Deck 4: Marine Sediments
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Marine Sediments
1
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
oolites
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
oolites
Answers: B
2
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
metal sulfides
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
metal sulfides
Answers: B
3
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
stromatolites
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
stromatolites
Answers: D
4
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)depth at which calcium carbonate begins to dissolve
B)microscopic biogenous sediment
C)associated with submarine canyons and deep-sea alluvial fans
D)depth at which all calcium carbonate is in solution (i.e. dissolved)
E)associated with glacial deposits
F)particle size classification
ice rafting
A)depth at which calcium carbonate begins to dissolve
B)microscopic biogenous sediment
C)associated with submarine canyons and deep-sea alluvial fans
D)depth at which all calcium carbonate is in solution (i.e. dissolved)
E)associated with glacial deposits
F)particle size classification
ice rafting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
manganese nodules
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
manganese nodules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
tektites
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
tektites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A glacial deposit is well sorted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
coccolithophores
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
coccolithophores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
diatomaceous ooze
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
diatomaceous ooze

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)depth at which calcium carbonate begins to dissolve
B)microscopic biogenous sediment
C)associated with submarine canyons and deep-sea alluvial fans
D)depth at which all calcium carbonate is in solution (i.e. dissolved)
E)associated with glacial deposits
F)particle size classification
Wentworth Scale
A)depth at which calcium carbonate begins to dissolve
B)microscopic biogenous sediment
C)associated with submarine canyons and deep-sea alluvial fans
D)depth at which all calcium carbonate is in solution (i.e. dissolved)
E)associated with glacial deposits
F)particle size classification
Wentworth Scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)depth at which calcium carbonate begins to dissolve
B)microscopic biogenous sediment
C)associated with submarine canyons and deep-sea alluvial fans
D)depth at which all calcium carbonate is in solution (i.e. dissolved)
E)associated with glacial deposits
F)particle size classification
lysocline
A)depth at which calcium carbonate begins to dissolve
B)microscopic biogenous sediment
C)associated with submarine canyons and deep-sea alluvial fans
D)depth at which all calcium carbonate is in solution (i.e. dissolved)
E)associated with glacial deposits
F)particle size classification
lysocline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
siliceous ooze
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
siliceous ooze

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)depth at which calcium carbonate begins to dissolve
B)microscopic biogenous sediment
C)associated with submarine canyons and deep-sea alluvial fans
D)depth at which all calcium carbonate is in solution (i.e. dissolved)
E)associated with glacial deposits
F)particle size classification
turbidite
A)depth at which calcium carbonate begins to dissolve
B)microscopic biogenous sediment
C)associated with submarine canyons and deep-sea alluvial fans
D)depth at which all calcium carbonate is in solution (i.e. dissolved)
E)associated with glacial deposits
F)particle size classification
turbidite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Coastal sand dunes are usually well sorted due to winds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)depth at which calcium carbonate begins to dissolve
B)microscopic biogenous sediment
C)associated with submarine canyons and deep-sea alluvial fans
D)depth at which all calcium carbonate is in solution (i.e. dissolved)
E)associated with glacial deposits
F)particle size classification
CCD
A)depth at which calcium carbonate begins to dissolve
B)microscopic biogenous sediment
C)associated with submarine canyons and deep-sea alluvial fans
D)depth at which all calcium carbonate is in solution (i.e. dissolved)
E)associated with glacial deposits
F)particle size classification
CCD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
halite
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
halite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Match the term or person with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
abyssal clay
A)cosmogenous sediment
B)hydrogenous sediment
C)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment
D)biogenous sediment
abyssal clay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Texture refers to the size and shape of sediment particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Wentworth scale is used to arrange the amount of sorting in a sediment deposit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Sediments derived from weathered rock and volcanic activities are called biogenous sediments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following contains calcium carbonate (CaCO₃)?
A)diatoms
B)foraminiferans
C)glauconite
D)phosphorites
E)radiolarians
A)diatoms
B)foraminiferans
C)glauconite
D)phosphorites
E)radiolarians

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Calcareous shells will not accumulate on the ocean floor when the water depth exceeds about 4,500 meters (around 15,000 feet).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Phosphate nodules are found on the continental shelf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following contains silica (SiO₂)?
