Deck 14: Cardiovascular Diagnostic Procedures
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Cardiovascular Diagnostic Procedures
1
Pulsus paradoxus may be seen on intra-arterial blood pressure monitoring when
A) there is a decrease of more than 10 mm Hg in the arterial waveform before inhalation.
B) there is a single, nonperfused beat.
C) the waveform demonstrates tall, tented T waves.
D) the pulse pressure is greater than 20 mm Hg on exhalation.
A) there is a decrease of more than 10 mm Hg in the arterial waveform before inhalation.
B) there is a single, nonperfused beat.
C) the waveform demonstrates tall, tented T waves.
D) the pulse pressure is greater than 20 mm Hg on exhalation.
there is a decrease of more than 10 mm Hg in the arterial waveform before inhalation.
2
When assessing the pulmonary arterial waveform,the nurse notices dampening.After tightening the stopcocks and flushing the line,the nurse decides to calibrate the transducer.What are two essential components included in calibration?
A) Obtaining a baseline blood pressure and closing the transducer to air
B) Leveling the air-fluid interface to the phlebostatic axis and opening the transducer to air
C) Having the patient lay flat and closing the transducer to air
D) Obtaining blood return on line and closing all stopcocks
A) Obtaining a baseline blood pressure and closing the transducer to air
B) Leveling the air-fluid interface to the phlebostatic axis and opening the transducer to air
C) Having the patient lay flat and closing the transducer to air
D) Obtaining blood return on line and closing all stopcocks
Leveling the air-fluid interface to the phlebostatic axis and opening the transducer to air
3
Which of the following findings would be indicative reasons to abort an exercise stress test?
A) Ventricular axis of +90
B) Increase in blood pressure
C) Inverted U wave
D) ST segment depression or elevation
A) Ventricular axis of +90
B) Increase in blood pressure
C) Inverted U wave
D) ST segment depression or elevation
ST segment depression or elevation
4
The value of SVO? monitoring is to determine
A) oxygen saturation at the capillary level.
B) an imbalance between oxygen supply and metabolic tissue demand.
C) the diffusion of gases at the alveolar capillary membrane.
D) the predicted cardiac output for acute pulmonary edema.
A) oxygen saturation at the capillary level.
B) an imbalance between oxygen supply and metabolic tissue demand.
C) the diffusion of gases at the alveolar capillary membrane.
D) the predicted cardiac output for acute pulmonary edema.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
ST segment monitoring for ischemia has gained increasing importance with the advent of thrombolytic therapy.The most accurate method for monitoring the existence of true ischemic changes is
A) T-wave inversion in leads overlying the ischemia.
B) ST segment depression in leads overlying the ischemia.
C) adjusting the gain control on bedside monitoring for best visualization.
D) 12-lead ECG for confirmation.
A) T-wave inversion in leads overlying the ischemia.
B) ST segment depression in leads overlying the ischemia.
C) adjusting the gain control on bedside monitoring for best visualization.
D) 12-lead ECG for confirmation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The mean arterial pressure (MAP)is calculated by
A) averaging three of the patient's blood pressure readings over a 6-hour period.
B) dividing the systolic pressure by the diastolic pressure.
C) adding the systolic pressure and two diastolic pressures and then dividing by 3.
D) dividing the diastolic pressure by the pulse pressure.
A) averaging three of the patient's blood pressure readings over a 6-hour period.
B) dividing the systolic pressure by the diastolic pressure.
C) adding the systolic pressure and two diastolic pressures and then dividing by 3.
D) dividing the diastolic pressure by the pulse pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When assessing a patient with PVCs,the nurse knows that the ectopic beat is multifocal because it appears
A) in various shapes in the same lead.
B) with increasing frequency.
C) to widen the QRS width.
D) in a specific pattern in the same lead.
A) in various shapes in the same lead.
B) with increasing frequency.
C) to widen the QRS width.
D) in a specific pattern in the same lead.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following diagnostic tests is most effective for measuring overall heart size?
A) Twelve-lead electrocardiography
B) Echocardiography
C) Chest radiography
D) Vectorcardiography
A) Twelve-lead electrocardiography
B) Echocardiography
C) Chest radiography
D) Vectorcardiography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following criteria are representative of the patient in normal sinus rhythm?
