Deck 52: Animal Behavior
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/249
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 52: Animal Behavior
1
A woodchuck in your yard has learned to associate the jingle of your dog's license and rabies tags with the appearance of your dog.Immediately before the dog races around the corner, upon hearing the jingle, the woodchuck disappears into its burrow.In this situation, the _______ is the _______.
A) sound of the tags; unconditioned stimulus
B) sight of the dog; conditioned response
C) sight of the dog; unconditioned response
D) sound of the tags; conditioned stimulus
E) sound of the tags; conditioned response
A) sound of the tags; unconditioned stimulus
B) sight of the dog; conditioned response
C) sight of the dog; unconditioned response
D) sound of the tags; conditioned stimulus
E) sound of the tags; conditioned response
D
2
Identify the incorrect pairing of a well-known behavioral biologist with a discovery made by that biologist.
A) Ivan Pavlov: a simple behavior can be modified through conditioning
B) Niko Tinbergen: strong bonds between parent and offspring can develop during a critical period following birth
C) B. F. Skinner: any random action can become a conditioned response to a stimulus if a reward is temporally associated with the action and the stimulus
D) Konrad Lorenz: stereotypic motor patterns of duck courtship displays are inherited
E) Karl von Frisch: the dance language of bees
A) Ivan Pavlov: a simple behavior can be modified through conditioning
B) Niko Tinbergen: strong bonds between parent and offspring can develop during a critical period following birth
C) B. F. Skinner: any random action can become a conditioned response to a stimulus if a reward is temporally associated with the action and the stimulus
D) Konrad Lorenz: stereotypic motor patterns of duck courtship displays are inherited
E) Karl von Frisch: the dance language of bees
B
3
Refer to the figure showing the steps in a conditioned reflex experiment. 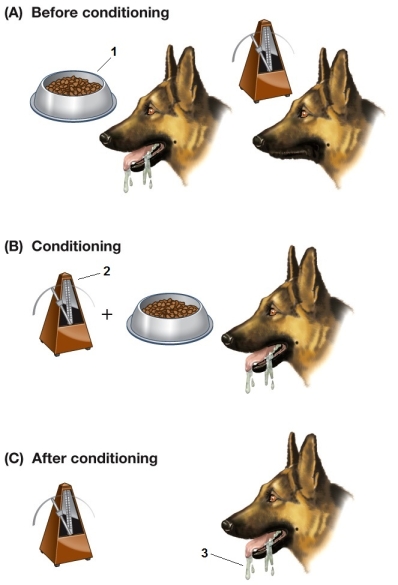 Based on the figure, the object at point 1 is the
Based on the figure, the object at point 1 is the
A) conditioned stimulus.
B) conditioned reflex.
C) unconditioned reflex.
D) unconditioned stimulus.
E) unconditioned response.
 Based on the figure, the object at point 1 is the
Based on the figure, the object at point 1 is theA) conditioned stimulus.
B) conditioned reflex.
C) unconditioned reflex.
D) unconditioned stimulus.
E) unconditioned response.
D
4
Refer to the graph showing the locomotor activity of Drosophila melanogaster flies that have been subjected to various gene-knockout experiments.  What can be inferred about the normal function of gene B in the graph?
What can be inferred about the normal function of gene B in the graph?
A) Gene B has little or no effect on locomotor activity.
B) Gene B interacts with gene A in controlling locomotor activity.
C) Gene B interacts with gene C in controlling locomotor activity.
D) Gene B is required for locomotor activity.
E) There is insufficient data to make an inference.
 What can be inferred about the normal function of gene B in the graph?
What can be inferred about the normal function of gene B in the graph?A) Gene B has little or no effect on locomotor activity.
B) Gene B interacts with gene A in controlling locomotor activity.
C) Gene B interacts with gene C in controlling locomotor activity.
D) Gene B is required for locomotor activity.
E) There is insufficient data to make an inference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Adult male mice are usually aggressive toward newborn mice.You suspect that the hormone prolactin being expressed in the adult males underlies this aggression and have identified a gene for prolactin receptors.The next logical step in your study would be to
A) knock out the gene for prolactin receptors and test the knockout male mice with newborns.
B) conduct breeding experiments between aggressive and nonaggressive mice.
C) conduct deprivation experiments in which male mice are raised in isolation and then tested for their response to newborns.
D) test whether aggression is a fixed action pattern by exposing male mice to objects that mimic specific features of newborns.
E) conduct hybridization experiments between different mouse species.
A) knock out the gene for prolactin receptors and test the knockout male mice with newborns.
B) conduct breeding experiments between aggressive and nonaggressive mice.
C) conduct deprivation experiments in which male mice are raised in isolation and then tested for their response to newborns.
D) test whether aggression is a fixed action pattern by exposing male mice to objects that mimic specific features of newborns.
E) conduct hybridization experiments between different mouse species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A hungry rat placed in a Skinner box explores its new surroundings and at some point presses a bar.This action immediately results in delivery of a food pellet, which the rat eats.The food reward increases the likelihood that the rat will press the bar again.This is an example of
A) a fixed action pattern.
B) insight learning.
C) a conditioned reflex.
D) habituation.
E) operant conditioning.
A) a fixed action pattern.
B) insight learning.
C) a conditioned reflex.
D) habituation.
E) operant conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following was not characteristic of the field of study that became known as ethology?
A) It used deprivation experiments.
B) It involved comparative studies of a wide range of species.
C) It focused initially on fixed action patterns.
D) It involved studies that were designed to investigate conditioned behavior.
E) It involved experiments that were conducted under field conditions.
A) It used deprivation experiments.
B) It involved comparative studies of a wide range of species.
C) It focused initially on fixed action patterns.
D) It involved studies that were designed to investigate conditioned behavior.
E) It involved experiments that were conducted under field conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Male three-spined sticklebacks occupy inland coastal waters where they aggressively defend their territories against intruding males.When tested with models of various shapes, sizes, and colors in the laboratory, males attacked crude models with red bellies more frequently than they attacked realistic models that lacked the characteristic red belly.These data suggest that
A) aggression is learned.
B) the red color of the male's underside is an unconditioned response.
C) the red color of the male's underside is a conditioned reflex.
D) the red color of the male's underside is a fixed action pattern.
E) the red color of the male's underside is a releaser for aggression.
A) aggression is learned.
