Deck 22: Speciation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/247
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Speciation
1
The genes F and G act in accordance with the Dobzhansky-Muller model, leading to sterility in hybrids between two species of monkeyflowers.Any combination of the F1 and the G2 alleles causes hybrids to be sterile.Based on the Dobzhansky-Muller model, which genotype was the ancestor of the two species unlikely to have?
A) F1F1; G1G1
B) F1F1; G2G2
C) F0F0; G2G2
D) F2F2; G0G0
E) F2F2; G2G2
A) F1F1; G1G1
B) F1F1; G2G2
C) F0F0; G2G2
D) F2F2; G0G0
E) F2F2; G2G2
B
2
Which statement about the Dobzhansky-Muller model of speciation is true?
A) It requires a phase in which some individuals are reproductively incompatible with other individuals in the same population.
B) It involves a single gene.
C) It is supported by empirical examples.
D) It requires millions of years to produce a new species.
E) It does not apply to the bat genus (Rhogeessa).
A) It requires a phase in which some individuals are reproductively incompatible with other individuals in the same population.
B) It involves a single gene.
C) It is supported by empirical examples.
D) It requires millions of years to produce a new species.
E) It does not apply to the bat genus (Rhogeessa).
C
3
The notion of potentiality in Mayr's definition of "potentially interbreeding" species would likely apply in which case?
A) Populations of mice on different islands
B) Two sparrow species that exist in a hybrid zone
C) Sympatric species of snails
D) Asexual fungi
E) Populations of fish that live in the same coral reef
A) Populations of mice on different islands
B) Two sparrow species that exist in a hybrid zone
C) Sympatric species of snails
D) Asexual fungi
E) Populations of fish that live in the same coral reef
A
4
Refer to the figure. 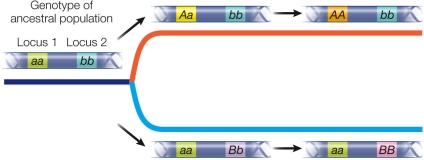 The figure shows the Dobzhansky-Muller model of the evolution of reproductive isolation.The F1 hybrids between the species at the end of this process have reduced fitness.Which genotype has reduced fitness?
The figure shows the Dobzhansky-Muller model of the evolution of reproductive isolation.The F1 hybrids between the species at the end of this process have reduced fitness.Which genotype has reduced fitness?
A) aabb
B) AAbb
C) AaBb
D) aaBB
E) aaBb
 The figure shows the Dobzhansky-Muller model of the evolution of reproductive isolation.The F1 hybrids between the species at the end of this process have reduced fitness.Which genotype has reduced fitness?
The figure shows the Dobzhansky-Muller model of the evolution of reproductive isolation.The F1 hybrids between the species at the end of this process have reduced fitness.Which genotype has reduced fitness?A) aabb
B) AAbb
C) AaBb
D) aaBB
E) aaBb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement best supports all three species concepts?
A) Biological diversity does not vary in a smooth, incremental way.
B) In some cases, it may be difficult to predict whether incipient species will continue to diverge.
C) Virtually all species exhibit some degree of genetic recombination among individuals.
D) Hybrid zones may form if reproductive isolation is incomplete.
E) A single lineage may evolve over time without giving rise to a new species.
A) Biological diversity does not vary in a smooth, incremental way.
B) In some cases, it may be difficult to predict whether incipient species will continue to diverge.
C) Virtually all species exhibit some degree of genetic recombination among individuals.
D) Hybrid zones may form if reproductive isolation is incomplete.
E) A single lineage may evolve over time without giving rise to a new species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which characteristic is least likely to be used to determine the difference between two cryptic species of Hyla treefrogs?
A) Behavior
B) Genotype
C) Mating calls
D) Morphology
E) Physiology
A) Behavior
B) Genotype
C) Mating calls
D) Morphology
E) Physiology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The biological species concept does not apply to which group of organisms?
A) Birds
B) Mammals that form monogamous pair bonds
C) Asexual fungi
D) Fungi that engage in sexual reproduction
E) Cryptic species
A) Birds
B) Mammals that form monogamous pair bonds
C) Asexual fungi
D) Fungi that engage in sexual reproduction
E) Cryptic species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The genes F and G act in accordance with the Dobzhansky-Muller model leading to sterility in hybrids between two species of monkeyflowers.Any combination of the F1 and the G2 alleles causes hybrids to be sterile.Based on the Dobzhansky-Muller model, which genotype should have high fitness?
A) F1F1; G1G1
B) F1F2; G2G2
C) F1F0; G2G2
D) F1F2; G0G2
E) F1F2; G1G2
A) F1F1; G1G1
B) F1F2; G2G2
C) F1F0; G2G2
D) F1F2; G0G2
E) F1F2; G1G2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which situation would most likely pose a major difficulty for applying the biological species concept?
A) Two populations of sexually reproducing plants that can be bred easily in the same location under field conditions
B) Two populations of sexually reproducing insects that can be bred easily in the same location under field conditions
C) Five snail fossils taken from the same locality during a 400,000-year time span
D) Dimorphic mating pairs of birds
E) Monomorphic mating pairs of birds
A) Two populations of sexually reproducing plants that can be bred easily in the same location under field conditions
B) Two populations of sexually reproducing insects that can be bred easily in the same location under field conditions
C) Five snail fossils taken from the same locality during a 400,000-year time span
D) Dimorphic mating pairs of birds
E) Monomorphic mating pairs of birds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is a major limitation of the morphological species concept?
A) It requires detailed knowledge of genetics and mating behavior.
B) Individuals that don't look alike don't always belong to different species.
C) It is a very recent concept.
D) It is incompatible with the binomial system of classification.
E) It cannot be used in creating field guides.
A) It requires detailed knowledge of genetics and mating behavior.
B) Individuals that don't look alike don't always belong to different species.
C) It is a very recent concept.
D) It is incompatible with the binomial system of classification.
E) It cannot be used in creating field guides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
You are a biologist going to an island that few scientists have studied.You will most likely be able to first distinguish new species based on the _______ species concept.Having a computer and rudimentary lab permits you to analyze DNA samples collected and compare them with known species.This will allow you to also make inferences about species based on a _______ species concept.
A) biological; lineage
B) biological; morphological
C) morphological; biological
D) morphological; lineage
E) lineage; biological
A) biological; lineage
B) biological; morphological
C) morphological; biological
D) morphological; lineage
E) lineage; biological

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Ginkgo trees grow in Asia and North America and thus are divided into two groups that are geographically separated.Mayr's framing of the biological species concept would classify these populations as belonging to the same species because they
A) are reproductively isolated.
B) are potentially capable of exchanging genes.
C) exchange genes across the Pacific Ocean.
D) have different evolutionary ancestries.
E) have formed a large hybrid zone.
A) are reproductively isolated.
B) are potentially capable of exchanging genes.
C) exchange genes across the Pacific Ocean.
D) have different evolutionary ancestries.
