Deck 44: Neurons, Glia, and Nervous Systems
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/250
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 44: Neurons, Glia, and Nervous Systems
1
A disease in which antibodies destroy myelin produced by oligodendrocytes would most likely cause which of the following?
A) The blood-brain barrier would be weakened and toxins would easily pass into the brain.
B) Neurons in the brain and spinal cord would conduct action potentials more slowly.
C) Action potential conduction in neurons in the peripheral nerves would be slower.
D) Neurons in the brain would be deprived of nutrients.
E) The dendrites of peripheral nerves would not process information from other neurons.
A) The blood-brain barrier would be weakened and toxins would easily pass into the brain.
B) Neurons in the brain and spinal cord would conduct action potentials more slowly.
C) Action potential conduction in neurons in the peripheral nerves would be slower.
D) Neurons in the brain would be deprived of nutrients.
E) The dendrites of peripheral nerves would not process information from other neurons.
B
2
Which statement about microglia is true?
A) They are activated by damage to neural tissue.
B) They act as macrophages in the peripheral nervous system.
C) They form synapses with brain neurons and conduct action potentials.
D) They form myelin sheaths around neurons of the peripheral nervous system.
E) They supply neurons of the brain and spinal cord with nutrients.
A) They are activated by damage to neural tissue.
B) They act as macrophages in the peripheral nervous system.
C) They form synapses with brain neurons and conduct action potentials.
D) They form myelin sheaths around neurons of the peripheral nervous system.
E) They supply neurons of the brain and spinal cord with nutrients.
A
3
Astrocytes influence the connectivity between a pre- and postsynaptic neuron by
A) causing additional storage of glycogen within neurons, thereby increasing their metabolism.
B) increasing myelination of neurons, which results in faster action potentials.
C) decreasing the permeability of blood vessels, thereby aiding in the supply of nutrients to neurons.
D) taking up and releasing neurotransmitters and therefore altering the activity of neurons.
E) conducting action potentials, which increase the flow of information.
A) causing additional storage of glycogen within neurons, thereby increasing their metabolism.
B) increasing myelination of neurons, which results in faster action potentials.
C) decreasing the permeability of blood vessels, thereby aiding in the supply of nutrients to neurons.
D) taking up and releasing neurotransmitters and therefore altering the activity of neurons.
E) conducting action potentials, which increase the flow of information.
D
4
Refer to the figure showing two types of neurons. 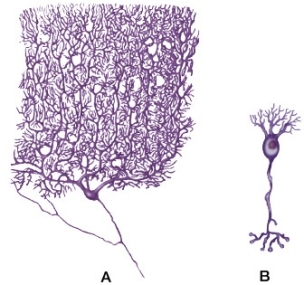 Compared with neuron B, neuron A would be more likely to
Compared with neuron B, neuron A would be more likely to
A) communicate information over a short distance.
B) collect information from more cells.
C) process information from fewer cells.
D) depolarize after receiving an action potential.
E) process information more quickly from a single synapse.
 Compared with neuron B, neuron A would be more likely to
Compared with neuron B, neuron A would be more likely toA) communicate information over a short distance.
B) collect information from more cells.
C) process information from fewer cells.
D) depolarize after receiving an action potential.
E) process information more quickly from a single synapse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following represents the correct order of the parts of neurons that are involved in the flow of information, beginning with the presynaptic cell and ending where a synapse is made with a postsynaptic cell?
A) Dendrites, cell body, axon hillock, axon, axon terminals
B) Cell body, axon terminals, axon hillock, axon, dendrites
C) Axon, cell body, dendrites
D) Axon terminals, axon hillock, cell body, dendrites
E) Synapse, axon, cell body, dendrites
A) Dendrites, cell body, axon hillock, axon, axon terminals
B) Cell body, axon terminals, axon hillock, axon, dendrites
C) Axon, cell body, dendrites
D) Axon terminals, axon hillock, cell body, dendrites
E) Synapse, axon, cell body, dendrites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a thin section through brain tissue, you see a cell that is wrapped around the axon of a neuron, forming concentric layers of cell membrane.This cell most likely
A) is part of the blood‒brain barrier.
B) supplies nutrients to neurons.
C) gives structural support to the axon.
D) insulates the axon for rapid conduction of action potentials.
E) recycles neurotransmitter in the synapses.
A) is part of the blood‒brain barrier.
B) supplies nutrients to neurons.
C) gives structural support to the axon.
D) insulates the axon for rapid conduction of action potentials.
E) recycles neurotransmitter in the synapses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The area where a neuron comes extremely close to a target cell and transmits information to the target cell is
A) the ganglion.
B) the axon hillock.
C) the synapse.
D) the node of Ranvier.
E) insulated with myelin.
A) the ganglion.
B) the axon hillock.
C) the synapse.
D) the node of Ranvier.
E) insulated with myelin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A disease that destroys astrocytes would cause all of the following except
A) neurons in the brain would be deprived of nutrients.
B) the blood‒brain barrier could be weakened, allowing toxins to pass into the brain.
C) modulation of many synapses would be impaired.
D) peripheral nerves would show degradation of the myelin sheath.
E) calcium waves would decline in neural tissue.
A) neurons in the brain would be deprived of nutrients.
B) the blood‒brain barrier could be weakened, allowing toxins to pass into the brain.
C) modulation of many synapses would be impaired.
D) peripheral nerves would show degradation of the myelin sheath.
E) calcium waves would decline in neural tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Neurons have different shapes and sizes depending on their roles.A bipolar cell in the retina of the eye collects information from a few inputs and transmits it a short distance to one or more closely spaced neurons.What shape would you predict it to have?
A) A few dendrites and a short axon with one or more terminals
B) A long axon with many axon terminals
C) A dense field of dendrites and a single axon
D) Numerous dendrites and a long axon
E) Dendrites and a highly branched axon
A) A few dendrites and a short axon with one or more terminals
B) A long axon with many axon terminals
C) A dense field of dendrites and a single axon
D) Numerous dendrites and a long axon
E) Dendrites and a highly branched axon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A challenge to modern medicine is to design drugs that target the brain.Existing knowledge about the ability of _______ to cross the blood‒brain barrier seems to be the best starting point in the design of new treatments.
A) antibodies
B) glucose
C) astrocytes
D) gases
E) lipid-soluble substances
A) antibodies
B) glucose
C) astrocytes
D) gases
E) lipid-soluble substances

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Diseases that destroy myelin
A) also destroy astrocytes.
B) are restricted to the central nervous system.
C) can be cured.
D) also destroy tripartite synapses.
E) impair conduction of action potentials.
A) also destroy astrocytes.
B) are restricted to the central nervous system.
C) can be cured.
D) also destroy tripartite synapses.
E) impair conduction of action potentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In looking at a section through the brain, you see a neuron with a number of shrublike projections extending from one side of the cell body and a single long projection extending from the other side.The shrublike projections are most likely _______, and the single long projection is most likely _______.
