Deck 7: Cell Communication and Multicellularity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/246
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Cell Communication and Multicellularity
1
A cascade of events initiated by a signal that causes several different intracellular responses is an example of signal
A) phosphorylation.
B) activation.
C) binding.
D) transcription.
E) transduction.
A) phosphorylation.
B) activation.
C) binding.
D) transcription.
E) transduction.
E
2
A juxtacrine signal affects
A) the cell that secreted the signal.
B) cells distant from the cell that secreted the signal.
C) cells adjacent to the cell that secreted the signal.
D) cells in the local area of the cell that secreted the signal.
E) cells in another organism.
A) the cell that secreted the signal.
B) cells distant from the cell that secreted the signal.
C) cells adjacent to the cell that secreted the signal.
D) cells in the local area of the cell that secreted the signal.
E) cells in another organism.
C
3
Refer to the figures below. 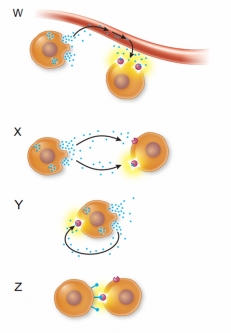 Each of the four figures represents a different type of cell signal.Which of the following correctly matches each figure with its cell signal type?
Each of the four figures represents a different type of cell signal.Which of the following correctly matches each figure with its cell signal type?
A) W = juxtacrine, X = paracrine, Y = hormone, Z = autocrine
B) W = hormone, X = paracrine, Y = autocrine, Z = juxtacrine
C) W = autocrine, X = hormone, Y = juxtacrine, Z = paracrine
D) W = paracrine, X = autocrine, Y = juxtacrine, Z = hormone
E) W = hormone, X = juxtacrine, Y = autocrine, Z = paracrine
 Each of the four figures represents a different type of cell signal.Which of the following correctly matches each figure with its cell signal type?
Each of the four figures represents a different type of cell signal.Which of the following correctly matches each figure with its cell signal type?A) W = juxtacrine, X = paracrine, Y = hormone, Z = autocrine
B) W = hormone, X = paracrine, Y = autocrine, Z = juxtacrine
C) W = autocrine, X = hormone, Y = juxtacrine, Z = paracrine
D) W = paracrine, X = autocrine, Y = juxtacrine, Z = hormone
E) W = hormone, X = juxtacrine, Y = autocrine, Z = paracrine
B
4
If a cell that normally produces juxtacrine signals is unable to produce signals during development, which cells will be most affected?
A) Cells that are nearby but not in contact with the signaling cell's membrane
B) The signaling cell itself
C) Cells that serve as distant targets for the signals
D) Cells that normally receive signals through the circulatory system
E) Cells immediately adjacent to the signaling cell
A) Cells that are nearby but not in contact with the signaling cell's membrane
B) The signaling cell itself
C) Cells that serve as distant targets for the signals
D) Cells that normally receive signals through the circulatory system
E) Cells immediately adjacent to the signaling cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Paracrine signals bind to
A) receptors on the cell that produced them.
B) receptors on cells far away from the cell that produced them.
C) receptors on adjacent cells.
D) internal receptors located inside cells.
E) receptors on neighboring cells.
A) receptors on the cell that produced them.
B) receptors on cells far away from the cell that produced them.
C) receptors on adjacent cells.
D) internal receptors located inside cells.
E) receptors on neighboring cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Autocrine signals bind to
A) receptors on adjacent cells.
B) receptors on neighboring cells.
C) receptors on the cell that produced them.
D) internal receptors located inside cells.
E) receptors on cells far away from the cell that produced them.
A) receptors on adjacent cells.
B) receptors on neighboring cells.
C) receptors on the cell that produced them.
D) internal receptors located inside cells.
E) receptors on cells far away from the cell that produced them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which is an example that explains how a juxtacrine signal functions in the human body?
A) At the junction of two nerve cells, one of the cells secretes a neurotransmitter molecule that diffuses over to the neighboring cell, where it binds and stimulates an electrochemical response.
B) To signal hunger, cells in the stomach secrete a peptide that circulates through the blood and binds to receptors on cells in the hypothalamus in the brain.
C) When the skin is injured, chemical signals are sent from nearby blood cells to aid in healing.
D) T lymphocytes secrete a chemical signal that stimulates those same T lymphocytes to undergo cell division.
E) A cell in a developing embryo has a cell surface protein that directly contacts a receptor on a neighboring cell, causing it to change its gene expression pattern.
A) At the junction of two nerve cells, one of the cells secretes a neurotransmitter molecule that diffuses over to the neighboring cell, where it binds and stimulates an electrochemical response.
B) To signal hunger, cells in the stomach secrete a peptide that circulates through the blood and binds to receptors on cells in the hypothalamus in the brain.
C) When the skin is injured, chemical signals are sent from nearby blood cells to aid in healing.
D) T lymphocytes secrete a chemical signal that stimulates those same T lymphocytes to undergo cell division.
E) A cell in a developing embryo has a cell surface protein that directly contacts a receptor on a neighboring cell, causing it to change its gene expression pattern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Signals that travel to distant cells through the circulatory system are
A) paracrine signals.
B) parasitic signals.
C) autocrine signals.
D) juxtacrine signals.
E) hormones.
A) paracrine signals.
B) parasitic signals.
C) autocrine signals.
D) juxtacrine signals.
E) hormones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Aldosterone is a steroid compound synthesized in the adrenal glands that binds to receptors in kidney cells.How would aldosterone be classified?
A) Paracrine signal
B) Parasitic signal
C) Autocrine signal
D) Juxtacrine signal
E) Hormone
A) Paracrine signal
B) Parasitic signal
C) Autocrine signal
D) Juxtacrine signal
E) Hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which statement about signal transduction in cells can be used to explain how specificity is achieved in a signal transduction pathway?
A) Receptors that bind chemical signals are either membrane receptors located on the cell surface or internal receptors present in the interior of a cell.
B) The sensitivity of a cell to a chemical signal is determined in part by the affinity of the cell's receptors for the signal molecule.
C) The binding of a small molecule to a site on a receptor is reversible, and equilibrium is reached when the rate of binding equals the rate of dissociation.
D) Agonists are chemicals that bind to a receptor and stimulate a signal transduction pathway just as the natural ligand does.
E) A receptor protein changes its conformation only when its binding site is occupied by a small molecule with a shape complementary to the site.
A) Receptors that bind chemical signals are either membrane receptors located on the cell surface or internal receptors present in the interior of a cell.
B) The sensitivity of a cell to a chemical signal is determined in part by the affinity of the cell's receptors for the signal molecule.
C) The binding of a small molecule to a site on a receptor is reversible, and equilibrium is reached when the rate of binding equals the rate of dissociation.
D) Agonists are chemicals that bind to a receptor and stimulate a signal transduction pathway just as the natural ligand does.
E) A receptor protein changes its conformation only when its binding site is occupied by a small molecule with a shape complementary to the site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A deer smells a predator as it passes by and quickly bounds to safety.Which sequence represents the correct order of steps in the signal transduction pathway that is involved?
A) Receptor binds signal, conformational change occurs in signal, signal travels to target cell, signal is transduced within cell, effects from signal transduction occur
B) Signal travels to target cell, receptor binds signal, conformational change occurs in receptor, signal is transduced within cell, effects from signal transduction occur
C) Signal travels to target cell, conformational change occurs in signal, signal is transduced within cell, effects from signal transduction occur
D) Signal is transduced within cell, signal causes conformational change in receptor, cell responds to signal, effects from signal transduction occur
E) Cell responds to signal, signal travels to target cell, signal is transduced within cell, effects from signal transduction occur
A) Receptor binds signal, conformational change occurs in signal, signal travels to target cell, signal is transduced within cell, effects from signal transduction occur
B) Signal travels to target cell, receptor binds signal, conformational change occurs in receptor, signal is transduced within cell, effects from signal transduction occur
C) Signal travels to target cell, conformational change occurs in signal, signal is transduced within cell, effects from signal transduction occur
D) Signal is transduced within cell, signal causes conformational change in receptor, cell responds to signal, effects from signal transduction occur
E) Cell responds to signal, signal travels to target cell, signal is transduced within cell, effects from signal transduction occur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Chemical signals called paracrine signals are transported from the secreting cell to a target cell by
A) nearby cells.
B) the nervous system.
C) the circulatory system.
D) gap junctions.
E) the surrounding extracellular fluid.
A) nearby cells.
B) the nervous system.
C) the circulatory system.
D) gap junctions.
E) the surrounding extracellular fluid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Some of the stem cells in bone become osteoclasts during differentiation.Researchers have shown that chemical signals called cytokines are released into the extracellular fluid by bone stem cells in response to environmental stimuli.The researchers also have shown that the cytokines induce these same bone stem cells to differentiate into osteoclasts.This example illustrates how a(n) _______ signal functions in the human body.
A) autocrine
B) hormone
C) paracrine
D) juxtacrine
E) intracellular
A) autocrine
B) hormone
C) paracrine
D) juxtacrine
E) intracellular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which experimental technique would be useful in determining whether a particular chemical signal is a juxtacrine or a paracrine signal?
