Deck 9: Bacterial Genomes and Evolution
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Bacterial Genomes and Evolution
1
Which of the following forms of horizontal gene transfer involves a prophage?
A) generalized transduction
B) specialized transduction
C) F factor conjugation
D) competence-mediated transformation
A) generalized transduction
B) specialized transduction
C) F factor conjugation
D) competence-mediated transformation
B
2
Meaningful evolution occurs when
A) a changed trait affects survival.
B) a changed trait gives an organism an advantage.
C) a changed trait gives an organism a disadvantage.
D) environmental factors change.
A) a changed trait affects survival.
B) a changed trait gives an organism an advantage.
C) a changed trait gives an organism a disadvantage.
D) environmental factors change.
A
3
Why can antibiotics be used to treat the nematode cause of filarial disease?
A) Antibiotics kill off Wolbachia, which is important for the embryonic development of the worm.
B) Antibiotics always kill off nematodes.
C) Antibiotics stimulate the immune system to more effectively fight off the nematodes.
D) Antibiotics are not used to treat filarial disease.
A) Antibiotics kill off Wolbachia, which is important for the embryonic development of the worm.
B) Antibiotics always kill off nematodes.
C) Antibiotics stimulate the immune system to more effectively fight off the nematodes.
D) Antibiotics are not used to treat filarial disease.
A
4
Wolbachia appears to be developing into a(n)________ of its host.
A) mitochondria
B) chloroplast
C) organelle
D) endosymbiont
A) mitochondria
B) chloroplast
C) organelle
D) endosymbiont

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following does NOT lead to divergence?
A) fossilization
B) mutations
C) transposition
D) transduction
A) fossilization
B) mutations
C) transposition
D) transduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Why might an organism transform DNA that is homologous to its own?
A) as a food source
B) to obtain new DNA
C) to repair its own damaged genome
D) Organisms are not capable of transforming homologous DNA.
A) as a food source
B) to obtain new DNA
C) to repair its own damaged genome
D) Organisms are not capable of transforming homologous DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The elements that form living organisms first originated from
A) viruses.
B) stardust.
C) water.
D) the oceans.
A) viruses.
B) stardust.
C) water.
D) the oceans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What specifically is passed from the donor cell to the recipient cell during conjugation?
A) single-stranded DNA
B) double-stranded DNA
C) protein subunits
D) F factor pilus
A) single-stranded DNA
B) double-stranded DNA
C) protein subunits
D) F factor pilus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Without selective pressure,a species is at risk of experiencing
A) random mutation.
B) natural selection.
C) reductive evolution.
D) endosymbiosis.
A) random mutation.
B) natural selection.
C) reductive evolution.
D) endosymbiosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is NOT a step in the transduction process?
A) The DNA phage enters a bacterial cell by endocytosis.
B) The phage DNA commandeers host protein synthesis machinery.
C) The phage uses host cell DNA replication machinery.
D) Completed phage particles are released into the environment by lysing.
A) The DNA phage enters a bacterial cell by endocytosis.
B) The phage DNA commandeers host protein synthesis machinery.
C) The phage uses host cell DNA replication machinery.
D) Completed phage particles are released into the environment by lysing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Examine the figure shown.What happened to transform the original MRSA isolate into the small-colony variant?
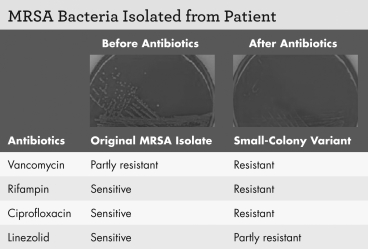
A) evolution
B) natural selection
C) speciation
D) fitness reduction

A) evolution
B) natural selection
C) speciation
D) fitness reduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following domains of life contain ether linkages in their membranes?
A) viral
B) eukarya
C) bacteria
D) archaea
A) viral
B) eukarya
C) bacteria
D) archaea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Examine the figure shown.Which of the following correctly describes how the two organisms pictured would fare if grown in an environment without antibiotics?
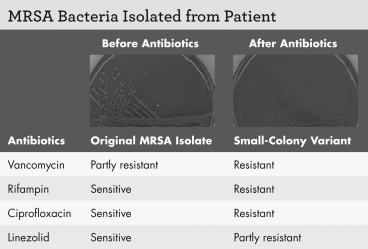
A) The small-colony variant would outcompete the original isolate.
