Deck 37: Economics of College and University Education
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/82
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 37: Economics of College and University Education
1
From 1995 to 2013 the share of revenue to public institutions of higher education attributable to appropriations
A)increased to 57% from 44%.
B)increased to 44% from 26%.
C)remained constant.
D)decreased to 44% from 57%.
A)increased to 57% from 44%.
B)increased to 44% from 26%.
C)remained constant.
D)decreased to 44% from 57%.
D
2
From 2007 to 2013 total tuition revenue to public institutions of higher education
A)increased 52%.
B)increased 26%.
C)remained constant.
D)decreased 15%.
A)increased 52%.
B)increased 26%.
C)remained constant.
D)decreased 15%.
B
3
In 2014, more than ________ was spent to educate _________ college students.
A)$223 million; 152 million
B)$315 billion; 52 million
C)$517 billion; 20 million
D)$661 billion; 8 million
A)$223 million; 152 million
B)$315 billion; 52 million
C)$517 billion; 20 million
D)$661 billion; 8 million
C
4
To a prospective full-time college student, the cost of a college education reflects the cost of
A)tuition.
B)tuition and fees.
C)tuition, fees, books and supplies.
D)tuition, fees, books and supplies plus any income foregone while in school.
A)tuition.
B)tuition and fees.
C)tuition, fees, books and supplies.
D)tuition, fees, books and supplies plus any income foregone while in school.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
From 2007 to 2013 total federal, state, and local appropriations to public institutions of higher education
A)increased $230 billion.
B)increased $47 billion.
C)remained constant.
D)decreased $71 billion.
A)increased $230 billion.
B)increased $47 billion.
C)remained constant.
D)decreased $71 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
From 1995 to 2013 the share of revenue to public institutions of higher education attributable to tuition
A)increased to 41% from 29%.
B)increased to 5% from 26%.
C)remained constant.
D)decreased to 29% from 41%.
A)increased to 41% from 29%.
B)increased to 5% from 26%.
C)remained constant.
D)decreased to 29% from 41%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
From 1995 to 2013 total revenues to public institutions attributable to tuition increases
A)increased $230 billion.
B)increased $47 billion.
C)remained constant.
D)decreased.
A)increased $230 billion.
B)increased $47 billion.
C)remained constant.
D)decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
From 2002 to 2014 long-term debt at four-year public institutions of higher education
A)increased four-fold.
B)doubled.
C)remained constant.
D)decreased by half.
A)increased four-fold.
B)doubled.
C)remained constant.
D)decreased by half.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In 2014, expenditure per student in higher education was approximately
A)$4,289.
B)$9,053.
C)$14,846.
D)$25,850.
A)$4,289.
B)$9,053.
C)$14,846.
D)$25,850.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Examine Figure 37.1. What is the tuition charged in a market that has no subsidy? 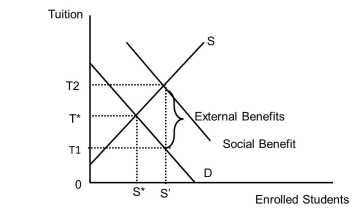 Figure 37.1
Figure 37.1
A)T1
B)T2
C)T*
D)The answer is unknown from this diagram.
 Figure 37.1
Figure 37.1A)T1
B)T2
C)T*
D)The answer is unknown from this diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
From 1995 to 2013 total revenues public institutions
A)increased $230 billion.
B)increased $47 billion.
C)remained constant.
D)decreased.
A)increased $230 billion.
B)increased $47 billion.
C)remained constant.
D)decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A university education costs more per student than a high school education because
A)college professors teach less than high school teachers.
B)college professors earn more than high school teachers.
C)colleges are typically in a monopoly position.
D)
A)and B).
A)college professors teach less than high school teachers.
B)college professors earn more than high school teachers.
C)colleges are typically in a monopoly position.
D)
A)and B).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Examine Figure 37.1. What is the tuition and subsidy revenue per student in a market that has a subsidy equal to the external benefit? 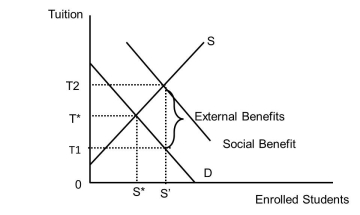 Figure 37.1
Figure 37.1
A)T1
B)T2
C)T*
D)The answer is unknown from this diagram.