A) Heart rate, 64 beats/min; rhythm regular; PR interval, 0.10 second; QRS, 0.04 second
B) Heart rate, 88 beats/min; rhythm regular; PR interval, 0.18 second; QRS, 0.06 second
C) Heart rate, 54 beats/min; rhythm regular; PR interval, 0.16 second; QRS, 0.08 second
D) Heart rate, 92 beats/min; rhythm irregular; PR interval, 0.16 second; QRS, 0.04 second
A) Heart rate, 64 beats/min; rhythm regular; PR interval, 0.10 second; QRS, 0.04 second
B) Heart rate, 88 beats/min; rhythm regular; PR interval, 0.18 second; QRS, 0.06 second
C) Heart rate, 54 beats/min; rhythm regular; PR interval, 0.16 second; QRS, 0.08 second
D) Heart rate, 92 beats/min; rhythm irregular; PR interval, 0.16 second; QRS, 0.04 second

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A characteristic event in junctional dysrhythmias is
A) irregular rhythm.
B) rapid depolarization to the ventricles.
C) the spread of the impulse in two directions at once.
D) a widened QRS.
A) irregular rhythm.
B) rapid depolarization to the ventricles.
C) the spread of the impulse in two directions at once.
D) a widened QRS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The rationale for giving the patient additional fluids after a cardiac catheterization is that
A) fluids help keep the femoral vein from clotting at the puncture site.
B) the patient had a nothing-by-mouth order before the procedure.
C) the radiopaque contrast acts as an osmotic diuretic.
D) fluids increase cardiac output.
A) fluids help keep the femoral vein from clotting at the puncture site.
B) the patient had a nothing-by-mouth order before the procedure.
C) the radiopaque contrast acts as an osmotic diuretic.
D) fluids increase cardiac output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which portion of the ECG is most valuable in diagnosing atrioventricular (AV)conduction disturbances?
A) P wave
B) PR interval
C) QRS complex
D) QT interval
A) P wave
B) PR interval
C) QRS complex
D) QT interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The physiologic effect of left ventricular afterload reduction is
A) decreased left atrial tension.
B) decreased systemic vascular resistance.
C) increased filling pressures.
D) decreased cardiac output.
A) decreased left atrial tension.
B) decreased systemic vascular resistance.
C) increased filling pressures.
D) decreased cardiac output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Contractility of the left side of the heart is measured by
A) pulmonary artery wedge pressure.
B) left atrial pressure.
C) systemic vascular resistance.
D) left ventricular stroke work index.
A) pulmonary artery wedge pressure.
B) left atrial pressure.
C) systemic vascular resistance.
D) left ventricular stroke work index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following interventions should be strictly followed to ensure accurate cardiac output readings?
A) Use 5 mL of iced injectate only.
B) Inject the fluid into the pulmonary artery port only.
C) Ensure a difference of at least 5° C between injectate temperature and the patient's body temperature.
D) Administer the injectate within 4 seconds.
A) Use 5 mL of iced injectate only.
B) Inject the fluid into the pulmonary artery port only.
C) Ensure a difference of at least 5° C between injectate temperature and the patient's body temperature.
D) Administer the injectate within 4 seconds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A patient with ventricular fibrillation (VF)is
A) hypertensive.
B) bradypneic.
C) diaphoretic.
D) pulseless.
A) hypertensive.
B) bradypneic.
C) diaphoretic.
D) pulseless.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A patient with heart failure may be at risk for hypomagnesemia as a result of
A) pump failure.
B) diuretic use.
C) fluid overload.
D) hemodilution.
A) pump failure.
B) diuretic use.
C) fluid overload.
D) hemodilution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A patient with a serum potassium level of 6.8 mEq/L may exhibit electrocardiographic changes of
A) a prominent U wave.
B) tall, peaked T waves.
C) a narrowed QRS.
D) sudden ventricular dysrhythmias.
A) a prominent U wave.
B) tall, peaked T waves.
C) a narrowed QRS.
D) sudden ventricular dysrhythmias.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The major key to the clinical significance of atrial flutter is the
A) atrial rate.
