Deck 20: Mechanisms of Evolution
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/243
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Mechanisms of Evolution
1
Which vegetable was produced from wild mustard, Brassica oleracea, through continued selection for larger stems and flowers?
A) Kale
B) Brussels sprouts
C) Cabbage
D) Cauliflower
E) Broccoli
A) Kale
B) Brussels sprouts
C) Cabbage
D) Cauliflower
E) Broccoli
E
2
Which phrase best describes natural selection?
A) The differential survival and reproduction of individuals
B) Chance variations in traits
C) The processes that lead individuals to resemble their parents
D) The potential for all species to increase rapidly in number
E) Individuals evolving in response to environmental change
A) The differential survival and reproduction of individuals
B) Chance variations in traits
C) The processes that lead individuals to resemble their parents
D) The potential for all species to increase rapidly in number
E) Individuals evolving in response to environmental change
A
3
The graph shows the range of variation among population members for a trait determined by multiple genes. 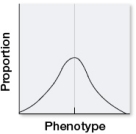 Suppose that there were no genetic component to this trait.If this population were subject to stabilizing selection for several generations, which distributions would be most likely to result? Assume that the environment stayed the same.
Suppose that there were no genetic component to this trait.If this population were subject to stabilizing selection for several generations, which distributions would be most likely to result? Assume that the environment stayed the same. 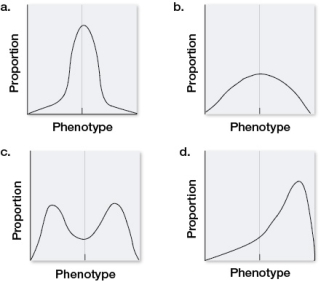
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) None of the above; there would be no change in the distribution.
 Suppose that there were no genetic component to this trait.If this population were subject to stabilizing selection for several generations, which distributions would be most likely to result? Assume that the environment stayed the same.
Suppose that there were no genetic component to this trait.If this population were subject to stabilizing selection for several generations, which distributions would be most likely to result? Assume that the environment stayed the same. 
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) None of the above; there would be no change in the distribution.
E
4
Suppose mutation and selection no longer occurred in a small, isolated population of nematodes.Which process would most likely continue operating, and what would be the most likely effect on the extent of genetic variation?
A) Gene flow would lead to an increase in genetic variation.
B) Gene flow would lead to a decrease in genetic variation.
C) Genetic drift would lead to an increase in genetic variation.
D) Genetic drift would lead to a decrease in genetic variation.
E) Genetic drift would operate but would have no effect on genetic variation.
A) Gene flow would lead to an increase in genetic variation.
B) Gene flow would lead to a decrease in genetic variation.
C) Genetic drift would lead to an increase in genetic variation.
D) Genetic drift would lead to a decrease in genetic variation.
E) Genetic drift would operate but would have no effect on genetic variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Yeast cells are sequenced periodically to examine them for new mutations.The table shows the results. 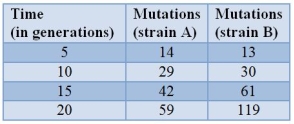 What is the approximate mutation rate per generation for strain A?
What is the approximate mutation rate per generation for strain A?
A) 3
B) 6
C) 14
D) 43
E) 59
 What is the approximate mutation rate per generation for strain A?
What is the approximate mutation rate per generation for strain A?A) 3
B) 6
C) 14
D) 43
E) 59

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Polydactyly (having more than five fingers on a hand) is much more common in some isolated human populations than it is elsewhere.This is most likely an example of a(n) _______, which is due to the evolutionary mechanism called _______.
A) founder effect; gene flow
B) founder effect; genetic drift
C) adaptation; gene flow
D) genetic ratchet; gene flow
E) genetic ratchet; genetic drift
A) founder effect; gene flow
B) founder effect; genetic drift
C) adaptation; gene flow
D) genetic ratchet; gene flow
E) genetic ratchet; genetic drift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The artificial selection experiments with bristle numbers in Drosophila illustrated which generality?
A) In such experiments, it is difficult to obtain individuals with traits that fall outside the range found in the original population.
B) Populations often contain considerable genetic variation upon which selection can operate.
C) Such experiments usually take thousands of generations to achieve their results.
D) Mutations occur to suit the needs of the population.
E) New species can be created via artificial selection.
A) In such experiments, it is difficult to obtain individuals with traits that fall outside the range found in the original population.
B) Populations often contain considerable genetic variation upon which selection can operate.
C) Such experiments usually take thousands of generations to achieve their results.
D) Mutations occur to suit the needs of the population.
E) New species can be created via artificial selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If variation at a given locus has no effect on the phenotypes of individuals, which evolutionary process will still occur at that locus?
A) Genetic drift
B) Natural selection
C) Nonrandom mating
D) Purifying selection
E) Positive selection
A) Genetic drift
B) Natural selection
C) Nonrandom mating
D) Purifying selection
E) Positive selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which two evolutionary processes would most likely act in opposite ways regarding their effects on the extent of genetic variation in a population?
A) Mutation and gene flow
B) Genetic drift and directional selection
C) Mutation and diversifying selection
D) Gene flow and diversifying selection
E) Mutation and directional selection
A) Mutation and gene flow
B) Genetic drift and directional selection
C) Mutation and diversifying selection
D) Gene flow and diversifying selection
E) Mutation and directional selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Different populations of mice that were previously isolated now experience gene flow.What is the most likely outcome after several generations?
A) The populations will become more genetically similar to one another.
B) The populations will become less genetically similar to one another.