 Figure 37.1
Figure 37.1A)T1
B)T2
C)T*
D)The answer is unknown from this diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Examine Figure 37.1. What is the tuition charged the student in a market that has a subsidy equal to the external benefit? 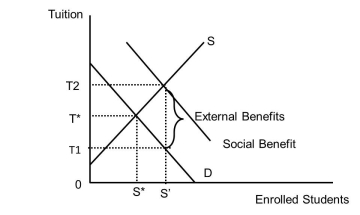 Figure 37.1
Figure 37.1
A)T1
B)T2
C)T*
D)The answer is unknown from this diagram.
 Figure 37.1
Figure 37.1A)T1
B)T2
C)T*
D)The answer is unknown from this diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Examine Figure 37.1. What is the number of students educated in a market that has no subsidy? 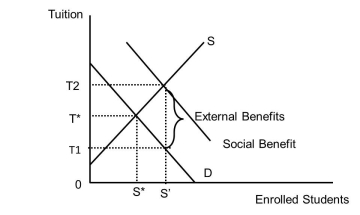 Figure 37.1
Figure 37.1
A)S'
B)S*
C)All who have any desire for it
D)The answer is unknown from this diagram.
 Figure 37.1
Figure 37.1A)S'
B)S*
C)All who have any desire for it
D)The answer is unknown from this diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When textbooks are produced, the idea for a new book typically comes from
A)the publisher.
B)faculty needing a book for their class.
C)faculty thinking they have a better idea.
D)department chairs.
A)the publisher.
B)faculty needing a book for their class.
C)faculty thinking they have a better idea.
D)department chairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Examine Figure 37.1. What is the number of students educated in a market that has a subsidy equal to the external benefit? 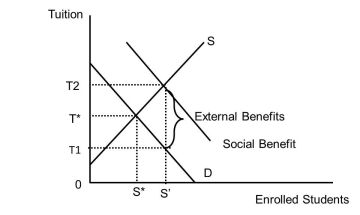 Figure 37.1
Figure 37.1
A)S'
B)S*
C)All who have any desire for it
D)The answer is unknown from this diagram.
 Figure 37.1
Figure 37.1A)S'
B)S*
C)All who have any desire for it
D)The answer is unknown from this diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An "advance" is called that because
A)it is paid before there are royalties but any royalties will be reduced by the amount of the advance.
B)it is paid after there are royalties.
C)it is paid instead of royalties.
D)it is paid before there are royalties though actual royalties are not reduced by the amount of the advance.
A)it is paid before there are royalties but any royalties will be reduced by the amount of the advance.
B)it is paid after there are royalties.
C)it is paid instead of royalties.
D)it is paid before there are royalties though actual royalties are not reduced by the amount of the advance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Over the last 34 years, costs of college tuition, room and board have increased by
A)32%.
B)87%.
C)138%.
D)702%.
A)32%.
B)87%.
C)138%.
D)702%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
College textbooks royalties are typically expressed as a
A)percentage of net sales.
B)percentage of gross sales.
C)fixed dollar amount per edition.
D)fixed dollar amount for all editions.
A)percentage of net sales.
B)percentage of gross sales.
C)fixed dollar amount per edition.
D)fixed dollar amount for all editions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If a college textbook costs $80 (for a new book)at a college bookstore, it probably cost the bookstore
A)$100.
B)$80.
C)$60.
D)$40.
A)$100.
B)$80.
C)$60.
D)$40.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
College textbook royalties are paid based on the sales to
A)faculty.
B)students.
C)bookstores.
D)internet outlets.
A)faculty.
B)students.
C)bookstores.
D)internet outlets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The royalty that an author receives on the resale of a used college textbook is
A)typically 15%.
B)half the typical new sale rate, or 7.5%.
C)set at 2%.
D)zero.
A)typically 15%.
B)half the typical new sale rate, or 7.5%.
C)set at 2%.
