Deck 37: Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/247
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 37: Reproduction in Flowering Plants
1
The two cells in a mature pollen grain are formed by
A) one meiotic division and one mitotic division.
B) two meiotic divisions and one mitotic division.
C) one meiotic division and two mitotic divisions.
D) two meiotic divisions and two mitotic divisions.
E) one meiotic division in which one of the four cells degenerates.
A) one meiotic division and one mitotic division.
B) two meiotic divisions and one mitotic division.
C) one meiotic division and two mitotic divisions.
D) two meiotic divisions and two mitotic divisions.
E) one meiotic division in which one of the four cells degenerates.
A
2
The microgametophyte of a flowering plant is
A) a flower.
B) an egg.
C) a pollen grain.
D) an anther.
E) the entire plant.
A) a flower.
B) an egg.
C) a pollen grain.
D) an anther.
E) the entire plant.
C
3
Which statement about the stamen and the carpel or pistil is true?
A) The stamen has two named parts, whereas the pistil has three.
B) The stamen produces microgametophytes, whereas the carpel produces megagametophytes.
C) The carpel is yellow and the stamen is brown.
D) The stamens are long, whereas the pistil is short.
E) The stamen is always taller than the pistil.
A) The stamen has two named parts, whereas the pistil has three.
B) The stamen produces microgametophytes, whereas the carpel produces megagametophytes.
C) The carpel is yellow and the stamen is brown.
D) The stamens are long, whereas the pistil is short.
E) The stamen is always taller than the pistil.
B
4
An angiosperm megagametophyte with 110 cells would be a highly unusual specimen because the flowering plant typically has a megagametophyte consisting of
A) one pollen grain.
B) a pollen tube.
C) an embryo sac with eight haploid nuclei.
D) microspores.
E) a megasporangium and the cells within it.
A) one pollen grain.
B) a pollen tube.
C) an embryo sac with eight haploid nuclei.
D) microspores.
E) a megasporangium and the cells within it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which processes are required in order for a megasporocyte to produce an egg cell?
A) Meiosis followed by mitosis
B) Mitosis followed by meiosis
C) Several meiotic divisions only
D) Several mitotic divisions only
E) Several nuclear fusion events
A) Meiosis followed by mitosis
B) Mitosis followed by meiosis
C) Several meiotic divisions only
D) Several mitotic divisions only
E) Several nuclear fusion events

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose you are studying fertilization in petunias.From what part of the flower would you extract material to study?
A) Petal
B) Ovule
C) Stigma
D) Sepal
E) Style
A) Petal
B) Ovule
C) Stigma
D) Sepal
E) Style

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
List the correct order of events in female gametophyte development.
A) Megagametophyte megasporocyte megaspore
B) Megagametophyte megaspore megasporocyte
C) Megasporocyte megaspore megagametophyte
D) Megaspore megasporocyte megagametophyte
E) Megaspore megagametophyte megasporocyte
A) Megagametophyte megasporocyte megaspore
B) Megagametophyte megaspore megasporocyte
C) Megasporocyte megaspore megagametophyte
D) Megaspore megasporocyte megagametophyte
E) Megaspore megagametophyte megasporocyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A flower that is wind-pollinated would be least likely to
A) have numerous anthers.
B) have sticky or feathery stigmas.
C) produce large numbers of pollen grains.
D) have a colorful corolla.
E) have unscented flowers.
A) have numerous anthers.
B) have sticky or feathery stigmas.
C) produce large numbers of pollen grains.
D) have a colorful corolla.
E) have unscented flowers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The embryo sac is also called the
A) megaspore.
B) megasporangium.
C) megasporocyte.
D) megasporophyll.
E) megagametophyte.
A) megaspore.
B) megasporangium.
C) megasporocyte.
D) megasporophyll.
E) megagametophyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Refer to the figure showing the typical life cycle of a plant. 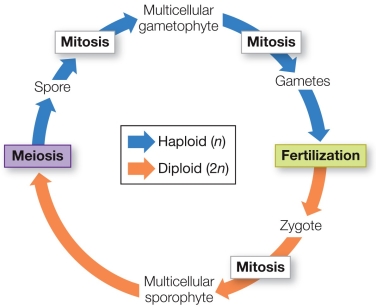 Suppose a botanist is studying a part of a flowering plant represented on the blue part of the figure.What is she studying?
Suppose a botanist is studying a part of a flowering plant represented on the blue part of the figure.What is she studying?
