Deck 12: Formation of Ð Bonds by Elimination Processes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/84
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Formation of Ð Bonds by Elimination Processes
1
What would be the product of the reaction shown below? 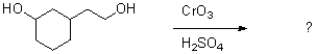
A)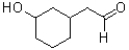
B)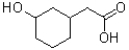
C)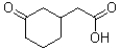
D)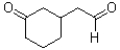
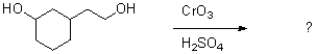
A)

B)

C)

D)


2
Which of the following reagents would achieve the transformation shown below? 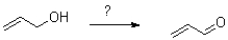
A)PCC,CH2Cl2
B)Na2Cr2O7,H2SO4
C)CrO3,H2SO4
D)H3O+

A)PCC,CH2Cl2
B)Na2Cr2O7,H2SO4
C)CrO3,H2SO4
D)H3O+
PCC,CH2Cl2
3
Which of the following reaction mechanisms would you expect to dominate from the reaction and conditions shown below? 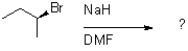
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2
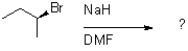
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2
E2
4
Which of the following reaction mechanisms would you expect to dominate from the reaction and conditions shown below? 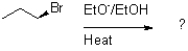
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2

A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following best describes an E1 elimination?
A)It is unimolecular and goes through a carbocation intermediate.
B)It is unimolecular and goes through a concerted mechanism.
C)It is bimolecular and goes through a carbocation intermediate.
D)It is bimolecular and goes through a concerted mechanism.
A)It is unimolecular and goes through a carbocation intermediate.
B)It is unimolecular and goes through a concerted mechanism.
C)It is bimolecular and goes through a carbocation intermediate.
D)It is bimolecular and goes through a concerted mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements best describes Zaitsev's rule?
A)An elimination reaction will favour the most stable product.
B)An elimination reaction will favour the most stable intermediate
C)An elimination reaction will favour the least stable product.
D)An elimination reaction will favour the least stable intermediate
A)An elimination reaction will favour the most stable product.
B)An elimination reaction will favour the most stable intermediate
C)An elimination reaction will favour the least stable product.
D)An elimination reaction will favour the least stable intermediate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What would be the expected product of the reaction shown below? 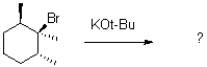
A)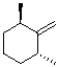
B)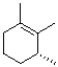
C)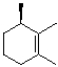
D)A mixture of

A)

B)

C)

D)A mixture of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the Hoffman product in an elimination reaction?
A)the kinetic product using a strong unhindered base
B)the thermodynamic product using a strong unhindered base
C)the kinetic product using a strong hindered base
D)the thermodynamic product using a strong hindered base
A)the kinetic product using a strong unhindered base
B)the thermodynamic product using a strong unhindered base
C)the kinetic product using a strong hindered base
D)the thermodynamic product using a strong hindered base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following best describes an E2 reaction mechanism?
A)The leaving group leaves,resulting in a carbocation,following by deprotonation of the â hydrogen and formation of a ð bond.
B)The â hydrogen is deprotonated,resulting in a carbocation,followed by loss of the leaving group and formation of a ð bond.
C)The â hydrogen is deprotonated and the leaving group leaves simultaneously,leading to the formation of a ð bond.
D)The â hydrogen is deprotonated,resulting in a carboanion,followed by loss of the leaving group and formation of a ð bond.
A)The leaving group leaves,resulting in a carbocation,following by deprotonation of the â hydrogen and formation of a ð bond.
B)The â hydrogen is deprotonated,resulting in a carbocation,followed by loss of the leaving group and formation of a ð bond.
C)The â hydrogen is deprotonated and the leaving group leaves simultaneously,leading to the formation of a ð bond.
D)The â hydrogen is deprotonated,resulting in a carboanion,followed by loss of the leaving group and formation of a ð bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following products will the E2 elimination reaction shown below lead to? 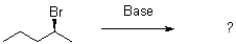
A)
B)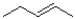
C)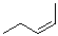
D)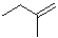
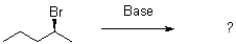
A)

