Deck 20: Infections of the Respiratory Tract
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/58
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Infections of the Respiratory Tract
1
A secondary bacterial infection is most likely in a patient who
A) smokes cigarettes.
B) breathes humidified air.
C) breathes dry air.
D) has thin mucus secretions.
A) smokes cigarettes.
B) breathes humidified air.
C) breathes dry air.
D) has thin mucus secretions.
A
2
A virus that primarily causes disease in the very young and may lead to complications such as low blood pressure and seizures is
A) type A influenza.
B) rhinovirus.
C) SARS virus.
D) respiratory syncytial virus.
A) type A influenza.
B) rhinovirus.
C) SARS virus.
D) respiratory syncytial virus.
D
3
The eyes are connected to the upper respiratory tract by the
A) pharynx.
B) Eustachian tube.
C) lacrimal ducts.
D) sinuses.
A) pharynx.
B) Eustachian tube.
C) lacrimal ducts.
D) sinuses.
C
4
Compared to individuals who receive vaccinations,individuals who do not receive any vaccinations are at higher risk of developing
A) sinusitis.
B) severe acute respiratory syndrome.
C) influenza.
D) croup.
A) sinusitis.
B) severe acute respiratory syndrome.
C) influenza.
D) croup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Coming into contact with respiratory secretions from an infected individual is LEAST likely to spread
A) the common cold.
B) respiratory syncytial disease.
C) influenza.
D) sinusitis.
A) the common cold.
B) respiratory syncytial disease.
C) influenza.
D) sinusitis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following structures is considered part of the upper respiratory tract?
A) trachea
B) primary bronchi
C) alveoli
D) larynx
A) trachea
B) primary bronchi
C) alveoli
D) larynx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Croup is most frequently seen in
A) the elderly.
B) middle-aged adults.
C) adolescents.
D) young children.
A) the elderly.
B) middle-aged adults.
C) adolescents.
D) young children.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The structure indicated on this figure is a(n)
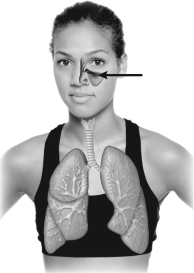
A) sinus.
B) lacrimal duct.
C) inner ear.
D) Eustachian tube.

A) sinus.
B) lacrimal duct.
C) inner ear.
D) Eustachian tube.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Of the viral respiratory diseases below,which is LEAST likely to present with a fever?
A) the common cold
B) croup
C) influenza
D) respiratory syncytial disease
A) the common cold
B) croup
C) influenza
D) respiratory syncytial disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A common home remedy used to treat a common cold is eating chicken soup or chicken broth.Why might this home remedy be useful?
A) Broth helps to prevent dehydration and thins mucus secretions.
B) The salt in broth draws water out of bacterial cells by osmosis.
C) Chicken meat contains antiviral properties.
D) Broth removes the top epithelial cell layers that contain viral particles.
A) Broth helps to prevent dehydration and thins mucus secretions.
B) The salt in broth draws water out of bacterial cells by osmosis.
C) Chicken meat contains antiviral properties.
D) Broth removes the top epithelial cell layers that contain viral particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following infections would affect the lower respiratory tract but NOT the upper respiratory tract?
A) acute otitis media
B) sinusitis
C) streptococcal pharyngitis
D) atypical pneumonia
A) acute otitis media
B) sinusitis
C) streptococcal pharyngitis
D) atypical pneumonia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Antigenic shift is best described as a
A) mixing of RNA segments to form a new form of the hemagglutinin gene in influenza.
B) shift of influenza antigen from one geographic location to another.
C) mutation that changes influenza RNA polymerase.
D) shift that occurs when an avian strain of influenza infects a pig.
A) mixing of RNA segments to form a new form of the hemagglutinin gene in influenza.
B) shift of influenza antigen from one geographic location to another.
C) mutation that changes influenza RNA polymerase.
D) shift that occurs when an avian strain of influenza infects a pig.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
As a result of an antigenic shift
A) influenza is able to evade the host immune system by presenting a new hemagglutinin structure.
B) the host immune system is better able to detect and respond to influenza viruses.
C) the influenza viral protein M2 becomes hidden within the virion envelope.
D) alpha 2,6 receptors are able to bind to the alpha 2,3 sialic acid residues.
A) influenza is able to evade the host immune system by presenting a new hemagglutinin structure.
B) the host immune system is better able to detect and respond to influenza viruses.
C) the influenza viral protein M2 becomes hidden within the virion envelope.
D) alpha 2,6 receptors are able to bind to the alpha 2,3 sialic acid residues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The Eustachian tubes connect the upper respiratory tract to the
A) sinuses.
B) middle ears.
C) inner ears.
D) eyes.
A) sinuses.
B) middle ears.
C) inner ears.
D) eyes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A viral disease of the lower respiratory tract would likely present with
A) runny nose.
B) sinus congestion.
C) facial pain.
D) cough.
A) runny nose.
B) sinus congestion.
C) facial pain.
D) cough.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following infections would affect the upper respiratory tract but NOT the lower respiratory tract?
A) the common cold
B) pneumonia
C) tuberculosis
D) bronchitis
A) the common cold
B) pneumonia
C) tuberculosis
D) bronchitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The most likely mutation to cause an influenza pandemic would be a mutation in
A) the head of hemagglutinin.
B) the stalk of hemagglutinin.
C) M2 protein inside the virion envelope.
D) influenza nucleoprotein.
A) the head of hemagglutinin.
B) the stalk of hemagglutinin.
C) M2 protein inside the virion envelope.
D) influenza nucleoprotein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Nicotine in cigarette smoke paralyzes the cilia found on epithelium within the respiratory tract.What is the normal function of these cilia?
A) They produce mucus that traps microorganisms.
B) They help to warm incoming air.
C) They aid in moving mucus to the nasal and oral cavities.
D) They contain macrophages that target microorganisms.
A) They produce mucus that traps microorganisms.
B) They help to warm incoming air.
C) They aid in moving mucus to the nasal and oral cavities.
D) They contain macrophages that target microorganisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the significance of the anatomical difference shown?
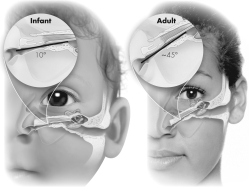
A) Adults are more prone to developing sinus infections.
B) Children are more prone to developing sinus infections.
C) Adults are more prone to developing middle ear infections.
D) Children are more prone to developing middle ear infections.

