Deck 35: Plant Nutrition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/248
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 35: Plant Nutrition
1
Which characteristic is not generally affected by nutrient deficiencies in plants?
A) Stature
B) Seed germination
C) Leaf color
D) Root growth
E) Location
A) Stature
B) Seed germination
C) Leaf color
D) Root growth
E) Location
E
2
_______ are available to the plant in unlimited supply _______.
A) Water and nitrogen; because there is plenty of soil around the plant
B) Sulfur and magnesium; because plants need such small amounts from the soil
C) Phosphorus and iron; because they dissolve readily in soil water
D) Calcium and chlorine; because they are easily absorbed by roots
E) Hydrogen and oxygen; as long as sufficient water is available
A) Water and nitrogen; because there is plenty of soil around the plant
B) Sulfur and magnesium; because plants need such small amounts from the soil
C) Phosphorus and iron; because they dissolve readily in soil water
D) Calcium and chlorine; because they are easily absorbed by roots
E) Hydrogen and oxygen; as long as sufficient water is available
E
3
Which nutrient would you add to the soil around a plant to help it form abundant membranes and nucleic acids?
A) Magnesium
B) Nitrogen
C) Phosphorus
D) Potassium
E) Iron
A) Magnesium
B) Nitrogen
C) Phosphorus
D) Potassium
E) Iron
C
4
Which element is a micronutrient in plants?
A) Potassium
B) Sulfur
C) Calcium
D) Zinc
E) Magnesium
A) Potassium
B) Sulfur
C) Calcium
D) Zinc
E) Magnesium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a corn plant lacks the micronutrient _______, it will not be able to complete synthesis of its chlorophyll.
A) magnesium
B) sulfur
C) phosphorus
D) potassium
E) iron
A) magnesium
B) sulfur
C) phosphorus
D) potassium
E) iron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Iron deficiencies cause _______ leaves to become _______.
A) old; yellow
B) young; yellow
C) old; orange
D) young; orange
E) old; brown-spotted
A) old; yellow
B) young; yellow
C) old; orange
D) young; orange
E) old; brown-spotted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In most plants, nitrogen deficiency is signaled by a(n) _______ color in the _______ leaves.
A) yellow; old
B) yellow; young
C) orange; old
D) orange; young
E) brown-spotted; old
A) yellow; old
B) yellow; young
C) orange; old
D) orange; young
E) brown-spotted; old

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A botanist performs a series of experiments in which different possible sources of oxygen to be used by plants are radioactively labeled.When photosynthetically derived compounds are examined, their oxygen will be found to have come from which source?
A) The atmosphere only
B) Soil minerals only
C) Water
D) Both the atmosphere and soil
E) Fertilizer
A) The atmosphere only
B) Soil minerals only
C) Water
D) Both the atmosphere and soil
E) Fertilizer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If a new essential nutrient were discovered, it would be a
A) macronutrient.
B) micronutrient.
C) rare metal.
D) small organism.
E) cytochrome.
A) macronutrient.
B) micronutrient.
C) rare metal.
D) small organism.
E) cytochrome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Refer to the graph showing data from a set of hydroponic experiments examining the dependence of germination on nickel levels.A number of plants are grown at different nickel concentrations for three generations.Some seeds from third generation plants are analyzed for nickel content, and some are germinated in solution lacking nickel.Many of the seeds germinate. 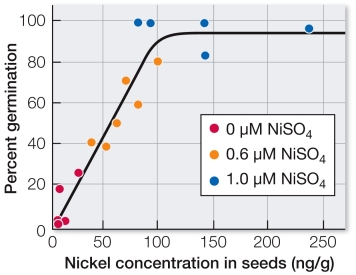 Which conclusion is valid?
Which conclusion is valid?
A) Since more seeds germinate in the low nickel conditions, there must be too much nickel present.
B) The lack of nickel in the germination solution compensates for too much nickel in the seeds.
C) High levels of nickel are toxic to the plant.
D) When plants are grown with sufficient nickel, their seeds contain enough nickel to allow germination.
E) There must be small amounts of nickel present in the germination solution to allow the seeds to germinate.
 Which conclusion is valid?
Which conclusion is valid?A) Since more seeds germinate in the low nickel conditions, there must be too much nickel present.
B) The lack of nickel in the germination solution compensates for too much nickel in the seeds.
C) High levels of nickel are toxic to the plant.
D) When plants are grown with sufficient nickel, their seeds contain enough nickel to allow germination.
E) There must be small amounts of nickel present in the germination solution to allow the seeds to germinate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which four elements are found in highest concentration in plants?
A) Phosphorus, calcium, hydrogen, carbon
B) Magnesium, phosphorus, calcium, potassium
C) Magnesium, iron, phosphorus, potassium
D) Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
E) Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, potassium
A) Phosphorus, calcium, hydrogen, carbon
B) Magnesium, phosphorus, calcium, potassium
C) Magnesium, iron, phosphorus, potassium
D) Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
E) Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, potassium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which mineral is a constituent of all proteins and nucleic acids?