C) The total amount of genetic variation across all of the populations will increase.
D) The total amount of genetic variation across all of the populations will decrease.
E) A founder effect will occur.
A) The populations will become more genetically similar to one another.
B) The populations will become less genetically similar to one another.
C) The total amount of genetic variation across all of the populations will increase.
D) The total amount of genetic variation across all of the populations will decrease.
E) A founder effect will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
High-throughput sequencing reveals that ten new mutations have occurred in the coding regions of genes in an individual bat.If the coding regions of this bat comprise 100 million nucleotides per haploid genome, what is the mutation rate per nucleotide?
A) 5 per billion
B) 10 per billion
C) 50 per billion
D) 5 per million
E) 10 per million
A) 5 per billion
B) 10 per billion
C) 50 per billion
D) 5 per million
E) 10 per million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the main difference between Darwin and Wallace with respect to their contributions to evolutionary biology?
A) Only Darwin had been a naturalist and had studied animals and plants in their natural settings.
B) Only Wallace had been a naturalist and had studied animals and plants in their natural settings.
C) Darwin presented more extensive evidence in support of evolution than Wallace.
D) Darwin developed a mathematical model of evolution.
E) Wallace developed a mathematical model of evolution.
A) Only Darwin had been a naturalist and had studied animals and plants in their natural settings.
B) Only Wallace had been a naturalist and had studied animals and plants in their natural settings.
C) Darwin presented more extensive evidence in support of evolution than Wallace.
D) Darwin developed a mathematical model of evolution.
E) Wallace developed a mathematical model of evolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The haploid human genome contains about 3 billion bp.Given a mutation rate of 5 × 10-9, how many new mutations would we expect on average in each diploid individual?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 15
D) 30
E) 60
A) 1
B) 3
C) 15
D) 30
E) 60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which statement about Darwin is true?
A) Even as a youth he recognized that life evolves.
B) He published his observations about evolution soon after the HMS Beagle arrived in England.
C) He recognized that animals on the Galápagos Islands were all identical to those on the mainland.
D) He had a keen interest in geology.
E) He was the first to present evidence that life has evolved.
A) Even as a youth he recognized that life evolves.
B) He published his observations about evolution soon after the HMS Beagle arrived in England.
C) He recognized that animals on the Galápagos Islands were all identical to those on the mainland.
D) He had a keen interest in geology.
E) He was the first to present evidence that life has evolved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Due to various causes, including DDT poisoning, the population size of whooping cranes was reduced to about a dozen during the 1970s.The population size has since rebounded, and there are now hundreds of whooping cranes.Which feature would not be expected in the current populations of whooping cranes?
A) Very low levels of genetic variation
B) Very few heterozygous individuals
C) Differences from historical populations in terms of allele frequencies
D) Considerable genetic polymorphism
E) A bottleneck effect
A) Very low levels of genetic variation
B) Very few heterozygous individuals
C) Differences from historical populations in terms of allele frequencies
D) Considerable genetic polymorphism
E) A bottleneck effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which understanding do modern biologists have that Darwin did not have?
A) The tendency of individuals to resemble their parents
B) The common ancestry of species that exist today
C) The details of genetic inheritance
D) The operation of natural selection on changes in species over time
E) The greater similarity of species in temperate and tropical regions of South America than of species in temperate regions of South America and Europe
A) The tendency of individuals to resemble their parents
B) The common ancestry of species that exist today
C) The details of genetic inheritance
D) The operation of natural selection on changes in species over time
E) The greater similarity of species in temperate and tropical regions of South America than of species in temperate regions of South America and Europe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Two populations of raccoons are similar in most respects, but the population on the east side of a river is much smaller than that on the west side.There is little gene flow between the populations.Which statement about these populations is most accurate?
A) The population on the west side of the river should experience more fluctuations in allele frequency due to genetic drift.
B) The population on the east side of the river should experience more fluctuations in allele frequency due to genetic drift.
C) The population on the west side of the river should have more fluctuations in allele frequency because it will experience a higher mutation rate.
D) The population on the east side of the river should have more fluctuations in allele frequency because it will experience a higher mutation rate.
E) The populations should experience similar degrees of fluctuations in allele frequency because mutation and genetic drift should affect them in the same way.
A) The population on the west side of the river should experience more fluctuations in allele frequency due to genetic drift.
B) The population on the east side of the river should experience more fluctuations in allele frequency due to genetic drift.
C) The population on the west side of the river should have more fluctuations in allele frequency because it will experience a higher mutation rate.
D) The population on the east side of the river should have more fluctuations in allele frequency because it will experience a higher mutation rate.
E) The populations should experience similar degrees of fluctuations in allele frequency because mutation and genetic drift should affect them in the same way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Biologists recently discovered that black wolves got their coat color from exchanging genes with dogs.This is an example of
A) genetic drift.
B) gene pools.
C) gene flow.
D) a founder effect.
E) an adaptation.
A) genetic drift.
B) gene pools.
C) gene flow.
D) a founder effect.
E) an adaptation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose there are three isolated populations of a beetle: population A has had a constant population size of 10,000, population B has had a constant population size of 1,000, and population C has had a constant population size of 100.We would most expect to see an increase in the frequency of deleterious alleles in population _______ due to _______.
A) A; genetic drift
B) A; purifying selection
C) B; purifying selection
D) C; genetic drift
E) C; gene flow
A) A; genetic drift
B) A; purifying selection
C) B; purifying selection
D) C; genetic drift
E) C; gene flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A cricket has a diploid genome of 1.2 billion bp.Assume that there are about 200,000 individuals in the population and that the mutation rate is 1 per 100 million bp.About how many new mutations will occur in each generation of the population of crickets?