E) have formed a large hybrid zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Even trained biologists have difficulty telling females of Drosophila melanogaster and D.sechellia apart, yet these species are reproductively isolated.Thus, these species are considered _______ species.
A) lineage
B) morphological
C) cryptic
D) Darwinian
E) sympatric
A) lineage
B) morphological
C) cryptic
D) Darwinian
E) sympatric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The classification of organisms based on appearance alone is known as the _______ species concept.
A) biological
B) lineage
C) phylogenetic
D) allopatric
E) morphological
A) biological
B) lineage
C) phylogenetic
D) allopatric
E) morphological

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Populations of beetles from different localities in Europe are possible cryptic species.How would one determine whether they are cryptic species based on the biological species concept?
A) Cross them; if they have much reproductive isolation, then they are likely to be cryptic species.
B) Cross them; if they have little reproductive isolation, then they are likely to be cryptic species.
C) Subject their DNA to phylogenetic analysis; if they are distinct evolutionary branches, then they are likely to be cryptic species.
D) Subject their DNA to phylogenetic analysis; if they are distinct evolutionary branches, then they are unlikely to be cryptic species.
E) The biological species cannot be applied to determine whether they are cryptic species.
A) Cross them; if they have much reproductive isolation, then they are likely to be cryptic species.
B) Cross them; if they have little reproductive isolation, then they are likely to be cryptic species.
C) Subject their DNA to phylogenetic analysis; if they are distinct evolutionary branches, then they are likely to be cryptic species.
D) Subject their DNA to phylogenetic analysis; if they are distinct evolutionary branches, then they are unlikely to be cryptic species.
E) The biological species cannot be applied to determine whether they are cryptic species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Under what circumstance would applications of the lineage species concept most face limitations?
A) When studying asexual species of plants
B) When specimens have been collected under different environmental conditions
C) When determining the extent of divergence in DNA sequences necessary to determine whether different populations of salamanders should be considered one species or not
D) When determining the extent of reproductive isolation necessary to determine whether different populations of flies should be considered species.
E) When working with DNA collected from museum specimens of birds.
A) When studying asexual species of plants
B) When specimens have been collected under different environmental conditions
C) When determining the extent of divergence in DNA sequences necessary to determine whether different populations of salamanders should be considered one species or not
D) When determining the extent of reproductive isolation necessary to determine whether different populations of flies should be considered species.
E) When working with DNA collected from museum specimens of birds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The _______ species concept holds that species are groups of actually or potentially interbreeding natural populations that are reproductively isolated from other such groups.
A) Darwinian
B) biological
C) morphological
D) Linnaean
E) lineage
A) Darwinian
B) biological
C) morphological
D) Linnaean
E) lineage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Platyfish with spots have an X-linked gene that produces the spots.All platyfish have an autosomal repressor that inhibits the expression of the spot-producing gene.The closely related swordtail lacks both the spot-producing gene and the repressor.In backcrosses between these two species, some hybrids receive the spot-producing gene, but not the repressor.These hybrid individuals should have reduced viability because they often develop malignant tumors due to improper regulation of the expression of the spot-producing gene.What can we conclude?
A) The ancestor of these fish likely had the spot-producing gene without the repressor.
B) This scenario is inconsistent with the Dobzhansky-Muller model.
C) Hybrids with the repressor, but not the spot-producing gene, should have high viability.
D) Reinforcement is likely to occur.
E) An adaptive radiation will likely occur.
A) The ancestor of these fish likely had the spot-producing gene without the repressor.
B) This scenario is inconsistent with the Dobzhansky-Muller model.
C) Hybrids with the repressor, but not the spot-producing gene, should have high viability.
D) Reinforcement is likely to occur.
E) An adaptive radiation will likely occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The genes F and G act in accordance with the Dobzhansky-Muller model, leading to sterility in hybrids between two species of monkeyflowers.Any combination of the F1 and the G2 alleles causes hybrids to be sterile.Based on the Dobzhansky-Muller model, which genotype should have low fitness?
A) F1F1; G1G1
B) F1F1; G2G2
C) F0F0; G2G2
D) F2F2; G0G0
E) F2F2; G2G2
A) F1F1; G1G1
B) F1F1; G2G2
C) F0F0; G2G2
D) F2F2; G0G0
E) F2F2; G2G2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The content of most standard field guides to identification of organisms reflects _______ species concept.
A) the biological
B) the lineage
C) Mayr's
D) the ecological
E) the morphological
A) the biological
B) the lineage
C) Mayr's
D) the ecological
E) the morphological

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which is a key distinction between allopatric and non-polyploid sympatric speciation?
A) Differences in selective pressures usually precede geographic barriers in allopatric, but not sympatric, speciation.
B) Differences in selective pressures usually precede geographic barriers in sympatric, but not allopatric, speciation.
C) Allopatric, but not sympatric, speciation involves genetic changes.
D) Sympatric, but not allopatric, speciation involves genetic change.
E) Sympatric speciation is usually a much longer process than allopatric speciation.
A) Differences in selective pressures usually precede geographic barriers in allopatric, but not sympatric, speciation.
B) Differences in selective pressures usually precede geographic barriers in sympatric, but not allopatric, speciation.
C) Allopatric, but not sympatric, speciation involves genetic changes.
D) Sympatric, but not allopatric, speciation involves genetic change.
E) Sympatric speciation is usually a much longer process than allopatric speciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Refer to the table. 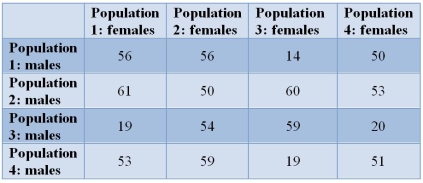 Certain populations of a copepod (a planktonic crustacean) may be reproductively isolated, even though females will mate with any male.Here, three females from one of the populations are placed with three males from another population.The diagonals represent crosses made between males and females of the same population.The numbers of offspring produced are listed in the table.Which cross shows reproductive isolation?
Certain populations of a copepod (a planktonic crustacean) may be reproductively isolated, even though females will mate with any male.Here, three females from one of the populations are placed with three males from another population.The diagonals represent crosses made between males and females of the same population.The numbers of offspring produced are listed in the table.Which cross shows reproductive isolation?
A) Population 3 males and population 2 females
B) Population 3 males and population 3 females
C) Population 3 males and population 4 females
D) Population 4 males and population 2 females
E) Population 4 males and population 4 females
 Certain populations of a copepod (a planktonic crustacean) may be reproductively isolated, even though females will mate with any male.Here, three females from one of the populations are placed with three males from another population.The diagonals represent crosses made between males and females of the same population.The numbers of offspring produced are listed in the table.Which cross shows reproductive isolation?
Certain populations of a copepod (a planktonic crustacean) may be reproductively isolated, even though females will mate with any male.Here, three females from one of the populations are placed with three males from another population.The diagonals represent crosses made between males and females of the same population.The numbers of offspring produced are listed in the table.Which cross shows reproductive isolation?A) Population 3 males and population 2 females
B) Population 3 males and population 3 females
C) Population 3 males and population 4 females
D) Population 4 males and population 2 females
E) Population 4 males and population 4 females

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the most likely sequence of events in allopatric speciation?