A) Magnesium
B) Nitrogen
C) Phosphorus
D) Potassium
E) Iron
A) Magnesium
B) Nitrogen
C) Phosphorus
D) Potassium
E) Iron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which list contains an element that is not essential for plant nutrition?
A) N, P, K
B) Ni, P, K
C) Cd, Mg, K
D) Ca, P, K
E) Mo, Ni, P
A) N, P, K
B) Ni, P, K
C) Cd, Mg, K
D) Ca, P, K
E) Mo, Ni, P

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Researchers discover that a species of maple tree cannot survive and complete its life cycle without tiny amounts of fluorine.For this tree, fluorine is a(n)
A) micronutrient.
B) macronutrient.
C) essential element.
D) amino acid.
E) essential micronutrient.
A) micronutrient.
B) macronutrient.
C) essential element.
D) amino acid.
E) essential micronutrient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which mineral is deficient in a tomato plant whose growth is stunted and whose oldest leaves turn yellow and die prematurely?
A) Calcium
B) Iron
C) Magnesium
D) Nitrogen
E) Phosphorus
A) Calcium
B) Iron
C) Magnesium
D) Nitrogen
E) Phosphorus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Proteins are macromolecules that account for much of a plant's demand for mineral nutrients.Protein molecular structure explains at least some of the need for carbon and which other elements?
A) Oxygen, sulfur, phosphorus, and potassium
B) Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus
C) Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur
D) Hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, and potassium
E) Hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and potassium
A) Oxygen, sulfur, phosphorus, and potassium
B) Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus
C) Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur
D) Hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, and potassium
E) Hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and potassium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Nitrogen is typically present in plants in concentrations of 15 g/kg dry weight.Thus, it is classified as a(n)
A) micronutrient.
B) macronutrient.
C) essential element.
D) nonessential element.
E) mineral nutrient.
A) micronutrient.
B) macronutrient.
C) essential element.
D) nonessential element.
E) mineral nutrient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Plants do not obtain _______ from the soil.
A) carbon
B) nitrogen
C) potassium
D) sulfur
E) zinc
A) carbon
B) nitrogen
C) potassium
D) sulfur
E) zinc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which mineral is necessary for a plant's water and ion balance?
A) Magnesium
B) Nitrogen
C) Phosphorus
D) Potassium
E) Iron
A) Magnesium
B) Nitrogen
C) Phosphorus
D) Potassium
E) Iron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
One of the defining characteristics of an essential element is that
A) it is necessary only for early growth of the seedling.
B) it can be replaced by another element.
C) the plant cannot survive without it.
D) it may function by relieving the toxicity of another element.
E) it is found in relatively high concentrations in the environment.
A) it is necessary only for early growth of the seedling.
B) it can be replaced by another element.
C) the plant cannot survive without it.
D) it may function by relieving the toxicity of another element.
E) it is found in relatively high concentrations in the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A newly identified species of trigger plant grows in unusual, extremely weathered soils but still deals with its mineral needs in conventional ways.It likely accesses new sources of mineral nutrients by
A) breaking down organic matter.
B) growing longer roots.
C) shading the plants below them.
D) evolving more elaborate photosystems.
E) absorbing minerals through leaves.
A) breaking down organic matter.
B) growing longer roots.
C) shading the plants below them.
D) evolving more elaborate photosystems.
E) absorbing minerals through leaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The ionization of carbonic acid
A) increases the amount of soil carbon available to plants.
B) raises the pH of soil.
C) reduces the leaching of phosphates and nitrates from soil.
D) causes it to evaporate from the A horizon of soil.
E) triggers the release of positively charged mineral ions from clay.
A) increases the amount of soil carbon available to plants.
B) raises the pH of soil.
C) reduces the leaching of phosphates and nitrates from soil.
D) causes it to evaporate from the A horizon of soil.
E) triggers the release of positively charged mineral ions from clay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In almost all land plants, roots get most of their oxygen from
A) air spaces in the soil.
B) water in the soil.
C) the leaves, by way of the phloem.
D) the leaves, which get oxygen from the air.
E) specific transport by symbionts.
A) air spaces in the soil.
B) water in the soil.
C) the leaves, by way of the phloem.
D) the leaves, which get oxygen from the air.
E) specific transport by symbionts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which mechanism is not used by plants to regulate nutrient uptake?
A) Specialized membrane transport systems
B) Casparian strips
C) A cuticle barrier
D) Active transport
E) Direct connection to symbiont cytoplasm
A) Specialized membrane transport systems
B) Casparian strips
C) A cuticle barrier
D) Active transport
E) Direct connection to symbiont cytoplasm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Chemical weathering, an important part of soil formation, includes the
A) splitting of clays.
B) effects of freezing and thawing.
C) hydrolysis of rock.
D) crushing of rock.
E) drying of soils.
A) splitting of clays.
B) effects of freezing and thawing.
C) hydrolysis of rock.
D) crushing of rock.
E) drying of soils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which sequence represents the correct order of these three mineral particles of the soil, from smallest to largest?
