Deck 19: Coevolution
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/26
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Coevolution
1
Why do we distinguish between inter- and intraspecific mutualism?
A)This distinction is for historical reasons only.
B)Mutualistic partners in the same species are part of the same gene pool, but this is not the case for intraspecific mutualisms.
C)The mutualistic partners do not benefit equally in interspecific mutualism.
D)Only intraspecific mutualism gives the opportunity for cheating.
A)This distinction is for historical reasons only.
B)Mutualistic partners in the same species are part of the same gene pool, but this is not the case for intraspecific mutualisms.
C)The mutualistic partners do not benefit equally in interspecific mutualism.
D)Only intraspecific mutualism gives the opportunity for cheating.
B
2
Provide one likely cost and one likely benefit for each of the mutualistic partners in the Iridomyrmex ant and imperial blue butterfly caterpillar relationship.
A.Benefit for ants:
B.Cost for ants:
C.Benefit for caterpillars:
D.Cost for caterpillar:
A.Benefit for ants:
B.Cost for ants:
C.Benefit for caterpillars:
D.Cost for caterpillar:
A)Food from caterpillar secretion; B)Risk of predation/parasitism when defending caterpillars; C)Protection from predation/parasitism; D)Fitness loss due to providing food secretion for ants
3
The apple host race (or biotype)of the Rhagoletis pomonella fruit flies evolved after apples were colonized by individuals of R.pomonella's hawthorn race (hawthorn is the original host of R.pomonella).If the two R.pomonella races become two different species over time,would this represent an example for cospeciation? Briefly justify your answer.
No,R.pomonella switched hosts and did not speciate when its host speciated.
4
Assume that the transmission of antibiotic-producing bacteria that live as mutualists with leaf cutter ants is strictly vertical (i.e.,bacteria are only transmitted from queens to their offspring).What would you expect the topology of a phylogeny for the bacteria to look like relative to the phylogeny of their ant partners?
A)The topologies should not correspond more than would be expected under a random model.
B)The topologies should closely correspond to one another.
C)The topologies should correspond less than would be expected under a random model.
D)Deep nodes will correspond, but not nodes that are located toward the tips of the tree.
A)The topologies should not correspond more than would be expected under a random model.
B)The topologies should closely correspond to one another.
C)The topologies should correspond less than would be expected under a random model.
D)Deep nodes will correspond, but not nodes that are located toward the tips of the tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following differs between intra- and interspecific interactions when it comes to the evolution and maintenance of cooperation?
A)Interacting partners from different species are not linked by inclusive fitness.
B)We cannot apply game theory to interspecific systems.
C)Cooperative interactions cannot shift into antagonistic ones in intraspecific systems.
D)All of the above
A)Interacting partners from different species are not linked by inclusive fitness.
B)We cannot apply game theory to interspecific systems.
C)Cooperative interactions cannot shift into antagonistic ones in intraspecific systems.
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When researchers examined the effects of withholding nitrogen from Bradyrhizobium japonicum,they used a "split root" treatment in which half of a soybean plant's root mass received gaseous nitrogen,whereas the other half did not.Why did the researchers use this split root treatment?
A)They were economizing on experimental soybean plants.
B)They were testing whether different parts of the root react differently to the absence of nitrogen.
C)They were testing the range of nitrogen in which soybean plants can thrive.
D)They were testing whether the potential "retaliation" against cheating symbionts was specific to root nodules that did not fix nitrogen.
A)They were economizing on experimental soybean plants.
B)They were testing whether different parts of the root react differently to the absence of nitrogen.
C)They were testing the range of nitrogen in which soybean plants can thrive.