B) the red color of the male's underside is an unconditioned response.
C) the red color of the male's underside is a conditioned reflex.
D) the red color of the male's underside is a fixed action pattern.
E) the red color of the male's underside is a releaser for aggression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which statement about gene cascades is false?
A) Alterations in a single gene within a gene cascade can affect an animal's behavior and fitness.
B) Gene cascades create opportunities for simple genetic changes to alter complex behavior.
C) Genes within cascades can influence several other genes.
D) A gene cascade controls sexual differentiation in fruit flies.
E) The fru gene is not part of the genetic cascade that controls sexual differentiation in fruit flies.
A) Alterations in a single gene within a gene cascade can affect an animal's behavior and fitness.
B) Gene cascades create opportunities for simple genetic changes to alter complex behavior.
C) Genes within cascades can influence several other genes.
D) A gene cascade controls sexual differentiation in fruit flies.
E) The fru gene is not part of the genetic cascade that controls sexual differentiation in fruit flies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Refer to the graph showing the locomotor activity of Drosophila melanogaster flies that have been subjected to various gene-knockout experiments. 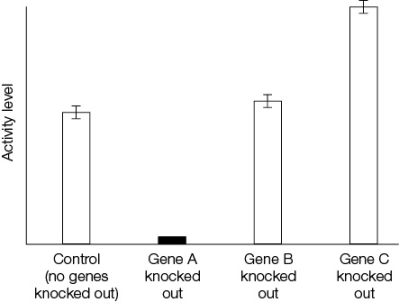 What can be inferred about the normal function of gene C in the graph?
What can be inferred about the normal function of gene C in the graph?
A) Gene C inhibits or regulates locomotor behavior; when the gene is knocked out, locomotor activity is elevated.
B) Gene C has little effect on locomotor activity.
C) Gene C has no effect at all on locomotor activity.
D) Gene C interacts with gene B in controlling locomotor activity.
E) There is insufficient data to make an inference.
 What can be inferred about the normal function of gene C in the graph?
What can be inferred about the normal function of gene C in the graph?A) Gene C inhibits or regulates locomotor behavior; when the gene is knocked out, locomotor activity is elevated.
B) Gene C has little effect on locomotor activity.
C) Gene C has no effect at all on locomotor activity.
D) Gene C interacts with gene B in controlling locomotor activity.
E) There is insufficient data to make an inference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following does not characterize deprivation experiments?
A) They were used by ethologists.
B) They provide opportunities to learn species-specific behaviors.
C) Web spinning by young spiders is an example of a natural deprivation experiment.
D) They involve raising individual animals without access to conspecifics.
E) They demonstrate that a behavior is genetically determined.
A) They were used by ethologists.
B) They provide opportunities to learn species-specific behaviors.
C) Web spinning by young spiders is an example of a natural deprivation experiment.
D) They involve raising individual animals without access to conspecifics.
E) They demonstrate that a behavior is genetically determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Tinbergen outlined four questions he thought behavioral biologists should be asking.Which of the following was not a consideration when investigating behavior, according to Tinbergen?
A) Function
B) Causation
C) Evolution
D) Ecology
E) Development
A) Function
B) Causation
C) Evolution
D) Ecology
E) Development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Refer to the figure showing the steps in a conditioned reflex experiment. 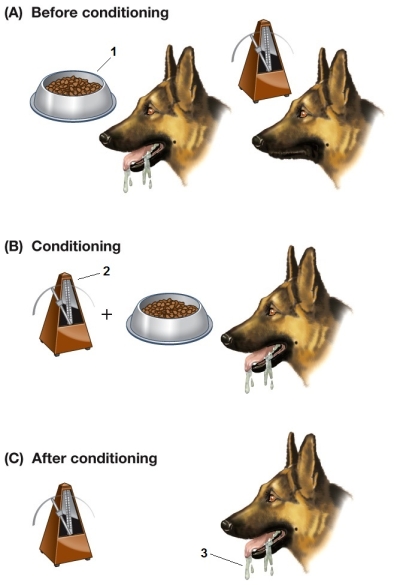 Which statement about the experiment shown in the figure is false?
Which statement about the experiment shown in the figure is false?
A) The object at point 2 is the conditioned stimulus.
B) In part B, the order of presentation of the stimuli is unimportant.
C) The object at point 1 produces an unconditioned response.
D) Point 3 shows the conditioned response.
E) In part B, the stimuli must be presented in quick succession.
 Which statement about the experiment shown in the figure is false?
Which statement about the experiment shown in the figure is false?A) The object at point 2 is the conditioned stimulus.
B) In part B, the order of presentation of the stimuli is unimportant.
C) The object at point 1 produces an unconditioned response.
D) Point 3 shows the conditioned response.
E) In part B, the stimuli must be presented in quick succession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which research question does not address ultimate causes of behavior?
A) Do prairie dogs that give alarm calls face increased risk of predation?
B) Do breeding pairs of scrub jays produce more young when they have helpers at the nest?
C) Does testosterone regulate courtship and copulation in male green anoles?
D) Why do lions live in groups, whereas other species in the genus Panthera do not?
E) How might siblicide (the killing of brothers and sisters) have evolved in egrets?
A) Do prairie dogs that give alarm calls face increased risk of predation?
B) Do breeding pairs of scrub jays produce more young when they have helpers at the nest?
C) Does testosterone regulate courtship and copulation in male green anoles?
D) Why do lions live in groups, whereas other species in the genus Panthera do not?
E) How might siblicide (the killing of brothers and sisters) have evolved in egrets?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which statement about genes and behavior is false?
A) Many patterns of complex behavior among different animals are coded for by a single gene.
B) Complex behaviors typically result from an interaction between genetic inheritance and learning.
C) Complex behaviors can be changed by alterations in a single gene.
D) Complex behaviors often are controlled by gene cascades.
E) Changes in the expression pattern of a gene can alter complex behaviors.
A) Many patterns of complex behavior among different animals are coded for by a single gene.
B) Complex behaviors typically result from an interaction between genetic inheritance and learning.
C) Complex behaviors can be changed by alterations in a single gene.
D) Complex behaviors often are controlled by gene cascades.
E) Changes in the expression pattern of a gene can alter complex behaviors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which research question does not address proximate causes of behavior?
A) Does oxytocin regulate social bonding in voles?
