Deck 13: Sterilization, Disinfection, and Antibiotic Therapy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/63
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Sterilization, Disinfection, and Antibiotic Therapy
1
Which of the following does NOT affect the sensitivity of a microorganism to food irradiation?
A) genome size
B) rate of repair of DNA damage
C) whether the food is fresh or frozen
D) the presence of heat-shock enzymes
A) genome size
B) rate of repair of DNA damage
C) whether the food is fresh or frozen
D) the presence of heat-shock enzymes
D
2
Which of the following is NOT a standard parameter of the Kirby-Bauer test?
A) the size of the agar plate
B) the depth of the medium
C) moderate composition
D) the method of spreading organisms onto the plate
A) the size of the agar plate
B) the depth of the medium
C) moderate composition
D) the method of spreading organisms onto the plate
D
3
Which of the following terms can describe the death rate of microbial cells when exposed to an antibacterial agent?
A) linear
B) exponential
C) reverse logarithmic
D) polar
A) linear
B) exponential
C) reverse logarithmic
D) polar
B
4
Hannibal Lecter,an infamous serial killer,is attempting to use H₂O₂ to remove pesky blood stains of his latest victim from his 100% cashmere scarf and for disinfection purposes.Why is it taking him so long to disinfect his scarf?
A) H₂O₂ is not a good disinfection agent.
B) This type of disinfection procedure is best completed at colder temperatures.
C) Blood is an example of organic load that can inhibit the process of disinfection.
D) The organisms on his scarf are resistant to H₂O₂.
A) H₂O₂ is not a good disinfection agent.
B) This type of disinfection procedure is best completed at colder temperatures.
C) Blood is an example of organic load that can inhibit the process of disinfection.
D) The organisms on his scarf are resistant to H₂O₂.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
________ with the structure R-CHO are very useful disinfectants.
A) Iodophors
B) Low-molecular-weight aldehydes
C) Anionic detergents
D) Cationic detergents
A) Iodophors
B) Low-molecular-weight aldehydes
C) Anionic detergents
D) Cationic detergents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of biofilms that makes it resistant to disinfectants?
A) presence of an extracellular matrix
B) stress-induced physiology of surface cells
C) stress-induced physiology of cells deep in the biofilm
D) metabolic collaboration between multiple species
A) presence of an extracellular matrix
B) stress-induced physiology of surface cells
C) stress-induced physiology of cells deep in the biofilm
D) metabolic collaboration between multiple species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Because it is an essential component for every individual,if enough vitamin C is not found in the diet,supplements may be required.Vitamin C is sensitive to heat.So that it can be safe for human consumption,how can vitamin C be sterilized before being packaged into supplements?
A) autoclave
B) pasteurization
C) filtration
D) lyophilization
A) autoclave
B) pasteurization
C) filtration
D) lyophilization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In which of the following mechanisms of microbial control might some pathogens still survive?
A) sanitization
B) antisepsis
C) disinfection
D) sterilization
A) sanitization
B) antisepsis
C) disinfection
D) sterilization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The term antibiotic is usually reserved for drugs that target
A) viruses.
B) bacteria.
C) fungi.
D) protozoa.
A) viruses.
B) bacteria.
C) fungi.
D) protozoa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Examine the table shown.Which disinfectant is the most effective against Salmonella typhi based on the phenol coefficient?
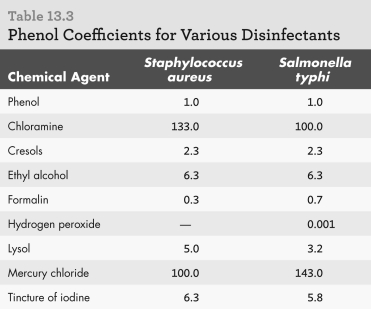
A) chloramine
B) mercury chloride
C) formalin
D) hydrogen peroxide

A) chloramine
B) mercury chloride
C) formalin
D) hydrogen peroxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is NOT a purpose of low temperatures in microbiology?
A) inhibit microbial growth
B) stop microbial metabolism
C) kill microorganisms
D) preserve microorganisms
A) inhibit microbial growth
B) stop microbial metabolism
C) kill microorganisms
D) preserve microorganisms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is NOT a factor affecting the efficacy of a disinfectant?
A) the barometric pressure
B) the presence of blood
C) the presence of endospore-forming bacteria
D) the corrosiveness of the disinfectant
A) the barometric pressure
B) the presence of blood
C) the presence of endospore-forming bacteria
D) the corrosiveness of the disinfectant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Glycerol is used to protect cells during
A) refrigeration.
