the nominal rate of interest based on the Fisher equation.
A) are most likely to be a borrower concerned mostly about the real interest rate you will earn.
B) are most likely to be a lender concerned mostly about the real interest rate you will earn.
C) are most likely to be a borrower concerned mostly about the nominal interest rate you will earn.
D) are most likely to be a lender concerned mostly about the nominal interest rate you will earn.
E) would only be concerned with whether inflation was greater or less than the nominal rate of interest based on the Fisher equation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If interest rates rise:
A) foreign entities that are borrowers of funds will borrow less.
B) governments that are savers of funds will save less.
C) households that are savers of funds will save more.
D) businesses that are savers of funds will borrow less.
E) it will reduce consumption smoothing.
A) foreign entities that are borrowers of funds will borrow less.
B) governments that are savers of funds will save less.
C) households that are savers of funds will save more.
D) businesses that are savers of funds will borrow less.
E) it will reduce consumption smoothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The interest rate is:
A) the price of money.
B) only a cost to savers.
C) a return to borrowers.
D) both a cost to savers and a return to borrowers.
E) both a return to savers and a cost to borrowers.
A) the price of money.
B) only a cost to savers.
C) a return to borrowers.
D) both a cost to savers and a return to borrowers.
E) both a return to savers and a cost to borrowers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The interest rate represents ________ to ________ and ________ to ________.
A) profit; foreign entities; the cost of funds; savers
B) the cost of funds; corporations; a return; governments
C) profit; governments; the marginal rate of arbitrage; foreign entities
D) the cost of borrowing; firms and governments; a return to saving; households
E) profit; arbitrage companies; loss; firms
A) profit; foreign entities; the cost of funds; savers
B) the cost of funds; corporations; a return; governments
C) profit; governments; the marginal rate of arbitrage; foreign entities
D) the cost of borrowing; firms and governments; a return to saving; households
E) profit; arbitrage companies; loss; firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Two nations are located next to one another.In Nation A,people are very thrifty and spend much less than their incomes; moreover,Nation A's government runs a balanced budget every year.In Nation B,people spend all of their incomes,but their government runs consistent deficits.Thus:
A) Nation A's extra savings would increase the supply of loanable funds to Nation B.
B) Nation B's government deficit would be a supply of loanable funds to Nation B.
C) Nation A's extra savings would increase the demand for loanable funds in Nation B.
D) Nation B would instantly default on all of its debt obligations.
E) Nation A's extra savings would decrease the supply of loanable funds to Nation B.
A) Nation A's extra savings would increase the supply of loanable funds to Nation B.
B) Nation B's government deficit would be a supply of loanable funds to Nation B.
C) Nation A's extra savings would increase the demand for loanable funds in Nation B.
D) Nation B would instantly default on all of its debt obligations.
E) Nation A's extra savings would decrease the supply of loanable funds to Nation B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Since firms are the primary:
A) demanders of loanable funds, they must borrow from households.
B) suppliers of loanable funds, they must lend to households.
C) suppliers of loanable funds, they must lend to the government.
D) agents of usury, they must be "reined in" by the people.
E) demanders of loanable funds, they must borrow from the government.
A) demanders of loanable funds, they must borrow from households.
B) suppliers of loanable funds, they must lend to households.
C) suppliers of loanable funds, they must lend to the government.
D) agents of usury, they must be "reined in" by the people.
E) demanders of loanable funds, they must borrow from the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Refer to the following graph to answer the questions that follow.

Assuming the figure represents the market for loanable funds,which of the following would represent the government running a larger budget deficit?
A) a shift from line 1 to line 4
B) a shift from line 4 to line 1
C) a shift from line 2 to line 3
D) a shift from line 3 to line 2
E) a new shortage of loanable funds represented by the distance from C to D

Assuming the figure represents the market for loanable funds,which of the following would represent the government running a larger budget deficit?
A) a shift from line 1 to line 4
B) a shift from line 4 to line 1
C) a shift from line 2 to line 3
D) a shift from line 3 to line 2
E) a new shortage of loanable funds represented by the distance from C to D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Foreign entities:
A) are generally borrowers of domestic (U.S.) loanable funds.
B) are generally lenders in the domestic (U.S.) loanable funds.
