Deck 5: Cell Biology of Bacteria and Eukaryotes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Cell Biology of Bacteria and Eukaryotes
1
In the image shown the circles and squares indicate molecules.The circles are at a higher concentration outside the cell and the squares are at a higher concentration inside the cell.Which of the following statements is correct?
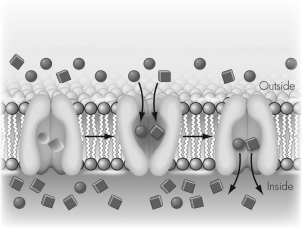
A) Energy is released if the circles move into the cell or if the squares move out of the cell.
B) Energy is released if the circles move into the cell or if the squares move into the cell.
C) Energy is released if the circles move out of the cell or if the squares move out of the cell.
D) Energy is released if the circles move out of the cell or if the squares move into the cell.

A) Energy is released if the circles move into the cell or if the squares move out of the cell.
B) Energy is released if the circles move into the cell or if the squares move into the cell.
C) Energy is released if the circles move out of the cell or if the squares move out of the cell.
D) Energy is released if the circles move out of the cell or if the squares move into the cell.
A
2
In this scanning electron micrograph of Borrelia burgdorferi,which of the following structures is visible?
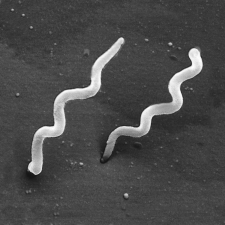
A) the outer sheath
B) cytoplasmic filaments
C) the genome
D) flagellar motors

A) the outer sheath
B) cytoplasmic filaments
C) the genome
D) flagellar motors
A
3
In this model of a Gram-negative bacterial cell envelope,which line is drawn to the periplasm?
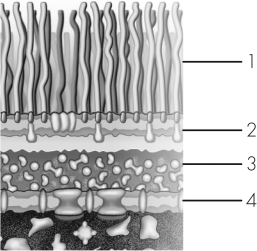
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
C
4
Which of the following is FALSE of teichoic acids?
A) They reinforce the cell wall.
B) They may help pathogens attach to host cells.
C) They are recognized by the host immune system.
D) They repel the Gram stain.
A) They reinforce the cell wall.
B) They may help pathogens attach to host cells.
C) They are recognized by the host immune system.
D) They repel the Gram stain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How does the cell wall protect bacterial cells from osmotic shock?
A) The wall forms a rigid cage that withstands turgor pressure.
B) The wall is impermeable to water, preventing turgor pressure.
C) The wall is impermeable to ions and other solutes, preventing osmotic imbalance.
D) The wall ensures cells are only found in environments where turgor pressure will not occur.
A) The wall forms a rigid cage that withstands turgor pressure.
B) The wall is impermeable to water, preventing turgor pressure.
C) The wall is impermeable to ions and other solutes, preventing osmotic imbalance.
D) The wall ensures cells are only found in environments where turgor pressure will not occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In an E.coli cell,which molecule is found in only 1-2 copies per cell?
A) DNA
B) RNA
C) protein
D) phospholipids
A) DNA
B) RNA
C) protein
D) phospholipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In this model of a Gram-negative bacterial cell envelope,which line is drawn to lipopolysaccharides?
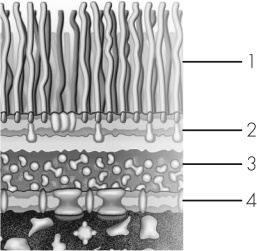
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In this image the energy released by the transport of the circles out of the cell is used to drive the import of the squares into the cell.This is an example of
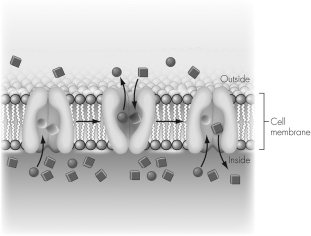
A) passive transport.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) symport coupled transport.
D) antiport coupled transport.

A) passive transport.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) symport coupled transport.
D) antiport coupled transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In Gram-negative bacteria,peptidoglycan is found in the
A) cytoplasm.
B) inner membrane.
C) outer membrane.
D) periplasm.
A) cytoplasm.
B) inner membrane.
C) outer membrane.
