Deck 17: Immune Disorders, Tools, and Vaccines
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Immune Disorders, Tools, and Vaccines
1
All of the following are true about B-cell neoplasms EXCEPT
A) cancers arise in B cells when genes that control cell division are dysregulated and fail to replicate.
B) follicular lymphoma occurs when the bcl-2 gene is activated and prevents apoptosis.
C) chronic lymphocytic leukemia occurs when there is a deletion in chromosome 13.
D) Burkitt's lymphoma develops when the c-myo gene moves next to expressed antibody genes.
A) cancers arise in B cells when genes that control cell division are dysregulated and fail to replicate.
B) follicular lymphoma occurs when the bcl-2 gene is activated and prevents apoptosis.
C) chronic lymphocytic leukemia occurs when there is a deletion in chromosome 13.
D) Burkitt's lymphoma develops when the c-myo gene moves next to expressed antibody genes.
A
2
Which of the following blood transfusions would be compatible?
A)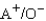
B)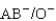
C)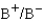
D)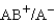
A)
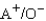
B)
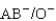
C)
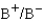
D)
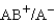
D
3
Leukemia refers to
A) a malignant lymphoid cell found in circulation or bone marrow.
B) a solid mass in a lymphoid organ.
C) growth of a plasma cell.
D) cancerous plasma cells that appear at multiple sites.
A) a malignant lymphoid cell found in circulation or bone marrow.
B) a solid mass in a lymphoid organ.
C) growth of a plasma cell.
D) cancerous plasma cells that appear at multiple sites.
A
4
Patients with primary immunodeficiencies and who are immunosuppressed are prone to developing cancers.Which is the most commonly developed cancer for these patients?
A) Epstein-Barr
B) B-cell lymphomas
C) myelomas
D) mononucleosis
A) Epstein-Barr
B) B-cell lymphomas
C) myelomas
D) mononucleosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How does immune surveillance work inside the host?
A) Cancer cells are sought out but not destroyed.
B) The immune system is suppressed.
C) Immune cells are unable to recognize cancerous cells.
D) Cancer cells are marked with surface antigens not present on normal cells.
A) Cancer cells are sought out but not destroyed.
B) The immune system is suppressed.
C) Immune cells are unable to recognize cancerous cells.
D) Cancer cells are marked with surface antigens not present on normal cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Anaphylaxis is the term for reactions caused when certain antigens combine with
A) IgE antibodies.
B) macrophages.
C) IgG antibodies.
D) histamine.
A) IgE antibodies.
B) macrophages.
C) IgG antibodies.
D) histamine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
All of the following are examples of antibody-mediated hypersensitivities EXCEPT ________ hypersensitivity.
A) IgE-mediated
B) antibody-mediated cytotoxic
C) immune complex-mediated
D) cell-mediated
A) IgE-mediated
B) antibody-mediated cytotoxic
C) immune complex-mediated
D) cell-mediated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
All of the following are examples of B-cell disorders EXCEPT
A) X-linked agammaglobulinemia (Burton's disease).
B) common variable immunodeficiency (CVID).
C) DiGeorge syndrome.
D) selective IgA deficiency.
A) X-linked agammaglobulinemia (Burton's disease).
B) common variable immunodeficiency (CVID).
C) DiGeorge syndrome.
D) selective IgA deficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is a symptom of systemic anaphylaxis?
A) sneezing
B) watery, itchy eyes
C) rhinitis
D) edema
A) sneezing
B) watery, itchy eyes
C) rhinitis
D) edema

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the end result of the reaction in the immune complex reaction demonstrated in the figure below?
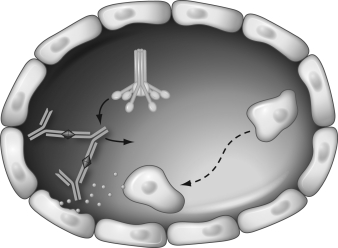
A) IgG is directed against cell membrane antigens.
B) Complement is activated.
C) Neutrophils are attracted and release enzymes.
D) Endothelial cells are damaged.

A) IgG is directed against cell membrane antigens.
B) Complement is activated.