A) 1.2
B) 12
C) 200,000
D) 1 million
E) 2.4 million
A) 1.2
B) 12
C) 200,000
D) 1 million
E) 2.4 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In a population of sea otters, the frequency of the alpha allele at locus Y6 is 0.8.If the population has 400 individuals, what is the expected number of alpha alleles in the population?
A) 320
B) 400
C) 480
D) 640
E) 800
A) 320
B) 400
C) 480
D) 640
E) 800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which statement about the relationship between genotype and phenotype is true?
A) A given genotype always produces a specific phenotype.
B) Genotype alone determines phenotype.
C) A particular phenotype can be produced by more than one genotype.
D) The phenotypic expression of dominance makes the study of the genetic basis of natural selection easy.
E) The genotype is the physical expression of an organism's genes.
A) A given genotype always produces a specific phenotype.
B) Genotype alone determines phenotype.
C) A particular phenotype can be produced by more than one genotype.
D) The phenotypic expression of dominance makes the study of the genetic basis of natural selection easy.
E) The genotype is the physical expression of an organism's genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Two populations of mice exist on either side of a river.After a bridge is constructed across the river, the two populations come to resemble each other more.What is the most likely explanation for this?
A) Stabilizing selection
B) Directional selection
C) Gene flow
D) Genetic drift
E) Nonrandom mating
A) Stabilizing selection
B) Directional selection
C) Gene flow
D) Genetic drift
E) Nonrandom mating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which statement about mutations is false?
A) Mutation rates are very low for most loci in most organisms.
B) Mutations are random with respect to the adaptive needs of organisms.
C) Most mutations are either harmful or neutral.
D) Only rarely does a human individual carry a new mutation in his or her genome.
E) A neutral mutation is one that neither benefits nor harms its carrier.
A) Mutation rates are very low for most loci in most organisms.
B) Mutations are random with respect to the adaptive needs of organisms.
C) Most mutations are either harmful or neutral.
D) Only rarely does a human individual carry a new mutation in his or her genome.
E) A neutral mutation is one that neither benefits nor harms its carrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In Mendel's peas, tall and short plant variants resulted from differences at a single genetic locus, with tall being dominant to short.The height of the plant is called its
A) allele.
B) gene pool.
C) phenotype.
D) genotype.
E) adaptation.
A) allele.
B) gene pool.
C) phenotype.
D) genotype.
E) adaptation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In Mendel's peas, tall and short plant variants resulted from differences at a single genetic locus, with tall being dominant to short.The differences between the tall and short plants were caused by their different
A) alleles.
B) gene pools.
C) alleles and genotypes.
D) alleles and gene pools.
E) None of the above
A) alleles.
B) gene pools.
C) alleles and genotypes.
D) alleles and gene pools.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which statement about genetic drift as an evolutionary factor is true?
A) It is more potent in a population with small numbers than in a population with large numbers.
B) It is responsible for the selection of mutations.
C) It is connected to the movements of alleles between populations of a single species.
D) Its strength is proportional to the size of a population: the larger the population, the greater the force.
E) It has the same effect as gene flow.
A) It is more potent in a population with small numbers than in a population with large numbers.
B) It is responsible for the selection of mutations.
C) It is connected to the movements of alleles between populations of a single species.
D) Its strength is proportional to the size of a population: the larger the population, the greater the force.
E) It has the same effect as gene flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Male earwigs that are DD at a locus have greater success in mating than those that are Dd or dd.Which type of selection is operating?
A) Frequency-dependent
B) Stabilizing
C) Diversifying
D) Sexual
E) Directional
A) Frequency-dependent
B) Stabilizing
C) Diversifying
D) Sexual
E) Directional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Malte Andersson's study of widowbirds demonstrated that
A) females prefer males with unaltered tails.
B) the preferences of females change according to the season.
C) sexually selected traits have no benefits or costs to survivorship.
D) long tails help males compete physically with other males.
E) females prefer males with longer-than-average tails.
A) females prefer males with unaltered tails.
B) the preferences of females change according to the season.
C) sexually selected traits have no benefits or costs to survivorship.
D) long tails help males compete physically with other males.
E) females prefer males with longer-than-average tails.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The ultimate origin of genetic variation is
A) genetic drift.
B) mutation.
C) natural selection.
D) a founder effect.
E) nonrandom mating.
A) genetic drift.
B) mutation.
C) natural selection.
D) a founder effect.
E) nonrandom mating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In a population of tree swallows, 18 individuals are homozygous for the c4 allele, 22 individuals are heterozygous for the allele, and 10 individuals lack the allele.What is the frequency of the c4 allele?
A) 0.29
B) 0.36
C) 0.40
D) 0.58
E) 0.80
A) 0.29
B) 0.36
C) 0.40
D) 0.58
E) 0.80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose variants at a single locus affect wing length in a species of crickets, with homozygotes for the L allele having long wings, homozygotes for the l allele having short wings, and heterozygotes having wings of intermediate length.In one population of 600 individuals, 400 have long wings, 160 have intermediate-length wings, and 40 have short wings.What is the frequency of the L allele?
A) 0.2
B) 0.35
C) 0.7
D) 0.8
E) 0.96
A) 0.2
B) 0.35
C) 0.7
D) 0.8
E) 0.96

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If there are only two alleles at a given locus and the frequency of one allele is 0.6, what is the frequency of the other allele?