A) The male gametophyte
B) The female sporophyte
C) The roots
D) The petals
E) The sepals
 Suppose a botanist is studying a part of a flowering plant represented on the blue part of the figure.What is she studying?
Suppose a botanist is studying a part of a flowering plant represented on the blue part of the figure.What is she studying?A) The male gametophyte
B) The female sporophyte
C) The roots
D) The petals
E) The sepals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which cells do not participate in double fertilization in apples?
A) Tube cells
B) Synergids
C) Eggs
D) Central cells
E) Antipodal cells
A) Tube cells
B) Synergids
C) Eggs
D) Central cells
E) Antipodal cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A newly discovered plant is thought to be wind-pollinated because of its exposure to regular, strong wind in spring and the lack of insect pollinators in its habitat.The presence of which characteristic would confirm this assumption?
A) Colorful petals
B) Smooth stigmas
C) Large quantities of pollen
D) Large quantities of nectar
E) Pollination before the opening of the flower bud
A) Colorful petals
B) Smooth stigmas
C) Large quantities of pollen
D) Large quantities of nectar
E) Pollination before the opening of the flower bud

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which list represents the correct evolutionary order, from earliest to most recent evolution?
A) Wind-pollinated plant plant with swimming sperm animal-pollinated plant
B) Plant with swimming sperm animal-pollinated plant wind-pollinated plant
C) Animal-pollinated plant wind-pollinated plant plant with swimming sperm
D) Animal-pollinated plant plant with swimming sperm wind-pollinated plant
E) Plant with swimming sperm wind-pollinated plant animal-pollinated plant
A) Wind-pollinated plant plant with swimming sperm animal-pollinated plant
B) Plant with swimming sperm animal-pollinated plant wind-pollinated plant
C) Animal-pollinated plant wind-pollinated plant plant with swimming sperm
D) Animal-pollinated plant plant with swimming sperm wind-pollinated plant
E) Plant with swimming sperm wind-pollinated plant animal-pollinated plant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Perfect and imperfect flowers differ from each other in that perfect flowers have all four types of flower parts but imperfect flowers are missing
A) either stamens or petals.
B) either sepals or carpels.
C) either stamens or carpels.
D) either petals or sepals.
E) sepals.
A) either stamens or petals.
B) either sepals or carpels.
C) either stamens or carpels.
D) either petals or sepals.
E) sepals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A scientist has perfected a technique, using a microcapillary, for catching sperm as they leave the pollen tube.At which structure should the microcapillary be placed for studying the earliest steps in sperm release?
A) The egg cell
B) The synergids
C) The integument
D) The antipodals
E) The central cell
A) The egg cell
B) The synergids
C) The integument
D) The antipodals
E) The central cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The first event that takes place after pollen is released from the anthers is the
A) fusion of the egg and sperm nuclei.
B) transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma.
C) development of the two-celled pollen grain.
D) growth of the pollen tube after pollen germination.
E) division of the generative nucleus to produce two sperm nuclei.
A) fusion of the egg and sperm nuclei.
B) transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma.
C) development of the two-celled pollen grain.
D) growth of the pollen tube after pollen germination.
E) division of the generative nucleus to produce two sperm nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the mature embryo sac, the cells closest to where the pollen tube enters the ovule (the micropyle) are the
A) polar nuclei.
B) synergids.
C) polar nuclei and synergids.
D) egg cell and polar nuclei.
E) egg cell and synergids.
A) polar nuclei.
B) synergids.
C) polar nuclei and synergids.
D) egg cell and polar nuclei.
E) egg cell and synergids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In flowering plants, the only structure to which pollen is directly transferred is the
A) micropyle.
B) ovary.
C) style.
D) ovule.
E) stigma.
A) micropyle.
B) ovary.
C) style.
D) ovule.
E) stigma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which list represents the correct order of events (from earliest to latest) in the reproduction of angiosperms?
A) Fertilization meiosis egg formation
B) Egg formation fertilization meiosis
C) Egg formation meiosis fertilization
D) Meiosis egg formation fertilization
E) Meiosis fertilization egg formation
A) Fertilization meiosis egg formation
B) Egg formation fertilization meiosis
C) Egg formation meiosis fertilization
D) Meiosis egg formation fertilization
E) Meiosis fertilization egg formation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If an insect chews through a flower, from outside to center, in what order will it eat the flower parts?