A) Chemical analysis of the signal molecule
B) Observations of the behavior of single cells
C) Gene expression analysis
D) Analysis of extracellular fluid surrounding cells
E) Analysis of blood from nearby capillaries
A) Chemical analysis of the signal molecule
B) Observations of the behavior of single cells
C) Gene expression analysis
D) Analysis of extracellular fluid surrounding cells
E) Analysis of blood from nearby capillaries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which statement about ligand‒receptor complexes is false?
A) For most ligand-receptor complexes, binding, as opposed to dissociation, is favored based on chemistry's law of mass action.
B) Ligand-receptor interactions are reversible.
C) Drugs that prevent binding of receptors' specific ligands can alter human behavior.
D) After binding to a cell membrane receptor, a ligand participates in the cellular response.
E) A ligand is a chemical signal.
A) For most ligand-receptor complexes, binding, as opposed to dissociation, is favored based on chemistry's law of mass action.
B) Ligand-receptor interactions are reversible.
C) Drugs that prevent binding of receptors' specific ligands can alter human behavior.
D) After binding to a cell membrane receptor, a ligand participates in the cellular response.
E) A ligand is a chemical signal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
After a signal arrives at a target cell, the next step in a signal transduction pathway involves
A) receptor binding.
B) hormone activation.
C) signal transcription.
D) signal regulation.
E) enzyme activation.
A) receptor binding.
B) hormone activation.
C) signal transcription.
D) signal regulation.
E) enzyme activation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
"Crosstalk" refers to the
A) ability of signaling molecules to communicate with one another.
B) activation of a signal transduction pathway.
C) communication between enzymes and transcription factors.
D) interaction of signal transduction pathways.
E) inactivation of multiple signal transduction pathways.
A) ability of signaling molecules to communicate with one another.
B) activation of a signal transduction pathway.
C) communication between enzymes and transcription factors.
D) interaction of signal transduction pathways.
E) inactivation of multiple signal transduction pathways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In designing a drug to function as an antagonist of a natural ligand in the human body, a pharmaceutical chemist would focus on mimicking which aspect of the natural ligand?
A) Mass
B) Number of atoms
C) Orientation of functional groups
D) Number of chemical bonds
E) Density
A) Mass
B) Number of atoms
C) Orientation of functional groups
D) Number of chemical bonds
E) Density

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Refer to the figure below. 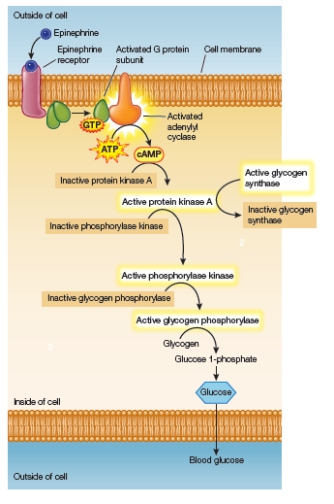 The figure shows a signal transduction pathway in a cell.How does adenylyl cyclase become activated so that it can relay the signal during a signal transduction event in this particular pathway?
The figure shows a signal transduction pathway in a cell.How does adenylyl cyclase become activated so that it can relay the signal during a signal transduction event in this particular pathway?
A) It becomes phosphorylated.
B) It becomes dephosphorylated.
C) It binds ATP.
D) It changes conformation.
E) It is hydrolyzed.
 The figure shows a signal transduction pathway in a cell.How does adenylyl cyclase become activated so that it can relay the signal during a signal transduction event in this particular pathway?
The figure shows a signal transduction pathway in a cell.How does adenylyl cyclase become activated so that it can relay the signal during a signal transduction event in this particular pathway?A) It becomes phosphorylated.
B) It becomes dephosphorylated.
C) It binds ATP.
D) It changes conformation.
E) It is hydrolyzed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Refer to the figure below. 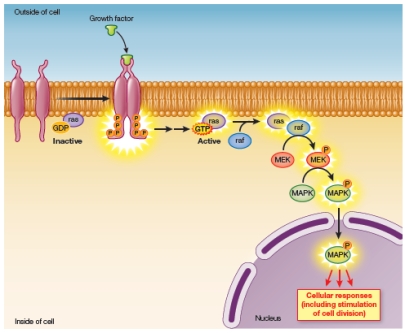 The figure shows a signal transduction pathway in a cell.Which of the following plays a role in signal transduction in this case?
The figure shows a signal transduction pathway in a cell.Which of the following plays a role in signal transduction in this case?
A) An internal receptor
B) A protein kinase cascade
C) A lipid-derived second messenger
D) A cyclic nucleotide second messenger
E) A calcium channel
 The figure shows a signal transduction pathway in a cell.Which of the following plays a role in signal transduction in this case?
The figure shows a signal transduction pathway in a cell.Which of the following plays a role in signal transduction in this case?A) An internal receptor
B) A protein kinase cascade
C) A lipid-derived second messenger
D) A cyclic nucleotide second messenger
E) A calcium channel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Refer to the figure below. 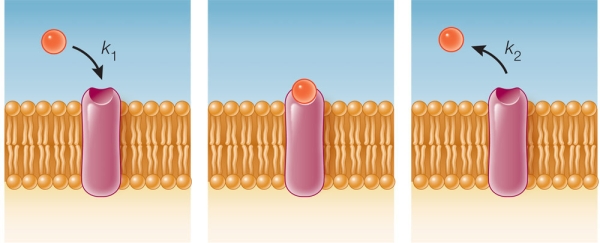 Which equation describes the rate of binding of a ligand to its receptor? In all equations shown, "R" represents a receptor with no ligand bound, "L" represents a free ligand in solution, and "RL" represents a receptor bound to a ligand.
Which equation describes the rate of binding of a ligand to its receptor? In all equations shown, "R" represents a receptor with no ligand bound, "L" represents a free ligand in solution, and "RL" represents a receptor bound to a ligand.
A)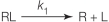
B)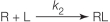
C)
D)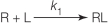
E)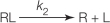
 Which equation describes the rate of binding of a ligand to its receptor? In all equations shown, "R" represents a receptor with no ligand bound, "L" represents a free ligand in solution, and "RL" represents a receptor bound to a ligand.
Which equation describes the rate of binding of a ligand to its receptor? In all equations shown, "R" represents a receptor with no ligand bound, "L" represents a free ligand in solution, and "RL" represents a receptor bound to a ligand.A)
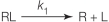
B)
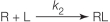
C)

D)
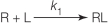
E)
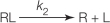

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In a signal transduction pathway involving G protein-coupled receptors, the receptor first binds the ligand and activates a G protein.After the GTP-bound subunit of the G protein separates from the rest of the G protein, it travels until it encounters
A) an activator.
B) a receptor.
C) an effector protein.
D) a protein kinase.
E) another G protein.
A) an activator.
B) a receptor.
C) an effector protein.
D) a protein kinase.
E) another G protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
To respond to a signal, a cell must have a(n) _______ molecule that can detect the signal.
A) paracrine
B) receptor
C) autocrine
D) response
E) recognition
A) paracrine
B) receptor
C) autocrine
D) response
E) recognition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A molecule functioning as an antagonist binds to a(n)
A) natural ligand.
B) artificial ligand, such as a drug.
C) adenosine molecule.
D) polar signal.
E) receptor protein.
A) natural ligand.
B) artificial ligand, such as a drug.
C) adenosine molecule.
D) polar signal.
E) receptor protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following has its receptors on a gated ion channel for sodium ions (Na+)?
A) Estrogen
B) Acetylcholine
C) Insulin
D) Caffeine
E) Protein kinase
A) Estrogen
B) Acetylcholine
C) Insulin
D) Caffeine
E) Protein kinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the table below. 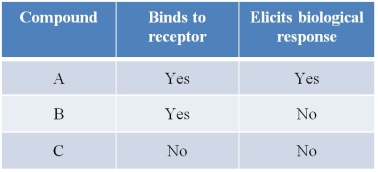 Compound X is the natural ligand that binds to a receptor and stimulates a signal transduction pathway associated with the receptor.Based on the information given in the table, what are the roles of compounds A, B, and C?
Compound X is the natural ligand that binds to a receptor and stimulates a signal transduction pathway associated with the receptor.Based on the information given in the table, what are the roles of compounds A, B, and C?
A) A is an antagonist, B is an agonist, and C is a ligand.
B) A is an agonist, B is an antagonist, and C has no role.
C) A is a ligand, B has no role, and C is an antagonist.
D) A is an agonist, B is an antagonist, and C is an agonist.
E) A has no role, B is an agonist, and C is an antagonist.
 Compound X is the natural ligand that binds to a receptor and stimulates a signal transduction pathway associated with the receptor.Based on the information given in the table, what are the roles of compounds A, B, and C?
Compound X is the natural ligand that binds to a receptor and stimulates a signal transduction pathway associated with the receptor.Based on the information given in the table, what are the roles of compounds A, B, and C?A) A is an antagonist, B is an agonist, and C is a ligand.
B) A is an agonist, B is an antagonist, and C has no role.
C) A is a ligand, B has no role, and C is an antagonist.
D) A is an agonist, B is an antagonist, and C is an agonist.
E) A has no role, B is an agonist, and C is an antagonist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Caffeine is an example of a(n) _______ because it binds to a receptor that recognizes adenosine but does not elicit the same cellular response as adenosine.