B)
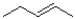
C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following products will the E2 elimination reaction below lead to? 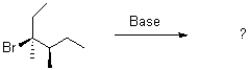
A)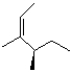
B)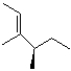
C)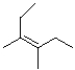
D)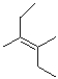

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following substrates is not suitable as an E1 substrate?
A)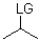
B)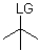
C)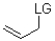
D)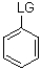
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following reaction mechanisms would you expect to dominate from the reaction and conditions shown below? 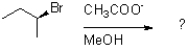
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2
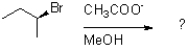
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following best describes the relationship between the leaving group and the â-hydrogen in an E2 elimination?
A)periplanar
B)antiperiplanar
C)scissile
D)enantiomeric
A)periplanar
B)antiperiplanar
C)scissile
D)enantiomeric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following best describes an E2 elimination reaction?
A)It is unimolecular and goes through a carbocation intermediate.
B)It is unimolecular and goes through a concerted mechanism.
C)It is bimolecular and goes through a carbocation intermediate.
D)It is bimolecular and goes through a concerted mechanism.
A)It is unimolecular and goes through a carbocation intermediate.
B)It is unimolecular and goes through a concerted mechanism.
C)It is bimolecular and goes through a carbocation intermediate.
D)It is bimolecular and goes through a concerted mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following compounds would be unsuitable for oxidation?
A)methanol
B)ethanol
C)2-propanol
D)2-methyl-2-propanol
A)methanol
B)ethanol
C)2-propanol
D)2-methyl-2-propanol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the first step in an E1 reaction mechanism?
A)The leaving group leaves,resulting in a carbocation.
B)The â hydrogen is deprotonated,resulting in a carbocation.
C)The â hydrogen is deprotonated and the leaving group leaves simultaneously.
D)The â hydrogen is deprotonated,resulting in a carboanion.
A)The leaving group leaves,resulting in a carbocation.
B)The â hydrogen is deprotonated,resulting in a carbocation.
C)The â hydrogen is deprotonated and the leaving group leaves simultaneously.
D)The â hydrogen is deprotonated,resulting in a carboanion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following represents the first mechanistic step in the oxidation reaction shown below? 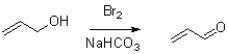
A)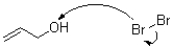
B)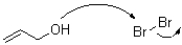
C)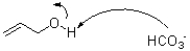
D)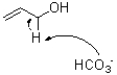

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following reaction mechanisms would you expect to dominate from the reaction and conditions shown below? 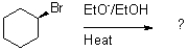
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2

A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
For an E2 elimination of bromocyclohexane to occur,what must the halogen group be?
A)axial
B)equatorial
C)either axial or equatorial
D)planar
A)axial
B)equatorial
C)either axial or equatorial
D)planar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following best describes sodium hydride?
A)It is a strong,non-nucleophilic base.
B)It is a strong,nucleophilic base.
C)It is a weak,non-nucleophilic base.
D)It is a weak,nucleophilic base.
A)It is a strong,non-nucleophilic base.
B)It is a strong,nucleophilic base.
C)It is a weak,non-nucleophilic base.
D)It is a weak,nucleophilic base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which cyclohexane derivative would you expect to react faster under E2 elimination conditions and why? 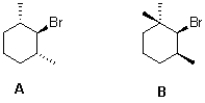
A)A because its less sterically hindered
B)B because its less sterically hindered
C)A because its scissile C-H bond is antiperiplanar
D)B because its scissile C-H bond is antiperiplanar

A)A because its less sterically hindered
B)B because its less sterically hindered
C)A because its scissile C-H bond is antiperiplanar
D)B because its scissile C-H bond is antiperiplanar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following reaction mechanisms would you expect to dominate from the reaction and conditions shown below? 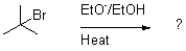
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2

A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following reaction mechanisms would you expect to dominate from the reaction and conditions shown below? 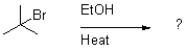
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2