A) Sepal carpel petal
B) Petal sepal carpel
C) Carpel petal sepal
D) Carpel sepal petal
E) Sepal petal carpel
A) Sepal carpel petal
B) Petal sepal carpel
C) Carpel petal sepal
D) Carpel sepal petal
E) Sepal petal carpel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Refer to the figure showing the initial stage of double fertilization. 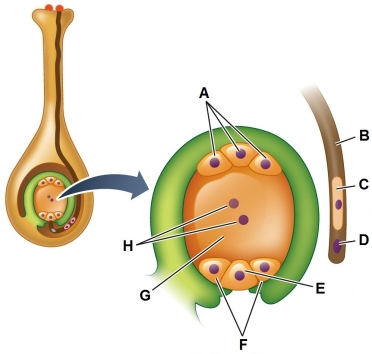 The female cell physically closest to structure C in the figure is the
The female cell physically closest to structure C in the figure is the
A) central cell.
B) egg cell.
C) synergid.
D) antipodal cell.
E) tube cell.
 The female cell physically closest to structure C in the figure is the
The female cell physically closest to structure C in the figure is theA) central cell.
B) egg cell.
C) synergid.
D) antipodal cell.
E) tube cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The endosperm is formed by a fusion between the _______ and _______.
A) egg nucleus; a sperm nucleus
B) egg nucleus; two sperm nuclei
C) synergid nuclei; a sperm nucleus
D) polar nuclei; a generative nucleus
E) polar nuclei; a sperm nucleus
A) egg nucleus; a sperm nucleus
B) egg nucleus; two sperm nuclei
C) synergid nuclei; a sperm nucleus
D) polar nuclei; a generative nucleus
E) polar nuclei; a sperm nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the fate of the seven cells of the embryo sac?
A) All but one disintegrates upon fertilization.
B) Two become fertilized; the others disintegrate.
C) Two become fertilized; the others fuse to form endosperm.
D) All are involved in nuclear fusion events.
E) They all become part of the seed tissue.
A) All but one disintegrates upon fertilization.
B) Two become fertilized; the others disintegrate.
C) Two become fertilized; the others fuse to form endosperm.
D) All are involved in nuclear fusion events.
E) They all become part of the seed tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The advantage of cross-fertilization in plants is that
A) it results in increased genetic diversity.
B) meiosis can occur.
C) it increases the chances of successful pollination.
D) no flowering is needed.
E) it requires less energy than self-fertilization.
A) it results in increased genetic diversity.
B) meiosis can occur.
C) it increases the chances of successful pollination.
D) no flowering is needed.
E) it requires less energy than self-fertilization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If you wanted to breed a plant to introduce self-incompatibility, which of the following mechanism(s) would be least useful to target in your breeding program?
A) Pollen recognition proteins on the stigma
B) Pollen germination on the stigma
C) Pollen tube growth through the style
D) Sperm nuclei fusion with the egg
E) Introduction of novel S alleles
A) Pollen recognition proteins on the stigma
B) Pollen germination on the stigma
C) Pollen tube growth through the style
D) Sperm nuclei fusion with the egg
E) Introduction of novel S alleles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A seed consists of a _______ embryo, a _______ endosperm, and a _______ seed coat.
A) diploid; triploid; diploid
B) haploid; triploid; diploid
C) diploid; triploid; haploid
D) diploid; diploid; diploid
E) haploid; diploid; haploid
A) diploid; triploid; diploid
B) haploid; triploid; diploid
C) diploid; triploid; haploid
D) diploid; diploid; diploid
E) haploid; diploid; haploid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which list represents the correct order of events (from earliest to latest) in the reproduction of angiosperms?
A) Pollination seed dispersal pollen formation
B) Pollen formation pollination seed dispersal
C) Seed dispersal pollen formation pollination
D) Seed dispersal pollination pollen formation
E) Pollen formation seed dispersal pollination
A) Pollination seed dispersal pollen formation
B) Pollen formation pollination seed dispersal
C) Seed dispersal pollen formation pollination
D) Seed dispersal pollination pollen formation
E) Pollen formation seed dispersal pollination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In flowering plants, fertilization occurs
A) where pollen lands on the stigma.
B) where the pollen tube germinates.
C) inside the pollen tube.
D) at the base of the embryo sac.
E) inside the seed.
A) where pollen lands on the stigma.
B) where the pollen tube germinates.
C) inside the pollen tube.
D) at the base of the embryo sac.
E) inside the seed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
After fertilization of the egg, the integument of the megasporangium develops into the
A) cotyledons.
B) embryo.
C) endosperm.
D) fruit.
E) seed coat.
A) cotyledons.
B) embryo.
C) endosperm.
D) fruit.
E) seed coat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Double fertilization in flowering plants results in the production of
A) one diploid embryo and a diploid endosperm.