A) axons; a dendrite
B) Purkinje fibers; the axon
C) dendrites; the axon
D) axon terminals; the postsynaptic process
E) presynaptic processes; the axon hillock
A) axons; a dendrite
B) Purkinje fibers; the axon
C) dendrites; the axon
D) axon terminals; the postsynaptic process
E) presynaptic processes; the axon hillock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Antibodies produced by the human immune system are typically prevented from getting to the brain by the blood‒brain barrier.Does this mean that the brain has no immune defenses?
A) No, microglia in the brain and spinal cord provide an immune function.
B) No, astrocytes carry out an immune function in addition to their other functions.
C) No, macrophages from the general circulation cross the blood‒brain barrier.
D) Yes, but there is no need for immune defenses in the central nervous system, since the blood‒brain barrier also protects it from infection.
E) Yes, this is why infections of the brain are so common.
A) No, microglia in the brain and spinal cord provide an immune function.
B) No, astrocytes carry out an immune function in addition to their other functions.
C) No, macrophages from the general circulation cross the blood‒brain barrier.
D) Yes, but there is no need for immune defenses in the central nervous system, since the blood‒brain barrier also protects it from infection.
E) Yes, this is why infections of the brain are so common.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In an active synapse composed of a presynaptic and postsynaptic cell, which part of the presynaptic cell is the last to participate in the action potential?
A) Axon
B) Axon hillock
C) Dendrites
D) Cell body
E) Axon terminals
A) Axon
B) Axon hillock
C) Dendrites
D) Cell body
E) Axon terminals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If a chemical prevents asymmetrical divisions of neuronal stem cells in the neural tube of a fish embryo, then
A) neuroblasts and gliablasts will not be produced.
B) microglia will not be produced.
C) excessive myelination will result.
D) immune function will be compromised.
E) blood-forming stems cells will replace neuronal stem cells.
A) neuroblasts and gliablasts will not be produced.
B) microglia will not be produced.
C) excessive myelination will result.
D) immune function will be compromised.
E) blood-forming stems cells will replace neuronal stem cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Anesthetics and alcohol can permeate the blood-brain barrier because
A) they are small molecules.
B) they are water-soluble.
C) they are lipid-soluble.
D) they pass through gated channels.
E) there are receptors for them on blood vessels.
A) they are small molecules.
B) they are water-soluble.
C) they are lipid-soluble.
D) they pass through gated channels.
E) there are receptors for them on blood vessels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Slowing of early divisions of neuronal stem cells in the neural tube of a vertebrate embryo would result in
A) fewer microglia.
B) a worsening of immune function.
C) fewer neuronal stem cells.
D) neurons without dendrites.
E) fewer blood-forming stem cells.
A) fewer microglia.
B) a worsening of immune function.
C) fewer neuronal stem cells.
D) neurons without dendrites.
E) fewer blood-forming stem cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The concept of a tripartite synapse is the idea that a synapse consists not only of pre- and postsynaptic neurons but also of connections from _______.This concept takes into account the _______ at the synapse.
A) dendrites; collection of information from neurotransmitters
B) axon terminals; release of neurotransmitters
C) astrocytes; contact of astrocytes with neuronal elements
D) microglia; macrophage activity
E) oligodendrocytes; myelination
A) dendrites; collection of information from neurotransmitters
B) axon terminals; release of neurotransmitters
C) astrocytes; contact of astrocytes with neuronal elements
D) microglia; macrophage activity
E) oligodendrocytes; myelination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The blood-brain barrier protects the brain
A) mostly during fetal development.
B) from fat-soluble substances.
C) by maintaining a brain blood supply that is separate from the circulation to the rest of the body.
D) through the action of astrocytes that reduce the permeability of small blood vessels.
E) and spinal cord and peripheral nervous system.
A) mostly during fetal development.
B) from fat-soluble substances.
C) by maintaining a brain blood supply that is separate from the circulation to the rest of the body.
D) through the action of astrocytes that reduce the permeability of small blood vessels.
E) and spinal cord and peripheral nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not a type of glial cell?
A) Oligodendrocyte
B) Bipolar cell
C) Schwann cell
D) Astrocyte
E) Microglia
A) Oligodendrocyte
B) Bipolar cell
C) Schwann cell
D) Astrocyte
E) Microglia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In a neuron at rest, the resting membrane potential is mainly due to
A) the number of voltage-gated channels in the membrane.
B) the difference in the concentrations of Na+ inside and outside of the cell.
C) passive leak currents in the cell membrane.
D) the active transport of K+ ions out of the cell.
E) the electrical charge in the extracellular fluid.
A) the number of voltage-gated channels in the membrane.
B) the difference in the concentrations of Na+ inside and outside of the cell.
C) passive leak currents in the cell membrane.
D) the active transport of K+ ions out of the cell.
E) the electrical charge in the extracellular fluid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Refer to the figure showing a cell membrane. 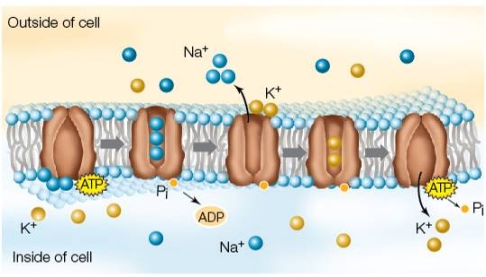 The figure illustrates the activity of a(n)
The figure illustrates the activity of a(n)
A) channel through which ions are diffusing.
B) sodium‒potassium pump.
C) leak channel.
D) ion channel.
E) concentration gradient.
 The figure illustrates the activity of a(n)
The figure illustrates the activity of a(n)A) channel through which ions are diffusing.
B) sodium‒potassium pump.
C) leak channel.
D) ion channel.
E) concentration gradient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
All of the following apply to the sodium-potassium pump in neurons except
A) it requires ATP to work.
B) it moves potassium ions to the inside of the neuron and sodium ions to the outside.
C) it works against a concentration gradient.
D) it consists of an enzyme complex.
E) it relies on facilitated diffusion.
A) it requires ATP to work.
B) it moves potassium ions to the inside of the neuron and sodium ions to the outside.
C) it works against a concentration gradient.
D) it consists of an enzyme complex.
E) it relies on facilitated diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following does not characterize an electrochemical gradient across a membrane?
A) It depends on the ion concentration gradient.
B) It depends on the voltage difference across the membrane.
C) It is a force acting on ions.
D) It determines the direction and amount of net movement of ions through ion channels.
E) It is unaffected by gates on channels.
A) It depends on the ion concentration gradient.
B) It depends on the voltage difference across the membrane.
C) It is a force acting on ions.
D) It determines the direction and amount of net movement of ions through ion channels.
E) It is unaffected by gates on channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If a physical or chemical stimulus causes a change in a cell's membrane potential, a direct effect of that change may be
A) an increase in Na+ concentration outside the cell.
B) increased permeability of the cell membrane to certain ions.
C) an increase in pumps.
