Deck 16: Cardiovascular Therapeutic Management
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Cardiovascular Therapeutic Management
1
The rationale for administration of a fibrinolytic agent is
A) dilation of the blocked coronary artery.
B) anticoagulation to prevent formation of new emboli.
C) dissolution of atherosclerotic plaque at the site of blockage.
D) restoration of blood flow to the obstructed coronary artery via lysis of the thrombus.
A) dilation of the blocked coronary artery.
B) anticoagulation to prevent formation of new emboli.
C) dissolution of atherosclerotic plaque at the site of blockage.
D) restoration of blood flow to the obstructed coronary artery via lysis of the thrombus.
restoration of blood flow to the obstructed coronary artery via lysis of the thrombus.
2
A nurse is providing care to a patient on fibrinolytic therapy.Which of the following statements from the patient warrants further assessment and intervention by the critical care nurse?
A) "My back is killing me!"
B) "There is blood on my toothbrush!"
C) "Look at the bruises on my arms!"
D) "My arm is bleeding where my IV is!"
A) "My back is killing me!"
B) "There is blood on my toothbrush!"
C) "Look at the bruises on my arms!"
D) "My arm is bleeding where my IV is!"
"My back is killing me!"
3
Which of the following statements regarding beta-blockers is correct?
A) They increase heart rate and are contraindicated in tachydysrhythmias.
B) They result in bronchospasm and should not be used in patients with COPD.
C) They increase cardiac output and help with left ventricular failure.
D) They are helpful in increasing atrioventricular node conduction and are used in heart blocks.
A) They increase heart rate and are contraindicated in tachydysrhythmias.
B) They result in bronchospasm and should not be used in patients with COPD.
C) They increase cardiac output and help with left ventricular failure.
D) They are helpful in increasing atrioventricular node conduction and are used in heart blocks.
They result in bronchospasm and should not be used in patients with COPD.
4
In analyzing the ECG strip,the nurse notices a spike before each QRS complex.The patient's heart rate is 70 beats/min.This phenomenon is reflective of
A) 60-cycle electrical interference; check equipment.
B) pacing artifact; the pacemaker is sensing and capturing.
C) electrical artifact; the pacemaker is not sensing.
D) patient movement; check electrodes.
A) 60-cycle electrical interference; check equipment.
B) pacing artifact; the pacemaker is sensing and capturing.
C) electrical artifact; the pacemaker is not sensing.
D) patient movement; check electrodes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When an intra-aortic balloon is in place,it is essential for the nurse to frequently assess
A) for a pulse deficit.
B) peripheral pulses distal to the catheter insertion site.
C) bilateral blood pressures.
D) coronary artery perfusion.
A) for a pulse deficit.
B) peripheral pulses distal to the catheter insertion site.
C) bilateral blood pressures.
D) coronary artery perfusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A pacemaker is connected to an external temporary pulse generator.The sensitivity control
A) determines heart rate to muscle activity.
B) determines the milliamperes needed to achieve capture.
C) regulates the ability of the pacemaker to detect the heart's intrinsic electrical activity.
D) allows for selection of intervals between atria and ventricles.
A) determines heart rate to muscle activity.
B) determines the milliamperes needed to achieve capture.
C) regulates the ability of the pacemaker to detect the heart's intrinsic electrical activity.
D) allows for selection of intervals between atria and ventricles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following doses of dopamine (Intropin)results in stimulation of beta? receptors and increased myocardial contractility?
A) 1 mcg/kg/min
B) 5 mcg/kg/min
C) 15 mcg/kg/min
D) 20 mcg/kg/min
A) 1 mcg/kg/min
B) 5 mcg/kg/min
C) 15 mcg/kg/min
D) 20 mcg/kg/min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Adenosine (Adenocard)is an antidysrhythmic agent given primarily to
A) convert supraventricular tachycardias.
B) act as a second-line drug for premature ventricular contractions (PVCs).
C) treat AV blocks.
D) coarsen ventricular fibrillation so that defibrillation is effective.
A) convert supraventricular tachycardias.
B) act as a second-line drug for premature ventricular contractions (PVCs).
C) treat AV blocks.