D) periplasm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Lipopolysaccharides are found in
A) Gram-positive bacteria.
B) Gram-negative bacteria.
C) archaea.
D) eukaryotic microbes.
A) Gram-positive bacteria.
B) Gram-negative bacteria.
C) archaea.
D) eukaryotic microbes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Mycoplasma lost their cell walls via reductive evolution.This was possible because
A) their cell membranes became extra thick to compensate.
B) it allowed them to not be sensitive to antibiotics that target the cell wall.
C) as obligate parasites they live in environments with constant osmolarity.
D) they live in soils with plenty of available moisture.
A) their cell membranes became extra thick to compensate.
B) it allowed them to not be sensitive to antibiotics that target the cell wall.
C) as obligate parasites they live in environments with constant osmolarity.
D) they live in soils with plenty of available moisture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
This image models a
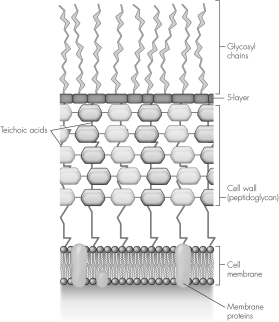
A) Gram-positive cell envelope.
B) Gram-negative cell envelope.
C) eukaryotic cell membrane.
D) mycobacterial envelope.

A) Gram-positive cell envelope.
B) Gram-negative cell envelope.
C) eukaryotic cell membrane.
D) mycobacterial envelope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In Gram-negative bacteria the cell membrane separates the
A) periplasm from the external environment.
B) cytoplasm from the external environment.
C) cytoplasm from the nucleoid.
D) DNA from the RNA.
A) periplasm from the external environment.
B) cytoplasm from the external environment.
C) cytoplasm from the nucleoid.
D) DNA from the RNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which bacterial cellular constituent is most liable to change under changing environmental conditions?
A) DNA
B) peptidoglycan
C) polyamines
D) proteins
A) DNA
B) peptidoglycan
C) polyamines
D) proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The bacterial cell wall is an attractive target for antibiotics because
A) bacterial cells cannot develop resistance to antibiotics that target the cell wall.
B) animal cells lack a cell wall.
C) the cell wall is unimportant for bacterial survival.
D) the cell wall is the only structure bacteria require for survival.
A) bacterial cells cannot develop resistance to antibiotics that target the cell wall.
B) animal cells lack a cell wall.
C) the cell wall is unimportant for bacterial survival.
D) the cell wall is the only structure bacteria require for survival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The majority of the bacterial cell cytoplasm (by total weight)is
A) DNA.
B) RNA.
C) protein.
D) water.
A) DNA.
B) RNA.
C) protein.
D) water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the cellular target of penicillin (the first antibiotic discovered)?
A) the DNA genome
B) the cell wall
C) ribosomes
D) ABC transporters
A) the DNA genome
B) the cell wall
C) ribosomes
D) ABC transporters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In this image a transmembrane protein moves circles out of the cell,providing energy to move squares into the cell.Which of the following is correct?
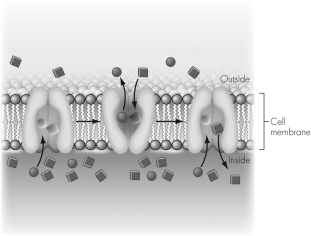
A) Both the circles and the squares move down their concentration gradients.
B) Both the circles and the squares move against their concentration gradients.
C) The circles move down their concentration gradient and the squares move against their concentration gradient.
D) The circles move against their concentration gradient and the squares move down their concentration gradient.

A) Both the circles and the squares move down their concentration gradients.
B) Both the circles and the squares move against their concentration gradients.
C) The circles move down their concentration gradient and the squares move against their concentration gradient.
D) The circles move against their concentration gradient and the squares move down their concentration gradient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The cell wall is part of the
A) cell membrane.
B) cytoplasm.
C) cell envelope.
D) proteome.
A) cell membrane.
B) cytoplasm.
C) cell envelope.
D) proteome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The cell membrane stores energy by maintaining a separation of
A) DNA.
B) proteins.
C) ions.
D) lipids.
A) DNA.
B) proteins.
C) ions.
D) lipids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Ribosomes associate with which endomembrane organelle?