B) Does dispersal increase reproductive success in naked mole-rats?
C) Does maternal behavior in chimpanzees change with age and experience?
D) Does the neural circuitry underlying crawling behavior disappear when a tobacco hornworm caterpillar becomes a pupa?
E) Do salmon use olfactory cues to return to their natal stream?
A) Does oxytocin regulate social bonding in voles?
B) Does dispersal increase reproductive success in naked mole-rats?
C) Does maternal behavior in chimpanzees change with age and experience?
D) Does the neural circuitry underlying crawling behavior disappear when a tobacco hornworm caterpillar becomes a pupa?
E) Do salmon use olfactory cues to return to their natal stream?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Refer to the graph showing the locomotor activity of Drosophila melanogaster flies that have been subjected to various gene-knockout experiments.  What can be inferred about the normal function of gene A in the graph?
What can be inferred about the normal function of gene A in the graph?
A) Gene A plays little role in locomotor activity.
B) Gene A interacts with gene B in controlling locomotor activity.
C) Gene A interacts with gene C in controlling locomotor activity.
D) Gene A is required for locomotor activity.
E) There is insufficient data to make an inference.
 What can be inferred about the normal function of gene A in the graph?
What can be inferred about the normal function of gene A in the graph?A) Gene A plays little role in locomotor activity.
B) Gene A interacts with gene B in controlling locomotor activity.
C) Gene A interacts with gene C in controlling locomotor activity.
D) Gene A is required for locomotor activity.
E) There is insufficient data to make an inference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following does not characterize male courtship behavior in the common fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster?
A) It is stereotypic.
B) Development of the behavior is controlled by the gene fruitless, which is embedded in a gene cascade.
C) The behavior changes with experience.
D) The behavior is species-specific.
E) The behavior involves multiple movements, including following a female, tapping her body, and vibrating one wing.
A) It is stereotypic.
B) Development of the behavior is controlled by the gene fruitless, which is embedded in a gene cascade.
C) The behavior changes with experience.
D) The behavior is species-specific.
E) The behavior involves multiple movements, including following a female, tapping her body, and vibrating one wing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following was not characteristic of the field of study called "behaviorism"?
A) It was focused on learning and memory.
B) It was carried out with a few model species.
C) It included the use of deprivation experiments.
D) Its practitioners were mostly psychologists.
E) It included experiments conducted under laboratory conditions.
A) It was focused on learning and memory.
B) It was carried out with a few model species.
C) It included the use of deprivation experiments.
D) Its practitioners were mostly psychologists.
E) It included experiments conducted under laboratory conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Knockout experiments concerning pheromone receptors in the vomeronasal organ (VNO) of mice have revealed that
A) there is a single gene controlling mating behavior in mice.
B) VNO receptors are necessary for a male mouse to identify whether another mouse is male or female.
C) mating behavior in male mice requires VNO receptors.
D) a male mouse without VNO receptors is aggressive toward other males.
E) a normal male mouse with VNO receptors will attempt to mate with another male.
A) there is a single gene controlling mating behavior in mice.
B) VNO receptors are necessary for a male mouse to identify whether another mouse is male or female.
C) mating behavior in male mice requires VNO receptors.
D) a male mouse without VNO receptors is aggressive toward other males.
E) a normal male mouse with VNO receptors will attempt to mate with another male.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which statement about songbirds is true?
A) The brains of male and female songbirds are more similar in the nonbreeding season than in the breeding season.
B) New neurons are not produced in the brains of adult songbirds.
C) Female songbirds form a memory of their species-specific song when courted by males in adulthood.
D) Testosterone causes the song-learning portions of the male songbird's brain to shrink.
E) The onset of autumn prompts changes in hormone levels in male songbirds that cause the portion of the brain related to song to grow larger.
A) The brains of male and female songbirds are more similar in the nonbreeding season than in the breeding season.
B) New neurons are not produced in the brains of adult songbirds.
C) Female songbirds form a memory of their species-specific song when courted by males in adulthood.
D) Testosterone causes the song-learning portions of the male songbird's brain to shrink.
E) The onset of autumn prompts changes in hormone levels in male songbirds that cause the portion of the brain related to song to grow larger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The critical periods that characterize imprinting
A) always occur early in life.
B) may be determined by a brief change in hormone levels.
C) are restricted to parent‒offspring recognition.
D) are unique to birds.
E) are windows of opportunity for learning characteristics that can easily be modified later.
A) always occur early in life.
B) may be determined by a brief change in hormone levels.
C) are restricted to parent‒offspring recognition.
D) are unique to birds.
E) are windows of opportunity for learning characteristics that can easily be modified later.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which male white-crowned sparrow will sing the species-typical song in adulthood?
A) A male raised in isolation and then exposed to the singing of other white-crowned sparrow males during its first breeding season
B) A male raised in isolation but exposed to tapes of white-crowned sparrow song at 6 months of age
C) A male raised in isolation, exposed to tapes of white-crowned sparrow song before 2 months of age, and deafened before he starts to sing
D) A male raised in isolation and deafened before he starts to sing
E) A male raised in isolation, exposed to tapes of white-crowned sparrow song before 2 months of age, and exposed to the singing of other white-crowned sparrow males during its first breeding season
A) A male raised in isolation and then exposed to the singing of other white-crowned sparrow males during its first breeding season
B) A male raised in isolation but exposed to tapes of white-crowned sparrow song at 6 months of age
C) A male raised in isolation, exposed to tapes of white-crowned sparrow song before 2 months of age, and deafened before he starts to sing
D) A male raised in isolation and deafened before he starts to sing
E) A male raised in isolation, exposed to tapes of white-crowned sparrow song before 2 months of age, and exposed to the singing of other white-crowned sparrow males during its first breeding season

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Researchers have demonstrated that collared flycatchers determine the quality of a habitat
A) by assessing the number of prey items in a small section of the habitat.
B) because of imprinting that took place shortly after hatching.
C) by estimating the amount of free water in the environment.
D) by observing the brood sizes of individuals already settled in the habitat.
E) by performing an opportunity-cost analysis.
A) by assessing the number of prey items in a small section of the habitat.
B) because of imprinting that took place shortly after hatching.
C) by estimating the amount of free water in the environment.
D) by observing the brood sizes of individuals already settled in the habitat.
E) by performing an opportunity-cost analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which female goat would recognize her offspring?
