Deck 33: The Plant Body
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/243
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 33: The Plant Body
1
Aboveground epidermal cells secrete a waxy layer called _______, which helps retard water loss from stems and leaves.
A) lignin
B) suberin
C) the cuticle
D) stomata
E) the pericycle
A) lignin
B) suberin
C) the cuticle
D) stomata
E) the pericycle
C
2
A phytomer can be broken down into which three very different parts of a plant?
A) Stem, petiole, and blade
B) Bud, trichome, and blade
C) Axillary bud, node, and internode
D) Petiole, axillary bud, and internode
E) Node, blade, and petiole
A) Stem, petiole, and blade
B) Bud, trichome, and blade
C) Axillary bud, node, and internode
D) Petiole, axillary bud, and internode
E) Node, blade, and petiole
C
3
Plasmodesmata passing between two plant cells must travel through
A) the primary cell wall.
B) the secondary cell wall.
C) the primary cell wall and the secondary cell wall (if present).
D) the secondary cell wall and sometimes the primary cell wall.
E) the apical-basal axis.
A) the primary cell wall.
B) the secondary cell wall.
C) the primary cell wall and the secondary cell wall (if present).
D) the secondary cell wall and sometimes the primary cell wall.
E) the apical-basal axis.
C
4
The polysaccharides that make up the primary cell wall
A) are strong but flexible.
B) form a water-tight matrix.
C) are rigid and allow no further expansion.
D) function independently.
E) are relatively minor contributors to the carbon balance of ecosystems.
A) are strong but flexible.
B) form a water-tight matrix.
C) are rigid and allow no further expansion.
D) function independently.
E) are relatively minor contributors to the carbon balance of ecosystems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A(n) _______ is the point at which a leaf attaches to a stem.
A) internode
B) bud
C) node
D) apical bud
E) petiole
A) internode
B) bud
C) node
D) apical bud
E) petiole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Grasses and other flowering plants with parallel-veined leaves and fibrous or adventitious roots are examples of
A) monocots.
B) gymnosperms.
C) eudicots.
D) magnoliids.
E) Both a and b
A) monocots.
B) gymnosperms.
C) eudicots.
D) magnoliids.
E) Both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The cell wall region between adjoining parenchyma cells, if peeled apart into its constituent layers, would be found to consist of
A) a middle lamella and a secondary cell wall.
B) lignin and cellulose.
C) a primary cell wall and a secondary cell wall.
D) a middle lamella and a primary cell wall.
E) lignin and a middle lamella.
A) a middle lamella and a secondary cell wall.
B) lignin and cellulose.
C) a primary cell wall and a secondary cell wall.
D) a middle lamella and a primary cell wall.
E) lignin and a middle lamella.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The large central vacuoles and rigid walls of plant cells
A) conserve energy.
B) make the plant less attractive to predators.
C) allow the plant to survive temperature extremes.
D) protect the plant from desiccation.
E) promote growth and provide support of the plant.
A) conserve energy.
B) make the plant less attractive to predators.
C) allow the plant to survive temperature extremes.
D) protect the plant from desiccation.
E) promote growth and provide support of the plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which statement about parenchyma cells is false?
A) They are the most common cells in a plant.
B) They may contain chloroplasts.
C) They are commonly used for food storage.
D) They are alive at maturity.
E) They usually have thick cell walls.
A) They are the most common cells in a plant.
B) They may contain chloroplasts.
C) They are commonly used for food storage.
D) They are alive at maturity.
E) They usually have thick cell walls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The main parts of the plant body are the
A) leaf and root systems.
B) root and shoot systems.
C) fruits and flowers.
D) leaves and tubers.
E) tubers and storage roots.
A) leaf and root systems.
B) root and shoot systems.
C) fruits and flowers.
D) leaves and tubers.
E) tubers and storage roots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is not a component of a phytomer?
A) Leaf
B) Root hair
C) Axillary buds
D) Internode
E) All of the above are components of a phytomer.
A) Leaf
B) Root hair
C) Axillary buds
D) Internode
E) All of the above are components of a phytomer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which statement would represent the best rephrasing of the following statement: "The basic body plan of a plant includes a root‒shoot axis."?
A) Plants have roots and shoots.
B) The root and shoot of a plant are connected.
C) The plant body is built of root and shoot systems connected in a linear arrangement.
D) A plant body can have a root system and/or a shoot system.
E) Plants grow via roots and shoots.