B) The small-colony variant would grow better than the original isolate.
C) The original isolate would outcompete the small-colony variant.
D) Neither organism would grow in this condition.

A) The small-colony variant would outcompete the original isolate.
B) The small-colony variant would grow better than the original isolate.
C) The original isolate would outcompete the small-colony variant.
D) Neither organism would grow in this condition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Examine the figure shown.Which organism does NOT share the same common ancestor as Escherichia and Erwinia carotovora?
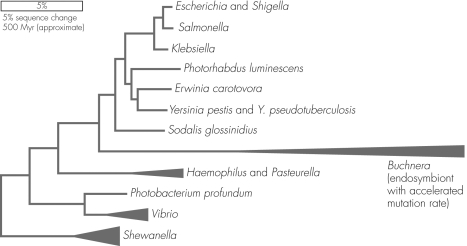
A) Sodalis glossinidius
B) Photorhabdus luminescens
C) Klebsiella
D) Salmonella

A) Sodalis glossinidius
B) Photorhabdus luminescens
C) Klebsiella
D) Salmonella

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is most important for determining the fitness of one organism versus another?
A) reproductive strategy
B) generation time
C) genetic composition
D) the environment
A) reproductive strategy
B) generation time
C) genetic composition
D) the environment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is NOT a good scenario for a molecular clock?
A) The gene used has the same function across all species being compared.
B) The generation time is the same for all species being compared.
C) The average mutation rate is constant among species.
D) The gene used is nonessential.
A) The gene used has the same function across all species being compared.
B) The generation time is the same for all species being compared.
C) The average mutation rate is constant among species.
D) The gene used is nonessential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How do bacteria protect their own DNA from restriction enzymes?
A) restriction digestion
B) methylation of target sequences
C) generalized recombination
D) site-specific recombination
A) restriction digestion
B) methylation of target sequences
C) generalized recombination
D) site-specific recombination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the mutation rate is not the same for all species being compared using a molecular clock,what does a phylogenetic tree demonstrate?
A) the time since two species diverged from a common ancestor
B) the amount of evolutionary distance between two species
C) the generation time for species
D) the induced mutation frequency between two species
A) the time since two species diverged from a common ancestor
B) the amount of evolutionary distance between two species
C) the generation time for species
D) the induced mutation frequency between two species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Griffith's observations from his experiments infecting mice with smooth and rough strain Streptococcus pneumoniae were later found to be due to
A) conjugation.
B) transposition.
C) transduction.
D) transformation.
A) conjugation.
B) transposition.
C) transduction.
D) transformation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A protein called integrase is encoded by ________ and allows for site-specific recombination in C.diphtheria.
A) E. coli
B) S. pneumoniae
C) C. diphtheria
D) beta phage
A) E. coli
B) S. pneumoniae
C) C. diphtheria
D) beta phage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
CASE HISTORY
Nine-month-old Eva had 12 clinic visits over a seven-month period due to runny nose and/or ear infections.During each episode,nasopharyngeal swabs were obtained for bacterial culture and Streptococcus pneumoniae was obtained.Although all the infections were resolved with antibiotics,scientists gained insight into pathogen evolution by seeing how the isolates compared.Each isolate was first analyzed for seven genes that can indicate strain variability,a process called multilocus sequence typing (MLST).The lab found two MLST types,indicating that the patient was infected with two divergent strains of S.pneumoniae.However,when the complete genomes of several of the isolates were sequenced and compared,four different genotypic strains were identified,all of which evolved as a result of 16 distinct recombination events between strains.Curiously,the technicians noticed that some recombined sequences did not seem to come from either of the two primary coinfecting strains.It appeared that this new DNA came from uncultured and undetected strains of S.pneumoniae that had colonized Eva's throat at one time or another.Horizontal gene transfers (transformation)between the undetected and detected isolates appear to have produced the new recombined strains of S.pneumoniae.The genome sequence data clearly support the idea that S.pneumoniae evolution is characterized by high rates of horizontal gene transfer and recombination.The scientists concluded that this and other related bacterial species use horizontal gene transfer to defeat the adaptive immunity of individual hosts,possibly explaining Eva's recurring infections.These types of bioinformatic comparisons suggest that horizontal gene transfers that produce most of the genetic variation pathogens develop while persisting within a host.