D) coarsen ventricular fibrillation so that defibrillation is effective.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Noninvasive emergency pacing is best achieved via the use of which type of temporary pacing?
A) Transvenous (endocardial)
B) Epicardial
C) Transthoracic
D) Transcutaneous
A) Transvenous (endocardial)
B) Epicardial
C) Transthoracic
D) Transcutaneous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The mechanism of dilation with percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA)is
A) stretching of the vessel wall, resulting in fracture of the plaque.
B) anticoagulation after the completion of the procedure, enhancing dilation.
C) plaque removal after balloon inflation.
D) compression of plaque against the vessel wall.
A) stretching of the vessel wall, resulting in fracture of the plaque.
B) anticoagulation after the completion of the procedure, enhancing dilation.
C) plaque removal after balloon inflation.
D) compression of plaque against the vessel wall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following mechanisms is responsible for the augmentation of coronary arterial blood flow and increased myocardial oxygen supply seen with the intra-aortic balloon pump?
A) The vacuum created in the aorta as a result of balloon deflation
B) Diastolic inflation with retrograde perfusion
C) Forward flow to the peripheral circulation
D) Inflation during systole to augment blood pressure
A) The vacuum created in the aorta as a result of balloon deflation
B) Diastolic inflation with retrograde perfusion
C) Forward flow to the peripheral circulation
D) Inflation during systole to augment blood pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The possibility of microshock when handling a temporary pacemaker can be minimized by
A) decreasing the milliamperes.
B) wearing gloves.
C) positioning the patient on the left side.
D) wearing rubber-soled shoes.
A) decreasing the milliamperes.
B) wearing gloves.
C) positioning the patient on the left side.
D) wearing rubber-soled shoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A patient is admitted with left-sided heart failure and a blood pressure of 220/118 mm Hg.Which of the following drugs will be most effective in decreasing the blood pressure and reducing afterload?
A) Dopamine (Intropin)
B) Verapamil (Calan)
C) Propranolol (Inderal)
D) Sodium nitroprusside (Nipride)
A) Dopamine (Intropin)
B) Verapamil (Calan)
C) Propranolol (Inderal)
D) Sodium nitroprusside (Nipride)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A patient is being monitored by continuous ECG after placement of a transvenous pacemaker."Loss of capture" is seen on the ECG.Which nursing intervention may correct this situation?
A) Position the patient on the left side.
B) Decrease the milliamperes as ordered.
C) Increase the rate as ordered.
D) Monitor the patient in a different lead.
A) Position the patient on the left side.
B) Decrease the milliamperes as ordered.
C) Increase the rate as ordered.
D) Monitor the patient in a different lead.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A reliable indicator of reperfusion after fibrinolytic therapy is
A) dysrhythmias.
B) Q waves.
C) elevated ST segments.
D) a rapid decrease in serum CK levels.
A) dysrhythmias.
B) Q waves.
C) elevated ST segments.
D) a rapid decrease in serum CK levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A patient has an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)for chronic ventricular tachydysrhythmias.If the patient's rhythm deteriorates to ventricular fibrillation,
A) an external defibrillator will need to be applied.
B) start CPR and call a code.
C) the ICD will defibrillate at a high energy level.
D) the ICD is programmed to cardiovert at a high energy level.
A) an external defibrillator will need to be applied.
B) start CPR and call a code.
C) the ICD will defibrillate at a high energy level.
D) the ICD is programmed to cardiovert at a high energy level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A transvenous pacemaker is inserted through the right subclavian vein and threaded into the right ventricle.The pacemaker is placed on demand at a rate of 70.The pacing mode for this pacemaker is
A) VVI.
B) AOO.
C) DDD.
D) VAT.
A) VVI.
B) AOO.
C) DDD.
D) VAT.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The most common complication of fibrinolytic therapy is
A) reperfusion chest pain.
B) lethargy.
C) bleeding.
D) heart blocks.
A) reperfusion chest pain.
B) lethargy.
C) bleeding.
D) heart blocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In caring for a postoperative cardiovascular patient,the nurse knows that the most frequent cause of a decreased cardiac output is
A) reduced preload.
B) increased afterload.
C) increased contractility.
D) bradycardia.
A) reduced preload.