A) Plants have roots and shoots.
B) The root and shoot of a plant are connected.
C) The plant body is built of root and shoot systems connected in a linear arrangement.
D) A plant body can have a root system and/or a shoot system.
E) Plants grow via roots and shoots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A newly discovered flowering plant found in an alpine meadow has broad leaves with branched veins.This plant is most likely a
A) monocot.
B) grass.
C) magnoliid.
D) eudicot.
E) gymnosperm.
A) monocot.
B) grass.
C) magnoliid.
D) eudicot.
E) gymnosperm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The bulk of nonwoody root cells are _______ cells.
A) parenchyma
B) sclerenchyma
C) companion
D) collenchyma
E) embryonic
A) parenchyma
B) sclerenchyma
C) companion
D) collenchyma
E) embryonic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
_______ cells perform their primary function when they are dead.
A) Parenchyma
B) Sclerenchyma
C) Collenchyma
D) Companion
E) Tracheid
A) Parenchyma
B) Sclerenchyma
C) Collenchyma
D) Companion
E) Tracheid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A _______ is an undeveloped shoot.
A) node
B) petiole
C) blade
D) bud
E) root
A) node
B) petiole
C) blade
D) bud
E) root

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Refer to the figure showing the basic plant body plan. 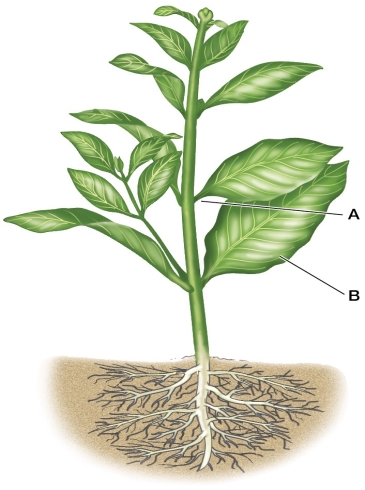 The taproot system shown in the figure indicates that this is a
The taproot system shown in the figure indicates that this is a
A) gymnosperm.
B) fern.
C) eudicot.
D) monocot.
E) magnoliid
 The taproot system shown in the figure indicates that this is a
The taproot system shown in the figure indicates that this is aA) gymnosperm.
B) fern.
C) eudicot.
D) monocot.
E) magnoliid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
One function of the parenchyma tissue in a plant is
A) photosynthesis.
B) to protect the plant.
C) to anchor the plant.
D) water conduction.
E) sugar conduction.
A) photosynthesis.
B) to protect the plant.
C) to anchor the plant.
D) water conduction.
E) sugar conduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The protective outer layer of cells of the plant is called the
A) vascular tissue.
B) endoderm.
C) epidermis.
D) ground tissue.
E) pericycle.
A) vascular tissue.
B) endoderm.
C) epidermis.
D) ground tissue.
E) pericycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Photosynthesis occurs in _______ cells.
A) collenchyma
B) sclerenchyma
C) parenchyma
D) tracheid
E) companion
A) collenchyma
B) sclerenchyma
C) parenchyma
D) tracheid
E) companion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Tracheids, vessel elements, and sclereids are similar in that they all
A) lack secondary cell walls.
B) serve their function when alive.
C) conduct water and minerals.
D) serve their function when dead.
E) have open ends.
A) lack secondary cell walls.
B) serve their function when alive.
C) conduct water and minerals.
D) serve their function when dead.
E) have open ends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In a young root, xylem cells can be observed in the
A) root cap.
B) apical meristem.
C) zone of cell division.
D) zone of cell elongation.
E) zone of cell maturation.
A) root cap.
B) apical meristem.
C) zone of cell division.
D) zone of cell elongation.
E) zone of cell maturation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The region of cell division in a primary root originates
A) in the root cap.
B) in the apical meristem.
C) in the region of elongation.
D) in the area containing differentiated tissues.
E) throughout the root.
A) in the root cap.
B) in the apical meristem.
C) in the region of elongation.
D) in the area containing differentiated tissues.
E) throughout the root.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is responsible for indeterminate growth in plants?
A) Regions of nondividing cells
B) Meristem tissues
C) Epidermis
D) Xylem
E) Vascular tissues
A) Regions of nondividing cells
B) Meristem tissues
C) Epidermis
D) Xylem
E) Vascular tissues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Sieve tube elements are joined to other sieve tube elements by sieve plates.Which statement about sieve plates is true?