Which of the following best explains Eva's recurring Streptococcus pneumoniae ear infections?
A) The strains with which she was infected were antibiotic resistant due to horizontal gene transfer.
B) Because she is a baby, she has low immunity.
C) The strains with which she was infected varied in antigen production due to horizontal gene transfer.
D) The strains with which she was infected were highly virulent due to horizontal gene transfer.
Nine-month-old Eva had 12 clinic visits over a seven-month period due to runny nose and/or ear infections.During each episode,nasopharyngeal swabs were obtained for bacterial culture and Streptococcus pneumoniae was obtained.Although all the infections were resolved with antibiotics,scientists gained insight into pathogen evolution by seeing how the isolates compared.Each isolate was first analyzed for seven genes that can indicate strain variability,a process called multilocus sequence typing (MLST).The lab found two MLST types,indicating that the patient was infected with two divergent strains of S.pneumoniae.However,when the complete genomes of several of the isolates were sequenced and compared,four different genotypic strains were identified,all of which evolved as a result of 16 distinct recombination events between strains.Curiously,the technicians noticed that some recombined sequences did not seem to come from either of the two primary coinfecting strains.It appeared that this new DNA came from uncultured and undetected strains of S.pneumoniae that had colonized Eva's throat at one time or another.Horizontal gene transfers (transformation)between the undetected and detected isolates appear to have produced the new recombined strains of S.pneumoniae.The genome sequence data clearly support the idea that S.pneumoniae evolution is characterized by high rates of horizontal gene transfer and recombination.The scientists concluded that this and other related bacterial species use horizontal gene transfer to defeat the adaptive immunity of individual hosts,possibly explaining Eva's recurring infections.These types of bioinformatic comparisons suggest that horizontal gene transfers that produce most of the genetic variation pathogens develop while persisting within a host.
Which of the following best explains Eva's recurring Streptococcus pneumoniae ear infections?
A) The strains with which she was infected were antibiotic resistant due to horizontal gene transfer.
B) Because she is a baby, she has low immunity.
C) The strains with which she was infected varied in antigen production due to horizontal gene transfer.
D) The strains with which she was infected were highly virulent due to horizontal gene transfer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The marine organism Chromohalobacter salexigens contains two homologous genes responsible for the conversion of a-ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA.A third gene contains a similar sequence and appears to have evolved from the other two genes to complete a different function.This is an example of ________ genes.
A) paralog
B) ortholog
C) degenerate
D) nonfunctional
A) paralog
B) ortholog
C) degenerate
D) nonfunctional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which is NOT an agreed-upon characteristic for microorganism species determination?
A) conjugation similarity
B) phylogeny
C) DNA relatedness
D) ecology
A) conjugation similarity
B) phylogeny
C) DNA relatedness
D) ecology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The traits of the hidden microbiota of humans can be predicted by analyzing
A) cellular structure.
B) DNA sequences.
C) microscopic appearance.
D) growth patterns.
A) cellular structure.
B) DNA sequences.
C) microscopic appearance.
D) growth patterns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The Enterobacteriaceae family is taxonomically considered a(n)
A) classification.
B) nomenclature.
C) identification.
D) homolog.
A) classification.
B) nomenclature.
C) identification.
D) homolog.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is a DISADVANTAGE of a probabilistic indicator compared to a dichotomous key?
A) more time-consuming
B) less applicable to microorganisms isolated in a clinical setting
C) more redundancy leading to fewer errors
D) There are no scientific disadvantages to using a probabilistic indicator.
A) more time-consuming
B) less applicable to microorganisms isolated in a clinical setting
C) more redundancy leading to fewer errors
D) There are no scientific disadvantages to using a probabilistic indicator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following can result in degenerative evolution?
A) natural selection
B) endosymbiosis
C) fitness reduction
D) parasitism
A) natural selection
B) endosymbiosis
C) fitness reduction
D) parasitism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which is NOT a useful way to identify a microorganism?
