Deck 17: Genomes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/249
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Genomes
1
The fluorescent dye attached to dNTPs in DNA sequencing
A) aids in identification of the last nucleotide added to a growing DNA strand.
B) acts as a catalyst for the reaction.
C) terminates the reaction.
D) aids in attaching DNA to a solid substrate for sequencing.
E) serves no function.
A) aids in identification of the last nucleotide added to a growing DNA strand.
B) acts as a catalyst for the reaction.
C) terminates the reaction.
D) aids in attaching DNA to a solid substrate for sequencing.
E) serves no function.
A
2
A universal adapter used in a sequencing run starts 5′-TCATAGT.What would be the sequence of the corresponding universal primer? (Note: "…" represents many nucleotides.)
A) 5′-TCATAGT…-3'
B) 5′-ACATAGT…-3'
C) 5′-…AGTATCA-3'
D) 5′-…AGUAUCA-3'
E) 5′-AGTTAGT…-3'
A) 5′-TCATAGT…-3'
B) 5′-ACATAGT…-3'
C) 5′-…AGTATCA-3'
D) 5′-…AGUAUCA-3'
E) 5′-AGTTAGT…-3'
C
3
Which procedure is not used in high-throughput DNA sequencing?
A) Cutting of the DNA into small fragments
B) Synthesis of RNA primers
C) Attaching of the DNA to a solid substrate
D) Denaturation of the DNA by heating
E) Amplification of the fragments by PCR
A) Cutting of the DNA into small fragments
B) Synthesis of RNA primers
C) Attaching of the DNA to a solid substrate
D) Denaturation of the DNA by heating
E) Amplification of the fragments by PCR
B
4
A DNA sequence is cut by two different restriction enzymes (1 and 2).Digestion from enzyme 1 yields the following fragments (read in the 5ʹ-to-3ʹ direction): CGATAC, GTCGTCGCC, and GTTATCGCGAC.Digestion from enzyme 2 yields the following fragments (read in the 5ʹ-to-3ʹ direction): CGACGTCGTCGCC and CGATACGTTATCG.What was the original sequence?
A) CGACGTCGTCGCCCGATACGTTATCG
B) GTCGTCGCCCGATACGTTATCGCGAC
C) CGATACGTTATCGCGACGTCGTCGCC
D) CGATACGTCGTCGCCGTTATCGCGAC
E) GTTATCGCGACGTCGTCGCCCGATAC
A) CGACGTCGTCGCCCGATACGTTATCG
B) GTCGTCGCCCGATACGTTATCGCGAC
C) CGATACGTTATCGCGACGTCGTCGCC
D) CGATACGTCGTCGCCGTTATCGCGAC
E) GTTATCGCGACGTCGTCGCCCGATAC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If the universal adapter sequence is 5′-GTCATTGCTTGCAATGTT-3′, which universal primer should be used for DNA sequencing?
A) 5′-GTCATTGCTTGCAATGTT-3′
B) 5′-TTGTAACGTTCGTTACTG-3′
C) 5′-CAGTAACGAACGTTACAA-3′
D) 5′-CCTGAATTGGTCGTACAA-3′
E) 5′-AACATGCTGGTTAAGTCC-3′
A) 5′-GTCATTGCTTGCAATGTT-3′
B) 5′-TTGTAACGTTCGTTACTG-3′
C) 5′-CAGTAACGAACGTTACAA-3′
D) 5′-CCTGAATTGGTCGTACAA-3′
E) 5′-AACATGCTGGTTAAGTCC-3′

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following would not be required for determining the sequence of a 400 bp DNA fragment by the high-throughput sequencing method?
A) The four dNTPs (dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP)
B) DNA polymerase
C) A short, artificially synthesized primer
D) A bacterial artificial chromosome
E) Heat-denatured DNA fragments
A) The four dNTPs (dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP)
B) DNA polymerase
C) A short, artificially synthesized primer
D) A bacterial artificial chromosome
E) Heat-denatured DNA fragments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the primary disadvantage of Sanger sequencing?
A) It requires automation.
B) It can only be done on eukaryotic DNA.
C) It can only be done on prokaryotic DNA.
D) It is a slow, laborious procedure.
E) It requires sequencing both complementary strands.
A) It requires automation.
B) It can only be done on eukaryotic DNA.
C) It can only be done on prokaryotic DNA.
D) It is a slow, laborious procedure.
E) It requires sequencing both complementary strands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which study is best characterized as one of comparative genomics?
A) Researchers investigating the relative frequencies of different transposable elements in a grasshopper species
B) Researchers investigating the relationship between the number of transposable elements and development time across different species of flies
C) Researchers attempting to find the regulatory sequences of a cell-signaling gene in a yeast species
D) Researchers using sequencing to assess the diversity of fungi in a soil sample
E) Researchers using sequencing to compare the diversity of bacteria across different parts of a stream
A) Researchers investigating the relative frequencies of different transposable elements in a grasshopper species
B) Researchers investigating the relationship between the number of transposable elements and development time across different species of flies
C) Researchers attempting to find the regulatory sequences of a cell-signaling gene in a yeast species
D) Researchers using sequencing to assess the diversity of fungi in a soil sample
E) Researchers using sequencing to compare the diversity of bacteria across different parts of a stream

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A DNA sequence is cut by two different restriction enzymes (1 and 2).Digestion from enzyme 1 yields the following fragments (read in the 5ʹ-to-3ʹ direction): CGATAC, GTCGTCGCC, and GTTATCGCGAC.Digestion from enzyme 2 yields the following fragments (read in the 5ʹ-to-3ʹ direction): CGACGTCGTCGCC and CGATACGTTATCG.Which sequence does enzyme 1 recognize as a site at which to cut? (Note that the enzyme cuts in the middle of its recognition sequence.)
A) GTTA
B) ACGT
C) TGGA
D) CGCG
E) GTCG
A) GTTA
B) ACGT
C) TGGA
D) CGCG
E) GTCG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Soon after the sequence of Haemophilus influenzae was announced, two additional prokaryotic sequences were announced: the smaller Mycoplasma genitalium and the larger E.coli.Having multiple genomes permitted the beginning of
A) metagenomics.
B) eukaryotic genomics.
C) proteomics.
D) comparative genomics.
E) haplotype mapping.
A) metagenomics.
B) eukaryotic genomics.
C) proteomics.
D) comparative genomics.
E) haplotype mapping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose a long sequence of DNA is cut with four different restriction enzymes.Which restriction enzyme should produce the fewest fragments?
A) One that cuts at the sequence GACT
B) One that cuts at the sequence GCCTCT
C) One that cuts at the sequence AGTTCTAT
D) One that cuts at the sequence CAGTTCTATG
E) All of these enzymes would produce roughly the same number of fragments.
A) One that cuts at the sequence GACT
B) One that cuts at the sequence GCCTCT
C) One that cuts at the sequence AGTTCTAT
D) One that cuts at the sequence CAGTTCTATG
E) All of these enzymes would produce roughly the same number of fragments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which is not used in functional genomics to identify the functions of genes?