A) Their pores are enlargements of meristems.
B) They allow conduction between sieve tube elements through tunnels.
C) They allow for the joining of cytoplasm between adjacent stomata.
D) They contain the organelles of the cell.
E) They are connected to other sieve plates via plasmodesmata.
A) Their pores are enlargements of meristems.
B) They allow conduction between sieve tube elements through tunnels.
C) They allow for the joining of cytoplasm between adjacent stomata.
D) They contain the organelles of the cell.
E) They are connected to other sieve plates via plasmodesmata.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In contrast to sclerenchyma cells, collenchyma cells
A) have more secondary cell wall materials.
B) have more variable shapes.
C) can be found in bundles.
D) provide support to the plant.
E) are more flexible.
A) have more secondary cell wall materials.
B) have more variable shapes.
C) can be found in bundles.
D) provide support to the plant.
E) are more flexible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A leaf skeleton, sometimes used in the art form known as nature printing, is very durable, lasting long after the mesophyll and epidermis have decomposed.This is because of the tough lignified cell walls of the
A) mesophyll cells.
B) guard cells.
C) stomata.
D) epidermal cells.
E) vascular cells.
A) mesophyll cells.
B) guard cells.
C) stomata.
D) epidermal cells.
E) vascular cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Unlike primary growth, secondary growth
A) involves growth in plant diameter.
B) involves growth in plant height.
C) is produced by meristems.
D) involves growth by cell elongation.
E) occurs in all eudicots.
A) involves growth in plant diameter.
B) involves growth in plant height.
C) is produced by meristems.
D) involves growth by cell elongation.
E) occurs in all eudicots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The spines of cactus plants originated from a modification of the same basic plant organ that forms the
A) trunks of coconut trees.
B) leaves of maple trees.
C) runners of strawberry plants.
D) tubers of potato plants.
E) adventitious roots of corn plants.
A) trunks of coconut trees.
B) leaves of maple trees.
C) runners of strawberry plants.
D) tubers of potato plants.
E) adventitious roots of corn plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which cells accomplish the function of water transport in stems?
A) Collenchyma cells
B) Companion cells
C) Parenchyma cells
D) Sclerenchyma cells
E) Vessel elements
A) Collenchyma cells
B) Companion cells
C) Parenchyma cells
D) Sclerenchyma cells
E) Vessel elements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The primary function of a typical leaf is
A) absorption.
B) food storage.
C) support.
D) anchoring.
E) photosynthesis.
A) absorption.
B) food storage.
C) support.
D) anchoring.
E) photosynthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is least likely to be formed from an axillary bud?
A) Flower
B) Branch
C) Runner
D) Leaf
E) Root
A) Flower
B) Branch
C) Runner
D) Leaf
E) Root

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Unlike tracheids, vessel elements
A) function when they are dead.
B) are spindle-shaped.
C) are found primarily in gymnosperms.
D) lose part or all of their end cell walls.
E) have evolved to be progressively longer.
A) function when they are dead.
B) are spindle-shaped.
C) are found primarily in gymnosperms.
D) lose part or all of their end cell walls.
E) have evolved to be progressively longer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Conducting cells called _______ are the part of xylem in which water and minerals are transported.
A) tracheids
B) sieve tubes
C) vessel elements
D) sclerenchyma
E) Both a and c
A) tracheids
B) sieve tubes
C) vessel elements
D) sclerenchyma
E) Both a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Stone cells of pears are an example of _______ cells.
A) parenchyma
B) sclerenchyma
C) collenchyma
D) companion
E) tracheid
A) parenchyma
B) sclerenchyma
C) collenchyma
D) companion
E) tracheid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following correctly represents the layers of a fiber cell, from inside to outside?
A) Primary cell wall secondary cell wall middle lamella
B) Primary cell wall middle lamella secondary cell wall
C) Middle lamella primary cell wall secondary cell wall
D) Middle lamella secondary cell wall primary cell wall
E) Secondary cell wall primary cell wall middle lamella
A) Primary cell wall secondary cell wall middle lamella
B) Primary cell wall middle lamella secondary cell wall
C) Middle lamella primary cell wall secondary cell wall
D) Middle lamella secondary cell wall primary cell wall
E) Secondary cell wall primary cell wall middle lamella

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The vascular tissue system of plants is analogous to the _______ system in animals.
