Deck 57: Ecosystems
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/238
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 57: Ecosystems
1
In the equation NPP = GPP - respiration, the term "GPP" is best defined by total
A) plant biomass produced.
B) plant and animal biomass produced.
C) carbon fixed by primary producers.
D) carbon fixed by producers and consumers.
E) carbon used by producers in all activities, including respiration.
A) plant biomass produced.
B) plant and animal biomass produced.
C) carbon fixed by primary producers.
D) carbon fixed by producers and consumers.
E) carbon used by producers in all activities, including respiration.
C
2
In which situation would bacteria be most likely to obtain energy through chemosynthesis, rather than photosynthesis?
A) At the ocean surface
B) At the soil surface
C) In an estuary with frequent mixing of water
D) Deep in the soil where no light penetrates
E) In a farm field that undergoes frequent plowing
A) At the ocean surface
B) At the soil surface
C) In an estuary with frequent mixing of water
D) Deep in the soil where no light penetrates
E) In a farm field that undergoes frequent plowing
D
3
Compared with the open ocean ecosystem, the continental shelf ecosystem
A) has higher net primary productivity on a per area basis.
B) covers more surface area.
C) has higher net primary productivity on a global basis.
D) is productive down to a greater depth.
E) is less limited by nutrients.
A) has higher net primary productivity on a per area basis.
B) covers more surface area.
C) has higher net primary productivity on a global basis.
D) is productive down to a greater depth.
E) is less limited by nutrients.
A
4
Compared with ocean productivity, land productivity
A) varies more with latitude and is much higher.
B) varies more with latitude and is much lower.
C) varies less with latitude and is much higher.
D) varies less with latitude and is much lower.
E) does not vary with latitude and is much lower.
A) varies more with latitude and is much higher.
B) varies more with latitude and is much lower.
C) varies less with latitude and is much higher.
D) varies less with latitude and is much lower.
E) does not vary with latitude and is much lower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When CO2 from the atmosphere dissolves into the oceans, it changes ocean water by
A) increasing its temperature.
B) decreasing its temperature.
C) increasing its acidity.
D) decreasing its acidity.
E) increasing its salinity.
A) increasing its temperature.
B) decreasing its temperature.
C) increasing its acidity.
D) decreasing its acidity.
E) increasing its salinity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A bacterial species lives deep in the ocean, where chemicals including hydrogen sulfide and methane seep out of superheated magma.The bacteria obtain their energy by breaking down these chemicals and building organic chemicals from them.They are carrying out which biological process?
A) Chemosynthesis
B) Photosynthesis
C) Secondary production
D) Heterotrophy
E) Metabolism
A) Chemosynthesis
B) Photosynthesis
C) Secondary production
D) Heterotrophy
E) Metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which statement best describes a key difference between movement of energy and movement of nutrients through an ecosystem?
A) Nutrients always move rapidly through an ecosystem; energy always moves slowly.
B) The same energy is used over and over; nutrients move through a system and do not return.
C) The same nutrients are used over and over; energy moves through a system, and some is lost as heat.
D) The amount of energy determines the amount of production that can occur; the amount of nutrients is not relevant.
E) The amount of nutrients determines the amount of production that can occur; the amount of energy is not relevant.
A) Nutrients always move rapidly through an ecosystem; energy always moves slowly.
B) The same energy is used over and over; nutrients move through a system and do not return.
C) The same nutrients are used over and over; energy moves through a system, and some is lost as heat.
D) The amount of energy determines the amount of production that can occur; the amount of nutrients is not relevant.
E) The amount of nutrients determines the amount of production that can occur; the amount of energy is not relevant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Algal beds contribute very little to Earth's total net primary production because they are limited by
A) insufficient light.
B) oxygen depletion.
C) insufficient phosphorus.
D) being at very low latitudes.
E) being a tiny fraction of Earth's surface.
A) insufficient light.
B) oxygen depletion.
C) insufficient phosphorus.
D) being at very low latitudes.
E) being a tiny fraction of Earth's surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An organism obtains its nutrients from inorganic chemicals present in soil, water, and air.It incorporates these materials into its tissues in the form of organic compounds.This organism is a(n)
A) autotroph.
B) heterotroph.
C) detritivore.
D) decomposer.
E) predator.
A) autotroph.
B) heterotroph.
C) detritivore.
D) decomposer.
E) predator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Both desert and tundra have very low NPP values.What factor or factors determine NPP values in these two biomes?
A) Both deserts and tundra are limited by temperature.
B) Both deserts and tundra are limited by precipitation.
C) Deserts are limited by precipitation and tundra by temperature.
D) Deserts are limited by temperature and tundra by precipitation.
E) Deserts and tundra are limited by nutrients, not by temperature or precipitation.
A) Both deserts and tundra are limited by temperature.
B) Both deserts and tundra are limited by precipitation.
C) Deserts are limited by precipitation and tundra by temperature.
D) Deserts are limited by temperature and tundra by precipitation.
E) Deserts and tundra are limited by nutrients, not by temperature or precipitation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Refer to the figure. 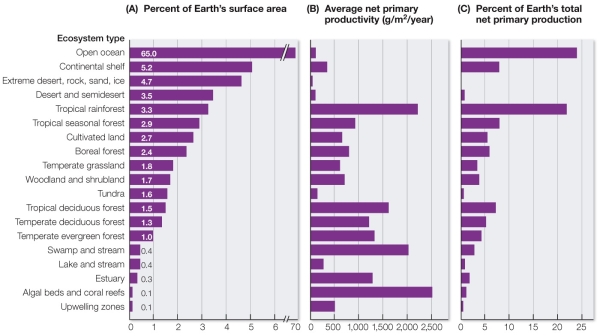 The algal bed and coral reef ecosystem type and the swamp and stream ecosystem type each have an average net primary productivity close to that of tropical rainforests.However, each makes up a much smaller percentage of Earth's net primary production than do rainforests.What factor accounts for this difference?
The algal bed and coral reef ecosystem type and the swamp and stream ecosystem type each have an average net primary productivity close to that of tropical rainforests.However, each makes up a much smaller percentage of Earth's net primary production than do rainforests.What factor accounts for this difference?
A) Latitude with tropical rainforest ecosystems
B) Percent of Earth's surface with tropical rainforest ecosystems
C) Type of ecosystem
D) Average temperature
E) Average precipitation
 The algal bed and coral reef ecosystem type and the swamp and stream ecosystem type each have an average net primary productivity close to that of tropical rainforests.However, each makes up a much smaller percentage of Earth's net primary production than do rainforests.What factor accounts for this difference?
The algal bed and coral reef ecosystem type and the swamp and stream ecosystem type each have an average net primary productivity close to that of tropical rainforests.However, each makes up a much smaller percentage of Earth's net primary production than do rainforests.What factor accounts for this difference?A) Latitude with tropical rainforest ecosystems
B) Percent of Earth's surface with tropical rainforest ecosystems
C) Type of ecosystem
D) Average temperature
E) Average precipitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Research ecologists often specialize in one level of ecology.Which question would most likely be studied by a Yellowstone National Park ecologist specializing in biogeochemical cycles in ecosystems?
A) What is the sex ratio of the elk living in the park?
B) How does nitrogen move among the organisms, soil, water, air, and rocks of the park?
C) How does the reintroduction of wolves influence other large mammal populations in the park?
D) What types of species interactions occur among the major species in the park's food webs?
E) What geological history led to the development of the park's environment?
A) What is the sex ratio of the elk living in the park?
B) How does nitrogen move among the organisms, soil, water, air, and rocks of the park?
C) How does the reintroduction of wolves influence other large mammal populations in the park?
D) What types of species interactions occur among the major species in the park's food webs?
E) What geological history led to the development of the park's environment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of these land ecosystems would be expected to have the highest total net primary productivity?