B) one diploid embryo and a triploid endosperm.
C) two diploid embryos.
D) two diploid embryos and a haploid endosperm.
E) two diploid embryos and a diploid seed coat.
A) one diploid embryo and a diploid endosperm.
B) one diploid embryo and a triploid endosperm.
C) two diploid embryos.
D) two diploid embryos and a haploid endosperm.
E) two diploid embryos and a diploid seed coat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Refer to the figure showing the initial stage of double fertilization. 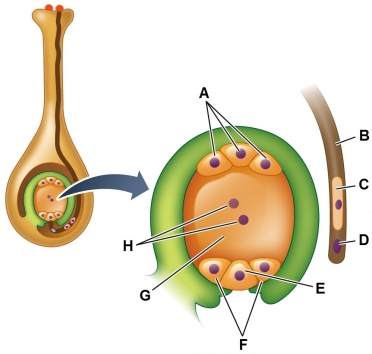 Identify the cell from the microgametophyte that will form the sperm.
Identify the cell from the microgametophyte that will form the sperm.
A) Tube cell (B)
B) Central cell (G)
C) Generative cell (C)
D) One of the synergids (F)
E) One of the antipodal cells (A)
 Identify the cell from the microgametophyte that will form the sperm.
Identify the cell from the microgametophyte that will form the sperm.A) Tube cell (B)
B) Central cell (G)
C) Generative cell (C)
D) One of the synergids (F)
E) One of the antipodal cells (A)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The egg can be fertilized by
A) one tube nucleus.
B) one sperm cell.
C) two sperm nuclei.
D) one generative nucleus.
E) two synergid nuclei.
A) one tube nucleus.
B) one sperm cell.
C) two sperm nuclei.
D) one generative nucleus.
E) two synergid nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Refer to the figure showing the initial stage of double fertilization. 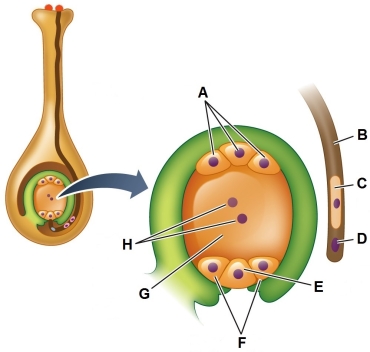 Identify the cell(s) of the embryo sac or pollen tube that do(es) not participate in double fertilization.
Identify the cell(s) of the embryo sac or pollen tube that do(es) not participate in double fertilization.
A) Antipodal cells (A)
B) Synergids (F)
C) Egg cell (E)
D) Tube cell (B)
E) Generative cell (C)
 Identify the cell(s) of the embryo sac or pollen tube that do(es) not participate in double fertilization.
Identify the cell(s) of the embryo sac or pollen tube that do(es) not participate in double fertilization.A) Antipodal cells (A)
B) Synergids (F)
C) Egg cell (E)
D) Tube cell (B)
E) Generative cell (C)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which characteristic is representative of all angiosperms?
A) Double cotyledons
B) Fleshy cotyledons
C) Seeds with stored nutrients
D) Double fertilization
E) Pollen production
A) Double cotyledons
B) Fleshy cotyledons
C) Seeds with stored nutrients
D) Double fertilization
E) Pollen production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How do the seed and the embryo sac differ from each other?
A) One is made from the embryo; the other is the embryo.
B) One is found inside the ovary; the other is inside the sepals.
C) One is made by fertilization; the other is made by apomixis.
D) One is microscopic; the other is submicroscopic.
E) One has parts of varied ploidy; the other is all haploid.
A) One is made from the embryo; the other is the embryo.
B) One is found inside the ovary; the other is inside the sepals.
C) One is made by fertilization; the other is made by apomixis.
D) One is microscopic; the other is submicroscopic.
E) One has parts of varied ploidy; the other is all haploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
After pollination, which of the following events is crucial for fertilization?
A) Sperm must swim to the egg and the polar nuclei.
B) Petals must close around the reproductive parts.
C) Meiosis must occur within the pollen grain.
D) A pollen tube must grow from the stigma to the ovule.
E) An insect must deliver pollen to the stigma.
A) Sperm must swim to the egg and the polar nuclei.
B) Petals must close around the reproductive parts.
C) Meiosis must occur within the pollen grain.
D) A pollen tube must grow from the stigma to the ovule.
E) An insect must deliver pollen to the stigma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which statement about a genetically self-incompatible species of plant is false?
A) It has many S alleles.