A) Golgi complex
B) endoplasmic reticulum
C) lysosomes
D) peroxisomes
A) Golgi complex
B) endoplasmic reticulum
C) lysosomes
D) peroxisomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which organelle arose via endosymbiosis?
A) chloroplast
B) Golgi apparatus
C) lysosome
D) nucleus
A) chloroplast
B) Golgi apparatus
C) lysosome
D) nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Flagella are required for bacterial
A) chemotaxis.
B) growth.
C) adherence.
D) buoyancy.
A) chemotaxis.
B) growth.
C) adherence.
D) buoyancy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following shows the correct path a secreted protein takes in a eukaryotic cell?
A) Golgi complex, rough ER, vesicle, cell membrane
B) vesicle, rough ER, Golgi complex, cell membrane
C) rough ER, Golgi complex, vesicle, cell membrane
D) rough ER, Golgi complex, cell membrane, vesicle
A) Golgi complex, rough ER, vesicle, cell membrane
B) vesicle, rough ER, Golgi complex, cell membrane
C) rough ER, Golgi complex, vesicle, cell membrane
D) rough ER, Golgi complex, cell membrane, vesicle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
ATP synthase is found in bacterial cell membranes.In eukaryotic cells,ATP synthase is found in the
A) cell membrane.
B) cytoplasm.
C) mitochondrial inner membrane.
D) mitochondrial matrix.
A) cell membrane.
B) cytoplasm.
C) mitochondrial inner membrane.
D) mitochondrial matrix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is a function of lipopolysaccharide?
A) helps cells resist phagocytosis
B) aids in outer membrane cell wall attachment
C) allows for mobility to promote chemotaxis
D) provides energy to the cell
A) helps cells resist phagocytosis
B) aids in outer membrane cell wall attachment
C) allows for mobility to promote chemotaxis
D) provides energy to the cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Magnetotactic bacteria swim along a magnetic field.To do this these bacteria have which of the following structures that are not present in all bacterial species?
A) storage granules
B) sulfur granules
C) flagella
D) gas vesicles
A) storage granules
B) sulfur granules
C) flagella
D) gas vesicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which organelle houses a eukaryotic cell's genome?
A) rough endoplasmic reticulum
B) contractile vacuole
C) ribosome
D) nucleus
A) rough endoplasmic reticulum
B) contractile vacuole
C) ribosome
D) nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Pili and stalks enable bacterial
A) adherence.
B) chemotaxis.
C) photosynthesis.
D) symport.
A) adherence.
B) chemotaxis.
C) photosynthesis.
D) symport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is true of growing bacteria?
A) DNA synthesis occurs continuously.
B) DNA synthesis occurs during a defined period.
C) They suspend flagella rotation to put energy toward DNA replication.
D) DNA synthesis cannot occur at the same time as transcription.
A) DNA synthesis occurs continuously.
B) DNA synthesis occurs during a defined period.
C) They suspend flagella rotation to put energy toward DNA replication.
D) DNA synthesis cannot occur at the same time as transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following structures is obligatory for all bacterial cells?
A) nucleoid
B) flagella
C) pili
D) magnetosomes
A) nucleoid
B) flagella
C) pili
D) magnetosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
This transmission electron micrograph of a marine microbe shows internal structures such as thylakoids.This microbe has what capability that is not present in all bacterial species?
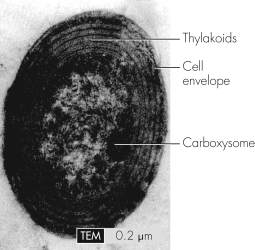
A) adherence
B) chemotaxis
C) DNA replication
D) photosynthesis

A) adherence
B) chemotaxis
C) DNA replication
D) photosynthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The arrows indicate the partition that separates a bacterial cell into two new daughter cells.This partition is called the
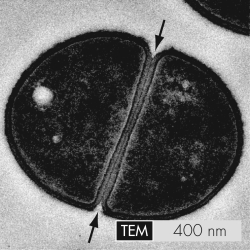
A) stalk.
B) S-layer.
C) septum.
D) termination site.

A) stalk.
B) S-layer.
C) septum.