A) circulatory
B) digestive
C) excretory
D) reproductive
E) respiratory
A) circulatory
B) digestive
C) excretory
D) reproductive
E) respiratory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Suppose you have a plant cell from a redwood tree.It has a secondary cell wall with pits and is shaped like a spindle—thicker in the middle and tapered down at the ends.It is most likely a
A) fiber cell.
B) tracheid.
C) vessel element.
D) sieve tube element.
E) companion cell.
A) fiber cell.
B) tracheid.
C) vessel element.
D) sieve tube element.
E) companion cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which cells function as "life support systems" for sieve tube elements?
A) Vessel elements
B) Tracheary elements
C) Fiber cells
D) Companion cells
E) Collenchyma cells
A) Vessel elements
B) Tracheary elements
C) Fiber cells
D) Companion cells
E) Collenchyma cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The meristem is
A) located the tip of the stem.
B) the location on a stem where a bud forms.
C) supporting tissue.
D) composed of undifferentiated cells.
E) located at the base of leaves.
A) located the tip of the stem.
B) the location on a stem where a bud forms.
C) supporting tissue.
D) composed of undifferentiated cells.
E) located at the base of leaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In a laboratory for this course, you are told to examine a slide of a root that is branching and find the origins of the lateral roots.What part of the root are you examining?
A) Epidermis
B) Pericycle
C) Endodermis
D) Cortex
E) Pith
A) Epidermis
B) Pericycle
C) Endodermis
D) Cortex
E) Pith

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The _______ is the centermost tissue in a nonwoody eudicot stem.
A) pith
B) xylem
C) phloem
D) pericycle
E) endodermis
A) pith
B) xylem
C) phloem
D) pericycle
E) endodermis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A newly discovered plant growing in a tropical forest has parallel veins in its leaves and pith in its roots.The location of the pith helps to determine whether this plant is a monocot or dicot because pith is found
A) only in eudicot roots.
B) only in monocot stems.
C) in both monocot stems and eudicot roots.
D) in both monocot roots and eudicot stems.
E) only in monocot and eudicot roots.
A) only in eudicot roots.
B) only in monocot stems.
C) in both monocot stems and eudicot roots.
D) in both monocot roots and eudicot stems.
E) only in monocot and eudicot roots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A root is called adventitious if it
A) forms a mycorrhizal association.
B) has a branched tip.
C) originates from a stem.
D) is modified for storage.
E) is actively growing.
A) forms a mycorrhizal association.
B) has a branched tip.
C) originates from a stem.
D) is modified for storage.
E) is actively growing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The body of a cactus plant is mostly a modified
A) stem.
B) leaf.
C) root.
D) spine.
E) tuber.
A) stem.
B) leaf.
C) root.
D) spine.
E) tuber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A species of carnivorous plant has special red root ends that are found just above the region where most cell division stops.Therefore, red color of the root ends is in the
A) root cap.
B) zone of cell division.
C) zone of cell elongation.
D) quiescent center.
E) zone of cell maturation.
A) root cap.
B) zone of cell division.
C) zone of cell elongation.
D) quiescent center.
E) zone of cell maturation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A fibrous root system
A) grows deep into the substrate.
B) consists of thick roots.
C) holds soil well.
D) is typical of many eudicots.
E) functions as a food storage organ.
A) grows deep into the substrate.
B) consists of thick roots.
C) holds soil well.
D) is typical of many eudicots.
E) functions as a food storage organ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Root hairs are produced by which layer of the plant body?
A) Epidermis
B) Cortex
C) Ground tissue
D) Xylem
E) Phloem
A) Epidermis
B) Cortex
C) Ground tissue
D) Xylem
E) Phloem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A region in the root apical meristem where cell division does not occur is the
A) root cap.
B) center of cell division.
C) zone of cell elongation.
D) quiescent center.
E) zone of cell maturation.
A) root cap.
B) center of cell division.
C) zone of cell elongation.
D) quiescent center.
E) zone of cell maturation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Lateral roots originate in the
A) epidermis.
B) cortex.
C) ground tissue.
D) pericycle.
E) root hairs.
A) epidermis.
B) cortex.
C) ground tissue.
D) pericycle.
E) root hairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A common function of roots, but not stems, is
A) branching.
B) transport.
C) storage.
D) support.
E) absorption.
A) branching.
B) transport.
C) storage.
D) support.
E) absorption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Root hairs are adaptations that
A) increase surface area.
B) defend a plant.
