Deck 12: Ecology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Ecology
1
All ecosystems need energy.What is the originating source for most of the energy that powers ecosystems on this planet?
A) Geothermal energy
B) Wind energy
C) Solar energy
D) Potential energy
A) Geothermal energy
B) Wind energy
C) Solar energy
D) Potential energy
C
2
A community in ecology is defined as ________.
A) a group of organisms, all from the same species, and their surrounding environment
B) organisms from multiple species interacting in the same place
C) organisms from multiple species interacting in the same place, and their surrounding environment
D) the global ecosystem
A) a group of organisms, all from the same species, and their surrounding environment
B) organisms from multiple species interacting in the same place
C) organisms from multiple species interacting in the same place, and their surrounding environment
D) the global ecosystem
B
3
What is the difference between a community and an ecosystem?
A) A community and an ecosystem are the same thing in ecology.
B) A community includes abiotic factors, while an ecosystem does not.
C) A community includes interacting populations with their surrounding environment, while an ecosystem does not include the surrounding environment.
D) A community includes interacting populations without their surrounding environment, while an ecosystem includes the surrounding environment.
A) A community and an ecosystem are the same thing in ecology.
B) A community includes abiotic factors, while an ecosystem does not.
C) A community includes interacting populations with their surrounding environment, while an ecosystem does not include the surrounding environment.
D) A community includes interacting populations without their surrounding environment, while an ecosystem includes the surrounding environment.
C
4
Which of the following is not an example of an abiotic factor?
A) Temperature
B) Energy
C) Bacteria
D) Nutrients
A) Temperature
B) Energy
C) Bacteria
D) Nutrients

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A wolf eats a rabbit that eats grass.The wolf is a(n)________.
A) consumer
B) detritivore
C) producer
D) autotroph
A) consumer
B) detritivore
C) producer
D) autotroph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A wolf eats a rabbit that eats grass.The grass is a ________.
A) consumer
B) detritivore
C) producer
D) heterotroph
A) consumer
B) detritivore
C) producer
D) heterotroph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Ecology is a science that can be carried out by ________.
A) learning via discovery
B) having hypotheses that are then tested
C) both A and B
D) neither C nor D
A) learning via discovery
B) having hypotheses that are then tested
C) both A and B
D) neither C nor D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Imagine you were the manager of a national park with cheetahs.The cheetahs feed primarily on gazelles,while the gazelles eat grass.It takes an acre of grassland to feed one gazelle,and it takes ten gazelles to feed one cheetah.You have a maximum of ten cheetahs when the system is functioning optimally.You would like to increase the cheetah population because people pay money to see the cheetahs.How much grassland do you need to double the cheetah population supported by this grassland?
A) 500 acres
B) 200 acres
C) 100 acres
D) 10 acres
A) 500 acres
B) 200 acres
C) 100 acres
D) 10 acres

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Identify the biotic factor of an ecosystem among the following options.
A) Amount of nitrogen available for the moss to grow on cliffs
B) Nesting spots on the edge of a cliff that birds can use
C) Average wind forces that the cliffs withstand daily
D) Amount of moss available to the consumers
A) Amount of nitrogen available for the moss to grow on cliffs
B) Nesting spots on the edge of a cliff that birds can use
C) Average wind forces that the cliffs withstand daily
D) Amount of moss available to the consumers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An ecosystem is a collection of all the ________ in a given area.
A) abiotic factors
B) plants and animals
C) plants and climate
D) living and nonliving things
A) abiotic factors
B) plants and animals
C) plants and climate
D) living and nonliving things