A) Tundra
B) Boreal forest
C) Temperate deciduous forest
D) Temperate grassland
E) Tropical rainforest
A) Tundra
B) Boreal forest
C) Temperate deciduous forest
D) Temperate grassland
E) Tropical rainforest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A major difference between primary and secondary production in ecosystems is that secondary production involves
A) using metabolism to release nutrients for use, whereas primary production does not.
B) obtaining energy from organic, rather than inorganic, compounds.
C) obtaining energy from sunlight, rather than from chemical compounds.
D) plants, seaweeds, and algae, whereas primary production involves animals.
E) production of different classes of organic compounds than primary production does.
A) using metabolism to release nutrients for use, whereas primary production does not.
B) obtaining energy from organic, rather than inorganic, compounds.
C) obtaining energy from sunlight, rather than from chemical compounds.
D) plants, seaweeds, and algae, whereas primary production involves animals.
E) production of different classes of organic compounds than primary production does.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In which situation are humans not directly affecting the NPP of aquatic ecosystems by altering nutrient concentrations? That is, which situation is natural, rather than caused by humans?
A) Rising CO2 from global warming increases NPP of ocean phytoplankton.
B) Phytoplankton blooms occur when iron sulfite is added to ocean water.
C) Artificial fertilizers from land cause plankton blooms in the Gulf of Mexico.
D) Sewage and wastewater cause eutrophication in Lake Erie.
E) High nitrogen levels in the Pacific Ocean keep NPP high.
A) Rising CO2 from global warming increases NPP of ocean phytoplankton.
B) Phytoplankton blooms occur when iron sulfite is added to ocean water.
C) Artificial fertilizers from land cause plankton blooms in the Gulf of Mexico.
D) Sewage and wastewater cause eutrophication in Lake Erie.
E) High nitrogen levels in the Pacific Ocean keep NPP high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which description does not fit the definition of an ecosystem study?
A) The transformation of energy through a group of forest-floor species
B) The cycling of carbon through a group of soil bacteria on the forest floor
C) Measurement of primary production by all producers in a large forest
D) Atmospheric nitrogen fixation by plants in a forest environment
E) Competitive and cooperative interactions among forest-floor beetle species
A) The transformation of energy through a group of forest-floor species
B) The cycling of carbon through a group of soil bacteria on the forest floor
C) Measurement of primary production by all producers in a large forest
D) Atmospheric nitrogen fixation by plants in a forest environment
E) Competitive and cooperative interactions among forest-floor beetle species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Organisms in an estuary, including phytoplankton, seagrasses, crustaceans, and mollusks, are all exposed to increasing acidity as atmospheric CO2 levels rise.What effect does the increased acidity likely have on these organisms?
A) All organisms are adversely affected and some die.
B) All organisms are unaffected and live and reproduce normally.
C) Phytoplankton and seagrasses decrease photosynthesis, and crustaceans and mollusks reproduce less.
D) Phytoplankton and seagrasses increase photosynthesis, and crustaceans and mollusks reproduce more.
E) Phytoplankton and seagrasses increase photosynthesis, and crustaceans and mollusks have weaker shells.
A) All organisms are adversely affected and some die.
B) All organisms are unaffected and live and reproduce normally.
C) Phytoplankton and seagrasses decrease photosynthesis, and crustaceans and mollusks reproduce less.
D) Phytoplankton and seagrasses increase photosynthesis, and crustaceans and mollusks reproduce more.
E) Phytoplankton and seagrasses increase photosynthesis, and crustaceans and mollusks have weaker shells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which is the correct order of forest types, from lowest to highest total NPP.
A) Tropical, boreal, temperate deciduous
B) Tropical, temperate deciduous, boreal
C) Boreal, tropical, temperate deciduous
D) Boreal, temperate deciduous, tropical
E) Temperate deciduous, boreal, tropical
A) Tropical, boreal, temperate deciduous
B) Tropical, temperate deciduous, boreal
C) Boreal, tropical, temperate deciduous
D) Boreal, temperate deciduous, tropical
E) Temperate deciduous, boreal, tropical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An upwelling zone off the coast of Peru, in South America, has a very high net productivity.The factor that probably contributes most to the region's high NPP is its
A) low latitude.
B) arid regions on the coast.
C) long distance from the coast.
D) increased nutrients from deep water.
E) small geographic area.
A) low latitude.
B) arid regions on the coast.
C) long distance from the coast.
D) increased nutrients from deep water.
E) small geographic area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Two tropical forest regions receive extremely high rainfall (more than 400 cm/yr).The NPP of forest A is much higher than the NPP of forest B.Which factor is likely most associated with the difference in NPP?
A) Forest A has more cloud cover than forest B.
B) Forest A has less cloud cover than forest B.
C) Forest A is at a higher latitude than forest B.
D) Forest A is at a lower latitude than forest B.
E) Forest A has more flooding than forest B.
A) Forest A has more cloud cover than forest B.
B) Forest A has less cloud cover than forest B.
C) Forest A is at a higher latitude than forest B.
D) Forest A is at a lower latitude than forest B.
E) Forest A has more flooding than forest B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which factor is least likely to have an effect on the total number of trophic levels in an ecosystem?
A) Amount of NPP entering the ecosystem
B) Occasional disturbances to the ecosystem
C) Amount of disturbance affecting the ecosystem
D) Evolutionary constraints on top predators
E) Energy loss at each level of the ecosystem
A) Amount of NPP entering the ecosystem
B) Occasional disturbances to the ecosystem
C) Amount of disturbance affecting the ecosystem
D) Evolutionary constraints on top predators
E) Energy loss at each level of the ecosystem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which factor is not a consequence of eutrophication?
A) Declining water quality
B) Hypoxia (decrease in oxygen)
C) Algal blooms
D) Decomposition by bacteria
E) Continuous increase in biomass production
A) Declining water quality
B) Hypoxia (decrease in oxygen)
C) Algal blooms
D) Decomposition by bacteria
E) Continuous increase in biomass production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the 1990s, oceanographic researchers added iron sulfite to the surface waters around the Galápagos Islands.The result of this experiment showed that iron
A) was not necessary to NPP in oceans.
B) was toxic to primary producers in this region.
C) prevented the uptake of CO2 by ocean waters.
D) was the primary factor limiting NPP in this region.
E) increased the uptake of CO2 by ocean waters.
A) was not necessary to NPP in oceans.
B) was toxic to primary producers in this region.
C) prevented the uptake of CO2 by ocean waters.
D) was the primary factor limiting NPP in this region.
E) increased the uptake of CO2 by ocean waters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Refer to the graph. 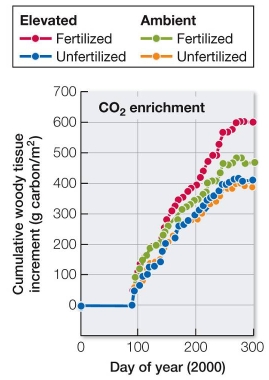 In the FACE experiment in a North Carolina forest, the amount of tree growth (change in carbon biomass per square meter) was measured under conditions of ambient CO2 (270 ppm in 2000, when measurements were done) and elevated CO2 (550 ppm).Half of both the ambient and elevated plots were given additional nitrogen (fertilized); the other half were not (unfertilized).According to the results shown, what can be concluded about the effectiveness of elevated CO2 on increasing rate of tree growth?
In the FACE experiment in a North Carolina forest, the amount of tree growth (change in carbon biomass per square meter) was measured under conditions of ambient CO2 (270 ppm in 2000, when measurements were done) and elevated CO2 (550 ppm).Half of both the ambient and elevated plots were given additional nitrogen (fertilized); the other half were not (unfertilized).According to the results shown, what can be concluded about the effectiveness of elevated CO2 on increasing rate of tree growth?
A) Elevated CO2 increases tree growth in all cases.
