Deck 13: Dna and Its Role in Heredity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/257
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Dna and Its Role in Heredity
1
Griffith's experiment with pneumococcus demonstrated that
A) DNA, not protein, is the genetic molecule.
B) a substance from one organism can alter heritable characteristics of another organism.
C) smooth bacteria can survive heating.
D) rough bacteria can survive heating.
E) bacteria must have rough capsules to be virulent.
A) DNA, not protein, is the genetic molecule.
B) a substance from one organism can alter heritable characteristics of another organism.
C) smooth bacteria can survive heating.
D) rough bacteria can survive heating.
E) bacteria must have rough capsules to be virulent.
B
2
The Hershey and Chase experiment proved that
A) DNA, not protein, is the hereditary material of bacteriophage T2.
B) protein, not DNA, is the hereditary material of bacteriophage T2.
C) protein and DNA are the hereditary materials of bacteriophage T2.
D) the hereditary material in bacteriophage T2 is neither protein nor DNA.
E) bacteriophage T2 does not contain hereditary material.
A) DNA, not protein, is the hereditary material of bacteriophage T2.
B) protein, not DNA, is the hereditary material of bacteriophage T2.
C) protein and DNA are the hereditary materials of bacteriophage T2.
D) the hereditary material in bacteriophage T2 is neither protein nor DNA.
E) bacteriophage T2 does not contain hereditary material.
A
3
The evidence suggesting that DNA is arranged in a double helix came from
A) Franklin's X-ray crystallography.
B) Chargaff's observations of relative abundances of base purines and pyrimidines in DNA.
C) Avery's studies of DNA as the transforming agent.
D) the Hershey and Chase blender experiment.
E) studies examining the density of DNA.
A) Franklin's X-ray crystallography.
B) Chargaff's observations of relative abundances of base purines and pyrimidines in DNA.
C) Avery's studies of DNA as the transforming agent.
D) the Hershey and Chase blender experiment.
E) studies examining the density of DNA.
A
4
If Hershey and Chase had found 32P in both the pellet and the supernatant of the phage-infected bacteria, what would have been their likely conclusion about the nature of genetic material?
A) A protein must be the information molecule.
B) DNA is the genetic information molecule.
C) Phage must have stuck to the bacteria.
D) Phosphorus was in the information molecule.
E) No conclusion would have been possible from these results.
A) A protein must be the information molecule.
B) DNA is the genetic information molecule.
C) Phage must have stuck to the bacteria.
D) Phosphorus was in the information molecule.
E) No conclusion would have been possible from these results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If 27 percent of the bases in a double-stranded DNA molecule are A, which of the following must be true?
A) Its bases must be 27 percent T.
B) Its bases must be 27 percent C.
C) Its bases must be 23 percent G.
D) Both a and b are true.
E) Both a and c are true.
A) Its bases must be 27 percent T.
B) Its bases must be 27 percent C.
C) Its bases must be 23 percent G.
D) Both a and b are true.
E) Both a and c are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In Griffith's experiments, when heat-killed S strain pneumococci were injected into a mouse along with live R strain pneumococci,
A) DNA from the live R cells was taken up by the heat-killed S cells, converting the latter to R cells and killing the mouse.
B) DNA from the heat-killed S cells was taken up by the live R cells, converting the latter to S cells and killing the mouse.
C) proteins released from the heat-killed S cells killed the mouse.
D) RNA from the heat-killed S cells was translated into proteins that killed the mouse.
E) there was no result.
A) DNA from the live R cells was taken up by the heat-killed S cells, converting the latter to R cells and killing the mouse.
B) DNA from the heat-killed S cells was taken up by the live R cells, converting the latter to S cells and killing the mouse.
C) proteins released from the heat-killed S cells killed the mouse.
D) RNA from the heat-killed S cells was translated into proteins that killed the mouse.
E) there was no result.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If 30 percent of the bases in a double-stranded DNA molecule are T, _______ percent must be G.
A) 20
B) 30
C) 40
D) 50
E) 60
A) 20
B) 30
C) 40
D) 50
E) 60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the 1920s, a dye (now called Feulgen stain) was developed that bound DNA in direct proportion to the amount of DNA present in cells.Upon binding, the DNA would turn a bright purple.This DNA staining technique
A) provided circumstantial evidence that DNA is the genetic material.
B) proved that DNA is the genetic material.
C) demonstrated that all species have the same amount of nuclear DNA.
D) confirmed that DNA is an important component of mitochondria and chloroplasts.
E) led to skepticism that DNA is the genetic material.
A) provided circumstantial evidence that DNA is the genetic material.
B) proved that DNA is the genetic material.
C) demonstrated that all species have the same amount of nuclear DNA.
D) confirmed that DNA is an important component of mitochondria and chloroplasts.
E) led to skepticism that DNA is the genetic material.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Experiments designed to identify the transforming substance were based on
A) purifying each of the macromolecule types from a cell-free extract.
B) removing each of the macromolecules from a cell, then testing its type.
C) selectively destroying the different macromolecules in a cell-free extract.
D) adding different macromolecules from a cell.
E) straining out the different macromolecules in a cell-free extract.