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Phytoplankton is an example of a ________.
A) producer
B) consumer
C) herbivore
D) decomposer
A) producer
B) consumer
C) herbivore
D) decomposer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Ecology is best defined as the study of ________.
A) the relationships between parasites and their hosts
B) the interactions between living organisms and their environments
C) plant succession
D) interactions between predator and prey populations
A) the relationships between parasites and their hosts
B) the interactions between living organisms and their environments
C) plant succession
D) interactions between predator and prey populations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Environmentalism is ________.
A) the study of ecosystems
B) a philosophical and social movement concerned with preserving the environment
C) a collection of citizens and scientists working together to support research and preserve biodiversity
D) the study of how energy flows through an ecosystem
A) the study of ecosystems
B) a philosophical and social movement concerned with preserving the environment
C) a collection of citizens and scientists working together to support research and preserve biodiversity
D) the study of how energy flows through an ecosystem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A population in ecology is defined as ________.
A) a group of organisms, all from the same species
B) a group of organisms, some from the same species, some from other species
C) a group of organisms, some from the same species, some from other species, and their surrounding environment
D) one organism and its surrounding environment
A) a group of organisms, all from the same species
B) a group of organisms, some from the same species, some from other species
C) a group of organisms, some from the same species, some from other species, and their surrounding environment
D) one organism and its surrounding environment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
All living things need carbon.How does carbon enter the living portion of an ecosystem?
A) Atmospheric CO₂ taken in by photosynthesis
B) Atmospheric CO₂ taken in by soil bacteria
C) Elemental carbon taken in by plant roots
D) Elemental carbon taken in by plant leaves
A) Atmospheric CO₂ taken in by photosynthesis
B) Atmospheric CO₂ taken in by soil bacteria
C) Elemental carbon taken in by plant roots
D) Elemental carbon taken in by plant leaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Abiotic factors are ________.
A) living components of an ecosystem
B) nonliving components of an ecosystem
C) living and nonliving components of an ecosystem
D) None of the above
A) living components of an ecosystem
B) nonliving components of an ecosystem
C) living and nonliving components of an ecosystem
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is not an example of goods and services provided by the environment?
A) Raw materials for goods we use every day, such as wood
B) Water treatment
C) The control of erosion
D) All of the above are examples of goods and services provided by the environment.
A) Raw materials for goods we use every day, such as wood
B) Water treatment
C) The control of erosion
D) All of the above are examples of goods and services provided by the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
All of the following are abiotic factors within an ecosystem except ________.
A) energy
B) fire
C) nutrients
D) All of the above are abiotic factors.
A) energy
B) fire
C) nutrients
D) All of the above are abiotic factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
All living things need nitrogen.How does nitrogen enter the living portion of an ecosystem?
A) Atmospheric N₂ taken in by photosynthesis
B) Atmospheric N₂ taken in by soil bacteria
C) Elemental nitrogen taken in by plant roots
D) Elemental nitrogen taken in by plant leaves
A) Atmospheric N₂ taken in by photosynthesis
B) Atmospheric N₂ taken in by soil bacteria
C) Elemental nitrogen taken in by plant roots
D) Elemental nitrogen taken in by plant leaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Ecology and environmentalism are the same scientific discipline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If you put some water in a bucket and left it in your backyard, the water level would rise and fall over time with the weather. The table represents data collected from a bucket that was initially filled to the halfway mark with water. The water depth was measured on the first of the month for 2 years. Although the water never completely dried up, it also never overflowed during this time. Answer the following question(s) based on the data.
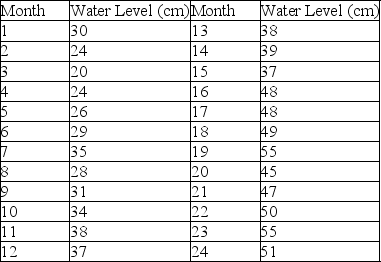
Which statement explains the general upward trend of the data over the 2-year time period?
A) Evaporation exceeded transpiration.
B) Transpiration exceeded precipitation.
C) Precipitation exceeded evaporation.
D) None of these statements explains the upward trend.

Which statement explains the general upward trend of the data over the 2-year time period?
A) Evaporation exceeded transpiration.
B) Transpiration exceeded precipitation.
C) Precipitation exceeded evaporation.
D) None of these statements explains the upward trend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Aquatic biomes cover most of the Earth's surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If you put some water in a bucket and left it in your backyard, the water level would rise and fall over time with the weather. The table represents data collected from a bucket that was initially filled to the halfway mark with water. The water depth was measured on the first of the month for 2 years. Although the water never completely dried up, it also never overflowed during this time. Answer the following question(s) based on the data.

