Deck 7: Bacterial Metabolism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Bacterial Metabolism
1
The human genome does NOT code for enzymes that can catabolize
A) cellulose.
B) starch.
C) fatty acids.
D) proteins.
A) cellulose.
B) starch.
C) fatty acids.
D) proteins.
A
2
What molecule is depicted here?
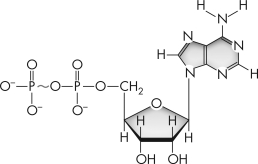
A) ADP
B) ATP
C) NAD+
D) NADH

A) ADP
B) ATP
C) NAD+
D) NADH
A
3
Which numbered arrow(s)point(s)to a step that indicates reactions carried out by autotrophs?
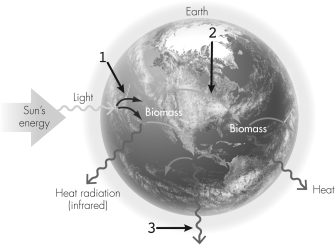
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 2

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 2
A
4
Which metabolic pathway is shown here?
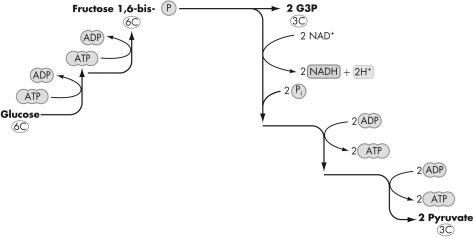
A) Calvin cycle
B) glycolysis
C) oxidative phosphorylation
D) tricarboxylic acid cycle

A) Calvin cycle
B) glycolysis
C) oxidative phosphorylation
D) tricarboxylic acid cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The hydrolysis of a protein into amino acids is an example of
A) anabolism.
B) catabolism.
C) lithotrophy.
D) nitrogen fixation.
A) anabolism.
B) catabolism.
C) lithotrophy.
D) nitrogen fixation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If cells cannot carry out fermentation or respiration,which numbered box indicates the first step of glycolysis to be affected?
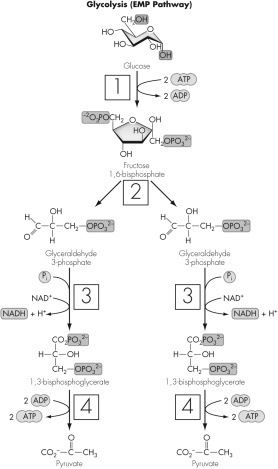
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What catabolite is produced first from the catabolism of starch and cellulose?
A) acetyl-CoA
B) amino acids
C) glucose
D) glycerol
A) acetyl-CoA
B) amino acids
C) glucose
D) glycerol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is true of metabolic reactions?
A) They are all catalyzed by enzymes.
B) They all release energy.
C) Reactions are unique to particular organisms.
D) They always use or produce ATP.
A) They are all catalyzed by enzymes.
B) They all release energy.
C) Reactions are unique to particular organisms.
D) They always use or produce ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which numbered box most clearly shows a redox reaction?
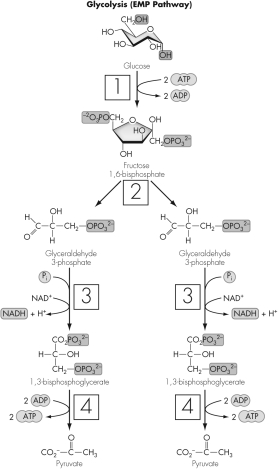
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An organism gains energy using H₂ as an electron donor and sulfate as an electron acceptor.This organism is categorized as an
A) aerobic lithotroph.
B) anaerobic lithotroph.
C) aerobic organotroph.
D) anaerobic organotroph.
A) aerobic lithotroph.
B) anaerobic lithotroph.
C) aerobic organotroph.
D) anaerobic organotroph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
During glycolysis glucose is ________ and NAD⁺ is ________.
A) oxidized; reduced
B) reduced; oxidized
C) oxidized; oxidized
D) reduced; reduced
A) oxidized; reduced
B) reduced; oxidized
C) oxidized; oxidized
D) reduced; reduced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In a metabolic reaction involving the conversion of NADH to NAD⁺
A) NADH loses electrons and gains energy.