C) typically require a greater inflation premium than domestic borrowers.
D) typically require a smaller inflation premium than domestic borrowers.
E) are not concerned about the U.S.interest rate compared to their own, since it is illegal for them to lend in the United States.
A) are generally borrowers of domestic (U.S.) loanable funds.
B) are generally lenders in the domestic (U.S.) loanable funds.
C) typically require a greater inflation premium than domestic borrowers.
D) typically require a smaller inflation premium than domestic borrowers.
E) are not concerned about the U.S.interest rate compared to their own, since it is illegal for them to lend in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Refer to the following graph to answer the questions that follow.

Assuming the figure represents the market for loanable funds,which of the following would represent a cut in corporate tax rates,causing business owners and managers to become more optimistic?
A) a shift from line 1 to line 4
B) movement from B to A
C) a shift from line 2 to line 3
D) movement from A to B
E) a shift from line 3 to line 2

Assuming the figure represents the market for loanable funds,which of the following would represent a cut in corporate tax rates,causing business owners and managers to become more optimistic?
A) a shift from line 1 to line 4
B) movement from B to A
C) a shift from line 2 to line 3
D) movement from A to B
E) a shift from line 3 to line 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If you deposit money in the bank,in essence,you are:
A) a supplier of funds, since the bank simply is an intermediary between those who want to borrow loanable funds and those who are willing to lend them (depositors).
B) a borrower, since all bank funds are borrowed from the federal government.
C) a supplier of funds, since the bank loans money to the government for daily operations.
D) neither a borrower nor supplier of funds in this case, since you have neither loaned nor borrowed money.
E) not a supplier of funds, since mutual funds are the source of lending to firms.
A) a supplier of funds, since the bank simply is an intermediary between those who want to borrow loanable funds and those who are willing to lend them (depositors).
B) a borrower, since all bank funds are borrowed from the federal government.
C) a supplier of funds, since the bank loans money to the government for daily operations.
D) neither a borrower nor supplier of funds in this case, since you have neither loaned nor borrowed money.
E) not a supplier of funds, since mutual funds are the source of lending to firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
By 1981:
A) interest rates were about 5%.
B) interest rates were about 7%.
C) interest rates were about 15%.
D) the real interest rate was negative.
E) the real interest rate was positive, but the nominal interest rate was less than the real rate.
A) interest rates were about 5%.
B) interest rates were about 7%.
C) interest rates were about 15%.
D) the real interest rate was negative.
E) the real interest rate was positive, but the nominal interest rate was less than the real rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The real interest rate:
A) equals the nominal rate minus the prime rate.
B) increases as inflation increases, ceteris paribus (all else equal).
C) is what you really pay if you borrow versus what you think you are paying.
D) equals the nominal rate plus the rate of inflation.
E) equals the nominal rate minus the rate of inflation.
A) equals the nominal rate minus the prime rate.
B) increases as inflation increases, ceteris paribus (all else equal).
C) is what you really pay if you borrow versus what you think you are paying.
D) equals the nominal rate plus the rate of inflation.
E) equals the nominal rate minus the rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Assume deflation is occurring in a nation; the implication(s)is/are that:
A) both real and nominal interest rates are positive.
B) both real and nominal interest rates are negative.
C) the nominal interest rate exceeds the real interest rate.
D) the real rate of interest exceeds the nominal rate of interest.
E) time preferences in the nation have fallen.
A) both real and nominal interest rates are positive.
B) both real and nominal interest rates are negative.
C) the nominal interest rate exceeds the real interest rate.
D) the real rate of interest exceeds the nominal rate of interest.
E) time preferences in the nation have fallen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Assume inflation is occurring in a nation; the implication(s)is/are that:
A) both real and nominal interest rates are positive.
B) both real and nominal interest rates are negative.
C) the nominal interest rate exceeds the real interest rate.
D) the real rate of interest exceeds the nominal rate of interest.
E) time preferences in the nation have risen.
A) both real and nominal interest rates are positive.
B) both real and nominal interest rates are negative.
C) the nominal interest rate exceeds the real interest rate.
D) the real rate of interest exceeds the nominal rate of interest.
E) time preferences in the nation have risen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The Fisher equation relates:
A) time preferences to the level of borrowing.