A) A female prevented from having direct contact with her offspring in the first 10 minutes after birth
B) A female whose olfactory system was blocked before she gave birth
C) A female unable to see her offspring but able to have direct contact in the first 10 minutes after birth
D) A female allowed direct physical contact with her offspring starting 60 minutes after birth
E) A female allowed visual and auditory contact, but no direct physical contact, with her offspring in the first 10 minutes after birth
A) A female prevented from having direct contact with her offspring in the first 10 minutes after birth
B) A female whose olfactory system was blocked before she gave birth
C) A female unable to see her offspring but able to have direct contact in the first 10 minutes after birth
D) A female allowed direct physical contact with her offspring starting 60 minutes after birth
E) A female allowed visual and auditory contact, but no direct physical contact, with her offspring in the first 10 minutes after birth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which statement about the impact of testosterone on brains of adult songbirds is false?
A) Increases in circulating testosterone in spring cause increases in the size of brain regions in adult males.
B) Adult females injected with testosterone in spring sing their species-specific song.
C) Under normal circumstances, adult females lack the hormonal stimulation to sing in spring.
D) Increases in the size of brain regions due to rising levels of testosterone reflect increases in size and number of neurons.
E) Females fail to form a memory of their species-specific song as nestlings.
A) Increases in circulating testosterone in spring cause increases in the size of brain regions in adult males.
B) Adult females injected with testosterone in spring sing their species-specific song.
C) Under normal circumstances, adult females lack the hormonal stimulation to sing in spring.
D) Increases in the size of brain regions due to rising levels of testosterone reflect increases in size and number of neurons.
E) Females fail to form a memory of their species-specific song as nestlings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is not a characteristic of imprinting?
A) It occurs during a critical (sensitive) period.
B) Its effects can last a long time.
C) It is a form of learning.
D) It occurs during parent-offspring recognition.
E) Its effects are easily reversed.
A) It occurs during a critical (sensitive) period.
B) Its effects can last a long time.
C) It is a form of learning.
D) It occurs during parent-offspring recognition.
E) Its effects are easily reversed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which statement does not characterize individual variation in the singing behavior of a bird species?
A) Variation may help a bird arriving in a region adopt the local dialect.
B) Birds on neighboring territories can vary in their songs.
C) White-crowned sparrows in nature always sing their species-specific song.
D) Individual variation may be key to attracting mates.
E) Individual variation may be key to maintaining a bond between mates.
A) Variation may help a bird arriving in a region adopt the local dialect.
B) Birds on neighboring territories can vary in their songs.
C) White-crowned sparrows in nature always sing their species-specific song.
D) Individual variation may be key to attracting mates.
E) Individual variation may be key to maintaining a bond between mates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which hormone is most immediately responsible for causing increases each spring in song-learning regions of the brains of male songbirds?
A) Estrogen
B) Norepinephrine
C) Testosterone
D) Melatonin
E) Aldosterone
A) Estrogen
B) Norepinephrine
C) Testosterone
D) Melatonin
E) Aldosterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Refer to the figure showing a series of experiments carried out on female rats. 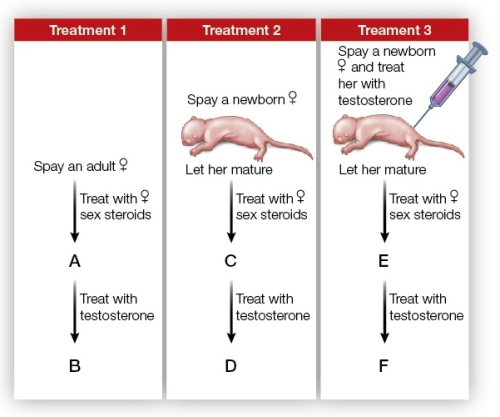 Based on the figure, which statement about sex steroids and rat sexual behavior is false?
Based on the figure, which statement about sex steroids and rat sexual behavior is false?
A) In treatment 1, a female rat at point A would display female sexual behavior (lordosis).
B) In treatment 2, a female rat at point D would show no sexual behavior.
C) In treatment 3, a female rat's nervous system would be masculinized.
D) In treatment 1, a female rat at point B would show male sexual behavior.
E) In treatment 2, a female rat at point C would display female sexual behavior (lordosis).
 Based on the figure, which statement about sex steroids and rat sexual behavior is false?
Based on the figure, which statement about sex steroids and rat sexual behavior is false?A) In treatment 1, a female rat at point A would display female sexual behavior (lordosis).
B) In treatment 2, a female rat at point D would show no sexual behavior.
C) In treatment 3, a female rat's nervous system would be masculinized.
D) In treatment 1, a female rat at point B would show male sexual behavior.
E) In treatment 2, a female rat at point C would display female sexual behavior (lordosis).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
It has been discovered that certain planktonic larvae of marine organisms select their settlement site using signals that indicate the suitability of the site for sustaining life.Which of the following is the most likely signal initiating this settling response?
A) Visual cue indicating an appropriate physical substrate
B) Visual cue indicating the absence of conspecifics
C) Visual cue indicating the presence of conspecifics
D) Chemical cue indicating the presence of nesting sites
E) Chemical cue indicating the presence of conspecifics
A) Visual cue indicating an appropriate physical substrate
B) Visual cue indicating the absence of conspecifics
C) Visual cue indicating the presence of conspecifics
D) Chemical cue indicating the presence of nesting sites
E) Chemical cue indicating the presence of conspecifics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which rat will show female sexual behavior (lordosis) in adulthood?
A) A female rat treated with testosterone as a newborn and with estrogen as an adult
B) A female rat spayed as a newborn and treated with estrogen as an adult
C) A male rat castrated as a newborn and not treated with hormones as an adult
D) A female rat treated with testosterone both as a newborn and as an adult
E) A female rat spayed as a newborn and not treated with hormones as an adult
A) A female rat treated with testosterone as a newborn and with estrogen as an adult
B) A female rat spayed as a newborn and treated with estrogen as an adult
C) A male rat castrated as a newborn and not treated with hormones as an adult
D) A female rat treated with testosterone both as a newborn and as an adult
E) A female rat spayed as a newborn and not treated with hormones as an adult

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A scientist interested in studying imprinting would study
A) parent-offspring interactions.
B) aggressive behavior.
C) territorial behavior.
D) foraging behavior.