B) ventricular response rate.
C) PR interval.
D) QRS duration.
A) atrial rate.
B) ventricular response rate.
C) PR interval.
D) QRS duration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A 52-year-old patient presents to the emergency department with reports of substernal chest pain.A history is taken; serum creatine kinase (CK)and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)isoenzymes and serum lipid studies are ordered,as is a 12-lead ECG.Which of the following results is most significant in diagnosing an MI during the first 12 hours of chest pain?
A) ECG-inverted T waves
B) Serum enzymes-elevated LDH4
C) Serum enzymes-elevated CK-MB
D) Patient history-substernal chest pain
A) ECG-inverted T waves
B) Serum enzymes-elevated LDH4
C) Serum enzymes-elevated CK-MB
D) Patient history-substernal chest pain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the ECG findings would be positive for an inferior wall MI?
A) ST segment depression in leads I, aVL, and V? to V?
B) Q waves in leads V? to V?
C) Q waves in leads II, III, and aVF
D) T-wave inversion in leads V? to V?, I, and aVL
A) ST segment depression in leads I, aVL, and V? to V?
B) Q waves in leads V? to V?
C) Q waves in leads II, III, and aVF
D) T-wave inversion in leads V? to V?, I, and aVL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A physician orders removal of the central venous catheter (CVC)line.The patient has a diagnosis of heart failure with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.The nurse would place the patient in what position for this procedure?
A) Supine in bed
B) Supine in a chair
C) Flat in bed
D) Reverse Trendelenburg position
A) Supine in bed
B) Supine in a chair
C) Flat in bed
D) Reverse Trendelenburg position

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A patient's bedside ECG strips show the following changes: increased PR interval; increased QRS width; and tall,peaked T waves.Vital signs are T 98.2° F; HR 118 beats/min; BP 146/90 mm Hg; and RR 18 breaths/min.The patient is receiving the following medications: digoxin 0.125 mg PO every day; D?1/2 normal saline with 40 mEq potassium chloride at 125 mL/hr; Cardizem at 30 mg PO q8h; and aldosterone at 300 mg PO q12h.The physician is notified of the ECG changes.What orders should the nurse expect to receive?
A) Change IV fluid to D51/2 normal saline and draw blood chemistry.
B) Give normal saline with 40 mEq of potassium chloride over a 6-hour period.
C) Hold digoxin and draw serum digoxin level.
D) Hold Cardizem and give 500 mL normal saline fluid challenge over a 2-hour period.
A) Change IV fluid to D51/2 normal saline and draw blood chemistry.
B) Give normal saline with 40 mEq of potassium chloride over a 6-hour period.
C) Hold digoxin and draw serum digoxin level.
D) Hold Cardizem and give 500 mL normal saline fluid challenge over a 2-hour period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The most common complication of a central venous catheter (CVC)is
A) air embolus.
B) infection.
C) thrombus formation.
D) pneumothorax.
A) air embolus.
B) infection.
C) thrombus formation.
D) pneumothorax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Mechanical contraction of the heart occurs during which of the following phases of the cardiac cycle?
A) Phase 0
B) Phase 2
C) Phase 3
D) Phase 4
A) Phase 0
B) Phase 2
C) Phase 3
D) Phase 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following cardiac enzymes is a highly specific biomarker for myocardial damage?
A) CK-MB
B) Troponin I
C) Troponin T
D) LDH
A) CK-MB
B) Troponin I
C) Troponin T
D) LDH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The P wave represents which of the following?
A) Atrial contraction
B) Atrial depolarization
C) Sinus node discharge
D) Ventricular contraction
A) Atrial contraction
B) Atrial depolarization
C) Sinus node discharge
D) Ventricular contraction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which serum lipid value is a significant predictor of future acute MI in persons with established coronary artery atherosclerosis?
A) High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
B) Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
C) Triglycerides
D) Very-low-density lipoprotein
A) High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
B) Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
C) Triglycerides
D) Very-low-density lipoprotein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Why is the measurement of the QT interval important?
A) It represents ventricular depolarization.
B) It represents ventricular contraction.