B) Elevated CO2 increases tree growth only when they are fertilized as well.
C) Elevated CO2 has little effect on tree growth at any time.
D) Elevated CO2 increases tree growth most when trees are unfertilized.
E) Tree growth is highest under ambient, not elevated, CO2 levels.
 In the FACE experiment in a North Carolina forest, the amount of tree growth (change in carbon biomass per square meter) was measured under conditions of ambient CO2 (270 ppm in 2000, when measurements were done) and elevated CO2 (550 ppm).Half of both the ambient and elevated plots were given additional nitrogen (fertilized); the other half were not (unfertilized).According to the results shown, what can be concluded about the effectiveness of elevated CO2 on increasing rate of tree growth?
In the FACE experiment in a North Carolina forest, the amount of tree growth (change in carbon biomass per square meter) was measured under conditions of ambient CO2 (270 ppm in 2000, when measurements were done) and elevated CO2 (550 ppm).Half of both the ambient and elevated plots were given additional nitrogen (fertilized); the other half were not (unfertilized).According to the results shown, what can be concluded about the effectiveness of elevated CO2 on increasing rate of tree growth?A) Elevated CO2 increases tree growth in all cases.
B) Elevated CO2 increases tree growth only when they are fertilized as well.
C) Elevated CO2 has little effect on tree growth at any time.
D) Elevated CO2 increases tree growth most when trees are unfertilized.
E) Tree growth is highest under ambient, not elevated, CO2 levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A large pond receives sewage runoff from a cattle feedlot and fertilizer runoff from surrounding fields.The runoff contains large quantities of nitrogen and phosphorus.The pond undergoes an algal bloom.The algae die off and are decomposed by bacteria, which depletes the pond's oxygen content.Fish and invertebrates begin to die.What process is the pond undergoing, and changes in what limiting factor or factors initiated the process?
A) Eutrophication; nitrogen only
B) Eutrophication; nitrogen, phosphorus, or both
C) Trophic efficiency; phosphorus only
D) Trophic efficiency; nitrogen, phosphorus, or both
E) Biogeochemical cycling; nitrogen only
A) Eutrophication; nitrogen only
B) Eutrophication; nitrogen, phosphorus, or both
C) Trophic efficiency; phosphorus only
D) Trophic efficiency; nitrogen, phosphorus, or both
E) Biogeochemical cycling; nitrogen only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Some people have suggested that fertilizing the oceans with iron would help combat the effects of global warming on oceans.However, it is unlikely that this method will be used extensively, because iron fertilization
A) does not affect the impacts of global warming on oceans.
B) causes more CO2 to be dissolved in oceans.
C) increases photosynthesis, thereby decreasing dissolved CO2.
D) would be very difficult to do on a large scale.
E) would be ineffective because its effects are indirect, not direct.
A) does not affect the impacts of global warming on oceans.
B) causes more CO2 to be dissolved in oceans.
C) increases photosynthesis, thereby decreasing dissolved CO2.
D) would be very difficult to do on a large scale.
E) would be ineffective because its effects are indirect, not direct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the table. 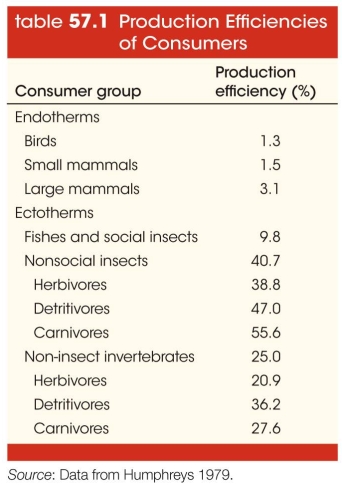 In general, according to the table, which group of ectotherms is most efficient at storing energy as biomass?
In general, according to the table, which group of ectotherms is most efficient at storing energy as biomass?
A) Nonsocial insect carnivores
B) Nonsocial insect detritivores
C) Nonsocial insect herbivores
D) Non-insect invertebrate detritivores
E) Non-insect invertebrate carnivores
 In general, according to the table, which group of ectotherms is most efficient at storing energy as biomass?
In general, according to the table, which group of ectotherms is most efficient at storing energy as biomass?A) Nonsocial insect carnivores
B) Nonsocial insect detritivores
C) Nonsocial insect herbivores
D) Non-insect invertebrate detritivores
E) Non-insect invertebrate carnivores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Refer to the figure. 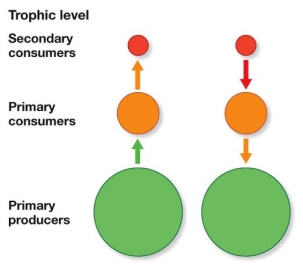 In an ecosystem, nutrients are highly limiting and prevent NPP from increasing above a certain level.This represents which type of control of energy flow?
In an ecosystem, nutrients are highly limiting and prevent NPP from increasing above a certain level.This represents which type of control of energy flow?
A) Top-down control, shown at left
B) Top-down control, shown at right
C) Bottom-up control, shown at left
D) Bottom-up control, shown at right
E) Either top-down or bottom-up, depending on the ecosystem
 In an ecosystem, nutrients are highly limiting and prevent NPP from increasing above a certain level.This represents which type of control of energy flow?
In an ecosystem, nutrients are highly limiting and prevent NPP from increasing above a certain level.This represents which type of control of energy flow?A) Top-down control, shown at left
B) Top-down control, shown at right
C) Bottom-up control, shown at left
D) Bottom-up control, shown at right
E) Either top-down or bottom-up, depending on the ecosystem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the figure. 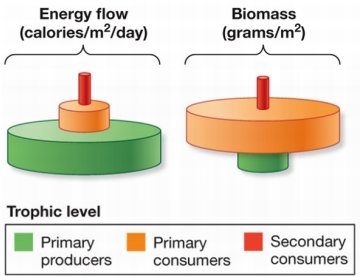 In these pyramid diagrams of the open ocean ecosystem, energy flow of primary producers is very large, while their biomass is very small.What does this suggest about the ocean ecosystem?
In these pyramid diagrams of the open ocean ecosystem, energy flow of primary producers is very large, while their biomass is very small.What does this suggest about the ocean ecosystem?
A) It is dying because primary producer biomass is too small to support higher-level consumers.
B) Producers are tiny and reproduce rapidly, so even though they maintain a small biomass, they can support a large biomass of primary consumers.
C) Producers are mostly large and therefore can support a large biomass of primary producers.
D) Trophic efficiencies are very low, so not much primary producer biomass can be supported.
E) Primary producers must work very hard to provide enough food for consumers; they have little energy left over to build up biomass.
 In these pyramid diagrams of the open ocean ecosystem, energy flow of primary producers is very large, while their biomass is very small.What does this suggest about the ocean ecosystem?
In these pyramid diagrams of the open ocean ecosystem, energy flow of primary producers is very large, while their biomass is very small.What does this suggest about the ocean ecosystem?A) It is dying because primary producer biomass is too small to support higher-level consumers.
B) Producers are tiny and reproduce rapidly, so even though they maintain a small biomass, they can support a large biomass of primary consumers.
C) Producers are mostly large and therefore can support a large biomass of primary producers.
D) Trophic efficiencies are very low, so not much primary producer biomass can be supported.
E) Primary producers must work very hard to provide enough food for consumers; they have little energy left over to build up biomass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
As CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere increase, how might the increase be expected to influence land-based NPP rates?
A) NPP will increase because the CO2 will replace other nutrients.
B) NPP will decrease because the extra CO2 will be toxic.
C) NPP will not change because photosynthesis is not limited by CO2.
D) NPP will increase because CO2 will inhibit respiration.
E) NPP will decrease because CO2 will stimulate respiration.
A) NPP will increase because the CO2 will replace other nutrients.
B) NPP will decrease because the extra CO2 will be toxic.
C) NPP will not change because photosynthesis is not limited by CO2.
