Deck 24: Infections of the Central Nervous System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Infections of the Central Nervous System
1
Initial treatment for tetanus in an unimmunized person with a puncture wound is
A) tetanus immune globulin.
B) tetanus toxoid.
C) penicillin.
D) debridement.
A) tetanus immune globulin.
B) tetanus toxoid.
C) penicillin.
D) debridement.
A
2
Which of the following is true about myelin sheaths?
A) They slow down the speed of nerve impulses.
B) They are made up of a protein molecule called myelin.
C) They are destroyed in certain disorders such as multiple sclerosis.
D) They cover all neuronal axons.
A) They slow down the speed of nerve impulses.
B) They are made up of a protein molecule called myelin.
C) They are destroyed in certain disorders such as multiple sclerosis.
D) They cover all neuronal axons.
C
3
The symptoms of tetanus are due to
A) tetanospasmin.
B) endospore formation.
C) inflammation.
D) the relaxation of muscles.
A) tetanospasmin.
B) endospore formation.
C) inflammation.
D) the relaxation of muscles.
A
4
Viral diseases of the central nervous system are transmitted by all of the following EXCEPT
A) sexual contact.
B) mosquito bites.
C) the fecal-oral route.
D) stepping on a contaminated nail.
A) sexual contact.
B) mosquito bites.
C) the fecal-oral route.
D) stepping on a contaminated nail.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Vaccination is available for all the following EXCEPT
A) Neisseria meningitis.
B) tetanus.
C) rabies.
D) botulism.
A) Neisseria meningitis.
B) tetanus.
C) rabies.
D) botulism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the correct order of the meninges from most outer to inner structures?
A) pia mater,dura mater,arachnoid
B) pia mater,arachnoid,dura mater
C) dura mater,arachnoid,pia mater
D) dura mater,pia mater,arachnoid
A) pia mater,dura mater,arachnoid
B) pia mater,arachnoid,dura mater
C) dura mater,arachnoid,pia mater
D) dura mater,pia mater,arachnoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following vaccines can cause the disease it is designed to prevent?
A) tetanus toxoid
B) oral polio
C) inactivated polio
D) meningococcal capsule
A) tetanus toxoid
B) oral polio
C) inactivated polio
D) meningococcal capsule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Motor neurons send
A) information from the CNS to the periphery.
B) information from the periphery to the CNS.
C) information in both directions.
D) information.
A) information from the CNS to the periphery.
B) information from the periphery to the CNS.
C) information in both directions.
D) information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The part of the nervous system that collects data from the environment is the
A) meninges.
B) central nervous system.
C) cerebrospinal fluid.
D) peripheral nervous system.
A) meninges.
B) central nervous system.
C) cerebrospinal fluid.
D) peripheral nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Refer to this image showing a CT scan of a brain displaying disease.To what does the arrow point?
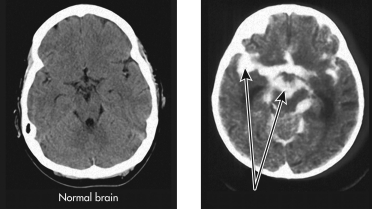
A) a brain abscess
B) encephalitis
C) myelitis
D) a normal brain

A) a brain abscess
B) encephalitis
C) myelitis
D) a normal brain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Bacterial encephalitis and meningitis are difficult to treat because
A) no medications exist for treatment of these infections.
B) antibiotics damage nervous tissue.
C) many antibiotics cannot cross the blood-brain barrier.
D) it is very difficult to determine the causative microbe.
A) no medications exist for treatment of these infections.
B) antibiotics damage nervous tissue.
C) many antibiotics cannot cross the blood-brain barrier.
D) it is very difficult to determine the causative microbe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Using the table below,which patient is most likely infected by a bacterium?
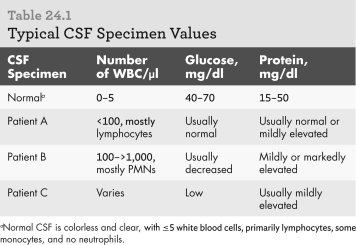
A) Patient A
B) Patient B
C) Patient C
D) none

A) Patient A
B) Patient B
C) Patient C
D) none

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Microorganisms reach the CNS by all of the following EXCEPT
A) migrating to the CNS from distal sites.
B) toxins traveling along peripheral nerves.
C) infecting bone.
D) inhalation of the organism.
A) migrating to the CNS from distal sites.
B) toxins traveling along peripheral nerves.
C) infecting bone.
D) inhalation of the organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following vaccine characteristics is/are mismatched with its/their respective vaccine type?
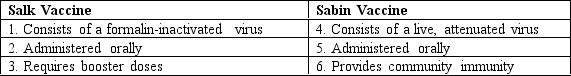
A) 1,3,and 5
B) 4,5,and 6
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 2 only