D)zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The college textbook adoption decision is made by
A)students.
B)university administrators.
C)state governing bodies.
D)faculty or faculty committees.
A)students.
B)university administrators.
C)state governing bodies.
D)faculty or faculty committees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
New editions of college textbooks come out
A)every year regardless of the degree to which new material warrants it.
B)when the publisher gets the urge.
C)when the author gets the urge.
D)in part, because authors and publishers only profit on new sales.
A)every year regardless of the degree to which new material warrants it.
B)when the publisher gets the urge.
C)when the author gets the urge.
D)in part, because authors and publishers only profit on new sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
One side effect of the increased speed with which used books circulate is
A)used books are cheaper.
B)used books are more expensive.
C)new editions come out more frequently.
D)new editions come out less frequently.
A)used books are cheaper.
B)used books are more expensive.
C)new editions come out more frequently.
D)new editions come out less frequently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a book has a royalty rate of 15%, 10,000 copies are sold to bookstores at $50 each, and the bookstore sells the books to students for $62.50, the author will be paid
A)$75,000 (.15*50*10,000).
B)$125,000 ((62.50-50)*10,000).
C)$93,750 (.15*62.50*10,000).
D)nothing.
A)$75,000 (.15*50*10,000).
B)$125,000 ((62.50-50)*10,000).
C)$93,750 (.15*62.50*10,000).
D)nothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Without a copyright, the high fixed costs of textbook creation
A)would be more easily recoverable.
B)would be nearly impossible to recover.
C)would be lower.
D)would be higher.
A)would be more easily recoverable.
B)would be nearly impossible to recover.
C)would be lower.
D)would be higher.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
College textbooks are marketed to faculty for adoption by
A)selling it to them for the full price.
B)selling it to them for half price.
C)giving it to them free of charge.
D)paying them money to use the book.
A)selling it to them for the full price.
B)selling it to them for half price.
C)giving it to them free of charge.
D)paying them money to use the book.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
One feature of the new textbook market is that publishers face ____ fixed costs and ____ variable costs.
A)high; high
B)high; low
C)low; high
D)low; low
A)high; high
B)high; low
C)low; high
D)low; low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The variable cost of producing a college textbook is usually around _____ of its price.
A)80%
B)50%
C)40%
D)20%
A)80%
B)50%
C)40%
D)20%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Once the breakeven level of sales has been reached, each additional book sold earns _______ for the publisher.
A)a decreasing, but positive additional profit
B)a substantial, positive additional profit
C)nothing
D)a small, negative additional profit
A)a decreasing, but positive additional profit
B)a substantial, positive additional profit
C)nothing
D)a small, negative additional profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A book that sells new for $125 will typically sell used for around
A)$25.
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.
A)$25.
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
College calculus textbooks change from edition to edition because
A)even elementary calculus is an ever-changing discipline.
B)recent discoveries challenge the legitimacy of Newton's methods.
C)it's the only way for the publisher and author to make money.
D)faculty demand it.
A)even elementary calculus is an ever-changing discipline.
B)recent discoveries challenge the legitimacy of Newton's methods.
C)it's the only way for the publisher and author to make money.
D)faculty demand it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Once faculty receive textbooks and choose not to use them they are
A)required to mail them back to the publisher.
B)free to do what they wish with the book, including selling it.
C)required to destroy the book.
D)required to give the book to a student or library.
A)required to mail them back to the publisher.
B)free to do what they wish with the book, including selling it.
C)required to destroy the book.
D)required to give the book to a student or library.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If a college textbook costs $80 (for a new book)at a college bookstore, the royalty paid on the book is likely
A)$15.
B)$12.
C)$9.
D)$5.
A)$15.
B)$12.
C)$9.
D)$5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The copyright gives its owner
A)the exclusive right to sell a work of intellectual property.
B)the ability to protect its "brand" like Coca-Cola.
C)the exclusive right to sell an invention.
D)(usually students)the right to make photocopies for friends.
A)the exclusive right to sell a work of intellectual property.
B)the ability to protect its "brand" like Coca-Cola.
C)the exclusive right to sell an invention.