A) ligand
B) agonist
C) antagonist
D) signal molecule
E) hormone
A) ligand
B) agonist
C) antagonist
D) signal molecule
E) hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Refer to the table below. 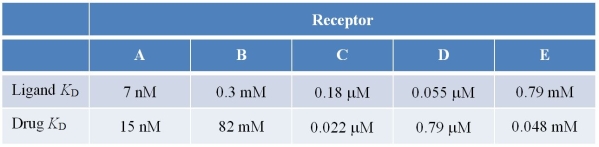 A pharmaceutical company is developing five new drugs to act as antagonists with respect to five different receptor proteins.Listed in the table are dissociation constants for ligand and drug in each case.In which case will the dosage of drug necessary to achieve a biological effect be the smallest?
A pharmaceutical company is developing five new drugs to act as antagonists with respect to five different receptor proteins.Listed in the table are dissociation constants for ligand and drug in each case.In which case will the dosage of drug necessary to achieve a biological effect be the smallest?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
 A pharmaceutical company is developing five new drugs to act as antagonists with respect to five different receptor proteins.Listed in the table are dissociation constants for ligand and drug in each case.In which case will the dosage of drug necessary to achieve a biological effect be the smallest?
A pharmaceutical company is developing five new drugs to act as antagonists with respect to five different receptor proteins.Listed in the table are dissociation constants for ligand and drug in each case.In which case will the dosage of drug necessary to achieve a biological effect be the smallest?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the figure below. 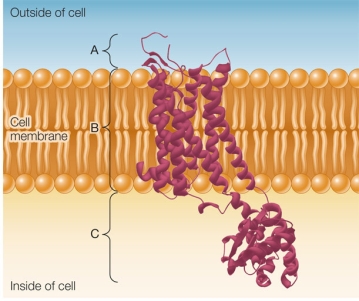 The figure shows a protein receptor that functions in a signal transduction pathway.This receptor binds a ligand and then later binds an antagonist molecule.How do sections of the receptor shown in the figure change in response to the binding of each molecule?
The figure shows a protein receptor that functions in a signal transduction pathway.This receptor binds a ligand and then later binds an antagonist molecule.How do sections of the receptor shown in the figure change in response to the binding of each molecule?
A) Section B, but not section C, undergoes a conformational change in response to the ligand and to the antagonist molecule.
B) Section C, but not section B, undergoes conformational change in response to the ligand and to the antagonist molecule.
C) Both sections C and B undergo conformational change in response to the ligand and to the antagonist molecule.
D) Both sections C and B undergo conformational change in response to the ligand but not to the antagonist molecule.
E) Both sections C and B undergo conformational change in response to the antagonist molecule but not to the ligand.
 The figure shows a protein receptor that functions in a signal transduction pathway.This receptor binds a ligand and then later binds an antagonist molecule.How do sections of the receptor shown in the figure change in response to the binding of each molecule?
The figure shows a protein receptor that functions in a signal transduction pathway.This receptor binds a ligand and then later binds an antagonist molecule.How do sections of the receptor shown in the figure change in response to the binding of each molecule?A) Section B, but not section C, undergoes a conformational change in response to the ligand and to the antagonist molecule.
B) Section C, but not section B, undergoes conformational change in response to the ligand and to the antagonist molecule.
C) Both sections C and B undergo conformational change in response to the ligand and to the antagonist molecule.
D) Both sections C and B undergo conformational change in response to the ligand but not to the antagonist molecule.
E) Both sections C and B undergo conformational change in response to the antagonist molecule but not to the ligand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When a G protein is activated in a signal transduction pathway,
A) GDP is released from the G protein, and GTP occupies the nucleotide-binding site.
B) GTP is released from the G protein, and GDP occupies the nucleotide-binding site.
C) cGMP occupies the otherwise empty nucleotide-binding site on the G protein.
D) cGMP leaves the otherwise occupied nucleotide-binding site on the G protein.
E) GDP causes a conformational change in the G protein.
A) GDP is released from the G protein, and GTP occupies the nucleotide-binding site.
B) GTP is released from the G protein, and GDP occupies the nucleotide-binding site.
C) cGMP occupies the otherwise empty nucleotide-binding site on the G protein.
D) cGMP leaves the otherwise occupied nucleotide-binding site on the G protein.
E) GDP causes a conformational change in the G protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which statement about the insulin receptor is false?
A) It autophosphorylates.
B) It is a transmembrane receptor with an extracellular binding domain.
C) It catalyzes the phosphorylation of insulin-response substrates inside a cell.
D) When activated, it allows insulin to enter the cell.
E) It is a protein kinase receptor.
A) It autophosphorylates.
B) It is a transmembrane receptor with an extracellular binding domain.
C) It catalyzes the phosphorylation of insulin-response substrates inside a cell.
D) When activated, it allows insulin to enter the cell.
E) It is a protein kinase receptor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The reversibility of ligand‒receptor binding
A) ensures that the ligands are not metabolized.
B) maintains the specificity of the receptor.
C) prevents the receptor from being continuously stimulated.
D) initiates a cellular response.
E) controls the number of ligand‒receptor interactions.
A) ensures that the ligands are not metabolized.
B) maintains the specificity of the receptor.
C) prevents the receptor from being continuously stimulated.
D) initiates a cellular response.
E) controls the number of ligand‒receptor interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which molecule binds directly to a protein kinase receptor?
A) Insulin
B) Estrogen
C) Acetylcholine
D) Sodium
E) G protein
A) Insulin
B) Estrogen
C) Acetylcholine
D) Sodium
E) G protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Refer to the table below.  The table shows data collected from studies comparing normal and mutant cells.Mutant cells differ from normal cells in having a mutation in the gene encoding a receptor protein.The mutation results in a single amino acid change from a glutamic acid to a lysine.Which is a possible effect of the mutation?
The table shows data collected from studies comparing normal and mutant cells.Mutant cells differ from normal cells in having a mutation in the gene encoding a receptor protein.The mutation results in a single amino acid change from a glutamic acid to a lysine.Which is a possible effect of the mutation?
A) The receptor protein cannot activate intracellular signal transduction.
B) The receptor protein loses its ability to embed in the cell membrane.
C) The receptor protein is not synthesized in mutant cells.
D) The receptor protein binds the signal molecule with lower affinity.
E) The receptor protein no longer recognizes the signal molecule.
 The table shows data collected from studies comparing normal and mutant cells.Mutant cells differ from normal cells in having a mutation in the gene encoding a receptor protein.The mutation results in a single amino acid change from a glutamic acid to a lysine.Which is a possible effect of the mutation?
The table shows data collected from studies comparing normal and mutant cells.Mutant cells differ from normal cells in having a mutation in the gene encoding a receptor protein.The mutation results in a single amino acid change from a glutamic acid to a lysine.Which is a possible effect of the mutation?A) The receptor protein cannot activate intracellular signal transduction.
B) The receptor protein loses its ability to embed in the cell membrane.
C) The receptor protein is not synthesized in mutant cells.
D) The receptor protein binds the signal molecule with lower affinity.
E) The receptor protein no longer recognizes the signal molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Refer to the table below. 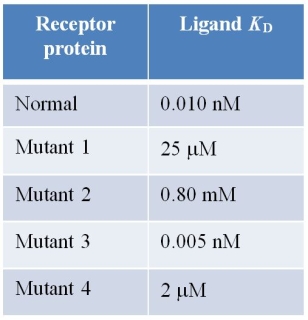 Listed in the first row of the table is the dissociation constant for a ligand and its receptor.Listed below this are the dissociation constants for the same ligand and four different mutants of the same receptor.Which sequence displays the range of affinities of the receptor for the ligand in order, from lowest to highest affinity?
Listed in the first row of the table is the dissociation constant for a ligand and its receptor.Listed below this are the dissociation constants for the same ligand and four different mutants of the same receptor.Which sequence displays the range of affinities of the receptor for the ligand in order, from lowest to highest affinity?
A) Mutant 1, mutant 4, mutant 2, normal, mutant 3
B) Mutant 3, mutant 1, normal, mutant 2, mutant 4
C) Mutant 1, mutant 3, mutant 1, normal, mutant 4
D) Mutant 4, mutant 2, mutant 1, normal, mutant 3
E) Mutant 3, normal, mutant 2, mutant 4, mutant 1
 Listed in the first row of the table is the dissociation constant for a ligand and its receptor.Listed below this are the dissociation constants for the same ligand and four different mutants of the same receptor.Which sequence displays the range of affinities of the receptor for the ligand in order, from lowest to highest affinity?
Listed in the first row of the table is the dissociation constant for a ligand and its receptor.Listed below this are the dissociation constants for the same ligand and four different mutants of the same receptor.Which sequence displays the range of affinities of the receptor for the ligand in order, from lowest to highest affinity?A) Mutant 1, mutant 4, mutant 2, normal, mutant 3
B) Mutant 3, mutant 1, normal, mutant 2, mutant 4
C) Mutant 1, mutant 3, mutant 1, normal, mutant 4
D) Mutant 4, mutant 2, mutant 1, normal, mutant 3
E) Mutant 3, normal, mutant 2, mutant 4, mutant 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose scientists discover a new extracellular protein that causes increases in cell size.In order to investigate whether cell surface receptors are involved in binding this protein, they could
A) increase the concentration of the protein outside the cell.
