Deck 8: Bacterial Genetics and Biotechnology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Bacterial Genetics and Biotechnology
1
Each bacterial species has a unique
A) cell shape.
B) cell wall.
C) genome.
D) glycolytic pathway.
A) cell shape.
B) cell wall.
C) genome.
D) glycolytic pathway.
C
2
DNA replication begins at a chromosomal region called the
A) activator.
B) initiator.
C) origin.
D) promoter.
A) activator.
B) initiator.
C) origin.
D) promoter.
C
3
An E.coli cell whose DNA contains N¹⁴ is placed in media with dNTPs containing a heavy isotope of nitrogen,N¹⁵,which incorporates into newly synthesized DNA.After one cell division,what will the DNA in the daughter cells look like?
A) One cell will have both strands of the helix N14; the other cell will have both strands of the helix N15.
B) One cell will have mostly N14 with a little bit of N15; the other cell will have mostly N15 with a little N14.
C) Each cell will have one strand of N14 and one strand of N15.
D) It is impossible to predict what the DNA in the daughter cells will look like.
A) One cell will have both strands of the helix N14; the other cell will have both strands of the helix N15.
B) One cell will have mostly N14 with a little bit of N15; the other cell will have mostly N15 with a little N14.
C) Each cell will have one strand of N14 and one strand of N15.
D) It is impossible to predict what the DNA in the daughter cells will look like.
C
4
The activity of what enzyme is modeled here?
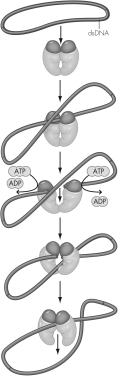
A) gyrase
B) helicase
C) DNA polymerase
D) primase

A) gyrase
B) helicase
C) DNA polymerase
D) primase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The image shown is a space-filling model of
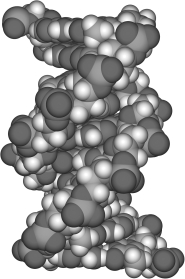
A) DNA.
B) peptidoglycan.
C) protein.
D) lipid.

A) DNA.
B) peptidoglycan.
C) protein.
D) lipid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A mutation known as a pyrimidine dimer is usually caused by
A) acridine orange.
B) DNA polymerase errors.
C) UV light.
D) X-rays.
A) acridine orange.
B) DNA polymerase errors.
C) UV light.
D) X-rays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
During gel electrophoresis the ________ DNA fragments migrate more quickly and move further down the gel toward the ________ pole.
A) larger; negative
B) larger; positive
C) smaller; negative
D) smaller; positive
A) larger; negative
B) larger; positive
C) smaller; negative
D) smaller; positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
TAT is a codon for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr).If a mutation changes TAT to TAA,what kind of mutation has occurred?

A) frameshift
B) missense
C) nonsense
D) silent

A) frameshift
B) missense
C) nonsense
D) silent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the active site of DNA polymerase,which monomer will form correct base pairs with a C in the template strand?
A) dATP
B) dCTP
C) dGTP
D) dTTP
A) dATP
B) dCTP
C) dGTP
D) dTTP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In this image of a nucleoside,which arrow is pointing to the 2¢ carbon of deoxyribose?
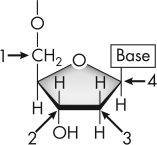
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Plasmids usually contain genes that are
A) important for cell survival in all environments.
B) important for cell survival in particular environments.
C) not important for cell survival in any environments.
D) composed of single-stranded DNA.
A) important for cell survival in all environments.
B) important for cell survival in particular environments.
C) not important for cell survival in any environments.
D) composed of single-stranded DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the choices below has the correct 5¢ and 3¢ DNA end designations?
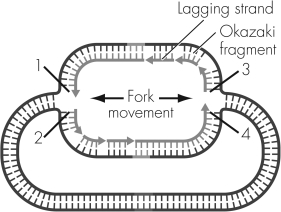
A) 1 = 5¢ 2 = 3¢ 3 = 5¢ 4 = 3¢
B) 1 = 3¢ 2 = 5¢ 3 = 5¢ 4 = 3¢
C) 1 = 5¢ 2 = 5¢ 3 = 3¢ 4 = 3¢
D) 1 = 3¢ 2 = 3¢ 3 = 5¢ 4 = 5¢

A) 1 = 5¢ 2 = 3¢ 3 = 5¢ 4 = 3¢
B) 1 = 3¢ 2 = 5¢ 3 = 5¢ 4 = 3¢
C) 1 = 5¢ 2 = 5¢ 3 = 3¢ 4 = 3¢
D) 1 = 3¢ 2 = 3¢ 3 = 5¢ 4 = 5¢

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If you wanted to radioactively tag newly synthesized DNA,which numbered phosphate would need to be radioactive?
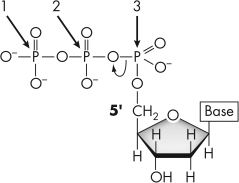
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) Either 1, 2, or 3 would work.