A) -0.6
B) 0
C) 0.4
D) 0.6
E) 1
A) -0.6
B) 0
C) 0.4
D) 0.6
E) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A small population of sawflies that was once connected to a larger population but is now isolated is no longer experiencing
A) enhanced genetic drift.
B) gene flow.
C) reproductive isolation.
D) natural selection.
E) genotypic equilibrium.
A) enhanced genetic drift.
B) gene flow.
C) reproductive isolation.
D) natural selection.
E) genotypic equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What was Darwin's explanation for the evolution of bright colors and other apparently useless (and potentially deleterious) but conspicuous characters in males of many species?
A) Sexual selection
B) Genetic drift
C) Stabilizing selection
D) Disruptive selection
E) Gene flow
A) Sexual selection
B) Genetic drift
C) Stabilizing selection
D) Disruptive selection
E) Gene flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Three different alleles (b1, b2, and b3) at the b locus exist in a hypothetical population of juniper trees.If the frequency of b1 is 0.4, what can be said about the frequency of b3?
A) It cannot be less than 0.4.
B) It cannot be greater than 0.6.
C) It is 0.3.
D) It is 0.
E) More information is required to answer this question.
A) It cannot be less than 0.4.
B) It cannot be greater than 0.6.
C) It is 0.3.
D) It is 0.
E) More information is required to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Male earwigs that are DD at a locus have greater success in mating than those that are Dd or dd.Which statement is correct?
A) DD is an allele.
B) dd is an allele.
C) Dd is a genotype.
D) There are two genotypes in this population.
E) There are three alleles in this population.
A) DD is an allele.
B) dd is an allele.
C) Dd is a genotype.
D) There are two genotypes in this population.
E) There are three alleles in this population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Yeast cells are sequenced periodically to examine them for new mutations.The table shows the results. 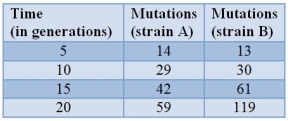 In strain, mutations are accumulating at a(n)
In strain, mutations are accumulating at a(n)
A) linear rate of about 3 per generation.
B) linear rate of about 6 per generation.
C) linear rate of about 30 per generation.
D) accelerating (faster than linear) rate.
E) decelerating (slower than linear) rate.
 In strain, mutations are accumulating at a(n)
In strain, mutations are accumulating at a(n)A) linear rate of about 3 per generation.
B) linear rate of about 6 per generation.
C) linear rate of about 30 per generation.
D) accelerating (faster than linear) rate.
E) decelerating (slower than linear) rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Yeast cells are sequenced periodically to examine them for new mutations.The table shows the results. 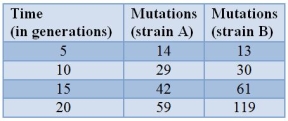 Assuming the mutation rate remains the same and mutations accumulate linearly, about how many mutations should there be in strain A after 50 generations?
Assuming the mutation rate remains the same and mutations accumulate linearly, about how many mutations should there be in strain A after 50 generations?
A) 50
B) 150
C) 300
D) 590
E) 700
 Assuming the mutation rate remains the same and mutations accumulate linearly, about how many mutations should there be in strain A after 50 generations?
Assuming the mutation rate remains the same and mutations accumulate linearly, about how many mutations should there be in strain A after 50 generations?A) 50
B) 150
C) 300
D) 590
E) 700

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is not an example of adaptation?
A) A plant population that is very drought-resistant due to the action of natural selection
B) The process by which a plant population becomes drought-resistant
C) The increased ability of an individual plant (above baseline) to withstand further drought after it has received a heat shock, which causes the expression of specific proteins that enable more efficient use of water
D) A mammal species that has evolved an increased ability to store water through the operation of natural selection
E) A mammal species that has evolved measures to use water more efficiently through the operation of natural selection
A) A plant population that is very drought-resistant due to the action of natural selection
B) The process by which a plant population becomes drought-resistant
C) The increased ability of an individual plant (above baseline) to withstand further drought after it has received a heat shock, which causes the expression of specific proteins that enable more efficient use of water
D) A mammal species that has evolved an increased ability to store water through the operation of natural selection
E) A mammal species that has evolved measures to use water more efficiently through the operation of natural selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose that a particular species of flowering plant that lives only one year can produce red, pink, or white blossoms, depending on its genotype: AA, Aa, and aa produce, respectively, red, pink, and white blossoms.Biologists studying a population of this species count 300 red-flowering, 600 pink-flowering, and 800 white-flowering plants.In a census in the same area the following year, biologists find a population with 600 red-flowering, 900 pink-flowering, and 1,000 white-flowering plants.Which color has the highest fitness?
A) Red has the highest fitness.
B) White has the highest fitness.
C) Pink has the highest fitness.
D) Pink and white have higher fitnesses than red.
E) All colors have equal fitness.
A) Red has the highest fitness.
B) White has the highest fitness.
C) Pink has the highest fitness.
D) Pink and white have higher fitnesses than red.
E) All colors have equal fitness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
You discover a population of mustard plants and find it to be at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium with respect to the R locus.Suppose there are two alleles at this locus and the frequency of one of those alleles (the r-6 allele) is 0.2.Of the individuals that carry at least one r-6 allele, what fraction will be heterozygotes?
A) 1/9
B) 1/5
C) 1/3
D) 4/5
E) 8/9
A) 1/9
B) 1/5
C) 1/3
D) 4/5
E) 8/9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which statement about Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium is true?
A) It explains why dominant alleles do not necessarily replace recessive alleles in a population.
B) It applies only to populations in which there is gene flow.
C) It assumes that populations are small.