D) NPP will increase because CO2 will inhibit respiration.
E) NPP will decrease because CO2 will stimulate respiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the food chain shown below, which type of organism would have the lowest biomass and why? 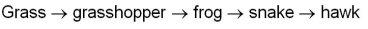
A) Grass; all organisms depend on it, and it does not have time to build up biomass.
B) Grasshopper; it is much smaller than organisms at other levels.
C) Hawk; energy is lost at each level, thus the highest level supports the smallest biomass.
D) Either hawk or snake; both are at high levels and both would lose energy.
E) Either grasshopper or frog; both are small organisms and therefore have small biomass.
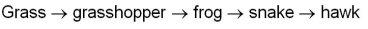
A) Grass; all organisms depend on it, and it does not have time to build up biomass.
B) Grasshopper; it is much smaller than organisms at other levels.
C) Hawk; energy is lost at each level, thus the highest level supports the smallest biomass.
D) Either hawk or snake; both are at high levels and both would lose energy.
E) Either grasshopper or frog; both are small organisms and therefore have small biomass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Primary consumers on land consume an average of 13 percent of the biomass; in aquatic ecosystems, primary consumers consume about 35 percent.What does this say about aquatic ecosystems, compared with terrestrial ecosystems?
A) Aquatic ecosystems have much higher trophic efficiencies.
B) Aquatic ecosystems have much lower trophic efficiencies.
C) Organisms in aquatic ecosystems need more food than those in terrestrial ecosystems.
D) Organisms in aquatic ecosystems need less food than those in terrestrial ecosystems.
E) Primary production in aquatic ecosystems far exceeds rates of herbivory.
A) Aquatic ecosystems have much higher trophic efficiencies.
B) Aquatic ecosystems have much lower trophic efficiencies.
C) Organisms in aquatic ecosystems need more food than those in terrestrial ecosystems.
D) Organisms in aquatic ecosystems need less food than those in terrestrial ecosystems.
E) Primary production in aquatic ecosystems far exceeds rates of herbivory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Refer to the figure. 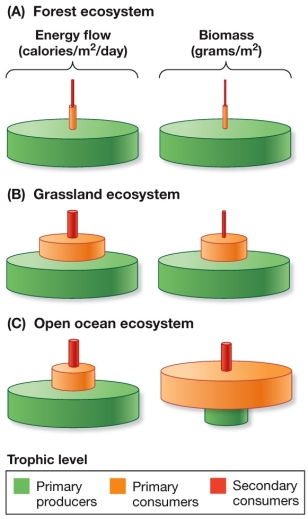 Compare the forest with the grassland ecosystem in the diagram.What is the most likely reason the grassland ecosystem has comparatively higher energy flow and biomass, particularly at the second (primary consumer) level?
Compare the forest with the grassland ecosystem in the diagram.What is the most likely reason the grassland ecosystem has comparatively higher energy flow and biomass, particularly at the second (primary consumer) level?
A) Trophic efficiency of the forest is lower because of the large proportion of wood in the forest.
B) The large proportion of wood in the forest means less energy is available to higher levels, but trophic efficiency is not affected.
C) Trophic efficiency of the forest is higher because of the large proportion of wood in the forest.
D) Grasslands have smaller plants and thus are less able to transfer energy efficiently.
E) Forest trees process energy faster, but they have to develop wood, so they cannot produce biomass as quickly.
 Compare the forest with the grassland ecosystem in the diagram.What is the most likely reason the grassland ecosystem has comparatively higher energy flow and biomass, particularly at the second (primary consumer) level?
Compare the forest with the grassland ecosystem in the diagram.What is the most likely reason the grassland ecosystem has comparatively higher energy flow and biomass, particularly at the second (primary consumer) level?A) Trophic efficiency of the forest is lower because of the large proportion of wood in the forest.
B) The large proportion of wood in the forest means less energy is available to higher levels, but trophic efficiency is not affected.
C) Trophic efficiency of the forest is higher because of the large proportion of wood in the forest.
D) Grasslands have smaller plants and thus are less able to transfer energy efficiently.
E) Forest trees process energy faster, but they have to develop wood, so they cannot produce biomass as quickly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The southwestern desert of the United States has very hot temperatures, low precipitation, and high evaporation rates.The soil is alkaline and low in nutrients.These factors result in minimal plant growth and very few species, compared with, for example, the tropical rainforest.One result of this is that desert food webs tend to have, on average, fewer trophic levels than rainforests.This suggests that in deserts the length of a food web is likely limited by
A) net primary productivity.
B) top predators.
C) human activity.
D) nutrient levels.
E) types of species present.
A) net primary productivity.
B) top predators.
C) human activity.
D) nutrient levels.
E) types of species present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Of the following food webs, which would likely have the highest NPP?
A) Two trophic levels
B) Three trophic levels with omnivory
C) Three trophic levels without omnivory
D) Five trophic levels with omnivory
E) Four trophic levels without omnivory
A) Two trophic levels
B) Three trophic levels with omnivory
C) Three trophic levels without omnivory
D) Five trophic levels with omnivory
E) Four trophic levels without omnivory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In forest ecosystems, bears often eat a varied diet.Two food chains in which they may participate are: 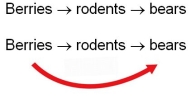 If bears eat only rodents, they are secondary consumers.If they eat both rodents and berries, they are omnivores.How will ecosystem NPP change if bears act as omnivores rather than secondary consumers?
If bears eat only rodents, they are secondary consumers.If they eat both rodents and berries, they are omnivores.How will ecosystem NPP change if bears act as omnivores rather than secondary consumers?
A) NPP will not change; the ecosystem needs a certain amount of primary production and will produce it.
B) NPP will increase; the ecosystem will produce enough berry bushes to feed both bears and rodents.
C) NPP will increase; bears control the populations of both rodents and berry bushes, resulting in higher NPP.
D) NPP will decrease; rodents control berry bushes, but bears cannot control rodent populations because rodents are too numerous.
E) NPP will decrease; bears benefit berry bushes by controlling rodents, but they also eat berries, which decreases NPP.
 If bears eat only rodents, they are secondary consumers.If they eat both rodents and berries, they are omnivores.How will ecosystem NPP change if bears act as omnivores rather than secondary consumers?
If bears eat only rodents, they are secondary consumers.If they eat both rodents and berries, they are omnivores.How will ecosystem NPP change if bears act as omnivores rather than secondary consumers?A) NPP will not change; the ecosystem needs a certain amount of primary production and will produce it.
B) NPP will increase; the ecosystem will produce enough berry bushes to feed both bears and rodents.
C) NPP will increase; bears control the populations of both rodents and berry bushes, resulting in higher NPP.
D) NPP will decrease; rodents control berry bushes, but bears cannot control rodent populations because rodents are too numerous.
E) NPP will decrease; bears benefit berry bushes by controlling rodents, but they also eat berries, which decreases NPP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Refer to the figure. 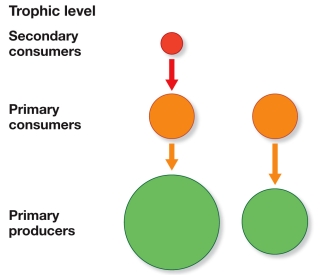 How would the NPP of a three-level food web (left) compare with that of a two-level web (right) and why?
How would the NPP of a three-level food web (left) compare with that of a two-level web (right) and why?
A) The three-level web would have a higher NPP because the extra level requires more primary producers.
B) The three-level web would have a higher NPP because the top level controls the middle level, enabling greater production at the primary producer level.
C) The three-level web would have a lower NPP because it is longer and more consumption takes place.
D) The three-level web would have a lower NPP because it takes more energy to maintain three levels than to maintain two.
E) The two- and three-level webs would have approximately the same NPP because length of the food web does not affect NPP.