C) reduce water loss.
D) provide active growth.
E) support a plant.
A) increase surface area.
B) defend a plant.
C) reduce water loss.
D) provide active growth.
E) support a plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Some species of rose, which are dicots, can grow on steep hillsides because of a taproot system that helps
A) maximize the surface area for absorption.
B) the plants use their roots as food storage organs.
C) anchor the plant.
D) hold the soil together.
E) transport water and minerals to the stem.
A) maximize the surface area for absorption.
B) the plants use their roots as food storage organs.
C) anchor the plant.
D) hold the soil together.
E) transport water and minerals to the stem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following represents the correct order of the cell layers encountered by an insect boring into a maple leaf, from the upper surface of the leaf toward the center of the leaf?
A) Mesophyll xylem phloem epidermis
B) Epidermis xylem mesophyll phloem
C) Xylem phloem mesophyll epidermis
D) Mesophyll epidermis xylem phloem
E) Epidermis mesophyll xylem phloem
A) Mesophyll xylem phloem epidermis
B) Epidermis xylem mesophyll phloem
C) Xylem phloem mesophyll epidermis
D) Mesophyll epidermis xylem phloem
E) Epidermis mesophyll xylem phloem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A maple sapling is discovered to have roots growing in random directions instead of down.It most likely has a mutation affecting its
A) root cap.
B) pericycle.
C) apical meristem.
D) protoderm.
E) region of elongation.
A) root cap.
B) pericycle.
C) apical meristem.
D) protoderm.
E) region of elongation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In an upright woody stem, vascular rays are composed of _______ cells and conduct materials in a _______ direction.
A) fiber and secondary xylem; vertical
B) guard and fiber; horizontal
C) parenchyma and secondary xylem; horizontal
D) fiber and parenchyma; vertical
E) parenchyma and guard; vertical
A) fiber and secondary xylem; vertical
B) guard and fiber; horizontal
C) parenchyma and secondary xylem; horizontal
D) fiber and parenchyma; vertical
E) parenchyma and guard; vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A mutant mustard plant has a number of novel features; for example, it does not absorb water and minerals from the soil as readily as wild-type plants do.The abnormality of the mutant plant is most likely in its
A) cortex structure.
B) root hairs.
C) endodermis structure.
D) xylem placement.
E) pith diameter.
A) cortex structure.
B) root hairs.
C) endodermis structure.
D) xylem placement.
E) pith diameter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which is the correct order of the regions of a root tip, from the quiescent center upward?
A) Zone of cell elongation zone of cell division zone of cell maturation
B) Zone of cell maturation zone of cell elongation zone of cell division
C) Zone of cell division zone of cell maturation zone of cell elongation
D) Zone of cell elongation zone of cell maturation zone of cell division
E) Zone of cell division zone of cell elongation zone of cell maturation
A) Zone of cell elongation zone of cell division zone of cell maturation
B) Zone of cell maturation zone of cell elongation zone of cell division
C) Zone of cell division zone of cell maturation zone of cell elongation
D) Zone of cell elongation zone of cell maturation zone of cell division
E) Zone of cell division zone of cell elongation zone of cell maturation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The shoot apical meristem is found _______ the nodes of mature leaves on the stem.
A) above
B) below
C) among
D) to the left of
E) behind
A) above
B) below
C) among
D) to the left of
E) behind

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A botanist working high on the slopes of a Hawaiian volcano finds a member of the daisy family that has adapted to dry conditions with traits that are structurally similar to cacti.What part of this plant has become enlarged in order to function as a water storage organ?
A) Stems
B) Roots
C) Branches
D) Leaves
E) Buds
A) Stems
B) Roots
C) Branches
D) Leaves
E) Buds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The _______ is the collective term for phelloderm, cork cambium, and cork.
A) pericycle
B) periderm
C) phloem
D) procambium
E) protoderm
A) pericycle
B) periderm
C) phloem
D) procambium
E) protoderm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which statement about cork cells is true?
A) They are located interior to cork cambium.
B) They contain waxy suberin.
C) They function in water storage.
D) They are characterized by active cell division.
E) They exist in abundance in monocots.
A) They are located interior to cork cambium.
B) They contain waxy suberin.
C) They function in water storage.
D) They are characterized by active cell division.
E) They exist in abundance in monocots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The vascular cambium is located between the _______ and _______.