B) deep-freezing.
C) lyophilization.
D) filtration.
A) refrigeration.
B) deep-freezing.
C) lyophilization.
D) filtration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following organisms is NOT killed by a germicidal agent?
A) bacteria
B) virus
C) fungi
D) endospore
A) bacteria
B) virus
C) fungi
D) endospore

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The cotreatment of septic Enterococcus infections with vancomycin and an aminoglycoside is an example of antibiotic
A) synergism.
B) antagonism.
C) sensitivity.
D) resistance.
A) synergism.
B) antagonism.
C) sensitivity.
D) resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Drug A has a toxic dose of 17 g/kg of body weight and a therapeutic dose of 8 g/kg of body weight.Drug B has a toxic dose of 6 g/kg of body weight and a therapeutic dose of 4 g/kg of body weight.Which of the following statements is true?
A) Drug B is the safer drug.
B) Drug A is the safer drug.
C) Drug B has a higher therapeutic index.
D) Drug A has a lower therapeutic index.
A) Drug B is the safer drug.
B) Drug A is the safer drug.
C) Drug B has a higher therapeutic index.
D) Drug A has a lower therapeutic index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following disinfectants has a high CDC level of activity?
A) hydrogen peroxide
B) quarternary ammonium compounds
C) phenol
D) chlorine gas
A) hydrogen peroxide
B) quarternary ammonium compounds
C) phenol
D) chlorine gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Drug sensitivity occurs when a(n)
A) drug is broken down by a pathogenic organism.
B) organism is inhibited by a drug.
C) individual develops an allergic reaction to a drug he or she is taking.
D) drug that is used to inhibit the growth of an organism is no longer capable.
A) drug is broken down by a pathogenic organism.
B) organism is inhibited by a drug.
C) individual develops an allergic reaction to a drug he or she is taking.
D) drug that is used to inhibit the growth of an organism is no longer capable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements regarding the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)is FALSE?
A) The MIC is the same for one drug regardless of bacterial species.
B) The MIC is the lowest concentration of a drug that will prevent the growth of an organism.
C) The MIC can be affected by how well a drug penetrates a cell.
D) The MIC can be affected by the affinity of the drug for the intracellular target.
A) The MIC is the same for one drug regardless of bacterial species.
B) The MIC is the lowest concentration of a drug that will prevent the growth of an organism.
C) The MIC can be affected by how well a drug penetrates a cell.
D) The MIC can be affected by the affinity of the drug for the intracellular target.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Standard conditions for sterilization by ________ are 121°C and 15 psi for 20 minutes.
A) autoclaving
B) pasteurization
C) tyndallization
D) lyophilization
A) autoclaving
B) pasteurization
C) tyndallization
D) lyophilization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What would inhibition of viral envelope acidification do to an influenza infection?
A) It would inhibit it.
B) It would enhance it.
C) It would have no effect.
D) It would speed it up.
A) It would inhibit it.
B) It would enhance it.
C) It would have no effect.
D) It would speed it up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the major downside to the often necessary long-term treatment with fungal drugs?
A) dry skin
B) high cost
C) antifungal resistance
D) potential toxic side effects
A) dry skin
B) high cost
C) antifungal resistance
D) potential toxic side effects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
CASE HISTORY
Three-year-old Molly was brought to the emergency department crying.She had a stiff neck and high fever (40° C,or 104° F).Gram stain of her cerebrospinal fluid revealed Gram-positive cocci,generally in pairs.The attending physician diagnosed Molly with meningitis and immediately prescribed intravenous ampicillin.Unfortunately,the child's condition worsened,so antibiotic treatment was changed to a third-generation cephalosporin (ceftriaxone).Molly began to improve within hours and was released after two days.A report from the clinical microbiology laboratory two days later identified the organism as Streptococcus pneumoniae.The report also included antibiotic susceptibility results,which revealed that this strain of S.pneumoniae was resistant to ampicillin but remained susceptible to cephalosporin.
The first antibiotic used to treat Molly,ampicillin,has activity against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria;however,the bacterium that made Molly ill was resistant to this agent.At the time the antibiotic was prescribed,neither the type of agent nor its resistances were known.Based on this information,which of the following is true?
A) Ampicillin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
B) Gram-positive bacteria are resistant to ampicillin, so it should be used only for Gram-negative infections.
C) Molly's illness should have been treated with a narrow-spectrum antibiotic.
D) Molly's infection is resistant to a broad variety of antibiotics.