A) Adults are more prone to developing sinus infections.
B) Children are more prone to developing sinus infections.
C) Adults are more prone to developing middle ear infections.
D) Children are more prone to developing middle ear infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The structure indicated on this figure is
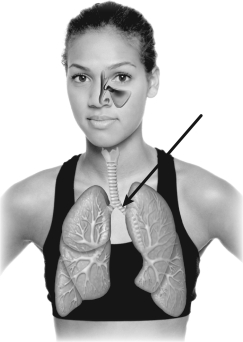
A) a bronchiole.
B) the trachea.
C) a main bronchus.
D) an alveolar duct.

A) a bronchiole.
B) the trachea.
C) a main bronchus.
D) an alveolar duct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The graph shown indicates the incidence of whooping cough in the United States.What information can you determine from this graph?
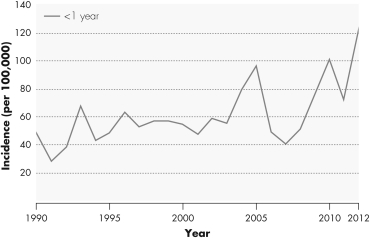
A) Approximately 40,000 individuals were infected with whooping cough in 2007.
B) The incidence of whooping cough in infants under one year of age in 2013 was higher than the incidence in 2012.
C) Vaccination against whooping cough has become less effective in infants under the age of one year over time.
D) The incidence of whooping cough declined dramatically between 2005 and 2007.

A) Approximately 40,000 individuals were infected with whooping cough in 2007.
B) The incidence of whooping cough in infants under one year of age in 2013 was higher than the incidence in 2012.
C) Vaccination against whooping cough has become less effective in infants under the age of one year over time.
D) The incidence of whooping cough declined dramatically between 2005 and 2007.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Acute otitis media is infection within the
A) sinuses.
B) outer ear.
C) middle ear.
D) inner ear.
A) sinuses.
B) outer ear.
C) middle ear.
D) inner ear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The graph shown indicates the incidence of whooping cough in the United States.What information can you determine from this graph?
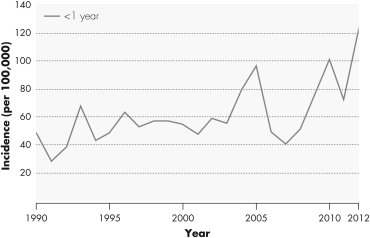
A) There was a decline in vaccination rates of infants under one year of age during the early 1990s.
B) The incidence of whooping cough in infants under one year of age was declining prior to 1990.
C) Waning immunity in adult populations has led to an increase in whooping cough.
D) The incidence of whooping cough in infants under one year of age was higher in 2010 than it was in 1995.