E) antipredator behavior.
A) parent-offspring interactions.
B) aggressive behavior.
C) territorial behavior.
D) foraging behavior.
E) antipredator behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which statement about sex steroids and sexual behavior in rats is false?
A) Estrogen around the time of birth is not required for development of female sexual behavior.
B) Whereas sex steroids early in life determine behavioral potential, sex steroids later in life determine when a pattern of behavior will be expressed.
C) Testosterone around the time of birth is required for development of male sexual behavior.
D) Once a young male has been masculinized through exposure to testosterone, he can subsequently display sexual behavior in the absence of testosterone.
E) Testosterone around the time of birth can masculinize the nervous systems of males and females.
A) Estrogen around the time of birth is not required for development of female sexual behavior.
B) Whereas sex steroids early in life determine behavioral potential, sex steroids later in life determine when a pattern of behavior will be expressed.
C) Testosterone around the time of birth is required for development of male sexual behavior.
D) Once a young male has been masculinized through exposure to testosterone, he can subsequently display sexual behavior in the absence of testosterone.
E) Testosterone around the time of birth can masculinize the nervous systems of males and females.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Female zebra finches
A) prefer the directed song of their mate.
B) prefer the song of a closely related species.
C) prefer the undirected song of their mate.
D) display no preference when presented with the directed and undirected song of their mate.
E) cannot distinguish between the directed and undirected song of their mate.
A) prefer the directed song of their mate.
B) prefer the song of a closely related species.
C) prefer the undirected song of their mate.
D) display no preference when presented with the directed and undirected song of their mate.
E) cannot distinguish between the directed and undirected song of their mate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which white-crowned sparrow will only sing the species-typical song in adulthood?
A) A male raised in isolation and exposed to tapes of lark sparrow song before 2 months of age
B) A male raised in isolation and exposed to tapes of lark sparrow song at 6 months of age
C) A male raised in isolation and exposed to tapes of white-crowned sparrow song before 2 months of age while housed next to an adult male lark sparrow
D) A male raised in isolation, exposed to tapes of white-crowned sparrow song before 2 months of age, and deafened after his song has crystallized
E) A wild-caught female that heard her father sing while she was a nestling
A) A male raised in isolation and exposed to tapes of lark sparrow song before 2 months of age
B) A male raised in isolation and exposed to tapes of lark sparrow song at 6 months of age
C) A male raised in isolation and exposed to tapes of white-crowned sparrow song before 2 months of age while housed next to an adult male lark sparrow
D) A male raised in isolation, exposed to tapes of white-crowned sparrow song before 2 months of age, and deafened after his song has crystallized
E) A wild-caught female that heard her father sing while she was a nestling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which statement about the cues used by animals to select a habitat in which to settle is false?
A) Cues can be simple.
B) The presence of conspecifics is used by some animals to select a habitat.
C) An abundance of select foods is used as a cue by some species with specialized food requirements.
D) In some species, individuals monitor the reproductive success of conspecifics when deciding where to settle the following year.
E) Cues regarding predators are usually given the lowest priority in habitat selection.
A) Cues can be simple.
B) The presence of conspecifics is used by some animals to select a habitat.
C) An abundance of select foods is used as a cue by some species with specialized food requirements.
D) In some species, individuals monitor the reproductive success of conspecifics when deciding where to settle the following year.
E) Cues regarding predators are usually given the lowest priority in habitat selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Refer to the figure showing a series of experiments carried out on female rats. 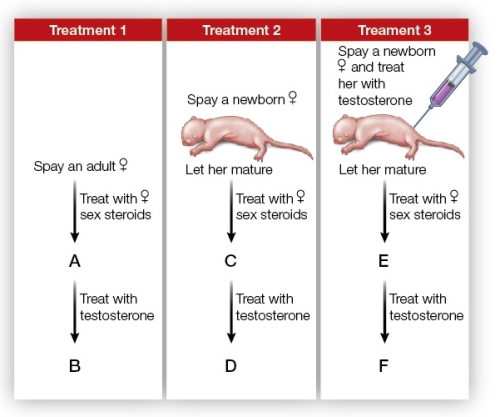 Based on the figure, which statement about sex steroids and rat sexual behavior is false?
Based on the figure, which statement about sex steroids and rat sexual behavior is false?
A) In treatment 3, a female rat at point E would not show female sexual behavior (lordosis).
B) In treatment 2, a female at point D would have a masculinized nervous system.
C) In treatment 3, a female rat at point F would show male sexual behavior.
D) The brain of a newborn female rat does not require exposure to estrogen for female sexual behavior to develop.
E) Estrogen in adulthood is needed to activate female sexual behavior.
 Based on the figure, which statement about sex steroids and rat sexual behavior is false?
Based on the figure, which statement about sex steroids and rat sexual behavior is false?A) In treatment 3, a female rat at point E would not show female sexual behavior (lordosis).
B) In treatment 2, a female at point D would have a masculinized nervous system.
C) In treatment 3, a female rat at point F would show male sexual behavior.
D) The brain of a newborn female rat does not require exposure to estrogen for female sexual behavior to develop.
E) Estrogen in adulthood is needed to activate female sexual behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Most female songbirds do not sing the songs of the males of their species because
A) they lack the necessary vocal structures.
B) they lack the appropriate hormonal stimulation.
C) their brains do not respond to the hormones needed for song learning.
D) they lack the necessary neural structures.
E) they are not exposed to song as nestlings.
A) they lack the necessary vocal structures.
B) they lack the appropriate hormonal stimulation.
C) their brains do not respond to the hormones needed for song learning.
D) they lack the necessary neural structures.
E) they are not exposed to song as nestlings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which rat will show male sexual behavior (mounting) in adulthood?
A) A female rat treated with testosterone both as a newborn and as an adult
B) A female rat spayed as a newborn and treated with testosterone as an adult
C) A male rat castrated as a newborn and not treated with hormones as an adult
D) A male rat castrated as a newborn and treated with testosterone as an adult
E) A female rat treated with testosterone as an adult
A) A female rat treated with testosterone both as a newborn and as an adult
B) A female rat spayed as a newborn and treated with testosterone as an adult
C) A male rat castrated as a newborn and not treated with hormones as an adult
D) A male rat castrated as a newborn and treated with testosterone as an adult
E) A female rat treated with testosterone as an adult

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which statement about leks is false?