B) NADH gains electrons and gains energy.
C) NADH loses electrons and loses energy.
D) NADH gains electrons and loses energy.
A) NADH loses electrons and gains energy.
B) NADH gains electrons and gains energy.
C) NADH loses electrons and loses energy.
D) NADH gains electrons and loses energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which statement describes the reaction shown?
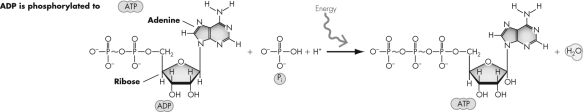
A) It is an anabolic reaction.
B) It is a hydrolysis reaction.
C) It is a redox reaction.
D) It has a negative change in free energy.

A) It is an anabolic reaction.
B) It is a hydrolysis reaction.
C) It is a redox reaction.
D) It has a negative change in free energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is true of energy and living cells?
A) Organisms can create their own energy.
B) Organisms do not require inputs of energy from the environment.
C) Organisms require inputs of energy from the environment to survive.
D) Only heterotrophic organisms require environmental energy inputs to survive.
A) Organisms can create their own energy.
B) Organisms do not require inputs of energy from the environment.
C) Organisms require inputs of energy from the environment to survive.
D) Only heterotrophic organisms require environmental energy inputs to survive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Humans harness microbial ________ to preserve foods and retain caloric value.
A) glycolysis
B) fermentation
C) TCA cycle
D) aerobic respiration
A) glycolysis
B) fermentation
C) TCA cycle
D) aerobic respiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which numbered arrow(s)point(s)to a step that indicates reactions carried out by heterotrophs?
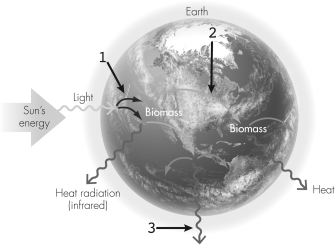
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 2

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A metabolic reaction can only provide energy to cells if
A) DG is negative.
B) DG is positive.
C) DS is negative.
D) DS is positive.
A) DG is negative.
B) DG is positive.
C) DS is negative.
D) DS is positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Starting with one glucose molecule,the products of glycolysis include
A) 1 pyruvate, 2 net ATP, and 2 NADPH.
B) 1 pyruvate, 4 net ATP, and 2 NADH.
C) 2 pyruvate, 4 net ATP, and 4 NADH.
D) 2 pyruvate, 2 net ATP, and 2 NADH.
A) 1 pyruvate, 2 net ATP, and 2 NADPH.
B) 1 pyruvate, 4 net ATP, and 2 NADH.
C) 2 pyruvate, 4 net ATP, and 4 NADH.
D) 2 pyruvate, 2 net ATP, and 2 NADH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which reactions both require energy?
A) ATP hydrolysis and reduction of NAD+
B) ATP hydrolysis and oxidation of NADH
C) ATP production and reduction of NAD+
D) ATP production and oxidation of NADH
A) ATP hydrolysis and reduction of NAD+
B) ATP hydrolysis and oxidation of NADH
C) ATP production and reduction of NAD+
D) ATP production and oxidation of NADH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Enzymes increase reaction rates by
A) increasing activation energies.
B) decreasing activation energies.
C) increasing the concentration of reactants.
D) increasing the concentration of products.
A) increasing activation energies.
B) decreasing activation energies.
C) increasing the concentration of reactants.
D) increasing the concentration of products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If in the ETS electrons are passed from a to b and finally accepted by c, then
A) a is a stronger electron acceptor than b.
B) a is a stronger electron acceptor than c.
C) a is a stronger electron donor than b.
D) c is a stronger electron donor than b.
A) a is a stronger electron acceptor than
B)
B)
B)
A) a is a stronger electron acceptor than b.
B) a is a stronger electron acceptor than c.
C) a is a stronger electron donor than b.
D) c is a stronger electron donor than b.