A) purifying each of the macromolecule types from a cell-free extract.
B) removing each of the macromolecules from a cell, then testing its type.
C) selectively destroying the different macromolecules in a cell-free extract.
D) adding different macromolecules from a cell.
E) straining out the different macromolecules in a cell-free extract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The Hershey and Chase blender experiment was designed to
A) prove that DNA is found in the nucleus.
B) test isotope labeling of DNA and proteins.
C) disprove that DNA is the genetic molecule.
D) identify the genetic material in bacteriophage T2.
E) develop a DNA isolation method.
A) prove that DNA is found in the nucleus.
B) test isotope labeling of DNA and proteins.
C) disprove that DNA is the genetic molecule.
D) identify the genetic material in bacteriophage T2.
E) develop a DNA isolation method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Chargaff's rule states that
A) DNA must be replicated before a cell can divide.
B) a virus can enter a cell only without its protein coat.
C) only protein from the infecting phage can also be detected in progeny phages.
D) only nucleic acids enter the cell during infection.
E) the amount of cytosine equals the amount of guanine.
A) DNA must be replicated before a cell can divide.
B) a virus can enter a cell only without its protein coat.
C) only protein from the infecting phage can also be detected in progeny phages.
D) only nucleic acids enter the cell during infection.
E) the amount of cytosine equals the amount of guanine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In one Hershey and Chase experiment, bacteriophage nucleic acids were labeled by carrying out an infection of E.coli cells growing in
A) 14C-labeled CO2.
B) 3H-labeled water.
C) 32P-labeled phosphate.
D) 35S-labeled sulfate.
E) 18O-labeled water.
A) 14C-labeled CO2.
B) 3H-labeled water.
C) 32P-labeled phosphate.
D) 35S-labeled sulfate.
E) 18O-labeled water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An alien DNA-like molecule is isolated from the frozen remains of a life form found beneath the Martian polar ice caps.In this sample, for every base designated Q, there is twice that amount of base R; for every base Z, there is twice that amount of base S.If the molecule contains 33.33 percent S, you expect to find _______ percent Z.
A) 8.33
B) 16.67
C) 50
D) 66.66
E) 66.67
A) 8.33
B) 16.67
C) 50
D) 66.66
E) 66.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is true of nitrogenous bases?
A) Cytosine is the only purine.
B) Adenine is the only purine.
C) Adenine and thymine are purines.
D) Cytosine and thymine are purines.
E) Adenine and guanine are purines.
A) Cytosine is the only purine.
B) Adenine is the only purine.
C) Adenine and thymine are purines.
D) Cytosine and thymine are purines.
E) Adenine and guanine are purines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which type of molecule functions to transfer information from one generation to the next in eukaryotes?
A) DNA
B) mRNA
C) tRNA
D) Protein
E) Lipid
A) DNA
B) mRNA
C) tRNA
D) Protein
E) Lipid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
According to Chargaff's rule, a pyrimidine on one strand of DNA must be paired with a(n) _______ on the other strand.
A) purine
B) pyrimidine
C) adenine
D) guanine
E) cytosine
A) purine
B) pyrimidine
C) adenine
D) guanine
E) cytosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Prior to the Hershey and Chase blender experiment, many biologists were skeptical that DNA was the genetic material.These biologists thought that proteins might be the genetic material because proteins
A) are twice as abundant in somatic cells as they are in the gametes.
B) can be labeled with isotopes.
C) are more structurally diverse than DNA is.
D) can transform bacteria.
E) contain sulfur.
A) are twice as abundant in somatic cells as they are in the gametes.
B) can be labeled with isotopes.
C) are more structurally diverse than DNA is.
D) can transform bacteria.
E) contain sulfur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The DNA binding dye that was developed about 100 years ago (and is now called Feulgen stain) binds to DNA and stains nuclei a bright purple in direct proportion to the amount of DNA present in cells.As a consequence of this property, the dye revealed that gametes have _______ DNA as somatic cells have.
A) one-third as much
B) one-half as much
C) as much
D) twice as much
E) four times as much
A) one-third as much
B) one-half as much
C) as much
D) twice as much
E) four times as much

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A deoxyribose nucleotide is a
A) deoxyribose plus a nitrogenous base.
B) sugar and a phosphate.
C) deoxyribose plus a nitrogenous base and a phosphate.
D) ribose plus a nitrogenous base.
E) nitrogenous base bonded at the 5ʹ end to a sugar-phosphate backbone.
A) deoxyribose plus a nitrogenous base.
B) sugar and a phosphate.
C) deoxyribose plus a nitrogenous base and a phosphate.
D) ribose plus a nitrogenous base.
E) nitrogenous base bonded at the 5ʹ end to a sugar-phosphate backbone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An alien DNA-like molecule is isolated from the frozen remains of a life form found beneath the Martian polar ice caps.In this sample, for every base designated Q, there is twice that amount of base R; for every base Z, there is twice that amount of base S.Assuming that there is base bonding, a likely conclusion from these observed ratios is that one base _______ bonds with _______ base _______.