A) Geographic barrier, reproductive isolation, genetic divergence
B) Geographic barrier, genetic divergence, reproductive isolation
C) Genetic divergence, geographic barrier, reproductive isolation
D) Genetic divergence, reproductive isolation, geographic barrier
E) Reproductive isolation, genetic divergence, geographic barrier
A) Geographic barrier, reproductive isolation, genetic divergence
B) Geographic barrier, genetic divergence, reproductive isolation
C) Genetic divergence, geographic barrier, reproductive isolation
D) Genetic divergence, reproductive isolation, geographic barrier
E) Reproductive isolation, genetic divergence, geographic barrier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which statement about the Dobzhansky-Muller model of speciation is false?
A) It can involve combinations of single genes.
B) It can involve combinations of chromosomal rearrangements.
C) It requires different mutations occurring in each of the two populations.
D) It requires selection to act differently in the two populations.
E) It requires genetic divergence.
A) It can involve combinations of single genes.
B) It can involve combinations of chromosomal rearrangements.
C) It requires different mutations occurring in each of the two populations.
D) It requires selection to act differently in the two populations.
E) It requires genetic divergence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which factor or process does the Dobzhansky-Muller model of speciation necessarily require?
A) Natural selection
B) Reinforcement
C) Interaction between alleles at different loci
D) Chromosomal rearrangements, particularly centric fusions
E) Temporal isolation
A) Natural selection
B) Reinforcement
C) Interaction between alleles at different loci
D) Chromosomal rearrangements, particularly centric fusions
E) Temporal isolation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which situation is least likely to lead to geographic isolation and allopatric speciation?
A) An eight-lane highway dividing a population of snails with limited mobility
B) A deep, narrow river dividing a population of hummingbirds
C) A deep, narrow river dividing a population of white-footed mice (not known for their swimming ability)
D) A patch of land bisecting a river and divides a population of minnows
E) A mountain range divideing a population of moths
A) An eight-lane highway dividing a population of snails with limited mobility
B) A deep, narrow river dividing a population of hummingbirds
C) A deep, narrow river dividing a population of white-footed mice (not known for their swimming ability)
D) A patch of land bisecting a river and divides a population of minnows
E) A mountain range divideing a population of moths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the table. 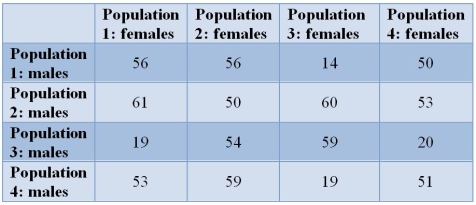 Certain populations of a copepod (a planktonic crustacean) may be reproductively isolated, even though females will mate with any male.Here, three females from one of the populations are placed with three males from another population.The diagonals represent crosses made between males and females of the same population.The numbers of offspring produced are listed in the table.Which cross shows reproductive isolation?
Certain populations of a copepod (a planktonic crustacean) may be reproductively isolated, even though females will mate with any male.Here, three females from one of the populations are placed with three males from another population.The diagonals represent crosses made between males and females of the same population.The numbers of offspring produced are listed in the table.Which cross shows reproductive isolation?
A) Population 1 males and population 2 females
B) Population 1 males and population 3 females
C) Population 2 males and population 1 females
D) Population 2 males and population 3 females
E) Population 2 males and population 4 females
 Certain populations of a copepod (a planktonic crustacean) may be reproductively isolated, even though females will mate with any male.Here, three females from one of the populations are placed with three males from another population.The diagonals represent crosses made between males and females of the same population.The numbers of offspring produced are listed in the table.Which cross shows reproductive isolation?
Certain populations of a copepod (a planktonic crustacean) may be reproductively isolated, even though females will mate with any male.Here, three females from one of the populations are placed with three males from another population.The diagonals represent crosses made between males and females of the same population.The numbers of offspring produced are listed in the table.Which cross shows reproductive isolation?A) Population 1 males and population 2 females
B) Population 1 males and population 3 females
C) Population 2 males and population 1 females
D) Population 2 males and population 3 females
E) Population 2 males and population 4 females

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Refer to the figure. 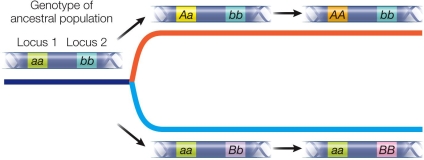 The figure shows the Dobzhansky-Muller model of the evolution of reproductive isolation.The F1 hybrids between the species at the end of this process have reduced fitness.Which genotype has high fitness?
The figure shows the Dobzhansky-Muller model of the evolution of reproductive isolation.The F1 hybrids between the species at the end of this process have reduced fitness.Which genotype has high fitness?
A) AaBB
B) aaBB
C) AaBb
D) AABB
E) AABb
 The figure shows the Dobzhansky-Muller model of the evolution of reproductive isolation.The F1 hybrids between the species at the end of this process have reduced fitness.Which genotype has high fitness?
The figure shows the Dobzhansky-Muller model of the evolution of reproductive isolation.The F1 hybrids between the species at the end of this process have reduced fitness.Which genotype has high fitness?A) AaBB
B) aaBB
C) AaBb
D) AABB
E) AABb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which conclusion is best supported by results of the studies of apple maggot flies?
A) Speciation requires geographic barriers.
B) Reproductive isolation evolves during speciation.
C) Polyploidy is a frequent cause of speciation.
D) Speciation requires gametic isolation.
E) Speciation requires dietary change.
A) Speciation requires geographic barriers.
B) Reproductive isolation evolves during speciation.
C) Polyploidy is a frequent cause of speciation.
D) Speciation requires gametic isolation.
E) Speciation requires dietary change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The Isthmus of Panama cut off gene flow between Atlantic and Pacific populations of a species of fish.The cessation of gene flow led to the accumulation of genetic differences between the populations, which then led to reproductive isolation.Now, Atlantic and Pacific populations of this fish are separate species that cannot interbreed, even if they were again to come into contact with each other.The process described here is that of
A) sympatric speciation.
B) parapatric speciation.
C) allopatric speciation.
D) reinforcement.
E) temporal isolation.
A) sympatric speciation.
B) parapatric speciation.
C) allopatric speciation.
D) reinforcement.
E) temporal isolation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which statement about Darwin's finches is true?
A) Several, but not all, of the finches eat mostly seeds.
B) There are more species of these finches than there are of the Hawaiian Drosophila.
C) They arose from at least three different species from the South American mainland.
D) They show little differentiation in their beak shape and differ mainly in their size.
E) None of the finches eat insects.
A) Several, but not all, of the finches eat mostly seeds.
B) There are more species of these finches than there are of the Hawaiian Drosophila.
C) They arose from at least three different species from the South American mainland.
D) They show little differentiation in their beak shape and differ mainly in their size.