Three-year-old Molly was brought to the emergency department crying.She had a stiff neck and high fever (40° C,or 104° F).Gram stain of her cerebrospinal fluid revealed Gram-positive cocci,generally in pairs.The attending physician diagnosed Molly with meningitis and immediately prescribed intravenous ampicillin.Unfortunately,the child's condition worsened,so antibiotic treatment was changed to a third-generation cephalosporin (ceftriaxone).Molly began to improve within hours and was released after two days.A report from the clinical microbiology laboratory two days later identified the organism as Streptococcus pneumoniae.The report also included antibiotic susceptibility results,which revealed that this strain of S.pneumoniae was resistant to ampicillin but remained susceptible to cephalosporin.
The first antibiotic used to treat Molly,ampicillin,has activity against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria;however,the bacterium that made Molly ill was resistant to this agent.At the time the antibiotic was prescribed,neither the type of agent nor its resistances were known.Based on this information,which of the following is true?
A) Ampicillin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
B) Gram-positive bacteria are resistant to ampicillin, so it should be used only for Gram-negative infections.
C) Molly's illness should have been treated with a narrow-spectrum antibiotic.
D) Molly's infection is resistant to a broad variety of antibiotics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Administering antibiotics before knowing the cause of the infection is specifically known as
A) chemotherapy.
B) empirical therapy.
C) prophylactic therapy.
D) persistence therapy.
A) chemotherapy.
B) empirical therapy.
C) prophylactic therapy.
D) persistence therapy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How do DNA analogs act to inhibit replication of an RNA virus?
A) DNA analogs do not inhibit RNA viruses.
B) by inhibiting RNA polymerase
C) by inhibiting DNA polymerase
D) by preventing protein synthesis
A) DNA analogs do not inhibit RNA viruses.
B) by inhibiting RNA polymerase
C) by inhibiting DNA polymerase
D) by preventing protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The function of polymyxin is similar to that of a detergent.What cell structure will be most affected by this drug?
A) cell membrane
B) cell wall
C) ribosome
D) chromosome
A) cell membrane
B) cell wall
C) ribosome
D) chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which antibiotic inhibits the formation of the peptide side chain of NAM?
A) vancomycin
B) cycloserine
C) bacitracin
D) cephalexin
A) vancomycin
B) cycloserine
C) bacitracin
D) cephalexin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How is griseofulvin selectively toxic?
A) it inhibits DNA synthesis of fungal DNA only
B) it disrupts the mitotic spindle of fungi but not humans
C) it blocks synthesis of a fungal cell wall
D) it inhibits synthesis of fungal-specific ergosterol
A) it inhibits DNA synthesis of fungal DNA only
B) it disrupts the mitotic spindle of fungi but not humans
C) it blocks synthesis of a fungal cell wall
D) it inhibits synthesis of fungal-specific ergosterol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Highly active antiretroviral therapy is used to treat
A) HPV.
B) HIV.
C) hepatitis C.
D) influenza.
A) HPV.
B) HIV.
C) hepatitis C.
D) influenza.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which antibiotic resistance mechanism is exemplified by beta-lactamase?
A) destroy the antibiotic before it gets into the cell
B) modify the target so that it no longer binds the antibiotic
C) add modifying groups that inactivate the antibiotic
D) pump the antibiotic out of the cell
A) destroy the antibiotic before it gets into the cell
B) modify the target so that it no longer binds the antibiotic
C) add modifying groups that inactivate the antibiotic
D) pump the antibiotic out of the cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Viruses cause more illnesses on an everyday basis than do bacteria.Why are there so few antiviral agents compared to antibacterial agents?
A) Viruses are a bigger problem in developing countries where they do not have the funds to develop antiviral drugs.
B) Since viruses are not living, there are no drugs that can stop their proliferation.
C) Viruses use functions of the host to replicate themselves, so achieving selective toxicity is difficult.
D) Viruses do not cause as many deadly diseases and therefore have not been targeted with antivirals.
A) Viruses are a bigger problem in developing countries where they do not have the funds to develop antiviral drugs.
B) Since viruses are not living, there are no drugs that can stop their proliferation.
C) Viruses use functions of the host to replicate themselves, so achieving selective toxicity is difficult.
D) Viruses do not cause as many deadly diseases and therefore have not been targeted with antivirals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Fungal cells grown in the presence of fluconazole have
A) impaired cell division.
B) mutations in DNA.
C) defective cell walls.
D) defective cell membranes.
A) impaired cell division.