A) Q; one; R
B) Q; two; Rs
C) R; two; Qs
D) Z; one; S
E) S; two; Rs
A) Q; one; R
B) Q; two; Rs
C) R; two; Qs
D) Z; one; S
E) S; two; Rs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Before Watson and Crick built their DNA model, the American chemist and Nobel laureate Linus Pauling proposed a triple-helix model for DNA.What evidence convinced Watson and Crick to reject this model for the double-helix model?
A) Franklin's X-ray crystallography
B) Chargaff's observations of base pairing
C) Avery's studies of DNA as the transforming agent
D) The Hershey and Chase blender experiment
E) Studies examining the stability of DNA
A) Franklin's X-ray crystallography
B) Chargaff's observations of base pairing
C) Avery's studies of DNA as the transforming agent
D) The Hershey and Chase blender experiment
E) Studies examining the stability of DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which three major properties of genes can be attributed to the structure of DNA?
A) They contain information, direct the synthesis of proteins, and are contained in the cell nucleus.
B) They contain nitrogenous bases, direct the synthesis of RNA, and are contained in the cell nucleus.
C) They replicate exactly, are contained in the cell nucleus, and direct the synthesis of cellular proteins.
D) They encode the organism's phenotype, are passed on from one generation to the next, and contain nitrogenous bases.
E) They contain information, replicate exactly, and can change to produce a mutation.
A) They contain information, direct the synthesis of proteins, and are contained in the cell nucleus.
B) They contain nitrogenous bases, direct the synthesis of RNA, and are contained in the cell nucleus.
C) They replicate exactly, are contained in the cell nucleus, and direct the synthesis of cellular proteins.
D) They encode the organism's phenotype, are passed on from one generation to the next, and contain nitrogenous bases.
E) They contain information, replicate exactly, and can change to produce a mutation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
DNA is held together in a double helix by the force of
A) the twists.
B) covalent bonds.
C) ionic bonds.
D) ionic interactions.
E) hydrogen bonds.
A) the twists.
B) covalent bonds.
C) ionic bonds.
D) ionic interactions.
E) hydrogen bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The nitrogenous bases of the two complementary strands in the DNA double helix are held together by
A) van der Waals forces.
B) covalent bonds.
C) hydrogen bonds.
D) covalent and hydrogen bonds.
E) van der Waals forces and covalent bonds.
A) van der Waals forces.
B) covalent bonds.
C) hydrogen bonds.
D) covalent and hydrogen bonds.
E) van der Waals forces and covalent bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The characteristic of DNA that allows it to make an exact copy of itself is its
A) sugar-phosphate backbone.
B) complementary base pairing.
C) phosphodiester bonding of the helices.
D) twisting of the molecule to form an α helix.
E) antiparallel strands.
A) sugar-phosphate backbone.
B) complementary base pairing.
C) phosphodiester bonding of the helices.
D) twisting of the molecule to form an α helix.
E) antiparallel strands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the figure, which illustrates the chemical structure of DNA. 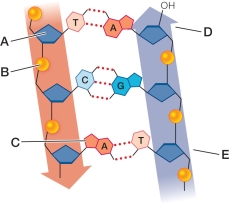 Which label corresponds to a deoxyribose sugar?
Which label corresponds to a deoxyribose sugar?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
 Which label corresponds to a deoxyribose sugar?
Which label corresponds to a deoxyribose sugar?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the figure, which illustrates the chemical structure of DNA. 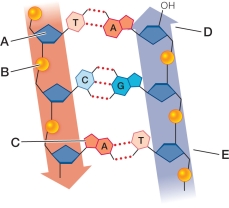 In which position would new DNA be added?
In which position would new DNA be added?
A) above A
B) above B
C) above D
D) below D
E) below E
 In which position would new DNA be added?
In which position would new DNA be added?A) above A
B) above B
C) above D
D) below D
E) below E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which physical feature of DNA is affected by the pairing of purines with pyrimidines?
A) Its length
B) Its width
C) Its parallel nature
D) Its helical structure
E) Its helix length
A) Its length
B) Its width
C) Its parallel nature
D) Its helical structure
E) Its helix length

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The strands that make up DNA are antiparallel, meaning that
A) one strand is positively charged, and the other is negatively charged.
B) the base pairings create unequal spacing between the two DNA strands.
C) the 5ʹ-to-3ʹ direction of one strand is opposite to the 5ʹ-to-3ʹ direction of the other strand.
D) the twisting of the DNA molecule has shifted the two strands.
E) purines bond with purines, and pyrimidines bond with pyrimidines.
A) one strand is positively charged, and the other is negatively charged.
B) the base pairings create unequal spacing between the two DNA strands.
C) the 5ʹ-to-3ʹ direction of one strand is opposite to the 5ʹ-to-3ʹ direction of the other strand.
D) the twisting of the DNA molecule has shifted the two strands.
E) purines bond with purines, and pyrimidines bond with pyrimidines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If a mutation changes a G to an A on one strand of a DNA molecule, with a corresponding change in its complement, which attribute of DNA will most likely be affected?
A) The width of the DNA molecule
B) The length of the DNA molecule
C) The nature of protein‒DNA interactions
D) The number of purines in the double-stranded molecule
E) All of the above are equally likely to be affected.