E) None of the finches eat insects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which statement about the evolution of reproductive isolation is false?
A) Reproductive isolation evolves at about the same rate in nearly all groups of organisms.
B) Reproductive isolation can evolve gradually in the lab, even if the researchers do not directly select for it.
C) Reproductive isolation generally increases gradually with increasing genetic distance.
D) Reproductive isolation is not "all-or-nothing"; intermediate levels of reproductive isolation can be found.
E) Reproductive isolation can be man-made, and it can occur naturally.
A) Reproductive isolation evolves at about the same rate in nearly all groups of organisms.
B) Reproductive isolation can evolve gradually in the lab, even if the researchers do not directly select for it.
C) Reproductive isolation generally increases gradually with increasing genetic distance.
D) Reproductive isolation is not "all-or-nothing"; intermediate levels of reproductive isolation can be found.
E) Reproductive isolation can be man-made, and it can occur naturally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which condition is most likely to lead to allopatric speciation?
A) A river dividing a population of small, nonflying crickets
B) A lake dividing a population of large butterflies
C) A highway dividing a population of deer
D) A mudslide dividing a population of hawks
E) A fire dividing a population of bats
A) A river dividing a population of small, nonflying crickets
B) A lake dividing a population of large butterflies
C) A highway dividing a population of deer
D) A mudslide dividing a population of hawks
E) A fire dividing a population of bats

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A fly is separating into two different groups-one that lays eggs on cherries and one that lays eggs on apples.The two types of flies, which are found in the same locality, prefer to mate with their own type.This fly species is most likely demonstrating
A) allopatric speciation due to their preference for cherry or apple
B) allopatric speciation due to directional selection.
C) sympatric speciation due to their preference for cherry or apple.
D) the formation of new species by polyploidy.
E) reinforcement.
A) allopatric speciation due to their preference for cherry or apple
B) allopatric speciation due to directional selection.
C) sympatric speciation due to their preference for cherry or apple.
D) the formation of new species by polyploidy.
E) reinforcement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which adaptation is not found among any of the species of Darwin's finches?
A) Large bills for crushing large, hard seeds
B) Beaks that can open cactus fruits and extract seeds
C) Long beaks for probing dead wood, crevices, and bark for insects
D) Heavy bills for twisting apart wood to reach larvae inside
E) Hooked bills for opening banana fruit
A) Large bills for crushing large, hard seeds
B) Beaks that can open cactus fruits and extract seeds
C) Long beaks for probing dead wood, crevices, and bark for insects
D) Heavy bills for twisting apart wood to reach larvae inside
E) Hooked bills for opening banana fruit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which condition is least likely to lead to geographic isolation, hence inhibiting allopatric speciation?
A) A lava flow in Iceland dividing a population of white Angora rabbits into two populations
B) A fire dividing a population of bats into two populations
C) A hurricane destroying a large portion of grassland, thereby creating two populations of snails
D) A deep gorge dividing a population of slow-moving snails
E) A land bridge dividing a population of tuna
A) A lava flow in Iceland dividing a population of white Angora rabbits into two populations
B) A fire dividing a population of bats into two populations
C) A hurricane destroying a large portion of grassland, thereby creating two populations of snails
D) A deep gorge dividing a population of slow-moving snails
E) A land bridge dividing a population of tuna

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which factor did not contribute to the genetic diversification of the Galápagos Island finches studied by Darwin?
A) Environmental conditions varying among the different islands
B) Most of the islands being sufficiently distant from one another such that movement among their populations was limited
C) The islands being only 100 km from Ecuador, so they received a continual input of new genes from the mainland
D) Occasional migrants to new islands rarely interbreeding with endemic species
E) Over time, the residents of each island developed their own genetic distinctiveness
A) Environmental conditions varying among the different islands
B) Most of the islands being sufficiently distant from one another such that movement among their populations was limited
C) The islands being only 100 km from Ecuador, so they received a continual input of new genes from the mainland
D) Occasional migrants to new islands rarely interbreeding with endemic species
E) Over time, the residents of each island developed their own genetic distinctiveness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The evolution of chromosomal rearrangements in Rhogeessa bats supports the role of _______ in speciation.
A) the Dobzhansky-Muller model
B) autopolyploidy
C) chromosome duplication
D) gametic isolation
E) genetic convergence
A) the Dobzhansky-Muller model
B) autopolyploidy
C) chromosome duplication
D) gametic isolation
E) genetic convergence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which process or event was required for sympatric speciation in the apple maggot fly?
A) Genetic drift
B) Stabilizing selection
C) Disruptive selection
D) Geographic barriers
E) Polyploidy
A) Genetic drift
B) Stabilizing selection
C) Disruptive selection
D) Geographic barriers
E) Polyploidy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Studies with Rhogeessa bats show that the Dobzhansky-Muller model
A) also applies to prezygotic reproductive isolation.
B) cannot be applied to prezygotic reproductive isolation.
C) cannot be applied to postzygotic reproductive isolation.
D) is restricted to genetic changes that are single nucleotide changes.
E) is not restricted to genetic changes that are single nucleotide changes.
A) also applies to prezygotic reproductive isolation.
B) cannot be applied to prezygotic reproductive isolation.
C) cannot be applied to postzygotic reproductive isolation.
D) is restricted to genetic changes that are single nucleotide changes.
E) is not restricted to genetic changes that are single nucleotide changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Two populations of snails are allopatric, living in areas that have different compositions of soil types.The snails live in soil and are not very mobile.Researchers are interested in whether the populations have acquired different types of reproductive isolation.Which method would be best to determine whether two populations exhibited behavioral isolation?
A) Move them into a common experimental setting to see if they will produce offspring. If they produce offspring, they exhibit behavioral isolation.
B) Move them into a common experimental setting to see if they will produce offspring. If they do not produce offspring, they exhibit behavioral isolation.
C) Bring them into the lab. Observe single pairs of a male from one population and a female from the other. If they mate, then they exhibit behavioral isolation.
D) Bring them into the lab. Observe single pairs of a male from one population and a female from the other. If they do not mate, then they exhibit behavioral isolation.
E) Observe when each population is active. If they are active at the same time, then they exhibit behavioral isolation.
A) Move them into a common experimental setting to see if they will produce offspring. If they produce offspring, they exhibit behavioral isolation.
B) Move them into a common experimental setting to see if they will produce offspring. If they do not produce offspring, they exhibit behavioral isolation.
C) Bring them into the lab. Observe single pairs of a male from one population and a female from the other. If they mate, then they exhibit behavioral isolation.
D) Bring them into the lab. Observe single pairs of a male from one population and a female from the other. If they do not mate, then they exhibit behavioral isolation.
E) Observe when each population is active. If they are active at the same time, then they exhibit behavioral isolation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which statement about polyploidy is true?
A) Autopolyploids may be produced when individuals of two different but closely related species hybridize.
B) Botanists estimate that 95 percent of fern species are polyploids.
C) Autopolyploids are often fertile, because each of the chromosomes has a nearly identical partner to pair with during meiosis.