C) An increasing QT interval increases the risk of torsades de pointes.
D) A decreasing QT interval increases the risk of torsades de pointes.
A) It represents ventricular depolarization.
B) It represents ventricular contraction.
C) An increasing QT interval increases the risk of torsades de pointes.
D) A decreasing QT interval increases the risk of torsades de pointes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The patient's admitting 12-lead ECG shows peaked P waves.Which of the following admitting diagnoses could be responsible for this finding?
A) Mitral stenosis
B) Pulmonary edema
C) Ischemia
D) Pericarditis
A) Mitral stenosis
B) Pulmonary edema
C) Ischemia
D) Pericarditis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
To accurately measure the heart rate of a patient in normal sinus rhythm,which technique would be the most accurate?
A) The number of R waves in a 6-second strip
B) The number of large boxes in a 6-second strip
C) The number of small boxes between QRS complexes divided into 1500
D) The number of large boxes between consecutive R waves divided into 300
A) The number of R waves in a 6-second strip
B) The number of large boxes in a 6-second strip
C) The number of small boxes between QRS complexes divided into 1500
D) The number of large boxes between consecutive R waves divided into 300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which lead is best to monitor a patient?
A) Varies based on the patient's clinical condition and recent clinical history
B) Lead MCL1
C) Lead V?
D) Lead II
A) Varies based on the patient's clinical condition and recent clinical history
B) Lead MCL1
C) Lead V?
D) Lead II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When performing a 12-lead ECG,how many wires are connected to the patient?
A) 3
B) 5
C) 10
D) 12
A) 3
B) 5
C) 10
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A new-onset MI can be recognized by which of the following ECG changes?
A) Q waves
B) Smaller R waves
C) Widened QRS
D) ST segment elevation
A) Q waves
B) Smaller R waves
C) Widened QRS
D) ST segment elevation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When comparing a portable chest radiograph taken in an intensive care unit bed with one taken with the patient upright in the radiology department,one significant difference is that the
A) portable chest radiograph is usually clearer.
B) one in the intensive care unit is considered a posterior view.
C) portable chest radiograph magnifies some thoracic structures and decreases the sharpness of the structures.
D) departmental chest radiograph enlarges some thoracic structures.
A) portable chest radiograph is usually clearer.
B) one in the intensive care unit is considered a posterior view.
C) portable chest radiograph magnifies some thoracic structures and decreases the sharpness of the structures.
D) departmental chest radiograph enlarges some thoracic structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The physician anticipates the CVC dwelling time to be 10 to 20 days.The nurse anticipates that the CVC will be placed in the
A) SC vein.
B) IJ vein.
C) EJ vein.
D) femoral vein.
A) SC vein.
B) IJ vein.
C) EJ vein.
D) femoral vein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A nurse is obtaining the history of a patient who reveals that he had an MI 5 years ago.When the admission 12-lead ECG is reviewed,Q waves are noted in leads V? and V? only.Which of the following conclusions is most consistent with this situation?
A) The patient may have had a posterior wall MI.
B) The patient must have had a right ventricular MI.
C) The admission 12-lead ECG was done incorrectly.
D) The patient may have had an anterior MI.
A) The patient may have had a posterior wall MI.
B) The patient must have had a right ventricular MI.
C) The admission 12-lead ECG was done incorrectly.
D) The patient may have had an anterior MI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A patient with a potassium level of 2.8 mEq/L is given 60 mEq over a 12-hour period,and a repeat potassium level is obtained after the bolus.The current potassium level is 2.9 mEq/L.Which of the following should now be considered?
A) Stopping the patient's Aldactone
B) Drawing a serum magnesium level
C) Rechecking the potassium level
D) Monitoring the patient's urinary output
A) Stopping the patient's Aldactone
B) Drawing a serum magnesium level
C) Rechecking the potassium level
D) Monitoring the patient's urinary output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A patient asks why he had to take a deep breath when the radiology technician took his chest radiograph.Which of the following would be the best response?
A) It gets the chest wall closer to the machine.
B) Lungs filled with air give a clearer picture.
C) It decreases the error caused by motion.
D) It makes the heart appear larger.
A) It gets the chest wall closer to the machine.