A) Males do not eat, drink, or sleep until they are displaced.
B) Females mates with males on prime sites.
C) Males defend nesting sites.
D) Females gain because their offspring will receive good genes.
E) Males benefit from the chance to mate with many females and maximize fitness.
A) Males do not eat, drink, or sleep until they are displaced.
B) Females mates with males on prime sites.
C) Males defend nesting sites.
D) Females gain because their offspring will receive good genes.
E) Males benefit from the chance to mate with many females and maximize fitness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Chimps appear to eat the toxic pith of Vernonia amygdalina plants
A) for its antiparasite properties.
B) because doing so reduces opportunity costs.
C) for its caloric benefits.
D) because it wards off potential predators.
E) for its nutrient content.
A) for its antiparasite properties.
B) because doing so reduces opportunity costs.
C) for its caloric benefits.
D) because it wards off potential predators.
E) for its nutrient content.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which experimental manipulation would make a mammal arrhythmic?
A) Maintenance in complete darkness
B) Maintenance in complete darkness with short pulses of light administered every 24 hours
C) Maintenance in complete darkness and at constant temperature
D) Destruction of the suprachiasmatic nuclei
E) Destruction of the medial preoptic area
A) Maintenance in complete darkness
B) Maintenance in complete darkness with short pulses of light administered every 24 hours
C) Maintenance in complete darkness and at constant temperature
D) Destruction of the suprachiasmatic nuclei
E) Destruction of the medial preoptic area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
_______ rhythms are biological rhythms that occur on an annual basis.
A) Circannual
B) Circalunidian
C) Circadian
D) Crepuscular
E) Photoperiod
A) Circannual
B) Circalunidian
C) Circadian
D) Crepuscular
E) Photoperiod

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In Moore and Marler's study of Yarrow's spiny lizards, males were implanted with testosterone capsules in the summer, when testosterone levels are normally low.Which of the following was not a result of this study?
A) They developed larger brains than control males.
B) They survived less well than control males.
C) They suffered opportunity costs related to decreased opportunity to feed.
D) They spent more time in territorial behavior.
E) They suffered energetic costs.
A) They developed larger brains than control males.
B) They survived less well than control males.
C) They suffered opportunity costs related to decreased opportunity to feed.
D) They spent more time in territorial behavior.
E) They suffered energetic costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Suppose you have two groups of hamsters: one group consisting of animals with short circadian periods and the other consisting of animals with long circadian periods.The suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) of the long-day hamsters have been destroyed and short-day fetal SCN tissue has been transplanted into the lesioned tissue.What will be the result?
A) The long-day adults will remain arrhythmic.
B) The long-day adults will demonstrate long-day rhythms.
C) The long-day adult will demonstrate short-day rhythms.
D) The rhythms of the adults will become entrained to the laboratory lighting.
E) The long-day adults will exhibit free-running rhythms.
A) The long-day adults will remain arrhythmic.
B) The long-day adults will demonstrate long-day rhythms.
C) The long-day adult will demonstrate short-day rhythms.
D) The rhythms of the adults will become entrained to the laboratory lighting.
E) The long-day adults will exhibit free-running rhythms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
While hiking, you come upon a scene in which individual male birds seem to be defending small territories devoid of resources such as food and nest sites.Individual females walk through the territories, mate with males on the most central territories, and leave the area.What have you found?
A) A lek
B) A territorial system based on defense of females
C) A situation in which males help females with parental care
D) A situation in which males, but not females, benefit
E) A situation with low costs to males
A) A lek
B) A territorial system based on defense of females
C) A situation in which males help females with parental care
D) A situation in which males, but not females, benefit
E) A situation with low costs to males

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which activity would you least expect to have a circannual rhythm?
A) Migration
B) Molting of feathers or hair
C) Reproduction
D) Hibernation
E) Sleep
A) Migration
B) Molting of feathers or hair
C) Reproduction
D) Hibernation
E) Sleep

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If an animal with a circadian clock of about 25 hours is kept in the dark without environmental time cues, it will
A) become active one hour later each day.
B) become active at the same time each day.
C) become active one hour earlier each day.
D) become active two hours earlier each day.
E) have an unpredictable pattern of activity.
A) become active one hour later each day.
B) become active at the same time each day.
C) become active one hour earlier each day.
D) become active two hours earlier each day.
E) have an unpredictable pattern of activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Choose the incorrectly paired term and definition.
A) Free-running: length of circadian period when an animal is in constant conditions
B) Entrainment: resetting a circadian rhythm to environmental conditions, such as the light-dark cycle
C) Circadian rhythm: daily cycles
D) Suprachiasmatic nuclei: area of the brain that controls circannual rhythms
E) In phase: one rhythm completely matches another
A) Free-running: length of circadian period when an animal is in constant conditions
B) Entrainment: resetting a circadian rhythm to environmental conditions, such as the light-dark cycle
C) Circadian rhythm: daily cycles
D) Suprachiasmatic nuclei: area of the brain that controls circannual rhythms
E) In phase: one rhythm completely matches another

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which statement about leks is false?
A) Males defend small territories.
B) The system involves high energetic costs to males.
C) Groups of females are defended.
D) Males on centrally located territories typically mate with the most females.
E) Females benefit by receiving genes from a successful competitor.
A) Males defend small territories.
B) The system involves high energetic costs to males.
C) Groups of females are defended.
D) Males on centrally located territories typically mate with the most females.
E) Females benefit by receiving genes from a successful competitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
On a territory within a lek, which of the following is/are defended?
A) Females within the territory
B) Nesting or denning sites within the territory
C) Energy-rich food within the territory
D) Food that is rich in rare minerals or micronutrients within the territory
E) The territory itself (display site), which, depending on its location, can provide access to females
A) Females within the territory
B) Nesting or denning sites within the territory
C) Energy-rich food within the territory
D) Food that is rich in rare minerals or micronutrients within the territory
E) The territory itself (display site), which, depending on its location, can provide access to females

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which statement about the cost-benefit approach to animal behavior is false?
A) Benefits are measured in terms of fitness gained by performing the behavior.
B) The approach assumes that animals have limited time and energy.
C) The approach includes opportunity costs of performing the behavior.
D) The approach assumes that animals cannot engage in behaviors whose benefits exceed their costs.
