Deck 10: Financial Markets and Securities
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/124
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Financial Markets and Securities
1
Indirect finance occurs when:
A) savers go directly to borrowers for funds.
B) borrowers deposit funds into banks, which then loan these funds to savers.
C) savers deposit funds into banks, which then loan these funds to borrowers.
D) borrowers go directly to savers for funds.
E) firms give bonds.
A) savers go directly to borrowers for funds.
B) borrowers deposit funds into banks, which then loan these funds to savers.
C) savers deposit funds into banks, which then loan these funds to borrowers.
D) borrowers go directly to savers for funds.
E) firms give bonds.
savers deposit funds into banks, which then loan these funds to borrowers.
2
Firms that help to channel funds from savers to borrowers are known as:
A) financial intermediaries.
B) securities.
C) channelers.
D) marketers.
E) treasury securities.
A) financial intermediaries.
B) securities.
C) channelers.
D) marketers.
E) treasury securities.
financial intermediaries.
3
The sellers (or lenders) in financial markets are:
A) financial intermediaries.
B) firms and governments in search of funds to undertake their daily operations.
C) savers looking for opportunities to earn a return on their savings.
D) not concerned with the interest rate in the market.
E) located on the demand side of the loanable funds market.
A) financial intermediaries.
B) firms and governments in search of funds to undertake their daily operations.
C) savers looking for opportunities to earn a return on their savings.
D) not concerned with the interest rate in the market.
E) located on the demand side of the loanable funds market.
savers looking for opportunities to earn a return on their savings.
4
When firms seek funding to pay for resources for production:
A) they always use indirect financing.
B) they always use direct financing.
C) they can use indirect or direct financing.
D) they must borrow money.
E) the government must play a role.
A) they always use indirect financing.
B) they always use direct financing.
C) they can use indirect or direct financing.
D) they must borrow money.
E) the government must play a role.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The buyers (or borrowers) in financial markets are:
A) financial intermediaries.
B) firms and governments in search of funds to undertake their daily operations.
C) savers looking for opportunities to earn a return on their savings.
D) not concerned with the interest rate in the market.
E) located on the supply side of the loanable funds market.
A) financial intermediaries.
B) firms and governments in search of funds to undertake their daily operations.
C) savers looking for opportunities to earn a return on their savings.
D) not concerned with the interest rate in the market.
E) located on the supply side of the loanable funds market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When borrowers go directly to savers for funds,it is called:
A) indirect finance.
B) direct finance.
C) security finance.
D) bond finance.
E) banking finance.
A) indirect finance.
B) direct finance.
C) security finance.
D) bond finance.
E) banking finance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A tradable contract that entitles its owner to certain rights is called:
A) a security.
B) an alternative.
C) a maturity.
D) an entitlement.
E) a financial statement.
A) a security.
B) an alternative.
C) a maturity.
D) an entitlement.
E) a financial statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Banks:
A) are the only type of financial intermediary.
B) are savers looking for opportunities to earn a return on their savings.
C) have been owned by the government since the Great Depression.
D) are private firms that accept deposits and extend loans.
E) complicate the connection between borrowers and savers.
A) are the only type of financial intermediary.
B) are savers looking for opportunities to earn a return on their savings.
C) have been owned by the government since the Great Depression.
D) are private firms that accept deposits and extend loans.
E) complicate the connection between borrowers and savers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The two different paths through the loanable funds market are:
A) indirect finance and security finance.
B) internal finance and external finance.
C) saver finance and borrower finance.
D) indirect finance and direct finance.
E) bond finance and stock finance.
A) indirect finance and security finance.
B) internal finance and external finance.
C) saver finance and borrower finance.
D) indirect finance and direct finance.
E) bond finance and stock finance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A security is:
A) a private firm that accepts deposits and extends loans.
B) when savers deposit funds into banks, which then loan these funds to borrowers.
C) the date on which the loan repayment is due.
D) a tradable contract that entitles its owner to certain rights.
E) the risk that the borrower will not pay the face value of a bond on the maturity date.
A) a private firm that accepts deposits and extends loans.
B) when savers deposit funds into banks, which then loan these funds to borrowers.
C) the date on which the loan repayment is due.
D) a tradable contract that entitles its owner to certain rights.
E) the risk that the borrower will not pay the face value of a bond on the maturity date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A security that represents a debt to be paid is known as:
A) a stock.
B) a bond.
C) a bank.
D) a rating.
E) an index.
A) a stock.
B) a bond.
C) a bank.
D) a rating.
E) an index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Banks are:
A) always owned by the government.
B) one example of direct finance.