D) It assumes that individuals prefer to mate with individuals with certain genotypes.
E) It assumes that selection is occurring.
A) It explains why dominant alleles do not necessarily replace recessive alleles in a population.
B) It applies only to populations in which there is gene flow.
C) It assumes that populations are small.
D) It assumes that individuals prefer to mate with individuals with certain genotypes.
E) It assumes that selection is occurring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Several populations of copepods are sampled for variation at the G locus.Population A is found to be 30 percent GG, 60 percent Gg, and 10 percent gg.Population B is 62 percent GG, 36 percent Gg, and 2 percent gg.Population C is 30 percent GG, 40 percent Gg, and 30 percent gg.Which of these populations shows a heterozygote deficiency?
A) Only population A
B) Only population B
C) Only population C
D) Both populations A and B
E) Both populations B and C
A) Only population A
B) Only population B
C) Only population C
D) Both populations A and B
E) Both populations B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If a population is monomorphic for an allele at one locus, the population is _______ for that allele, and the frequency of the allele is _______.
A) homozygous; 1
B) fixed; 0.5
C) heterozygous; 0
D) fixed; 1
E) heterozygous; 1
A) homozygous; 1
B) fixed; 0.5
C) heterozygous; 0
D) fixed; 1
E) heterozygous; 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In a population of 200 individuals at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, 72 are homozygous recessive for the character of eye color (cc).One hundred individuals from this population die from a fatal disease.Thirty-six of the survivors are homozygous recessive.In the original population, the frequency of the dominant allele was
A) 0.16.
B) 0.36.
C) 0.40.
D) 0.48.
E) 0.60.
A) 0.16.
B) 0.36.
C) 0.40.
D) 0.48.
E) 0.60.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which mode(s) of selection lead(s) to a reduction in variation but no change in the mean?
A) Stabilizing selection only
B) Directional selection only
C) Disruptive selection only
D) Both stabilizing and disruptive selection
E) Both directional and disruptive selection
A) Stabilizing selection only
B) Directional selection only
C) Disruptive selection only
D) Both stabilizing and disruptive selection
E) Both directional and disruptive selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In a population of 200 individuals at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, 72 were homozygous recessive for the character of eye color (cc).One hundred individuals from this population died from a fatal disease.If 36 of the survivors are homozygous recessive, how many heterozygous individuals are in the new population?
A) 16
B) 36
C) 40
D) 48
E) 60
A) 16
B) 36
C) 40
D) 48
E) 60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Following a flood, migration from neighboring populations alters genotypic frequencies of a population of river bottom midges.Assuming that the conditions for Hardy-Weinberg subsequently will be met, how many generations of random mating will be required to restore the genotypic frequencies to Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A) 1
B) 2
C) Between 3 and 10
D) Between 11 and 20
E) More than 20
A) 1
B) 2
C) Between 3 and 10
D) Between 11 and 20
E) More than 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Suppose variants at a single locus affect wing length in a species of crickets, with homozygotes for the L allele having long wings, homozygotes for the l allele having short wings, and heterozygotes having wings of intermediate length.In one population of 600 individuals, 400 have long wings, 160 have intermediate-lengths wings, and 40 have short wings.What is the expected number of individuals with long wings under Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A) 216
B) 300
C) 384
D) 400
E) 480
A) 216
B) 300
C) 384
D) 400
E) 480

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose a population of flour beetles has 1,000 individuals.Normally the beetles are red; however, this population is polymorphic for a mutant autosomal body color, black, designated by bb.Red is dominant to black, so BB and Bb genotypes result in red beetles.Assume the population is at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, with equal frequencies of the two alleles.What would be the expected red and black allele frequencies if 1,000 black individuals migrated into the population?
A) 0.75 red, 0.25 black
B) 0.33 red, 0.67 black
C) 0.25 red, 0.75 black
D) All black
E) None of the above because the population would still be at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
A) 0.75 red, 0.25 black
B) 0.33 red, 0.67 black
C) 0.25 red, 0.75 black
D) All black
E) None of the above because the population would still be at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In Mendel's crosses with peas, seed shape is due to a single allele, and the allele for smooth seeds is dominant to the allele for wrinkled.If 20 percent of a population has the smooth allele, _______ percent of the plants should have wrinkled seeds at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
A) 4
B) 20
C) 36
C) 80
D) 64
A) 4
B) 20
C) 36
C) 80
D) 64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In a population of 200 individuals at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, 72 are homozygous recessive for the character of eye color (cc).One hundred individuals from this population die from a fatal disease.Thirty-six of the survivors are homozygous recessive.In the new population, the frequency of the dominant allele is
A) 0.16.
B) 0.36.
C) 0.40.
D) 0.48.
E) 0.60.
A) 0.16.
B) 0.36.
C) 0.40.
D) 0.48.
E) 0.60.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which is not a condition for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A) Absence of gene flow
B) Absence of differential survival among genotypes
C) Random mating of individuals with respect to genotype
D) Absence of genetic drift that would cause chance fluctuations of allele frequencies
E) Small population size
A) Absence of gene flow
B) Absence of differential survival among genotypes
C) Random mating of individuals with respect to genotype
D) Absence of genetic drift that would cause chance fluctuations of allele frequencies
E) Small population size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If a population with two alleles is at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and the frequency of one allele is 0.7, what is the heterozygote frequency?
A) 0.21
B) 0.3
C) 0.42
D) 0.7
E) More information is required to answer this question.