B) Its self pollen germinates poorly.
C) Its self pollen tubes grow poorly.
D) Its self pollen attaches poorly to pollinators.
E) Its recognition of self pollen involves proteins.
A) It has many S alleles.
B) Its self pollen germinates poorly.
C) Its self pollen tubes grow poorly.
D) Its self pollen attaches poorly to pollinators.
E) Its recognition of self pollen involves proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the seed, nutrients for the seedling are generally stored as
A) macromolecules.
B) monomers in solution.
C) monomers in fat storage.
D) cellular enzymes.
E) cellular organelles.
A) macromolecules.
B) monomers in solution.
C) monomers in fat storage.
D) cellular enzymes.
E) cellular organelles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The advantage of self-fertilization in plants is that
A) it results in increased genetic recombination.
B) meiosis can occur.
C) it increases the chances of successful pollination.
D) no flowering is needed.
E) only asexual reproduction is necessary.
A) it results in increased genetic recombination.
B) meiosis can occur.
C) it increases the chances of successful pollination.
D) no flowering is needed.
E) only asexual reproduction is necessary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A scientist has perfected a technique for capturing individual cells during the process of reproduction.What will she capture along with one of the synergids just before fertilization?
A) Sperm cells
B) Generative nuclei
C) Tube nuclei
D) Pollen nuclei
E) Microspores
A) Sperm cells
B) Generative nuclei
C) Tube nuclei
D) Pollen nuclei
E) Microspores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The fruit generally develops from which part of the flower?
A) Petals
B) Sepals
C) Ovary
D) Stamens
E) Pedicel
A) Petals
B) Sepals
C) Ovary
D) Stamens
E) Pedicel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is a temporal pattern of plant flowering?
A) Annual
B) Biannual
C) Monopausal
D) Diapausal
E) Peregrine
A) Annual
B) Biannual
C) Monopausal
D) Diapausal
E) Peregrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The ability of plants to measure night length was determined by experiments in which
A) plants were grown in 12 hours of darkness alternating with 12 hours of light.
B) plants were grown in continuous light.
C) plants were grown in dark periods that were interrupted with brief pulses of light.
D) flowering was measured in plants of different ages that had been placed on the same light-dark schedule.
E) plants were grown in a 24-hour cycle in which the length of the light period was increased gradually.
A) plants were grown in 12 hours of darkness alternating with 12 hours of light.
B) plants were grown in continuous light.
C) plants were grown in dark periods that were interrupted with brief pulses of light.
D) flowering was measured in plants of different ages that had been placed on the same light-dark schedule.
E) plants were grown in a 24-hour cycle in which the length of the light period was increased gradually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Technically, short-day plants flower when the _______ period _______ a critical period.
A) light; exceeds
B) light; is less than
C) light; equals
D) dark; exceeds
E) dark; is less than
A) light; exceeds
B) light; is less than
C) light; equals
D) dark; exceeds
E) dark; is less than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The seeds of a new kind of mangrove are not viviparous, which is unusual for that kind of tree.How do these seeds differ from other mangrove seeds?
A) They produce roots.
B) They die if not germinated within one season.
C) They are released from the fruit.
D) They become dormant.
E) They are protected from animal predators.
A) They produce roots.
B) They die if not germinated within one season.
C) They are released from the fruit.
D) They become dormant.
E) They are protected from animal predators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The integuments of the ovule develop into the _______, and the carpels ultimately become the wall of the _______.
A) cotyledons; endosperm
B) seed coat; fruit
C) cotyledons; seed coat
D) endosperm; seed coat
E) cotyledons; fruit
A) cotyledons; endosperm
B) seed coat; fruit
C) cotyledons; seed coat
D) endosperm; seed coat
E) cotyledons; fruit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Refer to the figure. 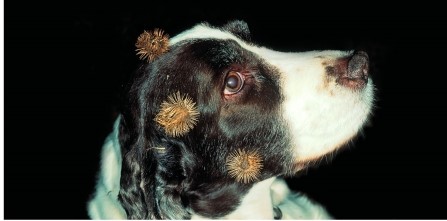 What function is this dog serving for the plant whose fruits are stuck to its head?
What function is this dog serving for the plant whose fruits are stuck to its head?
A) Consumption
B) Fertilization
C) Pollination
D) Seed dispersal
E) Disposal
 What function is this dog serving for the plant whose fruits are stuck to its head?
What function is this dog serving for the plant whose fruits are stuck to its head?A) Consumption
B) Fertilization
C) Pollination
D) Seed dispersal
E) Disposal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A plant's transition to a flowering state is often marked by a(n)
A) increased rate of photosynthesis.
