Deck 46: The Mammalian Nervous System: Structure and Higher Functions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/254
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 46: The Mammalian Nervous System: Structure and Higher Functions
1
Refer to the figure, which shows a cross section of an adult human brain. 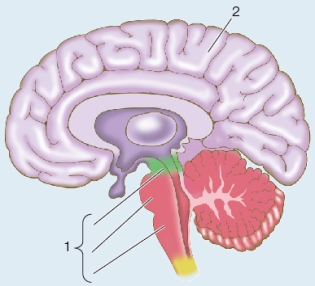 The three parts of structure 1 develop from the midbrain and regions of the hindbrain of an embryo and control many autonomic functions, such as breathing and basic motor patterns.Collectively these three parts are known as the
The three parts of structure 1 develop from the midbrain and regions of the hindbrain of an embryo and control many autonomic functions, such as breathing and basic motor patterns.Collectively these three parts are known as the
A) brainstem.
B) cerebellum.
C) cerebrum.
D) spinal cord.
E) cerebral cortex.
 The three parts of structure 1 develop from the midbrain and regions of the hindbrain of an embryo and control many autonomic functions, such as breathing and basic motor patterns.Collectively these three parts are known as the
The three parts of structure 1 develop from the midbrain and regions of the hindbrain of an embryo and control many autonomic functions, such as breathing and basic motor patterns.Collectively these three parts are known as theA) brainstem.
B) cerebellum.
C) cerebrum.
D) spinal cord.
E) cerebral cortex.
brainstem.
2
The ascending pathways of the reticular activating system in the brainstem promote wakefulness.If a person's spinal cord is damaged below the level of this area,
A) the person will be awake more than usual.
B) the person will be in a coma.
C) the person will be unable to sleep normal amounts of time.
D) the person's sleep‒wake cycles will be reversed.
E) paralysis can result, but there will be no effect on the person's sleep‒wake cycles.
A) the person will be awake more than usual.
B) the person will be in a coma.
C) the person will be unable to sleep normal amounts of time.
D) the person's sleep‒wake cycles will be reversed.
E) paralysis can result, but there will be no effect on the person's sleep‒wake cycles.
E
3
If a patient is in a coma, the primary region of the brain that is not activating neurons in the cortex is the
A) relay station in the thalamus.
B) forebrain.
C) limbic system.
D) reticular-activating system.
E) cerebellum.
A) relay station in the thalamus.
B) forebrain.
C) limbic system.
D) reticular-activating system.
E) cerebellum.
D
4
At the core of the forebrain are evolutionarily older structures that govern instincts, long-term memory formation, and physiological drives.These are known as the _______, and they develop from the embryonic _______.
A) hypothalamus; forebrain
B) homeostatic system; hindbrain
C) limbic system; forebrain
D) cerebral cortex; forebrain
E) cerebrum; hindbrain
A) hypothalamus; forebrain
B) homeostatic system; hindbrain
C) limbic system; forebrain
D) cerebral cortex; forebrain
E) cerebrum; hindbrain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Damage to the embryonic telencephalon could affect development of the _______, which plays major roles in _______.
A) cerebrum; learning and memory
B) cerebellum; coordination and balance
C) hypothalamus; controlling the pituitary gland
D) pons; regulating breathing
E) thalamus; conscious behavior
A) cerebrum; learning and memory
B) cerebellum; coordination and balance
C) hypothalamus; controlling the pituitary gland
D) pons; regulating breathing
E) thalamus; conscious behavior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Neurons localized in the brainstem that control autonomic functions communicate with their effectors via the
A) central nervous system.
B) cranial nerves.
C) pons.
D) nuclei.
E) spinal cord.
A) central nervous system.
B) cranial nerves.
C) pons.
D) nuclei.
E) spinal cord.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Conscious afferents are part of the _______ nervous system and carry information from _______.
A) central; sensory receptor cells
B) enteric; endocrine glands
C) peripheral; sensory receptor cells
D) peripheral; the central nervous system to muscles
E) central; the central nervous system to glands
A) central; sensory receptor cells
B) enteric; endocrine glands
C) peripheral; sensory receptor cells
D) peripheral; the central nervous system to muscles
E) central; the central nervous system to glands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is not true of the hypothalamus?
A) It controls the pituitary gland.
B) It develops from the telencephalon.
C) It is located below the thalamus.
D) It regulates many physiological functions.
E) It regulates biological drives.
A) It controls the pituitary gland.
B) It develops from the telencephalon.
C) It is located below the thalamus.
D) It regulates many physiological functions.
E) It regulates biological drives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Refer to the figure, which shows a cross section of an adult human brain. 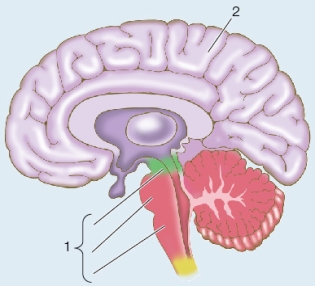 Structure 2 is the _______, which develops from the embryonic ______.
Structure 2 is the _______, which develops from the embryonic ______.
A) cerebellum; telencephalon
B) cerebellum; hindbrain
C) cerebrum; telencephalon
D) cerebrum; diencephalon
E) cerebellum; forebrain
 Structure 2 is the _______, which develops from the embryonic ______.
Structure 2 is the _______, which develops from the embryonic ______.A) cerebellum; telencephalon
B) cerebellum; hindbrain
C) cerebrum; telencephalon
D) cerebrum; diencephalon
E) cerebellum; forebrain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which pathway is correct?
A) Unconscious efferents to central nervous system to autonomic afferents
B) Unconscious afferents to peripheral nervous system to autonomic efferents
C) Conscious afferents to peripheral nervous system to voluntary efferents
D) Voluntary efferents to central nervous system to conscious afferents
E) Unconscious afferents to central nervous system to autonomic efferents
A) Unconscious efferents to central nervous system to autonomic afferents
B) Unconscious afferents to peripheral nervous system to autonomic efferents
C) Conscious afferents to peripheral nervous system to voluntary efferents
D) Voluntary efferents to central nervous system to conscious afferents
E) Unconscious afferents to central nervous system to autonomic efferents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
As you are driving home one night, you see a dark animal bound across the road.You quickly apply the brakes as you feel your heart starting to pound in your chest.Which of the following best describes the flow of information leading to these two responses?