What is the most likely expectation during the third year?
A) The water level will return to 30 cm.
B) The water will overflow the bucket or nearly so.
C) The water in the bucket will dry up.
D) None of these are indicated by the data.

What is the most likely expectation during the third year?
A) The water level will return to 30 cm.
B) The water will overflow the bucket or nearly so.
C) The water in the bucket will dry up.
D) None of these are indicated by the data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Of the biomes listed,which is best adapted to seasonal fires?
A) Coniferous forests
B) Tundra
C) Broadleaf forests
D) Chaparral
A) Coniferous forests
B) Tundra
C) Broadleaf forests
D) Chaparral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The distribution of terrestrial biomes on Earth depends mostly on ________.
A) temperature
B) rainfall
C) both temperature and rainfall
D) neither temperature nor rainfall; it depends on latitude and longitude
A) temperature
B) rainfall
C) both temperature and rainfall
D) neither temperature nor rainfall; it depends on latitude and longitude

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Aquatic biomes are defined primarily by ________.
A) the animals that live there
B) the plants that live there
C) their temperature
D) their salinity
A) the animals that live there
B) the plants that live there
C) their temperature
D) their salinity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The bird-rhino relationship is an example of ________.
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) predator-prey
D) commensalism
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) predator-prey
D) commensalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Where would a coral reef most likely be found?
A) In the oceanic benthic realm below the continental shelf
B) In an estuary
C) In the deep sea
D) In the oceanic photic zone
A) In the oceanic benthic realm below the continental shelf
B) In an estuary
C) In the deep sea
D) In the oceanic photic zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A biome characterized by warm,fairly dry climate that primarily contains grasses with scattered,isolated trees is a ________.
A) savanna
B) chaparral
C) tundra
D) temperate grasslands
A) savanna
B) chaparral
C) tundra
D) temperate grasslands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The bird-tick relationship is an example of ________.
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) predator-prey
D) commensalism
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) predator-prey
D) commensalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Although freshwater biomes cover less than 1% of the Earth's surface,they are important because ________.
A) we depend on them for drinking water
B) they are home to lots of species
C) they are the source of our irrigation for agriculture
D) All of the above are reasons why freshwater biomes are important.
A) we depend on them for drinking water
B) they are home to lots of species
C) they are the source of our irrigation for agriculture
D) All of the above are reasons why freshwater biomes are important.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How might the removal of a wetland affect a nearby city?
A) Wetlands cause flooding.
B) Wetlands reduce flooding.
C) Wetlands reduce water quality.
D) Wetlands support a rich supply of nutrients.
A) Wetlands cause flooding.
B) Wetlands reduce flooding.
C) Wetlands reduce water quality.
D) Wetlands support a rich supply of nutrients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Why is an estuary considered an intermediate biome?
A) It is the transition zone between freshwater and saltwater biomes.
B) It is intermediate in size, smaller than the largest biomes but larger than the smallest biomes.
C) It will seasonally dry up and cease to be a biome.
D) It is only a biome during high tide.
A) It is the transition zone between freshwater and saltwater biomes.
B) It is intermediate in size, smaller than the largest biomes but larger than the smallest biomes.
C) It will seasonally dry up and cease to be a biome.
D) It is only a biome during high tide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The tick-rhino relationship is an example of ________.
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) predator-prey
D) commensalism
A) parasitism
B) mutualism
C) predator-prey
D) commensalism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Terrestrial biomes are defined in a large part by ________.
A) the animals that live there
B) the plants that live there
C) the altitude
D) the longitude
A) the animals that live there
B) the plants that live there
C) the altitude
D) the longitude