B) decrease in vegetative growth.
C) increase in root development.
D) decreased rate of respiration.
E) increase in lateral bud growth.
A) increased rate of photosynthesis.
B) decrease in vegetative growth.
C) increase in root development.
D) decreased rate of respiration.
E) increase in lateral bud growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A vegetative meristem must _______ in order to begin switching to floral development.
A) experience determinate growth
B) be influenced by meristem identity genes
C) experience indeterminate growth
D) be influenced by other meristems
E) be exposed to long nights
A) experience determinate growth
B) be influenced by meristem identity genes
C) experience indeterminate growth
D) be influenced by other meristems
E) be exposed to long nights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Flowers can occur singly or in an orderly cluster known as a(n)
A) inflorescence.
B) flower cluster.
C) head.
D) grouping.
E) daisy chain.
A) inflorescence.
B) flower cluster.
C) head.
D) grouping.
E) daisy chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Refer to the figure. 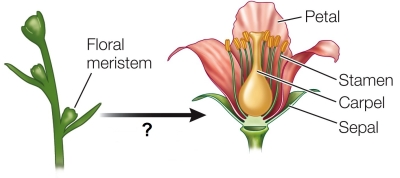 After an apical meristem has been redirected toward developing into a floral meristem, _______ are responsible for further refinement of the floral development pathway.
After an apical meristem has been redirected toward developing into a floral meristem, _______ are responsible for further refinement of the floral development pathway.
A) unknown hormones
B) light signals
C) floral identity genes
D) other, more mature floral meristems
E) abscisic acids
 After an apical meristem has been redirected toward developing into a floral meristem, _______ are responsible for further refinement of the floral development pathway.
After an apical meristem has been redirected toward developing into a floral meristem, _______ are responsible for further refinement of the floral development pathway.A) unknown hormones
B) light signals
C) floral identity genes
D) other, more mature floral meristems
E) abscisic acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If a seed is dormant, it likely contains high concentrations of
A) abscisic acid.
B) auxin.
C) cytokinin.
D) ethylene.
E) gibberellin.
A) abscisic acid.
B) auxin.
C) cytokinin.
D) ethylene.
E) gibberellin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When a vegetative apical meristem ceases production of leaves and axillary buds and instead produces structures such as bracts, it has become a(n)
A) axillary meristem.
B) inflorescence.
C) inflorescence meristem.
D) leaf.
E) branch.
A) axillary meristem.
B) inflorescence.
C) inflorescence meristem.
D) leaf.
E) branch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Angiosperm seeds develop
A) on a normal leaf.
B) in a fruit.
C) at the base of the flower next to sepals.
D) in the style.
E) in the stalk of the stamen.
A) on a normal leaf.
B) in a fruit.
C) at the base of the flower next to sepals.
D) in the style.
E) in the stalk of the stamen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A conifer is found with homologs of the genes that determine the location of floral parts in the flower.These are homologs of _______ genes.
A) meristem identity
B) whorl
C) flowering time
D) apical meristem
E) floral organ identity
A) meristem identity
B) whorl
C) flowering time
D) apical meristem
E) floral organ identity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Some wind-dispersed seeds use _______ to help them travel.
A) animal fur
B) bird feathers
C) winglike structures
D) velcro-like attachment structures
E) air sacs
A) animal fur
B) bird feathers
C) winglike structures
D) velcro-like attachment structures
E) air sacs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A newly discovered fruit has a thick, sweet flesh that is relished by bears.This fruit wall is
A) nourishing the embryo.
B) attracting seed eaters.
C) attracting pollinators.
D) attracting seed dispersers.
E) ensuring that the seeds fall close to the parent plant.
A) nourishing the embryo.
B) attracting seed eaters.
C) attracting pollinators.
D) attracting seed dispersers.
E) ensuring that the seeds fall close to the parent plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which characteristic is representative of some wind-dispersed seeds?
A) Abundant pollen
B) Hooked extensions
C) Fleshy fruit
D) Air chambers
E) A winglike structure
A) Abundant pollen
B) Hooked extensions
C) Fleshy fruit
D) Air chambers
E) A winglike structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A new kind of mustard plant is found to flower with any length of day or night as long as it is at least 2 months old.What kind of plant is this?