C) Neutrophils are attracted and release enzymes.
D) Endothelial cells are damaged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Symptoms of an immune complex reaction are due to
A) destruction of the antigen.
B) complement activation.
C) phagocytosis.
D) cytokines.
A) destruction of the antigen.
B) complement activation.
C) phagocytosis.
D) cytokines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An autoimmune response is generated within the host when
A) immune tolerance against self is lost.
B) immune cells attack foreign antigens.
C) NK cells bind host tissue.
D) T cells deactivate self-reacting B cells.
A) immune tolerance against self is lost.
B) immune cells attack foreign antigens.
C) NK cells bind host tissue.
D) T cells deactivate self-reacting B cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Allergic contact dermatitis is due to
A) sensitized T cells.
B) IgE antibodies.
C) IgG antibodies.
D) IgM antibodies.
A) sensitized T cells.
B) IgE antibodies.
C) IgG antibodies.
D) IgM antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
All of the following are consequences of bare lymphocyte syndrome (MHC II deficiency)EXCEPT
A) the MHC II molecule is expressed on APCs.
B) T cells will not form into TH₁, TH₂ , or other types of helper T cells.
C) cytotoxic T cells cannot be activated.
D) B cells do not isotype switch.
A) the MHC II molecule is expressed on APCs.
B) T cells will not form into TH₁, TH₂ , or other types of helper T cells.
C) cytotoxic T cells cannot be activated.
D) B cells do not isotype switch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is true regarding T-cell deficiencies?
A) A mutation in the IL-2 receptor affects T-cell proliferation.
B) A deficiency in ATP causes apoptosis in T, B, or NK cells.
C) Immunoglobulin protection is permanent.
D) Severe combined immunodeficiencies (SCIDs) are characterized by a lack of B cells.
A) A mutation in the IL-2 receptor affects T-cell proliferation.
B) A deficiency in ATP causes apoptosis in T, B, or NK cells.
C) Immunoglobulin protection is permanent.
D) Severe combined immunodeficiencies (SCIDs) are characterized by a lack of B cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Complement deficiencies are
A) acquired during life.
B) X-linked.
C) inherited autosomal traits.
D) treated with antivirals.
A) acquired during life.
B) X-linked.
C) inherited autosomal traits.
D) treated with antivirals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An example of a primary immunodeficiency would be
A) DiGeorge syndrome.
B) HIV.
C) severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome.
D) IgA deficiency.
A) DiGeorge syndrome.
B) HIV.
C) severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome.
D) IgA deficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
All of the following are true about Hodgkin's lymphoma EXCEPT that
A) it is often caused by the herpes simplex virus.
B) symptoms include fever, night sweats, and weight loss.
C) tumors contain neoplastic, multinucleated Reed-Sternberg cells.
D) the release of cytokines such as TNF-alpha contributes to the fever and chronic inflammation.
A) it is often caused by the herpes simplex virus.
B) symptoms include fever, night sweats, and weight loss.
C) tumors contain neoplastic, multinucleated Reed-Sternberg cells.
D) the release of cytokines such as TNF-alpha contributes to the fever and chronic inflammation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Type II hypersensitivities differ from type III sensitivities in that only type II involves
A) surface antigens.
B) soluble antigens.
C) antibodies.
D) histamine.
A) surface antigens.
B) soluble antigens.
C) antibodies.
D) histamine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Epinephrine is used to reverse anaphylaxis.This is achieved by all of the following EXCEPT
A) stimulating adenylate cyclase activity.
B) decreasing cAMP levels.
C) relaxing smooth muscle.
D) preventing degranulation of the mast cell.
A) stimulating adenylate cyclase activity.
B) decreasing cAMP levels.
C) relaxing smooth muscle.
D) preventing degranulation of the mast cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The following are all true about herd immunity EXCEPT that it
A) only works for diseases that are contagious.
B) occurs when a large portion of a population is immunized.
C) is possible for non-contagious infections like tetanus.
D) protects unimmunized individuals.
A) only works for diseases that are contagious.
B) occurs when a large portion of a population is immunized.
C) is possible for non-contagious infections like tetanus.