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The processes of chemical cycling would be studied mainly by ________.
A) an environmentalist
B) a community ecologist
C) a population ecologist
D) an ecosystem ecologist
A) an environmentalist
B) a community ecologist
C) a population ecologist
D) an ecosystem ecologist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The tendency of toxins to accumulate in top predators is called biological ________.
A) magnification
B) remediation
C) mitigation
D) concentration
A) magnification
B) remediation
C) mitigation
D) concentration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which principle states that no two species competing for the exact same resources can coexist?
A) Complex community network principle
B) Resource partitioning principle
C) Dominance species principle
D) Competitive exclusion principle
A) Complex community network principle
B) Resource partitioning principle
C) Dominance species principle
D) Competitive exclusion principle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which month was the wettest? (Remember that the readings are taken at the first of each month.)
A) Month 19
B) Month 16
C) Month 22
D) Month 15
A) Month 19
B) Month 16
C) Month 22
D) Month 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Species diversity is highest when ________.
A) species richness is high and relative abundance is unevenly distributed
B) species richness is low and relative abundance is unevenly distributed
C) species richness is high and relative abundance is evenly distributed
D) species richness is low and relative abundance is evenly distributed
A) species richness is high and relative abundance is unevenly distributed
B) species richness is low and relative abundance is unevenly distributed
C) species richness is high and relative abundance is evenly distributed
D) species richness is low and relative abundance is evenly distributed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which is the dominant greenhouse gas leading to global warming?
A) CH₄
B) H₂O
C) NO₂
D) CO₂
A) CH₄
B) H₂O
C) NO₂
D) CO₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What type of species,if removed from the community,could lead to the collapse of the entire community?
A) Endemic species
B) Keystone species
C) Indicator species
D) Flagship species
A) Endemic species
B) Keystone species
C) Indicator species
D) Flagship species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Asian kudzu bug (Megacopta cribaria)arrived in Atlanta in 2009 and is quickly spreading across the South.In addition to eating kudzu,it also eats soybeans and can decimate entire crops.The kudzu bug is a type of ________ species.
A) control
B) keystone
C) umbrella
D) invasive
A) control
B) keystone
C) umbrella
D) invasive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the term used to describe relatively small areas with unusually high concentrations of species found there and nowhere else,including many species in high risk of extinction? These areas receive the focus of global conservation efforts.
A) Natural wildlife reserve
B) Biodiversity hot spot
C) Protective wilderness refuge
D) Protective conservation zone
A) Natural wildlife reserve
B) Biodiversity hot spot
C) Protective wilderness refuge
D) Protective conservation zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What category describes a species that,while not presently at risk of extinction,could likely be at risk of extinction in the near future?
A) An endangered species
B) A species of concern
C) A threatened species
D) An endemic species
A) An endangered species
B) A species of concern
C) A threatened species
D) An endemic species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The responsible management (use and conservation)of the earth's resources indefinitely is called ________.
A) the maximum sustainable yield
B) landscape ecology
C) an environmental conservation trust
D) sustainable development
A) the maximum sustainable yield
B) landscape ecology
C) an environmental conservation trust
D) sustainable development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An age pyramid with a broad base that quickly slopes up to a narrow top would be indicative of ________.
A) an industrialized nation
B) a developing nation
C) a population with a high average age
D) a population with a low survivorship of children
A) an industrialized nation
B) a developing nation
C) a population with a high average age
D) a population with a low survivorship of children

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The use of multiple forms of pest control including biological,chemical,and the planting of pest-resistant crops is a strategy commonly called ________.
A) intermediate species control
B) integrated pest management
C) multilevel systems approach
D) none of the above
A) intermediate species control
B) integrated pest management
C) multilevel systems approach
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A sudden natural catastrophe resulting in massive die-offs would be categorized as a density-________ limiting factor.
A) independent
B) dependent
C) reliant
D) autonomous
A) independent
B) dependent
C) reliant
D) autonomous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
There have been several mass extinctions in the planet's history,such as the extinction of the dinosaurs,but the current mass extinction is different.Greater numbers of species are now going extinct faster than ever before.Also unique to the current mass extinction is the cause.What is causing the current mass extinction?
A) Man's direct activities
B) Climate change
C) Rising sea levels
D) Solar flares
A) Man's direct activities
B) Climate change
C) Rising sea levels
D) Solar flares