A) Biennial
B) Long-day plant
C) Long short-day plant
D) Short long-day plant
E) Short-day annual plant
A) Biennial
B) Long-day plant
C) Long short-day plant
D) Short long-day plant
E) Short-day annual plant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Suppose you are stranded on a desert island that is devoid of vegetation.One day at low tide, you notice a coconut that was not present the day before.It was most likely dispersed from its parent plant by
A) monkeys.
B) the wind.
C) fruit bats.
D) water.
E) birds.
A) monkeys.
B) the wind.
C) fruit bats.
D) water.
E) birds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which characteristic is a benefit of sexual reproduction in plants?
A) The great number of progeny that result
B) Ease of pollination
C) The creation of new combinations of genes and diverse phenotypes
D) The creation of a diploid plant from a haploid plant
E) Greater dispersal of progeny
A) The great number of progeny that result
B) Ease of pollination
C) The creation of new combinations of genes and diverse phenotypes
D) The creation of a diploid plant from a haploid plant
E) Greater dispersal of progeny

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A horticulturalist who wants to induce flowering in a crop of short-day plants should carry out the induction
A) in the spring.
B) when day length is below a critical maximum.
C) in midsummer.
D) when day length is above a critical maximum.
E) throughout the summer.
A) in the spring.
B) when day length is below a critical maximum.
C) in midsummer.
D) when day length is above a critical maximum.
E) throughout the summer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which protein(s) is/are most directly and physically involved in turning on gene expression for the transition to flower production?
A) FT
B) CO
C) FD
D) AP1
E) Both FT and FD
A) FT
B) CO
C) FD
D) AP1
E) Both FT and FD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which mechanism is not used by plants that flower independent of an external stimulus?
A) An internal clock
B) An unknown internal signal
C) A genetic program insensitive to the environment
D) A signal pathway dependent on bud position
E) A photoreceptor
A) An internal clock
B) An unknown internal signal
C) A genetic program insensitive to the environment
D) A signal pathway dependent on bud position
E) A photoreceptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Self-pollination results in progeny that
A) are identical to the parent.
B) are somewhat different from the parent because mutations are common.
C) can express only alleles that were present in the parent.
D) may be heterozygous in a locus where the parent is homozygous.
E) may be as varied as progeny resulting from cross-pollination.
A) are identical to the parent.
B) are somewhat different from the parent because mutations are common.
C) can express only alleles that were present in the parent.
D) may be heterozygous in a locus where the parent is homozygous.
E) may be as varied as progeny resulting from cross-pollination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A new variety of oats that requires vernalization must _______ before it will produce seeds.
A) be exposed to cold
B) have a source of soil calcium
C) experience a minimal day length
D) have sufficient moisture for a minimum period
E) experience a full year of growth
A) be exposed to cold
B) have a source of soil calcium
C) experience a minimal day length
D) have sufficient moisture for a minimum period
E) experience a full year of growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Winter wheat can be planted in the spring for fall harvest if it is
A) sprayed with gibberellins.
B) vernalized.
C) planted under a full moon.
D) stored in the dark for 50 days.
E) soaked in water.
A) sprayed with gibberellins.
B) vernalized.
C) planted under a full moon.
D) stored in the dark for 50 days.
E) soaked in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
You are given an extract of DNA from vernalized winter wheat seeds and asked to decide whether vernalization has gone on long enough for flowering to occur.In order to make this judgment, you should examine an extract of the cell nucleus under an electron microscope and look for
A) signs of degradation.
B) contamination with lipids.
C) compacted chromatin.
D) extra protein coating the DNA.
E) increased binding of histones.
A) signs of degradation.
B) contamination with lipids.
C) compacted chromatin.
D) extra protein coating the DNA.
E) increased binding of histones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Asexual reproduction is the best strategy for plants
A) that are well adapted to a stable environment.
B) as winter approaches.
C) when new genes must be introduced.
D) that have underground stems.
E) that have low seed production during a particular season.
A) that are well adapted to a stable environment.
B) as winter approaches.
C) when new genes must be introduced.
D) that have underground stems.
E) that have low seed production during a particular season.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Even if a plant receives an inductive stimulus that would normally lead to flowering, the flowering may be prevented by immediate removal of the
A) floral meristem.
B) vegetative apical meristem.
C) stems.
D) leaves.
E) roots.
A) floral meristem.
B) vegetative apical meristem.
C) stems.
D) leaves.
E) roots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Flowering is known to be triggered by
A) phytochrome.
B) NO.
C) ethylene.
D) abscisic acid.
E) florigen.
A) phytochrome.
B) NO.
C) ethylene.
D) abscisic acid.