B) mutations in DNA.
C) defective cell walls.
D) defective cell membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following will result from inhibited topoisomerases?
A) no cell wall synthesis
B) deficient plasma membrane
C) impaired DNA synthesis
D) impaired RNA synthesis
A) no cell wall synthesis
B) deficient plasma membrane
C) impaired DNA synthesis
D) impaired RNA synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
________ is the process of heating foods to a moderately high temperature long enough to kill most heat-resistant,non-spore-forming pathogens known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Protease inhibitors are a common antiviral drug targeting
A) HPV.
B) HIV.
C) hepatitis C.
D) influenza.
A) HPV.
B) HIV.
C) hepatitis C.
D) influenza.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The presence of ________,such as blood,can require longer exposure times to a chemical in order to achieve true disinfection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The removal of 99.9% of airborne particulate matter larger than 0.3µm in size can be accomplished with a(n)________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following actions of an individual will NOT inhibit the need for antibiotics?
A) frequent hand washing
B) aromatherapy
C) avoiding the use of antibiotics for viral infections
D) vaccinations
A) frequent hand washing
B) aromatherapy
C) avoiding the use of antibiotics for viral infections
D) vaccinations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
________ is the process by which all living cells,spores,and viruses are destroyed on an object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is NOT a category of antifungal agents?
A) polyenes
B) azoles
C) allylamines
D) cephalosporins
A) polyenes
B) azoles
C) allylamines
D) cephalosporins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Explain why penicillin is toxic for susceptible bacteria that are actively growing but has no effect on dormant bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A drug is classified as bactericidal if its minimum bactericidal concentration is no more than ________ its minimum inhibitory concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Neuraminidase inhibitors that target viral release can be used to treat infections with ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Explain how organisms can develop resistance to chemical disinfectants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Explain how DNA chain-terminating analog antivirals are selectively toxic despite the fact that the viruses they target and the host cell both contain DNA genomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Explain why norovirus and the prion that causes bovine spongiform encephalopathy are not susceptible to irradiation of food.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
________ is when infecting bacteria "play dead" when an antibiotic is present,only to grow again when the antibiotic is gone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Describe how the antibiotic resistance mechanism using drug efflux pumps works.How could the medical community respond to this resistance mechanism to overcome it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The presence (+)or absence (-)of growth of a specific organism after exposure to the shown dilutions of phenol and disinfectant A for 5,10,or 15 minutes is shown in the table below.Calculate the phenol coefficient for this disinfectant.
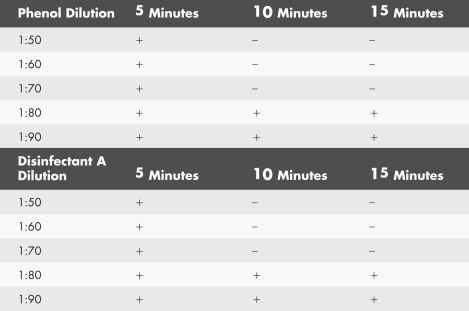


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Explain what the therapeutic index is.If two antibiotics can be used to treat an infection and they are equal except for their therapeutic indexes,should the doctor prescribe the drug with a high therapeutic index or a low therapeutic index?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Explain how a bacteriostatic antibiotic is useful even if it does not result in the death of the pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
________ is a category of antifungal agents that inhibits DNA synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Penicillin targets peptidoglycan synthesis to inhibit ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Examine the image provided.Determine the decimal reduction time and describe what this means in words.
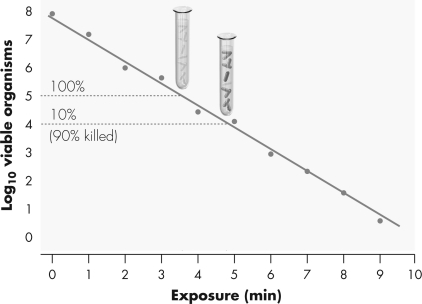


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Wescodyne and betadine are examples of ________ complexed with organic carriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Describe how avoiding the use of antibiotics for viral infections can prevent the spread of antibiotic resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Aminoglycosides inhibit translation by binding to the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Why does lyophilization offer longer-term storage of mesophilic cells than refrigeration?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Give an example of when you would want to use a broad-spectrum antibiotic and when you would want to use a narrow-spectrum antibiotic.Give a disadvantage to using a broad-spectrum antibiotic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The presence of ________ in the bacterial cell wall is one of the mechanisms of antibiotic selective toxicity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
CASE HISTORY
Titus,a nine-month-old infant,suffered from a series of chronic problems after birth,including respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis (infection and inflammation of the bronchioles)and neonatal group B Streptococcal sepsis.(Neonatal sepsis happens soon after birth and is often caused by lancefield group B Streptococcus agalactiae,passed to the newborn from an infected mother. )As a result of his weakened state,Titus was fitted with a gastrostomy feeding tube so that his parents could feed him.Within a week of being sent home,however,Titus was rushed to the Johns Hopkins Hospital with an acute onset of fever,cough,regurgitation from his gastrostomy feeding tube,and dehydration.Physical exam confirmed that the boy had a severe cough resulting in respiratory distress,a rapid heart rate,and moderate dehydration.A nasopharyngeal aspirate (the nasopharynx is the nasal part of the pharynx)was positive for influenza A antigen.Titus was diagnosed with influenza and treated with the antiviral drug oseltamivir.He gradually improved and was discharged four days after admission.