A) Clay silt sand
B) Sand clay humus
C) Sand silt clay
D) Humus silt sand
E) Silt sand loam
A) Clay silt sand
B) Sand clay humus
C) Sand silt clay
D) Humus silt sand
E) Silt sand loam

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If you dig through the A and B soil horizons in your garden, you will know that you have reached the C horizon when your shovel is no longer full of
A) plant roots.
B) earthworms.
C) parent rock.
D) roots and earthworms.
E) roots and parent rock.
A) plant roots.
B) earthworms.
C) parent rock.
D) roots and earthworms.
E) roots and parent rock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which is not a reason that clay is a useful additive to sandy soil?
A) Clay provides a reservoir of cation nutrients.
B) Clay holds moisture.
C) Clay binds positively charged mineral ions.
D) Clay prevents leaching.
E) Clay allows water to filter through quickly.
A) Clay provides a reservoir of cation nutrients.
B) Clay holds moisture.
C) Clay binds positively charged mineral ions.
D) Clay prevents leaching.
E) Clay allows water to filter through quickly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the graph showing the response of a hydroponic plant being transferred into a new solution.The dependent variable is the number of phosphate transporters per unit area of root epidermis as a function of time after transfer. 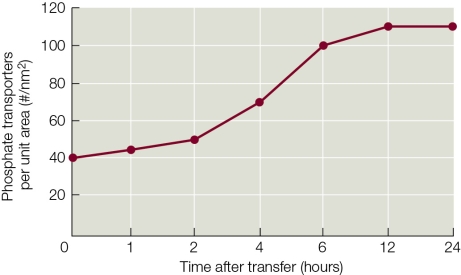 According to the graph, the plant was most likely moved from _______ to a _______.
According to the graph, the plant was most likely moved from _______ to a _______.
A) a high nitrogen solution; low nitrogen solution
B) a low phosphate solution; high phosphate solution
C) a high phosphate solution; low phosphate solution
D) a low nitrogen solution; high nitrogen solution
E) pure water; complete nutrient solution
 According to the graph, the plant was most likely moved from _______ to a _______.
According to the graph, the plant was most likely moved from _______ to a _______.A) a high nitrogen solution; low nitrogen solution
B) a low phosphate solution; high phosphate solution
C) a high phosphate solution; low phosphate solution
D) a low nitrogen solution; high nitrogen solution
E) pure water; complete nutrient solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Cation exchange is an important process that facilitates the uptake of nutrients by plants.How is this accomplished?
A) Cation exchange allows more incorporation of air into soil.
B) Because of the positive charge on clay particles, cation exchange gets rid of the clay.
C) Roots secrete protons (H+) or acids into the soil, which displace positive nutrient ions from soil particles.
D) Negative ions such as phosphate, nitrate, and sulfate are exchanged for cations.
E) Cation exchange is most effective when performed in the C horizon.
A) Cation exchange allows more incorporation of air into soil.
B) Because of the positive charge on clay particles, cation exchange gets rid of the clay.
C) Roots secrete protons (H+) or acids into the soil, which displace positive nutrient ions from soil particles.
D) Negative ions such as phosphate, nitrate, and sulfate are exchanged for cations.
E) Cation exchange is most effective when performed in the C horizon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A common bean plant is growing in a spot in a garden with variable nutrient availability in the surrounding soil.Some small soil patches contain large rocks, others contain sand, and still others contain animal droppings.What could the bean plant do to access the available nutrients most successfully?
A) Grow stems over the nutrient-rich patches to prevent competing plants from growing there.
B) Release allelopathic chemicals to prevent competition for resources.
C) Remodel its shoot system to grow around the poorer soil areas.
D) Attract ants to destroy any competing seedlings.
E) Increase the growth of roots toward the animal droppings.
A) Grow stems over the nutrient-rich patches to prevent competing plants from growing there.
B) Release allelopathic chemicals to prevent competition for resources.
C) Remodel its shoot system to grow around the poorer soil areas.
D) Attract ants to destroy any competing seedlings.
E) Increase the growth of roots toward the animal droppings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Soil scientists recognize _______ major soil horizons: _______.
A) two; A and B
B) two; upper and lower
C) three; A, B, and C
D) four; top, top middle, middle, and lower
E) seven; 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7
A) two; A and B
B) two; upper and lower
C) three; A, B, and C
D) four; top, top middle, middle, and lower
E) seven; 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An advantage to using inorganic fertilizers (as opposed to organic fertilizers) is that
A) they improve the physical properties of the soil.
B) they can be taken up by roots rapidly after application.
C) their quality is better than that of organic fertilizers.
D) they contain minerals in their proper ionic form.
E) they contain larger particles.
A) they improve the physical properties of the soil.
B) they can be taken up by roots rapidly after application.
C) their quality is better than that of organic fertilizers.
D) they contain minerals in their proper ionic form.
E) they contain larger particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Plants generally do not thrive in topsoil composed only of clay because such soil tends to
A) create too many air spaces.
B) retain too much water.
C) hold mineral nutrients too tightly.
D) retain too much water and hold minerals too tightly.
E) create too many air spaces and retain too much water.
A) create too many air spaces.
B) retain too much water.