D) an increase in the number of K+ ions needed to reach equilibrium.
E) an increase in the lipid composition of the membrane.
A) an increase in Na+ concentration outside the cell.
B) increased permeability of the cell membrane to certain ions.
C) an increase in pumps.
D) an increase in the number of K+ ions needed to reach equilibrium.
E) an increase in the lipid composition of the membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Because of the voltage difference across the membrane of a neuron and the different ion concentrations on either side of the membrane, ions would cross the membrane if they could.What is the importance, therefore, of a neuron maintaining a membrane potential?
A) It maintains an electrical balance in the cell.
B) Cellular activity requires more Na+ than K+.
C) If the ions were in equilibrium, the cell would shrink by losing water through osmosis.
D) It prevents the electrical and chemical gradients from reaching equilibrium, a process that would require a great deal of energy.
E) It allows a cell to respond to a stimulus that changes its permeability to ions.
A) It maintains an electrical balance in the cell.
B) Cellular activity requires more Na+ than K+.
C) If the ions were in equilibrium, the cell would shrink by losing water through osmosis.
D) It prevents the electrical and chemical gradients from reaching equilibrium, a process that would require a great deal of energy.
E) It allows a cell to respond to a stimulus that changes its permeability to ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Consider the following statement: Voltage is to the flow of electrically charged particles as pressure is to the flow of water.This statement indicates that voltage is the
A) force that moves charged particles.
B) rate at which charged particles move.
C) resistance against moving charged particles.
D) number of charged particles moving between two points.
E) conduction of charged particles along a pathway.
A) force that moves charged particles.
B) rate at which charged particles move.
C) resistance against moving charged particles.
D) number of charged particles moving between two points.
E) conduction of charged particles along a pathway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
To maintain the resting potential of the nerve cell membrane, the sodium‒potassium pump keeps the concentration of
A) K+ and Na+ inside the cell lower than in the extracellular fluid.
B) Na+ inside the cell greater than outside the cell, and that of K+ inside the cell lower than outside the cell.
C) K+ inside the cell greater than in the extracellular fluid, and that of Na+ inside the cell lower than outside the cell.
D) Na+ and K+ inside the cell greater than outside the cell.
E) negative ions higher inside the cell by pumping negative ions across the membrane.
A) K+ and Na+ inside the cell lower than in the extracellular fluid.
B) Na+ inside the cell greater than outside the cell, and that of K+ inside the cell lower than outside the cell.
C) K+ inside the cell greater than in the extracellular fluid, and that of Na+ inside the cell lower than outside the cell.
D) Na+ and K+ inside the cell greater than outside the cell.
E) negative ions higher inside the cell by pumping negative ions across the membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which statement about voltage-gated channels is true?
A) They open or close in response to a change in voltage across the cell membrane.
B) They all open and close at the same time in response to an action potential.
C) Ions can move through the channels only if the overall membrane potential stays the same.
D) Ions are pumped through the channels to maintain the existing membrane potential.
E) They open only in response to an action potential.
A) They open or close in response to a change in voltage across the cell membrane.
B) They all open and close at the same time in response to an action potential.
C) Ions can move through the channels only if the overall membrane potential stays the same.
D) Ions are pumped through the channels to maintain the existing membrane potential.
E) They open only in response to an action potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is most likely to cause the opening of a voltage-gated channel in a cell membrane?
A) Light causing a response in a photoreceptor
B) A taste molecule binding to a taste receptor
C) Mechanical pressure exerting a pull on a membrane
D) Bathing a neuron in fluid with a high concentration of Na+ ions
E) A rise in the membrane potential of a nerve cell
A) Light causing a response in a photoreceptor
B) A taste molecule binding to a taste receptor
C) Mechanical pressure exerting a pull on a membrane
D) Bathing a neuron in fluid with a high concentration of Na+ ions
E) A rise in the membrane potential of a nerve cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If Na+ channels open and sodium ions diffuse into the cell,
A) the cell will become hyperpolarized.
B) other sodium ions will move out of the cell.
C) voltage-gated channels will remain closed.
D) the inside of the cell will become less negative.
E) action potentials will be triggered.
A) the cell will become hyperpolarized.
B) other sodium ions will move out of the cell.
C) voltage-gated channels will remain closed.
D) the inside of the cell will become less negative.
E) action potentials will be triggered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The potassium equilibrium potential is reached when the diffusion of K+ out of the cell due to the concentration gradient is balanced by the movement of K+ into the cell due to the negative electric potential.This potassium equilibrium potential
A) is always equivalent to the membrane potential.
B) requires the activity of voltage-gated ion channels.
C) is due to electrochemical gradients.
D) is equivalent to the resting potential.
E) was discovered through patch clamping.
A) is always equivalent to the membrane potential.
B) requires the activity of voltage-gated ion channels.
C) is due to electrochemical gradients.
D) is equivalent to the resting potential.
E) was discovered through patch clamping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Nernst and Goldman equations shown are used to predict membrane potentials. 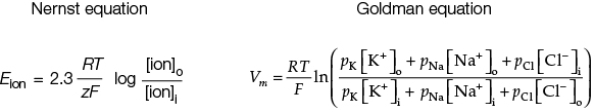 In the Goldman equation, "o" stands for outside or extracellular, "i" stands for inside or intracellular, and "p" stands for permeability.To use the Goldman equation as expressed to calculate the membrane potential of a cell, you must know the _______, as well as the membrane permeability for these ions.
In the Goldman equation, "o" stands for outside or extracellular, "i" stands for inside or intracellular, and "p" stands for permeability.To use the Goldman equation as expressed to calculate the membrane potential of a cell, you must know the _______, as well as the membrane permeability for these ions.
A) total number of ions crossing the membrane
B) intracellular and extracellular concentrations of ions that cross the membrane
C) fraction of the ions crossing the membrane that are positive
D) concentration of the ions that are entering the cell
E) different charges on all the ions involved
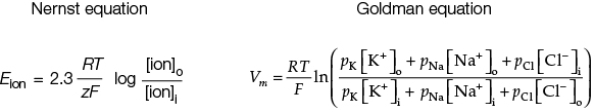 In the Goldman equation, "o" stands for outside or extracellular, "i" stands for inside or intracellular, and "p" stands for permeability.To use the Goldman equation as expressed to calculate the membrane potential of a cell, you must know the _______, as well as the membrane permeability for these ions.
In the Goldman equation, "o" stands for outside or extracellular, "i" stands for inside or intracellular, and "p" stands for permeability.To use the Goldman equation as expressed to calculate the membrane potential of a cell, you must know the _______, as well as the membrane permeability for these ions.A) total number of ions crossing the membrane
B) intracellular and extracellular concentrations of ions that cross the membrane
C) fraction of the ions crossing the membrane that are positive
D) concentration of the ions that are entering the cell
E) different charges on all the ions involved

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The Nernst and Goldman equations shown are used to predict membrane potentials. 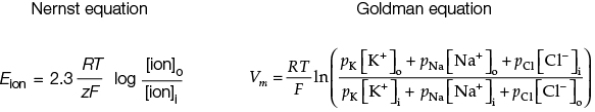 Which equation is more likely to be accurate in predicting the resting membrane potential, and why?