A)coccolithophores
B)corals
C)foraminiferans
D)phosphorites
E)radiolarians
A)coccolithophores
B)corals
C)foraminiferans
D)phosphorites
E)radiolarians

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Tektites are glassy rock fragments created during impact events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
All of the following are lithogenous sediments except:
A)beach sand.
B)diatom ooze.
C)glacial deposits.
D)clays.
E)volcanic particles.
A)beach sand.
B)diatom ooze.
C)glacial deposits.
D)clays.
E)volcanic particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The deposition of radiolarian oozes is affected by the carbonate compensation depth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The organisms that contribute to biogenous sediment are chiefly algae and protozoans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Calcium carbonate, phosphates, and manganese may precipitate out of solution to form deposits on the ocean floor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Sediments derived from pre-existing rocks on land are called:
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)lithogenous.
E)volcanogenic.
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)lithogenous.
E)volcanogenic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The four main classifications of marine sediment include:
A)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment.
B)biogenous sediment.
C)hydrogenous sediment.
D)cosmogenous sediment.
E)All of the above.
A)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment.
B)biogenous sediment.
C)hydrogenous sediment.
D)cosmogenous sediment.
E)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Radiolarian oozes typically form near the equator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Sediments that are poorly sorted were most likely deposited by:
A)a glacier.
B)a river delta.
C)organisms
D)a volcanic eruption.
E)the wind.
A)a glacier.
B)a river delta.
C)organisms
D)a volcanic eruption.
E)the wind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Sediment that begins as rocks on continents or islands is called:
A)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment.
B)biogenous sediment.
C)hydrogenous sediment.
D)cosmogenous sediment.
E)All of the above.
A)lithogenous (terrigenous)sediment.
B)biogenous sediment.
C)hydrogenous sediment.
D)cosmogenous sediment.
E)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Macroscopic biogenous sediment is the most abundant biogenous sediment in the marine environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Calcium carbonate is most likely to dissolve in water with which characteristics?
A)low carbon dioxide and warmer temperatures
B)lots of carbon dioxide and colder temperatures
C)lots of carbon dioxide and warmer temperatures
D)low pressure and warmer temperatures
E)low pressure and colder temperatures
A)low carbon dioxide and warmer temperatures
B)lots of carbon dioxide and colder temperatures
C)lots of carbon dioxide and warmer temperatures
D)low pressure and warmer temperatures
E)low pressure and colder temperatures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Sediments produced by plants and animals in the sea are called:
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)terrigenous.
E)volcanogenic.
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)terrigenous.
E)volcanogenic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
High-energy environments are most likely to deposit which one of the following?
A)clay-sized particles
B)cosmogenous sediments
C)large particles such as gravel
D)manganese nodules
E)silt-sized particles
A)clay-sized particles
B)cosmogenous sediments
C)large particles such as gravel
D)manganese nodules
E)silt-sized particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Calcareous ooze is found in cooler waters at depth around the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Organisms that live on the ocean floor may be responsible for keeping manganese nodules from being buried in the sediment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Phosphate-rich nodules form in:
A)continental shelf waters.
B)estuaries.
C)hydrothermal vent areas.
D)intermediate to shallow depth water.
E)mid-ocean ridges.
A)continental shelf waters.
B)estuaries.
C)hydrothermal vent areas.
D)intermediate to shallow depth water.
E)mid-ocean ridges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Manganese nodules are an example of:
A)biogenous sediments.
B)cosmogenous sediments.
C)hydrogenous sediments.
D)terrigenous sediments.
E)volcagenic sediments.
A)biogenous sediments.
B)cosmogenous sediments.
C)hydrogenous sediments.
D)terrigenous sediments.
E)volcagenic sediments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
All of the following statements are true of ocean sediments except:
A)ocean sediments are thickest in pelagic waters overlying the oceanic ridges.
B)ocean sediments can include the fossilized remains of ancient marine life.