B) nominal interest rates to the level of borrowing.
C) real interest rates to the level of borrowing.
D) real interest rates, nominal interest rates, and inflation.
E) real interest rates, nominal interest rates, and the level of saving.
A) time preferences to the level of borrowing.
B) nominal interest rates to the level of borrowing.
C) real interest rates to the level of borrowing.
D) real interest rates, nominal interest rates, and inflation.
E) real interest rates, nominal interest rates, and the level of saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The gap between the real and nominal interest rate represents:
A) inflation.
B) the time preference.
C) the difference from what the lender receives and the borrower pays.
D) consumption smoothing.
E) a surplus of loanable funds.
A) inflation.
B) the time preference.
C) the difference from what the lender receives and the borrower pays.
D) consumption smoothing.
E) a surplus of loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
You borrow $10,000 today at a nominal rate of 5%; inflation for the past 10 years has been exactly 2%.Today,inflation instantly rises to 7% and stays that way for the duration of your loan.Based on the above information,ceteris paribus (all else equal),today:
A) the real rate of interest on your loan is 14%.
B) the real rate of interest on your loan was previously 10% and is now 35%.
C) the real rate of interest on your loan is now -2%.
D) you will pay the lender back exactly $9,500.
E) you will pay the lender back exactly $10,700.
A) the real rate of interest on your loan is 14%.
B) the real rate of interest on your loan was previously 10% and is now 35%.
C) the real rate of interest on your loan is now -2%.
D) you will pay the lender back exactly $9,500.
E) you will pay the lender back exactly $10,700.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When making decisions about saving and borrowing,people care most about:
A) inflation.
B) the real rate of interest.
C) the nominal rate of interest.
D) the rate of saving minus the rate of borrowing.
E) the risk premium portion of the rate of interest.
A) inflation.
B) the real rate of interest.
C) the nominal rate of interest.
D) the rate of saving minus the rate of borrowing.
E) the risk premium portion of the rate of interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If interest rates rise,holding all else constant,this would cause a(n):
A) increase in both the demand and supply of loanable funds.
B) decrease in both the demand and supply of loanable funds.
C) increase in the supply of loanable funds but a decrease in the demand for loanable funds.
D) increase in the quantity supplied of loanable funds but a decrease in the quantity demanded of loanable funds.
E) increase in the demand for loanable funds but a decrease in the supply of loanable funds.
A) increase in both the demand and supply of loanable funds.
B) decrease in both the demand and supply of loanable funds.
C) increase in the supply of loanable funds but a decrease in the demand for loanable funds.
D) increase in the quantity supplied of loanable funds but a decrease in the quantity demanded of loanable funds.
E) increase in the demand for loanable funds but a decrease in the supply of loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If a depositor puts money in the bank,the interest rate that the bank will pay the depositor:
A) is the real rate of interest.
B) is the nominal rate of interest.
C) is the inflation-adjusted rate of interest.
D) must by law equal the rate of inflation times the bank's risk premium.
E) must by law equal the rate of inflation plus the bank's risk premium.
A) is the real rate of interest.
B) is the nominal rate of interest.
C) is the inflation-adjusted rate of interest.
D) must by law equal the rate of inflation times the bank's risk premium.
E) must by law equal the rate of inflation plus the bank's risk premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Assuming inflation is positive,the real interest rate:
A) must always be larger than the nominal interest rate.
B) must always be smaller than the nominal interest rate.
C) could be larger or smaller than the nominal interest rate, depending on the rate of inflation.
D) would normally be larger than the nominal interest rate.
E) increases exactly as fast as inflation.
A) must always be larger than the nominal interest rate.
B) must always be smaller than the nominal interest rate.
C) could be larger or smaller than the nominal interest rate, depending on the rate of inflation.
D) would normally be larger than the nominal interest rate.
E) increases exactly as fast as inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Inflation reached its peak (of at least 14%)in the late 1970s and early 1980s.If this statement is true,then:
A) it is certain the real rate of interest was greater than the nominal rate.
B) it is certain the nominal rate of interest was greater than the real rate.
C) borrowers would have borrowed more because, automatically, real rates would have fallen.
D) the real rate of interest must have been constant, even if the nominal rate varied because of consumption smoothing.