 How would the NPP of a three-level food web (left) compare with that of a two-level web (right) and why?
How would the NPP of a three-level food web (left) compare with that of a two-level web (right) and why?A) The three-level web would have a higher NPP because the extra level requires more primary producers.
B) The three-level web would have a higher NPP because the top level controls the middle level, enabling greater production at the primary producer level.
C) The three-level web would have a lower NPP because it is longer and more consumption takes place.
D) The three-level web would have a lower NPP because it takes more energy to maintain three levels than to maintain two.
E) The two- and three-level webs would have approximately the same NPP because length of the food web does not affect NPP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
According to the second law of thermodynamics, in every energy exchange, some energy becomes unavailable for further use.What happens to the energy that becomes unavailable?
A) It returns to a biogeochemical cycle to be reused later.
B) It cycles back to the environment to be reused later.
C) It dissipates and no longer exists as energy.
D) It is lost into the environment as heat.
E) It eventually becomes part of the energy heating Earth's core.
A) It returns to a biogeochemical cycle to be reused later.
B) It cycles back to the environment to be reused later.
C) It dissipates and no longer exists as energy.
D) It is lost into the environment as heat.
E) It eventually becomes part of the energy heating Earth's core.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Agricultural researchers are interested in the effect of production efficiency on economic impacts, sustainability, and production of greenhouse gases by cattle.Two groups of cattle were fed different diets.One group was fed exclusively on grass.The other was fed an energy-rich diet that included grain supplements.How would the two diets most likely affect production efficiency of the cattle?
A) Grass-fed cattle would have a higher production efficiency.
B) Grain-fed cattle would have a higher production efficiency.
C) Production efficiencies would always be equal under the two diets.
D) As long as both groups ate the same amount of food, production efficiencies would be equal.
E) As long as grain-fed cattle ate more food than grass-fed cattle, production efficiencies would be equal.
A) Grass-fed cattle would have a higher production efficiency.
B) Grain-fed cattle would have a higher production efficiency.
C) Production efficiencies would always be equal under the two diets.
D) As long as both groups ate the same amount of food, production efficiencies would be equal.
E) As long as grain-fed cattle ate more food than grass-fed cattle, production efficiencies would be equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Studies in agricultural science show that the net efficiency of energy utilization differs in beef cattle and dairy cattle, with beef cattle being more efficient.This is because beef cattle store more body fat than dairy cattle, although the two store the same amount of protein.This information suggests that the researchers are measuring which type of efficiency?
A) Consumption efficiency
B) Assimilation efficiency
C) Production efficiency
D) Trophic efficiency
E) Nutrient efficiency
A) Consumption efficiency
B) Assimilation efficiency
C) Production efficiency
D) Trophic efficiency
E) Nutrient efficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
More than half of the water from the hydrologic cycle that travels over and through the land eventually reaches the ocean from which source?
A) Rainfall
B) Coastal runoff
C) Groundwater flow
D) Evapotranspiration
E) Earth's largest rivers
A) Rainfall
B) Coastal runoff
C) Groundwater flow
D) Evapotranspiration
E) Earth's largest rivers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Rising CO2 levels have many effects on Earth's ecosystems and organisms.Which effect would have the most immediate impact on Arctic organisms?
A) Melting sea ice
B) Rising sea levels
C) Increasing ocean acidity
D) Shifting of bird ranges northward
E) Increased coastal flooding
A) Melting sea ice
B) Rising sea levels
C) Increasing ocean acidity
D) Shifting of bird ranges northward
E) Increased coastal flooding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The major photosynthesizing organisms in the ocean are phytoplankton and algae.These organisms obtain most of the CO2 necessary for photosynthesis from which source?
A) They take it directly from the atmosphere.
B) They use CO2 dissolved in ocean water.
C) They use CO2 respired by surrounding organisms.
D) They break down organic molecules in the ocean.
E) They break down carbonate from ocean sediments.
A) They take it directly from the atmosphere.
B) They use CO2 dissolved in ocean water.
C) They use CO2 respired by surrounding organisms.
D) They break down organic molecules in the ocean.
E) They break down carbonate from ocean sediments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Refer to the figure. 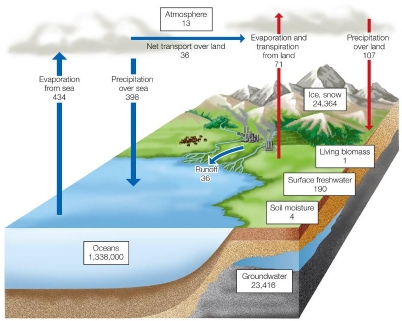 An examination of the fluxes of water over both land and sea, as measured by evaporation and precipitation, shows that
An examination of the fluxes of water over both land and sea, as measured by evaporation and precipitation, shows that
A) total evaporation is greater than total precipitation.
B) total precipitation is greater than total evaporation.
C) there is more evaporation over land and more precipitation at sea.
D) evaporation and precipitation are exactly balanced.
E) values for runoff make up for the variation between land and sea.
 An examination of the fluxes of water over both land and sea, as measured by evaporation and precipitation, shows that
An examination of the fluxes of water over both land and sea, as measured by evaporation and precipitation, shows thatA) total evaporation is greater than total precipitation.
B) total precipitation is greater than total evaporation.
C) there is more evaporation over land and more precipitation at sea.
D) evaporation and precipitation are exactly balanced.
E) values for runoff make up for the variation between land and sea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Carbon is currently being released into the atmosphere by fossil-fuel burning.Why does this release of carbon cause global warming, when carbon released by organism respiration does not?
A) Unlike respiratory CO2, it is being released faster than oceans or organisms can absorb it.
B) It is a stronger greenhouse gas because it has been buried for millions of years.
C) It is a different form of carbon than is currently present in the atmosphere.
D) Unlike respiratory CO2, it is released throughout the year instead of seasonally.
E) It is being burned by humans, who do not use safeguards as other animals do.
A) Unlike respiratory CO2, it is being released faster than oceans or organisms can absorb it.
B) It is a stronger greenhouse gas because it has been buried for millions of years.
C) It is a different form of carbon than is currently present in the atmosphere.
D) Unlike respiratory CO2, it is released throughout the year instead of seasonally.
E) It is being burned by humans, who do not use safeguards as other animals do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Refer to the figure. 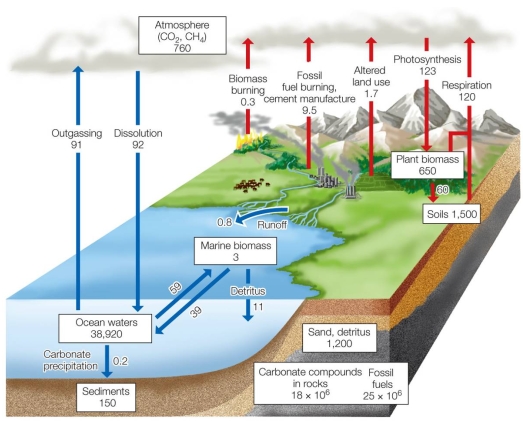 Based on the diagram, the carbon pool storing the largest amount of carbon is the
Based on the diagram, the carbon pool storing the largest amount of carbon is the
A) organisms.
B) atmosphere.
C) rocks and fossil fuels.
D) ocean sediments.
E) ocean water.
 Based on the diagram, the carbon pool storing the largest amount of carbon is the
Based on the diagram, the carbon pool storing the largest amount of carbon is theA) organisms.
B) atmosphere.
C) rocks and fossil fuels.
D) ocean sediments.
E) ocean water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The shortest residence time for water in pools of the hydrologic cycle occurs in
A) aquifers.
B) lakes.
C) rivers.
D) glaciers.
E) oceans.
A) aquifers.
B) lakes.
C) rivers.
D) glaciers.