A) Sequence comparisons between organisms
B) Amino acid sequences of proteins
C) Regulatory sequences
D) Open reading frames
E) RNA genes
A) Sequence comparisons between organisms
B) Amino acid sequences of proteins
C) Regulatory sequences
D) Open reading frames
E) RNA genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A stretch of one strand of a DNA fragment is 5′-GTCATCGTACT-3′.What is the complementary strand?
A) 5′-GTCATCGTACT-3′
B) 3′-GTCATCGTACT-5′
C) 5′-CAGTAGCATGA-3′
D) 3′-CAGTAGCATGA-5′
E) 5′-GTCAGACTACA-3′
A) 5′-GTCATCGTACT-3′
B) 3′-GTCATCGTACT-5′
C) 5′-CAGTAGCATGA-3′
D) 3′-CAGTAGCATGA-5′
E) 5′-GTCAGACTACA-3′

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A promoter is an example of a(n)
A) open reading frame.
B) transposable element.
C) chromatin sequence.
D) rRNA gene.
E) regulatory sequence.
A) open reading frame.
B) transposable element.
C) chromatin sequence.
D) rRNA gene.
E) regulatory sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which case best fits the description of functional genomics?
A) Collecting sequence data of bacteria from various soil samples to examine how the presence of nematodes affects bacterial diversity
B) Collecting sequence data of the microbiome from the stools of people with irritable bowel syndrome and healthy controls
C) Examining the sequences of bacteria that live inside aphids compared with free-living bacteria
D) Examining the genomes of domesticated animals compared with their nondomesticated relatives to look for genomic signatures of domestication
E) Examining which sequences in genomes are involved in regulation of transcriptional activity
A) Collecting sequence data of bacteria from various soil samples to examine how the presence of nematodes affects bacterial diversity
B) Collecting sequence data of the microbiome from the stools of people with irritable bowel syndrome and healthy controls
C) Examining the sequences of bacteria that live inside aphids compared with free-living bacteria
D) Examining the genomes of domesticated animals compared with their nondomesticated relatives to look for genomic signatures of domestication
E) Examining which sequences in genomes are involved in regulation of transcriptional activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A DNA sequence has been cut into the following three overlapping sequence fragments: (1) CCGCGCGTAGCGAGTCAG
(2) GGCTAGTTAGCTCCGCGCG
(3) AGTCAGTCAAAAT
What is the correct assembled sequence of these fragments?
A) GGCTAGTTAGCTCCGCGCGTAGCGAGTCAGTCAAAAT
B) CCGCGCGTAGCGTTAGCTCCGCGCGCAAAGTCAAAAT
C) CCGCGCGTAGCGAGTCAGGGCTAGTTAGCTCCGCGCG
D) AGTCAGTCAAAATGTCAGCAGTCAAAAT
E) GGCTAGTTAGCTCCGCGCGAGTCAGTCAAAAT
(2) GGCTAGTTAGCTCCGCGCG
(3) AGTCAGTCAAAAT
What is the correct assembled sequence of these fragments?
A) GGCTAGTTAGCTCCGCGCGTAGCGAGTCAGTCAAAAT
B) CCGCGCGTAGCGTTAGCTCCGCGCGCAAAGTCAAAAT
C) CCGCGCGTAGCGAGTCAGGGCTAGTTAGCTCCGCGCG
D) AGTCAGTCAAAATGTCAGCAGTCAAAAT
E) GGCTAGTTAGCTCCGCGCGAGTCAGTCAAAAT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Under which circumstance will a researcher most likely use Sanger sequencing instead of high-throughput sequencing?
A) If the researcher is undertaking a metagenomic study and is sequencing primarily prokaryotes
B) If the researcher is undertaking a metagenomic study and is sequencing primarily eukaryotes
C) If the researcher has a small lab, lacks miniaturization equipment, and plans to sequence only a relatively small amount
D) If the researcher is doing a comparative genomic study
E) If the researcher is doing a functional genomic study
A) If the researcher is undertaking a metagenomic study and is sequencing primarily prokaryotes
B) If the researcher is undertaking a metagenomic study and is sequencing primarily eukaryotes
C) If the researcher has a small lab, lacks miniaturization equipment, and plans to sequence only a relatively small amount
D) If the researcher is doing a comparative genomic study
E) If the researcher is doing a functional genomic study

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A DNA sequence has been cut into the following four overlapping sequence fragments: (1) AGGGGCCTATAGCATACGTACA
(2) CGTACATCTGAGGGTACGATCATGGC
(3) CATGGCTAGCAAACGCGATCCCAAG
(4) AGGCTAGTTACGATATAGGGGCC
What is the correct order of these fragments?
A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 1, 3, 2, 4
C) 2, 3, 1, 4
D) 4, 1, 2, 3
E) 4, 1, 3, 2
(2) CGTACATCTGAGGGTACGATCATGGC
(3) CATGGCTAGCAAACGCGATCCCAAG
(4) AGGCTAGTTACGATATAGGGGCC
What is the correct order of these fragments?
A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 1, 3, 2, 4
C) 2, 3, 1, 4
D) 4, 1, 2, 3
E) 4, 1, 3, 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which sequence type will not be included in an open reading frame?
A) Intron consensus sequences
B) A start codon
C) A stop codon
D) Regulatory sequences
E) Coding regions of genes
A) Intron consensus sequences
B) A start codon
C) A stop codon
D) Regulatory sequences
E) Coding regions of genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The noncoding strand of a 10 bp fragment of DNA was cut in three different ways to yield the following subfragments: cut 1 yielded TG, ATG, and CCTAC; cut 2 yielded AT, GCC, and TACTG; and cut 3 yielded CTG, CTA, and ATGC.What is the correct sequence of the large fragment?
A) GTCATCCGTA
B) ATGCCTACTG
C) ATGACTGCCT
D) GTCATGTACC
E) Insufficient information is given to determine the sequence.
A) GTCATCCGTA
B) ATGCCTACTG
C) ATGACTGCCT
D) GTCATGTACC
E) Insufficient information is given to determine the sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Refer to the table showing several prokaryote (bacterial) species (labeled A-E) that have been sequenced, along with the findings of the genes they contain.(Note: "x" marks the species possessing a functional copy of the gene.) Gene 1 is essential for the synthesis of several amino acids.Gene 2 encodes a protein involved in strengthening the cell wall.Gene 3 produces an enzyme that breaks down methane.The functions of the other five genes are currently unknown. 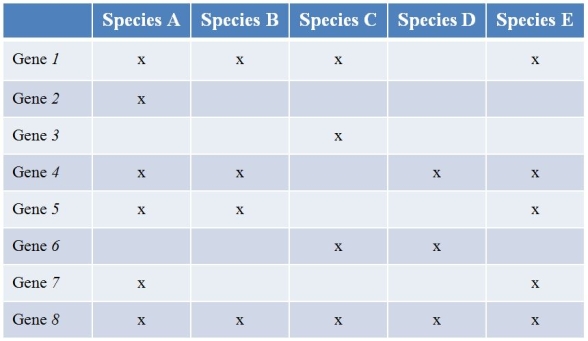 What type of study best characterizes what the researchers did?
What type of study best characterizes what the researchers did?
A) Functional genomics
B) Metagenomics
C) Comparative genomics
D) Haplotype mapping
E) Microbiomics
 What type of study best characterizes what the researchers did?