E) The approach includes energetic costs of performing the behavior.
A) Benefits are measured in terms of fitness gained by performing the behavior.
B) The approach assumes that animals have limited time and energy.
C) The approach includes opportunity costs of performing the behavior.
D) The approach assumes that animals cannot engage in behaviors whose benefits exceed their costs.
E) The approach includes energetic costs of performing the behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Daily activity cycles are _______ rhythms.
A) circannual
B) circalunidian
C) circadian
D) crepuscular
E) photoperiod
A) circannual
B) circalunidian
C) circadian
D) crepuscular
E) photoperiod

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
While singing, a male songbird increases his chances of acquiring a mate but also makes himself more obvious to predators.The male bird's chance of being killed by a predator is an example of a(n) _______ cost.
A) reproductive
B) delayed
C) risk
D) energetic
E) opportunity
A) reproductive
B) delayed
C) risk
D) energetic
E) opportunity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When studying moose foraging behavior, you note that moose spend some time eating aquatic plants even though the leaves of deciduous trees along the shore have higher energy content.What might explain this observation?
A) Feeding in the water increases opportunity costs.
B) Aquatic plants have an essential nutrient that is low or lacking in the leaves of deciduous leaves.
C) Feeding in the water has no influence on energetic costs.
D) Aquatic plants take more time to consume and process than the leaves of deciduous trees.
E) Feeding in the water increases risk costs.
A) Feeding in the water increases opportunity costs.
B) Aquatic plants have an essential nutrient that is low or lacking in the leaves of deciduous leaves.
C) Feeding in the water has no influence on energetic costs.
D) Aquatic plants take more time to consume and process than the leaves of deciduous trees.
E) Feeding in the water increases risk costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If you were interested in studying how animals defend food resources, you might select a study species
A) whose food is widely distributed in space.
B) whose costs of food defense outweigh the benefits.
C) that feeds on fish in the open ocean.
D) for whom food availability fluctuates greatly.
E) whose food can be economically defended.
A) whose food is widely distributed in space.
B) whose costs of food defense outweigh the benefits.
C) that feeds on fish in the open ocean.
D) for whom food availability fluctuates greatly.
E) whose food can be economically defended.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A mosquito feeding on mammalian blood benefits nutritionally but also places itself in danger.The insect's chance of being killed by that mammal is an example of a(n) _______ cost.
A) energetic
B) opportunity
C) acceptable
D) risk
E) territory
A) energetic
B) opportunity
C) acceptable
D) risk
E) territory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A dung beetle engaged in mating behavior has thereby forfeited time it could have spent foraging.The lost food is an example of
A) an energetic cost.
B) an opportunity cost.
C) the Concorde fallacy.
D) a risk cost.
E) a territory cost.
A) an energetic cost.
B) an opportunity cost.
C) the Concorde fallacy.
D) a risk cost.
E) a territory cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Collared flycatchers will likely settle in a habitat in which
A) brood sizes of conspecifics were large the previous year.
B) few adult conspecifics are present.
C) accurate assessment of nest site availability is difficult.
D) food abundance was variable the previous year.
E) access to mates appears unpredictable.
A) brood sizes of conspecifics were large the previous year.
B) few adult conspecifics are present.
C) accurate assessment of nest site availability is difficult.
D) food abundance was variable the previous year.
E) access to mates appears unpredictable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following would result in an effective alarm signal that also would be the most difficult for predators to localize?
A) An acoustic signal with a broad range of frequencies
B) A pheromone with low volatility
C) An acoustic signal with a single frequency and few starts and stops
D) An acoustic signal with a complex temporal structure
E) A visual signal
A) An acoustic signal with a broad range of frequencies
B) A pheromone with low volatility
C) An acoustic signal with a single frequency and few starts and stops
D) An acoustic signal with a complex temporal structure
E) A visual signal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Orienting by landmarks, such as done by gray whales migrating along the coast of western North America, is known as
A) bicoordinate navigation.
B) true navigation.
C) piloting.
D) distance-and-direction navigation.
E) homing.
A) bicoordinate navigation.
B) true navigation.
C) piloting.
D) distance-and-direction navigation.
E) homing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Pigeons have been shown to use the position of the sun as a compass.A pigeon is trained to feed from the south end of a circular cage and then is placed in a light-controlled room and is phase-advanced by 6 hours.If the bird is returned to the circular cage, where will it search for food at sunrise?
A) North
B) East
C) South
D) West
E) Northwest
A) North
B) East
C) South
D) West
E) Northwest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The ability of pigeons to return to their loft after being transported to remote sites is based on a navigational capacity called
A) behavioral communication.
B) clock-shifting.
C) mechanosensory signaling.
D) pheromone signaling.
E) homing.
A) behavioral communication.
B) clock-shifting.
C) mechanosensory signaling.
D) pheromone signaling.
E) homing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
At noon in the Northern Hemisphere, a bee is performing a waggle dance that is oriented 90 degrees to the right of vertical on the honeycomb.The waggle portion of the dance has a long duration.What is she communicating to her hivemates?
A) Food is close to the hive, and when you leave the hive, go right.
B) Food is far from the hive and to the west.
C) Food is close to the hive and to the east.
D) Food is in the direction of the sun.
E) The food source was in the east when I found it early this morning.
A) Food is close to the hive, and when you leave the hive, go right.
B) Food is far from the hive and to the west.
C) Food is close to the hive and to the east.
D) Food is in the direction of the sun.
E) The food source was in the east when I found it early this morning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
An observer of the night sky in the Northern Hemisphere would be able to see that
A) Polaris (the "North Star") and the constellations move as Earth rotates.
B) Polaris and the constellations are fixed.
C) Polaris moves, but the constellations are fixed.
D) the constellations move, but Polaris is fixed.
E) it is impossible for nocturnal migrants to use stars to navigate.
A) Polaris (the "North Star") and the constellations move as Earth rotates.
B) Polaris and the constellations are fixed.
C) Polaris moves, but the constellations are fixed.
D) the constellations move, but Polaris is fixed.
E) it is impossible for nocturnal migrants to use stars to navigate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A bee is performing a waggle dance straight down on the honeycomb, with waggle runs of very long duration.What is she communicating to her hivemates?
A) Food is close to the hive.
B) Food is at a location that is very distant from the hive and is in the direction opposite the sun.