A) 0.21
B) 0.3
C) 0.42
D) 0.7
E) More information is required to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Suppose a population of flour beetles has 1,000 individuals.Normally the beetles are red; however, this population is polymorphic for a mutant autosomal body color, black, designated by bb.Red is dominant to black, so BB and Bb genotypes result in red beetles.Assume the population is at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, with equal frequencies of the two alleles.What would be the expected frequencies of the red and black phenotypes?
A) 0.5 red and 0.5 black
B) 0.75 red and 0.25 black
C) 0.25 red and 0.75 black
D) All red
E) More information is required to answer this question.
A) 0.5 red and 0.5 black
B) 0.75 red and 0.25 black
C) 0.25 red and 0.75 black
D) All red
E) More information is required to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose variants at a single locus affect wing length in a species of crickets, with homozygotes for the L allele having long wings, homozygotes for the l allele having short wings, and heterozygotes having wings of intermediate length.In one population of 600 individuals, 400 have long wings, 160 have intermediate-length wings, and 40 have short wings.Is there an excess or a deficiency of heterozygotes in the population with respect to Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? By how many individuals?
A) An excess of 64 individuals
B) An excess of 32 individuals
C) An excess of 16 individuals
D) A deficiency of 16 individuals
E) A deficiency of 32 individuals
A) An excess of 64 individuals
B) An excess of 32 individuals
C) An excess of 16 individuals
D) A deficiency of 16 individuals
E) A deficiency of 32 individuals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Suppose a population of flour beetles has 1,000 individuals.Normally the beetles are red; however, this population is polymorphic for a mutant autosomal body color, black, designated by bb.Red is dominant to black, so BB and Bb genotypes are red.Assume the population is at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, with equal frequencies of the two alleles.What would be the expected frequencies of the homozygous dominant, heterozygous, and homozygous recessive genotypes (in that order) after 100 generations, assuming that no selection or other evolutionary processes were operating?
A) 0.25, 0.5, 0.25
B) 0.75, 0.20, 0.05
C) 0, 0.5, 0.5
D) 0, 0, 1
E) 1, 0, 0
A) 0.25, 0.5, 0.25
B) 0.75, 0.20, 0.05
C) 0, 0.5, 0.5
D) 0, 0, 1
E) 1, 0, 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Suppose a population of flour beetles has 1,000 individuals.Normally the beetles are red; however, this population is polymorphic for a mutant autosomal body color, black, designated by bb.Red is dominant to black, so BB and Bb genotypes are red.Assume the population is at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, with equal frequencies of the two alleles.What would be the allele frequencies if a population bottleneck occurred and only four individuals survived: one female red heterozygote and three black males?
A) 0.125 red, 0.875 black
B) 0.875 red, 0.125 black
C) 0.25 red, 0.75 black
D) 0.75 red, 0.25 black
E) 0.5 red, 0.5 black
A) 0.125 red, 0.875 black
B) 0.875 red, 0.125 black
C) 0.25 red, 0.75 black
D) 0.75 red, 0.25 black
E) 0.5 red, 0.5 black

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In a population of spiders, 40 percent of the individuals are homozygous for the A allele at a locus, and 20 percent are homozygous for the G allele at that locus.If A and G are the only alleles at the locus, then _______ percent of the population is heterozygous, which is ______ heterozygotes than would be expected under Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
A) 30; fewer
B) 30; more
C) 40; fewer
D) 40; more
E) 50; fewer
A) 30; fewer
B) 30; more
C) 40; fewer
D) 40; more
E) 50; fewer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Disruptive selection for body size would most likely occur when
A) there is heterozygote advantage.
B) predators prefer to consume larger individuals.
C) small individuals are more likely to become desiccated.
D) intermediate-sized individuals are less able to find a food source.
E) individuals at either size extreme have difficulty during development.
A) there is heterozygote advantage.
B) predators prefer to consume larger individuals.
C) small individuals are more likely to become desiccated.
D) intermediate-sized individuals are less able to find a food source.
E) individuals at either size extreme have difficulty during development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The table shows the number of offspring produced by genotype at the A locus in three different populations.Assuming all other things are equal, in which population(s) would you expect variation at the A locus to be maintained? 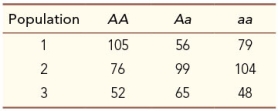
A) Population 1 only
B) Population 2 only
C) Population 3 only
D) Both populations 1 and 2
E) Both populations 1 and 3

A) Population 1 only
B) Population 2 only
C) Population 3 only
D) Both populations 1 and 2
E) Both populations 1 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The numbers of fledged young of female swamp sparrows of different sizes were assayed and are presented in the table. 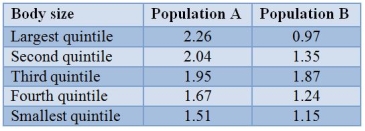 Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What is the most likely response to selection in population B?
Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What is the most likely response to selection in population B?
A) Body size would increase.
B) Body size would decrease.
C) Body size would stay more or less the same, but the variance would increase.
D) Body size would stay more or less the same, but the variance would decrease.
E) None of the above; there is no selection occuring.
 Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What is the most likely response to selection in population B?
Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What is the most likely response to selection in population B?A) Body size would increase.
B) Body size would decrease.
C) Body size would stay more or less the same, but the variance would increase.
D) Body size would stay more or less the same, but the variance would decrease.
E) None of the above; there is no selection occuring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which mode(s) of selection arise(s) when individuals at both extremes of the distribution have high fitness?