D) protects unimmunized individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is a test to determine a patient's blood type by mixing the patient's red blood cells with antibodies?
A) agglutination reaction
B) immunoprecipitation
C) enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
D) immunofluorescence
A) agglutination reaction
B) immunoprecipitation
C) enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
D) immunofluorescence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What type of vaccine is the live,weakened measles virus?
A) conjugated
B) subunit
C) DNA
D) attenuated whole-agent
A) conjugated
B) subunit
C) DNA
D) attenuated whole-agent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A hybridoma results from the fusion of a(n)
A) B cell with a T cell.
B) B cell with a myeloma cell.
C) antigen with an antibody.
D) antigen with a B cell.
A) B cell with a T cell.
B) B cell with a myeloma cell.
C) antigen with an antibody.
D) antigen with a B cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following does NOT use fluorescent-labeled antibodies?
A) agglutination
B) western blot
C) immunofluorescence microscopy
D) flow cytometry
A) agglutination
B) western blot
C) immunofluorescence microscopy
D) flow cytometry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
All of the following regarding immunoprecipitation are correct EXCEPT
A) it is observed both in vitro and in vivo.
B) too many antigens cause the test not to work.
C) too many antibody molecules cause the test not to work.
D) equivalence is the point at which there are roughly the same number of antigenic and antigen-binding sites.
A) it is observed both in vitro and in vivo.
B) too many antigens cause the test not to work.
C) too many antibody molecules cause the test not to work.
D) equivalence is the point at which there are roughly the same number of antigenic and antigen-binding sites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Determine the FALSE statement below.An effective vaccine
A) will deactivate B and T cells.
B) will generate memory.
C) should not require many boosters.
D) must protect against the natural pathogen.
A) will deactivate B and T cells.
B) will generate memory.
C) should not require many boosters.
D) must protect against the natural pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is the major player in transplant rejection?
A) MHC proteins of the donor
B) T helper cells of the donor
C) MHC proteins of the host
D) T helper cells of the host
A) MHC proteins of the donor
B) T helper cells of the donor
C) MHC proteins of the host
D) T helper cells of the host

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which item is from the patient in a direct ELISA test?
A) antigen
B) substrate for the enzyme
C) antibodies against the antigen
D) antihuman immune serum
A) antigen
B) substrate for the enzyme
C) antibodies against the antigen
D) antihuman immune serum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Graves' disease and Hashimoto's disease are different in the fact that Graves' disease
A) targets the thyroid.
B) involves autoantibodies.
C) causes hyperthyroidism.
D) causes hypothyroidism.
A) targets the thyroid.
B) involves autoantibodies.
C) causes hyperthyroidism.
D) causes hypothyroidism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Sensitivity differs from specificity in that sensitivity
A) measures how selective an antibody is.
B) occurs when antibodies bind dissimilar antigens.
C) reflects how few antigen or antibody molecules a test can detect.
D) is not important when conducting a serological test.
A) measures how selective an antibody is.
B) occurs when antibodies bind dissimilar antigens.
C) reflects how few antigen or antibody molecules a test can detect.
D) is not important when conducting a serological test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The image below is of a radial immunodiffusion assay embedded with anti-IgA antibodies.Which sample has the highest concentration of IgA antibodies?
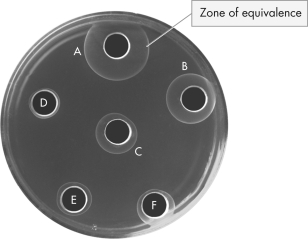
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A plasmid-encoding protein antigen from West Nile virus is injected into muscle cells.This is an example of a(n)
A) DNA vaccine.
B) attenuated vaccine.
C) subunit vaccine.
D) toxoid.
A) DNA vaccine.
B) attenuated vaccine.
C) subunit vaccine.
D) toxoid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
All of the following are examples of autoimmune diseases EXCEPT
A) lupus.
B) Lyme disease.
C) Graves' disease.
D) type-1 diabetes.
A) lupus.
B) Lyme disease.
C) Graves' disease.
D) type-1 diabetes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
All of the following are true of the generation of autoreactive antibodies EXCEPT
A) B cells escape the negative selection process.