C) one example of a financial intermediary.
D) firms and governments in search of funds to undertake their daily operations.
E) savers looking for opportunities to earn a return on their savings.
A) always owned by the government.
B) one example of direct finance.
C) one example of a financial intermediary.
D) firms and governments in search of funds to undertake their daily operations.
E) savers looking for opportunities to earn a return on their savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Private firms that accept deposits and extend loans are known as:
A) bonds.
B) banks.
C) stocks.
D) financials.
E) securities.
A) bonds.
B) banks.
C) stocks.
D) financials.
E) securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
One example of a financial intermediary is:
A) a bond.
B) a bank.
C) a stock.
D) a financial.
E) a security.
A) a bond.
B) a bank.
C) a stock.
D) a financial.
E) a security.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In financial markets,firms and governments in search of funds to undertake their daily operations would be the:
A) banks.
B) buyers and sellers.
C) financial intermediaries.
D) buyers.
E) sellers.
A) banks.
B) buyers and sellers.
C) financial intermediaries.
D) buyers.
E) sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Direct finance occurs when:
A) savers go directly to borrowers for funds.
B) borrowers deposit funds into banks, which then loan these funds to savers.
C) savers deposit funds into banks, which then loan these funds to borrowers.
D) borrowers go directly to savers for funds.
E) banks get involved with financing.
A) savers go directly to borrowers for funds.
B) borrowers deposit funds into banks, which then loan these funds to savers.
C) savers deposit funds into banks, which then loan these funds to borrowers.
D) borrowers go directly to savers for funds.
E) banks get involved with financing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When savers deposit funds into banks,which then loan these funds to borrowers,it is called:
A) indirect finance.
B) direct finance.
C) security finance.
D) bond finance.
E) banking finance.
A) indirect finance.
B) direct finance.
C) security finance.
D) bond finance.
E) banking finance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A bond is:
A) the creation of a new security by combining otherwise separate loan agreements.
B) an ownership of a firm.
C) a security that represents a debt to be paid.
D) a market in which securities are traded after their first sale.
E) a private firm that accepts deposits and extends loans.
A) the creation of a new security by combining otherwise separate loan agreements.
B) an ownership of a firm.
C) a security that represents a debt to be paid.
D) a market in which securities are traded after their first sale.
E) a private firm that accepts deposits and extends loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If you have a savings account at a bank,you participate in the loanable funds market as:
A) a borrower.
B) a buyer.
C) a borrower and a lender.
D) a buyer and a seller.
E) a lender.
A) a borrower.
B) a buyer.
C) a borrower and a lender.
D) a buyer and a seller.
E) a lender.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In financial markets,savers looking for opportunities to earn a return on their savings would be the:
A) banks.
B) buyers and sellers.
C) financial intermediaries.
D) buyers.
E) sellers.
A) banks.
B) buyers and sellers.
C) financial intermediaries.
D) buyers.
E) sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Consider the following scenario when answering the next five questions:
Your friend Carson is starting a new photography business that specializes in photographs of Central Park in New York City. Because his business is new and risky, he is unable to obtain a loan from the local bank. On June 21, 2013, you agree to pay a price of $4,000 for a bond from Carson. You will receive $5,000 in return on June 21, 2014.
The dollar price of the bond mentioned in the scenario is equal to:
A) $9,000.
B) $1,000.
C) $4,000.
D) $5,000.
E) $20,000.
Your friend Carson is starting a new photography business that specializes in photographs of Central Park in New York City. Because his business is new and risky, he is unable to obtain a loan from the local bank. On June 21, 2013, you agree to pay a price of $4,000 for a bond from Carson. You will receive $5,000 in return on June 21, 2014.
The dollar price of the bond mentioned in the scenario is equal to:
A) $9,000.
B) $1,000.
C) $4,000.
D) $5,000.
E) $20,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Consider the following scenario when answering the next five questions:
Your friend Carson is starting a new photography business that specializes in photographs of Central Park in New York City. Because his business is new and risky, he is unable to obtain a loan from the local bank. On June 21, 2013, you agree to pay a price of $4,000 for a bond from Carson. You will receive $5,000 in return on June 21, 2014.
The face value of the bond mentioned in the scenario is equal to:
A) $9,000.
B) $1,000.
C) $4,000.
D) $5,000.
E) $20,000.
Your friend Carson is starting a new photography business that specializes in photographs of Central Park in New York City. Because his business is new and risky, he is unable to obtain a loan from the local bank. On June 21, 2013, you agree to pay a price of $4,000 for a bond from Carson. You will receive $5,000 in return on June 21, 2014.