A) sequencing its genome
B) phenotypic trait analysis
C) microscopic observation alone
D) phylogenetic analysis
A) sequencing its genome
B) phenotypic trait analysis
C) microscopic observation alone
D) phylogenetic analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Ancient ________ give evidence to the fact that all life originated from microorganisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Genes for transfer RNA can be predicted through
A) amino acid sequence similarity.
B) protein function prediction.
C) gene function prediction.
D) conservation over vast phylogenetic distances.
A) amino acid sequence similarity.
B) protein function prediction.
C) gene function prediction.
D) conservation over vast phylogenetic distances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following can be used to provide evidence of horizontal gene transfer?
A) comparison of GC content
B) protein sequence similarity
C) cell structure modification
D) plasmid curing
A) comparison of GC content
B) protein sequence similarity
C) cell structure modification
D) plasmid curing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Consider the dichotomous key shown.What do the numbered organisms (0961,0914,and 021N)require?
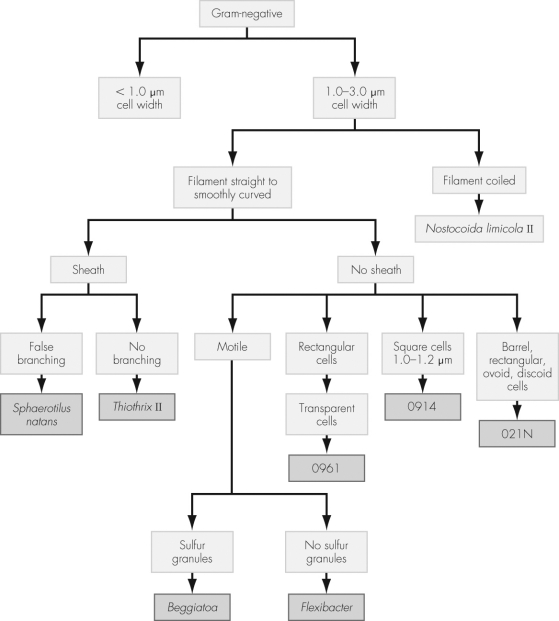
A) homology
B) classification
C) nomenclature
D) identification

A) homology
B) classification
C) nomenclature
D) identification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
How does one begin to identify a predicted protein?
A) experimentally determine its amino acid sequence
B) compare its predicted amino acid or DNA sequence to that of known proteins
C) analyze its RNA sequence
D) determine the sequence of its paralog
A) experimentally determine its amino acid sequence
B) compare its predicted amino acid or DNA sequence to that of known proteins
C) analyze its RNA sequence
D) determine the sequence of its paralog

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Renaming Pasteurella pestis to Yersinia pestis alters the ________ of the organism.
A) classification
B) nomenclature
C) identification
D) homology
A) classification
B) nomenclature
C) identification
D) homology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Serratia marcescens is taxonomically considered a
A) homolog.
B) identification.
C) nomenclature.
D) classification.
A) homolog.
B) identification.
C) nomenclature.
D) classification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is an example of functional genomics?
A) predicting the function of genes in Haemophilus influenzae from the genomic sequence
B) transforming antibiotic resistance genes into MRSA
C) measuring the pathogenesis of Corynebacterium diphtheria
D) eliminating the presence of Wolbachia endosymbionts
A) predicting the function of genes in Haemophilus influenzae from the genomic sequence
B) transforming antibiotic resistance genes into MRSA
C) measuring the pathogenesis of Corynebacterium diphtheria
D) eliminating the presence of Wolbachia endosymbionts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The enzyme ________ is important for generalized recombination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the best option for characterizing a completely unknown organism?
A) DNA sequencing
B) dichotomous key
C) probabilistic indicator
D) phylogenetic tree construction
A) DNA sequencing
B) dichotomous key
C) probabilistic indicator
D) phylogenetic tree construction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of an open reading frame?
A) DNA sequence long enough to encode an amino acid sequence of at least 50.
B) It begins with a translation start codon.
C) It ends with a translation termination codon.
D) It contains a promoter sequence.
A) DNA sequence long enough to encode an amino acid sequence of at least 50.
B) It begins with a translation start codon.
C) It ends with a translation termination codon.
D) It contains a promoter sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The gene proV codes for an ABC transport protein responsible for bringing proline or glycine betaine into the cell in response to osmotic stress.This gene serves a similar function in Salmonella and E.coli.This is an example of ________ genes.