A) Stabilizing selection only
B) Directional selection only
C) Disruptive selection only
D) Both stabilizing and disruptive selection
E) Both directional and disruptive selection
A) Stabilizing selection only
B) Directional selection only
C) Disruptive selection only
D) Both stabilizing and disruptive selection
E) Both directional and disruptive selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The frequency of an allele in a population of Drosophila melanogaster changes haphazardly over time, sometimes going up and sometimes going down.In this population, 17 percent had the allele in 1998 and 30 percent had it in 2016.Biologists found no effect of this allele (versus the other alleles in the population) on any phenotypic trait.What is the best explanation for this pattern?
A) The allele is a neutral allele whose frequency is affected by genetic drift.
B) The allele is a neutral allele whose frequency is affected by stabilizing selection.
C) The allele is undergoing Muller's ratchet.
D) The allele is experiencing frequency-dependent selection, and its frequency should decline.
E) The allele is experiencing frequency-dependent selection, and its frequency should increase.
A) The allele is a neutral allele whose frequency is affected by genetic drift.
B) The allele is a neutral allele whose frequency is affected by stabilizing selection.
C) The allele is undergoing Muller's ratchet.
D) The allele is experiencing frequency-dependent selection, and its frequency should decline.
E) The allele is experiencing frequency-dependent selection, and its frequency should increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A sparrow population currently eats seeds that are mostly of medium size.Which condition will most likely lead to more diversifying selection?
A) A decrease in size in the sparrow population
B) More seeds that are either considerably smaller or considerably larger than average, with fewer that are of intermediate size
C) More seeds that are intermediate in size
D) More seeds that are somewhat larger than average and fewer that are smaller than average
E) A reduction in the overall number of seeds, with no change in the distribution
A) A decrease in size in the sparrow population
B) More seeds that are either considerably smaller or considerably larger than average, with fewer that are of intermediate size
C) More seeds that are intermediate in size
D) More seeds that are somewhat larger than average and fewer that are smaller than average
E) A reduction in the overall number of seeds, with no change in the distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A sparrow population currently eats seeds that are mostly of medium size.Which condition will most likely lead to more directional selection?
A) A decrease in population size of the sparrow
B) More seeds that are either considerably smaller or considerably larger than average, with fewer of intermediate size
C) More seeds that are intermediate in size
D) More seeds that are somewhat larger than average and fewer that are smaller than average
E) A reduction in the overall number of seeds, with no change in the distribution
A) A decrease in population size of the sparrow
B) More seeds that are either considerably smaller or considerably larger than average, with fewer of intermediate size
C) More seeds that are intermediate in size
D) More seeds that are somewhat larger than average and fewer that are smaller than average
E) A reduction in the overall number of seeds, with no change in the distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which explanation has not been proposed for the existence of sexual reproduction?
A) Sexual reproduction facilitates repair of damaged DNA.
B) Sexual reproduction promotes the elimination of deleterious mutations.
C) Sexual reproduction accelerates Muller's ratchet.
D) Sexual reproduction creates a great diversity of genetic combinations that allows populations to adapt to the presence of pathogens.
E) Sexual reproduction maintains genetic variation.
A) Sexual reproduction facilitates repair of damaged DNA.
B) Sexual reproduction promotes the elimination of deleterious mutations.
C) Sexual reproduction accelerates Muller's ratchet.
D) Sexual reproduction creates a great diversity of genetic combinations that allows populations to adapt to the presence of pathogens.
E) Sexual reproduction maintains genetic variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which statement about fitness and natural selection is true?
A) The fitness of individuals of a particular phenotype is a function of the probability that such individuals survive, multiplied by the average number of offspring they produce.
B) The fitness of individuals of a particular phenotype is a function of the probability that such individuals survive, divided by the average number of offspring they produce.
C) Changes in the absolute numbers of offspring necessarily lead to changes in allele frequencies from one generation to the next.
D) Natural selection operates directly on the genotype.
E) The fitness of an individual is determined solely by its ability to survive.
A) The fitness of individuals of a particular phenotype is a function of the probability that such individuals survive, multiplied by the average number of offspring they produce.
B) The fitness of individuals of a particular phenotype is a function of the probability that such individuals survive, divided by the average number of offspring they produce.
C) Changes in the absolute numbers of offspring necessarily lead to changes in allele frequencies from one generation to the next.
D) Natural selection operates directly on the genotype.
E) The fitness of an individual is determined solely by its ability to survive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The sizes of eyes in a population of spiders are monitored over several generations.The average eye size does not noticeably change, but the range of variation decreases.Assuming that no other evolutionary processes are occurring, what type of selection is most likely taking place?
A) Frequency-dependent
B) Stabilizing
C) Diversifying
D) Sexual
E) None of the above; selection is not operating.
A) Frequency-dependent
B) Stabilizing
C) Diversifying
D) Sexual
E) None of the above; selection is not operating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The horn sizes in males of a particular beetle have an interesting distribution: the highest frequencies are around 15 millimeters and 30 millimeters, with few individuals in between.Based on this observation, which mode of selection is most likely to be operating on these horns?
A) Stabilizing selection
B) Directional selection
C) Concentrated selection
D) Disruptive selection
E) Purifying selection
A) Stabilizing selection
B) Directional selection
C) Concentrated selection
D) Disruptive selection
E) Purifying selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A benefit of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction is that sexual reproduction
A) generates new combinations of alleles upon which selection can act.
B) breaks up adaptive combinations of genes.
C) produces offspring of two different genders, thus increasing the overall reproductive rate.
D) promotes Muller's ratchet.
E) increases the rate at which females can pass genes on to their offspring.
A) generates new combinations of alleles upon which selection can act.
B) breaks up adaptive combinations of genes.