A) Afferent peripheral nerves central nervous system efferent peripheral nerves
B) Unconscious information conscious information central nervous system
C) Central nervous system autonomic nervous system central nervous system
D) Conscious information hormones peripheral nervous system
E) Autonomic commands peripheral nervous system central nervous system
A) Afferent peripheral nerves central nervous system efferent peripheral nerves
B) Unconscious information conscious information central nervous system
C) Central nervous system autonomic nervous system central nervous system
D) Conscious information hormones peripheral nervous system
E) Autonomic commands peripheral nervous system central nervous system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
All of the following characterize the cerebrum except
A) consists of right and left cerebral hemispheres.
B) has an inner layer called the cerebral cortex.
C) increases in size and complexity from fishes to mammals.
D) develops from the embryonic forebrain, specifically the telencephalon.
E) plays a role in sensory perception and conscious behavior.
A) consists of right and left cerebral hemispheres.
B) has an inner layer called the cerebral cortex.
C) increases in size and complexity from fishes to mammals.
D) develops from the embryonic forebrain, specifically the telencephalon.
E) plays a role in sensory perception and conscious behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Early in the embryonic development of a vertebrate, the neural tube forms.This tube will later develop into all of the following except
A) the hindbrain.
B) the heart.
C) the midbrain.
D) the spinal cord.
E) the forebrain.
A) the hindbrain.
B) the heart.
C) the midbrain.
D) the spinal cord.
E) the forebrain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Voluntary efferents are part of the _______ nervous system and carry information _______.
A) central; from sensory receptor cells
B) enteric; from endocrine glands
C) peripheral; related to physiological controls
D) peripheral; to skeletal muscles
E) central; to skeletal muscles
A) central; from sensory receptor cells
B) enteric; from endocrine glands
C) peripheral; related to physiological controls
D) peripheral; to skeletal muscles
E) central; to skeletal muscles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Neural information controlling heart rate would travel
A) from the peripheral nervous system to the central nervous system.
B) from the central nervous system to the heart via autonomic efferents.
C) from the central nervous system to the heart via unconscious afferents.
D) to the central nervous system via hormones.
E) from the peripheral nervous system to the heart via conscious afferents
A) from the peripheral nervous system to the central nervous system.
B) from the central nervous system to the heart via autonomic efferents.
C) from the central nervous system to the heart via unconscious afferents.
D) to the central nervous system via hormones.
E) from the peripheral nervous system to the heart via conscious afferents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Gymnasts rely on parts of their brains to execute their routines precisely.The region of the brain that is most important for coordinating motor commands and maintaining balance is the _______, which develops from the embryonic _______.
A) cerebrum; forebrain
B) cerebral cortex; hindbrain
C) cerebellum; hindbrain
D) right cerebral hemisphere; midbrain
E) diencephalon; forebrain
A) cerebrum; forebrain
B) cerebral cortex; hindbrain
C) cerebellum; hindbrain
D) right cerebral hemisphere; midbrain
E) diencephalon; forebrain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
All information from the spinal cord must pass through the _______ on its way to other regions of the brain for higher processing.
A) forebrain
B) telencephalon
C) brainstem
D) diencephalon
E) cerebrum
A) forebrain
B) telencephalon
C) brainstem
D) diencephalon
E) cerebrum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The diencephalon develops into the
A) cerebrum.
B) thalamus and hypothalamus.
C) brainstem.
D) spinal cord.
E) cerebellum.
A) cerebrum.
B) thalamus and hypothalamus.
C) brainstem.
D) spinal cord.
E) cerebellum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which is an incorrect match between embryonic brain region and structure that develops from that region?
A) Telencephalon; cerebrum
B) Hindbrain; pons
C) Midbrain: thalamus
D) Hindbrain; cerebellum
E) Diencephalon; hypothalamus
A) Telencephalon; cerebrum
B) Hindbrain; pons
C) Midbrain: thalamus
D) Hindbrain; cerebellum
E) Diencephalon; hypothalamus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which structures develop from the embryonic hindbrain?
A) Medulla; pons; cerebrum
B) Thalamus; hypothalamus
C) Association cortex; limbic system
D) Amygdala; hippocampus
E) Medulla; pons; cerebellum
A) Medulla; pons; cerebrum
B) Thalamus; hypothalamus
C) Association cortex; limbic system
D) Amygdala; hippocampus
E) Medulla; pons; cerebellum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system can be distinguished by their anatomy, neurotransmitters, and actions.Which of the following is not associated with the sympathetic division?
A) Acetylcholine
B) Increased heart rate
C) Relaxed airways
D) Increased activity of the digestive tract
E) Chain-like arrangement of ganglia
A) Acetylcholine
B) Increased heart rate
C) Relaxed airways
D) Increased activity of the digestive tract
E) Chain-like arrangement of ganglia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system can be distinguished by their anatomy, neurotransmitters, and actions.Which of the following is not associated with the parasympathetic division?
A) Increased activity of the digestive tract
B) Acetylcholine
C) Constriction of pupils
D) Fight-or-flight response
E) Location of ganglia close to target organs
A) Increased activity of the digestive tract
B) Acetylcholine
C) Constriction of pupils
D) Fight-or-flight response
E) Location of ganglia close to target organs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following would not result from stimulating sympathetic nerves?
A) Dilation of pupils
B) Increased heart rate
C) Increased breakdown of glycogen
D) Increased release of glucose
E) Contraction of the urinary bladder
A) Dilation of pupils
B) Increased heart rate
C) Increased breakdown of glycogen
D) Increased release of glucose
E) Contraction of the urinary bladder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following would not result from stimulating parasympathetic nerves?
A) Constriction of pupils
B) Contraction of urinary bladder
C) Inhibition of stomach motility
D) Constriction of airways
E) Increased uptake of glucose
A) Constriction of pupils
B) Contraction of urinary bladder
C) Inhibition of stomach motility
D) Constriction of airways
E) Increased uptake of glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which statement about mammal brain evolution is false?
A) Dolphins and humans have much larger brains that would be predicted based on body sizes.