D)They were testing whether the potential "retaliation" against cheating symbionts was specific to root nodules that did not fix nitrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Is there an alternative (genetic)explanation to cultural evolution for the correlation in songs of Darwin finches and their sons and grandsons? (The units on the x- and y-axes summarize multiple components of the finches' songs.) 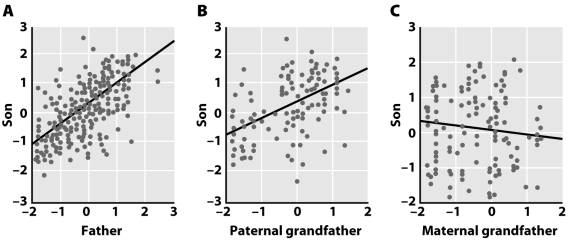
A)Mitochondrial inheritance
C)Y-linked inheritance
B)X-linked inheritance
D)No

A)Mitochondrial inheritance
C)Y-linked inheritance
B)X-linked inheritance
D)No

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Suppose that Epicephala moths are part of a larger group of moths whose members are all seed feeders,but none of the other seed-feeding genera are involved in the pollination of their host plant.What would you conclude to be the most parsimonious pathway for the evolution of the mutualistic relationship between Epicephala and Glochidion plants?
A)It evolved via a pollination mutualism without a seed-feeding relationship.
B)Epicephala started out eating Glochidion foliage before starting to pollinate the flowers of its host.
C)Pollination evolved as a byproduct of female moths laying their eggs in Glochidion flowers.
D)The ancestor of mutualistic Epicephala larvae had pollen-feeding larvae.
A)It evolved via a pollination mutualism without a seed-feeding relationship.
B)Epicephala started out eating Glochidion foliage before starting to pollinate the flowers of its host.
C)Pollination evolved as a byproduct of female moths laying their eggs in Glochidion flowers.
D)The ancestor of mutualistic Epicephala larvae had pollen-feeding larvae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is an example of Batesian mimicry?
A)Paper wasps and yellow jackets that both have black and yellow stripes
B)Defenseless spiders that look like ants
C)Crab spiders that mimic the color of flowers on which they live
D)Heliconius butterfly species that share warning patterns and that are both unpalatable
A)Paper wasps and yellow jackets that both have black and yellow stripes
B)Defenseless spiders that look like ants
C)Crab spiders that mimic the color of flowers on which they live
D)Heliconius butterfly species that share warning patterns and that are both unpalatable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What ecological role were the nitrogen-fixing Bradyrhizobium japonicum bacteria in soybean root nodules effectively playing when the experimenters cut off gaseous nitrogen?
A)Free rider
C)Commensal
B)Predator
D)Symbiont
A)Free rider
C)Commensal
B)Predator
D)Symbiont

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Clayton and colleagues discovered the relationship between feather-louse size and the body mass of their corresponding bird hosts illustrated in the figure below.What do the authors hypothesize about the mechanism of cospeciation in doves and lice from this relationship? 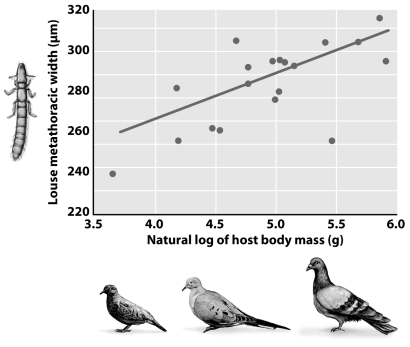
A)Lice are unlikely to switch to hosts that differ in body size from their original host.
B)Lice will tend to shift to the larger host regardless of their own size.
C)Larger lice are always better at holding onto their hosts.
D)Smaller lice are always better at evading the preening attempts than large lice species.

A)Lice are unlikely to switch to hosts that differ in body size from their original host.
B)Lice will tend to shift to the larger host regardless of their own size.
C)Larger lice are always better at holding onto their hosts.
D)Smaller lice are always better at evading the preening attempts than large lice species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Name two forms of antagonistic coevolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Geographically isolated subpopulations of a species can evolve partial reproductive isolation.If two subpopulations come into secondary contact,they can either become one mixed population,or,during a process called reinforcement,selection may lead to greater reproductive isolation.The latter will occur if mating between subpopulations results in hybrid offspring that have lower fitness.Could cultural evolution play a role in reinforcement?
A)Yes, if traits that affect reproductive isolation can be culturally transmitted.
B)Yes, but only if there is zero cultural transmission between subpopulations.
C)No, in order to form separate species, the changes have to be genetic.
D)No, culturally transmitted behavioral traits are bound to be "leaky" (allow for some level of gene flow).
A)Yes, if traits that affect reproductive isolation can be culturally transmitted.