E) if higher nominal rates were charged, it would be certain that higher real rates would have been received.
A) it is certain the real rate of interest was greater than the nominal rate.
B) it is certain the nominal rate of interest was greater than the real rate.
C) borrowers would have borrowed more because, automatically, real rates would have fallen.
D) the real rate of interest must have been constant, even if the nominal rate varied because of consumption smoothing.
E) if higher nominal rates were charged, it would be certain that higher real rates would have been received.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The nominal interest rate is:
A) the rate of interest charged to most large commercial borrowers.
B) equal to the real interest rate minus the inflation rate.
C) the rate charged on loans for automobiles and other personal loans but not the rate charged on home loans.
D) the interest rate that is not corrected for inflation.
E) the interest rate that is corrected for inflation.
A) the rate of interest charged to most large commercial borrowers.
B) equal to the real interest rate minus the inflation rate.
C) the rate charged on loans for automobiles and other personal loans but not the rate charged on home loans.
D) the interest rate that is not corrected for inflation.
E) the interest rate that is corrected for inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
You are thinking about buying a new car and will borrow $20,000 for this purchase at a 5% fixed rate for exactly one year.The lender (correctly)assumes that inflation will be 2% this year.Based on the above information and assuming you adhere to the terms of the loan,you will pay back the lender exactly ________,which will represent ________ of purchasing power.
A) $20,000; $19,000
B) $21,000; $21,000
C) $21,000; $21,400
D) $21,000; $20,600
E) $19,600; $20,000
A) $20,000; $19,000
B) $21,000; $21,000
C) $21,000; $21,400
D) $21,000; $20,600
E) $19,600; $20,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Assume you put money into an asset that pays you 7% interest and inflation is 5%.Which statement is correct?
A) This means the nominal rate of interest is 7% and the real rate is 5%.
B) This means the real rate of interest is 2%.
C) The textbook states that all interest rates would be assumed to be the real rate; thus, the nominal rate is 12%.
D) This means the nominal rate of interest is 35%.
E) If the rate of inflation falls, your real rate of interest from this asset would also fall.
A) This means the nominal rate of interest is 7% and the real rate is 5%.
B) This means the real rate of interest is 2%.
C) The textbook states that all interest rates would be assumed to be the real rate; thus, the nominal rate is 12%.
D) This means the nominal rate of interest is 35%.
E) If the rate of inflation falls, your real rate of interest from this asset would also fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If interest rates rise:
A) firms are willing to borrow more money because their rates of return have increased.
B) households are willing to borrow more money because their rates of return have increased.
C) firms are willing to borrow less money because their cost of borrowing has increased.
D) foreign entities are willing to borrow more money because their rates of return have increased.
E) it must mean that inflation has decreased because nominal rates have increased.
A) firms are willing to borrow more money because their rates of return have increased.
B) households are willing to borrow more money because their rates of return have increased.
C) firms are willing to borrow less money because their cost of borrowing has increased.
D) foreign entities are willing to borrow more money because their rates of return have increased.
E) it must mean that inflation has decreased because nominal rates have increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The interest rate represents:
A) the opportunity cost of saving.
B) the opportunity cost of consumption.
C) the opportunity cost of saving plus the opportunity cost of inflation.
D) only the opportunity cost of taking a different job.
E) the price of savings but not investment.
A) the opportunity cost of saving.
B) the opportunity cost of consumption.
C) the opportunity cost of saving plus the opportunity cost of inflation.
D) only the opportunity cost of taking a different job.
E) the price of savings but not investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Arguably,interest represents:
A) both a cost to lenders and a return to borrowers.
B) both a cost to borrowers and a return to savers.
C) the price of later availability (in terms of accrued interest) and a cost to borrowers.
D) the payment to the land factor of production and a return to savers.
E) the optimal rate of investment in depreciating assets and the price of earlier availability.
A) both a cost to lenders and a return to borrowers.
B) both a cost to borrowers and a return to savers.
C) the price of later availability (in terms of accrued interest) and a cost to borrowers.
D) the payment to the land factor of production and a return to savers.
E) the optimal rate of investment in depreciating assets and the price of earlier availability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The largest inflationary gap appeared:
A) in the 1960s.
B) in the 1950s during the great U.S.hyperinflation.