B) remove the protein from the extracellular medium.
C) measure enzymatic activity within the cell.
D) apply inhibitors known to block specific membrane receptors.
E) measure the growth of the cell over time.
A) increase the concentration of the protein outside the cell.
B) remove the protein from the extracellular medium.
C) measure enzymatic activity within the cell.
D) apply inhibitors known to block specific membrane receptors.
E) measure the growth of the cell over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The major difference between a cell that responds to a signal and one that does not is the presence of a
A) DNA sequence that binds to the signal.
B) nearby blood vessel.
C) receptor.
D) second messenger.
E) transduction pathway.
A) DNA sequence that binds to the signal.
B) nearby blood vessel.
C) receptor.
D) second messenger.
E) transduction pathway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The larger the dissociation constant KD is, the smaller will be
A) the rate at which a ligand dissociates from its receptors.
B) the affinity of the receptor for its ligand.
C) the effect of a ligand on a signal transduction pathway.
D) the number of ligand molecules needed to stimulate a signal transduction pathway.
E) the number of cell surface receptors that bind a ligand.
A) the rate at which a ligand dissociates from its receptors.
B) the affinity of the receptor for its ligand.
C) the effect of a ligand on a signal transduction pathway.
D) the number of ligand molecules needed to stimulate a signal transduction pathway.
E) the number of cell surface receptors that bind a ligand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which statement about cell signaling is false?
A) Cells are bombarded with numerous signals, but they do not respond to all of them.
B) A cell must possess the specific receptor to respond to a particular signal.
C) Chemical signaling molecules have specific binding sites.
D) Receptor specificity in cells allows a response to a specific signal.
E) There are only a few kinds of receptor proteins.
A) Cells are bombarded with numerous signals, but they do not respond to all of them.
B) A cell must possess the specific receptor to respond to a particular signal.
C) Chemical signaling molecules have specific binding sites.
D) Receptor specificity in cells allows a response to a specific signal.
E) There are only a few kinds of receptor proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Refer to the figure below. 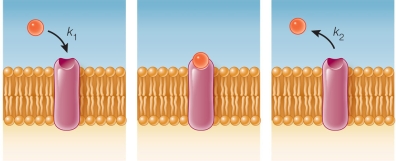 Which equation represents the equilibrium condition? In all equations shown, "R" represents a receptor with no ligand bound, "L" represents a free ligand in solution, and "RL" represents a receptor bound to a ligand.
Which equation represents the equilibrium condition? In all equations shown, "R" represents a receptor with no ligand bound, "L" represents a free ligand in solution, and "RL" represents a receptor bound to a ligand.
A)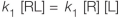
B)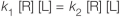
C)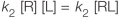
D)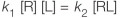
E)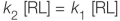
 Which equation represents the equilibrium condition? In all equations shown, "R" represents a receptor with no ligand bound, "L" represents a free ligand in solution, and "RL" represents a receptor bound to a ligand.
Which equation represents the equilibrium condition? In all equations shown, "R" represents a receptor with no ligand bound, "L" represents a free ligand in solution, and "RL" represents a receptor bound to a ligand.A)
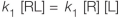
B)
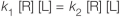
C)
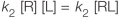
D)
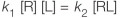
E)
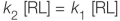

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Three second messengers involved in penile erections are
A) nitric oxide, inositol trisphosphate, and calcium ions.
B) adenylcyclase, phospholipase C, and calcium ions.
C) cyclic AMP, nitric oxide, and cyclic GMP.
D) adenylyl cyclase, calcium ions, and nitric oxide.
E) cyclic GMP, acetylcholine, and inositol trisphosphate.
A) nitric oxide, inositol trisphosphate, and calcium ions.
B) adenylcyclase, phospholipase C, and calcium ions.
C) cyclic AMP, nitric oxide, and cyclic GMP.
D) adenylyl cyclase, calcium ions, and nitric oxide.
E) cyclic GMP, acetylcholine, and inositol trisphosphate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A benefit of the many steps involved in a protein kinase cascade is that they involve
A) a large energy expenditure in communicating a signal.
B) amplification of the signal being communicated.
C) many genes that need to be expressed.
D) many enzymes whose biological activity must not be compromised.
E) transfer of a signal across large distances within a cell.
A) a large energy expenditure in communicating a signal.
B) amplification of the signal being communicated.
C) many genes that need to be expressed.
D) many enzymes whose biological activity must not be compromised.
E) transfer of a signal across large distances within a cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Refer to the figure below. 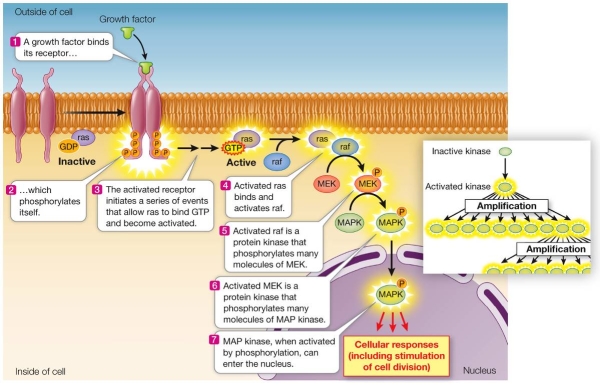 Consider that each time a growth factor binds to its receptor as shown in the figure, two ras G proteins are activated and each ras G protein activates one raf protein.If each raf then activates ten MEK molecules and each activated MEK activates ten molecules of MAP kinase, the original signal will be amplified by a factor of
Consider that each time a growth factor binds to its receptor as shown in the figure, two ras G proteins are activated and each ras G protein activates one raf protein.If each raf then activates ten MEK molecules and each activated MEK activates ten molecules of MAP kinase, the original signal will be amplified by a factor of
A) 20.
B) 22.
C) 100.
D) 200.
E) 1,000.
 Consider that each time a growth factor binds to its receptor as shown in the figure, two ras G proteins are activated and each ras G protein activates one raf protein.If each raf then activates ten MEK molecules and each activated MEK activates ten molecules of MAP kinase, the original signal will be amplified by a factor of
Consider that each time a growth factor binds to its receptor as shown in the figure, two ras G proteins are activated and each ras G protein activates one raf protein.If each raf then activates ten MEK molecules and each activated MEK activates ten molecules of MAP kinase, the original signal will be amplified by a factor ofA) 20.
B) 22.
C) 100.
D) 200.
E) 1,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which graph portrays the change in number of molecules activated at each successive step in a signal transduction pathway?
A)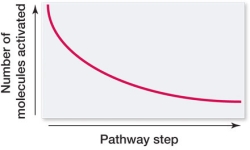
B)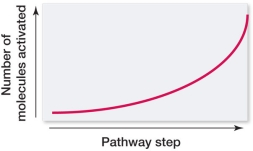
C)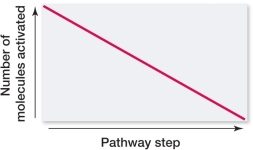
D)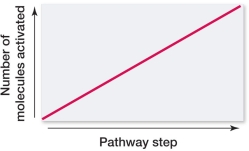
E)
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Vitamin D is a relatively small, lipid-soluble molecule that can behave as a hormone.Its receptor, therefore, most likely
A) is an ion channel receptor.
B) is a protein kinase receptor.
C) involves a G protein.
D) is located inside the cell.
E) does not exist, since the molecule can diffuse across the cell membrane.
A) is an ion channel receptor.
B) is a protein kinase receptor.
C) involves a G protein.
D) is located inside the cell.
E) does not exist, since the molecule can diffuse across the cell membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol-bisphosphate (PIP2) results in
A) inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol.
B) inositol trisphosphate and cyclic AMP.
C) one second-messenger molecule.
D) G protein activation.
E) shutdown of a signal transduction pathway.
A) inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol.
B) inositol trisphosphate and cyclic AMP.
C) one second-messenger molecule.
D) G protein activation.
E) shutdown of a signal transduction pathway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How does a protein kinase cascade amplify an intracellular signal?
A) It opens gap junctions, allowing the signal to spread to other cells.
B) The activated G protein in the cascade binds and activates a second protein, amplifying the signal.
C) Nitric oxide in the cascade opens gap junctions, allowing protein kinase molecules to move quickly from cell to cell.
D) Second messengers in the cascade create shortcuts that create multiple cascades.
E) Activation of the protein kinase receptors can trigger the activation of many other proteins.
A) It opens gap junctions, allowing the signal to spread to other cells.
B) The activated G protein in the cascade binds and activates a second protein, amplifying the signal.
C) Nitric oxide in the cascade opens gap junctions, allowing protein kinase molecules to move quickly from cell to cell.
D) Second messengers in the cascade create shortcuts that create multiple cascades.
E) Activation of the protein kinase receptors can trigger the activation of many other proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Inositol trisphosphate (IP3) is released into the cytoplasm when phosphatidyl inositol-bisphosphate (PIP2) is hydrolyzed.IP3 is one type of molecule that can directly
A) open Ca2+ channels and increase cytosolic calcium.
B) close Ca2+ channels and deplete intracellular calcium.
C) stimulate G protein activation of phospholipase.
D) activate cyclic AMP.