D) Polyploidy is more common in animals than in plants.
E) A tetraploid individual can usually produce viable offspring by mating with a diploid.
A) Autopolyploids may be produced when individuals of two different but closely related species hybridize.
B) Botanists estimate that 95 percent of fern species are polyploids.
C) Autopolyploids are often fertile, because each of the chromosomes has a nearly identical partner to pair with during meiosis.
D) Polyploidy is more common in animals than in plants.
E) A tetraploid individual can usually produce viable offspring by mating with a diploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which type of reproductive isolating mechanisms would most likely arise from the coevolution of male and female reproductive organs in two sympatric populations of insects?
A) Behavioral
B) Temporal
C) Allopatric
D) Habitat
E) Mechanical
A) Behavioral
B) Temporal
C) Allopatric
D) Habitat
E) Mechanical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The wheat that we commonly eat is hexaploid, derived from a cross between two distinct species, one a diploid and one a tetraploid.This is an example of
A) reinforcement.
B) the Dobzhansky-Muller model.
C) autopolyploidy.
D) allopolyploidy.
E) adaptive polyploidy.
A) reinforcement.
B) the Dobzhansky-Muller model.
C) autopolyploidy.
D) allopolyploidy.
E) adaptive polyploidy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Before transferring sperm to the female during mating, the males of some species of beetles use their copulatory organs to remove the sperm of other males.In cases in which a female mated first with a male of a different species, the male of her own species is particularly adept at removing the other male's sperm.This is an example of _______ isolation.
A) geographical
B) temporal
C) mechanical
D) postzygotic
E) precoital
A) geographical
B) temporal
C) mechanical
D) postzygotic
E) precoital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Two species of crickets have partially overlapping ranges, in which hybrids are never found.Individuals—whether taken from overlapping areas or from non-overlapping areas—will rarely mate in the lab, because the females reject the songs sung by males of the other species.Of the few hybrids that are produced in lab crosses, all have low viability.Based on the information given, which statement is true?
A) The two species exhibit postzygotic reproductive isolation, but not prezygotic isolation.
B) The two species exhibit prezygotic and postzygotic reproductive isolation.
C) There is no evidence for reinforcement.
D) A hybrid zone has formed.
E) Sympatric speciation has occurred.
A) The two species exhibit postzygotic reproductive isolation, but not prezygotic isolation.
B) The two species exhibit prezygotic and postzygotic reproductive isolation.
C) There is no evidence for reinforcement.
D) A hybrid zone has formed.
E) Sympatric speciation has occurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Suppose one incipient species of beetle prefers to live and mate in grassy areas and its sibling incipient species prefers sandy soils.This is an example of _______ isolation, and is a form of _______ zygotic isolation.
A) temporal; pre
B) temporal; post
C) behavioral; post
D) habitat; pre
E) habitat; post
A) temporal; pre
B) temporal; post
C) behavioral; post
D) habitat; pre
E) habitat; post

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A field contains two related species of flowering plants.Species A has a diploid chromosome number of 16, and species B has a diploid chromosome number of 18.If a third species arises as a result of hybridization between A and B, how many chromosomes will it have?
A) 17
B) 32
C) 34
D) 36
E) 68
A) 17
B) 32
C) 34
D) 36
E) 68

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Two populations of snails are allopatric, living in areas that have different compositions of soil types.The snails live in soil and are not very mobile.Researchers are interested in whether the populations have acquired different types of reproductive isolation.Which method would be best to determine if they exhibit temporal isolation?
A) Bring them into the lab. Observe single pairs of a male from one population and a female from the other. If they mate, then they exhibit temporal isolation.
B) Bring them into the lab. Observe single pairs of a male from one population and a female from the other. If they do not mate, then they exhibit temporal isolation.
C) Observe when each population is active. If they are active at very different times, then they exhibit temporal isolation.
D) Observe when each population is active. If they are active at the same time, then they exhibit temporal isolation.
E) Bring them into the lab. Have the females from one population mate with males from another. Count the number of offspring. If few offspring are produced, then they exhibit temporal isolation.
A) Bring them into the lab. Observe single pairs of a male from one population and a female from the other. If they mate, then they exhibit temporal isolation.
B) Bring them into the lab. Observe single pairs of a male from one population and a female from the other. If they do not mate, then they exhibit temporal isolation.
C) Observe when each population is active. If they are active at very different times, then they exhibit temporal isolation.
D) Observe when each population is active. If they are active at the same time, then they exhibit temporal isolation.
E) Bring them into the lab. Have the females from one population mate with males from another. Count the number of offspring. If few offspring are produced, then they exhibit temporal isolation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which statement about polyploidy in plants is false?
A) Both tetraploid and diploid individuals can produce viable gametes.
B) Tetraploid plants can self-fertilize.
C) Tetraploid plants crossed with diploid plants can produce viable offspring.
D) Offspring from crosses between tetraploid plants and diploid plant are reproductively isolated.
E) Crosses between tetraploid and diploid individuals produce tetraploid offspring.
A) Both tetraploid and diploid individuals can produce viable gametes.
B) Tetraploid plants can self-fertilize.
C) Tetraploid plants crossed with diploid plants can produce viable offspring.
D) Offspring from crosses between tetraploid plants and diploid plant are reproductively isolated.
E) Crosses between tetraploid and diploid individuals produce tetraploid offspring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Despite inhabiting overlapping ranges, the western spotted skunk and the eastern spotted skunk do not interbreed.One reason is that the western species breeds in early fall and the eastern species breeds in late winter to early spring.This is an example of _______ isolation.
A) chemical
B) gametic
C) postzygotic
D) temporal
E) mechanical
A) chemical
B) gametic
C) postzygotic
D) temporal
E) mechanical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The wheat that we commonly eat is hexaploid, derived from a cross between two distinct species, one a diploid and one a tetraploid.The diploid wheat has 14 chromosomes.How many chromosomes does the hexaploid wheat have?
A) 14
B) 28
C) 42
D) 56
E) 84
A) 14
B) 28
C) 42
D) 56
E) 84

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Females of the species Drosophila pseudoobscura respond less well to courtship signals from males of their close relative D.persimilis than they do to those of males of their own species.This is an example of
A) gametic isolation.
B) hybrid infertility.
C) behavioral isolation.
D) adaptive radiation.
E) sympatric speciation.
A) gametic isolation.
B) hybrid infertility.
C) behavioral isolation.
D) adaptive radiation.
E) sympatric speciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The sperm of one species of fish is chemically incompatible with the eggs of a closely related species.This type of reproductive isolating barrier is called
A) postzygotic isolation.
B) gametic isolation.
C) low hybrid zygote viability.
D) temporal isolation.
E) behavioral isolation.
A) postzygotic isolation.
B) gametic isolation.
C) low hybrid zygote viability.
D) temporal isolation.
E) behavioral isolation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Two species of crickets have partially overlapping ranges, in which hybrids are never found.Individuals—whether taken from overlapping areas or from non-overlapping areas—will rarely mate in the lab, because the females reject the songs sung by males of the other species.Of the few hybrids that are produced in lab crosses, all have low viability.The two cricket species described exhibit _______.