C) at the end of the 1970s and in the early 1980s.
D) during the Great Recession of 2007-2009.
E) in the 1990s.
A) in the 1960s.
B) in the 1950s during the great U.S.hyperinflation.
C) at the end of the 1970s and in the early 1980s.
D) during the Great Recession of 2007-2009.
E) in the 1990s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
You are thinking about building a new mall.Your economic consultants say the mall will bring a 7% rate of return.Because you know that you can borrow as much money as you need for 5%:
A) you will build the mall if it costs $50 million but not if it costs $100 million.
B) assuming conditions do not change, you will build the mall no matter how much it costs.
C) if the rate of return falls below 5%, you will still build the mall.
D) assuming conditions do not change, you will not build the mall because a 2% net rate of return is just too small to be worth it.
E) if the cost of borrowing rises to 8%, you would still build the mall.
A) you will build the mall if it costs $50 million but not if it costs $100 million.
B) assuming conditions do not change, you will build the mall no matter how much it costs.
C) if the rate of return falls below 5%, you will still build the mall.
D) assuming conditions do not change, you will not build the mall because a 2% net rate of return is just too small to be worth it.
E) if the cost of borrowing rises to 8%, you would still build the mall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The real interest rate in 2012 was:
A) about 9%.
B) about 7%.
C) about 5%.
D) about 3%.
E) a negative number.
A) about 9%.
B) about 7%.
C) about 5%.
D) about 3%.
E) a negative number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Assume foreign incomes rise.Ceteris paribus (all things equal),this would cause:
A) the demand for loanable funds to increase.
B) the supply of loanable funds to increase.
C) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to increase.
D) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to decrease.
E) the demand of loanable funds to decrease.
A) the demand for loanable funds to increase.
B) the supply of loanable funds to increase.
C) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to increase.
D) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to decrease.
E) the demand of loanable funds to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
T.D.Goneworth,a financial services firm,makes people want their money and want it now.If the firm is successful in advertising this message and convinces people to believe it; then,all else equal,T.D.Goneworth has:
A) caused people to increase their consumption smoothing.
B) caused people to reduce their time preferences.
C) equalized the real and nominal rates of interest.
D) increased the rate of inflation.
E) caused people to increase their time preferences.
A) caused people to increase their consumption smoothing.
B) caused people to reduce their time preferences.
C) equalized the real and nominal rates of interest.
D) increased the rate of inflation.
E) caused people to increase their time preferences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
As income and wealth rise,we would expect:
A) savings to increase as people save some of the extra wealth or income they have.
B) savings to fall, since people would spend the extra income or wealth.
C) interest rates to rise.
D) foreigners with more wealth to move their assets out of the United States to foreign markets.
E) people to have a negative rate of time preference.
A) savings to increase as people save some of the extra wealth or income they have.
B) savings to fall, since people would spend the extra income or wealth.
C) interest rates to rise.
D) foreigners with more wealth to move their assets out of the United States to foreign markets.
E) people to have a negative rate of time preference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Your roommate arrives home and says,"I am so hungry,I would give up my iPhone for a bowl of chili right now." You say,"Here is the chili-let's trade." Based on this information:
A) you have a lower time preference than your roommate because you get the iPhone now.
B) you have a lower time preference than your roommate because he gets the chili now.
C) the one willing to accept a lower nominal interest rate has a higher time preference.
D) your roommate would be a borrower and you a lender.
E) your roommate would engage in consumption smoothing but you would not.
A) you have a lower time preference than your roommate because you get the iPhone now.
B) you have a lower time preference than your roommate because he gets the chili now.
C) the one willing to accept a lower nominal interest rate has a higher time preference.
D) your roommate would be a borrower and you a lender.
E) your roommate would engage in consumption smoothing but you would not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Time preferences mean:
A) people prefer to have more free time rather than less.
B) people prefer to have less free time (work more) rather than more (being unemployed).
C) interest rates are higher for long-term loans than for short-term loans.
D) people prefer goods sooner rather than later.
E) people prefer goods later rather than sooner (save the best for last).
A) people prefer to have more free time rather than less.
B) people prefer to have less free time (work more) rather than more (being unemployed).
C) interest rates are higher for long-term loans than for short-term loans.