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) Either 1, 2, or 3 would work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In this image of a nucleoside,which arrow is pointing to the 5¢ carbon of deoxyribose?
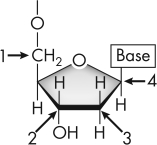
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following lists enzymes involved in DNA replication in the order they act?
A) primase, helicase, DNA polymerase
B) helicase, DNA polymerase, primase
C) primase, DNA polymerase, helicase
D) helicase, primase, DNA polymerase
A) primase, helicase, DNA polymerase
B) helicase, DNA polymerase, primase
C) primase, DNA polymerase, helicase
D) helicase, primase, DNA polymerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which repair process leads to an abasic site as part of the repair pathway?
A) base excision repair
B) methyl mismatch repair
C) recombination
D) SOS repair
A) base excision repair
B) methyl mismatch repair
C) recombination
D) SOS repair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
RFLP analysis requires which tools?
A) restriction enzymes and gel electrophoresis
B) restriction enzymes and PCR
C) gel electrophoresis and PCR
D) gel electrophoresis and DNA sequencing
A) restriction enzymes and gel electrophoresis
B) restriction enzymes and PCR
C) gel electrophoresis and PCR
D) gel electrophoresis and DNA sequencing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is true of plasmids?
A) They can be the entire genome.
B) They are common in eukaryotic cells.
C) They are usually linear.
D) They may contain antibiotic resistance genes.
A) They can be the entire genome.
B) They are common in eukaryotic cells.
C) They are usually linear.
D) They may contain antibiotic resistance genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is found in eukaryotic but not prokaryotic genomes?
A) promoters
B) operons
C) introns
D) genes
A) promoters
B) operons
C) introns
D) genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
TAT is a codon for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr).If a mutation changes TAT to CAT,what kind of mutation has occurred?

A) frameshift
B) missense
C) nonsense
D) silent

A) frameshift
B) missense
C) nonsense
D) silent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An antibiotic that inhibits peptidyl transferase activity likely binds to
A) aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
B) mRNA.
C) a 30S ribosome subunit.
D) a 50S ribosome subunit.
A) aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
B) mRNA.
C) a 30S ribosome subunit.
D) a 50S ribosome subunit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is most likely a signature of an operon?
A) large distances between consecutive coding regions and functional association of the gene products
B) large distances between consecutive coding regions and gene products involved in different pathways
C) short distances between consecutive coding regions and gene products involved in different pathways
D) short distances between consecutive coding regions and functional association of gene products
A) large distances between consecutive coding regions and functional association of the gene products
B) large distances between consecutive coding regions and gene products involved in different pathways
C) short distances between consecutive coding regions and gene products involved in different pathways
D) short distances between consecutive coding regions and functional association of gene products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What energy source is used to drive translation?
A) ATP
B) GTP
C) NADPH
D) the energy released when peptide bonds form
A) ATP
B) GTP
C) NADPH
D) the energy released when peptide bonds form

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If a portion of the template strand of a gene has the sequence 5¢ TTGCAGCT 3¢,what is the sequence of the RNA transcribed from this template?
A) 5¢AACGTCGA3¢
B) 5¢AACGUCGA3¢
C) 5¢ AGCUGCAA3¢
D) 5¢ AGCTGCAA3¢
A) 5¢AACGTCGA3¢
B) 5¢AACGUCGA3¢
C) 5¢ AGCUGCAA3¢
D) 5¢ AGCTGCAA3¢