B) Elephants and blue whales have large brains, but they fall close to the regression line of brain mass versus body mass.
C) The cerebral cortex is elaborated in mammals.
D) Convolutions in the brains of mammals decrease the surface area of the cortex.
E) The percent of cortex that is association cortex is greatest in humans.
A) Dolphins and humans have much larger brains that would be predicted based on body sizes.
B) Elephants and blue whales have large brains, but they fall close to the regression line of brain mass versus body mass.
C) The cerebral cortex is elaborated in mammals.
D) Convolutions in the brains of mammals decrease the surface area of the cortex.
E) The percent of cortex that is association cortex is greatest in humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Evolutionary change has resulted in the brains of some vertebrate species being larger than would be predicted based on their body size.The larger brain size is mostly due to an increase in surface area and is made possible by the convolutions of the cerebral cortex.This contributes primarily to
A) increased cognitive capacity.
B) increased running ability.
C) decreased energy needs.
D) less association cortex.
E) a larger brainstem.
A) increased cognitive capacity.
B) increased running ability.
C) decreased energy needs.
D) less association cortex.
E) a larger brainstem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Difficulty in planning future events as well as changes in personality can be attributed to many things, from drug abuse to mental illness.In assessing a new patient with these conditions, a physician should also evaluate possible trauma to the _______, because damage to this region can have the same effects.
A) primary motor cortex
B) primary somatosensory cortex
C) occipital lobe
D) temporal lobe
E) frontal lobe
A) primary motor cortex
B) primary somatosensory cortex
C) occipital lobe
D) temporal lobe
E) frontal lobe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is not produced by the sympathetic nervous system?
A) Increased heart rate
B) Increased secretion by the adrenal gland of epinephrine and norepinephrine
C) Increased glycogen breakdown and glucose release
D) Relaxation of airways and increased breathing rate
E) Increased intestinal activity
A) Increased heart rate
B) Increased secretion by the adrenal gland of epinephrine and norepinephrine
C) Increased glycogen breakdown and glucose release
D) Relaxation of airways and increased breathing rate
E) Increased intestinal activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which regions of the body have the greatest representation in the primary motor cortex?
A) Areas related to visual processing
B) Areas involved in fine motor control
C) Regions with the most muscle mass
D) Muscles involved in the fight-or-flight response
E) The palms of the hands
A) Areas related to visual processing
B) Areas involved in fine motor control
C) Regions with the most muscle mass
D) Muscles involved in the fight-or-flight response
E) The palms of the hands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A neurosurgeon is electrically stimulating different regions of a patient's primary motor cortex using fine electrodes.As the electrodes are moved to different areas, each stimulus causes the patient to experience
A) an increase in heart rate.
B) pain in different parts of the body.
C) greater visual sensitivity to light.
D) muscle twitches.
E) vivid memories.
A) an increase in heart rate.
B) pain in different parts of the body.
C) greater visual sensitivity to light.
D) muscle twitches.
E) vivid memories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
After an accident that caused damage to the left parietal lobe, a patient is unable to perform complex tasks on the right side of his body, such as shaving or dressing.This unusual condition is called _______ syndrome.
A) asymmetry
B) association
C) parietal
D) contralateral neglect
E) somatosensory
A) asymmetry
B) association
C) parietal
D) contralateral neglect
E) somatosensory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following about the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system is false?
A) Preganglionic neurons come from cranial nerves and the sacral region of the spinal cord.
B) It has preganglionic cholinergic neurons.
C) It inhibits salivation.
D) It has postganglionic noradrenergic neurons.
E) It relaxes the urinary bladder.
A) Preganglionic neurons come from cranial nerves and the sacral region of the spinal cord.
B) It has preganglionic cholinergic neurons.
C) It inhibits salivation.
D) It has postganglionic noradrenergic neurons.
E) It relaxes the urinary bladder.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The thalamus is the relay station for touch and pressure information from the body, which it sends to the _______ cortex of the _______ lobe for processing.
A) primary motor; frontal
B) primary somatosensory; parietal
C) auditory; temporal
D) visual; occipital
E) premotor; frontal
A) primary motor; frontal
B) primary somatosensory; parietal
C) auditory; temporal
D) visual; occipital
E) premotor; frontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Refer to the figure, which shows the human brain. 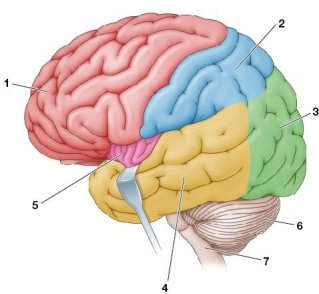 Which is an incorrect match between the numbered brain region and its name.
Which is an incorrect match between the numbered brain region and its name.
A) 1, frontal lobe
B) 2, parietal lobe
C) 3, occipital lobe
D) 4, temporal lobe
E) 5, hypothalamus
 Which is an incorrect match between the numbered brain region and its name.
Which is an incorrect match between the numbered brain region and its name.A) 1, frontal lobe
B) 2, parietal lobe
C) 3, occipital lobe
D) 4, temporal lobe
E) 5, hypothalamus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The region of the cerebral cortex that is involved in processing higher-order information is the
A) limbic system.
B) cortex system.
C) association cortex.
D) telencephalon.
E) thalamus.
A) limbic system.
B) cortex system.
C) association cortex.
D) telencephalon.
E) thalamus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of these pairs of actions will both cause an increase in salivation?
A) Stimulating sympathetic nerves to salivary glands, and applying norepinephrine to salivary gland cells
B) Stimulating parasympathetic nerves to salivary glands, and applying norepinephrine to salivary gland cells
C) Damaging parasympathetic nerves to salivary glands, and applying acetylcholine to salivary gland cells
D) Stimulating parasympathetic nerves to salivary glands, and applying acetylcholine to salivary gland cells
E) Damaging sympathetic nerves to salivary glands, and applying norepinephrine to salivary gland cells
A) Stimulating sympathetic nerves to salivary glands, and applying norepinephrine to salivary gland cells
B) Stimulating parasympathetic nerves to salivary glands, and applying norepinephrine to salivary gland cells
C) Damaging parasympathetic nerves to salivary glands, and applying acetylcholine to salivary gland cells
D) Stimulating parasympathetic nerves to salivary glands, and applying acetylcholine to salivary gland cells
E) Damaging sympathetic nerves to salivary glands, and applying norepinephrine to salivary gland cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The entire body surface can be mapped onto the primary somatosensory cortex, based on the density of mechanoreceptors and the ability to make fine discriminations in touch in a given area.Which of the following would require the smallest amount of cortical representation in comparison to its surface area?