Which equation is more likely to be accurate in predicting the resting membrane potential, and why?
A) The Goldman equation, because it also considers permeability of the membrane to all ions that cross it
B) The Nernst equation, because it takes into consideration the temperature of the cell
C) The Nernst equation, because it calculates permeability of the membrane to all ions that can be measured
D) The Goldman equation, because it calculates the potassium equilibrium potential
E) The Nernst equation, because it calculates the potassium equilibrium potential
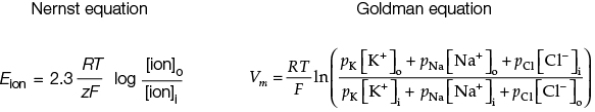 Which equation is more likely to be accurate in predicting the resting membrane potential, and why?
Which equation is more likely to be accurate in predicting the resting membrane potential, and why?A) The Goldman equation, because it also considers permeability of the membrane to all ions that cross it
B) The Nernst equation, because it takes into consideration the temperature of the cell
C) The Nernst equation, because it calculates permeability of the membrane to all ions that can be measured
D) The Goldman equation, because it calculates the potassium equilibrium potential
E) The Nernst equation, because it calculates the potassium equilibrium potential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is not one of the major ions that carry electrical charges across the cell membranes of neurons?
A) Sodium (Na+)
B) Potassium (K+)
C) Calcium (Ca2+)
D) Magnesium (Mg2+)
E) Chloride (Cl‒)
A) Sodium (Na+)
B) Potassium (K+)
C) Calcium (Ca2+)
D) Magnesium (Mg2+)
E) Chloride (Cl‒)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
You are looking at neural tissue that has been treated with calcium-sensitive dyes and you notice calcium ion waves traveling through the tissue.These waves represent
A) activity at a tripartite synapse.
B) action potentials of microglia.
C) communication among astrocytes.
D) toxins crossing the blood-brain barrier.
E) action potentials traveling along neurons whose axons have damaged myelin.
A) activity at a tripartite synapse.
B) action potentials of microglia.
C) communication among astrocytes.
D) toxins crossing the blood-brain barrier.
E) action potentials traveling along neurons whose axons have damaged myelin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When voltage-gated K+ channels open in the cell membrane of a neuron, K+ moves
A) into the cell, and the membrane becomes hyperpolarized.
B) into the cell, and the membrane becomes depolarized.
C) out of the cell, and the membrane becomes depolarized.
D) out of the cell, and the membrane becomes hyperpolarized.
E) through the leak channels, and leak channels for Na+ are opened.
A) into the cell, and the membrane becomes hyperpolarized.
B) into the cell, and the membrane becomes depolarized.
C) out of the cell, and the membrane becomes depolarized.
D) out of the cell, and the membrane becomes hyperpolarized.
E) through the leak channels, and leak channels for Na+ are opened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In their classic experiments to determine the electrical properties of neurons, Hodgkin and Huxley used
A) fluid-filled pipettes to sample the cytoplasm of a rat spinal cord neuron.
B) electrodes located on either side of the cell membrane of the squid giant axon.
C) batteries to cause electrical changes in the membrane potential of sensory neurons.
D) patch clamps to determine the activity of individual ion channels in brain neurons.
E) recording pipettes to measure the activity of ion channels in the giant axons of earthworms.
A) fluid-filled pipettes to sample the cytoplasm of a rat spinal cord neuron.
B) electrodes located on either side of the cell membrane of the squid giant axon.
C) batteries to cause electrical changes in the membrane potential of sensory neurons.
D) patch clamps to determine the activity of individual ion channels in brain neurons.
E) recording pipettes to measure the activity of ion channels in the giant axons of earthworms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which statement about the resting potential of a neuronal cell membrane is true?
A) The inside is about 60 mV more positive than the outside.
B) The outside is about 60 mV more positive than the inside.
C) The inside is about 30 mV more positive than the outside.
D) The outside is about 30 mV more positive than the inside.
E) The inside has about the same charge as the outside.
A) The inside is about 60 mV more positive than the outside.
B) The outside is about 60 mV more positive than the inside.
C) The inside is about 30 mV more positive than the outside.
D) The outside is about 30 mV more positive than the inside.
E) The inside has about the same charge as the outside.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Patch clamping
A) fixes a break in a cell membrane.
B) records the activity of Na+-K+ pumps.
C) can record ion movements through a single channel.
D) records ion movements through an entire nerve.
E) records an action potential through a single channel.
A) fixes a break in a cell membrane.
B) records the activity of Na+-K+ pumps.
C) can record ion movements through a single channel.
D) records ion movements through an entire nerve.
E) records an action potential through a single channel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Normally the acetylcholine receptor‒mediated channels in the motor end plate at a neuromuscular junction are closed.Which statement about this channel is true?
A) The channel opens when acetylcholine passes through it.
B) The binding of acetylcholinesterase opens the channel.
C) Activation of the channel by the binding of acetylcholine causes Na+ ions to enter the presynaptic cell.
D) When the channel opens, Na+ ions enter the muscle cell.
E) When the channel opens, the cell becomes hyperpolarized.
A) The channel opens when acetylcholine passes through it.
B) The binding of acetylcholinesterase opens the channel.
C) Activation of the channel by the binding of acetylcholine causes Na+ ions to enter the presynaptic cell.
D) When the channel opens, Na+ ions enter the muscle cell.
E) When the channel opens, the cell becomes hyperpolarized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When an action potential arrives at an axon terminal, the fusion of neurotransmitter vesicles with the cell membrane is triggered by
A) an increase in the concentration of calcium ions within the cell.
B) the removal of calcium ions from the cytoplasm of the cell.
C) the opening of K+ leak channels, which causes an increase in potassium ions within the cell.
D) the release of acetylcholine.
E) a sudden increase in chloride ions within the cytoplasm of the cell.
A) an increase in the concentration of calcium ions within the cell.
B) the removal of calcium ions from the cytoplasm of the cell.
C) the opening of K+ leak channels, which causes an increase in potassium ions within the cell.
D) the release of acetylcholine.
E) a sudden increase in chloride ions within the cytoplasm of the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Following the spike of an action potential, the return to resting membrane potential is facilitated by
A) Na+ ions moving into the cell through open Na+ channels.
B) K+ ions moving into the cell through K+ channels.
C) the closing of Cl- ion channels.
D) inactivation of leak channels.
E) the opening of voltage-gated K+ channels.
A) Na+ ions moving into the cell through open Na+ channels.
B) K+ ions moving into the cell through K+ channels.
C) the closing of Cl- ion channels.
D) inactivation of leak channels.
E) the opening of voltage-gated K+ channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which statement concerning the nodes of Ranvier is true?