A) mechanical
B) behavioral
C) habitat
D) temporal
E) gametic
A) mechanical
B) behavioral
C) habitat
D) temporal
E) gametic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Refer to the table. 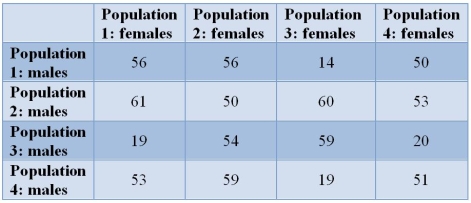 Certain populations of a copepod (a planktonic crustacean) may be reproductively isolated, even though females will mate with any male.Here, three females from one of the populations are placed with three males from another population.The diagonals represent crosses made between males and females of the same population.The numbers of offspring produced are listed in the table.In the crosses with reproductive isolation, what type of reproductive isolation exists?
Certain populations of a copepod (a planktonic crustacean) may be reproductively isolated, even though females will mate with any male.Here, three females from one of the populations are placed with three males from another population.The diagonals represent crosses made between males and females of the same population.The numbers of offspring produced are listed in the table.In the crosses with reproductive isolation, what type of reproductive isolation exists?
A) Behavioral
B) Mechanical
C) Temporal
D) Low hybrid viability
E) Hybrid inferility
 Certain populations of a copepod (a planktonic crustacean) may be reproductively isolated, even though females will mate with any male.Here, three females from one of the populations are placed with three males from another population.The diagonals represent crosses made between males and females of the same population.The numbers of offspring produced are listed in the table.In the crosses with reproductive isolation, what type of reproductive isolation exists?
Certain populations of a copepod (a planktonic crustacean) may be reproductively isolated, even though females will mate with any male.Here, three females from one of the populations are placed with three males from another population.The diagonals represent crosses made between males and females of the same population.The numbers of offspring produced are listed in the table.In the crosses with reproductive isolation, what type of reproductive isolation exists?A) Behavioral
B) Mechanical
C) Temporal
D) Low hybrid viability
E) Hybrid inferility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Two populations of snails are allopatric, living in areas that have different compositions of soil types.The snails live in soil and are not very mobile.Researchers are interested in whether the populations have acquired different types of reproductive isolation.What would be the best way to test whether these populations exhibit habitat isolation?
A) Examine the preference of soil types of each population. If they have similar preferences, then they likely exhibit habitat isolation.
B) Examine the preference of soil types of each population. If they have different preferences, then they likely exhibit habitat isolation.
C) Observe when each population is active. If they are active at very different times, then they likely exhibit habitat isolation.
D) Observe when each population is active. If they are active at the same time, then they likely exhibit habitat isolation.
E) Bring them into the lab. Have the females from one population mate with males from another. Count the number of offspring. If few offspring are produced, then they likely exhibit temporal isolation.
A) Examine the preference of soil types of each population. If they have similar preferences, then they likely exhibit habitat isolation.
B) Examine the preference of soil types of each population. If they have different preferences, then they likely exhibit habitat isolation.
C) Observe when each population is active. If they are active at very different times, then they likely exhibit habitat isolation.
D) Observe when each population is active. If they are active at the same time, then they likely exhibit habitat isolation.
E) Bring them into the lab. Have the females from one population mate with males from another. Count the number of offspring. If few offspring are produced, then they likely exhibit temporal isolation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The apple and the hawthorn groups of Rhagoletis flies display both behavioral and _______ isolation.
A) autopolyploidic
B) temporal
C) gametic
D) allopatric
E) mechanical
A) autopolyploidic
B) temporal
C) gametic
D) allopatric
E) mechanical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the expected ploidy level of an F1 hybrid offspring of a hexaploid father and a diploid mother?
A) Diploid (2n)
B) Triploid (3n)
C) Tetraploid (4n)
D) Hexaploid (6n)
E) Octaploid (8n)
A) Diploid (2n)
B) Triploid (3n)
C) Tetraploid (4n)
D) Hexaploid (6n)
E) Octaploid (8n)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the critical distinction between allopolyploidy and autopolyploidy?
A) Allopolyploidy involves disruptive selection; autopolyploidy does not
B) Autopolyploidy involves disruptive selection; allopolyploidy does not
C) If speciation is allopatric rather than sympatric, the mode of speciation is allopolyploidy; if speciation is sympatric rather than allopatric, the mode of speciation is autopolyploidy
D) In autopolyploidy, one parental species contributes to the polyploidy; in allopolyploidy, two parental species contribute to the polyploidy
E) In allopolyploidy, one parental species contributes to the polyploidy; in autopolyploidy, two parental species contribute to the polyploidy
A) Allopolyploidy involves disruptive selection; autopolyploidy does not
B) Autopolyploidy involves disruptive selection; allopolyploidy does not
C) If speciation is allopatric rather than sympatric, the mode of speciation is allopolyploidy; if speciation is sympatric rather than allopatric, the mode of speciation is autopolyploidy
D) In autopolyploidy, one parental species contributes to the polyploidy; in allopolyploidy, two parental species contribute to the polyploidy
E) In allopolyploidy, one parental species contributes to the polyploidy; in autopolyploidy, two parental species contribute to the polyploidy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Drosophila pseudoobscura and D.persimilis are two fly species that live in the western United States.The smaller geographic range of D.persimilis is enclosed within the range of D.pseudoobscura.Research shows that D.pseudoobscura taken from areas that overlap with D.persimilis are less likely to mate with D.persimilis than are the D.pseudoobscura flies from populations that do not come into contact D.persimilis.What is the most likely explanation for these results?
A) Temporal isolation
B) The Dobzhansky-Muller model of reproductive isolation
C) Reinforcement
D) Habitat Isolation
E) Adaptive radiation
A) Temporal isolation
B) The Dobzhansky-Muller model of reproductive isolation
C) Reinforcement
D) Habitat Isolation
E) Adaptive radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which statement about hybrid zones is false?
A) They occur where two different populations come into contact.
B) They may shift in location, due to environmental changes.
C) Their habitat may differ from that favored by the parent populations.
D) They may narrow, or even disappear, if strong isolating mechanisms develop.
E) Broad hybrid zones typically involve hybrids that have low fitness
A) They occur where two different populations come into contact.
B) They may shift in location, due to environmental changes.
C) Their habitat may differ from that favored by the parent populations.
D) They may narrow, or even disappear, if strong isolating mechanisms develop.
E) Broad hybrid zones typically involve hybrids that have low fitness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which scenario would not be considered an example of a prezygotic reproductive isolating mechanism?