A) 1,3,and 5
B) 4,5,and 6
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 2 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is true about CSF?
A) Inflammatory cells are found in both healthy and unhealthy CSF.
B) It helps to diagnose infections of the central nervous system.
C) The identification of PMNs in CSF indicates a viral infection.
D) CSF is collected via the placement of a shunt in the vertebral column.
A) Inflammatory cells are found in both healthy and unhealthy CSF.
B) It helps to diagnose infections of the central nervous system.
C) The identification of PMNs in CSF indicates a viral infection.
D) CSF is collected via the placement of a shunt in the vertebral column.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
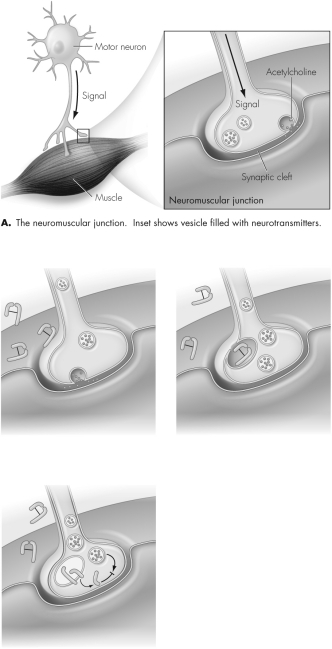
What is labeled as "C" in this figure?
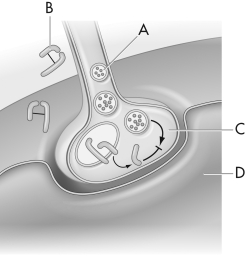
A) acetylcholine
B) toxin
C) motor neuron
D) muscle

A) acetylcholine
B) toxin
C) motor neuron
D) muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
All of the following are caused by prions EXCEPT
A) sheep scrapie.
B) kuru.
C) rabies.
D) bovine spongiform encephalopathy.
A) sheep scrapie.
B) kuru.
C) rabies.
D) bovine spongiform encephalopathy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Naegleria fowleri is commonly acquired through
A) mosquito bites.
B) ingestion of water contaminated with fecal material.
C) exposure to bird droppings.
D) swimming in warm ponds or streams.
A) mosquito bites.
B) ingestion of water contaminated with fecal material.
C) exposure to bird droppings.
D) swimming in warm ponds or streams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements about rabies is FALSE?
A) It is caused by lyssavirus.
B) Rabies virus is a neurotropic virus.
C) Hydrophobia is associated with the disease.
D) There are three basic forms: encephalitic,paralytic,and atypical.
A) It is caused by lyssavirus.
B) Rabies virus is a neurotropic virus.
C) Hydrophobia is associated with the disease.
D) There are three basic forms: encephalitic,paralytic,and atypical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
A) tetanus - releases potent neurotoxin
B) botulism - stimulates transmission of nerve impulse
C) poliomyelitis - multiplication of virus occurs in throat and small intestine
D) rabies - destroys cells of the CNS
A) tetanus - releases potent neurotoxin
B) botulism - stimulates transmission of nerve impulse
C) poliomyelitis - multiplication of virus occurs in throat and small intestine
D) rabies - destroys cells of the CNS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the images is the amebic form that infects humans?
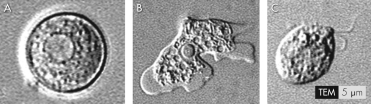
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) none

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) none

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
A) poliomyelitis - respiratory route
B) meningococcal meningitis - respiratory route
C) rabies - direct contact
D) listeriosis - ingestion
A) poliomyelitis - respiratory route
B) meningococcal meningitis - respiratory route
C) rabies - direct contact
D) listeriosis - ingestion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A 30-year-old woman was hospitalized after she experienced convulsions.On examination,she was alert and oriented and complained of a fever,headache,and stiff neck.Which of the following is most likely to provide rapid identification of the cause of her symptoms?
A) Gram stain of cerebrospinal fluid
B) Gram stain of throat culture
C) biopsy of brain tissue
D) check serum antibodies
A) Gram stain of cerebrospinal fluid
B) Gram stain of throat culture
C) biopsy of brain tissue
D) check serum antibodies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A 50-year-old man was hospitalized with dizziness,blurred vision,slurred speech,difficulty swallowing,and nausea.Examination revealed facial paralysis.He reported eating home-canned green beans 24 hours before the onset of his symptoms.The patient should be treated with
A) antibiotics.
B) vaccination.
C) toxins.
D) supportive care including respiratory assistance.
A) antibiotics.
B) vaccination.
C) toxins.
D) supportive care including respiratory assistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is a fungus that causes CNS disease?
A) C.albicans
B) T.gondii
C) T.brucei
D) C.tetani
A) C.albicans
B) T.gondii
C) T.brucei
D) C.tetani