D)(usually students)the right to make photocopies for friends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If a book has a royalty rate of 15% and 12,000 copies are sold to bookstores at $50 each the bookstore returns 2000 unsold books to publishers, and the bookstore sells the books to students for $62.50 the author will be paid
A)$90,000 (.15*50*12,000).
B)$75,000 (.15*50*10,000).
C)$93,750 (.15*62.50*10,000).
D)$112,500 (.15*62.50*12,000).
A)$90,000 (.15*50*12,000).
B)$75,000 (.15*50*10,000).
C)$93,750 (.15*62.50*10,000).
D)$112,500 (.15*62.50*12,000).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The copyright holder for most college textbooks is the
A)publisher.
B)author.
C)bookstore.
D)student.
A)publisher.
B)author.
C)bookstore.
D)student.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The profit a publisher makes on the sale of a used college textbook is
A)the same as when they sell it new.
B)half of the amount they made when it sold for the first time.
C)$2 per book.
D)zero.
A)the same as when they sell it new.
B)half of the amount they made when it sold for the first time.
C)$2 per book.
D)zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An e-book that sells new for $200 will typically be sold back to the bookstore "used" for
A)nothing (it can't be re-sold).
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.
A)nothing (it can't be re-sold).
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A physical book that sells new for $100 will rent for around
A)$25.
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.
A)$25.
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A book that sells new for $100 will typically sell used for around
A)$25.
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.
A)$25.
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If faculty choose to stay with an old edition of a book this is predicted to
A)increase royalty payments to authors.
B)decrease royalty payments to authors.
C)have no impact on royalty payments to authors.
D)Increase costs to students
A)increase royalty payments to authors.
B)decrease royalty payments to authors.
C)have no impact on royalty payments to authors.
D)Increase costs to students

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An e-book that sells new for $125 will typically be sold back to the bookstore "used" for
A)nothing (it can't be re-sold).
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.
A)nothing (it can't be re-sold).
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A physical book that sells new for $125 will rent for around
A)$50.
B)$62.50.
C)$75.
D)$100.
A)$50.
B)$62.50.
C)$75.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A book that sells new for $200 will typically be sold back to the bookstore "used" for
A)$26.50.
B)$50.
C)$100.
D)$150.
A)$26.50.
B)$50.
C)$100.
D)$150.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A book that sells new for $200 will typically sell used for around
A)$25.
B)$50.
C)$100.
D)$160.
A)$25.
B)$50.
C)$100.
D)$160.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Commercialization of the internet has helped to increase the price of new textbooks by facilitating
A)development of copyrighted material.
B)re-sale of used books.
C)advertising of new books.
D)shipment tracking at FedEx.
A)development of copyrighted material.
B)re-sale of used books.
C)advertising of new books.
D)shipment tracking at FedEx.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A physical book that sells new for $200 will typically sell as an e-book for around
A)$50.
B)$100.
C)$150.
D)$200.
A)$50.
B)$100.
C)$150.
D)$200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If faculty choose to stay with an old edition of a book this is predicted to cause
A)new textbook prices to rise.
B)used textbook prices to rise (for the current edition).
C)used textbook prices to rise (for the older edition).
D)used textbook prices to fall (for the older edition).
A)new textbook prices to rise.
B)used textbook prices to rise (for the current edition).
C)used textbook prices to rise (for the older edition).
D)used textbook prices to fall (for the older edition).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The payment to the author, usually expressed as a percentage of sales to bookstores, is called
A)a payoff.
B)a royalty.
C)the admiralty.
D)the annuity.
A)a payoff.
B)a royalty.
C)the admiralty.
D)the annuity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A physical book that sells new for $100 will typically sell as an e-book for around
A)$25.
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.
A)$25.
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A physical book that sells new for $125 will typically sell as an e-book for around
A)$50.
B)$62.50.
C)$75.
D)$100.
A)$50.
B)$62.50.
C)$75.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The rental market for textbooks is predicted to
A)increase royalty payments to authors.
B)decrease royalty payments to authors.
C)have no impact on royalty payments to authors.
D)increase costs to students
A)increase royalty payments to authors.