B) Lungs filled with air give a clearer picture.
C) It decreases the error caused by motion.
D) It makes the heart appear larger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A patient returns from the cardiac catheterization laboratory after angioplasty and stent placement (ECG changes had indicated an inferior wall myocardial infarction in progress).Which lead would best monitor this patient?
A) Varies based on the patient's clinical condition and recent clinical history
B) Lead MCL1
C) Lead V?
D) Lead II
A) Varies based on the patient's clinical condition and recent clinical history
B) Lead MCL1
C) Lead V?
D) Lead II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following statements made by a patient would indicate the need for further education before an electrophysiology procedure?
A) "I need to take all my heart medications the morning of the procedure."
B) "The doctor is going to make my heart beat wrong on purpose."
C) "I will be awake but relaxed during the procedure."
D) "I will be x-rayed during the procedure."
A) "I need to take all my heart medications the morning of the procedure."
B) "The doctor is going to make my heart beat wrong on purpose."
C) "I will be awake but relaxed during the procedure."
D) "I will be x-rayed during the procedure."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Ventricular tachycardia has which of the following hemodynamic effects?
A) Decreased cardiac output from increased ventricular filling time
B) Decreased cardiac output from decreased stroke volume
C) Decreased cardiac output from increased preload
D) Decreased cardiac output from decreased afterload
A) Decreased cardiac output from increased ventricular filling time
B) Decreased cardiac output from decreased stroke volume
C) Decreased cardiac output from increased preload
D) Decreased cardiac output from decreased afterload

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Allen test is used before radial arterial line placement to assess
A) collateral circulation to the hand.
B) patency of the radial artery.
C) neurologic function of the hand.
D) pain sensation at the insertion point.
A) collateral circulation to the hand.
B) patency of the radial artery.
C) neurologic function of the hand.
D) pain sensation at the insertion point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The patient is admitted to the ICU with a diagnosis of cardiogenic shock.The patient's VS includes HR 135 beats/min with weak peripheral pulses.The lungs have crackles in the bases bilaterally.O? saturation is 90% on 4L/NC.The physician orders diuretics and vasodilators.The nurse expects which responses to the medications.
A)3 SVR, 3 preload
B)5 SVR, 5 preload
C)3 SVR, 5 preload
D)5 SVR, 3 preload
A)3 SVR, 3 preload
B)5 SVR, 5 preload
C)3 SVR, 5 preload
D)5 SVR, 3 preload

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A positive signal-averaged ECG indicates that the patient
A) has had a heart attack.
B) is at increased risk of sudden cardiac death.
C) has no heart disease.
D) has no need for an electrophysiology study.
A) has had a heart attack.
B) is at increased risk of sudden cardiac death.
C) has no heart disease.
D) has no need for an electrophysiology study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The patient has an HR of 84 beats/min and an SV of 65 mL.Calculate the CO.
A) 149 mL
B) 500 mL
C) 4650 mL
D) 5460 mL
A) 149 mL
B) 500 mL
C) 4650 mL
D) 5460 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Zeroing the pressure transducer on hemodynamic monitoring equipment occurs when the displays reads
A) 0.
B) 250.
C) 600.
D) 760.
A) 0.
B) 250.
C) 600.
D) 760.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A patient becomes unresponsive.The patient's heart rate is 32 beats/min,idioventricular rhythm; blood pressure is 60/32 mm Hg; SpO? is 90%; and respiratory rate is 14 breaths/min.Which of the following interventions would the nurse do first?
A) Notify the physician and hang normal saline wide open.
B) Notify the physician and obtain the defibrillator.
C) Notify the physician and obtain a temporary pacemaker.
D) Notify the physician and obtain a 12-lead ECG.
A) Notify the physician and hang normal saline wide open.
B) Notify the physician and obtain the defibrillator.
C) Notify the physician and obtain a temporary pacemaker.
D) Notify the physician and obtain a 12-lead ECG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following AV blocks can be described as a gradually lengthening PR interval until ultimately the final P wave in the group fails to conduct?