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
After translation
A) all proteins are folded and secreted.
B) some proteins are folded but all are secreted.
C) all proteins are folded and some are also secreted.
D) some proteins are folded and another subset are secreted.
A) all proteins are folded and secreted.
B) some proteins are folded but all are secreted.
C) all proteins are folded and some are also secreted.
D) some proteins are folded and another subset are secreted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a typical two-component signal transduction system
A) the sensor kinase senses the environment and the response regulator directly alters transcription.
B) both the sensor kinase and the response regulator sense the environment.
C) both the sensor kinase and the response regulator directly alter transcription.
D) the sensor kinase directly alters transcription and the response regulator senses the environment.
A) the sensor kinase senses the environment and the response regulator directly alters transcription.
B) both the sensor kinase and the response regulator sense the environment.
C) both the sensor kinase and the response regulator directly alter transcription.
D) the sensor kinase directly alters transcription and the response regulator senses the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What technique is illustrated in this diagram?
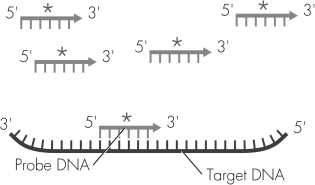
A) DNA hybridization
B) DNA sequencing
C) recombinant DNA production
D) PCR

A) DNA hybridization
B) DNA sequencing
C) recombinant DNA production
D) PCR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
PrfA protein is a global regulator of virulence genes in Listeria,a bacterium that can cause severe food poisoning.Below host body temperatures PrfA mRNA exists in a conformation that hides the ribosome binding site.Upon entry into a host and a rise in temperature,hydrogen bonds in the mRNA break,exposing the ribosome binding site.What level of gene regulation is seen here?
A) changing the DNA sequence
B) transcription control
C) translation control
D) posttranslational control
A) changing the DNA sequence
B) transcription control
C) translation control
D) posttranslational control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What enzyme is used to produce cDNA?
A) DNA polymerase III
B) DNA ligase
C) RNA polymerase
D) reverse transcriptase
A) DNA polymerase III
B) DNA ligase
C) RNA polymerase
D) reverse transcriptase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Except for the initiating fMet tRNA,what is the order of sites that tRNAs take through a ribosome?
A) first E, then P, and finally A
B) first A, then P, and finally E
C) first E, then A, and finally P
D) first P, then A, and finally E
A) first E, then P, and finally A
B) first A, then P, and finally E
C) first E, then A, and finally P
D) first P, then A, and finally E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following RNAs gets translated into protein?
A) mRNA
B) rRNA
C) tRNA
D) sRNA
A) mRNA
B) rRNA
C) tRNA
D) sRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
During transcription termination
A) sigma disengages from RNA polymerase.
B) RNA polymerase disengages from the DNA.
C) ribosomes disengage from the mRNA.
D) DNA replicates the termination sequence.
A) sigma disengages from RNA polymerase.
B) RNA polymerase disengages from the DNA.
C) ribosomes disengage from the mRNA.
D) DNA replicates the termination sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In the lac operon,a mutation in the operator,LacO,that prevents repressor binding will cause which of the following changes compared to wild type cells?
A) more expression of the lac operon when lactose is present
B) more expression of the lac operon when lactose is absent
C) less expression of the lac operon when lactose is present
D) less expression of the lac operon when lactose is absent
A) more expression of the lac operon when lactose is present
B) more expression of the lac operon when lactose is absent
C) less expression of the lac operon when lactose is present
D) less expression of the lac operon when lactose is absent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
EF-G is involved in
A) transcription initiation.
B) transcription elongation.
C) translation initiation.
D) translation elongation.
A) transcription initiation.
B) transcription elongation.
C) translation initiation.
D) translation elongation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Phase variation controls protein levels by
A) altering the DNA sequence.
B) changing the rate of mRNA translation.
C) changing the rate of mRNA stability.
D) changing the rate of protein stability.
A) altering the DNA sequence.
B) changing the rate of mRNA translation.
C) changing the rate of mRNA stability.
D) changing the rate of protein stability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Recombinant human insulin is safely produced in bacteria.Which of the following is the correct sequence of steps needed to produce such a transgenic bacterium?
A) transform bacteria, ligate, hybridize insulin cDNA and plasmid
B) hybridize insulin cDNA and plasmid, ligate, transform bacteria
C) hybridize insulin cDNA and plasmid, transform bacteria, ligate
D) ligate, hybridize insulin cDNA and plasmid, transform bacteria
A) transform bacteria, ligate, hybridize insulin cDNA and plasmid
B) hybridize insulin cDNA and plasmid, ligate, transform bacteria
C) hybridize insulin cDNA and plasmid, transform bacteria, ligate
D) ligate, hybridize insulin cDNA and plasmid, transform bacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Bacteria regulate virulence gene expression because