A) phloem; cork cambium
B) xylem; cork cambium
C) phloem; bark
D) xylem; phloem
E) phloem; ground tissue
A) phloem; cork cambium
B) xylem; cork cambium
C) phloem; bark
D) xylem; phloem
E) phloem; ground tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Guard cells
A) protect the plant from herbivores.
B) secrete a waxy cuticle to prevent evaporation.
C) contain chemicals that poison insects.
D) control gas exchange.
E) inhibit germination of fungal spores.
A) protect the plant from herbivores.
B) secrete a waxy cuticle to prevent evaporation.
C) contain chemicals that poison insects.
D) control gas exchange.
E) inhibit germination of fungal spores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Plants regulate gas exchange and water loss via
A) the cuticle.
B) xylem.
C) coated pits.
D) sieve plates.
E) stomata guard cells.
A) the cuticle.
B) xylem.
C) coated pits.
D) sieve plates.
E) stomata guard cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Lenticels are most like stomata in that both
A) are involved in gas exchange.
B) are located on the surface of the plant.
C) contain parenchyma cells.
D) open at dawn.
E) are part of secondary growth.
A) are involved in gas exchange.
B) are located on the surface of the plant.
C) contain parenchyma cells.
D) open at dawn.
E) are part of secondary growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
To stop the lateral expansion of a tree, you could apply a chemical to inhibit the action of the
A) apical meristem.
B) secondary phloem.
C) phelloderm.
D) vascular cambium.
E) primary xylem.
A) apical meristem.
B) secondary phloem.
C) phelloderm.
D) vascular cambium.
E) primary xylem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Refer to the figure showing a plant periderm. 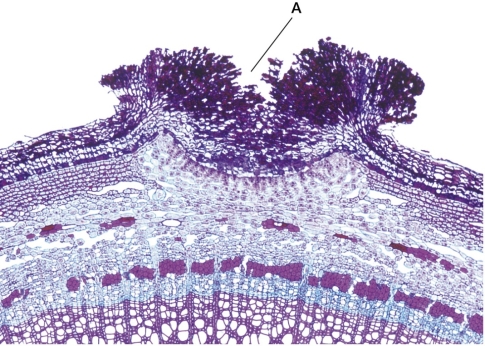 The periderm, which is the outer layer of the secondary plant body, provides protection for interior tissues by keeping water in and pathogens out.What function is provided by structure A in the figure?
The periderm, which is the outer layer of the secondary plant body, provides protection for interior tissues by keeping water in and pathogens out.What function is provided by structure A in the figure?
A) Location for mycorrhizal colonization
B) Uptake of water
C) Production of chemicals that deter herbivores
D) Gas exchange with the environment
E) Capture of wind-blown pollen
 The periderm, which is the outer layer of the secondary plant body, provides protection for interior tissues by keeping water in and pathogens out.What function is provided by structure A in the figure?
The periderm, which is the outer layer of the secondary plant body, provides protection for interior tissues by keeping water in and pathogens out.What function is provided by structure A in the figure?A) Location for mycorrhizal colonization
B) Uptake of water
C) Production of chemicals that deter herbivores
D) Gas exchange with the environment
E) Capture of wind-blown pollen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Primary phloem is always formed before
A) vascular cambium.
B) primary xylem.
C) secondary xylem.
D) stomata.
E) Both a and c
A) vascular cambium.
B) primary xylem.
C) secondary xylem.
D) stomata.
E) Both a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which statement represents the best rephrasing of the following statement: "Guard cells control gas exchange"?
A) Guard cells in the epidermis open and close the pores used for gas exchange.
B) Gases move through guard cells.
C) Guard cells are involved in photosynthesis.
D) Guard cells pump gases into and out of the leaf.
E) Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through epidermal cells.
A) Guard cells in the epidermis open and close the pores used for gas exchange.
B) Gases move through guard cells.
C) Guard cells are involved in photosynthesis.
D) Guard cells pump gases into and out of the leaf.
E) Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through epidermal cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
When the periderm of a cork oak is stripped for making wine bottle stoppers and other manufactured products, the removed material must be replaced by the tree because the periderm
A) transports sugars.
B) forms branches.
C) absorbs water.
D) protects the inner tissues.
E) supports the leaves.
A) transports sugars.
B) forms branches.
C) absorbs water.
D) protects the inner tissues.
E) supports the leaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The advantage of the spongy arrangement of mesophyll cells in the lower leaf layer is that it allows for
A) maximum absorption of sunlight for photosynthesis.