The face value of the bond mentioned in the scenario is equal to:
A) $9,000.
B) $1,000.
C) $4,000.
D) $5,000.
E) $20,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The value of the bond at maturity,or the payment due at repayment,is known as:
A) the face value.
B) the maturity value.
C) the real value.
D) the ending value.
E) the nominal value.
A) the face value.
B) the maturity value.
C) the real value.
D) the ending value.
E) the nominal value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
TARP stands for:
A) Troubled Asset Reassurance Project.
B) Targeted Assistance Relief Program.
C) Troubled Asset Relief Program.
D) Targeted Asset Reassurance Program.
E) Timed Assistance Relief Project.
A) Troubled Asset Reassurance Project.
B) Targeted Assistance Relief Program.
C) Troubled Asset Relief Program.
D) Targeted Asset Reassurance Program.
E) Timed Assistance Relief Project.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
As a result of the 2007 financial crisis,when financial institutions began faltering:
A) financial intermediaries all over the world became less inclined to extend loans.
B) financial intermediaries all over the world started to give out subprime loans.
C) the government did not get involved.
D) the government bailed out all institutions that failed.
E) financial intermediaries all over the world became more inclined to extend loans.
A) financial intermediaries all over the world became less inclined to extend loans.
B) financial intermediaries all over the world started to give out subprime loans.
C) the government did not get involved.
D) the government bailed out all institutions that failed.
E) financial intermediaries all over the world became more inclined to extend loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The TARP program:
A) led to the collapse of many large banks.
B) was one of the many causes of the financial crisis.
C) was implemented in an effort to assist poor households.
D) helped homeowners who had defaulted on their mortgages.
E) was very controversial from the beginning.
A) led to the collapse of many large banks.
B) was one of the many causes of the financial crisis.
C) was implemented in an effort to assist poor households.
D) helped homeowners who had defaulted on their mortgages.
E) was very controversial from the beginning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The TARP program:
A) allocated $700 million to keep banks from failing.
B) allocated $500 million to individuals who defaulted on their mortgages.
C) provided low-interest rate loans for students attending college.
D) allocated $700 billion to keep banks from failing.
E) provided low-interest rate loans for new homeowners.
A) allocated $700 million to keep banks from failing.
B) allocated $500 million to individuals who defaulted on their mortgages.
C) provided low-interest rate loans for students attending college.
D) allocated $700 billion to keep banks from failing.
E) provided low-interest rate loans for new homeowners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In 2012,the Target Corporation had $14.4 billion in bonds outstanding.This means that:
A) the Target Corporation was making a loss of $14.4 billion in 2012.
B) the Target Corporation was due $14.4 billion from the owners of those bonds.
C) the Target Corporation owed less than $14.4 billion to the owners of those bonds.
D) the Target Corporation owed more than $14.4 billion to the owners of those bonds.
E) the Target Corporation owed $14.4 billion to the owners of those bonds.
A) the Target Corporation was making a loss of $14.4 billion in 2012.
B) the Target Corporation was due $14.4 billion from the owners of those bonds.
C) the Target Corporation owed less than $14.4 billion to the owners of those bonds.
D) the Target Corporation owed more than $14.4 billion to the owners of those bonds.
E) the Target Corporation owed $14.4 billion to the owners of those bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The face value of a bond is:
A) the value of the bond at maturity plus the price of the bond at purchase.
B) the value of the bond at maturity minus the price of the bond at purchase.
C) the price of the bond at purchase.
D) the value of the bond at maturity; the amount due at repayment.
E) the price of the bond at purchase minus the face value of the bond.
A) the value of the bond at maturity plus the price of the bond at purchase.
B) the value of the bond at maturity minus the price of the bond at purchase.
C) the price of the bond at purchase.
D) the value of the bond at maturity; the amount due at repayment.
E) the price of the bond at purchase minus the face value of the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The value of the bond at maturity,or the payment due at repayment,is known as:
A) the par value.
B) the maturity value.
C) the real value.
D) the ending value.
E) the nominal value.
A) the par value.
B) the maturity value.
C) the real value.
D) the ending value.
E) the nominal value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The par value of a bond is:
A) the value of the bond at maturity plus the price of the bond at purchase.
B) the value of the bond at maturity minus the price of the bond at purchase.
C) the price of the bond at purchase.
D) the value of the bond at maturity; the amount due at repayment.
E) the price of the bond at purchase minus the face value of the bond.
A) the value of the bond at maturity plus the price of the bond at purchase.
B) the value of the bond at maturity minus the price of the bond at purchase.