E) oceans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Refer to the figure. 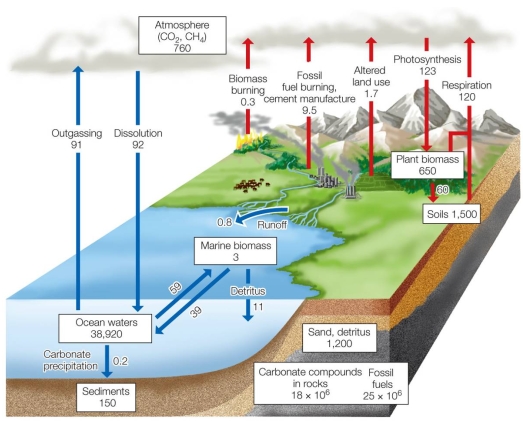 A major difference between carbon cycling on land and at sea is that on land
A major difference between carbon cycling on land and at sea is that on land
A) most of the carbon flux is due to human activity.
B) most of the carbon flux is ultimately stored in soils.
C) there is very little storage of carbon, compared with oceans.
D) all carbon participates in cycles, while little participates at sea.
E) the flux of carbon between air and land is less balanced than at sea.
 A major difference between carbon cycling on land and at sea is that on land
A major difference between carbon cycling on land and at sea is that on landA) most of the carbon flux is due to human activity.
B) most of the carbon flux is ultimately stored in soils.
C) there is very little storage of carbon, compared with oceans.
D) all carbon participates in cycles, while little participates at sea.
E) the flux of carbon between air and land is less balanced than at sea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Scientists know that increasing CO2 traps more heat in Earth's atmosphere and causes global temperatures to rise.What type of data provides the strongest evidence of this relationship?
A) Rising levels of atmospheric CO2 from the Mauna Loa measuring station
B) Comparisons of historical CO2 levels in ice cores and global temperatures over 800,000 years
C) The 1.8°F (1°C) rise in global temperatures since about 1880
D) The FACE experiments, which show increasing NPP with rising CO2 levels
E) Rising levels of carbonic acid in seawater, leading to decreasing ocean pH
A) Rising levels of atmospheric CO2 from the Mauna Loa measuring station
B) Comparisons of historical CO2 levels in ice cores and global temperatures over 800,000 years
C) The 1.8°F (1°C) rise in global temperatures since about 1880
D) The FACE experiments, which show increasing NPP with rising CO2 levels
E) Rising levels of carbonic acid in seawater, leading to decreasing ocean pH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
About half of the excess CO2 released into the atmosphere is dissolved into the oceans.What effect(s) does this added CO2 have on the oceans?
A) It has little or no effect.
B) It raises temperature, but only slightly.
C) It lowers pH.
D) It raises both temperature and pH.
E) It immediately sinks and is stored in the sediments.
A) It has little or no effect.
B) It raises temperature, but only slightly.
C) It lowers pH.
D) It raises both temperature and pH.
E) It immediately sinks and is stored in the sediments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Microbes, primarily bacteria, are responsible for all of the following aspects of the nitrogen cycle except
A) biological nitrogen fixation.
B) nitrification.
C) nitrate reduction.
D) denitrification.
E) industrial nitrogen fixation.
A) biological nitrogen fixation.
B) nitrification.
C) nitrate reduction.
D) denitrification.
E) industrial nitrogen fixation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Refer to the graph, showing a continual increase in CO2 since measurements began about 1960. 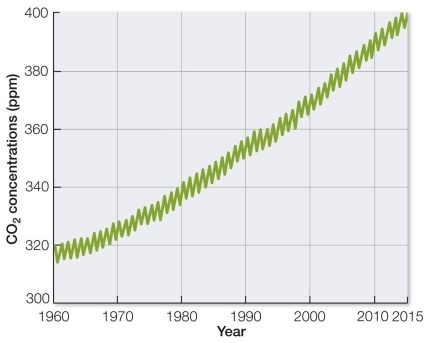 Which type of data, when added to the data in this graph, would not provide evidence of a connection between rising CO2 levels and rising global temperatures?
Which type of data, when added to the data in this graph, would not provide evidence of a connection between rising CO2 levels and rising global temperatures?
A) Atmospheric temperatures over thousands of years
B) Atmospheric temperatures since 1960
C) A climate model correlating rising temperatures with rising CO2
D) Chemistry experiment results showing that CO2 traps heat
E) Measurements showing CO2 being dissolved in the oceans
 Which type of data, when added to the data in this graph, would not provide evidence of a connection between rising CO2 levels and rising global temperatures?
Which type of data, when added to the data in this graph, would not provide evidence of a connection between rising CO2 levels and rising global temperatures?A) Atmospheric temperatures over thousands of years
B) Atmospheric temperatures since 1960
C) A climate model correlating rising temperatures with rising CO2
D) Chemistry experiment results showing that CO2 traps heat
E) Measurements showing CO2 being dissolved in the oceans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Coral reefs have been one of the ecosystems most seriously affected by climate change.Spikes of high temperature and acidity have killed more than half of all corals in some reef systems, including the Caribbean.A process called coral bleaching leaves the corals without color, appearing white.Coral bleaching occurs because the
A) high acidity causes the coral skeleton to disintegrate.
B) high temperature and acidity cause corals' algal symbionts to be expelled.
C) corals' algal symbionts change color as temperature and acidity rise.
D) acid caused by excess CO2 has a bleaching effect on corals.
E) increased water temperature has a bleaching effect on corals.
A) high acidity causes the coral skeleton to disintegrate.
B) high temperature and acidity cause corals' algal symbionts to be expelled.
C) corals' algal symbionts change color as temperature and acidity rise.
D) acid caused by excess CO2 has a bleaching effect on corals.
E) increased water temperature has a bleaching effect on corals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An animal dies near the forest edge.Almost immediately, its dead flesh is attacked and fed upon by bacteria, worms, insect larvae, and scavengers such as coyotes, crows, and vultures.The dead animal is undergoing the process of
A) autotrophy.
B) mineralization.
C) energy flow.
D) decomposition.
E) disturbance.
A) autotrophy.
B) mineralization.
C) energy flow.
D) decomposition.
E) disturbance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which is the least likely fate of a molecule of carbon dioxide dissolved in ocean water?
A) It will be diffused to the atmosphere.
B) It will be incorporated into a fossil fuel.
C) It will become part of a marine animal's shell.
D) It will be taken up by phytoplankton.
E) It will remain dissolved in the water.
A) It will be diffused to the atmosphere.
B) It will be incorporated into a fossil fuel.
C) It will become part of a marine animal's shell.
D) It will be taken up by phytoplankton.
E) It will remain dissolved in the water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The flesh of a dead animal is broken down by many types of decomposers.During the last part of this process, the flesh is turned into small soluble nutrients, such as ions of nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur, which can be used by plants in primary production.This final part of the decomposition process is known as
A) autotrophy.
B) mineralization.
C) energy flow.
D) disturbance.
E) omnivory.
A) autotrophy.
B) mineralization.
C) energy flow.
D) disturbance.
E) omnivory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
During which process of the hydrologic cycle is water most likely to help in the movement of nutrients through their biogeochemical cycles?
A) Runoff from the land into rivers, lakes, and oceans
B) Evapotranspiration from the land surface
C) Evaporation from the ocean surface
D) Pooling in groundwater
E) Storage in glaciers and ice sheets
A) Runoff from the land into rivers, lakes, and oceans
B) Evapotranspiration from the land surface
C) Evaporation from the ocean surface
D) Pooling in groundwater
E) Storage in glaciers and ice sheets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In a biogeochemical cycle, large amounts of an element can be stored for millions of years and remain relatively untouched.Which is the best example of such a pool?