A) a is a stronger electron acceptor than
B)
B)
B)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Under what environmental conditions might bacteria produce ATP more readily?
A) slightly acidic environment
B) slightly basic environment
C) greatly elevated temperature
D) greatly decreased temperature
A) slightly acidic environment
B) slightly basic environment
C) greatly elevated temperature
D) greatly decreased temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is a benefit to humans of the Calvin cycle?
A) It releases oxygen into the atmosphere, which humans require for aerobic respiration.
B) It creates biomass, which is the basis for food chains.
C) It synthesizes antibiotics that can help combat emerging pathogens.
D) It reduces nitrogen, eliminating the need for expensive fertilizers.
A) It releases oxygen into the atmosphere, which humans require for aerobic respiration.
B) It creates biomass, which is the basis for food chains.
C) It synthesizes antibiotics that can help combat emerging pathogens.
D) It reduces nitrogen, eliminating the need for expensive fertilizers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is NOT powered by the proton motive force in bacteria?
A) ATP synthase
B) DNA replication
C) drug efflux
D) flagella rotation
A) ATP synthase
B) DNA replication
C) drug efflux
D) flagella rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following plants can grow without fertilizer?
A) plants with rhizobia symbionts
B) plants that do not need proteins
C) plants that do not need nucleic acids
D) plants that can carry out the Calvin cycle
A) plants with rhizobia symbionts
B) plants that do not need proteins
C) plants that do not need nucleic acids
D) plants that can carry out the Calvin cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Oxidative phosphorylation requires
A) ATP synthase.
B) carbon dioxide.
C) NAD+.
D) pyruvate dehydrogenase.
A) ATP synthase.
B) carbon dioxide.
C) NAD+.
D) pyruvate dehydrogenase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What metabolic strategy is summarized in this equation: C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6H₂O + 6O₂ →12H₂O + 6CO₂
A) oxygenic photosynthesis
B) aerobic lithotrophy
C) anaerobic organotrophy
D) aerobic organotrophy
A) oxygenic photosynthesis
B) aerobic lithotrophy
C) anaerobic organotrophy
D) aerobic organotrophy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Nitrate contamination of water can poison infants.One source of nitrate is
A) lithotrophs that use ammonia as an electron donor.
B) anaerobes that use nitrate as a terminal electron acceptor.
C) methanogens that oxidize H₂ .
D) oxygenic photosynthesis.
A) lithotrophs that use ammonia as an electron donor.
B) anaerobes that use nitrate as a terminal electron acceptor.
C) methanogens that oxidize H₂ .
D) oxygenic photosynthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the phenol broth red test (shown),a yellow color and bubble (as shown in the far left vial)indicate



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is true of nitrogen fixation?
A) It requires ATP but not reducing agents.
B) It requires reducing agents but not ATP.
C) It is an important reaction carried out by organisms in all three domains of life.
D) Only prokaryotes have the metabolic capability to fix nitrogen.
A) It requires ATP but not reducing agents.
B) It requires reducing agents but not ATP.
C) It is an important reaction carried out by organisms in all three domains of life.
D) Only prokaryotes have the metabolic capability to fix nitrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the pathways below are in the correct order for the flow of electrons from glucose to oxygen in aerobic respiration?
A) glycolysis, ETS, TCA
B) glycolysis, fermentation, TCA
C) TCA, glycolysis, ETS
D) glycolysis, TCA, ETS
A) glycolysis, ETS, TCA
B) glycolysis, fermentation, TCA
C) TCA, glycolysis, ETS
D) glycolysis, TCA, ETS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
At the end of the TCA cycle most of the energy originally present in glucose is now found in
A) CO₂.
B) NADH.
C) NADPH.
D) ATP.
A) CO₂.
B) NADH.
C) NADPH.
D) ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The enzyme Rubisco is involved in
A) ATP production.
B) carbon fixation.
C) fermentation.
D) nitrogen fixation.
A) ATP production.
B) carbon fixation.
C) fermentation.
D) nitrogen fixation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Photosynthesis helps mitigate global warming by
A) adding O₂ to the atmosphere.
B) removing O₂ from the atmosphere.
C) removing CO₂ from the atmosphere.