C) the price of the bond at purchase.
D) the value of the bond at maturity; the amount due at repayment.
E) the price of the bond at purchase minus the face value of the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The date on which the repayment for a loan is due is called:
A) the maturity date.
B) the deferment date.
C) the deadline date.
D) the face value date.
E) the par date.
A) the maturity date.
B) the deferment date.
C) the deadline date.
D) the face value date.
E) the par date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Consider the following scenario when answering the next five questions:
Your friend Carson is starting a new photography business that specializes in photographs of Central Park in New York City. Because his business is new and risky, he is unable to obtain a loan from the local bank. On June 21, 2013, you agree to pay a price of $4,000 for a bond from Carson. You will receive $5,000 in return on June 21, 2014.
The par value of the bond mentioned in the scenario is equal to:
A) $9,000.
B) $1,000.
C) $4,000.
D) $5,000.
E) $20,000.
Your friend Carson is starting a new photography business that specializes in photographs of Central Park in New York City. Because his business is new and risky, he is unable to obtain a loan from the local bank. On June 21, 2013, you agree to pay a price of $4,000 for a bond from Carson. You will receive $5,000 in return on June 21, 2014.
The par value of the bond mentioned in the scenario is equal to:
A) $9,000.
B) $1,000.
C) $4,000.
D) $5,000.
E) $20,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Bonds contain three important pieces of information.These three pieces are:
A) the date of issue, the date of repayment, and the interest rate.
B) the name of the borrower, the name of the issuer, and the date of issue.
C) the maturity date, the face value of the bond, and the issuing bank.
D) the issuing bank, the interest rate, and the date of issue.
E) the name of the borrower, the repayment date, and the amount due at repayment.
A) the date of issue, the date of repayment, and the interest rate.
B) the name of the borrower, the name of the issuer, and the date of issue.
C) the maturity date, the face value of the bond, and the issuing bank.
D) the issuing bank, the interest rate, and the date of issue.
E) the name of the borrower, the repayment date, and the amount due at repayment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider the following scenario when answering the next five questions:
Your friend Carson is starting a new photography business that specializes in photographs of Central Park in New York City. Because his business is new and risky, he is unable to obtain a loan from the local bank. On June 21, 2013, you agree to pay a price of $4,000 for a bond from Carson. You will receive $5,000 in return on June 21, 2014.
In the scenario,the date June 21,2014,is known as:
A) the par value.
B) the maturity date.
C) the real value.
D) the ending value.
E) the nominal value.
Your friend Carson is starting a new photography business that specializes in photographs of Central Park in New York City. Because his business is new and risky, he is unable to obtain a loan from the local bank. On June 21, 2013, you agree to pay a price of $4,000 for a bond from Carson. You will receive $5,000 in return on June 21, 2014.
In the scenario,the date June 21,2014,is known as:
A) the par value.
B) the maturity date.
C) the real value.
D) the ending value.
E) the nominal value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The maturity date of a bond is:
A) the date on which the loan is given out.
B) the date on which the loan repayment is due.
C) always one year after the loan is given out.
D) always more than one year after the loan is given out.
E) the date on which the bond is worth the price of the bond.
A) the date on which the loan is given out.
B) the date on which the loan repayment is due.
C) always one year after the loan is given out.
D) always more than one year after the loan is given out.
E) the date on which the bond is worth the price of the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
During the Great Recession,firms found it _________ to borrow,leading to an ______________.
A) easier; economic contraction
B) easier; economic expansion
C) too easy; economic contraction
D) more difficult; economic contraction
E) more difficult; economic expansion
A) easier; economic contraction
B) easier; economic expansion
C) too easy; economic contraction
D) more difficult; economic contraction
E) more difficult; economic expansion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Consider the following scenario when answering the next five questions:
Your friend Carson is starting a new photography business that specializes in photographs of Central Park in New York City. Because his business is new and risky, he is unable to obtain a loan from the local bank. On June 21, 2013, you agree to pay a price of $4,000 for a bond from Carson. You will receive $5,000 in return on June 21, 2014.
The interest rate of the bond mentioned in the scenario is equal to:
A) 80%.
B) 20%.
C) 25%.
D) 10%.
E) 5%.
Your friend Carson is starting a new photography business that specializes in photographs of Central Park in New York City. Because his business is new and risky, he is unable to obtain a loan from the local bank. On June 21, 2013, you agree to pay a price of $4,000 for a bond from Carson. You will receive $5,000 in return on June 21, 2014.
The interest rate of the bond mentioned in the scenario is equal to:
A) 80%.
B) 20%.