C) hold mineral nutrients too tightly.
D) retain too much water and hold minerals too tightly.
E) create too many air spaces and retain too much water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A newly discovered species of earthworm is found to spend most of its time in the C horizon.This is unusual, since other species tend to stay mostly in the
A) bedrock only.
B) subsoil only.
C) topsoil only.
D) bedrock and subsoil.
E) bedrock and topsoil.
A) bedrock only.
B) subsoil only.
C) topsoil only.
D) bedrock and subsoil.
E) bedrock and topsoil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which list represents the correct order of soil horizons that you would encounter if you started digging in your garden?
A) Parent bedrock subsoil topsoil
B) Topsoil subsoil parent bedrock
C) Topsoil parent bedrock subsoil
D) Parent bedrock topsoil subsoil
E) Subsoil parent bedrock topsoil
A) Parent bedrock subsoil topsoil
B) Topsoil subsoil parent bedrock
C) Topsoil parent bedrock subsoil
D) Parent bedrock topsoil subsoil
E) Subsoil parent bedrock topsoil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The richest topsoils for agriculture are composed of
A) clay only.
B) sand only.
C) clay and sand only.
D) silt only.
E) a mixture of clay, sand, organic matter, and silt.
A) clay only.
B) sand only.
C) clay and sand only.
D) silt only.
E) a mixture of clay, sand, organic matter, and silt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In a typical approach to identifying essential elements in plants, a plant growing hydroponically in a solution containing all known nutrients is transplanted to a solution _______.This approach is most effective at detecting nutrients needed in _______ amounts.
A) lacking a single potential nutrient; small
B) lacking a single potential nutrient; large
C) lacking all known nutrients; small
D) lacking all known nutrients; large
E) having a single potential nutrient; small
A) lacking a single potential nutrient; small
B) lacking a single potential nutrient; large
C) lacking all known nutrients; small
D) lacking all known nutrients; large
E) having a single potential nutrient; small

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Cation exchange is the means by which
A) carbonic acid is added to soils.
B) positive ions are replaced by H+ on soil particles.
C) negative ions are incorporated into soils.
D) positive ions are replaced by negative ions on soil particles.
E) neutral atoms become ions in soils.
A) carbonic acid is added to soils.
B) positive ions are replaced by H+ on soil particles.
C) negative ions are incorporated into soils.
D) positive ions are replaced by negative ions on soil particles.
E) neutral atoms become ions in soils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Refer to the graph showing the response of a hydroponic plant being transferred into a new solution.The dependent variable is the number of phosphate transporters per unit area of root epidermis as a function of time after transfer. 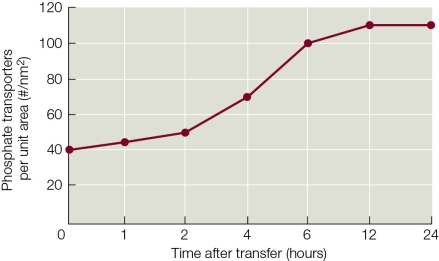 Why does the plot line level off after the plant has spent 12 hours in the new solution?
Why does the plot line level off after the plant has spent 12 hours in the new solution?
A) The roots have absorbed all of the phosphate from the solution after 12 hours.
B) After 12 hours, the activity of the phosphate transporters reaches maximal levels and levels off.
C) The phosphate that is taken up by the transporters has all been assimilated after 12 hours.
D) The level of phosphate in the cells has decreased after 12 hours, shutting down transcription of the phosphate transporter genes.
E) The transcription rate of the phosphate transporter genes goes down after 12 hours, when the roots have adjusted to the phosphate level in the new solution.
 Why does the plot line level off after the plant has spent 12 hours in the new solution?
Why does the plot line level off after the plant has spent 12 hours in the new solution?A) The roots have absorbed all of the phosphate from the solution after 12 hours.
B) After 12 hours, the activity of the phosphate transporters reaches maximal levels and levels off.
C) The phosphate that is taken up by the transporters has all been assimilated after 12 hours.
D) The level of phosphate in the cells has decreased after 12 hours, shutting down transcription of the phosphate transporter genes.
E) The transcription rate of the phosphate transporter genes goes down after 12 hours, when the roots have adjusted to the phosphate level in the new solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which three elements are most commonly added to agricultural soils as fertilizers?
A) Nitrogen, phosphorus, and iron
B) Nitrogen, potassium, and magnesium
C) Potassium, sulfur, and iron
D) Nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus
E) Nitrogen, sulfur, and calcium
A) Nitrogen, phosphorus, and iron
B) Nitrogen, potassium, and magnesium
C) Potassium, sulfur, and iron
D) Nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus
E) Nitrogen, sulfur, and calcium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The part of the root that is most important early in the formation of a root nodule is the
A) root cap.
B) cortex.
C) xylem.
D) phloem.
E) root hair.
A) root cap.
B) cortex.
C) xylem.
D) phloem.
E) root hair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If you wanted non-legumes to nodulate for the nutritional benefit of the plants, which part of the non-legumes would you work on?