A) The myelinated membrane adjacent to the nodes allows the firing of action potentials.
B) The nodes are regions where the nerve axon is myelinated.
C) Action potentials jump from node to node.
D) Voltage-gated ion channels are clustered in the regions between the nodes.
E) Positive current flows along the outside of the myelinated axon in between the nodes.
A) The myelinated membrane adjacent to the nodes allows the firing of action potentials.
B) The nodes are regions where the nerve axon is myelinated.
C) Action potentials jump from node to node.
D) Voltage-gated ion channels are clustered in the regions between the nodes.
E) Positive current flows along the outside of the myelinated axon in between the nodes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In the vertebrate neuromuscular junction, acetylcholine is transmitted from the presynaptic neuron to the postsynaptic motor end plate through
A) endocytosis of acetylcholine.
B) diffusion.
C) formation of vesicles in the motor end plate.
D) acetylcholine membrane pumps.
E) closing of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels.
A) endocytosis of acetylcholine.
B) diffusion.
C) formation of vesicles in the motor end plate.
D) acetylcholine membrane pumps.
E) closing of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which statement concerning graded potentials is true?
A) They are equivalent to the resting potential of the cell membrane.
B) They travel long distances to generate an action potential.
C) They are important in all sensory systems except neuromuscular junctions.
D) They allow a cell to integrate inputs and respond proportionally.
E) They are caused by ionic currents spreading over long distances.
A) They are equivalent to the resting potential of the cell membrane.
B) They travel long distances to generate an action potential.
C) They are important in all sensory systems except neuromuscular junctions.
D) They allow a cell to integrate inputs and respond proportionally.
E) They are caused by ionic currents spreading over long distances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following would result from the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase?
A) Release of neurotransmitter from the presynaptic membrane would be inhibited.
B) Synthesis of neurotransmitter in cells would be inhibited.
C) Breakdown of neurotransmitter in the synapse would be inhibited.
D) Stimulation of the postsynaptic membrane would be inhibited.
E) Cholinergic receptors would be inhibited.
A) Release of neurotransmitter from the presynaptic membrane would be inhibited.
B) Synthesis of neurotransmitter in cells would be inhibited.
C) Breakdown of neurotransmitter in the synapse would be inhibited.
D) Stimulation of the postsynaptic membrane would be inhibited.
E) Cholinergic receptors would be inhibited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When an action potential reaches an axon terminal, it can cause the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.Which of the following is a possible sequence of events that could follow?
A) Neurotransmitters diffuse from the presynaptic neuron and cause demyelination of the postsynaptic neuron.
B) Neurotransmitters are actively transported by vesicles into the postsynaptic neuron, causing a local potential.
C) Neurotransmitters are reabsorbed into the presynaptic neuron, exciting the presynaptic neuron.
D) Neurotransmitters remain in the synaptic cleft, changing the resting membrane potential of the postsynaptic neuron.
E) Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft, bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, and inhibit activity in the postsynaptic neuron.
A) Neurotransmitters diffuse from the presynaptic neuron and cause demyelination of the postsynaptic neuron.
B) Neurotransmitters are actively transported by vesicles into the postsynaptic neuron, causing a local potential.
C) Neurotransmitters are reabsorbed into the presynaptic neuron, exciting the presynaptic neuron.
D) Neurotransmitters remain in the synaptic cleft, changing the resting membrane potential of the postsynaptic neuron.
E) Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft, bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, and inhibit activity in the postsynaptic neuron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The frequency at which a single neuron can "fire" action potentials is limited by the
A) closure of the Na+ channel inactivation gates.
B) number of leak channels the neuron has.
C) number of synapses formed by the neuron.
D) time it takes for the voltage-gated Na+ channels to reopen.
E) speed at which Cl‒ ion channels can close.
A) closure of the Na+ channel inactivation gates.
B) number of leak channels the neuron has.
C) number of synapses formed by the neuron.
D) time it takes for the voltage-gated Na+ channels to reopen.
E) speed at which Cl‒ ion channels can close.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Acetylcholine is
A) a neurotransmitter.
B) released by muscle cells at neuromuscular junctions in vertebrates.
C) found in electrical synapses.
D) released when there is a drop in the cytoplasmic concentration of Ca2+ ions.
E) released by endocytosis.
A) a neurotransmitter.
B) released by muscle cells at neuromuscular junctions in vertebrates.
C) found in electrical synapses.
D) released when there is a drop in the cytoplasmic concentration of Ca2+ ions.
E) released by endocytosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In most vertebrate neurons, an action potential arrives at the axon terminal and causes the release of chemical messenger molecules.These molecules are
A) ATP.
B) glucose.
C) myelin.
D) neurotransmitters.
E) vesicles.
A) ATP.
B) glucose.
C) myelin.
D) neurotransmitters.
E) vesicles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The acetylcholine receptor is restored to its normal closed position by
A) diffusion of excess acetylcholine out of the synapse.
B) movement of Na+ ions into the muscle cell.
C) movement of Na+ ions out of the muscle cell.
D) exocytosis of acetylcholine.
E) the activity of acetylcholinesterase.
A) diffusion of excess acetylcholine out of the synapse.
B) movement of Na+ ions into the muscle cell.
C) movement of Na+ ions out of the muscle cell.
D) exocytosis of acetylcholine.
E) the activity of acetylcholinesterase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which statement about neurotransmitters is false?
A) Gases, such as nitric oxide, can act as neurotransmitters.
B) Each neurotransmitter has a single type of receptor.
C) Amino acids and their derivatives, monoamines, function as neurotransmitters.
D) Neurotransmitters have different effects in different tissues.
E) Some neurotransmitters are cleared from synapses by enzymes that destroy them.
A) Gases, such as nitric oxide, can act as neurotransmitters.
B) Each neurotransmitter has a single type of receptor.
C) Amino acids and their derivatives, monoamines, function as neurotransmitters.
D) Neurotransmitters have different effects in different tissues.
E) Some neurotransmitters are cleared from synapses by enzymes that destroy them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which statement concerning action potentials is false?
A) The magnitude of an action potential along an axon is the same, regardless of where it is measured.
B) Action potentials travel more quickly in large-diameter axons than in small-diameter axons.
C) Action potentials are conducted without loss of signal.
D) Whereas invertebrates rely on myelination of axons to increase conduction velocity, vertebrates rely on increased axon diameter.
E) Action potentials travel more quickly in myelinated axons than in nonmyelinated axons.
A) The magnitude of an action potential along an axon is the same, regardless of where it is measured.
B) Action potentials travel more quickly in large-diameter axons than in small-diameter axons.
C) Action potentials are conducted without loss of signal.
D) Whereas invertebrates rely on myelination of axons to increase conduction velocity, vertebrates rely on increased axon diameter.
E) Action potentials travel more quickly in myelinated axons than in nonmyelinated axons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which statement about acetylcholine receptors is false?
A) The motor end plate contains both chemically gated and voltage-gated acetylcholine receptors.