A) The width of the DNA molecule
B) The length of the DNA molecule
C) The nature of protein‒DNA interactions
D) The number of purines in the double-stranded molecule
E) All of the above are equally likely to be affected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Refer to the figure, which illustrates the chemical structure of DNA. 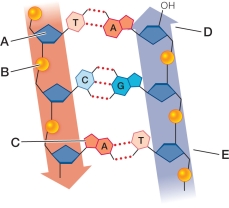 Which label corresponds to a phosphate group?
Which label corresponds to a phosphate group?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
 Which label corresponds to a phosphate group?
Which label corresponds to a phosphate group?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If a sequence in one strand of DNA is 5ʹ-AGCTGCTGA-3ʹ, what is the sequence in the complementary strand?
A) 5ʹ-AGCTGCTGA-3ʹ
B) 3ʹ-AGCTGCTGA-5ʹ
C) 5ʹ-TCGACGACT-3ʹ
D) 3ʹ-TCGATGACT-5ʹ
E) 3ʹ-TCGACGACT-5ʹ
A) 5ʹ-AGCTGCTGA-3ʹ
B) 3ʹ-AGCTGCTGA-5ʹ
C) 5ʹ-TCGACGACT-3ʹ
D) 3ʹ-TCGATGACT-5ʹ
E) 3ʹ-TCGACGACT-5ʹ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The bases from DNA isolated from a newly discovered single-stranded virus are found to be 32 percent A, 18 percent C, 18 percent G, and 32 percent T.During replication, this DNA forms a complementary strand.The bases of the complementary DNA would be _______ percent A, _______ percent C, _______ percent G, and _______ percent T.
A) 32; 17; 32; 19
B) 19; 32; 17; 32
C) 17; 32; 32; 19
D) 25; 25; 25; 25
E) 32; 18; 18; 32
A) 32; 17; 32; 19
B) 19; 32; 17; 32
C) 17; 32; 32; 19
D) 25; 25; 25; 25
E) 32; 18; 18; 32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Refer to the figure, which illustrates the chemical structure of DNA. 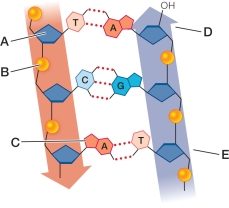 Which two labeled structures participate in a phosphodiester bond?
Which two labeled structures participate in a phosphodiester bond?
A) A and B
B) B and D
C) C and D
D) D and E
E) A and E
 Which two labeled structures participate in a phosphodiester bond?
Which two labeled structures participate in a phosphodiester bond?A) A and B
B) B and D
C) C and D
D) D and E
E) A and E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Information sources used by Watson and Crick to determine the structure of DNA included
A) electron micrographs of individual DNA molecules.
B) light micrographs of bacteriophage particles.
C) light micrographs of individual bacterial chromosomes.
D) nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of DNA.
E) X-ray crystallography of double-stranded DNA.
A) electron micrographs of individual DNA molecules.
B) light micrographs of bacteriophage particles.
C) light micrographs of individual bacterial chromosomes.
D) nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of DNA.
E) X-ray crystallography of double-stranded DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Recall that two hydrogen bonds bind A and T, but three hydrogen bonds bind G and C.Since the stability of DNA is affected by the number of hydrogen bonds, with more bonds promoting more stability, which of the following double-stranded DNA molecules would likely have the greatest stability?
A) A molecule with 20 percent A
B) A molecule with 26 percent G
C) A molecule with 32 percent C
D) A molecule with 38 percent T
E) More information is required to answer the question.
A) A molecule with 20 percent A
B) A molecule with 26 percent G
C) A molecule with 32 percent C
D) A molecule with 38 percent T
E) More information is required to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which molecular model describes the structure of the DNA molecule?
A) Single-stranded and antiparallel
B) Double-stranded and antiparallel
C) Single-stranded and parallel
D) Double-stranded and parallel
E) Triple-stranded and parallel
A) Single-stranded and antiparallel
B) Double-stranded and antiparallel
C) Single-stranded and parallel
D) Double-stranded and parallel
E) Triple-stranded and parallel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Double-stranded DNA looks like a ladder that has been twisted into a helix or spiral.The side supports of the ladder are
A) individual nitrogenous bases.
B) alternating bases and sugars.
C) alternating bases and phosphate groups.
D) alternating sugars and phosphates.
E) alternating bases, sugars, and phosphates.
A) individual nitrogenous bases.
B) alternating bases and sugars.
C) alternating bases and phosphate groups.
D) alternating sugars and phosphates.
E) alternating bases, sugars, and phosphates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Refer to the figure, which illustrates the chemical structure of DNA. 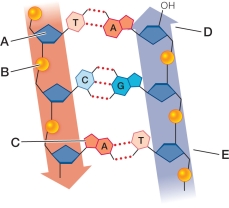 Which label corresponds to a 3ʹ end?
Which label corresponds to a 3ʹ end?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
 Which label corresponds to a 3ʹ end?
Which label corresponds to a 3ʹ end?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which statement about the molecular architecture of DNA is false?
A) The two strands run in opposite directions.