D) adding CO₂ to the atmosphere.
A) adding O₂ to the atmosphere.
B) removing O₂ from the atmosphere.
C) removing CO₂ from the atmosphere.
D) adding CO₂ to the atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Why does respiration yield more energy per glucose than fermentation?
A) Fermentation uses more enzymes, and enzymes are costly to make.
B) Fermentation requires oxygen.
C) In fermentation the carbons in glucose do not become fully oxidized.
D) Fermentation is only found in prokaryotic organisms; eukaryotes need more energy.
A) Fermentation uses more enzymes, and enzymes are costly to make.
B) Fermentation requires oxygen.
C) In fermentation the carbons in glucose do not become fully oxidized.
D) Fermentation is only found in prokaryotic organisms; eukaryotes need more energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which molecule is used as a reducing agent in biosynthetic reactions?
A) ATP
B) NADH
C) NADPH
D) glucose
A) ATP
B) NADH
C) NADPH
D) glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
During photosynthesis,ATP is produced via
A) oxidation of glucose.
B) transfer of a phosphate from NADPH onto ADP.
C) ATP synthase powered by a pmf.
D) ATP synthase powered directly by light.
A) oxidation of glucose.
B) transfer of a phosphate from NADPH onto ADP.
C) ATP synthase powered by a pmf.
D) ATP synthase powered directly by light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A bacterium that lacks a respiratory chain likely relies on what metabolic strategy for energy production?
A) aerobic lithotrophy
B) anaerobic lithotrophy
C) photosynthesis
D) glycolysis followed by fermentation
A) aerobic lithotrophy
B) anaerobic lithotrophy
C) photosynthesis
D) glycolysis followed by fermentation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Oxygenic photosynthesis strips electrons from
A) CO₂.
B) H₂O.
C) H₂ S.
D) O₂.
A) CO₂.
B) H₂O.
C) H₂ S.
D) O₂.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A bacterial electron transport system (ETS)is depicted.If the quinone pool were artificially depleted,what are the expected consequences?
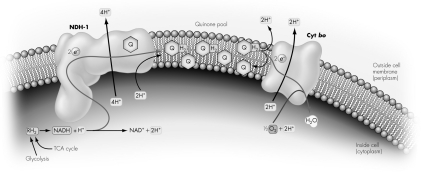
A) a buildup of NADH and increased H₂O production
B) a buildup of NADH and decreased H₂O production
C) a buildup of NAD+ and increased H₂O production
D) a buildup of NAD+ and decreased H₂O production

A) a buildup of NADH and increased H₂O production
B) a buildup of NADH and decreased H₂O production
C) a buildup of NAD+ and increased H₂O production
D) a buildup of NAD+ and decreased H₂O production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
CASE HISTORY
Tonya,age 32,was spending a warm June weekend at a beach in Massachusetts.The water near shore looked clear,although farther offshore the water had a reddish tint.Tonya dug up a pailful of clams and cooked them thoroughly.After dinner,her lips grew numb and her fingers tingled.She felt nauseated and had difficulty walking across the room.Her speech became slurred,but she managed to dial 911.The ambulance got her to the hospital in time for Tonya to have her stomach pumped and receive assistance breathing.The physician explained to Tonya that she had contracted paralytic shellfish poisoning from consumption of clams contaminated by an algal toxin.The toxin,called saxitoxin,accumulates in the clams as they feed on the algae;cooking does not affect the toxin.At that time,Massachusetts had a ban on shellfish because of a high population density of saxitoxin-producing algae,Alexandrium tamarense,a cause of "red tide."
Though Tonya suffered from consumption of saxitoxin,the organisms that produced it are valuable to humans as well.Explain how these myxotrophic organisms produce a product necessary to our respiration.