What type of study best characterizes what the researchers did?A) Functional genomics
B) Metagenomics
C) Comparative genomics
D) Haplotype mapping
E) Microbiomics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Refer to the table showing the properties of five different genomes. 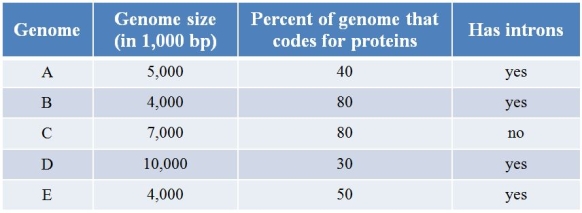 Which genome is most likely prokaryotic?
Which genome is most likely prokaryotic?
A) Genome A
B) Genome B
C) Genome C
D) Genome D
E) Genome E
 Which genome is most likely prokaryotic?
Which genome is most likely prokaryotic?A) Genome A
B) Genome B
C) Genome C
D) Genome D
E) Genome E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Refer to the hypothetical data set comparing the gene content of Salmonella and Shigella, of which all strains are pathogenic, and the pathogenic and nonpathogenic strains of E.coli.(Note: "x" denotes presence of the gene.) 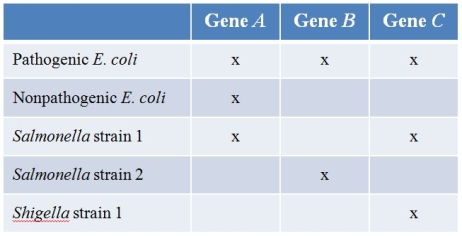 Which is the most likely conclusion about gene B?
Which is the most likely conclusion about gene B?
A) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Salmonella strain 1.
B) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Salmonella strain 2.
C) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Shigella.
D) It may be involved in pathogenicity, and its origin is unclear.
E) It is unlikely to be involved in pathogenicity.
 Which is the most likely conclusion about gene B?
Which is the most likely conclusion about gene B?A) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Salmonella strain 1.
B) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Salmonella strain 2.
C) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Shigella.
D) It may be involved in pathogenicity, and its origin is unclear.
E) It is unlikely to be involved in pathogenicity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Refer to the table showing several prokaryote (bacterial) species (labeled A-E) that have been sequenced, along with the findings of the genes they contain.(Note: "x" marks the species possessing a functional copy of the gene.) Gene 1 is essential for the synthesis of several amino acids.Gene 2 encodes a protein involved in strengthening the cell wall.Gene 3 produces an enzyme that breaks down methane.The functions of the other five genes are currently unknown. 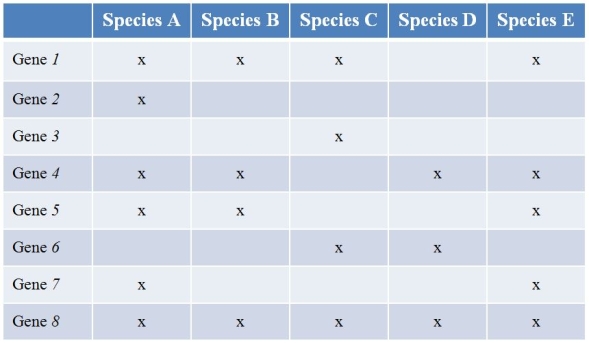 Which species has the most potential to be useful regarding studies of how global warming can be slowed?
Which species has the most potential to be useful regarding studies of how global warming can be slowed?
A) Species A
B) Species B
C) Species C
D) Species D
E) Species E
 Which species has the most potential to be useful regarding studies of how global warming can be slowed?
Which species has the most potential to be useful regarding studies of how global warming can be slowed?A) Species A
B) Species B
C) Species C
D) Species D
E) Species E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Where would you most likely find introns?
A) A tRNA gene of an archean species
B) A gene involved in central metabolism in an archean species
C) A gene involved in the formation of the cell wall of a bacterial species
D) A gene involved in central metabolism in a bacterial species
E) A tRNA gene of a bacterial species
A) A tRNA gene of an archean species
B) A gene involved in central metabolism in an archean species
C) A gene involved in the formation of the cell wall of a bacterial species
D) A gene involved in central metabolism in a bacterial species
E) A tRNA gene of a bacterial species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the hypothetical data set comparing the gene content of Salmonella and Shigella, of which all strains are pathogenic, and the pathogenic and nonpathogenic strains of E.coli.(Note: "x" denotes presence of the gene.) 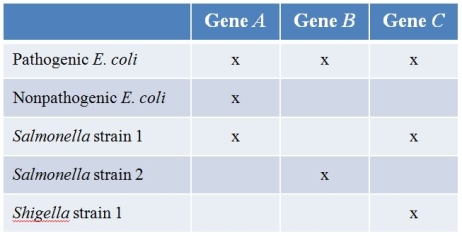 Which is the most likely conclusion about gene A?
Which is the most likely conclusion about gene A?
A) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Salmonella strain 1.
B) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Salmonella strain 2.
C) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Shigella.
D) It may be involved in pathogenicity, and its origin is unclear.
E) It is unlikely to be involved in pathogenicity.
 Which is the most likely conclusion about gene A?
Which is the most likely conclusion about gene A?A) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Salmonella strain 1.
B) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Salmonella strain 2.
C) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Shigella.
D) It may be involved in pathogenicity, and its origin is unclear.
E) It is unlikely to be involved in pathogenicity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A lab sequencing the DNA of various species of pathogenic bacteria with the goal of determining their evolutionary relationships would be practicing _______ genomics.
A) comparative
B) operational
C) meta-
D) functional
E) eukaryotic
A) comparative
B) operational
C) meta-
D) functional
E) eukaryotic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A genome is about 1.83 million bp long, it has 1,738 genes, and 99 percent of its sequence is coding sequence.This genome most likely belongs to a(n)
A) virus.
B) bacterium.
C) yeast.
D) plant.
E) animal.
A) virus.
B) bacterium.
C) yeast.
D) plant.
E) animal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which sequence is most likely to be interrupted by introns?
A) A tRNA gene from an archaean
B) A tRNA gene from a bacterium
C) An rRNA gene from a bacterium
D) An ordinary housekeeping gene from a bacterium
E) An ordinary housekeeping gene from an archaean
A) A tRNA gene from an archaean
B) A tRNA gene from a bacterium
C) An rRNA gene from a bacterium
D) An ordinary housekeeping gene from a bacterium
E) An ordinary housekeeping gene from an archaean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Studies have found that a bacterium of the genus Buchnera has been living as a parasite of aphids for many millions of years.This bacterium lacks certain genes that are involved in the production of the cell wall found in other related bacteria.The field of biology in which such studies were carried out is called
A) metagenomics.
B) eukaryotic genomics.
C) proteomics.
D) comparative genomics.
E) haplotype mapping.
A) metagenomics.
B) eukaryotic genomics.
C) proteomics.
D) comparative genomics.