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Human birth rate peaked in the 1980s and has been slowly declining ever since.How is this expected to affect our population size over the next several decades?
A) The human population size will begin to decline.
B) The human population size will continue to increase, but not as fast as before.
C) The human population size will level off.
D) The human population size will continue to increase at the same rate it has for the past 100 years.
A) The human population size will begin to decline.
B) The human population size will continue to increase, but not as fast as before.
C) The human population size will level off.
D) The human population size will continue to increase at the same rate it has for the past 100 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
How does an increase in atmospheric greenhouse gases increase global temperatures?
A) By preventing some of the heat from escaping the planet's surface
B) By decreasing the ozone layer in the atmosphere
C) By increasing the amount of heat from the sun that reaches the planet's surface
D) By reacting with each other
A) By preventing some of the heat from escaping the planet's surface
B) By decreasing the ozone layer in the atmosphere
C) By increasing the amount of heat from the sun that reaches the planet's surface
D) By reacting with each other

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What can a human population's age pyramid tell you about current and future needs?
A) How many schools to build or to close down
B) How many workers will be needed to support retirees
C) Neither of these
D) Both of these
A) How many schools to build or to close down
B) How many workers will be needed to support retirees
C) Neither of these
D) Both of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A dispersion pattern refers to ________.
A) the density of organisms in a habitat
B) the extinction rates of a species
C) the spacing of organism throughout a habitat
D) the diversity of species found in a habitat
A) the density of organisms in a habitat
B) the extinction rates of a species
C) the spacing of organism throughout a habitat
D) the diversity of species found in a habitat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What are the main causes of biodiversity loss?
A) Habitat destruction, overharvesting, and invasive species
B) Invasive species, pollution, and climate change
C) Habitat destruction, invasive species, and climate change
D) Habitat destruction, overharvesting, invasive species, pollution, and climate change
A) Habitat destruction, overharvesting, and invasive species
B) Invasive species, pollution, and climate change
C) Habitat destruction, invasive species, and climate change
D) Habitat destruction, overharvesting, invasive species, pollution, and climate change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which growth model would you expect to see in a stable population?
A) Logistic
B) Speculative
C) Factorial
D) Exponential
A) Logistic
B) Speculative
C) Factorial
D) Exponential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Using sunflower plants to naturally remove heavy toxins from contaminated soil is an example of ________.
A) land conservancy
B) bioremediation
C) the green revolution
D) biomagnification
A) land conservancy
B) bioremediation
C) the green revolution
D) biomagnification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The buildup of soil on bare rock by the decomposition of early colonizers is characteristic of ________ succession.
A) primary
B) ecological
C) opportunistic
D) secondary
A) primary
B) ecological
C) opportunistic
D) secondary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the name of the model of maximum rate of population growth?
A) Logistic
B) Speculative
C) Factorial
D) Exponential
A) Logistic
B) Speculative
C) Factorial
D) Exponential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
At what level is biodiversity often studied and measured?
A) The diversity of genes in a population
B) The diversity of species in a community
C) The diversity of ecosystems on the planet
D) All of the above
A) The diversity of genes in a population
B) The diversity of species in a community
C) The diversity of ecosystems on the planet
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Describe two ways (immediate and long term)in which burning a forest leads to an increase in atmospheric greenhouse gases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Why do some nonnative species spread so quickly and inflict so much devastation when introduced to a new area?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Imagine a hypothetical population of elephants and rabbits in which both species remain at carrying capacity over many generations.Who would have more offspring that survive to be adults and reproduce during their lifetime,a mating pair of elephants or a mating pair of rabbits? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Some species require a large and diverse range.Although it may not significantly decrease the overall size of the range,how might fragmenting the range with a freeway or neighborhood lead to the extinction of the entire population,even if sufficient food is available in either region to sustain two smaller populations? Suggest a compromise that would allow the population to survive and allow for the road project or neighborhood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Disturbances to an ecosystem,such as fires and floods,are often seen as negative.Describe a situation where regular disturbances are not only beneficial but are also required to sustain the ecosystem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The practice of "eating down the food chain" refers to eating more plant material and less herbivores.Explain how this is a more efficient use of energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