Tonya,age 32,was spending a warm June weekend at a beach in Massachusetts.The water near shore looked clear,although farther offshore the water had a reddish tint.Tonya dug up a pailful of clams and cooked them thoroughly.After dinner,her lips grew numb and her fingers tingled.She felt nauseated and had difficulty walking across the room.Her speech became slurred,but she managed to dial 911.The ambulance got her to the hospital in time for Tonya to have her stomach pumped and receive assistance breathing.The physician explained to Tonya that she had contracted paralytic shellfish poisoning from consumption of clams contaminated by an algal toxin.The toxin,called saxitoxin,accumulates in the clams as they feed on the algae;cooking does not affect the toxin.At that time,Massachusetts had a ban on shellfish because of a high population density of saxitoxin-producing algae,Alexandrium tamarense,a cause of "red tide."
Though Tonya suffered from consumption of saxitoxin,the organisms that produced it are valuable to humans as well.Explain how these myxotrophic organisms produce a product necessary to our respiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The Embden-Myerhof-Parnas (EMP)pathway is also known as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Compare and contrast anaerobic respiration and fermentation.How are they similar and how do they differ?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Lithotrophs donate electrons from inorganic reduced molecules directly to an ETS to generate a proton motive force.Why might these lithotrophs still possess the tricarboxylic acid cycle?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The ultimate goal of the Calvin cycle is to produce ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Yeast ferment hexose sugars into two molecules of ethanol and two molecules of CO₂.This reaction is used in bread making-the CO₂ causes the dough to rise.Explain why this reaction is so sensitive to temperature,slowing down considerably at lower temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Compare and contrast ATP production in chloroplasts and mitochondria.How are they similar and how do they differ?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Why does sugar production from CO₂ require NADPH in addition to ATP? In other words,why is ATP not sufficient?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
CASE HISTORY
Shane,a 21-year-old college student,was spending spring break at the beach in Cancun,where he frequently ordered drinks from the beachfront stands.Upon his return to classes,Shane fell ill with a fever of 38.9°C (102°F),severe abdominal cramps,and watery diarrhea.
By the second day,Shane had blood in his stools,a condition known as dysentery.Upon admission to the hospital,Shane showed dehydration,and his rectal exam was very painful with bleeding.
A fecal culture was performed on Hektoen agar,a selective medium for Gram-negative bacteria;bile salts exclude Gram-positives.Hektoen agar also differentiates among the enteric Gram-negative pathogens Salmonella,Shigella,and Escherichia.Most Salmonella species show black colonies due to H₂S formation from thiosulfate,whereas Escherichia species form colonies that are orange from lactose fermentation.Shane's culture produced translucent colonies,indicating Shigella species,which neither ferment lactose nor reduce thiosulfate to H₂S.
Serotyping (determining which antibodies react with the pathogen)confirmed the species Shigella flexneri,a common cause of "traveler's diarrhea" from drinking contaminated water.Shane received intravenous rehydration and was given the antibiotic quinolone,chosen based on laboratory tests of the pathogen's antibiotic sensitivity.Afterward,Shane made a full recovery.
On Hektoen agar,Salmonella colonies appear black,whereas Escherichia species form colonies that are orange.This helps microbiologists identify the organisms,and is actually representative of
A) differences in the enzymes produced by different species, which normally allow them to utilize nutrients in their environments.
B) differences in the color of the cells themselves.
C) how quickly the organisms are able to grow on this medium and how quickly they take up dyes.
D) the virulence or pathogenicity of the organisms (whether they can infect humans).
Shane,a 21-year-old college student,was spending spring break at the beach in Cancun,where he frequently ordered drinks from the beachfront stands.Upon his return to classes,Shane fell ill with a fever of 38.9°C (102°F),severe abdominal cramps,and watery diarrhea.
By the second day,Shane had blood in his stools,a condition known as dysentery.Upon admission to the hospital,Shane showed dehydration,and his rectal exam was very painful with bleeding.
A fecal culture was performed on Hektoen agar,a selective medium for Gram-negative bacteria;bile salts exclude Gram-positives.Hektoen agar also differentiates among the enteric Gram-negative pathogens Salmonella,Shigella,and Escherichia.Most Salmonella species show black colonies due to H₂S formation from thiosulfate,whereas Escherichia species form colonies that are orange from lactose fermentation.Shane's culture produced translucent colonies,indicating Shigella species,which neither ferment lactose nor reduce thiosulfate to H₂S.