D) termination site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
While most wild E.coli usually have flagella,many lab strains have lost their flagella.What is a likely cause of this loss?
A) reductive evolution due to an increased need for chemotaxis
B) reductive evolution due to an unchanging environment
C) reductive evolution due to an increased need for magnetotaxis
D) reductive evolution due to a decreased need for magnetotaxis
A) reductive evolution due to an increased need for chemotaxis
B) reductive evolution due to an unchanging environment
C) reductive evolution due to an increased need for magnetotaxis
D) reductive evolution due to a decreased need for magnetotaxis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Murein lipoprotein is a part of the ________ of the ________.
A) outer leaflet, outer membrane.
B) inner leaflet, outer membrane.
C) outer leaflet, inner membrane.
D) inner leaflet, inner membrane.
A) outer leaflet, outer membrane.
B) inner leaflet, outer membrane.
C) outer leaflet, inner membrane.
D) inner leaflet, inner membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
This transmission electron micrograph shows a
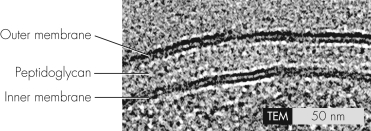
A) Gram-positive cell envelope.
B) Gram-negative cell envelope.
C) eukaryotic cell membrane.
D) mycobacterial envelope.

A) Gram-positive cell envelope.
B) Gram-negative cell envelope.
C) eukaryotic cell membrane.
D) mycobacterial envelope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Bacterial cells that expand their cell walls during septation (not before)and septate in parallel planes will form
A) chains of rods (bacilli).
B) tetrads of rods (bacilli).
C) chains of spheres (cocci).
D) tetrads of spheres (cocci).
A) chains of rods (bacilli).
B) tetrads of rods (bacilli).
C) chains of spheres (cocci).
D) tetrads of spheres (cocci).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following helps compact bacterial DNA?
A) the origin of replication site
B) supercoils
C) porins
D) pilins
A) the origin of replication site
B) supercoils
C) porins
D) pilins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which organelle is NOT part of the endomembrane system?
A) mitochondrion
B) lysosome
C) peroxisome
D) Golgi complex
A) mitochondrion
B) lysosome
C) peroxisome
D) Golgi complex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
This electron micrograph shows staphylococci,spherical cells that cluster together like grape bunches.This form occurs when cell wall expansion occurs
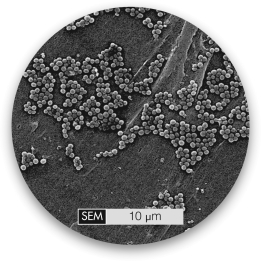
A) prior to septation and septation occurs in parallel planes.
B) prior to septation and septation occurs in random orientations.
C) during septation and septation occurs in parallel planes.
D) during septation and septation occurs in random orientations.

A) prior to septation and septation occurs in parallel planes.
B) prior to septation and septation occurs in random orientations.
C) during septation and septation occurs in parallel planes.
D) during septation and septation occurs in random orientations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Describe the two types of energy cells used to move molecules across membranes against their concentration gradients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The bacterial nucleoid contains loops of DNA that emanate from a central point called the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
CASE HISTORY
Jennifer,age 23,had just graduated from college with a Fulbright fellowship to study sociology in Africa.Before leaving the United States,she obtained a routine physical exam at a large city hospital.Upon returning home from the hospital,she developed a swelling in her leg.When she returned to the hospital,she was told that the swelling represented an allergic reaction and was given anti-inflammatory agents.The swelling grew,and within a day the skin ruptured with a bloody discharge.Upon return to the emergency room,Jennifer at last received the correct diagnosis of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus infection (MRSA).A nurse commented that hospital visitors can acquire MRSA;the infectious agent is endemic at many hospitals in the United States and is very difficult to eradicate.She showed Jennifer a micrograph of the bacteria,Staphylococcus aureus,which septate in alternating division planes,thus forming clusters of cells.Jennifer required many weeks of treatment with the antibiotics doxycycline and clindamycin (inhibits protein synthesis)before the infection resolved,and she had to postpone her fellowship for a year.
Methicillin,the antibiotic to which MRSA is characteristically resistant,targets the cell wall.Discuss the structure of the cell wall in a bacterial cell like those of MRSA and how antibiotics can target this structure without harming the patient.