B) The molecule's twist is usually right-handed.
C) The molecule is a double-stranded helix.
D) The molecule has a uniform diameter.
E) All of the above are true; none is false.
A) The two strands run in opposite directions.
B) The molecule's twist is usually right-handed.
C) The molecule is a double-stranded helix.
D) The molecule has a uniform diameter.
E) All of the above are true; none is false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In DNA replication, each newly made strand is
A) identical in DNA sequence to the strand from which it was copied.
B) complementary in sequence to the strand from which it was copied.
C) oriented in the same 3ʹ-to-5ʹ direction as the strand from which it was copied.
D) an incomplete copy of one of the parental strands.
E) a hybrid molecule consisting of both ribo- and deoxyribonucleotides.
A) identical in DNA sequence to the strand from which it was copied.
B) complementary in sequence to the strand from which it was copied.
C) oriented in the same 3ʹ-to-5ʹ direction as the strand from which it was copied.
D) an incomplete copy of one of the parental strands.
E) a hybrid molecule consisting of both ribo- and deoxyribonucleotides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The Meselson-Stahl experiment showed that DNA
A) replication is conservative.
B) is synthesized in only one direction.
C) replication is dispersive.
D) replication is semiconservative.
E) exists as a double helix.
A) replication is conservative.
B) is synthesized in only one direction.
C) replication is dispersive.
D) replication is semiconservative.
E) exists as a double helix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In eukaryotic cells, each chromosome has _______ origin(s) of replication.
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) multiple
E) no
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) multiple
E) no

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What local effect would an RNA synthesis inhibitor have on DNA replication?
A) Primase would not be able to add bases to the DNA.
B) Primase would not be able to use DNA as a template.
C) Primase would be blocked from joining the DNA replication complex.
D) Primase would not be able to provide primers for DNA polymerases.
E) There would be no effect on DNA replication.
A) Primase would not be able to add bases to the DNA.
B) Primase would not be able to use DNA as a template.
C) Primase would be blocked from joining the DNA replication complex.
D) Primase would not be able to provide primers for DNA polymerases.
E) There would be no effect on DNA replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose a double-stranded molecule similar to DNA replicates itself, such that one molecule contains two old strands and the other molecule contains two new strands.Such replication would be an instance of _______ replication.
A) semiconservative
B) conservative
C) dispersive
D) exact
E) complementary
A) semiconservative
B) conservative
C) dispersive
D) exact
E) complementary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Mutations are
A) permanent changes in DNA.
B) changes in the phosphate backbone of DNA.
C) mistakes in the incorporation of amino acids into proteins.
D) changes in the mRNA of an organism.
E) always harmful.
A) permanent changes in DNA.
B) changes in the phosphate backbone of DNA.
C) mistakes in the incorporation of amino acids into proteins.
D) changes in the mRNA of an organism.
E) always harmful.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
At the end of DNA replication, two DNA molecules are produced, each one consisting of a parental DNA strand and a new DNA strand.This process is known as _______ replication.
A) semiconservative
B) conservative
C) dispersive
D) exact
E) complementary
A) semiconservative
B) conservative
C) dispersive
D) exact
E) complementary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In the Meselson‒Stahl experiment, cesium chloride solution
A) helped the DNA polymerase replicate DNA.
B) was the template.
C) was used to assess the density of the DNA.
D) was used to label the DNA.
E) was a deoxyribonucleoside.
A) helped the DNA polymerase replicate DNA.
B) was the template.
C) was used to assess the density of the DNA.
D) was used to label the DNA.
E) was a deoxyribonucleoside.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In a growing DNA strand, to which carbon of the deoxyribose is each monomer added?
A) 1ʹ
B) 2ʹ
C) 3ʹ
D) 4ʹ
E) 5ʹ
A) 1ʹ
B) 2ʹ
C) 3ʹ
D) 4ʹ
E) 5ʹ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The molecules that function to replicate DNA in the cell are
A) DNA nucleoside triphosphates.
B) DNA polymerases.
C) nucleoside polymerases.
D) DNases.
E) ribonucleases.
A) DNA nucleoside triphosphates.
B) DNA polymerases.
C) nucleoside polymerases.
D) DNases.
E) ribonucleases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A researcher would like to separate viral DNA from the viral coat proteins using a density gradient.Which material would she use to set the density gradient?
A) Heavy nitrogen
B) Heavy oxygen
C) Radioactive carbon
D) Cesium chloride
E) Sodium chloride
A) Heavy nitrogen
B) Heavy oxygen
C) Radioactive carbon
D) Cesium chloride
E) Sodium chloride

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The energy necessary for making a DNA molecule comes directly from
A) sugar.
B) ATP.
C) the release of phosphates.
D) NADPH.
E) NADH.
A) sugar.
B) ATP.
C) the release of phosphates.
D) NADPH.
E) NADH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The nucleotides that make up DNA are composed of
A) deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate.
B) a sugar molecule and a phosphate group.
C) deoxyribose plus a phosphate group.
D) deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate.
E) a nitrogenous base bonded to three sugar molecules.
A) deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate.
B) a sugar molecule and a phosphate group.