E) haplotype mapping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Refer to the table showing several prokaryote (bacterial) species (labeled A-E) that have been sequenced, along with the findings of the genes they contain.(Note: "x" marks the species possessing a functional copy of the gene.) Gene 1 is essential for the synthesis of several amino acids.Gene 2 encodes a protein involved in strengthening the cell wall.Gene 3 produces an enzyme that breaks down methane.The functions of the other five genes are currently unknown. 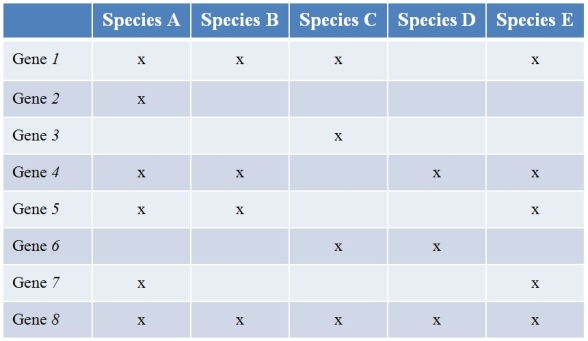 Which species would most likely have difficulty growing on a growth medium composed simply of a sugar as a carbon source?
Which species would most likely have difficulty growing on a growth medium composed simply of a sugar as a carbon source?
A) Species A
B) Species B
C) Species C
D) Species D
E) Species E
 Which species would most likely have difficulty growing on a growth medium composed simply of a sugar as a carbon source?
Which species would most likely have difficulty growing on a growth medium composed simply of a sugar as a carbon source?A) Species A
B) Species B
C) Species C
D) Species D
E) Species E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which statement about prokaryotic genomes is false?
A) All of their DNA is in protein-coding sequences or RNA genes.
B) They are usually organized into a single chromosome.
C) They usually do not have introns in their genes.
D) They often have smaller circular molecules called plasmids.
E) They range from about 160,000 to 12 million bp in length.
A) All of their DNA is in protein-coding sequences or RNA genes.
B) They are usually organized into a single chromosome.
C) They usually do not have introns in their genes.
D) They often have smaller circular molecules called plasmids.
E) They range from about 160,000 to 12 million bp in length.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Pathogenic strains of E.coli often exchange genes with other pathogenic bacteria such as Salmonella and Shigella.Refer to the table showing which bacteria contain various genes.(Note: "x" denotes presence of the gene.)  Which gene most likely got into pathogenic E.coli from the other pathogenic bacteria?
Which gene most likely got into pathogenic E.coli from the other pathogenic bacteria?
A) Gene A
B) Gene B
C) Gene C
D) Gene D
E) Gene E
 Which gene most likely got into pathogenic E.coli from the other pathogenic bacteria?
Which gene most likely got into pathogenic E.coli from the other pathogenic bacteria?A) Gene A
B) Gene B
C) Gene C
D) Gene D
E) Gene E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which genome is most likely to be that of a free-living prokaryote?
A) A genome that is 300 million bp long with over 50 percent repetitive DNA and many introns
B) A genome that is 16,000 bp long, arranged in a circle
C) A genome that is 3 million bp long, arranged in a single circular chromosome, and with little repetitive DNA
D) A genome that is 3 million bp long, arranged in many linear chromosomes, and with many introns
E) A genome that is 3 million bp long with many introns
A) A genome that is 300 million bp long with over 50 percent repetitive DNA and many introns
B) A genome that is 16,000 bp long, arranged in a circle
C) A genome that is 3 million bp long, arranged in a single circular chromosome, and with little repetitive DNA
D) A genome that is 3 million bp long, arranged in many linear chromosomes, and with many introns
E) A genome that is 3 million bp long with many introns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Refer to the table showing several prokaryote (bacterial) species (labeled A-E) that have been sequenced, along with the findings of the genes they contain.(Note: "x" marks the species possessing a functional copy of the gene.) Gene 1 is essential for the synthesis of several amino acids.Gene 2 encodes a protein involved in strengthening the cell wall.Gene 3 produces an enzyme that breaks down methane.The functions of the other five genes are currently unknown. 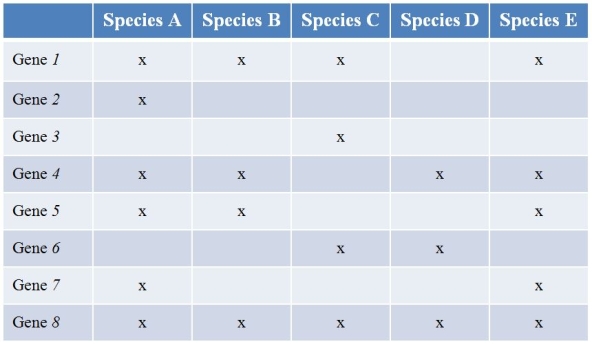 Species A and B are closely related, while the others are not.Which species pairs most likely exchanged genes?
Species A and B are closely related, while the others are not.Which species pairs most likely exchanged genes?
A) Species A and C
B) Species A and E
C) Species B and D
D) Species C and D
E) Species D and E
 Species A and B are closely related, while the others are not.Which species pairs most likely exchanged genes?
Species A and B are closely related, while the others are not.Which species pairs most likely exchanged genes?A) Species A and C
B) Species A and E
C) Species B and D
D) Species C and D
E) Species D and E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which statement about the pathogenic strain O157:H7 of E.coli is true?
A) It differs from the harmless laboratory strains of E. coli by only a few genes.
B) It shares several genes with other pathogenic bacteria, suggesting extensive genetic exchange among these species.
C) It is the primary cause of tuberculosis in the United States.
D) It kills more than 70,000 people a year in the United States.
E) It is not classified as one of the "superbugs" that share genes for antibiotic resistance.
A) It differs from the harmless laboratory strains of E. coli by only a few genes.
B) It shares several genes with other pathogenic bacteria, suggesting extensive genetic exchange among these species.
C) It is the primary cause of tuberculosis in the United States.
D) It kills more than 70,000 people a year in the United States.
E) It is not classified as one of the "superbugs" that share genes for antibiotic resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When scientists described the sequences of the proteins of Haemophilus influenzae based on its DNA sequence, what did they find to be the major difference between noninfective strains and highly infective strains?
A) The infective strains have genes for glycolysis that the noninfective strains lack.
B) The noninfective strains lack the enzymes needed to synthesize amino acids.
C) Only the infective strains have surface proteins that attach the bacterium to respiratory tracts.
D) The noninfective strains lack open reading frames.
E) The strains have different regulatory sequences.
A) The infective strains have genes for glycolysis that the noninfective strains lack.
B) The noninfective strains lack the enzymes needed to synthesize amino acids.
C) Only the infective strains have surface proteins that attach the bacterium to respiratory tracts.
D) The noninfective strains lack open reading frames.
E) The strains have different regulatory sequences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Under which circumstances would metagenomic studies be more useful than traditional methods?
A) The organisms are numerous and very small.
B) The organisms are relatively large and few in number.
C) The organisms are easily cultured.
D) The organisms have relatively large genomes.
E) The organisms have relatively small genomes.
A) The organisms are numerous and very small.
B) The organisms are relatively large and few in number.
C) The organisms are easily cultured.
D) The organisms have relatively large genomes.