A) Roots
B) Stems
C) Leaves
D) Flowers
E) Petioles
A) Roots
B) Stems
C) Leaves
D) Flowers
E) Petioles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Refer to the figure showing two different plant symbioses. 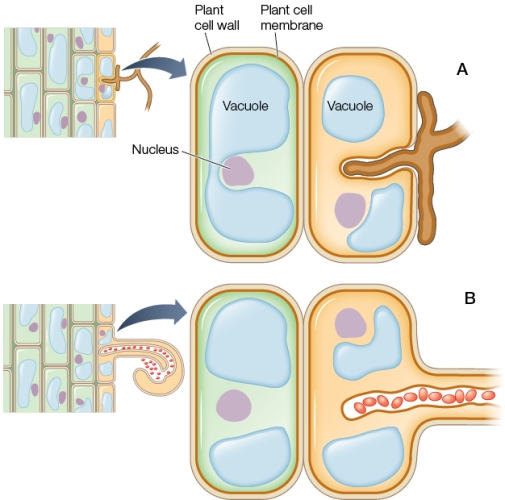 The symbiotic cells entering plant cell B in the figure are most likely
The symbiotic cells entering plant cell B in the figure are most likely
A) insect larvae.
B) actinomycetes.
C) Rhizobium.
D) fungi.
E) parasitic plants.
 The symbiotic cells entering plant cell B in the figure are most likely
The symbiotic cells entering plant cell B in the figure are most likelyA) insect larvae.
B) actinomycetes.
C) Rhizobium.
D) fungi.
E) parasitic plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Refer to the figure showing two different plant symbioses. 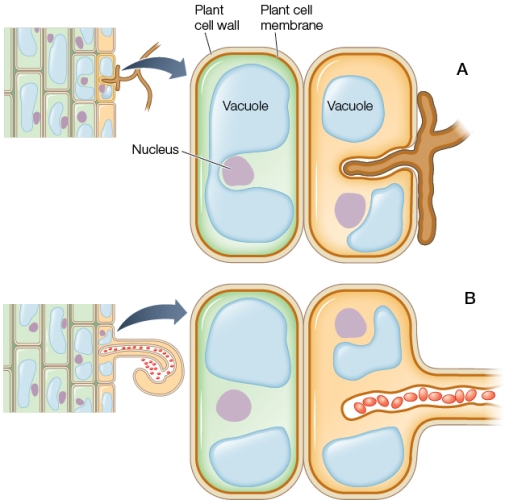 In plant cell A in the figure, what is being provided to the plant by the fungal structure entering between the two sections of vacuole?
In plant cell A in the figure, what is being provided to the plant by the fungal structure entering between the two sections of vacuole?
A) Additional plant cells
B) Connection to surface area for absorption
C) More plasmodesmata
D) Strands of cellulose
E) Air channels for gas exchange
 In plant cell A in the figure, what is being provided to the plant by the fungal structure entering between the two sections of vacuole?
In plant cell A in the figure, what is being provided to the plant by the fungal structure entering between the two sections of vacuole?A) Additional plant cells
B) Connection to surface area for absorption
C) More plasmodesmata
D) Strands of cellulose
E) Air channels for gas exchange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How do nitrogen-fixing microbes first become associated with their symbiotic plants?
A) They are carried in the seed.
B) They move into the vascular system and multiply.
C) They move in via openings in the plant cell walls.
D) They enter via modified root hairs.
E) They enter root nodules once they are produced by the plant.
A) They are carried in the seed.
B) They move into the vascular system and multiply.
C) They move in via openings in the plant cell walls.
D) They enter via modified root hairs.
E) They enter root nodules once they are produced by the plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which plant does not have nitrogen-fixing root nodules that contain Rhizobium?
A) Alfalfa
B) Beans
C) Clover
D) Peas
E) Rice
A) Alfalfa
B) Beans
C) Clover
D) Peas
E) Rice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Mycorrhizae help plants nutritionally by greatly increasing the _______ for absorption of mineral nutrients.
A) leaf area
B) number of roots
C) number of root hairs
D) surface area
E) driving force
A) leaf area
B) number of roots
C) number of root hairs
D) surface area
E) driving force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The nitrogen-fixing form of Rhizobium bacteria that can be found inside the roots of a legume are known as
A) endospores.
B) cyanobacteria.
C) bacteroids.
D) heterocysts.
E) eggs.
A) endospores.
B) cyanobacteria.
C) bacteroids.
D) heterocysts.
E) eggs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which statement about mycorrhizae is true?
A) They increase the functional surface area of a root system.
B) They involve an interaction between a bacterium and a plant.
C) They are very unusual in nature, found only in specialized plant groups.
D) They spread via plant seeds.
E) They form structures that exclude oxygen.
A) They increase the functional surface area of a root system.
B) They involve an interaction between a bacterium and a plant.
C) They are very unusual in nature, found only in specialized plant groups.
D) They spread via plant seeds.
E) They form structures that exclude oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Why might a farmer choose to add organic fertilizers (as opposed to inorganic fertilizers) to their farm soils?
A) Organic fertilizers allow for a more rapid increase in nutrients.