B) They are proteins.
C) Binding of the neurotransmitter allows ion movement across the cell membrane.
D) They are found in the postsynaptic cell membrane of a neuromuscular junction.
E) Acetylcholine binds to them, opening their channels to sodium ions.
A) The motor end plate contains both chemically gated and voltage-gated acetylcholine receptors.
B) They are proteins.
C) Binding of the neurotransmitter allows ion movement across the cell membrane.
D) They are found in the postsynaptic cell membrane of a neuromuscular junction.
E) Acetylcholine binds to them, opening their channels to sodium ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Action potentials
A) initially cause depolarization of the membrane, usually followed by hyperpolarization.
B) cause a return to resting potential when the sodium channels open.
C) can be triggered in rapid succession, with no measurable delay between spikes.
D) are initiated by the membrane's increased permeability to potassium.
E) result from inactivation of leak channels.
A) initially cause depolarization of the membrane, usually followed by hyperpolarization.
B) cause a return to resting potential when the sodium channels open.
C) can be triggered in rapid succession, with no measurable delay between spikes.
D) are initiated by the membrane's increased permeability to potassium.
E) result from inactivation of leak channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When an action potential arrives at an axon terminal, it causes the opening of _______ channels, which triggers fusion of neurotransmitter vesicles with the cell membrane.
A) calcium
B) sodium
C) potassium
D) chloride
E) acetylcholine
A) calcium
B) sodium
C) potassium
D) chloride
E) acetylcholine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Two electrodes, one on either side of the cell membrane of a resting neuron, show a difference of about ‒65 mV.If the value changes quickly to about +50 mV and then rapidly returns to ‒65 mV, the most likely explanation is that
A) the cell membrane briefly became hyperpolarized.
B) a graded potential passed by the electrodes.
C) an action potential was triggered by changes in voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels.
D) voltage-gated Na+ channels closed, causing a spike of depolarization, and then opened again.
E) leak K+ channels opened and then closed.
A) the cell membrane briefly became hyperpolarized.
B) a graded potential passed by the electrodes.
C) an action potential was triggered by changes in voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels.
D) voltage-gated Na+ channels closed, causing a spike of depolarization, and then opened again.
E) leak K+ channels opened and then closed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Refer to the figure showing the conduction of an action potential traveling from left to right in a myelinated axon.Note the action potential at node 2. 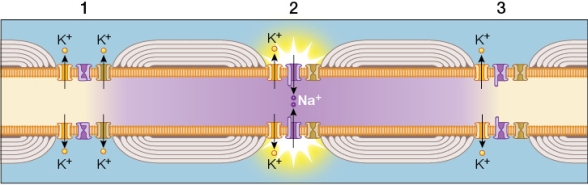 Which statement about this axon is false?
Which statement about this axon is false?
A) Area 1 is a node of Ranvier.
B) An action potential will be triggered at node 3 as a result of the action potential occurring at node 2.
C) Action potentials can jump rapidly from node 1 to node 2.
D) An action potential traveling from left to right will leave node 1 refractory because its Na+ channels are still open.
E) Node 1 participates in saltatory conduction.
 Which statement about this axon is false?
Which statement about this axon is false?A) Area 1 is a node of Ranvier.
B) An action potential will be triggered at node 3 as a result of the action potential occurring at node 2.
C) Action potentials can jump rapidly from node 1 to node 2.
D) An action potential traveling from left to right will leave node 1 refractory because its Na+ channels are still open.
E) Node 1 participates in saltatory conduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Refer to the figure showing the conduction of an action potential traveling from left to right in a myelinated axon.Note the action potential at node 2. 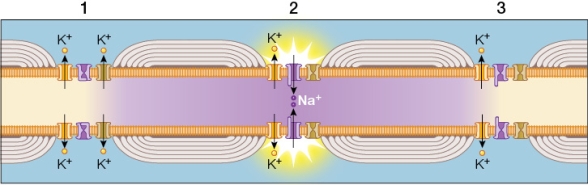 Which statement about section 2 of the axon is true?
Which statement about section 2 of the axon is true?
A) Depolarization is caused here by the opening of voltage-gated K+ channels.
B) The speed of the action potential in this axon depends mostly on its diameter.
C) Na+ channels remain open here until the action potential has reached the axon terminal.
D) A loss of signal will occur as the action potential travels to each adjacent node.
E) Na+ channels will inactivate at this node and enter a refractory state.
 Which statement about section 2 of the axon is true?
Which statement about section 2 of the axon is true?A) Depolarization is caused here by the opening of voltage-gated K+ channels.
B) The speed of the action potential in this axon depends mostly on its diameter.
C) Na+ channels remain open here until the action potential has reached the axon terminal.
D) A loss of signal will occur as the action potential travels to each adjacent node.
E) Na+ channels will inactivate at this node and enter a refractory state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Myasthenia gravis is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes weakness in skeletal muscle.It develops when a person's antibodies block or destroy _______ nicotinic receptors.
A) glutamate
B) acetylcholine
C) dopamine
D) GABA
E) glycine
A) glutamate
B) acetylcholine
C) dopamine
D) GABA
E) glycine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which statement about the process of summation in a neuron is false?
A) Slight perturbations of the membrane potential spread across the postsynaptic cell body.
B) The concentration of voltage-gated sodium channels is highest in the dendrites of the postsynaptic cell.
C) Spatial summation adds up the simultaneous influences of synapses at different locations on the postsynaptic cell.
D) Axons that terminate closer to the axon hillock have more influence on the summation process than those that do not.
E) The process is essentially a comparison of all the excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic inputs.
A) Slight perturbations of the membrane potential spread across the postsynaptic cell body.
B) The concentration of voltage-gated sodium channels is highest in the dendrites of the postsynaptic cell.
C) Spatial summation adds up the simultaneous influences of synapses at different locations on the postsynaptic cell.
D) Axons that terminate closer to the axon hillock have more influence on the summation process than those that do not.
E) The process is essentially a comparison of all the excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If the proteins that anchor acetylcholine-containing vesicles to the presynaptic membrane are damaged by botulism toxins, what effect will this have on the neuromuscular junction?
A) Reuptake by the presynaptic membrane will be impaired.
B) An action potential will not be able to open voltage-gated Ca2+ channels.
C) Neurotransmitter will not be released into the synaptic cleft.
D) Graded potentials will cause fusion of the vesicles with the cell membrane.
E) Endocytosis of acetylcholinesterase will be impaired.
A) Reuptake by the presynaptic membrane will be impaired.
B) An action potential will not be able to open voltage-gated Ca2+ channels.
C) Neurotransmitter will not be released into the synaptic cleft.
D) Graded potentials will cause fusion of the vesicles with the cell membrane.
E) Endocytosis of acetylcholinesterase will be impaired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When you decide to mark a particular answer to this question, your nervous system sends the command to your hand to do so.That command is carried to your hand by
A) afferent neurons.