E) The organisms have relatively small genomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Refer to the table showing several prokaryote (bacterial) species (labeled A-E) that have been sequenced, along with the findings of the genes they contain.(Note: "x" marks the species possessing a functional copy of the gene.) Gene 1 is essential for the synthesis of several amino acids.Gene 2 encodes a protein involved in strengthening the cell wall.Gene 3 produces an enzyme that breaks down methane.The functions of the other five genes are currently unknown. 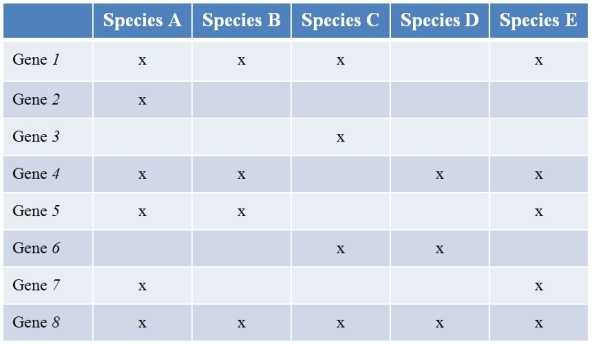 Which species would be most likely to withstand extreme conditions?
Which species would be most likely to withstand extreme conditions?
A) Species A
B) Species B
C) Species C
D) Species D
E) Species E
 Which species would be most likely to withstand extreme conditions?
Which species would be most likely to withstand extreme conditions?A) Species A
B) Species B
C) Species C
D) Species D
E) Species E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Refer to the hypothetical data set comparing the gene content of Salmonella and Shigella, of which all strains are pathogenic, and the pathogenic and nonpathogenic strains of E.coli.(Note: "x" denotes presence of the gene.) 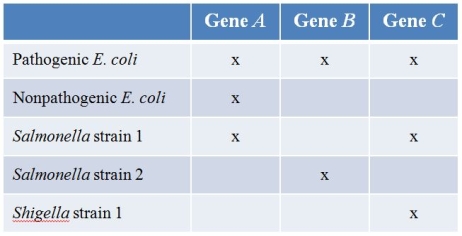 Which is the most likely conclusion about gene C?
Which is the most likely conclusion about gene C?
A) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Salmonella strain 1.
B) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Salmonella strain 2.
C) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Shigella.
D) It may be involved in pathogenicity, and its origin is unclear.
E) It is unlikely to be involved in pathogenicity.
 Which is the most likely conclusion about gene C?
Which is the most likely conclusion about gene C?A) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Salmonella strain 1.
B) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Salmonella strain 2.
C) It may be involved in pathogenicity and was acquired from Shigella.
D) It may be involved in pathogenicity, and its origin is unclear.
E) It is unlikely to be involved in pathogenicity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Refer to the figure showing the use of transposons as mutagens in Mycoplasma genitalium. 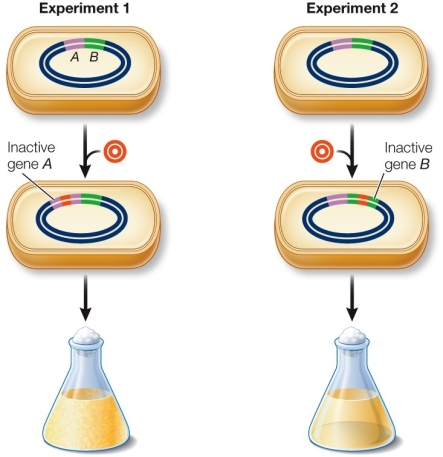 The transposon mutagenesis procedure shown in the figure
The transposon mutagenesis procedure shown in the figure
A) shows that all genes in Mycoplasma genitalium are essential for life.
B) is highly specific for the genes mutated.
C) results in a high percentage of mutant phenotypes when insertion of the transposable element is intergenic.
D) shows that many genes in M. genitalium are not essential for life.
E) cannot disrupt RNA genes.
 The transposon mutagenesis procedure shown in the figure
The transposon mutagenesis procedure shown in the figureA) shows that all genes in Mycoplasma genitalium are essential for life.
B) is highly specific for the genes mutated.
C) results in a high percentage of mutant phenotypes when insertion of the transposable element is intergenic.
D) shows that many genes in M. genitalium are not essential for life.
E) cannot disrupt RNA genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The most striking difference between the genomes of E.coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae is that the yeast genome contains many more genes devoted to
A) metabolism.
B) membrane transport.
C) DNA replication, repair, and recombination.
D) targeting proteins to organelles.
E) energy production and storage.
A) metabolism.
B) membrane transport.
C) DNA replication, repair, and recombination.
D) targeting proteins to organelles.
E) energy production and storage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When eukaryotic genomes and prokaryotic genomes are compared,
A) eukaryotic genomes tend to be smaller than prokaryotic genomes.
B) eukaryotic genomes tend to have fewer regulatory sequences than prokaryotic genomes.
C) the percentage of the genome devoted to coding sequences in eukaryotic genomes is lower than in prokaryotic genomes.
D) eukaryotic genomes have transposons, but prokaryotic genomes do not.
E) in eukaryotic genomes, there is a single origin of replication on each chromosome.
A) eukaryotic genomes tend to be smaller than prokaryotic genomes.
B) eukaryotic genomes tend to have fewer regulatory sequences than prokaryotic genomes.
C) the percentage of the genome devoted to coding sequences in eukaryotic genomes is lower than in prokaryotic genomes.
D) eukaryotic genomes have transposons, but prokaryotic genomes do not.
E) in eukaryotic genomes, there is a single origin of replication on each chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which technique is least likely to be associated with metagenomics?
A) Bacterial culture techniques
B) High-throughput sequencing
C) Comparative genomics
D) PCR
E) Sampling from the field
A) Bacterial culture techniques
B) High-throughput sequencing
C) Comparative genomics
D) PCR
E) Sampling from the field

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Refer to the figure showing microbial DNA being sequenced and analyzed. 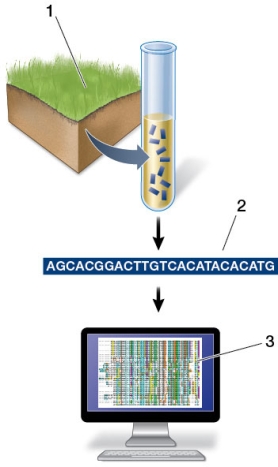 Studies like these would be most useful for questions related to
Studies like these would be most useful for questions related to
A) the metabolome.
B) proteomics.
C) metagenomics.
D) bacterial artificial chromosomes.
E) determining minimal genome size.
 Studies like these would be most useful for questions related to
Studies like these would be most useful for questions related toA) the metabolome.
B) proteomics.
C) metagenomics.
D) bacterial artificial chromosomes.
E) determining minimal genome size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Comparisons of yeast and bacterial cell genomes have revealed that
A) yeast cells have more genes devoted to the basic functions of survival than bacteria do.
B) eukaryotic cells are structurally similar to bacterial cells in terms of complexity.
C) bacteria and yeast are both haploid.
D) the histones of bacteria are very similar to those of yeast.
E) there are more genes for targeting proteins to organelles in yeast than in bacteria.
A) yeast cells have more genes devoted to the basic functions of survival than bacteria do.
B) eukaryotic cells are structurally similar to bacterial cells in terms of complexity.