E) stimulate gene expression.
A) open Ca2+ channels and increase cytosolic calcium.
B) close Ca2+ channels and deplete intracellular calcium.
C) stimulate G protein activation of phospholipase.
D) activate cyclic AMP.
E) stimulate gene expression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The receptor for estrogen is
A) an ion channel receptor.
B) a protein kinase receptor.
C) embedded in the plasma membrane.
D) located inside the cell.
E) nonpolar.
A) an ion channel receptor.
B) a protein kinase receptor.
C) embedded in the plasma membrane.
D) located inside the cell.
E) nonpolar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which statement about the IP3-DAG pathway is false?
A) Diacylglycerol can act as a second messenger.
B) Inositol trisphosphate can act as a second messenger.
C) Protein kinase C can phosphorylate a wide variety of proteins.
D) Inositol trisphosphate remains bound to the membrane after phospholipase C catalyzes its formation.
E) Inositol trisphosphate can open ion channels in the membranes of smooth endoplasmic reticulum, releasing calcium into the cytoplasm.
A) Diacylglycerol can act as a second messenger.
B) Inositol trisphosphate can act as a second messenger.
C) Protein kinase C can phosphorylate a wide variety of proteins.
D) Inositol trisphosphate remains bound to the membrane after phospholipase C catalyzes its formation.
E) Inositol trisphosphate can open ion channels in the membranes of smooth endoplasmic reticulum, releasing calcium into the cytoplasm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The concentration of cAMP in a cell is usually increased by activity of
A) phosphodiesterase.
B) cGMP.
C) a protein kinase.
D) a second messenger.
E) adenylyl cyclase.
A) phosphodiesterase.
B) cGMP.
C) a protein kinase.
D) a second messenger.
E) adenylyl cyclase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which molecule acts as a second messenger in the cascade by which epinephrine stimulates the activation of the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase in liver cells?
A) Adenosine
B) Caffeine
C) Citric acid
D) Cyclic AMP
E) Adenylyl cyclase
A) Adenosine
B) Caffeine
C) Citric acid
D) Cyclic AMP
E) Adenylyl cyclase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Receptors can be divided into two general classes according to their cellular location: _______ receptors and _______ receptors.
A) intracellular; membrane
B) membrane; protein kinase
C) ion channel; intracellular
D) G protein-coupled; intracellular
E) membrane; ion channel
A) intracellular; membrane
B) membrane; protein kinase
C) ion channel; intracellular
D) G protein-coupled; intracellular
E) membrane; ion channel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Refer to the table below, summarizing key features of two signal transduction pathways that result in the same cellular response. 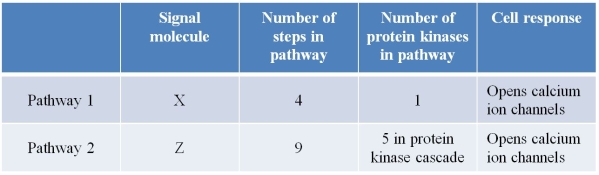 Based on this information, which comparison is most reasonable?
Based on this information, which comparison is most reasonable?
A) Pathway 1 requires more time to complete than pathway 2.
B) Pathway 1 requires more energy input than pathway 2.
C) Pathway 2 is less vulnerable than pathway 1 to becoming dysfunctional as the result of mutation events.
D) A single molecule of Z is able to open more calcium ion channels than a single molecule of X.
E) A single protein kinase in pathway 2 is able to activate more of its substrate than the single protein kinase in pathway 1.
 Based on this information, which comparison is most reasonable?
Based on this information, which comparison is most reasonable?A) Pathway 1 requires more time to complete than pathway 2.
B) Pathway 1 requires more energy input than pathway 2.
C) Pathway 2 is less vulnerable than pathway 1 to becoming dysfunctional as the result of mutation events.
D) A single molecule of Z is able to open more calcium ion channels than a single molecule of X.
E) A single protein kinase in pathway 2 is able to activate more of its substrate than the single protein kinase in pathway 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If a ligand binds to a G protein-coupled receptor but the normal exchange of GDP for GTP on the associated G protein does not take place, what will happen in the cell?
A) Cell responses that depend on an activated effector protein will not occur.
B) GDP binding will cause a conformational change in the G protein-coupled receptor.
C) The GDP-bound subunit will travel through the lipid bilayer.
D) The ligand will not be released from the G protein-coupled receptor.
E) Inactive G protein will be activated.
A) Cell responses that depend on an activated effector protein will not occur.
B) GDP binding will cause a conformational change in the G protein-coupled receptor.
C) The GDP-bound subunit will travel through the lipid bilayer.
D) The ligand will not be released from the G protein-coupled receptor.
E) Inactive G protein will be activated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Refer to the figure below. 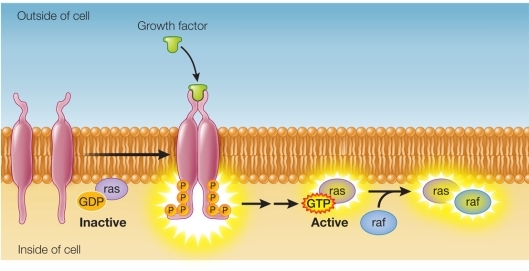 A portion of a signal transduction pathway is shown in the figure.The molecule raf is a protein kinase.This molecule becomes activated when a GTP-ras complex binds to it.Which equation describes how activated raf transmits the signal in this pathway?
A portion of a signal transduction pathway is shown in the figure.The molecule raf is a protein kinase.This molecule becomes activated when a GTP-ras complex binds to it.Which equation describes how activated raf transmits the signal in this pathway?
A)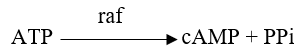
B)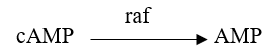
C)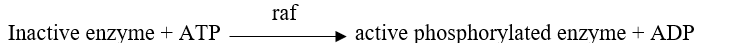
D)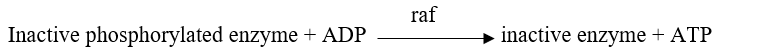
E)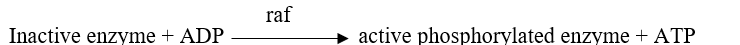
 A portion of a signal transduction pathway is shown in the figure.The molecule raf is a protein kinase.This molecule becomes activated when a GTP-ras complex binds to it.Which equation describes how activated raf transmits the signal in this pathway?
A portion of a signal transduction pathway is shown in the figure.The molecule raf is a protein kinase.This molecule becomes activated when a GTP-ras complex binds to it.Which equation describes how activated raf transmits the signal in this pathway?A)

B)
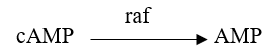
C)
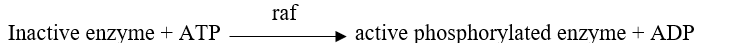
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Sometimes a transcription factor within the cytoplasm can act as an intracellular receptor for a ligand.When activated, such transcription factors can alter gene expression by
A) preventing chaperone proteins from entering the nucleus.
B) changing shape after binding their ligands and entering the nucleus.
C) attaching ligands to their extracellular binding sites.
D) activating effector proteins.
E) binding to the nuclear membrane.
A) preventing chaperone proteins from entering the nucleus.
B) changing shape after binding their ligands and entering the nucleus.
C) attaching ligands to their extracellular binding sites.
D) activating effector proteins.
E) binding to the nuclear membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A researcher working with mammalian kidney cells grown in culture observed that cells treated with a proteolytic enzyme (an enzyme that breaks down proteins) lost the ability to respond to the hormone vasopressin but not to the hormone aldosterone.Which is a reasonable explanation for this observation?
A) The vasopressin receptor is a protein, whereas the aldosterone receptor is composed of either lipids or carbohydrates.
B) The cells lost the ability to synthesize the vasopressin receptor but retained the ability to synthesize the aldosterone receptor.
C) The vasopressin receptor is embedded in the cell membrane with an external portion that binds its ligand, whereas the aldosterone receptor is an intracellular receptor.
D) A debilitating mutation was introduced into the gene encoding the vasopressin receptor, but no such mutation affected the aldosterone receptor gene.
E) Vasopressin requires a receptor to stimulate a signal transduction pathway, whereas aldosterone can stimulate a signal transduction pathway without binding to a receptor.
A) The vasopressin receptor is a protein, whereas the aldosterone receptor is composed of either lipids or carbohydrates.
B) The cells lost the ability to synthesize the vasopressin receptor but retained the ability to synthesize the aldosterone receptor.
C) The vasopressin receptor is embedded in the cell membrane with an external portion that binds its ligand, whereas the aldosterone receptor is an intracellular receptor.
D) A debilitating mutation was introduced into the gene encoding the vasopressin receptor, but no such mutation affected the aldosterone receptor gene.
E) Vasopressin requires a receptor to stimulate a signal transduction pathway, whereas aldosterone can stimulate a signal transduction pathway without binding to a receptor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which statement about cyclic AMP is false?
A) It has targets in multiple transduction pathways.
B) The enzyme adenylyl cyclase catalyzes its formation.
C) It is produced from ATP.
D) It is a second messenger.
E) It possesses enzymatic activity.
A) It has targets in multiple transduction pathways.
B) The enzyme adenylyl cyclase catalyzes its formation.