C) deoxyribose plus a phosphate group.
D) deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate.
E) a nitrogenous base bonded to three sugar molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
During DNA replication
A) one template strand must be degraded to allow the other strand to be copied.
B) the template strands must separate so that both can be copied.
C) the template strands come back together after the passage of the replication fork.
D) origins of replication always give rise to single replication forks.
E) two replication forks diverge from each origin, but one always lags behind the other.
A) one template strand must be degraded to allow the other strand to be copied.
B) the template strands must separate so that both can be copied.
C) the template strands come back together after the passage of the replication fork.
D) origins of replication always give rise to single replication forks.
E) two replication forks diverge from each origin, but one always lags behind the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
New DNA molecules can be synthesized in a test tube containing _______ as substrate.
A) deoxyribose nucleoside monophosphates
B) deoxyribose nucleoside diphosphates
C) deoxyribose nucleoside triphosphates
D) deoxyribose nucleotide diphosphates
E) deoxyribose nucleotide triphosphates
A) deoxyribose nucleoside monophosphates
B) deoxyribose nucleoside diphosphates
C) deoxyribose nucleoside triphosphates
D) deoxyribose nucleotide diphosphates
E) deoxyribose nucleotide triphosphates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
DNA polymerase lengthens a polynucleotide strand in a DNA molecule by
A) building short DNA fragments and linking them together.
B) adding lost DNA sequences to the 3ʹ end.
C) linking purines with pyrimidines.
D) covalently linking new nucleotides to the growing new strand.
E) threading the existing DNA through a replication complex.
A) building short DNA fragments and linking them together.
B) adding lost DNA sequences to the 3ʹ end.
C) linking purines with pyrimidines.
D) covalently linking new nucleotides to the growing new strand.
E) threading the existing DNA through a replication complex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If Meselson and Stahl had observed one intermediate, slightly smeared band after growing bacteria in the presence of 15N for one generation, and then after two generations in 14N again had found one slightly smeared band, they would most likely have concluded that DNA replicates
A) semiconservatively.
B) conservatively.
C) semidiscontinuously.
D) dispersively.
E) semicontinuously.
A) semiconservatively.
B) conservatively.
C) semidiscontinuously.
D) dispersively.
E) semicontinuously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the Meselson-Stahl experiment, which observation ruled out the conservative model of DNA replication?
A) No completely "heavy" DNA was observed after the first round of replication.
B) No completely "light" DNA ever appeared, even after several replications.
C) The product that accumulated after two rounds of replication was completely "heavy."
D) Completely "heavy" DNA was observed throughout the experiment.
E) Three different DNA densities were observed after a single round of replication.
A) No completely "heavy" DNA was observed after the first round of replication.
B) No completely "light" DNA ever appeared, even after several replications.
C) The product that accumulated after two rounds of replication was completely "heavy."
D) Completely "heavy" DNA was observed throughout the experiment.
E) Three different DNA densities were observed after a single round of replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
During replication, the new DNA strand is synthesized
A) in the 3ʹ-to-5ʹ direction.
B) in the 5ʹ-to-3ʹ direction.
C) in both the 3ʹ-to-5ʹ and 5ʹ-to-3ʹ directions from the replication fork.
D) from one end to the other, in the 3ʹ-to-5ʹ or the 5ʹ-to-3ʹ direction.
E) None of the above
A) in the 3ʹ-to-5ʹ direction.
B) in the 5ʹ-to-3ʹ direction.
C) in both the 3ʹ-to-5ʹ and 5ʹ-to-3ʹ directions from the replication fork.
D) from one end to the other, in the 3ʹ-to-5ʹ or the 5ʹ-to-3ʹ direction.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
To determine whether DNA replication is semiconservative, conservative, or dispersive, Meselson and Stahl labeled E.coli DNA with a regimen of heavy nitrogen for one round of replication and then transferred these cells to a light nitrogen regimen for two more rounds of replication.Which statement would not have been true within the context of this experiment?
A) If DNA replication was conservative, no DNA molecules of intermediate density would have been seen.
B) If DNA replication was dispersive, only DNA molecules that were of intermediate density would have been seen.
C) If DNA replication was semiconservative, the DNA molecules that were made would all be heavy.
D) If DNA replication was semiconservative, the DNA molecules would consist of one parental strand base paired to one newly replicated strand.
E) If DNA replication was semiconservative, a higher proportion of DNA molecules from future divisions would have been light.
A) If DNA replication was conservative, no DNA molecules of intermediate density would have been seen.
B) If DNA replication was dispersive, only DNA molecules that were of intermediate density would have been seen.
C) If DNA replication was semiconservative, the DNA molecules that were made would all be heavy.
D) If DNA replication was semiconservative, the DNA molecules would consist of one parental strand base paired to one newly replicated strand.
E) If DNA replication was semiconservative, a higher proportion of DNA molecules from future divisions would have been light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which statement about Okazaki fragments is true?
A) They occur because DNA polymerase operates in only one direction along a strand of DNA.
B) They act as a primer that initiates DNA replication.
C) If they did not exist, the ends of chromosomes would get shorter with every replication.