A) Carbon in rocks and fossil fuels
B) Oxygen in the atmosphere
C) Water in the atmosphere
D) Nitrogen in plant biomass
E) Sulfur in plant biomass
A) Carbon in rocks and fossil fuels
B) Oxygen in the atmosphere
C) Water in the atmosphere
D) Nitrogen in plant biomass
E) Sulfur in plant biomass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Refer to the figure. 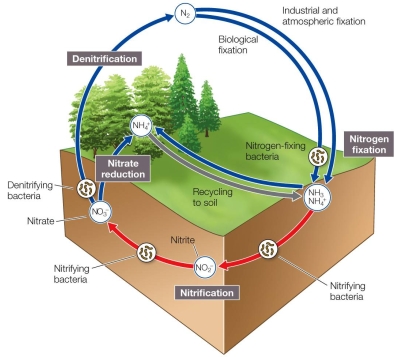 Based on the diagram, the process most responsible for returning nitrogen to the atmosphere as a gas is
Based on the diagram, the process most responsible for returning nitrogen to the atmosphere as a gas is
A) bacterial nitrogen fixation.
B) nitrification.
C) nitrate reduction.
D) denitrification.
E) industrial nitrogen fixation.
 Based on the diagram, the process most responsible for returning nitrogen to the atmosphere as a gas is
Based on the diagram, the process most responsible for returning nitrogen to the atmosphere as a gas isA) bacterial nitrogen fixation.
B) nitrification.
C) nitrate reduction.
D) denitrification.
E) industrial nitrogen fixation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In a biogeochemical cycle, an element is in flux when it is moving from one storage compartment to another.The element carbon shows the least flux (that is, shows the least movement, or stops moving) when it is
A) taken up during photosynthesis.
B) given off during respiration.
C) released during fossil-fuel burning.
D) deposited in ocean sediments.
E) broken down during decomposition.
A) taken up during photosynthesis.
B) given off during respiration.
C) released during fossil-fuel burning.
D) deposited in ocean sediments.
E) broken down during decomposition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of these ecosystem services could be considered a provisioning service?
A) Flood control
B) Soil stabilization
C) Pollination
D) Climate regulation
E) A national park
A) Flood control
B) Soil stabilization
C) Pollination
D) Climate regulation
E) A national park

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Coral reef fish provide the only source of protein for many people, and reef organisms are the source of many medicines.Because of their beauty, reefs are major tourist attractions.Because reefs can recycle and concentrate nutrients, rather than losing them to the open ocean, they can sustain large, diverse populations.Their structure protects shorelines from storms and erosion.These functions suggest that coral reefs provide which types of ecosystem services?
A) Provisioning and regulating only
B) Provisioning and supporting only
C) Provisioning, regulating, and supporting
D) Provisioning, regulating, and cultural
E) Provisioning, regulating, supporting, and cultural
A) Provisioning and regulating only
B) Provisioning and supporting only
C) Provisioning, regulating, and supporting
D) Provisioning, regulating, and cultural
E) Provisioning, regulating, supporting, and cultural

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A major difference between phosphorus cycling and nitrogen cycling is that unlike nitrogen, phosphorus
A) has its major pool in the atmosphere, rather than in rocks and marine sediments.
B) has its major pool in rocks and marine sediments, rather than in the atmosphere.
C) moves very rapidly through all parts of its cycle.
D) moves very rapidly through the geological parts of its cycle.
E) cannot lead to eutrophication in aquatic environments.
A) has its major pool in the atmosphere, rather than in rocks and marine sediments.
B) has its major pool in rocks and marine sediments, rather than in the atmosphere.
C) moves very rapidly through all parts of its cycle.
D) moves very rapidly through the geological parts of its cycle.
E) cannot lead to eutrophication in aquatic environments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Humans make many alterations to natural ecosystems.They turn natural areas into agricultural areas, build canals to transport offshore oil, cut down forests for lumber, build cities and highways, and more.How do these changes affect human societies?
A) They all have positive effects; humans live safer, healthier, more prosperous lives.
B) They all have positive effects; humans are meant to live with technology, not nature.
C) They involve trade-offs; for every benefit provided, an ecosystem service may be lost or altered.
D) They all have negative effects; the benefits are worth less than the ecosystem services lost.
E) They all have negative effects; humans are meant to live with nature, not technology.
A) They all have positive effects; humans live safer, healthier, more prosperous lives.
B) They all have positive effects; humans are meant to live with technology, not nature.
C) They involve trade-offs; for every benefit provided, an ecosystem service may be lost or altered.
D) They all have negative effects; the benefits are worth less than the ecosystem services lost.
E) They all have negative effects; humans are meant to live with nature, not technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The oxygen produced by photosynthesis is considered an ecosystem service because
A) it is a beneficial, but not required, service provided by nature.
B) it can only be produced by photosynthesis.
C) environmentalists consider it important.
D) it benefits humans and would be difficult or costly to replace.
E) it cannot be altered and will always be available from nature.
A) it is a beneficial, but not required, service provided by nature.
B) it can only be produced by photosynthesis.
C) environmentalists consider it important.
D) it benefits humans and would be difficult or costly to replace.
E) it cannot be altered and will always be available from nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
For most of human history, we have received many ecosystem services free and have taken them for granted.These include clean air, clean water, pollination, and flood control by wetlands.Compared with a century ago, these types of ecosystem services seem to be
A) unchanged.
B) degraded in quality.
C) improved in quality.
D) more available.
E) not measurable.
A) unchanged.
B) degraded in quality.
C) improved in quality.
D) more available.
E) not measurable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Industrial nitrogen fixation results in all of the following effects except
A) production of ammonia fertilizers.
B) production of nitrous oxide gas (N2O).
C) eutrophication of coastal waters.
D) increase in ozone and smog.
E) production of DMSP.
A) production of ammonia fertilizers.
B) production of nitrous oxide gas (N2O).
C) eutrophication of coastal waters.
D) increase in ozone and smog.
E) production of DMSP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following would be considered an ecosystem service?
A) The biogeochemical cycle of nitrogen
B) The food web of a forest
C) A city built on a coastline
D) The flood control provided by a salt marsh
E) Dams and levees built to control flooding
A) The biogeochemical cycle of nitrogen
B) The food web of a forest
C) A city built on a coastline
D) The flood control provided by a salt marsh
E) Dams and levees built to control flooding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Organisms both on land and in the oceans release some sulfur back into the atmosphere.On land, the gas released is _______; from the oceans, the gas released is _______.
A) hydrogen sulfide (H2S); hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
B) dimethyl sulfide (CH3SCH3); dimethyl sulfide (CH3SCH3)
C) dimethyl sulfide (CH3SCH3); hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
D) hydrogen sulfide (H2S); dimethyl sulfide (CH3SCH3)
E) DMSP; dimethyl sulfide (CH3SCH3)
A) hydrogen sulfide (H2S); hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
B) dimethyl sulfide (CH3SCH3); dimethyl sulfide (CH3SCH3)
C) dimethyl sulfide (CH3SCH3); hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
D) hydrogen sulfide (H2S); dimethyl sulfide (CH3SCH3)
E) DMSP; dimethyl sulfide (CH3SCH3)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Cities in China are greatly increasing the burning of coal in power plants and the use of automobiles.This is resulting in massive levels of air pollution.Which substances, produced during the burning of coal and oil, are likely causing much of China's air pollution?
A) H2S and DMSP
B) DMSP and CH3SCH3
C) CH3SCH3 and SO2
D) SO2 and N2
E) SO2 and NO2
A) H2S and DMSP
B) DMSP and CH3SCH3
C) CH3SCH3 and SO2
D) SO2 and N2
E) SO2 and NO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of these situations does not involve an ecosystem service trade-off?
A) Use of land to grow food prevents its use as a high-biodiversity prairie ecosystem.
B) Use of pesticides to kill crop-eating insects also kills pollinators.
C) Building a canal to transport offshore oil destroys a shrimp fishery.