B) self-reacting B cells can be activated without specific T-cell assistance.
C) some microbial antigens can also trigger autoimmune reactions.
D) self-reacting B cells do not take up and process self-antigens.
A) B cells escape the negative selection process.
B) self-reacting B cells can be activated without specific T-cell assistance.
C) some microbial antigens can also trigger autoimmune reactions.
D) self-reacting B cells do not take up and process self-antigens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
All of the following pertain to serology EXCEPT that they
A) can detect antibodies.
B) cannot detect antigens.
C) can be used to diagnose various diseases.
D) can reveal the contents of serum.
A) can detect antibodies.
B) cannot detect antigens.
C) can be used to diagnose various diseases.
D) can reveal the contents of serum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
All of the following are examples of passive immunization EXCEPT
A) injection of immune globulin.
B) breast-feeding.
C) antitoxins.
D) vaccinia virus.
A) injection of immune globulin.
B) breast-feeding.
C) antitoxins.
D) vaccinia virus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Refer to the image below.Which component came from the patient in this sandwich ELISA?
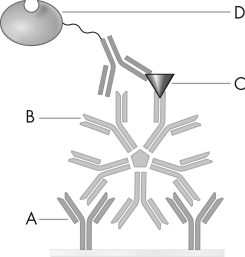
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The figure below illustrates a sandwich ELISA.What is happening in step 3?
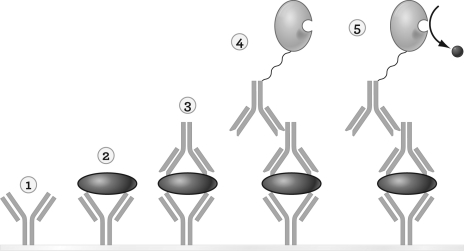
A) Enzyme-linked detection antibody is added.
B) Secondary antibody is added and binds to antigens.
C) The plate is coated with capture antibodies.
D) Serum sample is added.

A) Enzyme-linked detection antibody is added.
B) Secondary antibody is added and binds to antigens.
C) The plate is coated with capture antibodies.
D) Serum sample is added.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
All of the following are generally used in vaccines EXCEPT
A) toxoids.
B) parts of bacterial cells.
C) antibodies.
D) inactivated viruses.
A) toxoids.
B) parts of bacterial cells.
C) antibodies.
D) inactivated viruses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Using the figure below,please describe the steps taken to produce monoclonal antibodies and explain why they are used in diagnostic tests and disease treatments.
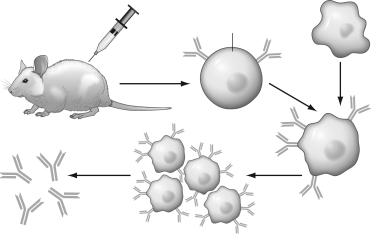


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Describe an ELISA test to detect the presence of hepatitis in a patient's blood sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
CASE HISTORY
Richard,who is blood group B,was undergoing surgery after a car accident and accidentally received a transfusion with type A blood.Within hours,Richard experienced chills and lowered blood pressure.His urine turned red with blood.All these symptoms indicate an ABO blood group incompatibility.
Is there an identifiable allergen present in this case study? How can you tell?
Richard,who is blood group B,was undergoing surgery after a car accident and accidentally received a transfusion with type A blood.Within hours,Richard experienced chills and lowered blood pressure.His urine turned red with blood.All these symptoms indicate an ABO blood group incompatibility.
Is there an identifiable allergen present in this case study? How can you tell?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Using the figure below,please describe in detail how this type IV sensitivity is produced and how tissue is ultimately damaged.
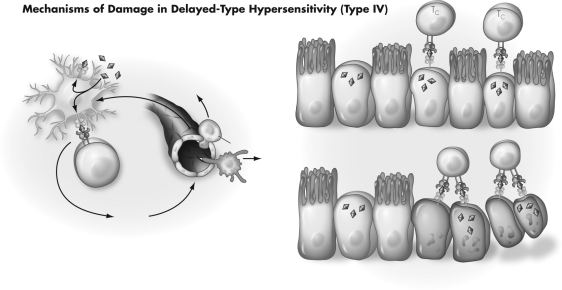


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
CASE HISTORY
The patient,Asuncion,is an eight-year-old girl from Argentina.She received the BCG vaccine for tuberculosis about one year before coming to the United States.Upon entering school in the United States,she must take a skin test for tuberculosis (TB).Asuncion tries to refuse but is told it is a requirement.She allows the nurse to apply the test to her arm.Three days later,the test site has a large red lesion and the skin is starting to slough (peel off).