D) It they did not exist, bases would pair with their complementary bases.
E) They reduce the mutation rate during DNA replication.
A) They occur because DNA polymerase operates in only one direction along a strand of DNA.
B) They act as a primer that initiates DNA replication.
C) If they did not exist, the ends of chromosomes would get shorter with every replication.
D) It they did not exist, bases would pair with their complementary bases.
E) They reduce the mutation rate during DNA replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
An individual inherits two defective copies of the MLH1 gene, a protein involved in mismatch repair of DNA during its replication.What do you predict will be the consequences of deficient mismatch repair upon DNA replication?
A) The fidelity of DNA polymerase activity will be decreased.
B) Mismatched nucleotides will no longer be detected by the replication complex.
C) Ligase will not be able to repair nicks in the DNA.
D) The excision repair proteins will no longer function.
E) A higher frequency of mutations will become fixed in the newly synthesized strand.
A) The fidelity of DNA polymerase activity will be decreased.
B) Mismatched nucleotides will no longer be detected by the replication complex.
C) Ligase will not be able to repair nicks in the DNA.
D) The excision repair proteins will no longer function.
E) A higher frequency of mutations will become fixed in the newly synthesized strand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The enzyme that restores the phosphodiester linkage between adjacent fragments in the lagging strand during DNA replication is
A) DNA ligase.
B) primase.
C) reverse transcriptase.
D) helicase.
E) DNA polymerase I.
A) DNA ligase.
B) primase.
C) reverse transcriptase.
D) helicase.
E) DNA polymerase I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which DNA repair system or mechanism acts as the second line of defense against mutational error that occurs as the result of DNA replication?
A) Excision
B) Mismatch
C) Proofreading
D) Telomerase
E) Ligation
A) Excision
B) Mismatch
C) Proofreading
D) Telomerase
E) Ligation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What joins Okazaki fragments together?
A) DNA polymerase
B) DNA ligase
C) DNA helicase
D) The leading strand
E) The lagging strand
A) DNA polymerase
B) DNA ligase
C) DNA helicase
D) The leading strand
E) The lagging strand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Refer to the figure. 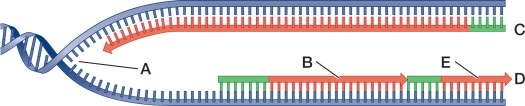 Which letter refers to an Okazaki fragment?
Which letter refers to an Okazaki fragment?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
 Which letter refers to an Okazaki fragment?
Which letter refers to an Okazaki fragment?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Refer to the figure. 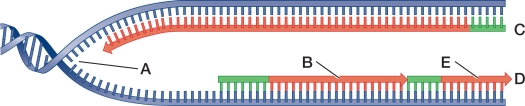 Which letter best indicates the lagging strand?
Which letter best indicates the lagging strand?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
 Which letter best indicates the lagging strand?
Which letter best indicates the lagging strand?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Refer to the figure. 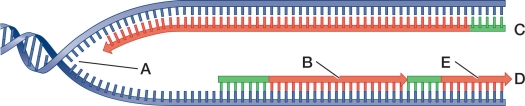 Which structure illustrates a replication fork?
Which structure illustrates a replication fork?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
 Which structure illustrates a replication fork?
Which structure illustrates a replication fork?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In organisms that contain circular DNA,
A) there are often multiple origins of replication.
B) DNA replication is conservative.
C) the replication complex moves in both directions around the circle.
D) the chromosome must first be linearized to enable replication.
E) DNA replication is slow.
A) there are often multiple origins of replication.
B) DNA replication is conservative.
C) the replication complex moves in both directions around the circle.
D) the chromosome must first be linearized to enable replication.
E) DNA replication is slow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The enzyme DNA ligase is required continuously during DNA replication in order for
A) fragments of the leading strand to be joined together.
B) fragments of the lagging strand to be joined together.
C) the parental strands to be joined back together.
D) 3ʹ-deoxynucleoside triphosphates to be converted to 5ʹ-deoxynucleoside triphosphates.
E) the complex of proteins that work together at the replication fork to remain intact.
A) fragments of the leading strand to be joined together.
B) fragments of the lagging strand to be joined together.
C) the parental strands to be joined back together.
D) 3ʹ-deoxynucleoside triphosphates to be converted to 5ʹ-deoxynucleoside triphosphates.
E) the complex of proteins that work together at the replication fork to remain intact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
During eukaryotic DNA synthesis, after repair the error rate is on the order of one wrong nucleotide per
A) 1,000.
B) 10,000.
C) 1 million.
D) 100 million.
E) 10 billion.
A) 1,000.
B) 10,000.
C) 1 million.
D) 100 million.
E) 10 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Refer to the figure. 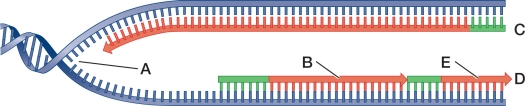 Which letter represents the leading strand?
Which letter represents the leading strand?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
 Which letter represents the leading strand?
Which letter represents the leading strand?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In DNA replication, a sliding DNA clamp
A) increases the number of nucleotides that can be polymerized at one time.