A) Legs
B) Hands
C) Fingers
D) Face
E) Lips
A) Legs
B) Hands
C) Fingers
D) Face
E) Lips

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Damage to which of the following structures could impair spatial memory?
A) Hypothalamus
B) Thalamus
C) Amygdala
D) Brainstem
E) Hippocampus
A) Hypothalamus
B) Thalamus
C) Amygdala
D) Brainstem
E) Hippocampus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Refer to the figure, which shows the human brain. 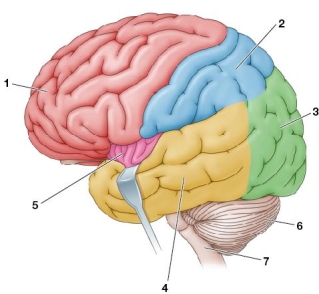 Choose the incorrect match between the numbered brain region and its primary function(s).
Choose the incorrect match between the numbered brain region and its primary function(s).
A) 1; controls muscles, contributes to personality, and allows future planning
B) 2; receives information about touch and pressure
C) 3; receives information about social interactions
D) 4; processes auditory information and functions in recognition and naming of objects
E) 5; receives somatosensory and autonomic regulatory information
 Choose the incorrect match between the numbered brain region and its primary function(s).
Choose the incorrect match between the numbered brain region and its primary function(s).A) 1; controls muscles, contributes to personality, and allows future planning
B) 2; receives information about touch and pressure
C) 3; receives information about social interactions
D) 4; processes auditory information and functions in recognition and naming of objects
E) 5; receives somatosensory and autonomic regulatory information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
After head trauma, an athlete cannot recognize his teammates' faces, but he can recognize them by their voices and other body features.This particular agnosia is most likely the result of damage to association areas of the
A) occipital lobe.
B) visual cortex.
C) temporal lobe.
D) motor cortex.
E) frontal lobe.
A) occipital lobe.
B) visual cortex.
C) temporal lobe.
D) motor cortex.
E) frontal lobe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Kuffler's experiments on cat retinas revealed that each retinal ganglion cell has a receptive field composed of
A) adjacent retinal ganglion cells.
B) a group of photoreceptors that respond to a portion of the visual field.
C) a group of photoreceptors and the ganglion cells with which they synapse.
D) a photoreceptor that responds to a single spot of light.
E) a group of binocular cells.
A) adjacent retinal ganglion cells.
B) a group of photoreceptors that respond to a portion of the visual field.
C) a group of photoreceptors and the ganglion cells with which they synapse.
D) a photoreceptor that responds to a single spot of light.
E) a group of binocular cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements about the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system is false?
A) Preganglionic and postganglionic neurons of the parasympathetic division are cholinergic.
B) Some preganglionic neurons of the parasympathetic division come from the sacral region of the spinal cord.
C) Ganglia of the parasympathetic division are close to target organs.
D) The parasympathetic division stimulates release of glucose from the liver.
E) The parasympathetic division stimulates stomach secretions.
A) Preganglionic and postganglionic neurons of the parasympathetic division are cholinergic.
B) Some preganglionic neurons of the parasympathetic division come from the sacral region of the spinal cord.
C) Ganglia of the parasympathetic division are close to target organs.
D) The parasympathetic division stimulates release of glucose from the liver.
E) The parasympathetic division stimulates stomach secretions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Refer to the figure, which shows the rate of action potentials in a ganglion cell. 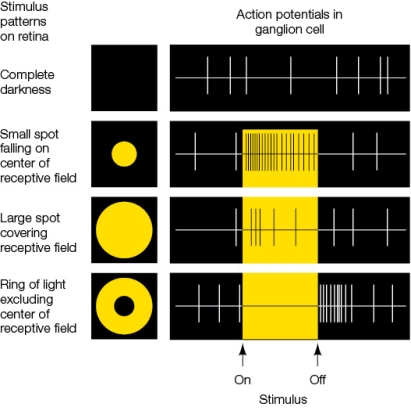 The ganglion cell being monitored is inhibited from firing action potentials when
The ganglion cell being monitored is inhibited from firing action potentials when
A) a small spot of light is received by the center of the receptive field.
B) the receptive field is in complete darkness.
C) the entire receptive field is presented with a large spot of light.
D) the receptive field is in the dark after a small spot of light is delivered.
E) a ring of light excluding the center of the receptive field is delivered.
 The ganglion cell being monitored is inhibited from firing action potentials when
The ganglion cell being monitored is inhibited from firing action potentials whenA) a small spot of light is received by the center of the receptive field.
B) the receptive field is in complete darkness.
C) the entire receptive field is presented with a large spot of light.
D) the receptive field is in the dark after a small spot of light is delivered.
E) a ring of light excluding the center of the receptive field is delivered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Photoreceptors in the surround portion of a receptive field modify the light information received by photoreceptors in the center of the receptive field.They accomplish this by
A) firing action potentials onto the photoreceptors in the center.
B) modifying communication between the center photoreceptors and their bipolar cells through horizontal and amacrine cells.
C) reducing the communication between the center and the surround.
D) expanding communication to adjacent receptive fields.
E) blocking bipolar cell transmission to retinal ganglion cells.
A) firing action potentials onto the photoreceptors in the center.
B) modifying communication between the center photoreceptors and their bipolar cells through horizontal and amacrine cells.
C) reducing the communication between the center and the surround.
D) expanding communication to adjacent receptive fields.
E) blocking bipolar cell transmission to retinal ganglion cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The receptive field of a retinal ganglion cell results from a pattern of synapses between photoreceptors, horizontal cells, amacrine cells, and bipolar cells.Which of the following demonstrates the balance between excitatory and inhibitory inputs to an on-center retinal ganglion cell?
A) When light covers the entire receptive field, it has very little effect on the firing rate of the ganglion cell for that receptive field.