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
All of the following are true regarding African trypanosomiasis EXCEPT that
A) it is also known as "sleeping sickness."
B) all subspecies of Trypanosoma brucei have multiple hosts.
C) it is transmitted by the tsetse fly.
D) death occurs without proper treatment.
A) it is also known as "sleeping sickness."
B) all subspecies of Trypanosoma brucei have multiple hosts.
C) it is transmitted by the tsetse fly.
D) death occurs without proper treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Fungal infections of the CNS are most commonly seen in
A) immunocompetent individuals.
B) young,healthy individuals.
C) AIDS patients.
D) newborns.
A) immunocompetent individuals.
B) young,healthy individuals.
C) AIDS patients.
D) newborns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A physician diagnoses a patient with Eastern equine encephalitis.All of the following pertain to the patient EXCEPT that he or she
A) most likely caught the virus from a bite from an infected mosquito.
B) was diagnosed by detecting an increase in antibody titer to the virus.
C) is infected with a neurotropic virus.
D) is infected with a rare disease.
A) most likely caught the virus from a bite from an infected mosquito.
B) was diagnosed by detecting an increase in antibody titer to the virus.
C) is infected with a neurotropic virus.
D) is infected with a rare disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following protozoan(s)use antigenic switching to avoid the host immune system?
A) T.gondii
B) T.brucei
C) T.cruzi
D) T.brucei and T.cruzi
A) T.gondii
B) T.brucei
C) T.cruzi
D) T.brucei and T.cruzi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is true about Candida albicans?
A) Normal flora helps this organism to cause disease.
B) It commonly causes disease in immunocompetent individuals.
C) Treatment includes amphotericin B and flucytosine.
D) Candida meningitis is seen more commonly in teenagers.
A) Normal flora helps this organism to cause disease.
B) It commonly causes disease in immunocompetent individuals.
C) Treatment includes amphotericin B and flucytosine.
D) Candida meningitis is seen more commonly in teenagers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In this figure,where does botulinum toxin act to prevent acetylcholine release?
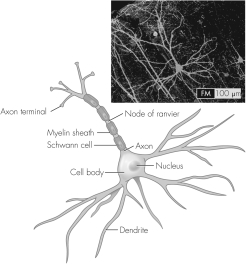
A) dendrite
B) Schwann cells
C) axon
D) axon terminal

A) dendrite
B) Schwann cells
C) axon
D) axon terminal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
All of the following are true of polio EXCEPT
A) the portal of entry is ingestion of contaminated water.
B) most cases are severe and result in paralysis.
C) it replicates in the throat and small intestines.
D) the Sabin vaccine contains attenuated strains of the virus.
A) the portal of entry is ingestion of contaminated water.
B) most cases are severe and result in paralysis.
C) it replicates in the throat and small intestines.
D) the Sabin vaccine contains attenuated strains of the virus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A pathologist detects Negri bodies while examining a brain section taken at autopsy.What was the cause of death?
A) rabies
B) poliomyelitis
C) spongiform encephalopathy
D) West Nile encephalitis
A) rabies
B) poliomyelitis
C) spongiform encephalopathy
D) West Nile encephalitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
This figure shows an India ink stain of C.neoformans in a patient's CSF.What is the purpose of the capsule depicted by the arrow?
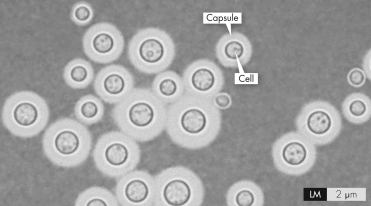
A) It protects the organism from the host immune response.
B) It allows the organism to spread the CNS.
C) The capsule causes the persistent headache seen in most cases of coccidioidal meningitis.
D) It is targeted by fluconazole as a treatment.