C) It is produced from ATP.
D) It is a second messenger.
E) It possesses enzymatic activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which statement about calcium ions is true?
A) Calcium ions are more concentrated in the cytoplasm than outside the cell.
B) Active transport maintains the concentration differences between intracellular and extracellular levels of calcium ions.
C) A cell can increase intracellular concentrations of calcium ions by making more calcium.
D) Inositol trisphosphate (IP3) is the only signal that causes calcium ion channels to open.
E) Calcium ions are involved in signal transduction but do not function as second messengers.
A) Calcium ions are more concentrated in the cytoplasm than outside the cell.
B) Active transport maintains the concentration differences between intracellular and extracellular levels of calcium ions.
C) A cell can increase intracellular concentrations of calcium ions by making more calcium.
D) Inositol trisphosphate (IP3) is the only signal that causes calcium ion channels to open.
E) Calcium ions are involved in signal transduction but do not function as second messengers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Connexons are channel structures that make up
A) plasmodesmata.
B) desmosomes.
C) gap junctions.
D) cell surface receptors.
E) desmotubules.
A) plasmodesmata.
B) desmosomes.
C) gap junctions.
D) cell surface receptors.
E) desmotubules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Refer to the two figures below. 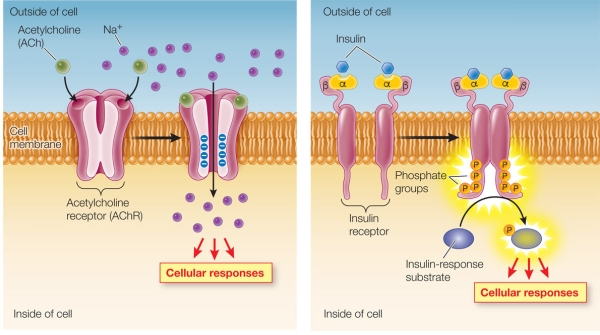 The receptor portions of two signal transduction pathways are shown.The two mechanisms underlying these pathways are similar in that they both involve
The receptor portions of two signal transduction pathways are shown.The two mechanisms underlying these pathways are similar in that they both involve
A) gated ion channels.
B) activating a kinase as part of the signaling process.
C) a protein binding to the same signal molecule.
D) a protein conformational change in response to a signal molecule.
E) an ion serving as a second messenger.
 The receptor portions of two signal transduction pathways are shown.The two mechanisms underlying these pathways are similar in that they both involve
The receptor portions of two signal transduction pathways are shown.The two mechanisms underlying these pathways are similar in that they both involveA) gated ion channels.
B) activating a kinase as part of the signaling process.
C) a protein binding to the same signal molecule.
D) a protein conformational change in response to a signal molecule.
E) an ion serving as a second messenger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Refer to the figure below. 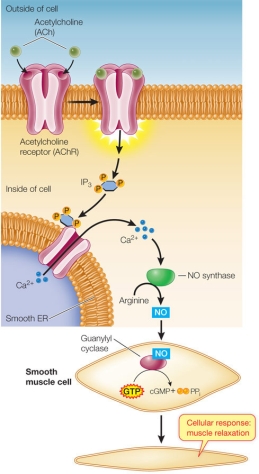 Which action could the cell use to turn off the signal transduction pathway shown, as part of a regulatory mechanism?
Which action could the cell use to turn off the signal transduction pathway shown, as part of a regulatory mechanism?
A) Increase the concentration of an NO synthase activator.
B) Turn off expression of the guanylyl cyclase gene.
C) Decrease the concentration of a calcium ion channel protein inhibitor.
D) Activate expression of the phospholipase C gene.
E) Increase arginine synthesis.
 Which action could the cell use to turn off the signal transduction pathway shown, as part of a regulatory mechanism?
Which action could the cell use to turn off the signal transduction pathway shown, as part of a regulatory mechanism?A) Increase the concentration of an NO synthase activator.
B) Turn off expression of the guanylyl cyclase gene.
C) Decrease the concentration of a calcium ion channel protein inhibitor.
D) Activate expression of the phospholipase C gene.
E) Increase arginine synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A researcher finds that mouse kidney cells and mouse muscle cells both use cAMP as a second messenger in two different signal transduction pathways that result in different cellular responses.Which other condition related to these two pathways would be expected in these cells?
A) Both cells have the same cell surface receptor for the two pathways.
B) One cell has a cell surface receptor and the other has an intracellular receptor for these pathways.
C) Both pathways in the two cells have the same target protein whose activity changes when it binds cAMP.
D) Both cell types express the adenylate cyclase gene.
E) One pathway involves cAMP inhibition of a target protein, while the other pathway involves cAMP activation of a target protein.
A) Both cells have the same cell surface receptor for the two pathways.
B) One cell has a cell surface receptor and the other has an intracellular receptor for these pathways.
C) Both pathways in the two cells have the same target protein whose activity changes when it binds cAMP.
D) Both cell types express the adenylate cyclase gene.
E) One pathway involves cAMP inhibition of a target protein, while the other pathway involves cAMP activation of a target protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Calcium ions can serve as second messengers in signal transduction pathways.Mechanisms in the cell can regulate calcium signals that have been activated during a signal transduction pathway.Which is a calcium regulation mechanism by which the cell returns to the state it was in before the pathway was initiated?
A) A protein binds calcium.
B) An enzyme is activated that degrades calcium ions.
C) Ion pumps move calcium ions into intracellular compartments.
D) Expression of the genes encoding calcium ion channel proteins is halted.
E) The concentration of activating molecules that open calcium ion channels is increased.
A) A protein binds calcium.
B) An enzyme is activated that degrades calcium ions.
C) Ion pumps move calcium ions into intracellular compartments.
D) Expression of the genes encoding calcium ion channel proteins is halted.
E) The concentration of activating molecules that open calcium ion channels is increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Refer to the table below. 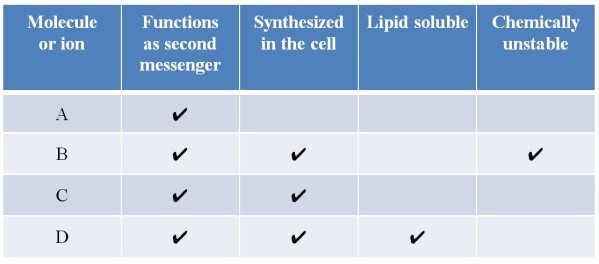 Which molecules and ions are matched appropriately to the letters in the table?
Which molecules and ions are matched appropriately to the letters in the table?
A) A = calcium ions; B = NO; C = cAMP; D = inositol trisphosphate
B) A = NO; B = inositol trisphosphate; C = cAMP; D = calcium ions
C) A = inositol trisphosphate; B = cAMP; C = calcium ions; D = NO
D) A = NO; B = cAMP; C = calcium ions; D = inositol trisphosphate
E) A = inositol trisphosphate; B = calcium ions; C = NO; D = cAMP
 Which molecules and ions are matched appropriately to the letters in the table?
Which molecules and ions are matched appropriately to the letters in the table?A) A = calcium ions; B = NO; C = cAMP; D = inositol trisphosphate
B) A = NO; B = inositol trisphosphate; C = cAMP; D = calcium ions
C) A = inositol trisphosphate; B = cAMP; C = calcium ions; D = NO
D) A = NO; B = cAMP; C = calcium ions; D = inositol trisphosphate
E) A = inositol trisphosphate; B = calcium ions; C = NO; D = cAMP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Refer to the table below, which lists three biological responses that result from cAMP-mediated signal transduction pathways.The "yes" and "no" references in the table indicate which cells are capable of displaying the three biological responses. 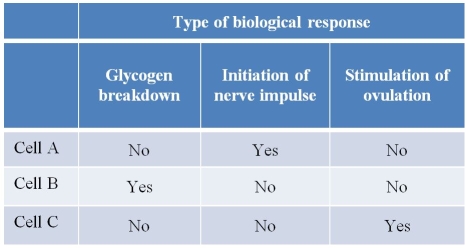 Which statement explains how the same second-messenger molecule, cAMP, can be involved in all of these different pathways?
Which statement explains how the same second-messenger molecule, cAMP, can be involved in all of these different pathways?
A) The cells carrying out these signal transduction pathways are located in different regions of the body.
B) The cells carrying out these signal transduction pathways do so at different points in time and never simultaneously.
C) The cells contain different proteins that carry out different functions but respond to the same small molecule.
D) Each cell has lost the ability to carry out signal transduction pathways other than the few that are most important to its survival.
E) Each cell is programmed in its DNA to respond only to signals that are most important to its survival.
 Which statement explains how the same second-messenger molecule, cAMP, can be involved in all of these different pathways?
Which statement explains how the same second-messenger molecule, cAMP, can be involved in all of these different pathways?A) The cells carrying out these signal transduction pathways are located in different regions of the body.
B) The cells carrying out these signal transduction pathways do so at different points in time and never simultaneously.
C) The cells contain different proteins that carry out different functions but respond to the same small molecule.
D) Each cell has lost the ability to carry out signal transduction pathways other than the few that are most important to its survival.