C)ocean sediments may form from the remains of living organisms falling to the ocean floor.
D)ocean sediments include the remains of ancient rocks of cosmic origin.
E)ocean sediments may be composed of chemical precipitates such as calcium carbonate or manganese dioxide.
A)ocean sediments are thickest in pelagic waters overlying the oceanic ridges.
B)ocean sediments can include the fossilized remains of ancient marine life.
C)ocean sediments may form from the remains of living organisms falling to the ocean floor.
D)ocean sediments include the remains of ancient rocks of cosmic origin.
E)ocean sediments may be composed of chemical precipitates such as calcium carbonate or manganese dioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
All of the following are hydrogenous sediments except:
A)evaporites.
B)halites.
C)manganese nodule.
D)phosphates.
E)stromatolites.
A)evaporites.
B)halites.
C)manganese nodule.
D)phosphates.
E)stromatolites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Sediments produced because of chemical reactions in seawater are called:
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)lithogenous.
E)volcanogenic.
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)lithogenous.
E)volcanogenic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The particles found in some sediment that suggests that an extraterrestrial impact event are:
A)tektites.
B)oozes.
C)clays.
D)silt.
E)evaporites.
A)tektites.
B)oozes.
C)clays.
D)silt.
E)evaporites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In general, polar neritic sediment tends to have more:
A)clay than in temperate waters.
B)coral debris than in tropical waters.
C)gravel than in tropical waters.
D)shell fragments than in temperate waters.
E)silt and sand than in tropical waters.
A)clay than in temperate waters.
B)coral debris than in tropical waters.
C)gravel than in tropical waters.
D)shell fragments than in temperate waters.
E)silt and sand than in tropical waters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Ocean sediments provide all of the following mineral resources except:
A)coal.
B)clathrates.
C)manganese nodules.
D)methane hydrates.
E)petroleum.
A)coal.
B)clathrates.
C)manganese nodules.
D)methane hydrates.
E)petroleum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
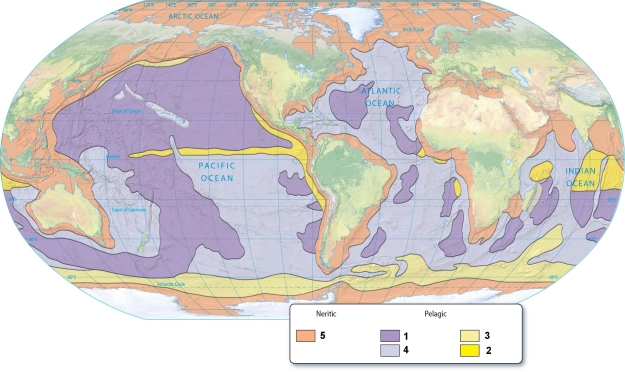
Calcareous oozes are represented by the number(s):
A)1)
B)2)
C)4)
D)2 & 3.
E)3 & 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Pelagic clays contain lots of material that settles to the seafloor through the water column and are:
A)less than 30% biogenous material.
B)more than 30% biogenous material.
C)more than 30% hydrogenous material.
D)less than 30% neritic material.
E)more than 30% neritic material.
A)less than 30% biogenous material.
B)more than 30% biogenous material.
C)more than 30% hydrogenous material.
D)less than 30% neritic material.
E)more than 30% neritic material.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The most likely place to find abundant manganese nodules is on the:
A)abyssal plain far from a continent.
B)continental rise.
C)continental shelf.
D)crest of a mid-ocean ridge.
E)All of the above locations contain manganese nodules.
A)abyssal plain far from a continent.
B)continental rise.
C)continental shelf.
D)crest of a mid-ocean ridge.
E)All of the above locations contain manganese nodules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Cosmogenous sediment consists of two main types of sediment:
A)microscopic spherules and macroscopic meteor debris.
B)microscopic spherules and abyssal clays.
C)biogenous oozes and macroscopic meteor debris.
D)abyssal clays and evaporites.
E)biogenous oozes and evaporites.
A)microscopic spherules and macroscopic meteor debris.