A) the genes need to be expressed all the time.
B) the genes do not need to be expressed all the time, and regulation saves energy.
C) the genes do not need to be expressed all the time; if they were, the bacterial cell would die.
D) it does not cost them any energy to keep the gene expressed all the time.
A) the genes need to be expressed all the time.
B) the genes do not need to be expressed all the time, and regulation saves energy.
C) the genes do not need to be expressed all the time; if they were, the bacterial cell would die.
D) it does not cost them any energy to keep the gene expressed all the time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The gene that codes for a protein involved in detoxifying an environmental toxin is only expressed in the presence of the toxin.A repressor protein controls transcription of the gene.Which of the following is true?
A) The toxin mediates induction of the gene by relieving repression imposed by the repressor.
B) The toxin mediates induction of the gene by stimulating activation mediated by an activator.
C) The toxin mediates repression of the gene by relieving repression imposed by the repressor.
D) The toxin mediates repression of the gene by stimulating activation mediated by an activator.
A) The toxin mediates induction of the gene by relieving repression imposed by the repressor.
B) The toxin mediates induction of the gene by stimulating activation mediated by an activator.
C) The toxin mediates repression of the gene by relieving repression imposed by the repressor.
D) The toxin mediates repression of the gene by stimulating activation mediated by an activator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is NOT normally found in human cells?
A) cDNA
B) DNA
C) mRNA
D) tRNA
A) cDNA
B) DNA
C) mRNA
D) tRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Ribosomes are composed of
A) protein only.
B) RNA only.
C) both protein and rRNA.
D) both protein and tRNA.
A) protein only.
B) RNA only.
C) both protein and rRNA.
D) both protein and tRNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
TAT is a codon for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr).If a mutation changes TAT to TAC,a ________-point mutation has occurred.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
CASE HISTORY
In San Francisco, a 3-year-old boy named Luke was admitted to the hospital after an abrupt onset of fever and a generalized seizure. The boy's cerebrospinal fluid was normal, and he had a normal chest radiograph, but his white blood cell count was 20,000/mm3 (normal is 5,000-10,000), with 85% polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMns). Luke's blood culture revealed bacteremia (bacteria in the blood). The bacteria were identified as "nontypeable" Haemophilus influenzae bacteria. The nontypeable H. influenzae strain was beta-lactamase-positive (expressed an enzyme to inactivate penicillin G, ampicillin, and amoxicillin) but proved sensitive to cefixime, a third-generation cephalosporin.
The diagnosis surprised the boy's two fathers. They showed the doctor Luke's full record of immunizations and booster shots, including the standard DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis), hepatitis B, pneumococcus, and Haemophilus influenzae b (Hib). Why was Luke not protected by the Hib vaccine? The doctor explained that the Hib vaccine protected only from H. influenzae type b, the most common virulent strain-but not the only virulent strain. Six strains, or serotypes, a through f, are "typed" based on the type of polysaccharide capsule surrounding the cell envelope. The Hib vaccine targets capsule type b. But some variant strains of H. influenzae, called "nontypeable," lack a capsule. These strains can be identified on the basis of other properties, such as enzyme activities, but they are unaffected by the vaccine. Fortunately, after seven days of intravenous antibiotic, Luke recovered fully.
The H. influenzae strain infecting Luke was beta-lactamase positive. Would the cell be likely to express the gene for this enzyme at all times? Describe one mechanism by which the cell could regulate the expression of this enzyme.
In San Francisco, a 3-year-old boy named Luke was admitted to the hospital after an abrupt onset of fever and a generalized seizure. The boy's cerebrospinal fluid was normal, and he had a normal chest radiograph, but his white blood cell count was 20,000/mm3 (normal is 5,000-10,000), with 85% polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMns). Luke's blood culture revealed bacteremia (bacteria in the blood). The bacteria were identified as "nontypeable" Haemophilus influenzae bacteria. The nontypeable H. influenzae strain was beta-lactamase-positive (expressed an enzyme to inactivate penicillin G, ampicillin, and amoxicillin) but proved sensitive to cefixime, a third-generation cephalosporin.
The diagnosis surprised the boy's two fathers. They showed the doctor Luke's full record of immunizations and booster shots, including the standard DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis), hepatitis B, pneumococcus, and Haemophilus influenzae b (Hib). Why was Luke not protected by the Hib vaccine? The doctor explained that the Hib vaccine protected only from H. influenzae type b, the most common virulent strain-but not the only virulent strain. Six strains, or serotypes, a through f, are "typed" based on the type of polysaccharide capsule surrounding the cell envelope. The Hib vaccine targets capsule type b. But some variant strains of H. influenzae, called "nontypeable," lack a capsule. These strains can be identified on the basis of other properties, such as enzyme activities, but they are unaffected by the vaccine. Fortunately, after seven days of intravenous antibiotic, Luke recovered fully.