B) efferent neurons.
C) interneurons.
D) sensory neurons.
E) ganglion cells.
A) afferent neurons.
B) efferent neurons.
C) interneurons.
D) sensory neurons.
E) ganglion cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Refer to the figure showing a neuromuscular junction. 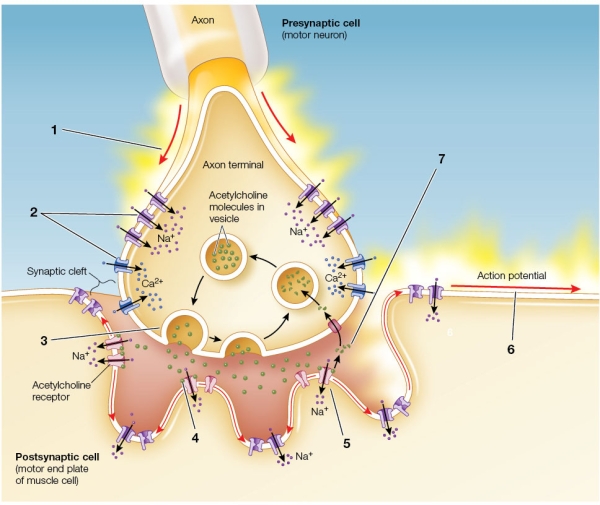 Which cellular event is paired correctly with the location where it occurs?
Which cellular event is paired correctly with the location where it occurs?
A) At position 2, calcium ions trigger fusion of vesicles with the presynaptic membrane.
B) At position 3, voltage-gated calcium channels open.
C) At position 4, acetylcholine molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
D) At position 6, acetylcholine is broken down and the components are recycled.
E) At position 7, neurotransmitter is released.
 Which cellular event is paired correctly with the location where it occurs?
Which cellular event is paired correctly with the location where it occurs?A) At position 2, calcium ions trigger fusion of vesicles with the presynaptic membrane.
B) At position 3, voltage-gated calcium channels open.
C) At position 4, acetylcholine molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
D) At position 6, acetylcholine is broken down and the components are recycled.
E) At position 7, neurotransmitter is released.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Information about a sensory stimulus such as touch can be prevented from reaching the central nervous system by chemically blocking
A) touch receptors in the central nervous system.
B) afferent neurons from the sensory cells detecting touch.
C) graded potentials in interneurons.
D) efferent neurons carrying information to the spinal cord.
E) neurotransmitter release from interneurons in the brain.
A) touch receptors in the central nervous system.
B) afferent neurons from the sensory cells detecting touch.
C) graded potentials in interneurons.
D) efferent neurons carrying information to the spinal cord.
E) neurotransmitter release from interneurons in the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is not necessary for the formation of a neural network?
A) Neurons carrying sensory information into the nervous system
B) Neurons carrying commands to effector structures such as muscles and glands
C) Neurons integrating information between incoming sensory neurons and outgoing efferent neurons
D) A brain that coordinates information between afferent and efferent neurons
E) Synapses between presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons
A) Neurons carrying sensory information into the nervous system
B) Neurons carrying commands to effector structures such as muscles and glands
C) Neurons integrating information between incoming sensory neurons and outgoing efferent neurons
D) A brain that coordinates information between afferent and efferent neurons
E) Synapses between presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Refer to the graphs showing action potentials occurring in response to multiple excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs). 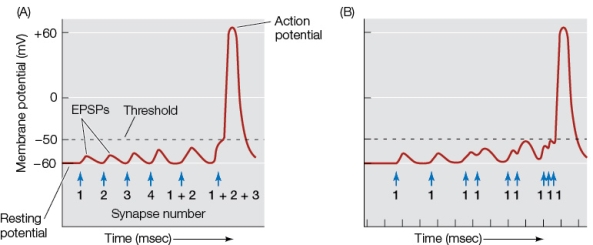 In graph B, the action potential is due to
In graph B, the action potential is due to
A) the rapid succession of EPSPs at one synapse.
B) the action of each EPSP, which raises the membrane potential above its threshold.
C) saltatory conduction along the axon receiving the EPSP.
D) the increase in strength of the EPSP as it spreads from the synapse.
E) the spatial summation of several simultaneous EPSPs.
 In graph B, the action potential is due to
In graph B, the action potential is due toA) the rapid succession of EPSPs at one synapse.
B) the action of each EPSP, which raises the membrane potential above its threshold.
C) saltatory conduction along the axon receiving the EPSP.
D) the increase in strength of the EPSP as it spreads from the synapse.
E) the spatial summation of several simultaneous EPSPs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which statement about the summation of postsynaptic potentials is false?
A) Summation typically takes place in the axon hillock.
B) It is the major mechanism for integrating information within the nervous system.
C) A neuron receives only excitatory or inhibitory input, but not both.
D) Temporal summation adds up potentials generated at the same site in rapid succession.
E) Spatial summation adds up potentials generated simultaneously at different sites on the cell.
A) Summation typically takes place in the axon hillock.
B) It is the major mechanism for integrating information within the nervous system.
C) A neuron receives only excitatory or inhibitory input, but not both.
D) Temporal summation adds up potentials generated at the same site in rapid succession.
E) Spatial summation adds up potentials generated simultaneously at different sites on the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which experimental stimulus would most likely produce the greatest response in a postsynaptic neuronal membrane?
A) A rapid stimulus that hyperpolarizes some parts of the membrane and depolarizes others
B) A sudden stimulus that opens Ca2+ channels
C) A single stimulus that increases neurotransmitter synthesis
D) A steady stimulus that makes the resting membrane potential more negative
E) A repeated stimulus that occurs at different sites on the postsynaptic cell
A) A rapid stimulus that hyperpolarizes some parts of the membrane and depolarizes others
B) A sudden stimulus that opens Ca2+ channels
C) A single stimulus that increases neurotransmitter synthesis
D) A steady stimulus that makes the resting membrane potential more negative
E) A repeated stimulus that occurs at different sites on the postsynaptic cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which statement about electrical synapses is false?
A) Electrical synapses do not perform temporal summation.
B) Signal transmission is rapid at electrical synapses.
C) Electrical synapses are mostly excitatory.
D) Electrical synapses are less common than chemical synapses in vertebrates.
E) Gap junctions are rare at electrical synapses.
A) Electrical synapses do not perform temporal summation.
B) Signal transmission is rapid at electrical synapses.
C) Electrical synapses are mostly excitatory.
D) Electrical synapses are less common than chemical synapses in vertebrates.
E) Gap junctions are rare at electrical synapses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A particular disease of the nervous system specifically involves the Ca2+ channels at the chemical synapses of motor neurons where neurotransmitter is stored and released.This disease therefore affects the
A) axon terminals of the presynaptic cell and the release of acetylcholine.
B) axon terminals of the postsynaptic cell and the release of K+.
C) movement of Na+ out of the postsynaptic cell.
D) axon terminals of the presynaptic cell and the release of K+.