C) 25%.
D) 10%.
E) 5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
After the Lehman Brothers bankruptcy,it appeared there might be a domino effect that would lead to the collapse of many large banks.To avoid this potential disaster,the U.S.government implemented the:
A) Troubled Asset Reassurance Project.
B) Targeted Assistance Relief Program.
C) Troubled Asset Relief Program.
D) Targeted Bank Bailout Program.
E) Troubled Bank Bailout Program.
A) Troubled Asset Reassurance Project.
B) Targeted Assistance Relief Program.
C) Troubled Asset Relief Program.
D) Targeted Bank Bailout Program.
E) Troubled Bank Bailout Program.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Coupon bonds are:
A) bonds with coupons attached that represent multiple interest rates.
B) bonds with coupons attached that represent periodic interest payments.
C) bonds with coupons attached that represent multiple bond issuers.
D) bonds with coupons attached that represent discounted repayments.
E) bonds with coupons attached that represent multiple bond holders.
A) bonds with coupons attached that represent multiple interest rates.
B) bonds with coupons attached that represent periodic interest payments.
C) bonds with coupons attached that represent multiple bond issuers.
D) bonds with coupons attached that represent discounted repayments.
E) bonds with coupons attached that represent multiple bond holders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If a borrower defaults on a bond,it means that:
A) the borrower has one year to pay before facing possible jail time.
B) the borrower did not pay back the loan on the maturity date.
C) the borrower only has to pay a portion of the loan back.
D) the borrower has paid back the loan on the maturity date.
E) the borrower has paid back the loan prior to the maturity date.
A) the borrower has one year to pay before facing possible jail time.
B) the borrower did not pay back the loan on the maturity date.
C) the borrower only has to pay a portion of the loan back.
D) the borrower has paid back the loan on the maturity date.
E) the borrower has paid back the loan prior to the maturity date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
You friend Michelle is starting a fitness center that specializes in helping people get in shape through exercise and eating healthy.Because her business is new and risky,she is unable to obtain a loan from the local bank.You agree to pay $7,500 for a one-year bond from Michelle with an interest rate of 5%.The face value of the bond is:
A) $7,875.00.
B) $7,500.00.
C) $7,142.86.
D) $7,000.00.
E) $375.
A) $7,875.00.
B) $7,500.00.
C) $7,142.86.
D) $7,000.00.
E) $375.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following supply and demand models for bonds issued by company X represents what happens when the default risk increases for company X?
A)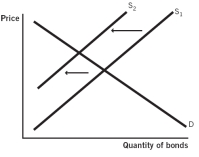
B)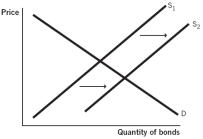
C)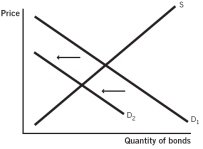
D)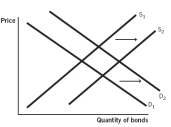
E)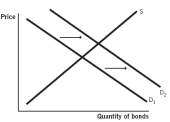
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements is true about bonds?
A) Bonds are ownership shares in a firm.
B) The dollar price and interest rate of a bond have an inverse relationship.
C) A bond's dollar price is calculated as growth rate.
D) Bonds can never default.
E) The dollar price and interest rate of a bond have a positive relationship.
A) Bonds are ownership shares in a firm.
B) The dollar price and interest rate of a bond have an inverse relationship.
C) A bond's dollar price is calculated as growth rate.
D) Bonds can never default.
E) The dollar price and interest rate of a bond have a positive relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The interest rate of a bond is computed as:
A) a sum.
B) an absolute value.
C) a growth rate.
D) a difference.
E) a multiplication.
A) a sum.
B) an absolute value.
C) a growth rate.
D) a difference.
E) a multiplication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the interest rate of a one-year bond is 15% and its dollar price is $3,250,the face value of the bond is:
A) $3,737.50.
B) $2826.09.
C) $373.75.
D) $282.61.
E) $3,350.00.
A) $3,737.50.
B) $2826.09.
C) $373.75.
D) $282.61.
E) $3,350.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The risk that the borrower will not pay the face value of a bond on the maturity date is called the:
A) default risk.
B) maturity risk.
C) timing risk.
D) full-pay risk.
E) par value risk.
A) default risk.
B) maturity risk.
C) timing risk.
D) full-pay risk.
E) par value risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Your friend Jamarcus is an award-winning chef.Jamarcus wants to start his own restaurant in Denver but is unable to obtain a loan from his local bank.Jamarcus has decided to issue a one-year bond with a face value of $6,000 and an interest rate of 10%.If you wanted to buy this bond,what would be the initial price?