A) It protects the organism from the host immune response.
B) It allows the organism to spread the CNS.
C) The capsule causes the persistent headache seen in most cases of coccidioidal meningitis.
D) It is targeted by fluconazole as a treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements about prions is correct?
A) Prions are small particles that contain DNA.
B) Chemical agents easily destroy prions.
C) Acanthamoeba encephalitis is caused by prions.
D) Prions can be passed by patient-to-patient contact.
A) Prions are small particles that contain DNA.
B) Chemical agents easily destroy prions.
C) Acanthamoeba encephalitis is caused by prions.
D) Prions can be passed by patient-to-patient contact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Arboviruses cause ________ and are transmitted by ________.
A) meningitis;bee stings
B) meningitis;mosquitoes
C) encephalitis;dog bites
D) encephalitis;mosquitoes
A) meningitis;bee stings
B) meningitis;mosquitoes
C) encephalitis;dog bites
D) encephalitis;mosquitoes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which part of this neuron receives information from the periphery?
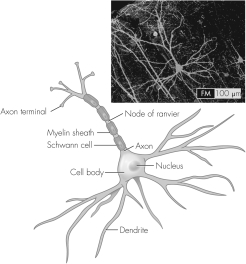
A) dendrite
B) Schwann cells
C) axon
D) axon terminal