A) One bird species forages in the tops of trees for flying insects, whereas another forages on the ground for worms and grubs
B) The males of one species of moth cannot detect and respond to the sex attractant chemicals produced by the females of another species
C) Sperm of one species of sea urchin are unable to penetrate the egg plasma membrane of another species
D) Mosquitoes of one species are active in foraging and searching for mates at dusk, whereas those of another species are active at dawn
E) Flowers of one orchid species mimic female bees of species A, whereas flowers of another orchid species mimic female bees of species B
A) One bird species forages in the tops of trees for flying insects, whereas another forages on the ground for worms and grubs
B) The males of one species of moth cannot detect and respond to the sex attractant chemicals produced by the females of another species
C) Sperm of one species of sea urchin are unable to penetrate the egg plasma membrane of another species
D) Mosquitoes of one species are active in foraging and searching for mates at dusk, whereas those of another species are active at dawn
E) Flowers of one orchid species mimic female bees of species A, whereas flowers of another orchid species mimic female bees of species B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Refer to the figure. 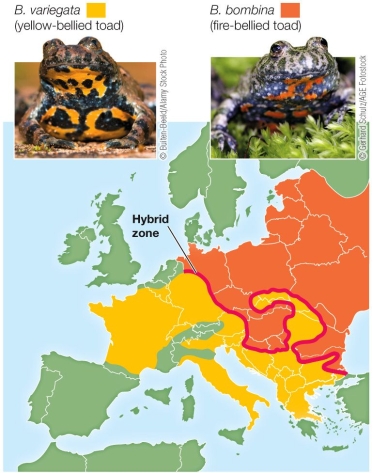 A long, narrow hybrid zone exists in Europe between the ranges of the fire-bellied toad and the yellow-bellied toad.The persistence of this zone can be attributed to which factor?
A long, narrow hybrid zone exists in Europe between the ranges of the fire-bellied toad and the yellow-bellied toad.The persistence of this zone can be attributed to which factor?
A) Hybrid fitness is high, but reinforcement strengthens the prezygotic barriers between the two species.
B) Hybrid offspring have the same fitness as non-hybrid offspring.
C) Both species travel long distances over the course of their lives.
D) Hybrid fitness is low, but individuals from outside the hybrid zone regularly move into the hybrid zone.
E) An adaptive radiation is occurring.
 A long, narrow hybrid zone exists in Europe between the ranges of the fire-bellied toad and the yellow-bellied toad.The persistence of this zone can be attributed to which factor?
A long, narrow hybrid zone exists in Europe between the ranges of the fire-bellied toad and the yellow-bellied toad.The persistence of this zone can be attributed to which factor?A) Hybrid fitness is high, but reinforcement strengthens the prezygotic barriers between the two species.
B) Hybrid offspring have the same fitness as non-hybrid offspring.
C) Both species travel long distances over the course of their lives.
D) Hybrid fitness is low, but individuals from outside the hybrid zone regularly move into the hybrid zone.
E) An adaptive radiation is occurring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Two species of narrowmouth frogs in the United States have mating calls that differ more in their region of sympatry than in those parts of their ranges that do not overlap.If this difference in their vocalizations has the function of preventing hybridization between the two species, it is an example of
A) a hybrid zone.
B) reinforcement.
C) sympatric speciation.
D) a postzygotic reproductive barrier.
E) an adaptive radiation.
A) a hybrid zone.
B) reinforcement.
C) sympatric speciation.
D) a postzygotic reproductive barrier.
E) an adaptive radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which mechanism can lead to selection against hybridization?
A) Temporal isolation
B) Behavioral isolation
C) Mechanical isolation
D) Hybrid sterility
E) Gametic isolation
A) Temporal isolation
B) Behavioral isolation
C) Mechanical isolation
D) Hybrid sterility
E) Gametic isolation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose that two populations that were once isolated come into contact.Which result would not be likely?
A) Little reinforcement of prezygotic barriers if the hybrids are unfit
B) Interbreeding between the two populations if reproductive isolation is not complete
C) Spread of hybrids through both populations if the hybrids are fit, resulting in gene flow between them
D) A lack of interbreeding if reproductive isolation had been established before contact
E) The development of hybrid zones that last for long periods of time
A) Little reinforcement of prezygotic barriers if the hybrids are unfit
B) Interbreeding between the two populations if reproductive isolation is not complete
C) Spread of hybrids through both populations if the hybrids are fit, resulting in gene flow between them
D) A lack of interbreeding if reproductive isolation had been established before contact
E) The development of hybrid zones that last for long periods of time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which is not a prezygotic reproductive isolating barrier?
A) Hybrid infertility
B) Mechanical isolation
C) Behavioral isolation
D) Temporal isolation
E) Habitat isolation
A) Hybrid infertility
B) Mechanical isolation
C) Behavioral isolation
D) Temporal isolation
E) Habitat isolation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Hybrid zones are likely to be narrow
A) in species that shift locations considerably during their lifetimes.
B) when reinforcement is occurring.
C) when there is strong selection against the hybrids.
D) when the hybrids are as fit as the original species.
E) when hybrids are formed in marine species.
A) in species that shift locations considerably during their lifetimes.
B) when reinforcement is occurring.
C) when there is strong selection against the hybrids.
D) when the hybrids are as fit as the original species.
E) when hybrids are formed in marine species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Natural selection would rarely favor the evolution of which type of reproductive isolating barriers?
A) Mechanical isolation
B) Gametic isolation
C) Behavioral isolation
D) Temporal isolation
E) Hybrid infertility
A) Mechanical isolation
B) Gametic isolation
C) Behavioral isolation
D) Temporal isolation
E) Hybrid infertility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A hybrid zone between two species of butterflies contains individuals with widely varying genotypes, ranging from those matching both parental species to those with varying proportions of genes from the parental species.From this information one can infer that
A) prezygotic isolating mechanisms are maintaining the hybrid zone.
B) postzygotic isolating mechanisms are maintaining the hybrid zone.
C) the hybrid zone is relatively old.
D) the hybrid zone is relatively new.
E) the hybrid zone has been reinforced.
A) prezygotic isolating mechanisms are maintaining the hybrid zone.
B) postzygotic isolating mechanisms are maintaining the hybrid zone.
C) the hybrid zone is relatively old.
D) the hybrid zone is relatively new.
E) the hybrid zone has been reinforced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Molecular genetic analysis shows that a turtle hybrid zone contains mainly F1 individuals with a few backcross individuals.What can you infer from this?
A) The hybrids have high fitness.
B) The hybrid zone probably started only a couple generations ago.
C) The hybrid zone has been around for more than 20 generations.
D) The main type of reproductive isolation operating is behavioral.
E) The main type of reproductive isolation operating is low hybrid viability.
A) The hybrids have high fitness.
B) The hybrid zone probably started only a couple generations ago.
C) The hybrid zone has been around for more than 20 generations.
D) The main type of reproductive isolation operating is behavioral.
E) The main type of reproductive isolation operating is low hybrid viability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Aquilegia formosa (columbine) flowers are normally pendant and pollinated by hummingbirds.A related species, A.pubescens, has flowers that are normally upright and pollinated by hawkmoths.Studies in which the flowers of A.formosa were turned upright and those of A.pubescens were turned downward showed that
A) hybrids rarely form between these species because the two species are not interfertile.