Jennifer,age 23,had just graduated from college with a Fulbright fellowship to study sociology in Africa.Before leaving the United States,she obtained a routine physical exam at a large city hospital.Upon returning home from the hospital,she developed a swelling in her leg.When she returned to the hospital,she was told that the swelling represented an allergic reaction and was given anti-inflammatory agents.The swelling grew,and within a day the skin ruptured with a bloody discharge.Upon return to the emergency room,Jennifer at last received the correct diagnosis of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus infection (MRSA).A nurse commented that hospital visitors can acquire MRSA;the infectious agent is endemic at many hospitals in the United States and is very difficult to eradicate.She showed Jennifer a micrograph of the bacteria,Staphylococcus aureus,which septate in alternating division planes,thus forming clusters of cells.Jennifer required many weeks of treatment with the antibiotics doxycycline and clindamycin (inhibits protein synthesis)before the infection resolved,and she had to postpone her fellowship for a year.
Methicillin,the antibiotic to which MRSA is characteristically resistant,targets the cell wall.Discuss the structure of the cell wall in a bacterial cell like those of MRSA and how antibiotics can target this structure without harming the patient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The ability of bacterial cells to swim toward favorable environments and away from harmful environments is known as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Explain how bacterial cells can divide so rapidly,some in as little as ten minutes between generations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the process of ________,a vesicle fuses with the cell membrane,releasing vesicle contents into the extracellular environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Would pili be more advantageous to bacteria in a rapidly changing or in an unchanging environment? Please explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
CASE HISTORY
Sharon,the CEO of a start-up company,lives in Westchester County,a wooded community north of New York City.She spends her summer weekends e-mailing her managers from the outdoor deck of her home,shaded by tall oak trees.The acorns attract mice and deer,and the leaf litter is full of ticks (Ixodes scapularis).
One evening Sharon's husband noticed a red rash on her back,consisting of a ring shape several centimeters across,surrounding another red spot in the middle.Sharon recalled seeing this "bull's-eye" type of rash on the Internet.The rash was described as the hallmark of Lyme disease,or borreliosis,caused in the United States by the tick-borne bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi (in Europe,by the closely related species Borrelia afzelii).The distinctive rash,erythema migrans ("migrating redness"),begins at the site of a tick bite and expands concentrically as the bacteria migrate outward.Sharon recalled that a neighbor's child had suffered crippling arthritis caused by an undetected case of Lyme disease.Another neighbor who contracted Lyme disease had suffered from meningitis (inflammation of the brain lining)and neurological abnormalities,including facial paralysis,ultimately losing his job and his million-dollar home.
The next day Sharon went to her doctor and was treated with the antibiotic doxycycline,a tetracycline derivative that targets the bacterial ribosome.Doxycycline is the antibiotic of choice for B.burgdorferi.Sharon was fortunate to make a full recovery before serious symptoms appeared.
The bull's-eye rash that is a hallmark of Sharon's infection is associated with movement of the bacteria from the initial site of tick bite and infection.Discuss how these bacteria move and the cell structures associated with movement.
Sharon,the CEO of a start-up company,lives in Westchester County,a wooded community north of New York City.She spends her summer weekends e-mailing her managers from the outdoor deck of her home,shaded by tall oak trees.The acorns attract mice and deer,and the leaf litter is full of ticks (Ixodes scapularis).
One evening Sharon's husband noticed a red rash on her back,consisting of a ring shape several centimeters across,surrounding another red spot in the middle.Sharon recalled seeing this "bull's-eye" type of rash on the Internet.The rash was described as the hallmark of Lyme disease,or borreliosis,caused in the United States by the tick-borne bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi (in Europe,by the closely related species Borrelia afzelii).The distinctive rash,erythema migrans ("migrating redness"),begins at the site of a tick bite and expands concentrically as the bacteria migrate outward.Sharon recalled that a neighbor's child had suffered crippling arthritis caused by an undetected case of Lyme disease.Another neighbor who contracted Lyme disease had suffered from meningitis (inflammation of the brain lining)and neurological abnormalities,including facial paralysis,ultimately losing his job and his million-dollar home.