B) Only organic fertilizers are available in specific nutrient formulas for specific problems.
C) Organic fertilizers are more successful in improving the structure of soil.
D) Organic fertilizers do a better job of leaching the soil.
E) Organic fertilizers add more clay particles to the soil.
A) Organic fertilizers allow for a more rapid increase in nutrients.
B) Only organic fertilizers are available in specific nutrient formulas for specific problems.
C) Organic fertilizers are more successful in improving the structure of soil.
D) Organic fertilizers do a better job of leaching the soil.
E) Organic fertilizers add more clay particles to the soil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Root nodules on plants of the legume family contain
A) cyanobacteria.
B) Nitrosococcus bacteria.
C) Rhizobium bacteria.
D) Pseudomonas bacteria.
E) Nitrobacter bacteria.
A) cyanobacteria.
B) Nitrosococcus bacteria.
C) Rhizobium bacteria.
D) Pseudomonas bacteria.
E) Nitrobacter bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Refer to the figure showing two different plant symbioses. 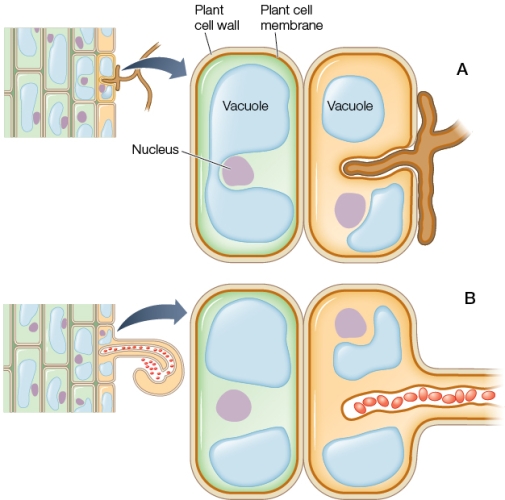 In both A and B, the fungal and bacterial cells remain surrounded by plant plasma membrane instead of directly entering the plant cells.What advantage does this separation provide for the plant?
In both A and B, the fungal and bacterial cells remain surrounded by plant plasma membrane instead of directly entering the plant cells.What advantage does this separation provide for the plant?
A) It prevents the fungus or bacteria from becoming pathogenic.
B) It allows the plant to control what nutrients enter the plant cells from the fungus or bacteria.
C) It provides more surface area for nutrient exchange with the fungus or bacteria.
D) It prevents fungus and bacteria from colonizing the same cells.
E) There is no advantage to the plant, only to the fungus or bacteria.
 In both A and B, the fungal and bacterial cells remain surrounded by plant plasma membrane instead of directly entering the plant cells.What advantage does this separation provide for the plant?
In both A and B, the fungal and bacterial cells remain surrounded by plant plasma membrane instead of directly entering the plant cells.What advantage does this separation provide for the plant?A) It prevents the fungus or bacteria from becoming pathogenic.
B) It allows the plant to control what nutrients enter the plant cells from the fungus or bacteria.
C) It provides more surface area for nutrient exchange with the fungus or bacteria.
D) It prevents fungus and bacteria from colonizing the same cells.
E) There is no advantage to the plant, only to the fungus or bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Refer to the table.Researchers grew seedlings with phosphate fertilizer, arbuscular mycorrhizae, or both, and then weighed the seedlings after six months. 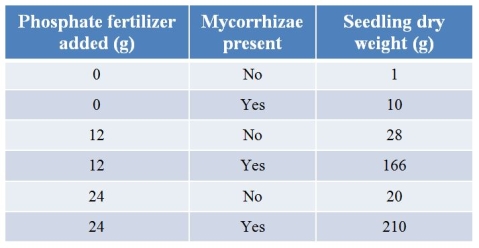 Which conclusion could be drawn from these data?
Which conclusion could be drawn from these data?
A) Phosphate fertilizer has no added effect on plants that have mycorrhizae.
B) More phosphate fertilizer will always result in more plant growth.
C) Mycorrhizae alone maximize plant growth.
D) Mycorrhizae make it easier for plants to take up any added nutrients.
E) Farmers should not bother considering mycorrhizal relationships with crops, since inorganic fertilizers are sufficient.
 Which conclusion could be drawn from these data?
Which conclusion could be drawn from these data?A) Phosphate fertilizer has no added effect on plants that have mycorrhizae.
B) More phosphate fertilizer will always result in more plant growth.
C) Mycorrhizae alone maximize plant growth.
D) Mycorrhizae make it easier for plants to take up any added nutrients.
E) Farmers should not bother considering mycorrhizal relationships with crops, since inorganic fertilizers are sufficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The haustoria of parasitic plants and the hyphae of mycorrhizae both _______ the tissues of their hosts.
A) digest
B) invade
C) color
D) benefit
E) make hydrophobic
A) digest
B) invade
C) color
D) benefit
E) make hydrophobic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Nitrogen-fixing rhizobia can associate with the roots of which common garden plant?