A) nonprotein coding
B) paralog
C) ortholog
D) degenerate
A) nonprotein coding
B) paralog
C) ortholog
D) degenerate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Describe how gene duplication leads to paralogs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
CASE HISTORY
Harrison was a 73-year-old man with kidney failure.He was admitted to the hospital with fever and hypotension,both of which are symptoms of bacteremia.When bacteria from Harrison's blood were grown on horse blood agar,it showed colonies typical of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)and confirmed the diagnosis of bacteremia.Further investigation uncovered his home dialysis line as the source of MRSA.He was treated with intravenous vancomycin (an antibiotic that targets cell wall synthesis),but the bacteremia persisted.The bacteria were tested and found to be partly resistant to vancomycin,though sensitive to rifampin (which targets RNA polymerase),ciprofloxacin (which targets DNA gyrase),and linezolid (which targets protein synthesis).The vancomycin was discontinued,and therapy was begun with rifampin,ciprofloxacin,and linezolid.Harrison's symptoms improved,but within three weeks the bacteremia returned.Bacteria cultured from his blood now showed resistance to rifampin and ciprofloxacin.Linezolid was administered alone for six weeks,but five days after linezolid treatment ended,the bacteremia recurred.Linezolid was administered again,for another six weeks.Then a new blood culture revealed a form of MRSA with small colonies.The small-colony variant was partly resistant to linezolid while fully resistant to all the other antibiotics.Harrison was now treated with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.These final antibiotics had to be administered indefinitely,as they could not fully eliminate MRSA from Harrison's system.
A laboratory technician cultures the small-colony form of MRSA for 100 generations on agar media without antibiotics,selecting the largest colony for passage at each generation.Would you predict the 100th generation would be more or less resistant to linezolid than the isolate from Harrison's highly resistant infection?
Harrison was a 73-year-old man with kidney failure.He was admitted to the hospital with fever and hypotension,both of which are symptoms of bacteremia.When bacteria from Harrison's blood were grown on horse blood agar,it showed colonies typical of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)and confirmed the diagnosis of bacteremia.Further investigation uncovered his home dialysis line as the source of MRSA.He was treated with intravenous vancomycin (an antibiotic that targets cell wall synthesis),but the bacteremia persisted.The bacteria were tested and found to be partly resistant to vancomycin,though sensitive to rifampin (which targets RNA polymerase),ciprofloxacin (which targets DNA gyrase),and linezolid (which targets protein synthesis).The vancomycin was discontinued,and therapy was begun with rifampin,ciprofloxacin,and linezolid.Harrison's symptoms improved,but within three weeks the bacteremia returned.Bacteria cultured from his blood now showed resistance to rifampin and ciprofloxacin.Linezolid was administered alone for six weeks,but five days after linezolid treatment ended,the bacteremia recurred.Linezolid was administered again,for another six weeks.Then a new blood culture revealed a form of MRSA with small colonies.The small-colony variant was partly resistant to linezolid while fully resistant to all the other antibiotics.Harrison was now treated with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.These final antibiotics had to be administered indefinitely,as they could not fully eliminate MRSA from Harrison's system.