A) First-degree AV block
B) Second-degree AV block, type I
C) Second-degree AV block, type II
D) Third-degree AV block
A) First-degree AV block
B) Second-degree AV block, type I
C) Second-degree AV block, type II
D) Third-degree AV block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is most often found in ventricular dysrhythmias?
A) Retrograde P waves
B) Wide QRS complexes
C) No P waves
D) An inverted T wave
A) Retrograde P waves
B) Wide QRS complexes
C) No P waves
D) An inverted T wave

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is the initial intervention in a patient with sinus tachycardia with the following vital signs: HR,136 beats/min; BP,102/60 mm Hg; RR,24 breaths/min; T,99.2° F; SpO?,94% on oxygen 2 L/min by nasal cannula?
A) Stat adenosine to decrease heart rate
B) Identification and correction of the cause of the increased heart rate
C) Sublingual nitroglycerine 0.4 mg
D) Lidocaine 75 mg IV push
A) Stat adenosine to decrease heart rate
B) Identification and correction of the cause of the increased heart rate
C) Sublingual nitroglycerine 0.4 mg
D) Lidocaine 75 mg IV push

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
New-onset atrial fibrillation can be serious for which of the following reasons?
A) It increases the risk of stroke and pulmonary embolism from atrial clots.
B) It increases the patient's risk of deep venous thrombosis.
C) It may increase cardiac output to dangerous levels.
D) It indicates that the patient is about to have an MI.
A) It increases the risk of stroke and pulmonary embolism from atrial clots.
B) It increases the patient's risk of deep venous thrombosis.
C) It may increase cardiac output to dangerous levels.
D) It indicates that the patient is about to have an MI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following expresses the correct order when working with an invasive pressure monitor?
A) Level the transducer, locate the phlebostatic axis, zero the transducer, and take the reading.
B) Locate the phlebostatic axis, level the transducer, zero the transducer, and take the reading.
C) Take the reading, level the transducer, locate the phlebostatic axis, and zero the transducer.
D) Locate the phlebostatic axis, zero the transducer, level the transducer, and take the reading.
A) Level the transducer, locate the phlebostatic axis, zero the transducer, and take the reading.
B) Locate the phlebostatic axis, level the transducer, zero the transducer, and take the reading.
C) Take the reading, level the transducer, locate the phlebostatic axis, and zero the transducer.
D) Locate the phlebostatic axis, zero the transducer, level the transducer, and take the reading.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The target INR range is
A) 1.0 to 2.0.
B) 1.5 to 3.0.
C) 1.5 to 2.5.
D) 2.0 to 3.0.
A) 1.0 to 2.0.
B) 1.5 to 3.0.
C) 1.5 to 2.5.
D) 2.0 to 3.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A patient presents with atrial flutter with an atrial rate of 280 beats/min and a ventricular rate of 70 beats/min.Which of the following best explains this discrepancy in rates?
A) The ventricles are too tired to respond to all the atrial signals.
B) The AV node does not conduct all the atrial signals to the ventricles.
C) Some of the atrial beats are blocked before reaching the AV node.
D) The ventricles are responding to a ventricular ectopic pacemaker.
A) The ventricles are too tired to respond to all the atrial signals.
B) The AV node does not conduct all the atrial signals to the ventricles.
C) Some of the atrial beats are blocked before reaching the AV node.
D) The ventricles are responding to a ventricular ectopic pacemaker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following has become the first-line hemodynamic assessment tool in the critical care unit?
A) Echocardiogram
B) ECG
C) Exercise stress test
D) 24-hour Holter monitor
A) Echocardiogram
B) ECG
C) Exercise stress test
D) 24-hour Holter monitor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The blood test used to standardize PT results among clinical laboratories worldwide is known as
A) aPTT.
B) ACT.
C) HDL.
D) INR.
A) aPTT.
B) ACT.
C) HDL.
D) INR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
On returning from the cardiac catheterization laboratory,the patient asks if he can get up in the chair.The most appropriate response would be
A) "You cannot get up because you may pass out."
B) "You cannot get up because you may start bleeding."
C) "You cannot get up because you may fall."
D) "You cannot get up until you urinate."
A) "You cannot get up because you may pass out."
B) "You cannot get up because you may start bleeding."