A) Tomato
B) Lettuce
C) Celery
D) Pepper
E) Bean
A) Tomato
B) Lettuce
C) Celery
D) Pepper
E) Bean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The industrial production of nitrogen-containing fertilizer is currently limited by
A) its high energy expense.
B) the inability to insert nitrogenase genes into plants.
C) the lack of nitrogenase for the industrial process.
D) the limited supply of N2 gas.
E) the need to exclude free oxygen in the process.
A) its high energy expense.
B) the inability to insert nitrogenase genes into plants.
C) the lack of nitrogenase for the industrial process.
D) the limited supply of N2 gas.
E) the need to exclude free oxygen in the process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which sequence represents the correct order of the locations where rhizobia develop as a root nodule is formed, from earliest to latest?
A) Soil root hair cortex
B) Soil cortex root hair
C) Root hair cortex soil
D) Root hair soil cortex
E) Cortex soil root hair
A) Soil root hair cortex
B) Soil cortex root hair
C) Root hair cortex soil
D) Root hair soil cortex
E) Cortex soil root hair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The part of the root that is most important for building the bulk of a root nodule is the
A) epidermis.
B) cortex.
C) xylem.
D) phloem.
E) root hair.
A) epidermis.
B) cortex.
C) xylem.
D) phloem.
E) root hair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A newly discovered parasitic plant is found to have special threadlike leaves that penetrate the stems of the plants from which it steals nutrients.These leaves, therefore, have some of the same properties as
A) mycorrhizae.
B) haustoria.
C) nodules.
D) both mycorrhizae and haustoria.
E) both mycorrhizae and nodules.
A) mycorrhizae.
B) haustoria.
C) nodules.
D) both mycorrhizae and haustoria.
E) both mycorrhizae and nodules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Nodules that are actively fixing nitrogen are pink, demonstrating the presence of
A) nitrogen.
B) chlorophyll.
C) leghemoglobin.
D) anthocyanin.
E) alkaloids.
A) nitrogen.
B) chlorophyll.
C) leghemoglobin.
D) anthocyanin.
E) alkaloids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The products of nitrogen-fixing organisms can be oxidized to form nitrites and nitrates by
A) all living organisms.
B) most living organisms that utilize oxygen.
C) many types of microorganisms.
D) a few specific genera of soil bacteria.
E) only the nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
A) all living organisms.
B) most living organisms that utilize oxygen.
C) many types of microorganisms.
D) a few specific genera of soil bacteria.
E) only the nitrogen-fixing bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which list is the correct order of the nitrogen cycle?
A) Nitrification nitrate reduction fixation
B) Fixation nitrate reduction nitrification
C) Fixation nitrification nitrate reduction
D) Nitrification fixation nitrate reduction
E) Nitrate reduction nitrification fixation
A) Nitrification nitrate reduction fixation
B) Fixation nitrate reduction nitrification
C) Fixation nitrification nitrate reduction
D) Nitrification fixation nitrate reduction
E) Nitrate reduction nitrification fixation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Carnivorous plants generally trap
A) molluscs.
B) velvet worms.
C) insects.
D) crustaceans.
E) vertebrates.
A) molluscs.
B) velvet worms.
C) insects.
D) crustaceans.
E) vertebrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Bacteria that function as denitrifiers would
A) oxidize ammonium ions to nitrate.
B) oxidize nitrate to nitrite.
C) reduce N2 to ammonia.
D) reduce nitrates to ammonia.
E) reduce nitrate to N2.
A) oxidize ammonium ions to nitrate.
B) oxidize nitrate to nitrite.
C) reduce N2 to ammonia.
D) reduce nitrates to ammonia.
E) reduce nitrate to N2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Root nodulation is beneficial to plants because plants
A) use the nodules as storehouses for nitrogen.
B) usually have limited nitrogen supplies.
C) benefit from the increased surface area provided by the nodules.
D) use the nodules to obtain phosphorous as well as nitrogen.
E) use the nodules to trap nitrogen-rich bacteria.
A) use the nodules as storehouses for nitrogen.
B) usually have limited nitrogen supplies.
C) benefit from the increased surface area provided by the nodules.
D) use the nodules to obtain phosphorous as well as nitrogen.
E) use the nodules to trap nitrogen-rich bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The enzyme that fixes nitrogen in Rhizobium is called
A) urease.
B) rubisco.
C) nitrogenase.
D) carbonic anhydrase.
E) DNase I.
A) urease.
B) rubisco.
C) nitrogenase.
D) carbonic anhydrase.
E) DNase I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If an environmental antibiotic temporarily stopped bacterial functioning in the nitrogen cycle, which process(es) could continue?
A) Denitrification
B) Nitrogen fixation
C) Nitrate reduction
D) Nitrification
E) Both b and c
A) Denitrification
B) Nitrogen fixation
C) Nitrate reduction
D) Nitrification
E) Both b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which nitrogen compound is used directly by plants to build proteins?
A) Ammonium
B) N2
C) Nitrate
D) Nitrite
E) Nitrous oxide
A) Ammonium
B) N2
C) Nitrate
D) Nitrite
E) Nitrous oxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The process of nitrogen fixation is the
A) uptake of atmospheric nitrogen by plants.
B) conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia.
C) production of nitrogen-bearing compounds in plants.
D) release of nitrogen into the atmosphere.
E) release of ammonia into the atmosphere.
A) uptake of atmospheric nitrogen by plants.
B) conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia.
C) production of nitrogen-bearing compounds in plants.
D) release of nitrogen into the atmosphere.
E) release of ammonia into the atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Nitrogen fixers are present among
A) bacteria.
B) fungi.
C) Plantae.
D) both bacteria and fungi.
E) both bacteria and Plantae.
A) bacteria.
B) fungi.
C) Plantae.
D) both bacteria and fungi.
E) both bacteria and Plantae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Nitrogen fixation converts
A) ammonia to N2.
B) nitrate to ammonia.
C) ammonia to nitrate.
D) N2 to ammonia.
E) N2 to nitrate.
A) ammonia to N2.
B) nitrate to ammonia.
C) ammonia to nitrate.
D) N2 to ammonia.
E) N2 to nitrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Refer to the table.Researchers grew seedlings with phosphate fertilizer, arbuscular mycorrhizae, or both, and then weighed the seedlings after six months. 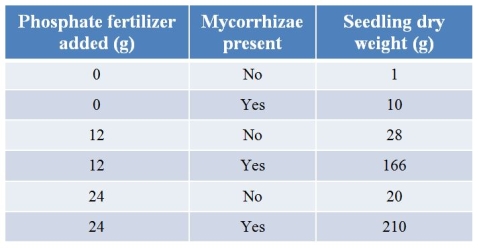 Which explanation best describes why the weight of the seedlings did not increase when the amount of phosphate was doubled in the absence of mycorrhizae?
Which explanation best describes why the weight of the seedlings did not increase when the amount of phosphate was doubled in the absence of mycorrhizae?
A) The amount of phosphate added was over and above the absorptive capacity of the plant roots.
B) Without mycorrhizae, no phosphate was available for uptake by the roots.
C) The additional phosphate is converted to unusable form in the soil.
D) Other plants compete for the added phosphate at higher concentrations.
E) There was experimental error in that plot of plants.
 Which explanation best describes why the weight of the seedlings did not increase when the amount of phosphate was doubled in the absence of mycorrhizae?
Which explanation best describes why the weight of the seedlings did not increase when the amount of phosphate was doubled in the absence of mycorrhizae?A) The amount of phosphate added was over and above the absorptive capacity of the plant roots.
B) Without mycorrhizae, no phosphate was available for uptake by the roots.
C) The additional phosphate is converted to unusable form in the soil.
D) Other plants compete for the added phosphate at higher concentrations.
E) There was experimental error in that plot of plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A carnivorous plant that produces one of the fastest motions known among plants is the
A) pitcher plant.
B) sundew.
C) Venus flytrap.
D) butterwort.
E) mimosa.
A) pitcher plant.
B) sundew.
C) Venus flytrap.
D) butterwort.
E) mimosa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
After nitrogen fixation, the ammonia can be converted by other bacteria to _______ and _______.
A) nitrite; ATP
B) nitrate; amino acids
C) nitrate; nucleic acids
D) nitrite; nitrate
E) nitrite; pigments
A) nitrite; ATP
B) nitrate; amino acids
C) nitrate; nucleic acids
D) nitrite; nitrate
E) nitrite; pigments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The most common gas in the atmosphere is
A) carbon dioxide.
B) ozone.
C) oxygen.
D) nitrogen.
E) water vapor.
A) carbon dioxide.
B) ozone.
C) oxygen.
D) nitrogen.
E) water vapor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which material is not essential to the process of biological nitrogen fixation in soybean (legume) nodules?
A) N2 gas
B) O2 gas
C) A strong reducing agent
D) A great deal of energy
E) The enzyme nitrogenase
A) N2 gas
B) O2 gas
C) A strong reducing agent
D) A great deal of energy
E) The enzyme nitrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If you were working in the lab with nitrogenase, and the nitrogenase stopped catalyzing the reaction, you might need to eliminate or reduce the _______ in the experimental system to get it working again.
A) hydrogen gas
B) calcium carbonate
C) water
D) CO2
E) oxygen
A) hydrogen gas
B) calcium carbonate
C) water
D) CO2
E) oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In the legume-Rhizobium symbiosis, the _______ partner produces leghemoglobin to provide _______ to the _______ partner.
A) legume; oxygen; Rhizobium
B) Rhizobium; oxygen; legume
C) legume; nitrogen; Rhizobium
D) Rhizobium; nitrogen; legume
E) legume; sugars; Rhizobium
A) legume; oxygen; Rhizobium
B) Rhizobium; oxygen; legume
C) legume; nitrogen; Rhizobium
D) Rhizobium; nitrogen; legume
E) legume; sugars; Rhizobium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Most of the nitrogen on Earth exists in the form of
A) ammonia.
B) nitrate ions.
C) N2 gas.
D) amino acids.
E) proteins.
A) ammonia.
B) nitrate ions.
C) N2 gas.
D) amino acids.
E) proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