B) When light falls only on the center of the receptive field, action potentials are maximally induced.
C) Where there is no light exposure, action potentials are infrequent.
D) When light reaches only the surround of the receptive field, action potentials are absent.
E) When light covers the entire receptive field, action potentials are absent.
A) When light covers the entire receptive field, it has very little effect on the firing rate of the ganglion cell for that receptive field.
B) When light falls only on the center of the receptive field, action potentials are maximally induced.
C) Where there is no light exposure, action potentials are infrequent.
D) When light reaches only the surround of the receptive field, action potentials are absent.
E) When light covers the entire receptive field, action potentials are absent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Neurons in the visual cortex are organized into _______ with _______ cells at the boarders of the columns.
A) centers and surrounds; binocular
B) columns; horizontal
C) rows; ganglion
D) columns; binocular
E) borders; bipolar
A) centers and surrounds; binocular
B) columns; horizontal
C) rows; ganglion
D) columns; binocular
E) borders; bipolar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Bipolar cells receive input from a large number of photoreceptors, and individual retinal ganglion cells collect information from a number of bipolar cells.The ability of individual ganglion cells to receive inputs from multiple neurons is called
A) convergence of information.
B) the visual field.
C) the visual cortex.
D) the on-center‒off-center system.
E) bipolar cell connectivity.
A) convergence of information.
B) the visual field.
C) the visual cortex.
D) the on-center‒off-center system.
E) bipolar cell connectivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Receptive fields have a center and concentric surround that stimulate the firing of action potentials in opposition to one another.Given this arrangement, the response and pattern of firing would you expect from an off-center retinal ganglion cell when a spot of light hits the center of its receptive field is that the ganglion cell would
A) be excited and would decrease its firing rate.
B) be inhibited and would increase its firing rate.
C) increase its firing rate, even though the photoreceptors would be inhibited.
D) be excited and its firing rate would increase.
E) be inhibited, and its firing rate would decrease.
A) be excited and would decrease its firing rate.
B) be inhibited and would increase its firing rate.
C) increase its firing rate, even though the photoreceptors would be inhibited.
D) be excited and its firing rate would increase.
E) be inhibited, and its firing rate would decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Species with front-facing eyes and overlapping visual fields have
A) the ability to see equally well to the front and to the sides.
B) selective vision.
C) binocular vision.
D) poor depth perception.
E) an extensive field of view.
A) the ability to see equally well to the front and to the sides.
B) selective vision.
C) binocular vision.
D) poor depth perception.
E) an extensive field of view.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Half of the information from each eye — that is, the information from the half of each retina that is closest to the nose — crosses to the opposite side of the brain for processing.What is the functional consequence of this crossing over?
A) The visual fields do not overlap.
B) The visual cortex does not distinguish which side of the visual field the information arrived from.
C) The splitting of information prevents too many action potentials from arriving in the cortex at the same time.
D) The thalamus reassembles the information from both eyes for processing.
E) All of the information from the left visual field goes to the right side of the brain, and all of the information from the right visual field goes to the left side of the brain.
A) The visual fields do not overlap.
B) The visual cortex does not distinguish which side of the visual field the information arrived from.
C) The splitting of information prevents too many action potentials from arriving in the cortex at the same time.
D) The thalamus reassembles the information from both eyes for processing.
E) All of the information from the left visual field goes to the right side of the brain, and all of the information from the right visual field goes to the left side of the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following correctly represents the flow of information about light, from the sensory cells in the retina to the brain?
A) Retina optic nerve retinal ganglion cells bipolar cells photoreceptors
B) Visual field photoreceptors retinal ganglion cells optic nerve brain
C) Photoreceptors bipolar cells retinal ganglion cells optic nerve brain
D) Bipolar cells retinal ganglion cells photoreceptors axons brain
E) Photoreceptors optic nerves bipolar cells retinal ganglion cells brain
A) Retina optic nerve retinal ganglion cells bipolar cells photoreceptors
B) Visual field photoreceptors retinal ganglion cells optic nerve brain
C) Photoreceptors bipolar cells retinal ganglion cells optic nerve brain
D) Bipolar cells retinal ganglion cells photoreceptors axons brain
E) Photoreceptors optic nerves bipolar cells retinal ganglion cells brain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Refer to the figure, which shows the rate of action potentials in a ganglion cell. 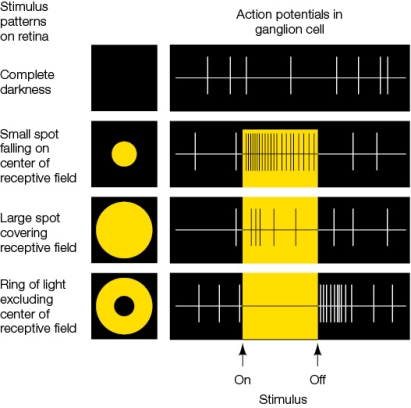 What can you conclude about the type of cell being monitored?
What can you conclude about the type of cell being monitored?
A) It is an off-center ganglion cell.
B) It is an on-center ganglion cell.
C) It is a photoreceptor.
D) It is a bipolar cell.
E) It is a horizontal cell.
 What can you conclude about the type of cell being monitored?
What can you conclude about the type of cell being monitored?A) It is an off-center ganglion cell.
B) It is an on-center ganglion cell.
C) It is a photoreceptor.
D) It is a bipolar cell.
E) It is a horizontal cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The optic nerves converge briefly in the _______ and then separate again.
A) occipital lobe
B) thalamus
C) retina
D) optic chiasm
E) visual cortex
A) occipital lobe
B) thalamus
C) retina
D) optic chiasm
E) visual cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Researchers experimenting on ganglion cells of the retina wish to produce the highest number of action potentials possible.To accomplish this, they should direct their beam of light to the _______ of an _______ ganglion cell's receptive field.