The H. influenzae strain infecting Luke was beta-lactamase positive. Would the cell be likely to express the gene for this enzyme at all times? Describe one mechanism by which the cell could regulate the expression of this enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Why might the insertion or deletion of three base pairs in a gene be less harmful than the insertion or deletion of only one or two base pairs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Transcription of genes starts at regions of the genome called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
CASE HISTORY
Tina,a 33-year-old store clerk from Peoria,Illinois,had her first dental exam in five years.She told the hygienist that her gums hurt and that stains appeared on her pillow where her jaw had rested.She also told the hygienist that she did not smoke or drink.
The hygienist found that Tina's gums were swollen and bled upon probing.The gums had receded from Tina's teeth,forming pockets about 5 mm deep,and X-rays revealed some loss of bone.
Tina then saw the dentist,who told her she had periodontitis,inflammatory disease of the gums and bone supporting the teeth.Periodontitis is caused by dental plaque,a biofilm of mixed bacterial species that grow on the teeth.Without regular oral hygiene,the biofilm grows beneath the gum and eventually causes loss of teeth.
Tina expressed surprise,as she thought that only elderly people suffered gum disease.The dentist asked her again whether she smoked,perhaps two packs a day.Tina denied smoking that much,but admitted to one pack a day.The dentist told her that smoking is a common factor in early gum disease,as are diabetes and genetic susceptibility.Under predisposing conditions,many different kinds of bacteria can cause gum disease.
To determine the bacterial species causing Tina's periodontitis,the dentist ordered a DNA test.The DNA test works by polymerase chain reaction (PCR),a technique in which a short piece of DNA is amplified (copied many times),making it possible to read the sequence of DNA base pairs.The DNA sequence reveals the bacterial species.Tina's DNA test revealed Porphyromonas gingivalis and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans,two Gram-negative anaerobes that are sensitive to metronidazole and amoxicillin,respectively.
The DNA test enabled the dentist to target the most effective antibiotics for Tina's condition.The dentist also enrolled Tina in a smoking cessation program.
Following amplification of the bacterial DNA from Tina's sample,one of the ways the bacteria involved may be identified is via sequencing of the amplified fragment of DNA.Explain how this process works and how it can be used to identify bacteria.
Tina,a 33-year-old store clerk from Peoria,Illinois,had her first dental exam in five years.She told the hygienist that her gums hurt and that stains appeared on her pillow where her jaw had rested.She also told the hygienist that she did not smoke or drink.
The hygienist found that Tina's gums were swollen and bled upon probing.The gums had receded from Tina's teeth,forming pockets about 5 mm deep,and X-rays revealed some loss of bone.
Tina then saw the dentist,who told her she had periodontitis,inflammatory disease of the gums and bone supporting the teeth.Periodontitis is caused by dental plaque,a biofilm of mixed bacterial species that grow on the teeth.Without regular oral hygiene,the biofilm grows beneath the gum and eventually causes loss of teeth.
Tina expressed surprise,as she thought that only elderly people suffered gum disease.The dentist asked her again whether she smoked,perhaps two packs a day.Tina denied smoking that much,but admitted to one pack a day.The dentist told her that smoking is a common factor in early gum disease,as are diabetes and genetic susceptibility.Under predisposing conditions,many different kinds of bacteria can cause gum disease.
To determine the bacterial species causing Tina's periodontitis,the dentist ordered a DNA test.The DNA test works by polymerase chain reaction (PCR),a technique in which a short piece of DNA is amplified (copied many times),making it possible to read the sequence of DNA base pairs.The DNA sequence reveals the bacterial species.Tina's DNA test revealed Porphyromonas gingivalis and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans,two Gram-negative anaerobes that are sensitive to metronidazole and amoxicillin,respectively.
The DNA test enabled the dentist to target the most effective antibiotics for Tina's condition.The dentist also enrolled Tina in a smoking cessation program.
Following amplification of the bacterial DNA from Tina's sample,one of the ways the bacteria involved may be identified is via sequencing of the amplified fragment of DNA.Explain how this process works and how it can be used to identify bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An enzyme that cuts the DNA phosphodiester backbone at a particular DNA sequence is called a ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A protein that affects the expression of many different genes is known as a ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
CASE HISTORY
In Wichita,Kansas,a 20-year-old college student named Lillian visited the college health practitioner for a routine gynecological exam.Lillian's periods had been regular,but she recently noted some spotting between periods.Her last menstrual period was four weeks prior.The practitioner asked Lillian whether she was sexually active.Lillian reported two male partners within the past six months.She reported no vaginal discharge,dyspareunia (painful intercourse),genital lesions,or sores.Her breast,thyroid,and abdominal exam were within normal limits,as were her vital signs-blood pressure: 118/68,pulse: 74,respiration: 18,temperature: 37.1°C (98.6°F).