E) axon terminals of the postsynaptic cell and the release of Cl-.
A) axon terminals of the presynaptic cell and the release of acetylcholine.
B) axon terminals of the postsynaptic cell and the release of K+.
C) movement of Na+ out of the postsynaptic cell.
D) axon terminals of the presynaptic cell and the release of K+.
E) axon terminals of the postsynaptic cell and the release of Cl-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Refer to the graphs showing action potentials occurring in response to multiple excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs). 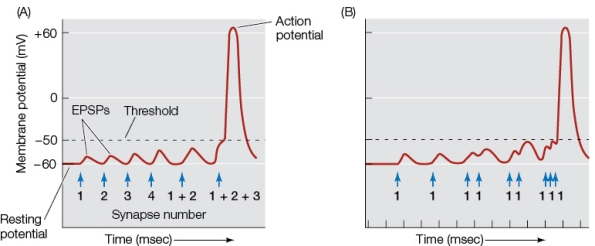 In graph A, the action potential is due to
In graph A, the action potential is due to
A) the action of each EPSP, which raises the membrane potential above its threshold.
B) the spatial summation of several simultaneous EPSPs.
C) the number of synapses on the cell body.
D) the rapid succession of EPSPs at one synapse.
E) the lack of inhibitory synapses.
 In graph A, the action potential is due to
In graph A, the action potential is due toA) the action of each EPSP, which raises the membrane potential above its threshold.
B) the spatial summation of several simultaneous EPSPs.
C) the number of synapses on the cell body.
D) the rapid succession of EPSPs at one synapse.
E) the lack of inhibitory synapses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The binding of acetylcholine results in a(n) _______ in the motor end plate membrane.
A) graded potential
B) equilibrium potential for K+
C) hyperpolarization
D) action potential
E) influx of acetylcholinesterase
A) graded potential
B) equilibrium potential for K+
C) hyperpolarization
D) action potential
E) influx of acetylcholinesterase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which statement about the ganglia of invertebrates is true?
A) They are found in animals whose neural networks are characterized by little or no integration of information.
B) Paired ganglia are present primarily in radially symmetrical organisms.
C) Paired ganglia are found in the nerve nets of cnidarians.
D) They are found primarily in organisms with nerve nets.
E) A large set of fused ganglia at the anterior end of an organism is a brain.
A) They are found in animals whose neural networks are characterized by little or no integration of information.
B) Paired ganglia are present primarily in radially symmetrical organisms.
C) Paired ganglia are found in the nerve nets of cnidarians.
D) They are found primarily in organisms with nerve nets.
E) A large set of fused ganglia at the anterior end of an organism is a brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If the clearance of neurotransmitter from the synaptic cleft is prevented, which of the following will be the most likely result?
A) The presynaptic cell will be unable to release more neurotransmitter.
B) The postsynaptic cell will return to its resting potential.
C) The postsynaptic cell will respond more quickly to a change in output of the presynaptic cell.
D) The buildup of neurotransmitter will cause activation of the presynaptic cell.
E) The postsynaptic cell will be constantly activated.
A) The presynaptic cell will be unable to release more neurotransmitter.
B) The postsynaptic cell will return to its resting potential.
C) The postsynaptic cell will respond more quickly to a change in output of the presynaptic cell.
D) The buildup of neurotransmitter will cause activation of the presynaptic cell.
E) The postsynaptic cell will be constantly activated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which statement about the withdrawal response to stepping on a piece of broken glass is false?
A) The withdrawal reflex involves a simpler neural circuit than does the knee-jerk reflex.
B) In the withdrawal reflex, sensory neurons transmit action potentials into the dorsal horn of the spinal cord.
C) Some interneurons coordinate withdrawal of the foot with the actions of muscles associated with shifting weight to the other leg.
D) The reflex by which the foot is withdrawn is a polysynaptic spinal reflex.
E) Some interneurons send pain information to the brain.
A) The withdrawal reflex involves a simpler neural circuit than does the knee-jerk reflex.
B) In the withdrawal reflex, sensory neurons transmit action potentials into the dorsal horn of the spinal cord.
C) Some interneurons coordinate withdrawal of the foot with the actions of muscles associated with shifting weight to the other leg.
D) The reflex by which the foot is withdrawn is a polysynaptic spinal reflex.
E) Some interneurons send pain information to the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Refer to the figure showing a neuromuscular junction. 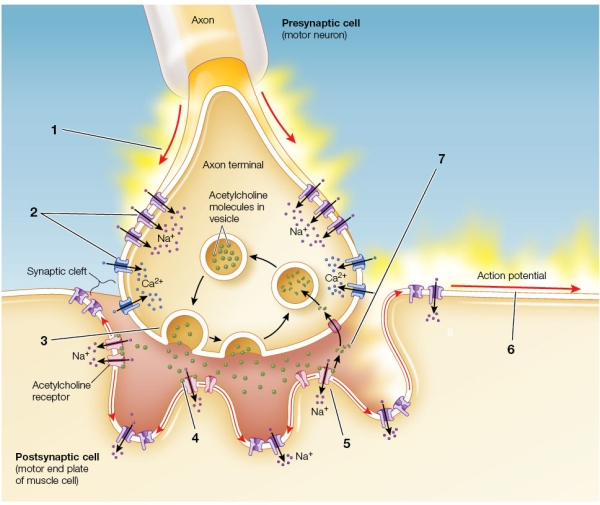 Which event is occurring at position 5?
Which event is occurring at position 5?
A) Acetylcholine molecules are entering the postsynaptic cell.
B) Ca2+ channels open after acetylcholine binding occurs.
C) Charged acetylcholine molecules cause a graded potential in the postsynaptic membrane.
D) The motor end plate is depolarized by the influx of Na+.
E) Acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine, and the channel closes again.
 Which event is occurring at position 5?
Which event is occurring at position 5?A) Acetylcholine molecules are entering the postsynaptic cell.
B) Ca2+ channels open after acetylcholine binding occurs.
C) Charged acetylcholine molecules cause a graded potential in the postsynaptic membrane.
D) The motor end plate is depolarized by the influx of Na+.
E) Acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine, and the channel closes again.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Sea stars are marine animals that have the simplest form of nervous system, a _______, located in each arm.
A) ganglion
B) brain
C) nerve net
D) peripheral nervous system
E) central nervous system
A) ganglion
B) brain
C) nerve net
D) peripheral nervous system
E) central nervous system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A chemical synapse differs from an electrical synapse in that a chemical synapse
A) allows for faster transmission of a signal.
B) allows for many more synaptic inputs per cell.
C) does not allow for temporal summation of synaptic inputs.
D) requires a larger area of cell‒cell contact.
E) cannot be inhibitory.
A) allows for faster transmission of a signal.
B) allows for many more synaptic inputs per cell.
C) does not allow for temporal summation of synaptic inputs.
D) requires a larger area of cell‒cell contact.
E) cannot be inhibitory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 250 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