B) increased afterload.
C) increased contractility.
D) bradycardia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)inhibitors such as captopril (Capoten)and enalapril (Vasotec)decrease peripheral vascular resistance and decrease blood pressure by the mechanism of
A) direct arterial vasodilation.
B) blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II.
C) increased fluid excretion at the loop of Henle in the renal tubules.
D) peripheral vasoconstriction and central vasodilation.
A) direct arterial vasodilation.
B) blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II.
C) increased fluid excretion at the loop of Henle in the renal tubules.
D) peripheral vasoconstriction and central vasodilation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The predominant form of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)is
A) Rotablator.
B) stents.
C) directional coronary atherectomy (DCA).
D) balloon angioplasty (PTCA).
A) Rotablator.
B) stents.
C) directional coronary atherectomy (DCA).
D) balloon angioplasty (PTCA).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A patient is admitted to the ICU after a positive exercise treadmill test with a diagnosis of CAD and stable angina.Radiographic test show that the patient has blockage in the left main coronary artery and four other vessels.The nurse anticipates that the patient will be scheduled for
A) medical therapy antianginal medications.
B) PCI.
C) TAVR.
D) CABG.
A) medical therapy antianginal medications.
B) PCI.
C) TAVR.
D) CABG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A patient suddenly develops a wide QRS complex tachycardia.The patient's heart rate is 220 beats/min and regular; blood pressure is 96/40 mm Hg; and respiratory rate is 22 breaths/min,and the patient is awake without complaint except for palpitations.Which of the following interventions would be best to try first?
A) Adenosine 6 mg rapid IV push
B) Lidocaine 1 mg/kg IV push
C) Verapamil 0.5 mg IV push
D) Digoxin 0.25 mg IV push
A) Adenosine 6 mg rapid IV push
B) Lidocaine 1 mg/kg IV push
C) Verapamil 0.5 mg IV push
D) Digoxin 0.25 mg IV push

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Identify complications with the above rhythm strip. 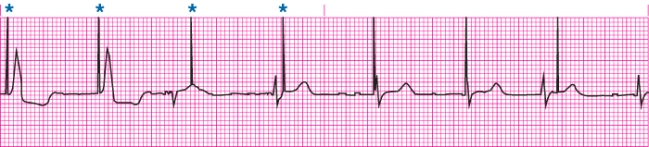
A) Undersensing from a pacemaker
B) Oversensing from a pacemaker
C) ICD firing caused by VF
D) Atrial pacing failure to capture

A) Undersensing from a pacemaker
B) Oversensing from a pacemaker
C) ICD firing caused by VF
D) Atrial pacing failure to capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The current standard of care for PCI typically includes dual antiplatelet therapy with oral
A) aspirin and Clopidogrel (Plavix).
B) aspirin and Abciximab (ReoPro).
C) aspirin and Eptifibatide (Integrilin).
D) aspirin and Tirofiban (Aggrastat).
A) aspirin and Clopidogrel (Plavix).
B) aspirin and Abciximab (ReoPro).
C) aspirin and Eptifibatide (Integrilin).
D) aspirin and Tirofiban (Aggrastat).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following patients would be a candidate for fibrinolytic therapy?
A) The patient's chest pain started 8 hours ago. She has a diagnosis of NSTEMI.
B) The patient's chest pain started 3 hours ago, and her ECG shows a new left bundle branch block.
C) The patient presents to the emergency department with chest pain of 30 minutes' duration. She has a history of cerebrovascular accident 1 month ago.
D) The patient has a history of unstable angina. He has been experiencing chest pain with sudden onset.
E) The patient's chest pain started 1 hour ago, and his ECG shows ST elevation.
A) The patient's chest pain started 8 hours ago. She has a diagnosis of NSTEMI.
B) The patient's chest pain started 3 hours ago, and her ECG shows a new left bundle branch block.
C) The patient presents to the emergency department with chest pain of 30 minutes' duration. She has a history of cerebrovascular accident 1 month ago.
D) The patient has a history of unstable angina. He has been experiencing chest pain with sudden onset.
E) The patient's chest pain started 1 hour ago, and his ECG shows ST elevation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Surgical repair of an AAA occurs when the aneurysm is
A) greater than 5 cm and asymptomatic.