A) center and surround; on-center
B) center and surround; off-center
C) center; off-center
D) center; on-center
E) surround; on-center
A) center and surround; on-center
B) center and surround; off-center
C) center; off-center
D) center; on-center
E) surround; on-center

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Refer to the figure, which shows the rate of action potentials in a ganglion cell. 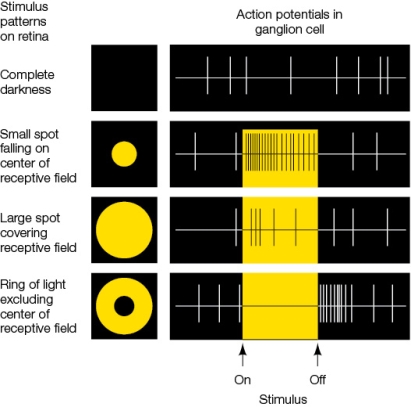 The rate of action potentials in the ganglion cell being monitored is highest when
The rate of action potentials in the ganglion cell being monitored is highest when
A) a small spot of light is delivered to the center of the receptive field.
B) the receptive field is in complete darkness.
C) the entire receptive field is presented with a large spot of light.
D) light outside of the receptive field is delivered.
E) a ring of light excluding the center of the receptive field is delivered.
 The rate of action potentials in the ganglion cell being monitored is highest when
The rate of action potentials in the ganglion cell being monitored is highest whenA) a small spot of light is delivered to the center of the receptive field.
B) the receptive field is in complete darkness.
C) the entire receptive field is presented with a large spot of light.
D) light outside of the receptive field is delivered.
E) a ring of light excluding the center of the receptive field is delivered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If you are looking at a pen that you are holding to the right of your visual field, the information about the image of the pen that is detected by the right eye will be processed by the
A) left visual cortex.
B) visual cortex on both sides of the brain.
C) right visual cortex.
D) optic chiasm.
E) left optic nerve.
A) left visual cortex.
B) visual cortex on both sides of the brain.
C) right visual cortex.
D) optic chiasm.
E) left optic nerve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following about the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system is false?
A) Its actions can be characterized as "rest and digest."
B) Its preganglionic neurons use acetylcholine as their neurotransmitter.
C) It relaxes airways.
D) Its postganglionic neurons use acetylcholine as their neurotransmitter.
E) It works in opposition to the sympathetic division in its effects on most target organs.
A) Its actions can be characterized as "rest and digest."
B) Its preganglionic neurons use acetylcholine as their neurotransmitter.
C) It relaxes airways.
D) Its postganglionic neurons use acetylcholine as their neurotransmitter.
E) It works in opposition to the sympathetic division in its effects on most target organs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
At the time of your oral presentation to the class, your mouth suddenly becomes incredibly dry, making it difficult to speak.This response results from
A) the effects of acetylcholine on salivary gland cells.
B) stimulation of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.
C) stimulation of preganglionic neurons coming from cranial nerves.
D) stimulation of noradrenergic neurons coming from the celiac ganglion.
E) stimulation of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.
A) the effects of acetylcholine on salivary gland cells.
B) stimulation of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.
C) stimulation of preganglionic neurons coming from cranial nerves.
D) stimulation of noradrenergic neurons coming from the celiac ganglion.
E) stimulation of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Choose the incorrect pairing of a division of the autonomic nervous system and one of its effects.
A) Parasympathetic division and slowing the heartbeat
B) Sympathetic division and stimulating stomach secretions
C) Sympathetic division and stimulating the breakdown of glycogen
D) Parasympathetic division and stimulating glucose uptake
E) Sympathetic division and relaxing the urinary bladder
A) Parasympathetic division and slowing the heartbeat
B) Sympathetic division and stimulating stomach secretions
C) Sympathetic division and stimulating the breakdown of glycogen
D) Parasympathetic division and stimulating glucose uptake
E) Sympathetic division and relaxing the urinary bladder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following statements about the autonomic nervous system (ANS) is false?
A) The ANS controls diverse organs and tissues, making its actions critical to homeostasis.
B) The ANS has two divisions, the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division.
C) The ANS controls many voluntary and involuntary functions.
D) The ANS includes components from both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
E) Every autonomic efferent pathway of the ANS begins with a cholinergic neuron.
A) The ANS controls diverse organs and tissues, making its actions critical to homeostasis.
B) The ANS has two divisions, the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division.
C) The ANS controls many voluntary and involuntary functions.
D) The ANS includes components from both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
E) Every autonomic efferent pathway of the ANS begins with a cholinergic neuron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Whether repeating a heard word or speaking a written word, the last area of the brain in each pathway is
A) Broca's area.
B) the angular gyrus.
C) Wernicke's area.
D) the primary motor cortex.
E) the primary somatosensory cortex.
A) Broca's area.
B) the angular gyrus.
C) Wernicke's area.
D) the primary motor cortex.
E) the primary somatosensory cortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In which sleep state does the electroencephalogram recording most closely resemble that of the awake brain, because depolarization of some neurons?
A) Non-REM Stage 1
B) Non-REM Stage 2
C) Non-REM Stage 3
D) REM
E) None
A) Non-REM Stage 1
B) Non-REM Stage 2
C) Non-REM Stage 3
D) REM
E) None

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If you were hooked up to electrodes that gave you a reading of only your eye movements (an electroocculogram, or EOG) during the night, would you be able to learn anything about your sleep cycles, and why?
A) No, because an electroencephalogram (EEG), which is recorded by scalp electrodes, is needed to monitor sleep states.
B) No, because both an EEG and an electromyogram (EMG) are needed to monitor sleep states.
C) Yes, because an EOG would tell you if your eyes were open.
D) Yes, because the EOG would measure jerky eye movements that characterize one type of sleep, called REM sleep.
E) No, because your breathing rate is also a factor and would not be monitored by an EOG.
A) No, because an electroencephalogram (EEG), which is recorded by scalp electrodes, is needed to monitor sleep states.
B) No, because both an EEG and an electromyogram (EMG) are needed to monitor sleep states.
C) Yes, because an EOG would tell you if your eyes were open.
D) Yes, because the EOG would measure jerky eye movements that characterize one type of sleep, called REM sleep.
E) No, because your breathing rate is also a factor and would not be monitored by an EOG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Language abilities are lateralized and are located in
A) one cerebral hemisphere, usually the left.
B) one cerebral hemisphere, usually the right.
C) both hemispheres equally.
D) the frontal lobe of the right cerebral hemisphere.
E) the thalamus.
A) one cerebral hemisphere, usually the left.
B) one cerebral hemisphere, usually the right.
C) both hemispheres equally.