A) $6,600.00.
B) $5,500.50.
C) $6,000.00.
D) $5,000.00.
E) $5,454.54.
A) $6,600.00.
B) $5,500.50.
C) $6,000.00.
D) $5,000.00.
E) $5,454.54.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
All else equal,the greater the default risk:
A) the higher the face value of the bond.
B) the higher the price of the bond.
C) the lower the price of the bond.
D) the lower the face value of the bond.
E) the lower the interest rate of the bond.
A) the higher the face value of the bond.
B) the higher the price of the bond.
C) the lower the price of the bond.
D) the lower the face value of the bond.
E) the lower the interest rate of the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the interest rate of a one-year bond is 10% and its face value is $5,000,the dollar price of the bond is:
A) $5,000.00.
B) $5,500.00.
C) $4,545.45.
D) $5,250.50.
E) $454.00.
A) $5,000.00.
B) $5,500.00.
C) $4,545.45.
D) $5,250.50.
E) $454.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Default risk is:
A) the risk that the lender will not pay the face value of the bond on the maturity date.
B) the risk that a stock will become worthless.
C) the risk that the borrower will renegotiate the maturity date on a bond.
D) the risk that the borrower will not pay the face value of the bond on the maturity date.
E) the risk that a stock will lose value.
A) the risk that the lender will not pay the face value of the bond on the maturity date.
B) the risk that a stock will become worthless.
C) the risk that the borrower will renegotiate the maturity date on a bond.
D) the risk that the borrower will not pay the face value of the bond on the maturity date.
E) the risk that a stock will lose value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Consider a supply and demand model of bonds for company X.Which of the following would you expect to happen if the default risk decreases for company X?
A) The demand curve will shift to the right, causing the price of the bond to rise.
B) The demand curve will shift to the left, causing the price of the bond to rise.
C) The supply curve will shift to the right, causing the price of the bond to fall.
D) The demand curve will shift the left, causing the price of the bond to fall.
E) The supply curve will shift to the left, causing the price of the bond to rise.
A) The demand curve will shift to the right, causing the price of the bond to rise.
B) The demand curve will shift to the left, causing the price of the bond to rise.
C) The supply curve will shift to the right, causing the price of the bond to fall.
D) The demand curve will shift the left, causing the price of the bond to fall.
E) The supply curve will shift to the left, causing the price of the bond to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The equation for the interest rate of a bond is:
A)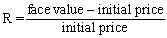
B)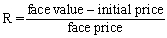
C)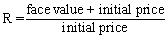
D)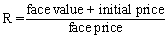
E)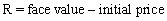
A)
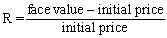
B)
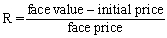
C)
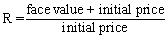
D)
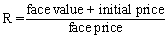
E)
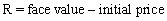

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
is the equation for:
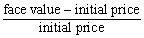
A) the interest rate of a stock.
B) the dividend of a stock.
C) the maturity value of a bond.
D) the par value of a bond.
E) the interest rate of a bond.
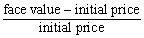
A) the interest rate of a stock.
B) the dividend of a stock.
C) the maturity value of a bond.
D) the par value of a bond.
E) the interest rate of a bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
All else equal,the smaller the default risk:
A) the higher the face value of the bond.
B) the higher the price of the bond.
C) the lower the price of the bond.
D) the lower the face value of the bond.
E) the higher the interest rate of the bond.
A) the higher the face value of the bond.
B) the higher the price of the bond.
C) the lower the price of the bond.
D) the lower the face value of the bond.
E) the higher the interest rate of the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The interest rate of a bond is equal to:
A) the difference between the face value and the initial price all divided by the face value.
B) the difference between the face value and the initial price.
C) the difference between the face value and the initial price all divided by the initial price.
D) the sum of the face value and the initial price all divided by the face value.
E) the sum of the face value and the initial price all divided by the initial price.
A) the difference between the face value and the initial price all divided by the face value.
B) the difference between the face value and the initial price.
C) the difference between the face value and the initial price all divided by the initial price.
D) the sum of the face value and the initial price all divided by the face value.
E) the sum of the face value and the initial price all divided by the initial price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Consider a supply and demand model of bonds for company X.Which of the following would you expect to happen if the default risk increases for company X?
A) The demand curve will shift to the right, causing the price of the bond to rise.
B) The demand curve will shift to the left, causing the price of the bond to rise.
C) The supply curve will shift to the right, causing the price of the bond to fall.