The genital exam revealed normal vulva and vagina.The practitioner found no cervical motion pain and no uterine or adnexal tenderness (areas that include and surround the fallopian tubes and ovaries).But Lillian's cervix appeared inflamed and bled easily,with a purulent discharge coming from the cervical os (opening).
The practitioner performed nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs)for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae.Within a day,the NAAT results were positive for Chlamydia and negative for N.gonorrhoeae.Wet-mount microscopy revealed no pathogens but many WBCs (white blood cells).The diagnosis was confirmed as chlamydia infection,an infection reportable to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The practitioner prescribed doxycycline to clear up the infection.To curtail transmission,the practitioner asked Lillian to identify all her sexual partners for partner notification.Lillian recalled a third partner seven months earlier.The practitioner also recommended use of condoms to decrease further infections.
Doxycycline is an antibiotic that binds to the bacterial ribosome.How does this antibiotic interfere with the creating of proteins in bacterial cells?
A) Binding to the ribosome prevents DNA strands from being separated properly, preventing transcription.
B) Binding to the ribosome prevents mRNA strands from being properly assembled from single-stranded DNA templates.
C) Binding to the ribosome prevents mRNA from being properly read and translated into an amino acid sequence.
D) Binding to the ribosome prevents completed proteins from being exported to the cell surface.
In Wichita,Kansas,a 20-year-old college student named Lillian visited the college health practitioner for a routine gynecological exam.Lillian's periods had been regular,but she recently noted some spotting between periods.Her last menstrual period was four weeks prior.The practitioner asked Lillian whether she was sexually active.Lillian reported two male partners within the past six months.She reported no vaginal discharge,dyspareunia (painful intercourse),genital lesions,or sores.Her breast,thyroid,and abdominal exam were within normal limits,as were her vital signs-blood pressure: 118/68,pulse: 74,respiration: 18,temperature: 37.1°C (98.6°F).
The genital exam revealed normal vulva and vagina.The practitioner found no cervical motion pain and no uterine or adnexal tenderness (areas that include and surround the fallopian tubes and ovaries).But Lillian's cervix appeared inflamed and bled easily,with a purulent discharge coming from the cervical os (opening).
The practitioner performed nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs)for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae.Within a day,the NAAT results were positive for Chlamydia and negative for N.gonorrhoeae.Wet-mount microscopy revealed no pathogens but many WBCs (white blood cells).The diagnosis was confirmed as chlamydia infection,an infection reportable to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The practitioner prescribed doxycycline to clear up the infection.To curtail transmission,the practitioner asked Lillian to identify all her sexual partners for partner notification.Lillian recalled a third partner seven months earlier.The practitioner also recommended use of condoms to decrease further infections.
Doxycycline is an antibiotic that binds to the bacterial ribosome.How does this antibiotic interfere with the creating of proteins in bacterial cells?
A) Binding to the ribosome prevents DNA strands from being separated properly, preventing transcription.
B) Binding to the ribosome prevents mRNA strands from being properly assembled from single-stranded DNA templates.
C) Binding to the ribosome prevents mRNA from being properly read and translated into an amino acid sequence.
D) Binding to the ribosome prevents completed proteins from being exported to the cell surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Proteins that assist the folding of newly formed proteins are known as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Is the mRNA shown a model of a bacterial mRNA or a eukaryotic mRNA? Please explain your rationale.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
During Sanger DNA sequencing,in addition to normal dNTPs used in cellular DNA synthesis,small amounts of modified DNA polymerase substrates are added to the reaction.How do these modified monomers differ from the normal dNTPs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In a two-component signal transduction system the response regulator activity is altered via phosphorylation.This is an example of
A) changing the DNA sequence.
B) transcription control.
C) translation control.
D) posttranslational control.
A) changing the DNA sequence.
B) transcription control.
C) translation control.
D) posttranslational control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If DNA polymerase misincorporates a base,leading to a mismatch,how do repair enzymes distinguish the parental and daughter DNA strands to specifically fix the daughter strand?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Two common levels of regulation of protein activity are transcriptional control and posttranslational control.Please discuss the differences between the two in terms of speed of response and energy efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