The reaction Asuncion is experiencing is most similar to someone who has
A) been exposed to poison ivy and now has contact dermatitis.
B) type A blood, but has been given a type B transfusion.
C) an urticarial rash in response to penicillin treatment.
D) an allergic reaction to bee venom injected during a sting.
The patient,Asuncion,is an eight-year-old girl from Argentina.She received the BCG vaccine for tuberculosis about one year before coming to the United States.Upon entering school in the United States,she must take a skin test for tuberculosis (TB).Asuncion tries to refuse but is told it is a requirement.She allows the nurse to apply the test to her arm.Three days later,the test site has a large red lesion and the skin is starting to slough (peel off).
The reaction Asuncion is experiencing is most similar to someone who has
A) been exposed to poison ivy and now has contact dermatitis.
B) type A blood, but has been given a type B transfusion.
C) an urticarial rash in response to penicillin treatment.
D) an allergic reaction to bee venom injected during a sting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
CASE HISTORY
The patient,Asuncion,is an eight-year-old girl from Argentina.She received the BCG vaccine for tuberculosis about one year before coming to the United States.Upon entering school in the United States,she must take a skin test for tuberculosis (TB).Asuncion tries to refuse but is told it is a requirement.She allows the nurse to apply the test to her arm.Three days later,the test site has a large red lesion and the skin is starting to slough (peel off).
From the information given in the case study,we cannot tell whether Asuncion could potentially pose a TB infection risk to her classmates.Why was this test an inappropriate one for Asuncion and what would be a more useful alternative?
The patient,Asuncion,is an eight-year-old girl from Argentina.She received the BCG vaccine for tuberculosis about one year before coming to the United States.Upon entering school in the United States,she must take a skin test for tuberculosis (TB).Asuncion tries to refuse but is told it is a requirement.She allows the nurse to apply the test to her arm.Three days later,the test site has a large red lesion and the skin is starting to slough (peel off).
From the information given in the case study,we cannot tell whether Asuncion could potentially pose a TB infection risk to her classmates.Why was this test an inappropriate one for Asuncion and what would be a more useful alternative?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Patients with ________ have normal or elevated serum IgM levels but low levels of other antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Using the figure below,describe what is happening in each figure.Explain the concept of herd immunity and how it protects the unvaccinated population.
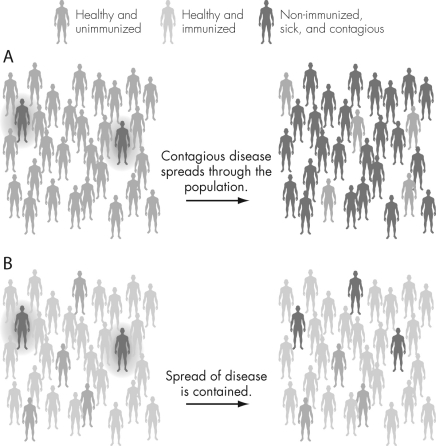


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the immune complex reaction shown in the figure below,the structure labeled as "B" is called a(n)________.
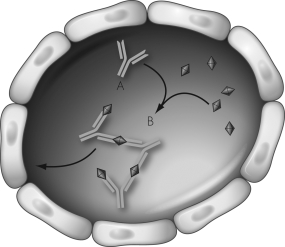


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Draw and label the key mediators of a type 1 hypersensitivity.Be sure to indicate where medical intervention can take place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Injecting an antigen such as a weakened or killed pathogen is called ________ immunization,while ________ immunization is a type of immunotherapy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Antigens that possess structures similar in shape to host structures are called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The process that detects and eliminates cancer cells as they arise is called a(n)________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