C) bacteria and yeast are both haploid.
D) the histones of bacteria are very similar to those of yeast.
E) there are more genes for targeting proteins to organelles in yeast than in bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which type of sequence is likely to be found in a eukaryotic genome but not in a prokaryotic genome?
A) Regulatory sequences
B) Coding sequences
C) Open reading frames
D) RNA genes
E) Telomeric sequences
A) Regulatory sequences
B) Coding sequences
C) Open reading frames
D) RNA genes
E) Telomeric sequences

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If a plant were to acquire mobility, such that it could more easily escape adverse conditions and enemies, some genes would be lost over evolutionary time.Which function category would most likely lose genes?
A) Photosynthesis
B) Cell signaling
C) Plant defense
D) Cell growth
E) Metabolism
A) Photosynthesis
B) Cell signaling
C) Plant defense
D) Cell growth
E) Metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Refer to the table showing the properties of five different genomes. 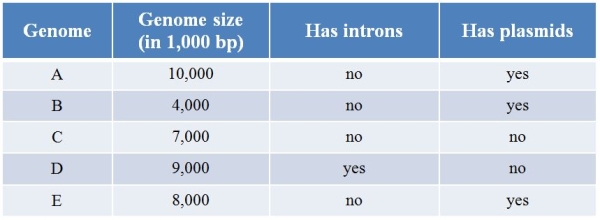 Which genome is most likely eukaryotic?
Which genome is most likely eukaryotic?
A) Genome A
B) Genome B
C) Genome C
D) Genome D
E) Genome E
 Which genome is most likely eukaryotic?
Which genome is most likely eukaryotic?A) Genome A
B) Genome B
C) Genome C
D) Genome D
E) Genome E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Refer to the table showing several prokaryote (bacterial) species (labeled A-E) that have been sequenced, along with the findings of the genes they contain.(Note: "x" marks the species possessing a functional copy of the gene.) Gene 1 is essential for the synthesis of several amino acids.Gene 2 encodes a protein involved in strengthening the cell wall.Gene 3 produces an enzyme that breaks down methane.The functions of the other five genes are currently unknown. 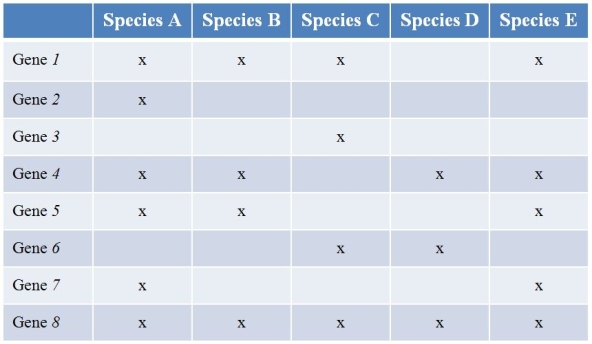 Which gene is most likely to be part of the prokaryotic minimal genome?
Which gene is most likely to be part of the prokaryotic minimal genome?
A) Gene 4
B) Gene 5
C) Gene 6
D) Gene 7
E) Gene 8
 Which gene is most likely to be part of the prokaryotic minimal genome?
Which gene is most likely to be part of the prokaryotic minimal genome?A) Gene 4
B) Gene 5
C) Gene 6
D) Gene 7
E) Gene 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which characteristic is least likely to be useful when choosing the next "model" plant genome to study agriculturally important traits?
A) Small size
B) Little redundancy
C) Good survival in laboratory cultures
D) Rapid life cycle
E) A large number of transposons
A) Small size
B) Little redundancy
C) Good survival in laboratory cultures
D) Rapid life cycle
E) A large number of transposons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which is required for the formation of gene families?
A) Repetitive DNA
B) Pseudogenes
C) Transposable elements
D) Regulatory sequences
E) Gene duplication
A) Repetitive DNA
B) Pseudogenes
C) Transposable elements
D) Regulatory sequences
E) Gene duplication

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Biologists are attempting to develop a small wasp called Nasonia vitripennis into a model system.Which characteristic would most likely limit this wasp's use as a model system for genomic studies?
A) It has a large number of genetic markers and genetic tools.
B) It has a short generation time.
C) It is easily reared in the lab.
D) Its small size permits large numbers of the wasp to fit in a small space.
E) Its biology is rather unusual, and not indicative of many other species.
A) It has a large number of genetic markers and genetic tools.
B) It has a short generation time.
C) It is easily reared in the lab.
D) Its small size permits large numbers of the wasp to fit in a small space.
E) Its biology is rather unusual, and not indicative of many other species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which statement comparing Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster is true?
A) D. melanogaster has a smaller genome.
B) D. melanogaster has fewer genes.
C) D. melanogaster has a higher percentage of the genome that codes for proteins.
D) D. melanogaster has fewer cells.
E) D. melanogaster is a smaller organism.
A) D. melanogaster has a smaller genome.
B) D. melanogaster has fewer genes.
C) D. melanogaster has a higher percentage of the genome that codes for proteins.
D) D. melanogaster has fewer cells.
E) D. melanogaster is a smaller organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Craig Venter, a leader of one of the teams that sequenced the human genome, turned his attention to cataloging the microbial life of the oceans.His studies, which involve PCR amplification of microbial DNA and a sequencing of the PCR products, are part of a field of biology called
A) functional genomics.
B) transposon tagging.
C) proteomics.
D) phenomics.
E) metagenomics.
A) functional genomics.
B) transposon tagging.
C) proteomics.
D) phenomics.
E) metagenomics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Refer to the figure showing microbial DNA being sequenced and analyzed. 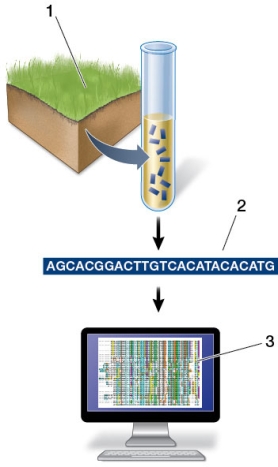 At what step(s) is/are DNA sequenced?
At what step(s) is/are DNA sequenced?
A) Only step 1
B) Only step 2
C) Only step 3
D) Both steps 1 and 2
E) Both steps 2 and 3
 At what step(s) is/are DNA sequenced?
At what step(s) is/are DNA sequenced?A) Only step 1
B) Only step 2
C) Only step 3
D) Both steps 1 and 2
E) Both steps 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Refer to the figure showing the use of transposons as mutagens in Mycoplasma genitalium. 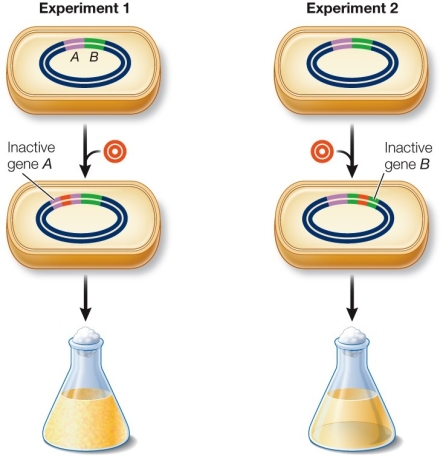 Which statement is true?
Which statement is true?