B) hawkmoths prefer one species over the other because of differences between the flowers in the color of light that they emit.
C) hawkmoths show equal preference for the two species if the flowers of A. formosa are turned upright.
D) hawkmoths show equal preference for the two species if the flowers of A. pubescens are turned downward.
E) hummingbirds show equal preference for the two species if the flowers of A. pubescens are turned downward.
A) hybrids rarely form between these species because the two species are not interfertile.
B) hawkmoths prefer one species over the other because of differences between the flowers in the color of light that they emit.
C) hawkmoths show equal preference for the two species if the flowers of A. formosa are turned upright.
D) hawkmoths show equal preference for the two species if the flowers of A. pubescens are turned downward.
E) hummingbirds show equal preference for the two species if the flowers of A. pubescens are turned downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which is not a postzygotic isolation mechanism?
A) Abnormal meiosis following fertilization
B) Infertile hybrids
C) Reduced viability of hybrids
D) Abnormal mitosis following fertilization
E) Variation in mating pheromones
A) Abnormal meiosis following fertilization
B) Infertile hybrids
C) Reduced viability of hybrids
D) Abnormal mitosis following fertilization
E) Variation in mating pheromones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Rank the following isolating mechanisms with respect to their time of occurrence in the life cycle, from earliest to latest.
A) Low hybrid zygotic viability, gametic isolation, behavioral isolation
B) Low hybrid zygotic viability, behavioral isolation, gametic isolation
C) Behavioral isolation, low hybrid zygotic viability, gametic isolation
D) Behavioral isolation, gametic isolation, low hybrid zygotic viability
E) Gametic isolation, behavioral isolation, low hybrid zygotic viability
A) Low hybrid zygotic viability, gametic isolation, behavioral isolation
B) Low hybrid zygotic viability, behavioral isolation, gametic isolation
C) Behavioral isolation, low hybrid zygotic viability, gametic isolation
D) Behavioral isolation, gametic isolation, low hybrid zygotic viability
E) Gametic isolation, behavioral isolation, low hybrid zygotic viability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which statement about hybrid zones is false?
A) They are excellent natural laboratories for speciation studies.
B) When they first appear, most contain primarily recombinant individuals.
C) They can persist for hundreds of years or longer.
D) Hybrids in hybrid zones can have morphological abnormalites
E) Hybrid zones only occur in plants
A) They are excellent natural laboratories for speciation studies.
B) When they first appear, most contain primarily recombinant individuals.
C) They can persist for hundreds of years or longer.
D) Hybrids in hybrid zones can have morphological abnormalites
E) Hybrid zones only occur in plants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Suppose that the natural ranges of horses and donkeys were to overlap.Which statement best describes what is likely to happen to the populations over time?
A) The hybrid offspring (mules) would become widespread and mate with members of both populations. b. The hybrid offspring would mate with other hybrid offspring to produce viable offspring.
C) The hybrid offspring would be less reproductively fit and reinforcement would strengthen postzygotic barriers.
D) Eventually all members of both populations would be hybrids.
E) The hybrid offspring would be less reproductively fit and reinforcement would strengthen prezygotic barriers.
A) The hybrid offspring (mules) would become widespread and mate with members of both populations. b. The hybrid offspring would mate with other hybrid offspring to produce viable offspring.
C) The hybrid offspring would be less reproductively fit and reinforcement would strengthen postzygotic barriers.
D) Eventually all members of both populations would be hybrids.
E) The hybrid offspring would be less reproductively fit and reinforcement would strengthen prezygotic barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
When hybrid offspring in amphibians are at a fitness disadvantage and reinforcement does not take place, what event or process is likely to occur?
A) The formation of a hybrid zone
B) An adaptive radiation
C) The formation of a new species via polyploidy
D) The spreading of hybrids through both populations, resulting in the combining of both gene pools and no new species
E) Habitat isolation
A) The formation of a hybrid zone
B) An adaptive radiation
C) The formation of a new species via polyploidy
D) The spreading of hybrids through both populations, resulting in the combining of both gene pools and no new species
E) Habitat isolation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Refer to the figure. 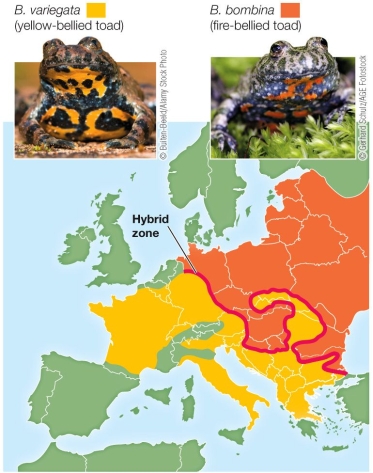 The figure shows two species, a fire-bellied toad and yellow-bellied toad, which occupy different areas of Europe.A small area of overlap between these regions constitutes a hybrid zone.If individuals from the two populations overcome prezygotic reproductive barriers, additional postzygotic barriers may prevent the formation of stable hybrids.Based on this data, which statement is true?
The figure shows two species, a fire-bellied toad and yellow-bellied toad, which occupy different areas of Europe.A small area of overlap between these regions constitutes a hybrid zone.If individuals from the two populations overcome prezygotic reproductive barriers, additional postzygotic barriers may prevent the formation of stable hybrids.Based on this data, which statement is true?
A) B. variegata individuals are moving into the range of B. bombina populations.
B) The ranges of the two species overlap in a long, wide hybrid zone.
C) The hybrid zone spreads from the middle of the range of overlap.
D) B. bombina does not like mountainous terrain.
E) The hybrid zone will likely persist for several generations of toads.
 The figure shows two species, a fire-bellied toad and yellow-bellied toad, which occupy different areas of Europe.A small area of overlap between these regions constitutes a hybrid zone.If individuals from the two populations overcome prezygotic reproductive barriers, additional postzygotic barriers may prevent the formation of stable hybrids.Based on this data, which statement is true?
The figure shows two species, a fire-bellied toad and yellow-bellied toad, which occupy different areas of Europe.A small area of overlap between these regions constitutes a hybrid zone.If individuals from the two populations overcome prezygotic reproductive barriers, additional postzygotic barriers may prevent the formation of stable hybrids.Based on this data, which statement is true?A) B. variegata individuals are moving into the range of B. bombina populations.
B) The ranges of the two species overlap in a long, wide hybrid zone.
C) The hybrid zone spreads from the middle of the range of overlap.
D) B. bombina does not like mountainous terrain.
E) The hybrid zone will likely persist for several generations of toads.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Crosses between the flour beetles Tribolium castaneum and T.freemani result in large numbers of hybrids that survive, but are sterile.This is an example of
A) low hybrid zygote viability.
B) behavioral isolation.
C) low hybrid adult viability.
D) postzygotic reproductive isolation.
E) prezygotic hybrid viability.
A) low hybrid zygote viability.
B) behavioral isolation.
C) low hybrid adult viability.
D) postzygotic reproductive isolation.
E) prezygotic hybrid viability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