B)Yes, but only if there is zero cultural transmission between subpopulations.
C)No, in order to form separate species, the changes have to be genetic.
D)No, culturally transmitted behavioral traits are bound to be "leaky" (allow for some level of gene flow).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Is any form of adaptation coevolution?
A)Yes, evolution always happens in response to environmental change.
B)Yes, other species are always part of an organism's environment.
C)No, only evolution as an action-reaction response to a selection pressure imposed by interacting organisms on each other qualifies as coevolution.
D)No, coevolution is by definition limited to mutualistic interactions.
A)Yes, evolution always happens in response to environmental change.
B)Yes, other species are always part of an organism's environment.
C)No, only evolution as an action-reaction response to a selection pressure imposed by interacting organisms on each other qualifies as coevolution.
D)No, coevolution is by definition limited to mutualistic interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Define "obligate mutualism" in one sentence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How did Lutzoni and Pagel conclude that the entire genome of mutualistic fungi evolved faster than the genome of free-living fungi?
A)They based their estimate on the branch lengths in the phylogeny of a single gene.
B)They compared the evolutionary rates of multiple genes.
C)They conducted a genome scan at a great number of variable loci using microarray technology.
D)Their "conclusion" is mere speculation and is not backed up by data.
A)They based their estimate on the branch lengths in the phylogeny of a single gene.
B)They compared the evolutionary rates of multiple genes.
C)They conducted a genome scan at a great number of variable loci using microarray technology.
D)Their "conclusion" is mere speculation and is not backed up by data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is a difference between genetic and cultural transmission?
A)Only cultural transmission involves the transfer of information.
B)Only genetic transmission is prone to errors (mutations).
C)Cultural transmission can work both vertically and horizontally.
D)None of the above
A)Only cultural transmission involves the transfer of information.
B)Only genetic transmission is prone to errors (mutations).
C)Cultural transmission can work both vertically and horizontally.
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
You want to study an aspect of the mosaic theory of coevolution,and you are looking for a suitable study system.Which of the following is the most important condition that your study system needs to fulfill?
A)It needs to involve an insect-plant interaction.
B)It needs to be a case of coevolution.
C)The system must be organized as a true metapopulation.
D)Coevolution is largely independent of differences in subpopulations.
A)It needs to involve an insect-plant interaction.
B)It needs to be a case of coevolution.
C)The system must be organized as a true metapopulation.
D)Coevolution is largely independent of differences in subpopulations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is a relationship between organisms that cannot evolve into a mutualistic relationship?
A)Parasite-host interaction
B)Predator-prey interaction
C)Neutral interaction
D)None of the above; any interaction can serve as a precursor
A)Parasite-host interaction
B)Predator-prey interaction
C)Neutral interaction
D)None of the above; any interaction can serve as a precursor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Why do woodland star flowers likely abort flower heads with Greya moth eggs in geographic locations where other nonflower-feeding pollinators are present?
A)Greya moths do not pollinate woodland stars in locations with multiple pollinators.
B)Pollination by Greya is not essential for the reproduction of these woodland stars.
C)Pollen becomes limited, and woodland stars can no longer afford to lose pollen to Greya larvae.
D)B and C
A)Greya moths do not pollinate woodland stars in locations with multiple pollinators.
B)Pollination by Greya is not essential for the reproduction of these woodland stars.
C)Pollen becomes limited, and woodland stars can no longer afford to lose pollen to Greya larvae.
D)B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Define "cultural transmission" in one sentence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Some species of tropical fireflies mimic the luminescent mating signals of females of a related species and will prey upon the males that have been attracted by the fake signal.How would you classify this behavior? Is it Batesian mimicry,Müllerian mimicry,a third form of mimicry,or no mimicry at all? Briefly justify your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How can cultural transmission of male songs facilitate the early stages of species formation in Darwin's finches?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Briefly define the three modes of cultural transmission: vertical cultural transmission,horizontal cultural transmission,and oblique cultural transmission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Describe the mosaic theory of coevolution in your own words.Limit your answer to one sentence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Why does cultural transmission have the potential to be faster than genetic transmission? Limit your answer to one sentence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