B) maximum diffusion of CO2 in the leaf.
C) maximum movement of water into leaf cells.
D) minimum water loss from the leaf.
E) minimum exchange of O2 within the leaf.
A) maximum absorption of sunlight for photosynthesis.
B) maximum diffusion of CO2 in the leaf.
C) maximum movement of water into leaf cells.
D) minimum water loss from the leaf.
E) minimum exchange of O2 within the leaf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following represents the correct order of vascular tissues, from the center to the outer part of a tree trunk?
A) Primary xylem secondary xylem vascular cambium secondary phloem primary phloem
B) Secondary xylem primary xylem vascular cambium primary phloem secondary phloem
C) Primary xylem primary phloem secondary xylem secondary phloem vascular cambium
D) Primary xylem primary phloem vascular cambium secondary phloem secondary xylem
E) Secondary xylem secondary phloem vascular cambium primary xylem primary phloem
A) Primary xylem secondary xylem vascular cambium secondary phloem primary phloem
B) Secondary xylem primary xylem vascular cambium primary phloem secondary phloem
C) Primary xylem primary phloem secondary xylem secondary phloem vascular cambium
D) Primary xylem primary phloem vascular cambium secondary phloem secondary xylem
E) Secondary xylem secondary phloem vascular cambium primary xylem primary phloem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose you are given a freeze-dried leaf and told to remove all of the cell layers except for the one that will provide the maximum amount of chlorophyll for an extract to be used in an experiment.You should scrape away all of the layers of cells except for the _______ cells.
A) upper epidermal
B) palisade mesophyll
C) bundle sheath
D) phloem
E) guard
A) upper epidermal
B) palisade mesophyll
C) bundle sheath
D) phloem
E) guard

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Refer to the figure showing a plant periderm. 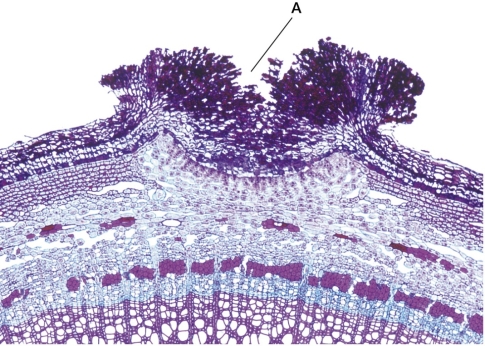 Structure A in the figure is found in the secondary body of a woody plant.Which structure found in the primary plant body has a similar function?
Structure A in the figure is found in the secondary body of a woody plant.Which structure found in the primary plant body has a similar function?
A) Stoma
B) Leaf hair
C) Root hair
D) Mesophyll cell
E) Vessel element
 Structure A in the figure is found in the secondary body of a woody plant.Which structure found in the primary plant body has a similar function?
Structure A in the figure is found in the secondary body of a woody plant.Which structure found in the primary plant body has a similar function?A) Stoma
B) Leaf hair
C) Root hair
D) Mesophyll cell
E) Vessel element

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The _______ of woody stems, though structured very differently from the stomata of leaves, function in some ways that are similar.
A) mesophyll cells
B) cuticles
C) lenticels
D) vessel elements
E) bundle sheath cells
A) mesophyll cells
B) cuticles
C) lenticels
D) vessel elements
E) bundle sheath cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Structures that protrude from bark for the purpose of gas exchange are called
A) leaves.
B) leaf hairs.
C) stomata.
D) lenticels.
E) root hairs.
A) leaves.
B) leaf hairs.
C) stomata.
D) lenticels.
E) root hairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Lenticels are spongy regions on the surface of some woody stems that function in
A) water uptake.
B) water conservation.
C) gas exchange.
D) protection of growing layers.
E) support of the plant.
A) water uptake.
B) water conservation.
C) gas exchange.
D) protection of growing layers.
E) support of the plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Some plants, such as cacti, have developed spines as a means of protection.Spines are most likely modifications of which plant structure?
A) Stems
B) Roots
C) Branches
D) Leaves
E) Seeds
A) Stems
B) Roots
C) Branches
D) Leaves
E) Seeds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Leaf scars indicate a previous presence of
A) trichomes.
B) flowers.
C) petioles.
D) stems.
E) fruit.
A) trichomes.
B) flowers.
C) petioles.
D) stems.
E) fruit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 243 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