A) There was a decline in vaccination rates of infants under one year of age during the early 1990s.
B) The incidence of whooping cough in infants under one year of age was declining prior to 1990.
C) Waning immunity in adult populations has led to an increase in whooping cough.
D) The incidence of whooping cough in infants under one year of age was higher in 2010 than it was in 1995.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following organisms is an intracellular pathogen capable of preventing fusion of a phagosome with a lysosome after phagocytosis has occurred?
A) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
B) Haemophilus influenzae
C) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
D) Legionella pneumophila
A) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
B) Haemophilus influenzae
C) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
D) Legionella pneumophila

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
This figure shows the relative incidence of pneumonia caused by various microorganisms.Vaccines are available to prevent
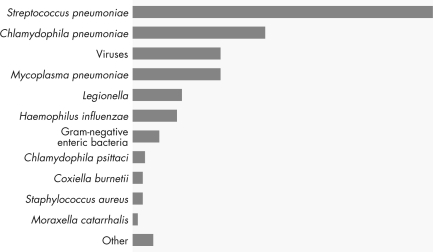
A) all of the bacterial forms of pneumonia.
B) the most common and least common bacterial causes of pneumonia.
C) viral forms of pneumonia.
D) the form of pneumonia that occurs most frequently in the elderly.

A) all of the bacterial forms of pneumonia.
B) the most common and least common bacterial causes of pneumonia.
C) viral forms of pneumonia.
D) the form of pneumonia that occurs most frequently in the elderly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Close contact with respiratory droplets from which of the following individuals is most likely to cause disease?
A) an individual with histoplasmosis
B) an individual with blastomycosis
C) an individual with cryptococcosis
D) an individual with tuberculosis
A) an individual with histoplasmosis
B) an individual with blastomycosis
C) an individual with cryptococcosis
D) an individual with tuberculosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A day-care worker reports that two young children have been coughing all day.She first noticed that both children had runny noses a few days ago,but is not sure if they had fevers.She states that they both sound like barking seals.Most likely these children have
A) the common cold.
B) croup.
C) influenza.
D) respiratory syncytial disease.
A) the common cold.
B) croup.
C) influenza.
D) respiratory syncytial disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A young man who enjoys spelunking,the recreational sport of exploring caves,develops a flu-like pulmonary illness along with erythema nodosum and arthralgia.The most likely fungal infection in this man is
A) histoplasmosis.
B) coccidioidomycosis.
C) cryptococcosis.
D) blastomycosis.
A) histoplasmosis.
B) coccidioidomycosis.
C) cryptococcosis.
D) blastomycosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A 23-year-old man arrives in the emergency room.He is currently in respiratory distress and is experiencing kidney failure and blood clots in one lung.His partner reports that he had a high fever,chills,and a cough for several days prior.The attending physician quickly orders a serum antibody test validated by the CDC when he suspects the individual may be infected with
A) type B influenza.
B) respiratory syncytial virus.
C) severe acute respiratory syndrome.
D) croup.
A) type B influenza.
B) respiratory syncytial virus.
C) severe acute respiratory syndrome.
D) croup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Due to the location of infection,bacterial sinusitis may lead to complications,including
A) meningitis.
B) pneumonia.
C) bronchitis.
D) epiglottitis.
A) meningitis.
B) pneumonia.
C) bronchitis.
D) epiglottitis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Some strains of the bacteria Haemophilus influenzae produce beta-lactamase enzyme that
A) confers antibiotic resistance to the bacteria.
B) allows attachment of the bacteria to cilia on host cells.
C) prevents immunity from forming in the host.
D) prevents lysosomes from fusing to phagosomes.
A) confers antibiotic resistance to the bacteria.
B) allows attachment of the bacteria to cilia on host cells.
C) prevents immunity from forming in the host.
D) prevents lysosomes from fusing to phagosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A young boy with a sore throat,cervical lymphadenopathy,and a low-grade fever is seen by his physician.Upon examination,his physician notes a thick,grayish membrane that bleeds when scraped covering the boy's tonsils and soft palate.A bacterial culture will most likely reveal the presence of
A) Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
B) Streptococcus pneumoniae.
C) Moraxella catarrhalis.
D) Bordetella pertussis.
A) Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
B) Streptococcus pneumoniae.
C) Moraxella catarrhalis.
D) Bordetella pertussis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Ghon complex shown in this figure is indicative of infection by
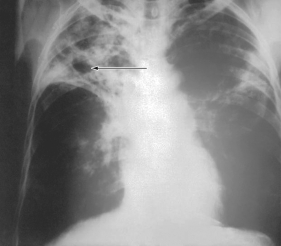
A) Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
B) Bacillus anthracis.
C) Blastomyces dermatitidis.
D) Coccidioides immitis.

A) Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
B) Bacillus anthracis.
C) Blastomyces dermatitidis.
D) Coccidioides immitis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A patient with a respiratory infection who is unresponsive to treatment with antibiotics,lacks a clearly defined presentation,and has seemingly unrelated symptoms
A) is more likely to be infected by a fungus than a virus or bacteria.
B) is more likely to be infected by a virus than a fungus or bacteria.
C) is most likely carrying an antibiotic-resistant form of bacteria.
D) would likely have a positive TB skin test.
A) is more likely to be infected by a fungus than a virus or bacteria.
B) is more likely to be infected by a virus than a fungus or bacteria.
C) is most likely carrying an antibiotic-resistant form of bacteria.
D) would likely have a positive TB skin test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The most prevalent form of cryptococcosis is found in
A) young children.
B) AIDS patients.
C) the elderly.
D) adolescents.
A) young children.
B) AIDS patients.
C) the elderly.
D) adolescents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The most common cause of bacterial pharyngitis is
A) Streptococcus pyogenes.
B) Streptococcus pneumoniae.
C) Haemophilus influenzae.
D) Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
A) Streptococcus pyogenes.
B) Streptococcus pneumoniae.
C) Haemophilus influenzae.
D) Corynebacterium diphtheriae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Respiratory syncytial virus and influenza are responsible for the majority of cases of
A) bacterial pneumonia.
B) viral pneumonia.
C) sinusitis.
D) kidney failure.
A) bacterial pneumonia.
B) viral pneumonia.
C) sinusitis.
D) kidney failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An AIDS patient with a fungal infection develops meningoencephalitis,which is the most prevalent form of
A) histoplasmosis.
B) coccidioidomycosis.
C) cryptococcosis.
D) blastomycosis.
A) histoplasmosis.
B) coccidioidomycosis.
C) cryptococcosis.
D) blastomycosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Close contact with respiratory droplets from which of the following individuals is LEAST likely to cause disease?
A) an individual with histoplasmosis
B) an individual with influenza
C) an individual with pertussis
D) an individual with tuberculosis
A) an individual with histoplasmosis
B) an individual with influenza
C) an individual with pertussis
D) an individual with tuberculosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The differential diagnosis for a patient presenting with a fever and productive cough with bloody sputum would likely include
A) tuberculosis and legionellosis.
B) walking pneumonia and Pseudomonas pneumonia.
C) inhalation anthrax and diphtheria.
D) whooping cough and tuberculosis.
A) tuberculosis and legionellosis.
B) walking pneumonia and Pseudomonas pneumonia.
C) inhalation anthrax and diphtheria.
D) whooping cough and tuberculosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
CASE HISTORY
Jacob,a rambunctious five-year-old boy brought to the clinic by his mother,was complaining of a scratchy sore throat,a nonproductive cough (a cough that does not produce sputum),rhinorrhea (a runny nose),nasal congestion (a stopped-up nose),and a headache that started the night before.He did not have a fever.His complete blood count (CBC)-the number of platelets and red and white blood cells in blood,along with its differential (the different types of red and white blood cells)-was normal,as was his chest X-ray.Jacob was diagnosed with the common cold and was advised to rest,drink plenty of clear liquids,and use over-the-counter cough suppressants and either ibuprofen or acetaminophen for pain.
Based on the symptoms described and what you know about this pathogen,which best describes Jacob's infection?
A) viral lower respiratory illness
B) viral upper respiratory illness
C) bacterial lower respiratory illness
D) bacterial upper respiratory illness
Jacob,a rambunctious five-year-old boy brought to the clinic by his mother,was complaining of a scratchy sore throat,a nonproductive cough (a cough that does not produce sputum),rhinorrhea (a runny nose),nasal congestion (a stopped-up nose),and a headache that started the night before.He did not have a fever.His complete blood count (CBC)-the number of platelets and red and white blood cells in blood,along with its differential (the different types of red and white blood cells)-was normal,as was his chest X-ray.Jacob was diagnosed with the common cold and was advised to rest,drink plenty of clear liquids,and use over-the-counter cough suppressants and either ibuprofen or acetaminophen for pain.
Based on the symptoms described and what you know about this pathogen,which best describes Jacob's infection?
A) viral lower respiratory illness
B) viral upper respiratory illness
C) bacterial lower respiratory illness
D) bacterial upper respiratory illness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A patient with a bacterial infection of the respiratory system presents with a fever and cough.What additional information regarding his or her cough would be useful in forming a differential diagnosis?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Moraxella catarrhalis may cause bacterial ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
CASE HISTORY
Jacob,a rambunctious five-year-old boy brought to the clinic by his mother,was complaining of a scratchy sore throat,a nonproductive cough (a cough that does not produce sputum),rhinorrhea (a runny nose),nasal congestion (a stopped-up nose),and a headache that started the night before.He did not have a fever.His complete blood count (CBC)-the number of platelets and red and white blood cells in blood,along with its differential (the different types of red and white blood cells)-was normal,as was his chest X-ray.Jacob was diagnosed with the common cold and was advised to rest,drink plenty of clear liquids,and use over-the-counter cough suppressants and either ibuprofen or acetaminophen for pain.
Why would prescription of an antibiotic likely do more to harm Jacob than help him recover in this case? Consider how this pathogen enters,leaves,and replicates in cells.
Jacob,a rambunctious five-year-old boy brought to the clinic by his mother,was complaining of a scratchy sore throat,a nonproductive cough (a cough that does not produce sputum),rhinorrhea (a runny nose),nasal congestion (a stopped-up nose),and a headache that started the night before.He did not have a fever.His complete blood count (CBC)-the number of platelets and red and white blood cells in blood,along with its differential (the different types of red and white blood cells)-was normal,as was his chest X-ray.Jacob was diagnosed with the common cold and was advised to rest,drink plenty of clear liquids,and use over-the-counter cough suppressants and either ibuprofen or acetaminophen for pain.
Why would prescription of an antibiotic likely do more to harm Jacob than help him recover in this case? Consider how this pathogen enters,leaves,and replicates in cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Stephanie,a one-year-old girl,frequently develops painful cases of acute otitis media within days of developing viral upper respiratory infections.Explain why viral infections of the upper respiratory tract may lead to acute otitis media.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A young patient arrives in the emergency room with a fever,chills,cough,and chest pains.At this point would it be more likely for a physician to make a differential diagnosis or a definitive diagnosis? Explain your reasoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Coccidioidomycosis is endemic in the ________ United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
How do fungal respiratory infections differ from bacterial respiratory infections in their transmission and treatment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Describe how a human infected simultaneously with an avian flu strain and a swine flu strain may cause an influenza pandemic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The two bacterial diseases of the respiratory system that are prevented by the DTaP vaccine are ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The lowest structure in the respiratory tract,used to produce sounds,is called the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The diffuse infiltrate shown in this figure is indicative of
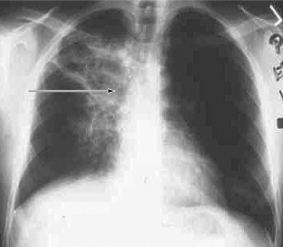
A) pertussis.
B) blastomycosis.
C) tuberculosis.
D) pneumococcal pneumonia.