A) dendrite
B) Schwann cells
C) axon
D) axon terminal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
All of the following are true of Neisseria meningitides EXCEPT
A) the capsule protects the organism from host complement proteins.
B) it does not cross the blood-brain barrier.
C) the organism uses type IV pili to invade epithelial cells.
D) it produces a nonblanching rash due to endotoxin release.
A) the capsule protects the organism from host complement proteins.
B) it does not cross the blood-brain barrier.
C) the organism uses type IV pili to invade epithelial cells.
D) it produces a nonblanching rash due to endotoxin release.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the prescribed treatment for Naegleria?
A) ketoconazole
B) eflornithine
C) penicillin
D) vaccine
A) ketoconazole
B) eflornithine
C) penicillin
D) vaccine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is treated with antibiotics?
A) botulism
B) tetanus
C) streptococcal pneumonia
D) polio
A) botulism
B) tetanus
C) streptococcal pneumonia
D) polio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Inflammation of the meninges is called ________,while inflammation of the brain is called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
CASE HISTORY
In June,Mitch,a 47-year-old resident of Oklahoma,was admitted to the hospital with rapid onset of progressive dizziness,blurred vision,slurred speech,difficulty swallowing,and nausea.Findings on examination included absence of fever,drooping eyelids,facial paralysis,and impaired gag reflex.He developed breathing difficulties and required mechanical ventilation.The patient reported that during the 24 hours before onset of symptoms,he had eaten home-canned green beans and a stew containing roast beef and potatoes.Analysis of the patient's stool detected botulinum type a toxin,but no Clostridium botulinum organisms were found.The patient was hospitalized for 49 days,including 42 days on mechanical ventilation,before being discharged.
What are the risk factors for botulism like that in Mitch's case? How can this disease be prevented?
In June,Mitch,a 47-year-old resident of Oklahoma,was admitted to the hospital with rapid onset of progressive dizziness,blurred vision,slurred speech,difficulty swallowing,and nausea.Findings on examination included absence of fever,drooping eyelids,facial paralysis,and impaired gag reflex.He developed breathing difficulties and required mechanical ventilation.The patient reported that during the 24 hours before onset of symptoms,he had eaten home-canned green beans and a stew containing roast beef and potatoes.Analysis of the patient's stool detected botulinum type a toxin,but no Clostridium botulinum organisms were found.The patient was hospitalized for 49 days,including 42 days on mechanical ventilation,before being discharged.
What are the risk factors for botulism like that in Mitch's case? How can this disease be prevented?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Explain the transmission,etiologies,and diagnosis of bacterial meningitis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
List and describe the defensive mechanisms that are in place to protect the central nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A small proteinaceous infectious particle is known as a ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
This figure shows the mechanism of action of botulinum toxin.Describe what is happening in each step.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The ________ collects data from the outside environment and communicates that information to the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
One of the complications of poliomyelitis is damage to the ________ nerve,which interferes with breathing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Fungal infections of the central nervous system are also known as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
CASE HISTORY
In June,Mitch,a 47-year-old resident of Oklahoma,was admitted to the hospital with rapid onset of progressive dizziness,blurred vision,slurred speech,difficulty swallowing,and nausea.Findings on examination included absence of fever,drooping eyelids,facial paralysis,and impaired gag reflex.He developed breathing difficulties and required mechanical ventilation.The patient reported that during the 24 hours before onset of symptoms,he had eaten home-canned green beans and a stew containing roast beef and potatoes.Analysis of the patient's stool detected botulinum type a toxin,but no Clostridium botulinum organisms were found.The patient was hospitalized for 49 days,including 42 days on mechanical ventilation,before being discharged.
Briefly describe the likely progress of Mitch's disease from exposure to hospitalization.Is antibiotic therapy likely to be useful in the treatment of Mitch's disease? Why or why not?
In June,Mitch,a 47-year-old resident of Oklahoma,was admitted to the hospital with rapid onset of progressive dizziness,blurred vision,slurred speech,difficulty swallowing,and nausea.Findings on examination included absence of fever,drooping eyelids,facial paralysis,and impaired gag reflex.He developed breathing difficulties and required mechanical ventilation.The patient reported that during the 24 hours before onset of symptoms,he had eaten home-canned green beans and a stew containing roast beef and potatoes.Analysis of the patient's stool detected botulinum type a toxin,but no Clostridium botulinum organisms were found.The patient was hospitalized for 49 days,including 42 days on mechanical ventilation,before being discharged.
Briefly describe the likely progress of Mitch's disease from exposure to hospitalization.Is antibiotic therapy likely to be useful in the treatment of Mitch's disease? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the Salk and Sabin vaccines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
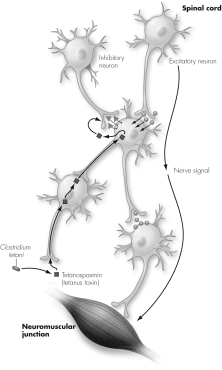
Describe what is happening in this figure's depiction of retrograde movement of tetanus toxin.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
CASE HISTORY
In April 2001,Abdul,a four-month-old infant from Saudi Arabia,was hospitalized with fever,tender neck,and purplish,nonblanching spots (petechiae and purpuric spots)on his trunk.Suspecting meningitis,the clinician took a CSF sample and examined it by Gram stain.The smear revealed Gram-negative diplococci inside PMNS.The CSF was turbid with 900 leukocytes/ml,and Neisseria meningitidis was confirmed by culture.The child was treated with cefotaxime and made a full recovery.His father,the person who brought him in,was clinically well.However,meningococcus was isolated from his oropharynx,as well as from the throat of the patient's two-year-old brother.Isolates from the patient,his father,and his brother were positive by agglutination with meningococcus a,c,y,W135 polyvalent reagent.The father's vaccination certificate confirmed that he had received a quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine.All three isolates were sent to the World Health Organization collaborating center,which confirmed meningococcus serogroup W135.DNA analysis of the three isolates found them to be indistinguishable,meaning that the father and his children were infected with the same strain of N.meningitidis.
Identify the INCORRECT statement regarding the pathogenesis and prevention of Abdul's meningitis.
A) N.meningitidis generally only infects infants,explaining why Abdul's father and brother showed no symptoms of disease.
B) Ten to twenty percent of the healthy population can be colonized by N.meningitidis and remain asymptomatic.
C) Complement deficiencies make individuals particularly susceptible to meningococcal meningitis.
D) N.meningitidis utilized type IV pili to disrupt tight junctions,allowing passage through the blood-brain barrier.
In April 2001,Abdul,a four-month-old infant from Saudi Arabia,was hospitalized with fever,tender neck,and purplish,nonblanching spots (petechiae and purpuric spots)on his trunk.Suspecting meningitis,the clinician took a CSF sample and examined it by Gram stain.The smear revealed Gram-negative diplococci inside PMNS.The CSF was turbid with 900 leukocytes/ml,and Neisseria meningitidis was confirmed by culture.The child was treated with cefotaxime and made a full recovery.His father,the person who brought him in,was clinically well.However,meningococcus was isolated from his oropharynx,as well as from the throat of the patient's two-year-old brother.Isolates from the patient,his father,and his brother were positive by agglutination with meningococcus a,c,y,W135 polyvalent reagent.The father's vaccination certificate confirmed that he had received a quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine.All three isolates were sent to the World Health Organization collaborating center,which confirmed meningococcus serogroup W135.DNA analysis of the three isolates found them to be indistinguishable,meaning that the father and his children were infected with the same strain of N.meningitidis.
Identify the INCORRECT statement regarding the pathogenesis and prevention of Abdul's meningitis.
A) N.meningitidis generally only infects infants,explaining why Abdul's father and brother showed no symptoms of disease.
B) Ten to twenty percent of the healthy population can be colonized by N.meningitidis and remain asymptomatic.
C) Complement deficiencies make individuals particularly susceptible to meningococcal meningitis.
D) N.meningitidis utilized type IV pili to disrupt tight junctions,allowing passage through the blood-brain barrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