A) Gene A is essential, because there was growth when gene A was mutagenized.
B) Gene A is not essential, because there was growth when gene A was mutagenized.
C) Gene A is not essential, because there was no growth when gene A was mutagenized.
D) Gene A is essential, because there was no growth when gene A was mutagenized.
E) Whether gene A is essential or not depends on gene B.
 Which statement is true?
Which statement is true?A) Gene A is essential, because there was growth when gene A was mutagenized.
B) Gene A is not essential, because there was growth when gene A was mutagenized.
C) Gene A is not essential, because there was no growth when gene A was mutagenized.
D) Gene A is essential, because there was no growth when gene A was mutagenized.
E) Whether gene A is essential or not depends on gene B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The genome of Arabidopsis is least like that of the typical plant in that the Arabidopsis genome
A) has very few plant defense genes.
B) has very few photosynthesis genes.
C) has much more repetitive DNA.
D) is much smaller.
E) does not have duplicate genes.
A) has very few plant defense genes.
B) has very few photosynthesis genes.
C) has much more repetitive DNA.
D) is much smaller.
E) does not have duplicate genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which technique or tool listed below is best suited to determining the minimal genome of a free-living bacterium?
A) Metagenomics
B) Haplotype mapping
C) Hierarchical sequencing
D) Bacterial artificial chromosomes
E) Selective inactivation of genes
A) Metagenomics
B) Haplotype mapping
C) Hierarchical sequencing
D) Bacterial artificial chromosomes
E) Selective inactivation of genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the most likely difference between the genomes of Drosophila and Caenorhabditis?
A) Caenorhabditis should have more genes devoted to metamorphosis than Drosophila.
B) Caenorhabditis should have fewer genes devoted to metamorphosis than Drosophila.
C) Caenorhabditis should have more genes devoted to DNA replication than Drosophila.
D) Caenorhabditis should have fewer genes devoted to DNA replication than Drosophila.
E) Caenorhabditis should have more genes devoted to general metabolism than Drosophila.
A) Caenorhabditis should have more genes devoted to metamorphosis than Drosophila.
B) Caenorhabditis should have fewer genes devoted to metamorphosis than Drosophila.
C) Caenorhabditis should have more genes devoted to DNA replication than Drosophila.
D) Caenorhabditis should have fewer genes devoted to DNA replication than Drosophila.
E) Caenorhabditis should have more genes devoted to general metabolism than Drosophila.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which field or approach is most likely to lead directly to a reduction in the negative side effects associated with a drug used to treat diabetes?
A) Comparative genomics
B) Metagenomics
C) Metabolomics
D) Pharmacogenomics
E) Selective inactivation
A) Comparative genomics
B) Metagenomics
C) Metabolomics
D) Pharmacogenomics
E) Selective inactivation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The Alu element, which accounts for over 10 percent of the human genome, uses an RNA intermediate and employs a "copy and paste" mechanism of replication.It is not translated.It is thus an example of a
A) LINE.
B) SINE.
C) haplotype.
D) LTR.
E) DNA transposon.
A) LINE.
B) SINE.
C) haplotype.
D) LTR.
E) DNA transposon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Two graduate students are working in the same lab.Jane is investigating the mariner transposon, a DNA transposon.Sam is studying Alu, a SINE.What property is shared by Jane's and Sam's elements?
A) Both are transcribed and translated.
B) Both use an RNA intermediary.
C) Both use a "copy and paste" mechanism.
D) Both use a "cut and paste" mechanism.
E) Both are short tandem repeats.
A) Both are transcribed and translated.
B) Both use an RNA intermediary.
C) Both use a "copy and paste" mechanism.
D) Both use a "cut and paste" mechanism.
E) Both are short tandem repeats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The Denisovans are an extinct species of human that lived in Siberia several tens of thousands of years ago.We now have sequence information from these Denisovans.What evidence would best support Denisovans having had the capacity for speech?
A) The Denisovan MC1R protein variant had the same activity as the typical human variant.
B) The Denisovan MC1R gene resembled the human but not the chimpanzee variant.
C) The Denisovan MC1R gene resembled the chimpanzee but not the human variant.
D) The Denisovan FOXP2 protein variant had lower activity than the typical human variant.
E) The Denisovan FOXP2 gene resembled the human but not the chimpanzee variant.
A) The Denisovan MC1R protein variant had the same activity as the typical human variant.
B) The Denisovan MC1R gene resembled the human but not the chimpanzee variant.
C) The Denisovan MC1R gene resembled the chimpanzee but not the human variant.
D) The Denisovan FOXP2 protein variant had lower activity than the typical human variant.
E) The Denisovan FOXP2 gene resembled the human but not the chimpanzee variant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which statement comparing the human and Neanderthal genomes is true?
A) The Neanderthal genome is only 90 percent identical to human DNA.
B) The higher activity of the MC1R gene in Neanderthals means that some of them may have had pale skin and red hair.
C) Genetic analysis reveals that humans and Neanderthals did interbreed.
D) The Neanderthal FOXP2 gene is not identical to that of humans, which means they were not capable of speech.
E) There are no human DNA sequences that are distinct from Neanderthal DNA sequences due to point mutations.
A) The Neanderthal genome is only 90 percent identical to human DNA.
B) The higher activity of the MC1R gene in Neanderthals means that some of them may have had pale skin and red hair.
C) Genetic analysis reveals that humans and Neanderthals did interbreed.
D) The Neanderthal FOXP2 gene is not identical to that of humans, which means they were not capable of speech.
E) There are no human DNA sequences that are distinct from Neanderthal DNA sequences due to point mutations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which statement about the globin genes is true?
A) They are all continually expressed in humans.
B) The globin genes first arose in invertebrates.
C) Different tissues in mammals will express different globin genes.
D) All the different globin genes carry out the exact same function in humans.
E) All forms of human globins bind oxygen with the same affinity.
A) They are all continually expressed in humans.
B) The globin genes first arose in invertebrates.
C) Different tissues in mammals will express different globin genes.
D) All the different globin genes carry out the exact same function in humans.
E) All forms of human globins bind oxygen with the same affinity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In some species of moths, the genes that make the protein-rich chorion for the eggshell are found in multiple copies in order to maximize the production of chorion at specific times.In this regard, these chorion genes are most like
A) pseudogenes.
B) highly repetitive DNA.
C) rRNA genes.
D) transposons.
E) introns.
A) pseudogenes.
B) highly repetitive DNA.
C) rRNA genes.
D) transposons.
E) introns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Genomic analysis of a fish reveals that this species has dozens of functional copies of a gene that are all nearly identical to one another.What is the most likely explanation for this finding?
A) The different copies of the gene perform different functions.
B) These genes are associated with heterochromatin.
C) A large amount of the gene product is needed in a relatively short time period.
D) These genes are pseudogenes.
E) These genes are transposable elements.
A) The different copies of the gene perform different functions.
B) These genes are associated with heterochromatin.
C) A large amount of the gene product is needed in a relatively short time period.
D) These genes are pseudogenes.
E) These genes are transposable elements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the biggest difference between the human genome and the genomes of model animal species such as Drosophila?
A) The human genome has many times the number of genes.
B) The human genome has many fewer genes.