A laboratory technician cultures the small-colony form of MRSA for 100 generations on agar media without antibiotics,selecting the largest colony for passage at each generation.Would you predict the 100th generation would be more or less resistant to linezolid than the isolate from Harrison's highly resistant infection?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Create an example that shows how random mutations lead to natural selection and divergence of organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Describe how horizontal gene transfer could lead to the emergence of a new bacterial pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
For each domain of life,list three characteristics that distinguish it from the other two domains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Would transformation be possible for an organism that does not produce nucleases? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
________ is important for analyzing and comparing the genomic sequences of organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Using the dichotomous key shown,determine the identity of an organism isolated in pure culture given the following characteristics:
Filament smoothly curved
Sheath
No branching
Motile
Transparent cells
Sulfur granules
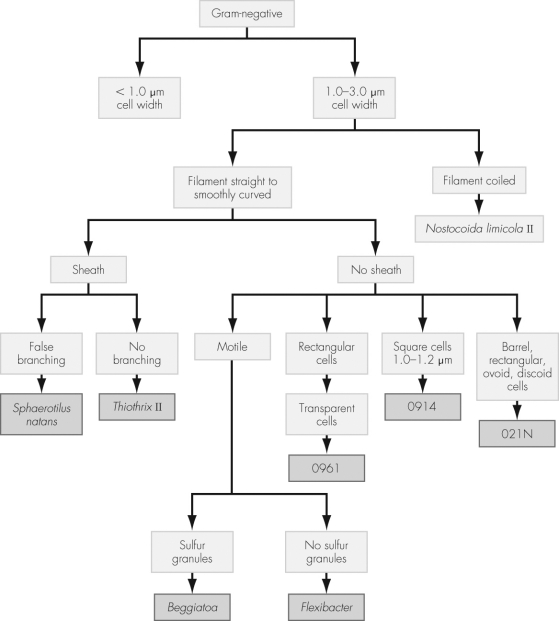
Filament smoothly curved
Sheath
No branching
Motile
Transparent cells
Sulfur granules


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Explain how natural selection quickly leads to antibiotic resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What are two reasons why the definition of a species is problematic for bacteria?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A ________ relationship develops between endosymbionts and their hosts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
CASE HISTORY
Nine-month-old Eva had 12 clinic visits over a seven-month period due to runny nose and/or ear infections.During each episode,nasopharyngeal swabs were obtained for bacterial culture and Streptococcus pneumoniae was obtained.Although all the infections were resolved with antibiotics,scientists gained insight into pathogen evolution by seeing how the isolates compared.Each isolate was first analyzed for seven genes that can indicate strain variability,a process called multilocus sequence typing (MLST).The lab found two MLST types,indicating that the patient was infected with two divergent strains of S.pneumoniae.However,when the complete genomes of several of the isolates were sequenced and compared,four different genotypic strains were identified,all of which evolved as a result of 16 distinct recombination events between strains.Curiously,the technicians noticed that some recombined sequences did not seem to come from either of the two primary coinfecting strains.It appeared that this new DNA came from uncultured and undetected strains of S.pneumoniae that had colonized Eva's throat at one time or another.Horizontal gene transfers (transformation)between the undetected and detected isolates appear to have produced the new recombined strains of S.pneumoniae.The genome sequence data clearly support the idea that S.pneumoniae evolution is characterized by high rates of horizontal gene transfer and recombination.The scientists concluded that this and other related bacterial species use horizontal gene transfer to defeat the adaptive immunity of individual hosts,possibly explaining Eva's recurring infections.These types of bioinformatic comparisons suggest that horizontal gene transfers that produce most of the genetic variation pathogens develop while persisting within a host.
Could antibiotic resistance from one strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae to another occur by transformation?
Nine-month-old Eva had 12 clinic visits over a seven-month period due to runny nose and/or ear infections.During each episode,nasopharyngeal swabs were obtained for bacterial culture and Streptococcus pneumoniae was obtained.Although all the infections were resolved with antibiotics,scientists gained insight into pathogen evolution by seeing how the isolates compared.Each isolate was first analyzed for seven genes that can indicate strain variability,a process called multilocus sequence typing (MLST).The lab found two MLST types,indicating that the patient was infected with two divergent strains of S.pneumoniae.However,when the complete genomes of several of the isolates were sequenced and compared,four different genotypic strains were identified,all of which evolved as a result of 16 distinct recombination events between strains.Curiously,the technicians noticed that some recombined sequences did not seem to come from either of the two primary coinfecting strains.It appeared that this new DNA came from uncultured and undetected strains of S.pneumoniae that had colonized Eva's throat at one time or another.Horizontal gene transfers (transformation)between the undetected and detected isolates appear to have produced the new recombined strains of S.pneumoniae.The genome sequence data clearly support the idea that S.pneumoniae evolution is characterized by high rates of horizontal gene transfer and recombination.The scientists concluded that this and other related bacterial species use horizontal gene transfer to defeat the adaptive immunity of individual hosts,possibly explaining Eva's recurring infections.These types of bioinformatic comparisons suggest that horizontal gene transfers that produce most of the genetic variation pathogens develop while persisting within a host.
Could antibiotic resistance from one strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae to another occur by transformation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The ________ gene was used as a molecular clock to reveal the divergence of three domains of life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