B) greater than 5 cm and symptomatic.
C) greater than 7 cm and asymptomatic.
D) greater than 7 cm and symptomatic.
A) greater than 5 cm and asymptomatic.
B) greater than 5 cm and symptomatic.
C) greater than 7 cm and asymptomatic.
D) greater than 7 cm and symptomatic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which calcium channel blocker is easily titrated and beneficial in treating hypertension in patients with CAD or CVA?
A) Nifedipine (Procardia)
B) Nicardipine (Cardene)
C) Clevidipine (Cleviprex)
D) Diltiazem (Cardizem)
A) Nifedipine (Procardia)
B) Nicardipine (Cardene)
C) Clevidipine (Cleviprex)
D) Diltiazem (Cardizem)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A patient is diagnosed with third-degree heart failure.The nurse reviews the patient's medication list because the following classifications of drugs should be avoided with patients with heart failure.
A) NSAIDs
B) Antidysrhythmics
C) ACE inhibitors
D) Calcium channel blockers
E) Beta-blockers
A) NSAIDs
B) Antidysrhythmics
C) ACE inhibitors
D) Calcium channel blockers
E) Beta-blockers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Nursing interventions after angioplasty would include which of the following?
A) Elevating the head of the bed to 45 degrees
B) Hydration as a renal protection measure
C) Assessing pedal pulses on the involved limb every 15 minutes for the first 2 hours after the procedure
D) Monitoring the vascular hemostatic device for signs of bleeding
E) Educating the patient on the necessity of staying supine for 1 to 2 hours after the procedure
A) Elevating the head of the bed to 45 degrees
B) Hydration as a renal protection measure
C) Assessing pedal pulses on the involved limb every 15 minutes for the first 2 hours after the procedure
D) Monitoring the vascular hemostatic device for signs of bleeding
E) Educating the patient on the necessity of staying supine for 1 to 2 hours after the procedure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which anticoagulant(s)enhances activity of antithrombin III and does not require aPTT or ACT monitoring?
A) Heparin
B) Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
C) Bivalirudin (Angiomax)
D) Argatroban (Argatroban)
A) Heparin
B) Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
C) Bivalirudin (Angiomax)
D) Argatroban (Argatroban)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following would indicate successful reperfusion after administration of a fibrinolytic agent?
A) Gradual decrease in chest pain
B) Intermittent, multifocal premature ventricular contractions
C) Rapid resolution of ST elevation
D) Rapid rise in creatine kinase MB fraction
A) Gradual decrease in chest pain
B) Intermittent, multifocal premature ventricular contractions
C) Rapid resolution of ST elevation
D) Rapid rise in creatine kinase MB fraction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A patient returns to the ICU after a femorotibial bypass graft of the left leg.Identify the primary focus of nursing care immediately in the postprocedural assessment period.
A) Prevention of skin breakdown
B) Hourly intake and urinary output
C) Monitor for ST segment changes
D) Frequent pulse checks to the affected limb
A) Prevention of skin breakdown
B) Hourly intake and urinary output
C) Monitor for ST segment changes
D) Frequent pulse checks to the affected limb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Vasopressors are used cautiously with critical care patients because they can cause
A) vasoconstriction of the smooth muscles.
B) vasodilation of the smooth muscles.
C) increased afterload of the heart.
D) decreased preload of the heart.
A) vasoconstriction of the smooth muscles.
B) vasodilation of the smooth muscles.
C) increased afterload of the heart.
D) decreased preload of the heart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The patient is 12 hours postoperative for a CABG.The patient's vital signs include: T 103° F,HR 112,RR 22,BP 134/78 mm Hg,and O? sat 94% on 3L/NC.The nurse suspects that the patient has developed
A) infection and notifies the physician immediately.
B) infection, which is common postoperatively, and monitors the patient's condition.
C) cardiac tamponade and notifies the physician immediately.
D) delirium caused by the elevated temperature.
A) infection and notifies the physician immediately.
B) infection, which is common postoperatively, and monitors the patient's condition.
C) cardiac tamponade and notifies the physician immediately.
D) delirium caused by the elevated temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