C) produces offspring of two different genders, thus increasing the overall reproductive rate.
D) promotes Muller's ratchet.
E) increases the rate at which females can pass genes on to their offspring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Muller's ratchet is the
A) breaking down of adaptive combinations of genes by recombination.
B) elimination of deleterious mutations through sexual reproduction.
C) maintenance of genetic variation via disruptive selection.
D) crossing over and independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis.
E) accumulation of deleterious mutations in asexual lineages.
A) breaking down of adaptive combinations of genes by recombination.
B) elimination of deleterious mutations through sexual reproduction.
C) maintenance of genetic variation via disruptive selection.
D) crossing over and independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis.
E) accumulation of deleterious mutations in asexual lineages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The numbers of fledged young of female swamp sparrows of different sizes were assayed and are presented in the table. 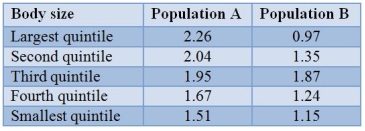 Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What type of selection is most likely occurring in population A? Assume that all other aspects (survival, etc.) are independent of size.
Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What type of selection is most likely occurring in population A? Assume that all other aspects (survival, etc.) are independent of size.
A) Stabilizing
B) Directional
C) Diversifying
D) Sexual
E) None of the above
 Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What type of selection is most likely occurring in population A? Assume that all other aspects (survival, etc.) are independent of size.
Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What type of selection is most likely occurring in population A? Assume that all other aspects (survival, etc.) are independent of size.A) Stabilizing
B) Directional
C) Diversifying
D) Sexual
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The numbers of fledged young of female swamp sparrows of different sizes were assayed and are presented in the table. 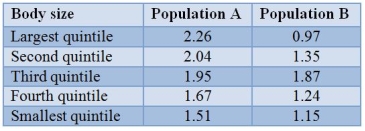 Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What is the most likely response to selection in population A?
Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What is the most likely response to selection in population A?
A) Body size would increase.
B) Body size would decrease.
C) Body size would stay more or less the same, but the variance would increase.
D) Body size would stay more or less the same, but the variance would decrease.
E) None of the above; there is no selection occuring.
 Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What is the most likely response to selection in population A?
Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What is the most likely response to selection in population A?A) Body size would increase.
B) Body size would decrease.
C) Body size would stay more or less the same, but the variance would increase.
D) Body size would stay more or less the same, but the variance would decrease.
E) None of the above; there is no selection occuring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The numbers of fledged young of female swamp sparrows of different sizes were assayed and are presented in the table. 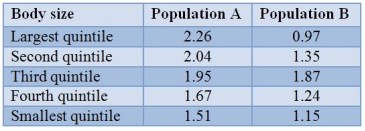 Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What type of selection is most likely occurring in population B? Assume that all other aspects (survival, etc.) are independent of size.
Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What type of selection is most likely occurring in population B? Assume that all other aspects (survival, etc.) are independent of size.
A) Stabilizing
B) Directional
C) Diversifying
D) Sexual
E) None of the above
 Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What type of selection is most likely occurring in population B? Assume that all other aspects (survival, etc.) are independent of size.
Assume that body size is at least partially heritable.What type of selection is most likely occurring in population B? Assume that all other aspects (survival, etc.) are independent of size.A) Stabilizing
B) Directional
C) Diversifying
D) Sexual
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A species of yeast can reproduce either sexually or asexually.Five populations of this yeast were initially asexual but were moved to different environments.Which population would likely evolve sexual reproduction and recombination?
A) Population A, which has a very large population size
B) Population B, which experiences steady temperatures
C) Population C, which has evolved a more efficient DNA repair system
D) Population D, which is in an environment without pathogens
E) Population E, which experiences a rapidly changing environment
A) Population A, which has a very large population size
B) Population B, which experiences steady temperatures
C) Population C, which has evolved a more efficient DNA repair system
D) Population D, which is in an environment without pathogens
E) Population E, which experiences a rapidly changing environment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which mode(s) of selection result(s) in a decrease in variation?
A) Stabilizing selection only
B) Directional selection only
C) Disruptive selection only
D) Both stabilizing and disruptive selection
E) Both directional and stabilizing selection
A) Stabilizing selection only
B) Directional selection only
C) Disruptive selection only
D) Both stabilizing and disruptive selection
E) Both directional and stabilizing selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If the exchange of allele b1 for b2 at the b locus does not affect the fitness of individuals, these alleles can be considered _______ alleles.
A) selected
B) neutral
C) neutered
D) Muller's
E) deleterious
A) selected
B) neutral
C) neutered
D) Muller's
E) deleterious

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The graph shows the range of variation among population members for a trait determined by multiple genes. 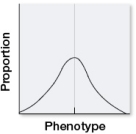 If this population were subject to stabilizing selection for several generations, which, if any, of the distributions shown would be most likely to result?
If this population were subject to stabilizing selection for several generations, which, if any, of the distributions shown would be most likely to result? 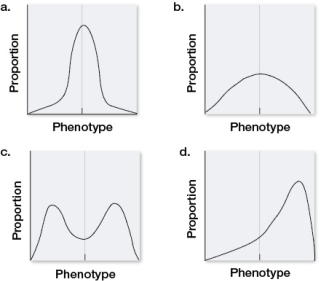
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) None of the above; there would be no change.
 If this population were subject to stabilizing selection for several generations, which, if any, of the distributions shown would be most likely to result?
If this population were subject to stabilizing selection for several generations, which, if any, of the distributions shown would be most likely to result? 
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) None of the above; there would be no change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