C) "You cannot get up because you may fall."
D) "You cannot get up until you urinate."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A patient's CVP reading suddenly increased from 10 to 48 mm Hg.His lungs are clear except for fine rales at the bases.Immediate response should be which of the following?
A) Nothing; this reading is still within normal limits.
B) Place a stat call into the physician.
C) Administer ordered prn Lasix.
D) Check the transducer level.
A) Nothing; this reading is still within normal limits.
B) Place a stat call into the physician.
C) Administer ordered prn Lasix.
D) Check the transducer level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
After an MI,a patient presents with an increasing frequency of PVCs.The patient's heart rate is 110 beats/min,and ECG indicates a sinus rhythm with up to five unifocal PVCs per minute.Which of the following should be done? The patient is alert and responsive and denies any chest pain or dyspnea.
A) Administer lidocaine 100 mg bolus IV push stat.
B) Administer Cardizem 20 mg IV push stat.
C) Notify the physician and monitor the patient closely.
D) Nothing; PVCs are expected in this patient.
A) Administer lidocaine 100 mg bolus IV push stat.
B) Administer Cardizem 20 mg IV push stat.
C) Notify the physician and monitor the patient closely.
D) Nothing; PVCs are expected in this patient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A 55-year-old patient is scheduled for a stress test.The patient's maximal predicted HR is estimated to be
A) 65 beats/min.
B) 155 beats/min.
C) 165 beats/min.
D) 265 beats/min.
A) 65 beats/min.
B) 155 beats/min.
C) 165 beats/min.
D) 265 beats/min.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Identify the rhythm. 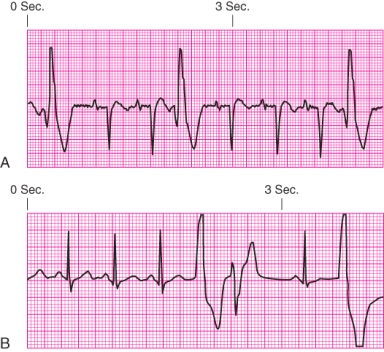
A) Junctional escape rhythm
B) Atrial fibrillation
C) Unifocal premature ventricular contractions
D) Ventricular tachycardia

A) Junctional escape rhythm
B) Atrial fibrillation
C) Unifocal premature ventricular contractions
D) Ventricular tachycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A patient's arterial line waveform has become damped.The nurse should
A) check for kinks, blood, and air bubbles in the tubing.
B) prepare for a normal saline fluid challenge for hypotension.
C) discontinue the arterial line.
D) check the patient's lung sounds.
A) check for kinks, blood, and air bubbles in the tubing.
B) prepare for a normal saline fluid challenge for hypotension.
C) discontinue the arterial line.
D) check the patient's lung sounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Identify the rhythm. 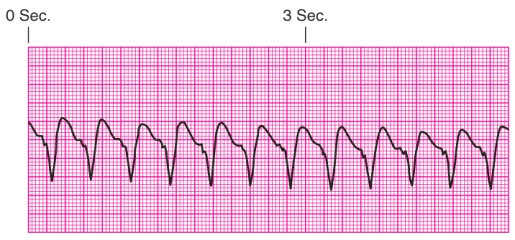
A) Junctional escape rhythm
B) Atrial fibrillation
C) Unifocal premature ventricular contractions
D) Ventricular tachycardia

A) Junctional escape rhythm
B) Atrial fibrillation
C) Unifocal premature ventricular contractions
D) Ventricular tachycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Identify the rhythm. 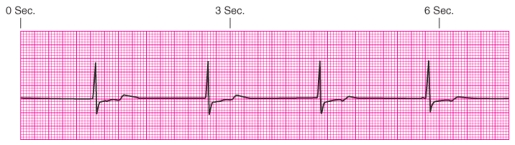
A) Junctional escape rhythm
B) Atrial fibrillation
C) Unifocal premature ventricular contractions
D) Ventricular tachycardia

A) Junctional escape rhythm
B) Atrial fibrillation
C) Unifocal premature ventricular contractions
D) Ventricular tachycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A patient is in shock.In this patient,
A) cuff pressures may be unreliable.