A) pertussis.
B) blastomycosis.
C) tuberculosis.
D) pneumococcal pneumonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Streptococcal pharyngitis,or strep throat,may be caused by an exotoxin-producing strain of Streptococcus pyogenes that causes fever and a red rash known as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Engaging in recreational or occupational activities that expose an individual to fungal spores in moist soils along the Mississippi or Ohio River valleys increases the risk of developing ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
CASE HISTORY
Chloe is a generally healthy two-year-old child who was brought to the clinic by her father.The child had had a fever since the previous night,was irritable,and kept pulling on her left ear.Chloe had also had a runny nose for the previous two weeks.Her temperature was 38.5° C (101.3° F)at the clinic,and the physical exam showed a red and swollen ear,an erythematous ear canal,and a bulging tympanic membrane.Chloe was diagnosed with acute otitis media and prescribed an antibiotic that she had to take for seven days.
If a complete blood count (CBC)was performed on Chloe as a part of her diagnosis,what clues would you expect to see supporting the nature of her infection?
Chloe is a generally healthy two-year-old child who was brought to the clinic by her father.The child had had a fever since the previous night,was irritable,and kept pulling on her left ear.Chloe had also had a runny nose for the previous two weeks.Her temperature was 38.5° C (101.3° F)at the clinic,and the physical exam showed a red and swollen ear,an erythematous ear canal,and a bulging tympanic membrane.Chloe was diagnosed with acute otitis media and prescribed an antibiotic that she had to take for seven days.
If a complete blood count (CBC)was performed on Chloe as a part of her diagnosis,what clues would you expect to see supporting the nature of her infection?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The ciliated epithelium in the respiratory tract that traps inhaled particles and microorganisms is referred to as the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Viruses that cause the common cold may also spread to the sinuses to cause ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Explain how the M proteins associated with some strains of Streptococcus pyogenes lead to streptococcal sequelae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