B)microscopic spherules and abyssal clays.
C)biogenous oozes and macroscopic meteor debris.
D)abyssal clays and evaporites.
E)biogenous oozes and evaporites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
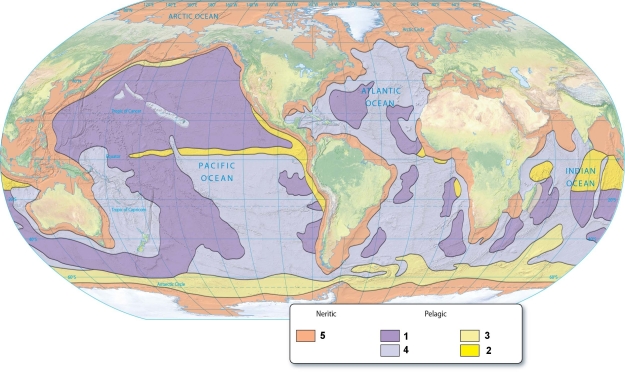
The sediments that are produced in areas of high primary productivity are indicated by the number(s):
A)1)
B)2)
C)3)
D)2 & 3.
E)3 & 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Sediments with an extraterrestrial origin are called:
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)lithogenous.
E)volcanogenic.
A)cosmogenous.
B)biogenous.
C)hydrogenous.
D)lithogenous.
E)volcanogenic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The type of marine sediment that forms the thickest deposits worldwide is:
A)abyssal clay deposits.
B)manganese nodule deposits.
C)neritic, lithogenous sediment deposits.
D)neritic siliceous sediment deposits.
E)pelagic biogenous calcareous deposits.
A)abyssal clay deposits.
B)manganese nodule deposits.
C)neritic, lithogenous sediment deposits.
D)neritic siliceous sediment deposits.
E)pelagic biogenous calcareous deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
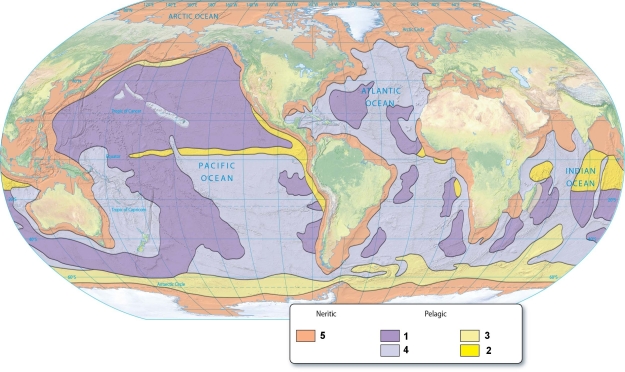
Biogenous sediments are indicated by the number(s):
A)1)
B)2 & 3.
C)2 & 4.
D)2, 3, & 4.
E)2, 3, 4, & 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is not an important control on oceanic sediment accumulation?
A)degree of preservation
B)dilution
C)input from other sediment types
D)rate of deposition
E)All of the above factors are important.
A)degree of preservation
B)dilution
C)input from other sediment types
D)rate of deposition
E)All of the above factors are important.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A very important way to increase the settling rate of fine particles in the open ocean is via:
A)carbonate dissolution.
B)deposit feeders.
C)fecal pellets.
D)precipitation.
E)wind.
A)carbonate dissolution.
B)deposit feeders.
C)fecal pellets.
D)precipitation.
E)wind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Sediments found on continental margins are called:
A)continental.
B)estuarine.
C)neritic.
D)oceanic.
E)pelagic.
A)continental.
B)estuarine.
C)neritic.
D)oceanic.
E)pelagic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
All of the following are true concerning neritic sediment deposits except:
A)they may contain coarse-grained sand and rock fragments in the sediments.
B)they may contain sediments of lithogenous origin.
C)they may contain sediments transported from rivers onto the continental shelf.
D)they may form in shallow coastal waters.
E)they are primarily composed of calcareous deposits of biological origin.
A)they may contain coarse-grained sand and rock fragments in the sediments.
B)they may contain sediments of lithogenous origin.