D) the frontal lobe of the right cerebral hemisphere.
E) the thalamus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Refer to the figure. 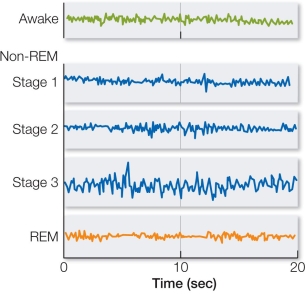 The figure shows electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings from a person who is awake and in different stages of sleep.Which of the following EEG recordings represents the period when bursts of action potentials fired by cells of the cortex are most synchronized over large areas, resulting in the slow-wave pattern?
The figure shows electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings from a person who is awake and in different stages of sleep.Which of the following EEG recordings represents the period when bursts of action potentials fired by cells of the cortex are most synchronized over large areas, resulting in the slow-wave pattern?
A) Awake
B) Non-REM Stage 1
C) Non-REM Stage 2
D) Non-REM Stage 3
E) REM
 The figure shows electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings from a person who is awake and in different stages of sleep.Which of the following EEG recordings represents the period when bursts of action potentials fired by cells of the cortex are most synchronized over large areas, resulting in the slow-wave pattern?
The figure shows electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings from a person who is awake and in different stages of sleep.Which of the following EEG recordings represents the period when bursts of action potentials fired by cells of the cortex are most synchronized over large areas, resulting in the slow-wave pattern?A) Awake
B) Non-REM Stage 1
C) Non-REM Stage 2
D) Non-REM Stage 3
E) REM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If you look at your finger and close one eye at a time, your finger seems to jump back and forth because the different positions of stimuli on your retinas.If you look at a distant object, however, there is less jumping of the image because
A) there is less disparity in the positions of the image on the two retinas.
B) binocular cells adjust for the distance of the object.
C) the time it takes to perceive the distant object reduces the disparity between the position of the image on the two retinas.
D) binocular vision is useful only for near objects.
E) more binocular cells are stimulated.
A) there is less disparity in the positions of the image on the two retinas.
B) binocular cells adjust for the distance of the object.
C) the time it takes to perceive the distant object reduces the disparity between the position of the image on the two retinas.
D) binocular vision is useful only for near objects.
E) more binocular cells are stimulated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
You are talking with a patient who has slow, halting speech but who is perfectly capable of understanding you when you talk.Moreover, the content of his answers is clear.This patient's brain may have sustained damage to _______, which is crucial for _______ of speech.
A) Wernicke's area; motor aspects
B) Wernicke's area; sensory aspects
C) Broca's area; motor aspects
D) Broca's area; sensory aspects
E) the angular gyrus; written and spoken integration
A) Wernicke's area; motor aspects
B) Wernicke's area; sensory aspects
C) Broca's area; motor aspects
D) Broca's area; sensory aspects
E) the angular gyrus; written and spoken integration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following represents the correct flow of information when a person repeats a heard word?
A) Broca's area Wernicke's area auditory cortex primary motor cortex
B) Auditory cortex Wernicke's area Broca's area primary motor cortex
C) Primary motor cortex auditory cortex Wernicke's area Broca's area
D) Broca's area primary motor cortex auditory cortex Wernicke's area
E) Wernicke's area auditory cortex Broca's area primary motor cortex
A) Broca's area Wernicke's area auditory cortex primary motor cortex
B) Auditory cortex Wernicke's area Broca's area primary motor cortex
C) Primary motor cortex auditory cortex Wernicke's area Broca's area
D) Broca's area primary motor cortex auditory cortex Wernicke's area
E) Wernicke's area auditory cortex Broca's area primary motor cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which statement about brain activity during the transition from wakefulness to sleep is false?
A) Specific nuclei in the brainstem decrease neurotransmitter release.
B) Neurons in the thalamus and cerebral cortex become hyperpolarized.
C) Resting potentials of neurons in the thalamus and cerebral cortex become more positive.
D) Neurons in the thalamus and cerebral cortex become less sensitive to excitatory synaptic input.
E) Processing of information by neurons in the cerebral cortex and thalamus is inhibited.
A) Specific nuclei in the brainstem decrease neurotransmitter release.
B) Neurons in the thalamus and cerebral cortex become hyperpolarized.
C) Resting potentials of neurons in the thalamus and cerebral cortex become more positive.
D) Neurons in the thalamus and cerebral cortex become less sensitive to excitatory synaptic input.
E) Processing of information by neurons in the cerebral cortex and thalamus is inhibited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Cells that are close to the borders of the columns of neurons in the visual cortex receive input from both eyes and are called _______ cells; they interpret distance by measuring the _______ between the stimulus locations on the two retinas.
A) photoreceptive; crossover
B) binocular; disparity
C) ganglion; distance
D) visual; action potentials
E) bipolar; movement
A) photoreceptive; crossover
B) binocular; disparity
C) ganglion; distance
D) visual; action potentials
E) bipolar; movement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Mammals experience two distinct types of sleep.A sleeping dog that starts to make noises and appears to be trying to chase something while remaining asleep is likely transitioning from _______ to _______.
A) wakefulness; slow-wave sleep
B) REM sleep; wakefulness
C) slow-wave sleep; high-amplitude sleep
D) REM sleep; slow-wave sleep
E) slow-wave sleep; REM sleep
A) wakefulness; slow-wave sleep
B) REM sleep; wakefulness
C) slow-wave sleep; high-amplitude sleep
D) REM sleep; slow-wave sleep
E) slow-wave sleep; REM sleep

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following represents the correct sequence of sleep stages that a person will cycle through several times, from the time of going to bed at night to the time of awakening in the morning? Which of the following represents the typical sequence of sleep stages that a person will cycle through several times, from the time of going to bed at night to the time of awakening in the morning?