D) The demand curve will shift the left, causing the price of the bond to fall.
E) The supply curve will shift to the left, causing the price of the bond to rise.
A) The demand curve will shift to the right, causing the price of the bond to rise.
B) The demand curve will shift to the left, causing the price of the bond to rise.
C) The supply curve will shift to the right, causing the price of the bond to fall.
D) The demand curve will shift the left, causing the price of the bond to fall.
E) The supply curve will shift to the left, causing the price of the bond to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following supply and demand models for bonds issued by company X represents what happens when the default risk decreases for company X?
A)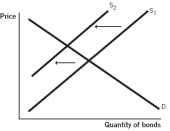
B)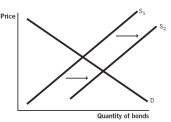
C)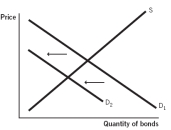
D)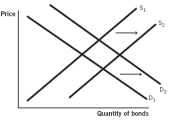
E)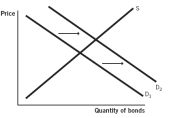
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If the dollar price of a bond is $7,500 and the face value of the bond is $8,000,the interest rate is equal to:
A) 7%.
B) 6.67%.
C) 6.25%.
D) 14%.
E) 5%.
A) 7%.
B) 6.67%.
C) 6.25%.
D) 14%.
E) 5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If the dollar price of a bond is $4,000 and its face value is $4,250,the interest rate is equal to:
A) 5.9%.
B) 5%.
C) 6.67%.
D) 6.25%.
E) 10%.
A) 5.9%.
B) 5%.
C) 6.67%.
D) 6.25%.
E) 10%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
As of January 2013,American Airlines had an S&P bond rating of:
A) A.
B) AA.
C) BB.
D) CCC.
E) D.
A) A.
B) AA.
C) BB.
D) CCC.
E) D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A higher bond rating directly translates into:
A) higher prices and higher interest rates on the firm's bonds.
B) higher prices and lower interest rates on the firm's bonds.
C) lower prices and lower interest rates on the firm's bonds.
D) lower prices and higher interest rates on the firm's bonds.
E) higher prices and higher default rates on the firm's bonds.
A) higher prices and higher interest rates on the firm's bonds.
B) higher prices and lower interest rates on the firm's bonds.
C) lower prices and lower interest rates on the firm's bonds.
D) lower prices and higher interest rates on the firm's bonds.
E) higher prices and higher default rates on the firm's bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
NYSE stands for:
A) New York Stock Exchange.
B) National Youth Stock Exchange.
C) New York Securities Exchange.
D) National Youth Student Ensemble.
E) New York Student Ensemble.
A) New York Stock Exchange.
B) National Youth Stock Exchange.
C) New York Securities Exchange.
D) National Youth Student Ensemble.
E) New York Student Ensemble.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A majority shareholder:
A) has total say in the decisions of the company.
B) owns less than 50% of the shares of the firm.
C) controls 100% of the ownership votes.
D) becomes the CEO of the company.
E) can determine the direction of the company.
A) has total say in the decisions of the company.
B) owns less than 50% of the shares of the firm.
C) controls 100% of the ownership votes.
D) becomes the CEO of the company.
E) can determine the direction of the company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Most people who purchase stocks and bonds use brokers,who buy the stocks and bonds in:
A) minor markets.
B) inferior markets.
C) alternate markets.
D) secondary markets.
E) primary markets.
A) minor markets.
B) inferior markets.
C) alternate markets.
D) secondary markets.
E) primary markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following statements about bonds is true?
A) Bond interest rates fall with increased default risk.
B) Bond interest rates and default risk are not related.
C) Bond prices rise with increased default risk.
D) Bond prices rise with increased interest rates.
E) Bond interest rates rise with increased default risk.
A) Bond interest rates fall with increased default risk.
B) Bond interest rates and default risk are not related.
C) Bond prices rise with increased default risk.
D) Bond prices rise with increased interest rates.
E) Bond interest rates rise with increased default risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Secondary markets are:
A) markets in which securities are bought for the first time.
B) markets in which securities are traded after their first sale.
C) available for stocks but not for bonds.
D) markets in which securities are traded on the maturity date.
E) available for bonds but not for stocks.
A) markets in which securities are bought for the first time.
B) markets in which securities are traded after their first sale.
C) available for stocks but not for bonds.
D) markets in which securities are traded on the maturity date.
E) available for bonds but not for stocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following would explain why a firm would want to sell stocks instead of bonds?
A) The owners are worried about the burden of debt.