C)they may contain sediments transported from rivers onto the continental shelf.
D)they may form in shallow coastal waters.
E)they are primarily composed of calcareous deposits of biological origin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. halite and other salts
B) manganese nodules
C) metal sulfides
D) phosphates
E) tektites
A. halite and other salts
B) manganese nodules
C) metal sulfides
D) phosphates
E) tektites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Compare and contrast neritic and pelagic sediment deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63

Compare and contrast marine environments that favor the deposition of siliceous and calcareous oozes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. chalk
B) coccolithophores
C) diatoms
D) limestone
E) stromatolites
A. chalk
B) coccolithophores
C) diatoms
D) limestone
E) stromatolites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Discuss the sources of biogenous sediments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. coccolithophores
B) diatoms
C) foraminiferans
D) oolites
E) radiolarians
A. coccolithophores
B) diatoms
C) foraminiferans
D) oolites
E) radiolarians

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. siliceous ooze
B) quartz sand
C) rock fragments
D) clay
E) volcanic ash
A. siliceous ooze
B) quartz sand
C) rock fragments
D) clay
E) volcanic ash

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
List and describe the four types of marine sediments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
How does the analysis of marine sediments provide information about the climate of the ancient Earth?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
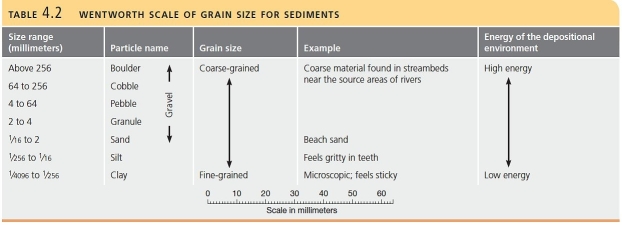
List the particle names and corresponding grain size, from smallest to largest, using the Wentworth scale of grain size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
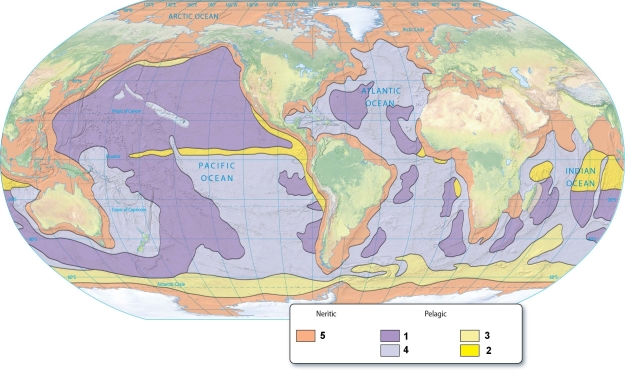
Compare and contrast how neritic and pelagic sediment deposits are distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. biogenous
B) calcareous
C) cosmogenous
D) hydrogenous
E) lithogenous
A. biogenous
B) calcareous
C) cosmogenous
D) hydrogenous
E) lithogenous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
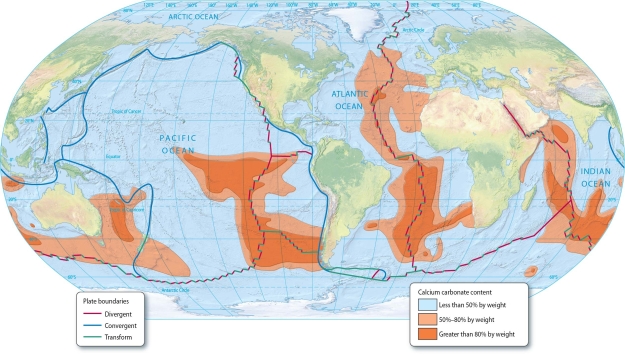
How is the carbonate compensation depth (CCD)related to the worldwide distribution of calcareous oozes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. glaciers
B) rivers
C) siliceous ooze
D) turbidity currents
E) volcanic ash
A. glaciers
B) rivers
C) siliceous ooze
D) turbidity currents
E) volcanic ash

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Create a table detailing the four types of marine sediments and their source (parent)material.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