B) cuff pressures are more accurate than A-line pressures.
C) cuff pressures and A-line pressures should be nearly identical.
D) A-lines should not be inserted.
A) cuff pressures may be unreliable.
B) cuff pressures are more accurate than A-line pressures.
C) cuff pressures and A-line pressures should be nearly identical.
D) A-lines should not be inserted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is most indicative of decreased left ventricular preload?
A) Increased PAOP/PAWP
B) Decreased PAOP/PAWP
C) Increased CVP
D) Decreased CVP
A) Increased PAOP/PAWP
B) Decreased PAOP/PAWP
C) Increased CVP
D) Decreased CVP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Identify the rhythm. 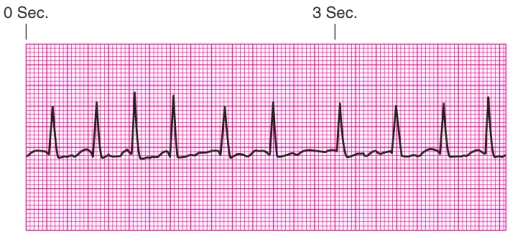
A) Junctional escape rhythm
B) Atrial fibrillation
C) Unifocal premature ventricular contractions
D) Ventricular tachycardia

A) Junctional escape rhythm
B) Atrial fibrillation
C) Unifocal premature ventricular contractions
D) Ventricular tachycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the noninvasive imaging technique which is useful in diagnosing complications of MI?
A) 12-lead ECG
B) CT
C) MRI
D) Echocardiography
A) 12-lead ECG
B) CT
C) MRI
D) Echocardiography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The patient's admitting 12-lead ECG shows wide,M-shaped P waves.Which of the following admitting diagnoses could be responsible for this finding?
A) Mitral stenosis
B) Chronic pulmonary disease
C) Hypotension
D) Pericarditis
A) Mitral stenosis
B) Chronic pulmonary disease
C) Hypotension
D) Pericarditis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following conditions can cause an artificial increase in the PAOP/PCWP?
A) Aortic regurgitation
B) Aortic stenosis
C) Mitral stenosis
D) Mitral regurgitation
A) Aortic regurgitation
B) Aortic stenosis
C) Mitral stenosis
D) Mitral regurgitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Identify the rhythm. 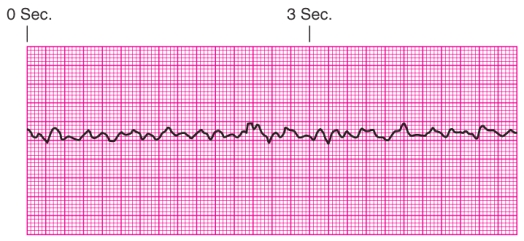
A) Ventricular tachycardia
B) Ventricular fibrillation
C) Supraventricular tachycardia
D) Torsades de pointes

A) Ventricular tachycardia
B) Ventricular fibrillation
C) Supraventricular tachycardia
D) Torsades de pointes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A 24-hour event monitor is commonly known as
A) a Holter monitor.
B) a transtelephonic monitor.
C) an external loop recorder.
D) a signal-averaged electrocardiogram.
A) a Holter monitor.
B) a transtelephonic monitor.
C) an external loop recorder.
D) a signal-averaged electrocardiogram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Increased preload
A) always increases cardiac output.
B) never increases cardiac output.
C) increases cardiac output in some cases.
D) has no relation to cardiac output.
A) always increases cardiac output.
B) never increases cardiac output.
C) increases cardiac output in some cases.
D) has no relation to cardiac output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
After bathing and repositioning a patient,the nurse notices the following readings on the bedside monitor: PAWP,20 mm Hg and PAP,28/12 mm Hg.Assessment notes no changes in patient condition.Which of the following statements would be true?
A) The patient may be having a silent MI.
B) The monitoring system is not functioning properly.
C) The patient is at increased risk for congestive heart failure.
D) The patient has pericardial tamponade.
A) The patient may be having a silent MI.
B) The monitoring system is not functioning properly.
C) The patient is at increased risk for congestive heart failure.
D) The patient has pericardial tamponade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