B) holds open the two strands of the DNA molecule for access to the bonds.
C) slides forward, separating additional strands of the DNA molecule.
D) temporarily holds the nucleotides together until phosphodiester bonds can form.
E) unwinds the double helix to allow DNA polymerase to bind.
A) increases the number of nucleotides that can be polymerized at one time.
B) holds open the two strands of the DNA molecule for access to the bonds.
C) slides forward, separating additional strands of the DNA molecule.
D) temporarily holds the nucleotides together until phosphodiester bonds can form.
E) unwinds the double helix to allow DNA polymerase to bind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What prevents the DNA repair system from "repairing" telomeres?
A) Telomerase is bound to telomeres and thus blocks the repair system from binding to telomeres.
B) Telomerase catalyzes reactions instead of the repair system.
C) DNA polymerase blocks the repair system from accessing the telomere DNA.
D) Telomeres are at the end of the chromosome, and DNA is replicated in only one direction.
E) Protective proteins bind to telomeres, and therefore the repair system does not recognize telomeres as breaks.
A) Telomerase is bound to telomeres and thus blocks the repair system from binding to telomeres.
B) Telomerase catalyzes reactions instead of the repair system.
C) DNA polymerase blocks the repair system from accessing the telomere DNA.
D) Telomeres are at the end of the chromosome, and DNA is replicated in only one direction.
E) Protective proteins bind to telomeres, and therefore the repair system does not recognize telomeres as breaks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Without DNA repair, the error rate of DNA polymerase is about one for every 100,000 bases replicated.If an organism has a haploid genome of 2 billion base pairs, how many mutations are likely to occur each time a diploid cell replicates its DNA?
A) 20
B) 40
C) 80
D) 20,000
E) 40,000
A) 20
B) 40
C) 80
D) 20,000
E) 40,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The telomeres at the ends of linear chromosomes allow
A) the 5ʹ ends of the chromosomes to undergo recombination.
B) the single-stranded DNA left by the terminal primer removal from lagging strands to be repaired by telomerase.
C) DNA repair enzymes to recognize those ends and remove them.
D) normal cells to divide continuously.
E) DNA breaks to be examined at cell division checkpoints.
A) the 5ʹ ends of the chromosomes to undergo recombination.
B) the single-stranded DNA left by the terminal primer removal from lagging strands to be repaired by telomerase.
C) DNA repair enzymes to recognize those ends and remove them.
D) normal cells to divide continuously.
E) DNA breaks to be examined at cell division checkpoints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The enzyme that unwinds the DNA prior to replication is called
A) DNA polymerase III.
B) DNA ligase.
C) single-stranded DNA binding protein.
D) primase.
E) helicase.
A) DNA polymerase III.
B) DNA ligase.
C) single-stranded DNA binding protein.
D) primase.
E) helicase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following provides the correct order of events in the synthesis of the lagging strand?
A) Primase adds RNA primer, DNA polymerase III creates a segment of new DNA, DNA polymerase I removes the primer, and ligase seals the gaps.
B) Primase adds primer, DNA polymerase I removes the primer, DNA polymerase III extends the segment, and ligase seals the gap.
C) Ligase adds bases to the primase, the primase generates polymerase I, polymerase III adds to the segment of new DNA, and helicase winds the DNA.
D) Helicase unwinds the DNA, primase creates a primer, DNA polymerase I elongates the segment of new DNA, DNA polymerase III removes the primer, and ligase seals the gaps in the DNA.
E) None of the above
A) Primase adds RNA primer, DNA polymerase III creates a segment of new DNA, DNA polymerase I removes the primer, and ligase seals the gaps.
B) Primase adds primer, DNA polymerase I removes the primer, DNA polymerase III extends the segment, and ligase seals the gap.
C) Ligase adds bases to the primase, the primase generates polymerase I, polymerase III adds to the segment of new DNA, and helicase winds the DNA.
D) Helicase unwinds the DNA, primase creates a primer, DNA polymerase I elongates the segment of new DNA, DNA polymerase III removes the primer, and ligase seals the gaps in the DNA.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In a population of cells on the inner surface of the intestine, the cells frequently divide.Therefore, these cells are likely to
A) have high levels of telomerase.
B) have very low levels of telomerase.
C) undergo the polymerase chain reaction.
D) lack DNA polymerase.
E) lack Okazaki fragments.
A) have high levels of telomerase.
B) have very low levels of telomerase.
C) undergo the polymerase chain reaction.
D) lack DNA polymerase.
E) lack Okazaki fragments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which statement about telomerase is true?
A) It prevents the ends of chromosomes from continuing to grow.
B) It prevents the ends of chromosomes from being eroded with each round of DNA replication.
C) It makes DNA repair possible.
D) It is necessary for the formation of Okazaki fragments.
E) It is necessary for the formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary bases.
A) It prevents the ends of chromosomes from continuing to grow.
B) It prevents the ends of chromosomes from being eroded with each round of DNA replication.
C) It makes DNA repair possible.
D) It is necessary for the formation of Okazaki fragments.
E) It is necessary for the formation of hydrogen bonds between complementary bases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 257 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