A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What would be the major product of the reaction shown below? 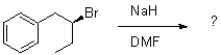
A)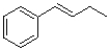
B)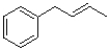
C)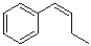
D)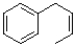
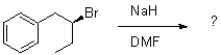
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following mechanisms are promoted by polar protic solvents?
A)SN1 and SN2
B)E1 and E2
C)SN2 and E2
D)SN1 and E1
A)SN1 and SN2
B)E1 and E2
C)SN2 and E2
D)SN1 and E1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following best describes the Hoffman product in an elimination reaction?
A)an unhindered base giving the less substituted product
B)an unhindered base giving the more substituted product
C)a hindered base giving the less substituted product
D)a hindered base giving the more substituted product
A)an unhindered base giving the less substituted product
B)an unhindered base giving the more substituted product
C)a hindered base giving the less substituted product
D)a hindered base giving the more substituted product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the role of Br2 in the first step of the oxidation of alcohols?
A)nucleophile
B)electrophile
C)leaving group
D)base
A)nucleophile
B)electrophile
C)leaving group
D)base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Why does the E2 mechanism require an antiperiplanar relationship between the leaving group X and the â hydrogen?
A)This conformation maximizes overlap between the C-H ó* orbital and the C-X ó orbital.
B)This staggered conformation minimizes steric repulsion.
C)This conformation maximizes overlap between the C-H ó orbital and the C-X ó* orbital.
D)This conformation leads to the more substituted alkene.
A)This conformation maximizes overlap between the C-H ó* orbital and the C-X ó orbital.
B)This staggered conformation minimizes steric repulsion.
C)This conformation maximizes overlap between the C-H ó orbital and the C-X ó* orbital.
D)This conformation leads to the more substituted alkene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the role of HCrO3+ in the first step of the oxidation of alcohols?
A)proton donor
B)proton acceptor
C)nucleophile
D)electrophile
A)proton donor
B)proton acceptor
C)nucleophile
D)electrophile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What sort of reaction mechanism is employed in an acid catalyzed dehydration reaction?
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following substrates will undergo the fastest E1 reaction?
A)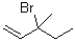
B)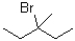
C)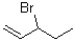
D)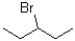
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the effect of adding heat to a reaction capable of both elimination and substitution mechanisms?
A)It pushes a reaction towards the thermodynamic elimination product.
B)It pushes a reaction towards the thermodynamic substitution product.
C)It pushes a reaction towards the kinetic elimination product.
D)It pushes a reaction towards the kinetic substitution product.
A)It pushes a reaction towards the thermodynamic elimination product.
B)It pushes a reaction towards the thermodynamic substitution product.
C)It pushes a reaction towards the kinetic elimination product.
D)It pushes a reaction towards the kinetic substitution product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following substrates would undergo the slowest elimination reaction?
A)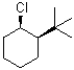
B)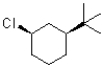
C)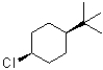
D)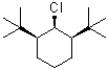
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which orbital interaction best describes the hyperconjugation that results in increased stability of a substituted alkene?
A)ó ð
B)ó ð*
C)ó* ð*
D)ð ð*
A)ó ð
B)ó ð*
C)ó* ð*
D)ð ð*