B) The owners don't want to give up ownership of the business.
C) The owners aren't trying to finance production.
D) Stocks are easier to issue than bonds are.
E) There are more fees associated with issuing bonds.
A) The owners are worried about the burden of debt.
B) The owners don't want to give up ownership of the business.
C) The owners aren't trying to finance production.
D) Stocks are easier to issue than bonds are.
E) There are more fees associated with issuing bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A shareholder who owns more than 50% of the shares of the firm is called the:
A) minority shareholder.
B) CEO.
C) majority shareholder.
D) overwhelming shareholder.
E) bulk shareholder.
A) minority shareholder.
B) CEO.
C) majority shareholder.
D) overwhelming shareholder.
E) bulk shareholder.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
As of January 2013,Microsoft had an S&P bond rating of:
A) A.
B) AA.
C) AAA.
D) A++.
E) BBB.
A) A.
B) AA.
C) AAA.
D) A++.
E) BBB.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Ownership shares in a firm are known as:
A) bonds.
B) stocks.
C) treasuries.
D) mortgages.
E) chips.
A) bonds.
B) stocks.
C) treasuries.
D) mortgages.
E) chips.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following is a secondary stock market?
A) North American Stock Exchange
B) The S&P 500
C) New York Stock Exchange
D) The Dow Jones Industrial Average
E) The United States Stock Exchange
A) North American Stock Exchange
B) The S&P 500
C) New York Stock Exchange
D) The Dow Jones Industrial Average
E) The United States Stock Exchange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The existence of a secondary market for a given security will:
A) increase the supply for that security.
B) decrease the supply for that security.
C) decrease the demand for that security.
D) increase the demand for that security.
E) increase both the supply and the demand for that security.
A) increase the supply for that security.
B) decrease the supply for that security.
C) decrease the demand for that security.
D) increase the demand for that security.
E) increase both the supply and the demand for that security.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Typical individuals have difficulty judging the default risk of any one company,let alone the thousands of firms that sell bonds in a developed economy.To address this problem:
A) the price of bonds increases as more information is made available to investors.
B) borrowing entities rate their own bonds.
C) individuals should never invest in bonds.
D) the government assigns ratings of borrowing entities.
E) private rating agencies evaluate and then grade the default risk of borrowing entities.
A) the price of bonds increases as more information is made available to investors.
B) borrowing entities rate their own bonds.
C) individuals should never invest in bonds.
D) the government assigns ratings of borrowing entities.
E) private rating agencies evaluate and then grade the default risk of borrowing entities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following statements is true about stocks?
A) Owners of stock securities are guaranteed a return on their investment.
B) Stocks have a maturity date.
C) Stocks represent a debt to be paid.
D) Owners of stock securities are actual owners of the firm.
E) Only institutional investors can own stock securities.
A) Owners of stock securities are guaranteed a return on their investment.
B) Stocks have a maturity date.
C) Stocks represent a debt to be paid.
D) Owners of stock securities are actual owners of the firm.
E) Only institutional investors can own stock securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is the highest rating a bond can receive from the rating firm Standard and Poor's (S&P)?
A) A+
B) A++
C) AA
D) AAA
E) A
A) A+
B) A++
C) AA
D) AAA
E) A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Markets in which securities are traded after their first sale are known as:
A) minor markets.
B) inferior markets.
C) alternate markets.
D) primary markets.
E) secondary markets.
A) minor markets.
B) inferior markets.
C) alternate markets.
D) primary markets.
E) secondary markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Private rating agencies evaluate and then grade the default risk of bonds to address which of the following problems?
A) the government's inability to judge default risks
B) companies hiding their finances
C) bond holders not having access to companies finances
D) individuals' inability to easily judge default risks
E) too many investors picking risky bonds for their portfolios
A) the government's inability to judge default risks
B) companies hiding their finances
C) bond holders not having access to companies finances
D) individuals' inability to easily judge default risks
E) too many investors picking risky bonds for their portfolios

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Stocks are:
A) ownership shares in a firm.
B) securities that represent a debt to be paid.
C) markets in which securities are bought and sold.
D) contracts that represent a guaranteed payment.
E) not available for individual investors.
A) ownership shares in a firm.
B) securities that represent a debt to be paid.
C) markets in which securities are bought and sold.
D) contracts that represent a guaranteed payment.
E) not available for individual investors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Non-investment grade bonds are bonds that receive an S&P bond rating of _______ and lower.
A) A
B) B
C) BB
D) BBB
E) CCC
A) A
B) B
C) BB
D) BBB
E) CCC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