The next day Sharon went to her doctor and was treated with the antibiotic doxycycline,a tetracycline derivative that targets the bacterial ribosome.Doxycycline is the antibiotic of choice for B.burgdorferi.Sharon was fortunate to make a full recovery before serious symptoms appeared.
The bull's-eye rash that is a hallmark of Sharon's infection is associated with movement of the bacteria from the initial site of tick bite and infection.Discuss how these bacteria move and the cell structures associated with movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The region within the inner and outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria is known as the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What evidence would suggest that a newly discovered eukaryotic organelle was formed via endosymbiosis?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Compare and contrast the Gram-negative and Gram-positive cell envelopes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If Na⁺ is at a higher concentration outside a cell than inside,________ is the most likely means for sodium ions to enter the cell (and for nothing else to enter or leave).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
CASE HISTORY
In the Indian state of Bihar,a school nurse noticed that a 13-year-old boy,Naranjan,had swelling on his nose and lips.When questioned,Naranjan complained of a pruritic (itchy)rash on his arms and legs.Upon examination,the nurse found pale patches of skin on his back.The pale patches lacked sensation,and there was partial loss of sensation in Naranjan's wrists and forearms.The patient was diagnosed with leprosy,caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae.The bacteria stain acid-fast and are spread primarily by nasal secretions.For unknown reasons,only 5% of people exposed to the bacteria are susceptible to infection.In a susceptible host,the bacteria can grow slowly for many years without symptoms.They infect the peripheral nerves,causing loss of sensation,and the body's immune reaction generates skin lesions.To halt the disease,Naranjan was started on a two-year course of multidrug therapy combining dapsone,clofazimine,and rifampin.To monitor hepatotoxicity,liver function tests were ordered.Naranjan's family and neighbors were screened;one member,an uncle,showed skin lesions.The uncle was treated also.Leprosy is difficult to eradicate because of the long incubation period and because people hide their symptoms,fearing stigma as "lepers."
Mycobacterium leprae,or leprosy disease,often takes years to develop.Naranjan must use a long-term multidrug therapy to cure it.Why is it necessary to take the drugs for such a long period,and why must he take so many drugs at once?
A) Mycobacteria are Gram-negative organisms. They must be killed slowly to prevent release of toxic LPS.
B) Mycolic acid within the cell wall reduces nutrient uptake, resulting in slow growth, and excludes some antibiotics.
C) Mycobacteria are all highly resistant to antibiotics.
D) Mycobacteria don't have cell walls, so must be treated with antibiotics that target other structures.
In the Indian state of Bihar,a school nurse noticed that a 13-year-old boy,Naranjan,had swelling on his nose and lips.When questioned,Naranjan complained of a pruritic (itchy)rash on his arms and legs.Upon examination,the nurse found pale patches of skin on his back.The pale patches lacked sensation,and there was partial loss of sensation in Naranjan's wrists and forearms.The patient was diagnosed with leprosy,caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae.The bacteria stain acid-fast and are spread primarily by nasal secretions.For unknown reasons,only 5% of people exposed to the bacteria are susceptible to infection.In a susceptible host,the bacteria can grow slowly for many years without symptoms.They infect the peripheral nerves,causing loss of sensation,and the body's immune reaction generates skin lesions.To halt the disease,Naranjan was started on a two-year course of multidrug therapy combining dapsone,clofazimine,and rifampin.To monitor hepatotoxicity,liver function tests were ordered.Naranjan's family and neighbors were screened;one member,an uncle,showed skin lesions.The uncle was treated also.Leprosy is difficult to eradicate because of the long incubation period and because people hide their symptoms,fearing stigma as "lepers."
Mycobacterium leprae,or leprosy disease,often takes years to develop.Naranjan must use a long-term multidrug therapy to cure it.Why is it necessary to take the drugs for such a long period,and why must he take so many drugs at once?
A) Mycobacteria are Gram-negative organisms. They must be killed slowly to prevent release of toxic LPS.
B) Mycolic acid within the cell wall reduces nutrient uptake, resulting in slow growth, and excludes some antibiotics.
C) Mycobacteria are all highly resistant to antibiotics.
D) Mycobacteria don't have cell walls, so must be treated with antibiotics that target other structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