Serotyping (determining which antibodies react with the pathogen)confirmed the species Shigella flexneri,a common cause of "traveler's diarrhea" from drinking contaminated water.Shane received intravenous rehydration and was given the antibiotic quinolone,chosen based on laboratory tests of the pathogen's antibiotic sensitivity.Afterward,Shane made a full recovery.
On Hektoen agar,Salmonella colonies appear black,whereas Escherichia species form colonies that are orange.This helps microbiologists identify the organisms,and is actually representative of
A) differences in the enzymes produced by different species, which normally allow them to utilize nutrients in their environments.
B) differences in the color of the cells themselves.
C) how quickly the organisms are able to grow on this medium and how quickly they take up dyes.
D) the virulence or pathogenicity of the organisms (whether they can infect humans).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If Fe³⁺ is the final electron acceptor at the end of an electron transport system,the waste product is ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The metabolic pathway used by cyanobacteria and plants to fix carbon dioxide into sugar is known as the ________ cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
CASE HISTORY
Brianna was a 2-month-old,formula-fed infant in a rural community in Nebraska.Brianna's mother noticed signs of blueness around the baby's mouth and fingers.One night after feeding,Brianna had trouble breathing,and her face had a peculiar lavender color.The infant became lethargic,salivated excessively,and had diarrhea and vomiting.An EMT came and took blood samples,which appeared brown and failed to turn pink when exposed to air.The EMT diagnosed methemoglobinemia,a condition in which toxic levels of nitrite oxidize hemoglobin and prevent it from receiving oxygen.The nitriteoxidized hemoglobin is called methemoglobin;elevated levels can cause asphyxiation and death.A solution of methylene blue,a reducing agent,was administered by IV to reduce (add electrons to)the hemoglobin in Brianna's blood.
Nitrite forms in the digestive tract by bacterial reduction of nitrate during anaerobic respiration.The well water from which Brianna's formula was prepared was tested and found to contain high levels of nitrate,enough to cause methemoglobinemia.Brianna's parents were surprised because they had felt no ill effect from the water.But an infant's stomach pH is high,allowing bacteria to reduce nitrate to nitrite,which may then oxidize hemoglobin.
The nitrite in the baby's blood was formed by her intestinal bacteria using nitrate (NO3⁻)as a terminal electron acceptor for anaerobic respiration,with nitrite (NO₂⁻)as the product.Bacteria can multiply more quickly by utilizing oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor in which process?
A) fermentation
B) the pentose phosphate pathway
C) aerobic respiration
D) lithotrophy
Brianna was a 2-month-old,formula-fed infant in a rural community in Nebraska.Brianna's mother noticed signs of blueness around the baby's mouth and fingers.One night after feeding,Brianna had trouble breathing,and her face had a peculiar lavender color.The infant became lethargic,salivated excessively,and had diarrhea and vomiting.An EMT came and took blood samples,which appeared brown and failed to turn pink when exposed to air.The EMT diagnosed methemoglobinemia,a condition in which toxic levels of nitrite oxidize hemoglobin and prevent it from receiving oxygen.The nitriteoxidized hemoglobin is called methemoglobin;elevated levels can cause asphyxiation and death.A solution of methylene blue,a reducing agent,was administered by IV to reduce (add electrons to)the hemoglobin in Brianna's blood.
Nitrite forms in the digestive tract by bacterial reduction of nitrate during anaerobic respiration.The well water from which Brianna's formula was prepared was tested and found to contain high levels of nitrate,enough to cause methemoglobinemia.Brianna's parents were surprised because they had felt no ill effect from the water.But an infant's stomach pH is high,allowing bacteria to reduce nitrate to nitrite,which may then oxidize hemoglobin.
The nitrite in the baby's blood was formed by her intestinal bacteria using nitrate (NO3⁻)as a terminal electron acceptor for anaerobic respiration,with nitrite (NO₂⁻)as the product.Bacteria can multiply more quickly by utilizing oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor in which process?
A) fermentation
B) the pentose phosphate pathway
C) aerobic respiration
D) lithotrophy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Biosynthetic reactions are also known as ________ reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