D) people prefer goods sooner rather than later.
E) people prefer goods later rather than sooner (save the best for last).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Those with the LEAST patience:
A) have the greatest time preference.
B) have the least time preference.
C) will demand a higher nominal interest rate but not a higher real rate.
D) will save the most.
E) will engage in the most consumption smoothing.
A) have the greatest time preference.
B) have the least time preference.
C) will demand a higher nominal interest rate but not a higher real rate.
D) will save the most.
E) will engage in the most consumption smoothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
You borrow some amount of money for five years at a fixed rate of 4%.For the first three years,inflation is 3%,and for the last two years,deflation is 3%.Based on this information,your:
A) real rate of interest was larger than your nominal rate only for the last two years.
B) real rate of interest was larger than your nominal rate only for the first three years.
C) real rate of interest exceeded your nominal rate for the entire five years.
D) nominal rate of interest exceeded your real rate for the entire five years.
E) nominal rate of interest equaled your real rate for the entire five years.
A) real rate of interest was larger than your nominal rate only for the last two years.
B) real rate of interest was larger than your nominal rate only for the first three years.
C) real rate of interest exceeded your nominal rate for the entire five years.
D) nominal rate of interest exceeded your real rate for the entire five years.
E) nominal rate of interest equaled your real rate for the entire five years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Stewart Shopaholic,a compulsive shopper who likes to spend a lot of money all the time:
A) has a high time preference.
B) has a low time preference.
C) prefers to borrow at the nominal rate, rather than the real rate of interest, if inflation is positive.
D) is likely a supplier of loanable funds.
E) would best be described as an "income smoother" rather than a "consumption smoother."
A) has a high time preference.
B) has a low time preference.
C) prefers to borrow at the nominal rate, rather than the real rate of interest, if inflation is positive.
D) is likely a supplier of loanable funds.
E) would best be described as an "income smoother" rather than a "consumption smoother."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
We could best describe the:
A) nominal rate of interest as the inflation-adjusted rate of interest.
B) real rate of interest as the inflation-adjusted rate of interest.
C) rate of inflation as the nominal interest rate.
D) loanable funds market as the market where only governments make loans.
E) supply of loanable funds as upward-sloping, with the slope equaling the rate of inflation.
A) nominal rate of interest as the inflation-adjusted rate of interest.
B) real rate of interest as the inflation-adjusted rate of interest.
C) rate of inflation as the nominal interest rate.
D) loanable funds market as the market where only governments make loans.
E) supply of loanable funds as upward-sloping, with the slope equaling the rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A young boy is saving money for a baseball bat but is tempted to buy an ice cream cone.If the boy successfully resists buying ice cream and continues to save for the bat,the boy has:
A) exchanged high time preferences for low.
B) exchanged low time preferences for high.
C) engaged in consumption smoothing.
D) increased his consumption variance.
E) increased his wealth.
A) exchanged high time preferences for low.
B) exchanged low time preferences for high.
C) engaged in consumption smoothing.
D) increased his consumption variance.
E) increased his wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Assume an epidemic hits a nation hard.As a result,people now have lower life expectancies.The most likely result would be:
A) a higher supply of loanable funds.
B) a higher demand for loanable funds.
C) a lower supply of loanable funds.
D) higher productivity of capital.
E) a decrease in equilibrium interest rates.
A) a higher supply of loanable funds.
B) a higher demand for loanable funds.
C) a lower supply of loanable funds.
D) higher productivity of capital.
E) a decrease in equilibrium interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
You borrow $10,000 today at a nominal rate of 5%; inflation for the past 10 years has been exactly 2%.Today,inflation instantly rises to 4% and stays that way for the duration of your loan.Based on the above information and all else being equal,today:
A) you are worse off because inflation has risen.
B) you are better off strictly because 5% is still more than 4%.
C) you are better off because you are paying back the loan with dollars that represent less purchasing power today than the dollars you borrowed before.
D) the lender is better off because the real rate of interest automatically increases when inflation increases.
E) both you and the lender are better off because real rates fall when inflation rises.
A) you are worse off because inflation has risen.
B) you are better off strictly because 5% is still more than 4%.
C) you are better off because you are paying back the loan with dollars that represent less purchasing power today than the dollars you borrowed before.