E) florigen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
You are asked to identify the version of florigen found in carnivorous sundew plants.You decide to start by using biochemical methods to isolate the florigen molecule, which is a(n)
A) RNA molecule.
B) nucleotide.
C) DNA molecule.
D) protein.
E) lipid.
A) RNA molecule.
B) nucleotide.
C) DNA molecule.
D) protein.
E) lipid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Experiments have shown that when a short-day plant (SDP) and a long-day plant (LDP) are grafted together and the SDP is exposed to a photoperiod that causes it to flower, the LDP flowers as well.This observation supports the theory that a specific flower-initiating hormone is produced in plants.A properly controlled experiment would repeat the grafting procedure but
A) graft together the two plants and not induce the SDP.
B) omit the LDP.
C) omit the SDP.
D) shorten the SDP photoperiod.
E) include an LDP photoperiod.
A) graft together the two plants and not induce the SDP.
B) omit the LDP.
C) omit the SDP.
D) shorten the SDP photoperiod.
E) include an LDP photoperiod.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
For plants that flower in response to photoperiodic stimuli, the most critical determinant in the light-dark cycle is the
A) temperature.
B) length of the dark period for short-day plants and length of the light period for long-day plants.
C) length of the light period for short-day plants and length of the dark period for long-day plants.
D) length of uninterrupted dark.
E) length of uninterrupted light.
A) temperature.
B) length of the dark period for short-day plants and length of the light period for long-day plants.
C) length of the light period for short-day plants and length of the dark period for long-day plants.
D) length of uninterrupted dark.
E) length of uninterrupted light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A horticulturalist who is producing strawberry plants clonally is relying on which biological process?
A) Cross-hybridization
B) Forced seed germination
C) Apomixis
D) A runner system
E) Vernalization
A) Cross-hybridization
B) Forced seed germination
C) Apomixis
D) A runner system
E) Vernalization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In a short-day plant like cocklebur with a critical day length of 15 hours, flowering can be induced by _______ hours of light alternating with _______.
A) 12; 12 hours of darkness
B) 16; 8 hours of darkness
C) 14; 8 hours of darkness
D) 8; 8 hours of darkness
E) 15; 9 hours of darkness, interrupted by one short burst of white light
A) 12; 12 hours of darkness
B) 16; 8 hours of darkness
C) 14; 8 hours of darkness
D) 8; 8 hours of darkness
E) 15; 9 hours of darkness, interrupted by one short burst of white light

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Short-day plants bloom
A) in the spring only.
B) in the fall only.
C) in the summer.
D) only after the second year of life.
E) in the spring or in the fall.
A) in the spring only.
B) in the fall only.
C) in the summer.
D) only after the second year of life.
E) in the spring or in the fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Refer to the figure showing two tobacco plants.  The large plant on the right has failed to flower in summer as normal tobacco plants do.A genetic mutation caused it to become a(n) _______ plant.
The large plant on the right has failed to flower in summer as normal tobacco plants do.A genetic mutation caused it to become a(n) _______ plant.
A) long-day
B) short-day
C) infertile
D) short-day-long-day
E) long-day-short-day
 The large plant on the right has failed to flower in summer as normal tobacco plants do.A genetic mutation caused it to become a(n) _______ plant.
The large plant on the right has failed to flower in summer as normal tobacco plants do.A genetic mutation caused it to become a(n) _______ plant.A) long-day
B) short-day
C) infertile
D) short-day-long-day
E) long-day-short-day

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
To stage long-day plants so they will produce blooms for a flower show, what can a greenhouse manager provide to the plants to prevent flowering?
A) A long, uninterrupted period of darkness
B) A period of daylight interrupted by a dark period
C) A period of daylight interrupted by a prolonged period of red light
D) A period of darkness interrupted by a period of far-red light
E) A period of daylight interrupted by a brief period of red light
A) A long, uninterrupted period of darkness
B) A period of daylight interrupted by a dark period
C) A period of daylight interrupted by a prolonged period of red light
D) A period of darkness interrupted by a period of far-red light
E) A period of daylight interrupted by a brief period of red light

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What could be expected from a mutant plant that lacks expression of the FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC) gene?
A) Earlier flowering than in the wild type
B) More leaves than in the wild type
C) More flower petals per flower than in the wild type
D) Fewer leaf hairs than in the wild type
E) Taller growth than in the wild type
A) Earlier flowering than in the wild type
B) More leaves than in the wild type
C) More flower petals per flower than in the wild type
D) Fewer leaf hairs than in the wild type
E) Taller growth than in the wild type

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 247 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