C) The human genome has a much greater percentage of noncoding DNA.
D) The human genome has a much lower percentage of noncoding DNA.
E) Genes in the human genome undergo much less posttranscriptional modification.
A) The human genome has many times the number of genes.
B) The human genome has many fewer genes.
C) The human genome has a much greater percentage of noncoding DNA.
D) The human genome has a much lower percentage of noncoding DNA.
E) Genes in the human genome undergo much less posttranscriptional modification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A piece of DNA that is 3 kb in length is found in many locations throughout the genome.How would you decide whether this was a LINE or a DNA transposon?
A) If it has more than 10,000 copies in the genome, it is a LINE; if not, it is a DNA transposon.
B) If it has more than 10,000 copies in the genome, it is a DNA transposon; if not, it is a LINE.
C) If it contains the sequence GCTCGATC, it is a LINE; if not, it is a DNA transposon.
D) If it uses an RNA intermediate, it is a LINE; if not, it is a DNA transposon.
E) If it uses a "copy and paste" mechanism, it is a DNA transposon; if not, it is a LINE.
A) If it has more than 10,000 copies in the genome, it is a LINE; if not, it is a DNA transposon.
B) If it has more than 10,000 copies in the genome, it is a DNA transposon; if not, it is a LINE.
C) If it contains the sequence GCTCGATC, it is a LINE; if not, it is a DNA transposon.
D) If it uses an RNA intermediate, it is a LINE; if not, it is a DNA transposon.
E) If it uses a "copy and paste" mechanism, it is a DNA transposon; if not, it is a LINE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which statement best supports the notion that humans and Neanderthals should be considered separate species?
A) Neanderthals have a FOXP2 protein that is identical to the human variant.
B) Some Neanderthals may have had red hair.
C) Neanderthals lived in Europe less than 50,000 years ago.
D) Humans and Neanderthals differ in chromosomal rearrangements.
E) Neanderthal DNA variants have been found in many human populations.
A) Neanderthals have a FOXP2 protein that is identical to the human variant.
B) Some Neanderthals may have had red hair.
C) Neanderthals lived in Europe less than 50,000 years ago.
D) Humans and Neanderthals differ in chromosomal rearrangements.
E) Neanderthal DNA variants have been found in many human populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The hypothetical antianxiety drug Epitome is inactive when taken, but it is activated by the rasputin enzyme a few hours after injection.Alleles 1 and 2 of the gene that encodes rasputin encode enzymes with similar activity levels.Individuals with one or both copies of allele 3, which is very rare, have much higher levels of enzyme activity.Individuals who have both copies of allele 4 have much lower levels of enzyme activity.Heterozygotes of allele 4 have normal levels of enzyme activity.The individuals who are most likely to experience negative side effects from Epitome are those whose genotypes have one copy of allele _______ and one copy of allele _______.
A) 1; 2
B) 2; 3
C) 2; 4
D) 2; 2
E) 4; 4
A) 1; 2
B) 2; 3
C) 2; 4
D) 2; 2
E) 4; 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The Denisovans are an extinct species of human that lived in Siberia several tens of thousands of years ago.We now have sequence information from these Denisovans.What evidence would best support Denisovans having had red hair?
A) The Denisovan MC1R protein variant had greater activity than the typical human variant.
B) The Denisovan MC1R protein variant had lower activity than the typical human variant.
C) The Denisovan FOXP2 protein variant had greater activity than the typical human variant.
D) The Denisovan FOXP2 gene was inactivated.
E) The Denisovan FOXP2 gene underwent accelerated evolution.
A) The Denisovan MC1R protein variant had greater activity than the typical human variant.
B) The Denisovan MC1R protein variant had lower activity than the typical human variant.
C) The Denisovan FOXP2 protein variant had greater activity than the typical human variant.
D) The Denisovan FOXP2 gene was inactivated.
E) The Denisovan FOXP2 gene underwent accelerated evolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which techniques, tools, or activities would be most directly useful in identifying the genetic variants associated with a complex human disease such as schizophrenia?
A) Haplotype mapping
B) Selective inactivation
C) Metagenomics
D) Determining the metabolome
E) Performing a pseudogene screen
A) Haplotype mapping
B) Selective inactivation
C) Metagenomics
D) Determining the metabolome
E) Performing a pseudogene screen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
As organisms increase in complexity from yeasts to fruit flies to humans, the number of protein-coding genes in the genome increases _______ than the number of nucleotides, and the proportion of the genome that codes for proteins _______.
A) more; greatly increases
B) more; greatly decreases
C) less; greatly increases
D) less; roughly stays the same
E) less; greatly decreases
A) more; greatly increases
B) more; greatly decreases
C) less; greatly increases
D) less; roughly stays the same
E) less; greatly decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What percentage of the human genome is DNA that codes for proteins?
A) Less than 5 percent
B) Between 5 and 15 percent
C) Between 15 and 25 percent
D) Between 25 and 40 percent
E) Over 40 percent
A) Less than 5 percent
B) Between 5 and 15 percent
C) Between 15 and 25 percent
D) Between 25 and 40 percent
E) Over 40 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In which species or population would haplotype mapping be particularly challenging or practically impossible?
A) A salamander species that has a particularly large genome size
B) Dogs, because of the large number of breeds
C) Pufferfish, which have a relatively small genome size (for a vertebrate)
D) Cheetahs, because they have extraordinarily little genetic diversity
E) A species of ant that has a large number of chromosomes
A) A salamander species that has a particularly large genome size
B) Dogs, because of the large number of breeds
C) Pufferfish, which have a relatively small genome size (for a vertebrate)
D) Cheetahs, because they have extraordinarily little genetic diversity
E) A species of ant that has a large number of chromosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which statement comparing the human genome to those of invertebrates such as Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster is true?
A) A larger fraction of DNA in the human genome is for coding proteins.
B) The human genome has more than ten times the number of genes.
C) The average human gene codes for more proteins than the average invertebrate gene.
D) Human genes, unlike invertebrate genes, code for a single protein.
E) Only human genes are evenly distributed over the genome.
A) A larger fraction of DNA in the human genome is for coding proteins.
B) The human genome has more than ten times the number of genes.
C) The average human gene codes for more proteins than the average invertebrate gene.
D) Human genes, unlike invertebrate genes, code for a single protein.
E) Only human genes are evenly distributed over the genome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Opsin genes are involved in vision.Which circumstance would most likely lead to the evolution of pseudogenes in the opsins of a salamander?
A) Living in caves
B) The presence of a new fish predator
C) The presence of a new colorful prey species
D) Selection for faster development
E) Selection for slower development
A) Living in caves
B) The presence of a new fish predator
C) The presence of a new colorful prey species
D) Selection for faster development
E) Selection for slower development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What is the most likely explanation for the abundance of transposons in eukaryotic genomes?
A) They are needed to provide mutations.
B) They are genomic parasites.
C) They are needed to increase genetic recombination.
D) They assist in the process of DNA repair.
E) They provide reverse transcriptase.
A) They are needed to provide mutations.
B) They are genomic parasites.
C) They are needed to increase genetic recombination.
D) They assist in the process of DNA repair.
E) They provide reverse transcriptase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