C) Food is close to the hive and is in the direction opposite the sun.
D) Food is at a moderate distance from the hive and is in the direction of the sun.
E) Food is at a moderate distance from the hive and is in the direction opposite the sun.
A) Food is close to the hive.
B) Food is at a location that is very distant from the hive and is in the direction opposite the sun.
C) Food is close to the hive and is in the direction opposite the sun.
D) Food is at a moderate distance from the hive and is in the direction of the sun.
E) Food is at a moderate distance from the hive and is in the direction opposite the sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
After an 8- to 9-year preadolescent period of wandering the southern oceans, gray-headed albatrosses navigate to their natal colony to find a mate and nest.Which of the following is not used by these birds to navigate to their natal breeding colony?
A) A map sense
B) Trial-and-error navigation
C) Bicoordinate navigation
D) True navigation
E) A compass sense
A) A map sense
B) Trial-and-error navigation
C) Bicoordinate navigation
D) True navigation
E) A compass sense

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which type of signal would be used by a nocturnal animal living in dense forest that wishes to quickly communicate its location to a distant family member?
A) Visual
B) Mechanosensory
C) Chemical signal with low volatility
D) Chemical signal with medium volatility
E) Acoustic
A) Visual
B) Mechanosensory
C) Chemical signal with low volatility
D) Chemical signal with medium volatility
E) Acoustic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A diurnal animal living in grassland habitat is marking its territory.What type of signal would it most likely use for maximum durability of the signal?
A) Visual
B) Chemical signal with low volatility
C) Acoustic
D) Mechanosensory
E) Chemical signal with high volatility
A) Visual
B) Chemical signal with low volatility
C) Acoustic
D) Mechanosensory
E) Chemical signal with high volatility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following would provide the strongest evidence that pigeons use magnetic cues when returning to their home loft?
A) The detection and description of a neurophysiological magnetic transducer
B) Observations that orienting behavior takes place even on cloudy days
C) Evidence that the attachment of small magnets disrupts pigeons' homing behavior
D) Observations of pigeons gaining latitude information from magnetic fields
E) The discovery of magnetite particles in the cells of pigeons
A) The detection and description of a neurophysiological magnetic transducer
B) Observations that orienting behavior takes place even on cloudy days
C) Evidence that the attachment of small magnets disrupts pigeons' homing behavior
D) Observations of pigeons gaining latitude information from magnetic fields
E) The discovery of magnetite particles in the cells of pigeons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
An animal living in the Northern Hemisphere is displaced within the Northern Hemisphere such that the sun rises earlier and is lower in the sky than it would be at the animal's home position.In which direction will the animal move to return home?
A) Southwest
B) Southeast
C) Northwest
D) Northeast
E) South
A) Southwest
B) Southeast
C) Northwest
D) Northeast
E) South

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following does not characterize visual signals?
A) They provide rapid transmission of information.
B) Their effective distance depends on the environment.
C) They can be intercepted by predators.
D) They make it difficult to localize the sender.
E) They are problematic at night and in dark environments.
A) They provide rapid transmission of information.
B) Their effective distance depends on the environment.
C) They can be intercepted by predators.
D) They make it difficult to localize the sender.
E) They are problematic at night and in dark environments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Pigeons have been shown to use the position of the sun as a compass.In an experiment, a pigeon is trained to feed from the southeast end of a circular cage.At sunrise, a mirror is used to shift the sun 45 degrees to the right (in a clockwise direction) from its real position.At which location in the cage will the pigeon attempt to feed?
A) North
B) East
C) South
D) West
E) Southwest
A) North
B) East
C) South
D) West
E) Southwest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which experimental manipulation could be used to determine whether an animal uses piloting?
A) Displacing the animal to see if it compensates for the displacement
B) Rearranging potential landmarks around its home
C) Looking for migratory restlessness in captive animals
D) Clock-shifting the animals
E) Displacing and clock-shifting the animals
A) Displacing the animal to see if it compensates for the displacement
B) Rearranging potential landmarks around its home
C) Looking for migratory restlessness in captive animals
D) Clock-shifting the animals
E) Displacing and clock-shifting the animals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Experimental evidence suggests that the ability to detect _______ allows pigeons that are displaced long distances to return home even on overcast days.
A) sound waves
B) ultraviolet (UV) light
C) the gravitational field
D) the magnetic field
E) landmarks
A) sound waves
B) ultraviolet (UV) light
C) the gravitational field
D) the magnetic field
E) landmarks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A bee is performing a waggle dance on the vertical surface of the honeycomb.The dance has a long waggle segment that goes straight upward.What is she communicating to her hivemates?
A) Food is close to the hive and located in the direction of the sun.
B) Food is far from the hive and located to the north.
C) Food is not available.
D) Food is far from the hive and located in the direction of the sun.
E) Food is far from the hive and located in the opposite direction from the sun.
A) Food is close to the hive and located in the direction of the sun.
B) Food is far from the hive and located to the north.
C) Food is not available.
D) Food is far from the hive and located in the direction of the sun.
E) Food is far from the hive and located in the opposite direction from the sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which statement is true?
A) Nonhuman animal communication differs from human communication because unlike humans, nonhuman animals do not practice deception.
B) Clarity of communication decreases as the number of sensory modalities increases.
C) Auditory signals are more efficient than visual signals in a structurally complex environment.
D) Pheromonal signals are very limited in terms of how much information they can provide about the signaler.
E) Most predators have difficulty intercepting visual signals.
A) Nonhuman animal communication differs from human communication because unlike humans, nonhuman animals do not practice deception.
B) Clarity of communication decreases as the number of sensory modalities increases.
C) Auditory signals are more efficient than visual signals in a structurally complex environment.
D) Pheromonal signals are very limited in terms of how much information they can provide about the signaler.
E) Most predators have difficulty intercepting visual signals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following requires an animal to "know" the latitude and longitude of its current position and its intended destination?
A) Bicoordinate navigation
B) Piloting
C) Distance-and-direction navigation
D) Homing
E) Migration
A) Bicoordinate navigation
B) Piloting
C) Distance-and-direction navigation
D) Homing
E) Migration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The waggle dance of bees is an example of a(n) _______ signal.
A) visual
B) tactile
C) auditory
D) electrical
E) chemical
A) visual
B) tactile
C) auditory
D) electrical
E) chemical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