D) the lender is better off because the real rate of interest automatically increases when inflation increases.
E) both you and the lender are better off because real rates fall when inflation rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Wealth increases in the United States because the value of the stock market increases; if all else is equal,this would cause:
A) a larger gap between the real and nominal rates of interest.
B) the demand for loanable funds to increase.
C) the supply of loanable funds to increase.
D) the supply of loanable funds to decrease.
E) corporations to be more willing to borrow.
A) a larger gap between the real and nominal rates of interest.
B) the demand for loanable funds to increase.
C) the supply of loanable funds to increase.
D) the supply of loanable funds to decrease.
E) corporations to be more willing to borrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Assume households become thriftier.This would cause:
A) the demand for loanable funds to increase.
B) the supply of loanable funds to increase.
C) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to increase.
D) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to decrease.
E) the supply of loanable funds to decrease.
A) the demand for loanable funds to increase.
B) the supply of loanable funds to increase.
C) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to increase.
D) both the demand and supply of loanable funds to decrease.
E) the supply of loanable funds to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A non-price determinant of the supply of loanable funds would be:
A) the interest rate.
B) business future profit expectations.
C) governments running higher deficits.
D) a change in the level of household time preferences.
E) better technology.
A) the interest rate.
B) business future profit expectations.
C) governments running higher deficits.
D) a change in the level of household time preferences.
E) better technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If real rates were higher than nominal rates in 2009,the implication is that:
A) inflation was greater than the real rate.
B) inflation was less than the real rate.
C) the nominal rate was equal to the real rate.
D) inflation was negative (deflation was occurring).
E) the real rate was equal to the rate of inflation.
A) inflation was greater than the real rate.
B) inflation was less than the real rate.
C) the nominal rate was equal to the real rate.
D) inflation was negative (deflation was occurring).
E) the real rate was equal to the rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If life expectancy falls due to AIDS and other diseases,we would expect:
A) time preference to fall and savings to increase.
B) time preference to rise and savings to increase.
C) time preference to fall and savings to decrease.
D) time preference to rise and savings to decrease.
E) interest rates to fall to zero.
A) time preference to fall and savings to increase.
B) time preference to rise and savings to increase.
C) time preference to fall and savings to decrease.
D) time preference to rise and savings to decrease.
E) interest rates to fall to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If foreign income and wealth decrease,this would most likely:
A) not affect the market for loanable funds.
B) cause the supply of loanable funds to increase.
C) cause the supply of loanable funds to decrease.
D) cause the demand for loanable funds to increase in order for foreigners to maintain consumption.
E) cause the demand for loanable funds to decrease.
A) not affect the market for loanable funds.
B) cause the supply of loanable funds to increase.
C) cause the supply of loanable funds to decrease.
D) cause the demand for loanable funds to increase in order for foreigners to maintain consumption.
E) cause the demand for loanable funds to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Higher education:
A) will generally result in higher lifetime earnings, ceteris paribus (all else equal).
B) is not generally worth the costs.
C) will generally result in lower lifetime earnings, ceteris paribus.
D) is worth the additional expense for bachelor's degrees and associate's degrees but not for master's degrees and higher.
E) is only worth the additional expense for professional degrees such as law and medical degrees.
A) will generally result in higher lifetime earnings, ceteris paribus (all else equal).
B) is not generally worth the costs.
C) will generally result in lower lifetime earnings, ceteris paribus.
D) is worth the additional expense for bachelor's degrees and associate's degrees but not for master's degrees and higher.
E) is only worth the additional expense for professional degrees such as law and medical degrees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A young girl is saving money for a soccer ball but is tempted to buy a book.If the girl buys a book rather than continuing to save for the ball,the:
A) girl has exchanged high time preferences for low.
B) girl has exchanged low time preferences for high.
C) girl has engaged in consumption smoothing.
D) bookseller has moved from being a lender of loanable funds to a borrower.
E) bookseller has moved from being a borrower to a lender of loanable funds.
A) girl has exchanged high time preferences for low.
B) girl has exchanged low time preferences for high.
C) girl has engaged in consumption smoothing.
D) bookseller has moved from being a lender of loanable funds to a borrower.
E) bookseller has moved from being a borrower to a lender of loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