A) REM non-REM stage 1 non-REM stage 2 non-REM stage 3
B) Non-REM stage 1 non-REM stage 2 non-REM stage 3 REM
C) Non-REM stage 1 non-REM stage 2 REM non-REM stage 3
D) Non-REM stage 3 REM non-REM stage 1 non-REM stage 2
E) REM non-REM stage 1 non-REM stage 2 REM
A) REM non-REM stage 1 non-REM stage 2 non-REM stage 3
B) Non-REM stage 1 non-REM stage 2 non-REM stage 3 REM
C) Non-REM stage 1 non-REM stage 2 REM non-REM stage 3
D) Non-REM stage 3 REM non-REM stage 1 non-REM stage 2
E) REM non-REM stage 1 non-REM stage 2 REM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Despite the lateralization of language to one cerebral hemisphere, the brain depends on the experience of the other hemisphere for full language function.This information travels between the hemispheres via the
A) gray matter.
B) temporal lobe.
C) thalamus.
D) corpus callosum.
E) brainstem.
A) gray matter.
B) temporal lobe.
C) thalamus.
D) corpus callosum.
E) brainstem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Positron emission tomography (PET) allows live imaging of brain regions that are most active during language tasks.Suppose that you see two sequential PET images of a person's brain.The visual cortex is most active in the first image, whereas Broca's area is most active in the second image.Which of the following is the most likely explanation for these different patterns of brain activation?
A) The person was talking and then viewing words.
B) The person was thinking of words and then reading.
C) The person was listening to conversation and then writing.
D) The person was reading and then writing.
E) The person was reading and then speaking.
A) The person was talking and then viewing words.
B) The person was thinking of words and then reading.
C) The person was listening to conversation and then writing.
D) The person was reading and then writing.
E) The person was reading and then speaking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A person makes several word-like sounds but does not form sensible speech or understand spoken or written language.This person may have sustained damage to _______, which is crucial for _______ of speech.
A) Wernicke's area; motor aspects
B) Wernicke's area; sensory aspects
C) Broca's area; motor aspects
D) Broca's area; sensory aspects
E) the angular gyrus; written and spoken integration
A) Wernicke's area; motor aspects
B) Wernicke's area; sensory aspects
C) Broca's area; motor aspects
D) Broca's area; sensory aspects
E) the angular gyrus; written and spoken integration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The flow of information in the brain that allows you to repeat spoken language is different from the flow of information that allows you to read a word out loud.Say the word: "biology." Which of the following represents the correct flow of information that allowed you to do this?
A) Primary visual area angular gyrus Wernicke's area Broca's area primary motor cortex
B) Angular gyrus Broca's area Wernicke's area primary visual area primary motor cortex
C) Primary motor cortex primary visual area angular gyrus Wernicke's area Broca's area
D) Angular gyrus primary visual area Wernicke's area Broca's area primary motor cortex
E) Broca's area angular gyrus Wernicke's area primary motor cortex primary visual cortex
A) Primary visual area angular gyrus Wernicke's area Broca's area primary motor cortex
B) Angular gyrus Broca's area Wernicke's area primary visual area primary motor cortex
C) Primary motor cortex primary visual area angular gyrus Wernicke's area Broca's area
D) Angular gyrus primary visual area Wernicke's area Broca's area primary motor cortex
E) Broca's area angular gyrus Wernicke's area primary motor cortex primary visual cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A sleep researcher who is monitoring the sleep of volunteers in the study notices that the electroencephalogram (EEG) of one person, who is sleeping quietly, is showing large peaks of activity at regular intervals.What is most likely occurring in the person's brain at the cellular level?
A) Cells in the thalamus and cortex are depolarized and are firing more action potentials.
B) Cortical cells are hyperpolarized, and the bursts of activity indicate slow-wave sleep.
C) The peaks indicate REM sleep and some depolarization of the brainstem.
D) Cells are responding to dreams that the person may be having and firing action potentials accordingly.
E) The peaks correspond to the activity of only a few neurons and do not indicate much about the overall cellular activity.
A) Cells in the thalamus and cortex are depolarized and are firing more action potentials.
B) Cortical cells are hyperpolarized, and the bursts of activity indicate slow-wave sleep.
C) The peaks indicate REM sleep and some depolarization of the brainstem.
D) Cells are responding to dreams that the person may be having and firing action potentials accordingly.
E) The peaks correspond to the activity of only a few neurons and do not indicate much about the overall cellular activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Electroencephalograms measure the activity
A) that exists between neurons and muscles.
B) of large numbers of neurons in the brain.
C) of eye movements while asleep.
D) of body temperature during sleep‒wake cycles.
E) of single cells.
A) that exists between neurons and muscles.
B) of large numbers of neurons in the brain.
C) of eye movements while asleep.
D) of body temperature during sleep‒wake cycles.
E) of single cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following does not characterize REM sleep?
A) Slow-wave patterns
B) Paralysis of the skeletal muscles
C) Jerky eye movements
D) Dreaming
E) Limb twitches
A) Slow-wave patterns
B) Paralysis of the skeletal muscles
C) Jerky eye movements
D) Dreaming
E) Limb twitches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Refer to the figure. 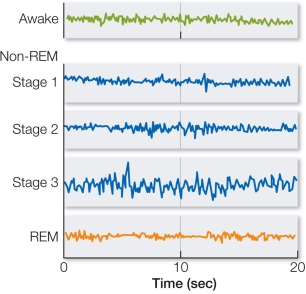 The figure shows electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings from a person who is awake and in different stages of sleep.Which of the following explains why EEG recordings show similar patterns when a person is awake and in REM sleep?
The figure shows electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings from a person who is awake and in different stages of sleep.Which of the following explains why EEG recordings show similar patterns when a person is awake and in REM sleep?
A) At least some brainstem nuclei are active in both phases.
B) Synchronized bursts of action potentials occur over broad areas of cortex during both phases.
C) Eye movements are similar in both phases.
D) The amounts of time that humans spend awake and in REM sleep are similar.
E) Activity of motor pathways is the same in both phases.
 The figure shows electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings from a person who is awake and in different stages of sleep.Which of the following explains why EEG recordings show similar patterns when a person is awake and in REM sleep?
The figure shows electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings from a person who is awake and in different stages of sleep.Which of the following explains why EEG recordings show similar patterns when a person is awake and in REM sleep?A) At least some brainstem nuclei are active in both phases.
B) Synchronized bursts of action potentials occur over broad areas of cortex during both phases.
C) Eye movements are similar in both phases.
D) The amounts of time that humans spend awake and in REM sleep are similar.
E) Activity of motor pathways is the same in both phases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 254 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