E) Each cell is programmed in its DNA to respond only to signals that are most important to its survival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Refer to the graph below. 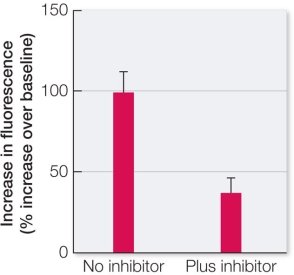 The graph shows results from an investigation using living cartilage cells extracted from slaughtered cows.The cells were treated so that they took up a fluorescent dye in their cytosols without losing viability.(This dye undergoes a change in fluorescence intensity upon binding calcium ions.) The treated cells were then exposed to forces that mimic the forces on cartilage during weight-bearing exercise.This experiment was then repeated with cells that were pretreated with a calcium ion channel inhibitor before exposure to forces of weight-bearing exercise.This inhibitor is specific for intracellular calcium ion channels.Which statement is consistent with the results shown in the graph?
The graph shows results from an investigation using living cartilage cells extracted from slaughtered cows.The cells were treated so that they took up a fluorescent dye in their cytosols without losing viability.(This dye undergoes a change in fluorescence intensity upon binding calcium ions.) The treated cells were then exposed to forces that mimic the forces on cartilage during weight-bearing exercise.This experiment was then repeated with cells that were pretreated with a calcium ion channel inhibitor before exposure to forces of weight-bearing exercise.This inhibitor is specific for intracellular calcium ion channels.Which statement is consistent with the results shown in the graph?
A) Calcium ions move out of the cytosol into other cell compartments in response to a mechanical stimulus.
B) Calcium ions are inhibited from moving out of the cytosol into other cell compartments as the result of a mechanical stimulus.
C) A mechanical stimulus induces cellular changes in cartilage that include the opening of intracellular calcium ion channels.
D) Extracellular calcium ion channels open as part of the response of cartilage cells to a mechanical stimulus.
E) Cartilage cells use an inhibitor molecule to prevent intracellular calcium ion release during weight-bearing exercise.
 The graph shows results from an investigation using living cartilage cells extracted from slaughtered cows.The cells were treated so that they took up a fluorescent dye in their cytosols without losing viability.(This dye undergoes a change in fluorescence intensity upon binding calcium ions.) The treated cells were then exposed to forces that mimic the forces on cartilage during weight-bearing exercise.This experiment was then repeated with cells that were pretreated with a calcium ion channel inhibitor before exposure to forces of weight-bearing exercise.This inhibitor is specific for intracellular calcium ion channels.Which statement is consistent with the results shown in the graph?
The graph shows results from an investigation using living cartilage cells extracted from slaughtered cows.The cells were treated so that they took up a fluorescent dye in their cytosols without losing viability.(This dye undergoes a change in fluorescence intensity upon binding calcium ions.) The treated cells were then exposed to forces that mimic the forces on cartilage during weight-bearing exercise.This experiment was then repeated with cells that were pretreated with a calcium ion channel inhibitor before exposure to forces of weight-bearing exercise.This inhibitor is specific for intracellular calcium ion channels.Which statement is consistent with the results shown in the graph?A) Calcium ions move out of the cytosol into other cell compartments in response to a mechanical stimulus.
B) Calcium ions are inhibited from moving out of the cytosol into other cell compartments as the result of a mechanical stimulus.
C) A mechanical stimulus induces cellular changes in cartilage that include the opening of intracellular calcium ion channels.
D) Extracellular calcium ion channels open as part of the response of cartilage cells to a mechanical stimulus.
E) Cartilage cells use an inhibitor molecule to prevent intracellular calcium ion release during weight-bearing exercise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A transcription factor located in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell
A) is able to regulate gene expression.
B) acts as an enzyme.
C) is inactive until it is transported to the nucleus.
D) catalyzes biochemical responses.
E) promotes signal binding.
A) is able to regulate gene expression.
B) acts as an enzyme.
C) is inactive until it is transported to the nucleus.
D) catalyzes biochemical responses.
E) promotes signal binding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which statement about gap junctions is true?
A) They generally occupy less than 5 percent of the area of the plasma membrane.
B) They permit metabolic cooperation among linked cells.
C) They occur only in plants.
D) They are made up of G proteins.
E) Their structure allows communication within a cell.
A) They generally occupy less than 5 percent of the area of the plasma membrane.
B) They permit metabolic cooperation among linked cells.
C) They occur only in plants.
D) They are made up of G proteins.
E) Their structure allows communication within a cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The figure below shows the oxytocin signal transduction pathway in uterine smooth muscle cells.The abbreviation "CaM" refers to calmodulin, and "MLCK" refers to myosin light chain kinase, an enzyme that phosphorylates the light chains of myosin, stimulating smooth muscle contractions. 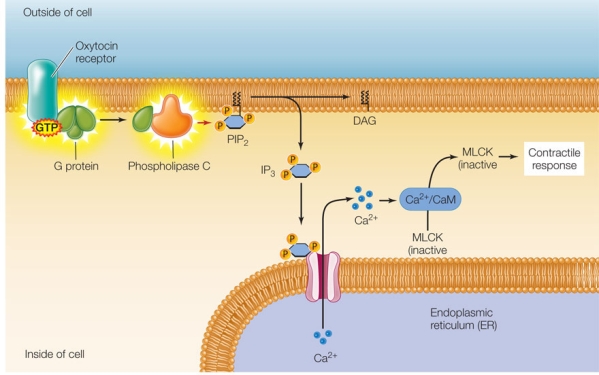 Which two components of this pathway share a similar mechanism in transmitting a biological signal by causing a conformation change in a target protein?
Which two components of this pathway share a similar mechanism in transmitting a biological signal by causing a conformation change in a target protein?
A) Phospholipase C and calcium ions
B) IP3 and MLCK
C) Oxytocin receptor and phospholipase C
D) Calcium ions and IP3
E) G protein and IP3
 Which two components of this pathway share a similar mechanism in transmitting a biological signal by causing a conformation change in a target protein?
Which two components of this pathway share a similar mechanism in transmitting a biological signal by causing a conformation change in a target protein?A) Phospholipase C and calcium ions
B) IP3 and MLCK
C) Oxytocin receptor and phospholipase C
D) Calcium ions and IP3
E) G protein and IP3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Refer to the figure and table below. 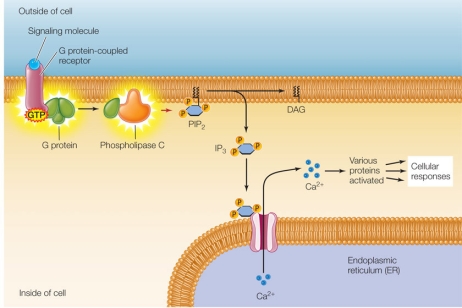
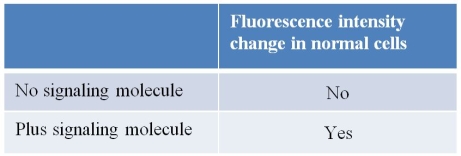 A researcher treated mouse kidney cells growing in culture so that they took up a fluorescent dye into their cytosols without losing viability.(This dye undergoes a change in fluorescence intensity upon binding calcium ions.) The treated cells were then incubated with and without a compound thought to act as a signaling molecule, and the cells were observed for changes in fluorescence.The researcher hypothesizes that the signaling molecule functions according to the pathway shown in the diagram above.As a next step, the researcher wants to acquire evidence that IP3 is involved in this pathway.Which procedure will provide needed evidence about IP3 as the entire experiment is repeated?
A researcher treated mouse kidney cells growing in culture so that they took up a fluorescent dye into their cytosols without losing viability.(This dye undergoes a change in fluorescence intensity upon binding calcium ions.) The treated cells were then incubated with and without a compound thought to act as a signaling molecule, and the cells were observed for changes in fluorescence.The researcher hypothesizes that the signaling molecule functions according to the pathway shown in the diagram above.As a next step, the researcher wants to acquire evidence that IP3 is involved in this pathway.Which procedure will provide needed evidence about IP3 as the entire experiment is repeated?
A) Using mouse kidney cells containing a mutation that knocks out GTP binding by G protein
B) Using mouse kidney cells containing a mutation that knocks out phospholipase C
C) Adding a calcium channel inhibitor during all trials
D) Replacing the signaling molecule with an agonist molecule
E) Replacing the signaling molecule with IP3

 A researcher treated mouse kidney cells growing in culture so that they took up a fluorescent dye into their cytosols without losing viability.(This dye undergoes a change in fluorescence intensity upon binding calcium ions.) The treated cells were then incubated with and without a compound thought to act as a signaling molecule, and the cells were observed for changes in fluorescence.The researcher hypothesizes that the signaling molecule functions according to the pathway shown in the diagram above.As a next step, the researcher wants to acquire evidence that IP3 is involved in this pathway.Which procedure will provide needed evidence about IP3 as the entire experiment is repeated?
A researcher treated mouse kidney cells growing in culture so that they took up a fluorescent dye into their cytosols without losing viability.(This dye undergoes a change in fluorescence intensity upon binding calcium ions.) The treated cells were then incubated with and without a compound thought to act as a signaling molecule, and the cells were observed for changes in fluorescence.The researcher hypothesizes that the signaling molecule functions according to the pathway shown in the diagram above.As a next step, the researcher wants to acquire evidence that IP3 is involved in this pathway.Which procedure will provide needed evidence about IP3 as the entire experiment is repeated?A) Using mouse kidney cells containing a mutation that knocks out GTP binding by G protein
B) Using mouse kidney cells containing a mutation that knocks out phospholipase C
C) Adding a calcium channel inhibitor during all trials
D) Replacing the signaling molecule with an agonist molecule
E) Replacing the signaling molecule with IP3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which statement about the abnormal form of the ras protein found in some cancer cells is true?