B)decrease royalty payments to authors.
C)have no impact on royalty payments to authors.
D)increase costs to students

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Payment of a share of prospective royalties to the author before publication is called the
A)advance.
B)bonus.
C)stipend.
D)allowance.
A)advance.
B)bonus.
C)stipend.
D)allowance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A book that sells new for $100 will typically be sold back to the bookstore "used" for
A)$26.50.
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.
A)$26.50.
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An e-book that sells new for $100 will typically be sold back to the bookstore "used" for
A)nothing (it can't be re-sold).
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.
A)nothing (it can't be re-sold).
B)$50.
C)$75.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A book that sells new for $125 will typically be sold back to the bookstore "used" for
A)$26.50.
B)$48.75.
C)$62.50.
D)$100.
A)$26.50.
B)$48.75.
C)$62.50.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A physical book that sells new for $200 will rent for around
A)$50.
B)$100.
C)$150.
D)$200.
A)$50.
B)$100.
C)$150.
D)$200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If e-books begin to be the most popular form of textbooks, it is
A)in the best interests of publishers and authors.
B)in the best interests of traditional book stores.
C)likely to increase costs to students.
D)likely to be self-defeating for publishers.
A)in the best interests of publishers and authors.
B)in the best interests of traditional book stores.
C)likely to increase costs to students.
D)likely to be self-defeating for publishers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the United States, the average government subsidy for a college education at a flagship, state institution is approximately __ for every $1 spent by the student.
A)$0.65
B)$2
C)$5
D)$10
A)$0.65
B)$2
C)$5
D)$10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Since 1960 the percentage of the population with a college degree has increased from __ to __.
A)less than 10%; near 35%
B)around 20%; near 85%
C)less than 2%; near 50%
D)near 40%; near 50%
A)less than 10%; near 35%
B)around 20%; near 85%
C)less than 2%; near 50%
D)near 40%; near 50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If e-books begin to be the most popular form of textbooks, it is
A)in the best interests of publishers and authors.
B)in the best interests of internet book sellers.
C)likely to increase costs to students.
D)likely to be self-defeating for publishers.
A)in the best interests of publishers and authors.
B)in the best interests of internet book sellers.
C)likely to increase costs to students.
D)likely to be self-defeating for publishers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Between 1992 and 2012, the percentage of students borrowing to pay for college
A)decreased from 18% to 13%.
B)remained constant at 30%.
C)increased from 34% to 57%.
D)decreased from 73% to 58%.
A)decreased from 18% to 13%.
B)remained constant at 30%.
C)increased from 34% to 57%.
D)decreased from 73% to 58%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If e-books begin to be the most popular form of textbooks, it is
A)the worst possible outcome for publishers and authors.
B)in the best interests of internet book sellers.
C)likely to increase costs to students.
D)likely to damage the physical used book market.
A)the worst possible outcome for publishers and authors.
B)in the best interests of internet book sellers.
C)likely to increase costs to students.
D)likely to damage the physical used book market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the 1980s, President Reagan shifted government education policies toward
A)repeal of the GI Bill.
B)increased availability of subsidized student loans.
C)education-related income tax deductions and credits.
D)increased reliance upon direct grants, such as Pell Grants.
A)repeal of the GI Bill.
B)increased availability of subsidized student loans.
C)education-related income tax deductions and credits.
D)increased reliance upon direct grants, such as Pell Grants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Estimates of the value of a college education to the student are that there is
A)a $330,000 net present value benefit.
B)a $30,000 per year benefit.
C)a $330,000 net present value loss.
D)an external benefit.
A)a $330,000 net present value benefit.
B)a $30,000 per year benefit.
C)a $330,000 net present value loss.
D)an external benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The strategy of faculty choosing to stay with an old edition of a book is
A)in the best interests of publishers.
B)in the best interests of authors.
C)likely to be unsustainable if too many try it.
D)likely to be replicated by everyone.
A)in the best interests of publishers.
B)in the best interests of authors.
C)likely to be unsustainable if too many try it.
D)likely to be replicated by everyone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Estimates of the value of a college education are based on
A)actual costs and benefits.
B)present value.