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which alkene isomer of an elimination reaction is more favoured and why?
A)the E product because there is better ó - ð* overlap
B)the Z product because there is better ó - ð* overlap
C)the E product because there is less steric hindrance
D)the Z product because there is less steric hindrance
A)the E product because there is better ó - ð* overlap
B)the Z product because there is better ó - ð* overlap
C)the E product because there is less steric hindrance
D)the Z product because there is less steric hindrance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following reaction mechanisms would you expect to dominate from the reaction and conditions shown below? 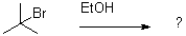
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2
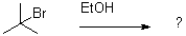
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)E1
D)E2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the role of HCO3- in the first step of the oxidation of alcohols?
A)acid
B)electrophile
C)leaving group
D)base
A)acid
B)electrophile
C)leaving group
D)base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following best describes tert-butoxide?
A)It is a strong,bulky base.
B)It is a strong,non-bulky base.
C)It is a weak,bulky base.
D)It is a weak,non-bulky base.
A)It is a strong,bulky base.
B)It is a strong,non-bulky base.
C)It is a weak,bulky base.
D)It is a weak,non-bulky base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following reagents is required for a dehydration reaction and why?
A)strong acid to protonate the alcohol group
B)strong base to deprotonate the alcohol group
C)strong base to deprotonate the â hydrogen
D)strong acid to stabilize the formed carbocation
A)strong acid to protonate the alcohol group
B)strong base to deprotonate the alcohol group
C)strong base to deprotonate the â hydrogen
D)strong acid to stabilize the formed carbocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Chromic acid oxidation of a secondary alcohol results in a carboxylic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The E alkene product is favoured because it is less sterically hindered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Br2 oxidation of a primary alcohol results in an aldehyde.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Deprotonation of the â hydrogen is the rate-limiting step in E1 eliminations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An E2 Elimination reaction occurs through a concerted mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The Hoffman product is typically the result of using a bulky base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An E2 reaction runs faster if the scissile C-H bond is antiperiplanar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Dehydration reactions can proceed under an E1 or E2 mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
E2 eliminations are susceptible to carbocation rearrangements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Bromine acts as an electrophile in the oxidation of alcohols.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
E1 eliminations go through a carbocation intermediate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Heat promotes an E1 reaction over an SN1 reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Dehydrohalogenation reactions can proceed under an E1 or E2 mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
PCC oxidation of a primary alcohol results in a carboxylic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Sodium Hydride is an example of a non-nucleophilic base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
E2 reactions are promoted by protic solvents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
E1 reactions are usually less stereoselective than E2 reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An E1 mechanism occurs through a single mechanistic step.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A strong bulky nucleophile will promote an SN2 reaction over an E2 reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Higher substituted alkenes are more stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Chromic acid oxidation of a primary alcohol will result in a(n)_______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Propose a mechanism of the following reaction to generate each of the observed products. 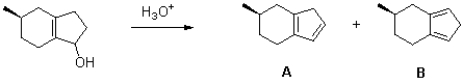


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Zaitsev's rule states that the elimination reaction favours the most _______________ alkene product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Carbocation rearrangements are a possible side reaction for _______________ elimination reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The following substrate is capable of undergoing SN1,SN2,E1 and E2 reaction mechanisms depending on the conditions used.Suggest a set of reagents and conditions that can be used to get each reaction mechanism as the dominant mechanism. 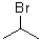


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Predict the product of the following elimination reaction and show the mechanism using a Newman projection. 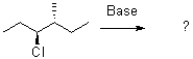


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
For an E2 elimination to occur,the scissile C-H bond and the leaving group must be _______________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Provide a set of reaction conditions to achieve the following transformation with the following major product. 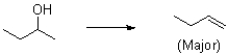


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Draw the mechanism for the transformation shown below. 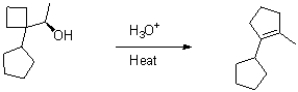


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The scissile C-H bond must be antiperiplanar to the leaving group in an E1 reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The less substituted alkene product of an elimination reaction is also known as the _______________ product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Chromic acid oxidation of a tertiary alcohol will result in _______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
E1 reaction rates are dependent on the concentration of the base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
For an E2 reaction to occur on a cyclohexyl ring,the leaving group must be in an equatorial position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
PCC oxidation of a secondary alcohol will result in a(n)_______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In a cyclohexyl ring,the leaving group must be _______________ for an E2 reaction to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In an E2 elimination reaction,the leaving group and the scissile C-H bond are _______________ to each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In hyperconjugation,the ó orbital of the C-H bond donates into the ð* orbital of the alkene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In an E2 mechanism,the ó orbital of the scissile C-H bond donates into the ð* bond of the leaving group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Dehydration reactions require the use of a(n)_______________ catalyst.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