A) Because it is inactive, it is unable to inhibit growth factors.
B) It is always active because it is continuously bound to GTP.
C) If it were inhibited, cells would continue to divide.
D) It acts as an ion channel receptor.
E) It directly stimulates epinephrine production.
A) Because it is inactive, it is unable to inhibit growth factors.
B) It is always active because it is continuously bound to GTP.
C) If it were inhibited, cells would continue to divide.
D) It acts as an ion channel receptor.
E) It directly stimulates epinephrine production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which represents the correct ordering from lowest number to highest number of molecules in a liver cell activated by a single molecule of epinephrine?
A) cAMP, protein kinase A, phosphorylase kinase, glycogen phosphorylase
B) Glycogen phosphorylase, phosphorylase kinase, protein kinase A, cAMP
C) cAMP, phosphorylase kinase, glycogen phosphorylase, protein kinase A
D) Glycogen phosphorylase, cAMP, protein kinase A, phosphorylase kinase
E) Phosphorylase kinase, glycogen phosphorylase, cAMP, protein kinase A
A) cAMP, protein kinase A, phosphorylase kinase, glycogen phosphorylase
B) Glycogen phosphorylase, phosphorylase kinase, protein kinase A, cAMP
C) cAMP, phosphorylase kinase, glycogen phosphorylase, protein kinase A
D) Glycogen phosphorylase, cAMP, protein kinase A, phosphorylase kinase
E) Phosphorylase kinase, glycogen phosphorylase, cAMP, protein kinase A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which statement about nitric oxide is true?
A) Because it is chemically stable, it is able to travel relatively long distances.
B) It does not diffuse readily.
C) It is made in the body from arginine.
D) The enzyme that catalyzes the formation of nitric oxide is inhibited by calcium ions.
E) It is produced by inactivation of NO synthase.
A) Because it is chemically stable, it is able to travel relatively long distances.
B) It does not diffuse readily.
C) It is made in the body from arginine.
D) The enzyme that catalyzes the formation of nitric oxide is inhibited by calcium ions.
E) It is produced by inactivation of NO synthase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Refer to the graphs below.  Human cells taken from the large intestine were cultured in dishes and divided into control and experimental groups.Control cells were incubated for 1 hour in a buffered solution, while experimental cells were incubated for 1 hour in a buffered solution that also contained 10 M dibutyryl cyclic AMP (db-cAMP).Dibutyryl cyclic AMP has biological activity similar to that of cyclic AMP (cAMP) but readily diffuses through the cell membrane.Following the incubations, researchers isolated a protein known to act as a transcription factor from the cells.They measured both the protein quantity (graph A) and the amount of phosphorylation of the protein (graph B).Which statement is consistent with these results?
Human cells taken from the large intestine were cultured in dishes and divided into control and experimental groups.Control cells were incubated for 1 hour in a buffered solution, while experimental cells were incubated for 1 hour in a buffered solution that also contained 10 M dibutyryl cyclic AMP (db-cAMP).Dibutyryl cyclic AMP has biological activity similar to that of cyclic AMP (cAMP) but readily diffuses through the cell membrane.Following the incubations, researchers isolated a protein known to act as a transcription factor from the cells.They measured both the protein quantity (graph A) and the amount of phosphorylation of the protein (graph B).Which statement is consistent with these results?
A) cAMP does not function as a second messenger in the signal transduction pathway that stimulates this transcription factor.
B) cAMP's role in this signal transduction pathway is to stimulate expression of the transcription factor's gene.
C) cAMP's role in this signal transduction pathway is to stimulate phosphorylation of the transcription factor.
D) Phosphorylation of the transcription factor occurs upstream of cAMP synthesis in this signal transduction pathway.
E) The transcription factor is activated by cAMP through an increase in its gene expression and through a chemical step in which the factor becomes phosphorylated.
 Human cells taken from the large intestine were cultured in dishes and divided into control and experimental groups.Control cells were incubated for 1 hour in a buffered solution, while experimental cells were incubated for 1 hour in a buffered solution that also contained 10 M dibutyryl cyclic AMP (db-cAMP).Dibutyryl cyclic AMP has biological activity similar to that of cyclic AMP (cAMP) but readily diffuses through the cell membrane.Following the incubations, researchers isolated a protein known to act as a transcription factor from the cells.They measured both the protein quantity (graph A) and the amount of phosphorylation of the protein (graph B).Which statement is consistent with these results?
Human cells taken from the large intestine were cultured in dishes and divided into control and experimental groups.Control cells were incubated for 1 hour in a buffered solution, while experimental cells were incubated for 1 hour in a buffered solution that also contained 10 M dibutyryl cyclic AMP (db-cAMP).Dibutyryl cyclic AMP has biological activity similar to that of cyclic AMP (cAMP) but readily diffuses through the cell membrane.Following the incubations, researchers isolated a protein known to act as a transcription factor from the cells.They measured both the protein quantity (graph A) and the amount of phosphorylation of the protein (graph B).Which statement is consistent with these results?A) cAMP does not function as a second messenger in the signal transduction pathway that stimulates this transcription factor.
B) cAMP's role in this signal transduction pathway is to stimulate expression of the transcription factor's gene.
C) cAMP's role in this signal transduction pathway is to stimulate phosphorylation of the transcription factor.
D) Phosphorylation of the transcription factor occurs upstream of cAMP synthesis in this signal transduction pathway.
E) The transcription factor is activated by cAMP through an increase in its gene expression and through a chemical step in which the factor becomes phosphorylated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The G protein-mediated cascade stimulated by epinephrine within a liver cell results in the phosphorylation of two key enzymes.The eventual results of this phosphorylation are the _______ of glycogen synthase and the _______ of glycogen phosphorylase, leading to the release of glucose.
A) inhibition; activation
B) activation; inhibition
C) inhibition; degradation
D) activation; activation
E) inhibition; inhibition
A) inhibition; activation
B) activation; inhibition
C) inhibition; degradation
D) activation; activation
E) inhibition; inhibition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The figure below shows the oxytocin signal transduction pathway in uterine smooth muscle cells.The abbreviation "CaM" refers to calmodulin, and "MLCK" refers to myosin light chain kinase, an enzyme that phosphorylates the light chains of myosin, stimulating smooth muscle contractions. 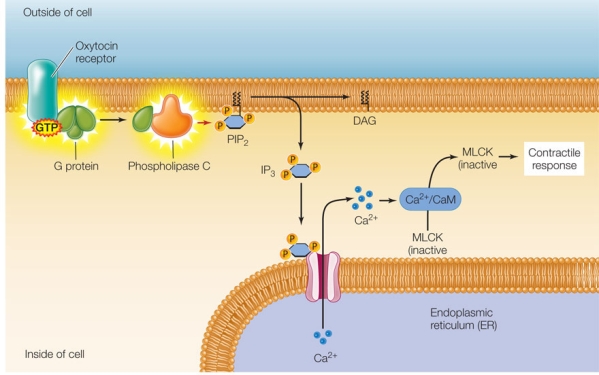 How could this signal transduction pathway be shut off?
How could this signal transduction pathway be shut off?
A) Activate a kinase that phosphorylates phospholipase C, which inactivates it.
B) Activate an enzyme that degrades DAG.
C) Add a compound that acts as an agonist of IP3 with respect to calcium ion channel binding.
D) Add a compound that acts as an agonist of calcium ion with respect to MLCK activation.
E) Add a compound that acts as an agonist of oxytocin with respect to oxytocin cell membrane receptor binding.
 How could this signal transduction pathway be shut off?
How could this signal transduction pathway be shut off?A) Activate a kinase that phosphorylates phospholipase C, which inactivates it.
B) Activate an enzyme that degrades DAG.
C) Add a compound that acts as an agonist of IP3 with respect to calcium ion channel binding.
D) Add a compound that acts as an agonist of calcium ion with respect to MLCK activation.
E) Add a compound that acts as an agonist of oxytocin with respect to oxytocin cell membrane receptor binding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Increased synthesis of phosphodiesterase would most likely lead to
A) an increased concentration of cyclic AMP.
B) an increased concentration of cyclic GMP.
C) an increased concentration of nitric oxide.
D) the inactivation of adenylyl cyclase.
E) decreased concentration of cyclic AMP or cyclic GMP.
A) an increased concentration of cyclic AMP.
B) an increased concentration of cyclic GMP.
C) an increased concentration of nitric oxide.
D) the inactivation of adenylyl cyclase.
E) decreased concentration of cyclic AMP or cyclic GMP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which are specialized cell junctions that allow neighboring cells to communicate directly with one another?
A) Gated channels
B) Gap junctions
C) Cytoplasmic junctions
D) Ion channels
E) G proteins
A) Gated channels
B) Gap junctions
C) Cytoplasmic junctions
D) Ion channels
E) G proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