C)enumerated costs and benefits.
D)plausible deniability.
A)actual costs and benefits.
B)present value.
C)enumerated costs and benefits.
D)plausible deniability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The strategy of faculty choosing to stay with an old edition of a book is
A)in the best interests of publishers.
B)in the best interests of authors.
C)likely to reduce the costs to students.
D)likely to be replicated by everyone.
A)in the best interests of publishers.
B)in the best interests of authors.
C)likely to reduce the costs to students.
D)likely to be replicated by everyone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
To compare the costs of a college education with its monetary benefits, economists use the concept of
A)actual costs and benefits.
B)present value.
C)enumerated costs and benefits.
D)plausible deniability.
A)actual costs and benefits.
B)present value.
C)enumerated costs and benefits.
D)plausible deniability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In the United States, the average government subsidy for a college education at a private institution is approximately __ for every $1 spent by the student.
A)Less than $0.65
B)$2
C)$5
D)$10
A)Less than $0.65
B)$2
C)$5
D)$10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose a college education is choosing between a modestly expensive school ($100,000 over 4 years)and a less expensive school ($40,000 over 4 years)the student should
A)Choose the more expensive school only if the present value of the difference in salary is $60,000 or more.
B)Choose the more expensive school only if the present value of the difference in salary is $60,000 or less.
C)Choose the more expensive school only if the difference in salary will total $60,000 or more.
D)Choose the more expensive school only if the difference in salary will total $60,000 or less.
A)Choose the more expensive school only if the present value of the difference in salary is $60,000 or more.
B)Choose the more expensive school only if the present value of the difference in salary is $60,000 or less.
C)Choose the more expensive school only if the difference in salary will total $60,000 or more.
D)Choose the more expensive school only if the difference in salary will total $60,000 or less.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In the United States, the average government subsidy for a college education at a regional, bachelors-only public institution is approximately __ for every $1 spent by the student.
A)$0.85
B)$2
C)$5
D)$10
A)$0.85
B)$2
C)$5
D)$10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Suppose a college education is choosing between an expensive school ($200,000 over 4 years)and a less expensive school ($40,000 over 4 years)the student should
A)Choose the more expensive school only if the present value of the difference in salary is $160,000 or more.
B)Choose the more expensive school only if the present value of the difference in salary is $160,000 or less.
C)Choose the more expensive school only if the difference in salary will total $160,000 or more.
D)Choose the more expensive school only if the difference in salary will total $160,000 or less.
A)Choose the more expensive school only if the present value of the difference in salary is $160,000 or more.
B)Choose the more expensive school only if the present value of the difference in salary is $160,000 or less.
C)Choose the more expensive school only if the difference in salary will total $160,000 or more.
D)Choose the more expensive school only if the difference in salary will total $160,000 or less.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
To compare the costs of a college education a wise student, when choosing between an expensive school with a high expected income and a less expensive school with a lower expected income would use the concept of
A)actual costs and benefits.
B)present value.
C)enumerated costs and benefits.
D)plausible deniability.
A)actual costs and benefits.
B)present value.
C)enumerated costs and benefits.
D)plausible deniability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Between 1992 and 2012, the percentage of college students receiving federally funded grants
A)increased from 8% to 13%.
B)slowly increased to around 47%.
C)increased from 58% to 73%.
D)decreased from 73% to 58%.
A)increased from 8% to 13%.
B)slowly increased to around 47%.
C)increased from 58% to 73%.
D)decreased from 73% to 58%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Between 1992 and 2012, the percentage of college students receiving some form of aid
A)increased from 8% to 13%.
B)remained constant at 35%.
C)increased from 58% to around 84%.
D)decreased from 73% to 58%.
A)increased from 8% to 13%.
B)remained constant at 35%.
C)increased from 58% to around 84%.
D)decreased from 73% to 58%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In the 1990s President Clinton worked for
A)the creation of the Pell Grant.
B)the GI Bill.
C)the introduction of student loans.
D)tax credits and deductions for education.
A)the creation of the Pell Grant.
B)the GI Bill.
C)the introduction of student loans.
D)tax credits and deductions for education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