What is the mechanism of action for the drug,oseltamivir,used to treat Titus's influenza infection? Why would antibiotics such as 50S ribosomal inhibitors have had no effect on this viral infection?
Titus,a nine-month-old infant,suffered from a series of chronic problems after birth,including respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis (infection and inflammation of the bronchioles)and neonatal group B Streptococcal sepsis.(Neonatal sepsis happens soon after birth and is often caused by lancefield group B Streptococcus agalactiae,passed to the newborn from an infected mother. )As a result of his weakened state,Titus was fitted with a gastrostomy feeding tube so that his parents could feed him.Within a week of being sent home,however,Titus was rushed to the Johns Hopkins Hospital with an acute onset of fever,cough,regurgitation from his gastrostomy feeding tube,and dehydration.Physical exam confirmed that the boy had a severe cough resulting in respiratory distress,a rapid heart rate,and moderate dehydration.A nasopharyngeal aspirate (the nasopharynx is the nasal part of the pharynx)was positive for influenza A antigen.Titus was diagnosed with influenza and treated with the antiviral drug oseltamivir.He gradually improved and was discharged four days after admission.
What is the mechanism of action for the drug,oseltamivir,used to treat Titus's influenza infection? Why would antibiotics such as 50S ribosomal inhibitors have had no effect on this viral infection?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
CASE HISTORY
Brian,a 14-year-old boy with fever (39° C,or 102.2° F),chills,and left-sided pleuritic chest pain (pain when inhaling)was referred to a hospital emergency department by his general practitioner.A chest X-ray showed left lower lobe pneumonia.The boy reported that he was allergic to amoxicillin and cephalosporins (as a child he had developed a rash to these agents)and had been taking daily doxycycline (tetracycline)for the previous three months to treat mild acne.He was admitted to the hospital and treated with intravenous erythromycin because of his reported beta-lactam allergies,but he continued to feel sick.The day after admission,both sputum and blood cultures grew Streptococcus pneumoniae.After 48 hours,antibiotic susceptibility results indicated that the microbe was resistant to penicillin,erythromycin,and tetracycline.Armed with this information,the clinician immediately changed antibiotic treatment to vancomycin,a drug still effective in the face of these resistance mechanisms.The boy's fever resolved over the next 12 hours,and he made a slow but full recovery over the next week.
Would you have predicted the resistance profile of the Streptococcus pneumoniae causing Brian's infection? Why?
Brian,a 14-year-old boy with fever (39° C,or 102.2° F),chills,and left-sided pleuritic chest pain (pain when inhaling)was referred to a hospital emergency department by his general practitioner.A chest X-ray showed left lower lobe pneumonia.The boy reported that he was allergic to amoxicillin and cephalosporins (as a child he had developed a rash to these agents)and had been taking daily doxycycline (tetracycline)for the previous three months to treat mild acne.He was admitted to the hospital and treated with intravenous erythromycin because of his reported beta-lactam allergies,but he continued to feel sick.The day after admission,both sputum and blood cultures grew Streptococcus pneumoniae.After 48 hours,antibiotic susceptibility results indicated that the microbe was resistant to penicillin,erythromycin,and tetracycline.Armed with this information,the clinician immediately changed antibiotic treatment to vancomycin,a drug still effective in the face of these resistance mechanisms.The boy's fever resolved over the next 12 hours,and he made a slow but full recovery over the next week.
Would you have predicted the resistance profile of the Streptococcus pneumoniae causing Brian's infection? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain why antifungal agents are less selectively toxic than antibacterial agents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