D) Fertilizer and pesticide runoff from agriculture prevent use of a stream as a clean water source.
E) A city apartment building is torn down and another, more modern, building is built.
A) Use of land to grow food prevents its use as a high-biodiversity prairie ecosystem.
B) Use of pesticides to kill crop-eating insects also kills pollinators.
C) Building a canal to transport offshore oil destroys a shrimp fishery.
D) Fertilizer and pesticide runoff from agriculture prevent use of a stream as a clean water source.
E) A city apartment building is torn down and another, more modern, building is built.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Nitrogen is often the limiting nutrient in ecosystems.This is because
A) there is very little nitrogen on Earth, compared with other nutrients.
B) most nitrogen is in the form of N2, which organisms cannot use.
C) the chemical reactions needed to produce usable nitrogen are difficult.
D) nitrogen is quickly removed from ecosystems and stored in rocks and sediments.
E) humans turn most available nitrogen into ammonia, which organisms cannot use.
A) there is very little nitrogen on Earth, compared with other nutrients.
B) most nitrogen is in the form of N2, which organisms cannot use.
C) the chemical reactions needed to produce usable nitrogen are difficult.
D) nitrogen is quickly removed from ecosystems and stored in rocks and sediments.
E) humans turn most available nitrogen into ammonia, which organisms cannot use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Refer to the graph. 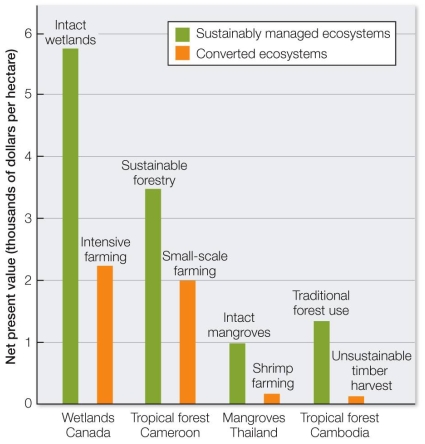 Based on the results in the graph, is sustainable management of ecosystems profitable, and on what do you base your response?
Based on the results in the graph, is sustainable management of ecosystems profitable, and on what do you base your response?
A) Yes; the values of all sustainable systems are more than double those of unsustainable systems.
B) Yes; the values of all sustainable systems are significantly greater than those of unsustainable systems.
C) Sometimes; the values of all systems except "tropical forest Cameroon" are great enough to be profitable.
D) No; factors other than dollar value must be taken into account to determine profitability.
E) No; the differences in values are not great enough to ensure profitability of sustainable systems.
 Based on the results in the graph, is sustainable management of ecosystems profitable, and on what do you base your response?
Based on the results in the graph, is sustainable management of ecosystems profitable, and on what do you base your response?A) Yes; the values of all sustainable systems are more than double those of unsustainable systems.
B) Yes; the values of all sustainable systems are significantly greater than those of unsustainable systems.
C) Sometimes; the values of all systems except "tropical forest Cameroon" are great enough to be profitable.
D) No; factors other than dollar value must be taken into account to determine profitability.
E) No; the differences in values are not great enough to ensure profitability of sustainable systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A farmer is growing corn, which requires high levels of nitrogen.Corn does not have root nodules with nitrogen-fixing bacteria and therefore cannot produce its own nitrogen.What will most likely happen to the soil's nitrogen content if corn is grown in the same place year after year?
A) It will increase rapidly, as nitrogen-fixing bacteria immediately move in.
B) It will decrease at first, then increase as nitrogen-fixing bacteria move in.
C) It will decrease continuously until it becomes nitrogen-deficient.
D) It will remain stable, as the corn becomes accustomed to lower nitrogen levels.
E) It will remain stable, as nitrogen will enter the field through runoff.
A) It will increase rapidly, as nitrogen-fixing bacteria immediately move in.
B) It will decrease at first, then increase as nitrogen-fixing bacteria move in.
C) It will decrease continuously until it becomes nitrogen-deficient.
D) It will remain stable, as the corn becomes accustomed to lower nitrogen levels.
E) It will remain stable, as nitrogen will enter the field through runoff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Offshore oil drilling in the United States provides oil that is refined to make many products to provide energy for human civilization.Making this provisioning service possible requires many changes to natural ecosystems.Along the Gulf Coast, thousands of canals, pipelines, and drilling rigs are installed, shipping lanes are dredged, and cypress swamps and other wetlands are destroyed.Which is one ecosystem service lost in trade-off as a result of these changes?
A) Flood control services by wetlands
B) Control over water supplies
C) Easy access to offshore oil
D) Delivery of upstream sediments to the wetlands
E) Control over pollution from oil rigs
A) Flood control services by wetlands
B) Control over water supplies
C) Easy access to offshore oil
D) Delivery of upstream sediments to the wetlands
E) Control over pollution from oil rigs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A recent study showed that in situations involving ecosystem service trade-offs, private interests usually win over public interests, and provisioning services win over more general services (such as regulating, supporting, or cultural).For example, harvesting a forest for timber wins over maintaining the forest for carbon storage, and agriculture wins over maintaining land for clean water and biodiversity.This suggests that in the future, we can expect to see
A) more use of regulating, supporting, and cultural services.
B) more careful consideration of the value of ecosystem services.
C) better methods for calculating the value of ecosystem services.
D) more use of economically profitable provisioning services.
E) replacement of ecosystem services by technological services.
A) more use of regulating, supporting, and cultural services.
B) more careful consideration of the value of ecosystem services.
C) better methods for calculating the value of ecosystem services.
D) more use of economically profitable provisioning services.
E) replacement of ecosystem services by technological services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Atmospheric sulfur participates in world climate by helping to form clouds, which decrease incoming solar radiation.Which sulfur compound is most associated with cloud formation?
A) Hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
B) dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP)
C) Dimethyl sulfide (CH3SCH3)
D) Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
E) Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
A) Hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
B) dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP)
C) Dimethyl sulfide (CH3SCH3)
D) Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
E) Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of these is not a factor that must be considered when determining the value of an ecosystem service?
A) The humans driving ecosystem change
B) The ecosystem processes or functions affected by the change
C) All ecosystem processes and functions, including those not affected by the change
D) How ecosystem processes and functions influence the goods and services
E) The social and economic values of all goods and services
A) The humans driving ecosystem change
B) The ecosystem processes or functions affected by the change
C) All ecosystem processes and functions, including those not affected by the change
D) How ecosystem processes and functions influence the goods and services
E) The social and economic values of all goods and services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A scientist studying the sulfur cycle is particularly interested in the movement of sulfur through organisms in terrestrial ecosystems.To see most of the interactions of sulfur with these organisms, she should concentrate her measurements on which environmental pool of sulfur?
A) Soil
B) Oceans
C) Atmosphere
D) Volcanoes
E) Rocks and ocean sediments
A) Soil
B) Oceans
C) Atmosphere
D) Volcanoes
E) Rocks and ocean sediments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In much of the open ocean, NPP is limited by nitrogen.But in the Gulf of Mexico, especially near the mouth of the Mississippi River, dead zones (regions of low or no oxygen, resulting in the death of marine organisms) form every summer.These dead zones result from
A) eutrophication caused by nitrogen fertilizer runoff from farms upstream.
B) very low nitrogen levels leading to inability of plants to reproduce.
C) an unknown combination of excess nutrients poisoning the system.
D) a lack of required nutrients, with the type of nutrient varying from year to year.
E) fertilizer production in the area producing smog, which limits photosynthesis.
A) eutrophication caused by nitrogen fertilizer runoff from farms upstream.
B) very low nitrogen levels leading to inability of plants to reproduce.
C) an unknown combination of excess nutrients poisoning the system.
D) a lack of required nutrients, with the type of nutrient varying from year to year.
E) fertilizer production in the area producing smog, which limits photosynthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 238 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



