Deck 4: Consumer Choice
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/125
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Consumer Choice
1
If a consumer prefers Apples to Bananas and prefers Bananas to Citrus Fruit,in order to satisfy assumptions about preferences she has to prefer
A) Bananas to Apples.
B) Citrus Fruit to Bananas.
C) Apples to Citrus Fruit.
D) Citrus Fruit to Apples.
A) Bananas to Apples.
B) Citrus Fruit to Bananas.
C) Apples to Citrus Fruit.
D) Citrus Fruit to Apples.
Apples to Citrus Fruit.
2
Indifference curves for perfect substitutes must be parallel lines with a slope of negative one.
False
3
A consumer's willingness to trade one good for another can be expressed by the consumer's
A) indifference curve.
B) marginal rate of substitution.
C) Both A and B above.
D) None of the above.
A) indifference curve.
B) marginal rate of substitution.
C) Both A and B above.
D) None of the above.
Both A and B above.
4
The principle that "More is better" results in indifference curves
A) sloping down.
B) not intersecting.
C) reflecting greater preferences the further they are from the origin.
D) All of the above.
A) sloping down.
B) not intersecting.
C) reflecting greater preferences the further they are from the origin.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Indifference curves that are upward-sloping violate
A) the assumption of transitivity.
B) the assumption of completeness.
C) the assumption that more is better.
D) none of the assumptions.
A) the assumption of transitivity.
B) the assumption of completeness.
C) the assumption that more is better.
D) none of the assumptions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The statement "There is no accounting for taste" implies
A) individuals all have the same preferences.
B) individuals all have different cardinal preferences but the same ordinal preferences.
C) individuals all have different ordinal preferences but the same cardinal preferences.
D) individuals all have different ordinal and cardinal preferences.
A) individuals all have the same preferences.
B) individuals all have different cardinal preferences but the same ordinal preferences.
C) individuals all have different ordinal preferences but the same cardinal preferences.
D) individuals all have different ordinal and cardinal preferences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An indifference curve represents bundles of goods that a consumer
A) views as equally desirable.
B) ranks from most preferred to least preferred.
C) refers to any other bundle of goods.
D) All of the above.
A) views as equally desirable.
B) ranks from most preferred to least preferred.
C) refers to any other bundle of goods.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Measuring "y" on the vertical axis and "x" on the horizontal axis,convexity of indifference curves implies that the MRS of "y" for "x"
A) is decreasing as "x" increases.
B) is increasing as "x" increases.
C) is constant as "x" increases.
D) cannot be calculated for large levels of "x".
A) is decreasing as "x" increases.
B) is increasing as "x" increases.
C) is constant as "x" increases.
D) cannot be calculated for large levels of "x".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Diminishing marginal rate of substitution can be seen when indifference curves
A) cross.
B) are convex.
C) are downward sloping.
D) become flatter as we move down and to the right.
A) cross.
B) are convex.
C) are downward sloping.
D) become flatter as we move down and to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Indifference curves cannot intersect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Indifference curves on the same indifference map can have different shapes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If two goods are perfect substitutes,then the indifference curves for those two goods would be
A) upward sloping and concave to the origin.
B) downward sloping and convex to the origin.
C) downward sloping and straight.
D) L-shaped.
A) upward sloping and concave to the origin.
B) downward sloping and convex to the origin.
C) downward sloping and straight.
D) L-shaped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Convexity of indifference curves implies that consumers are willing to
A) give up more "y" to get an extra "x" the more "x" they have.
B) give up more "y" to get an extra "x" the less "x" they have.
C) settle for less of both "x" and "y".
D) acquire more "x" only if they do not have to give up any "y".
A) give up more "y" to get an extra "x" the more "x" they have.
B) give up more "y" to get an extra "x" the less "x" they have.
C) settle for less of both "x" and "y".
D) acquire more "x" only if they do not have to give up any "y".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If two indifference curves were to intersect at a point,this would violate the assumption of
A) transitivity.
B) completeness.
C) Both A and B above.
D) None of the above.
A) transitivity.
B) completeness.
C) Both A and B above.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Indifference curves that are thick violate
A) the assumption of transitivity.
B) the assumption that more is better.
C) the assumption of completeness.
D) none of the assumptions.
A) the assumption of transitivity.
B) the assumption that more is better.
C) the assumption of completeness.
D) none of the assumptions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Economists use a preference map to illustrate that
A) more is better than less.
B) preferences are transitive.
C) preferences are complete.
D) All of the above.
A) more is better than less.
B) preferences are transitive.
C) preferences are complete.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Indifference curves cannot ever be concave for two goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The indifference curves for left shoes and right shoes would most likely be
A) upward sloping and concave to the origin.
B) downward sloping and convex to the origin.
C) downward sloping and straight lines.
D) L-shaped.
A) upward sloping and concave to the origin.
B) downward sloping and convex to the origin.
C) downward sloping and straight lines.
D) L-shaped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The assumption of completeness means that
A) the consumer can rank all possible consumption bundles.
B) more of a good is always better.
C) the consumers can rank all affordable consumption bundles.
D) all preferences conditions are met.
A) the consumer can rank all possible consumption bundles.
B) more of a good is always better.
C) the consumers can rank all affordable consumption bundles.
D) all preferences conditions are met.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Lisa views pizzas and burritos as goods.If she prefers a bundle of 4 burritos and 4 pizzas to a bundle of 4 burritos and 5 pizzas,which property of consumer preference is violated? What change in the assumptions could lead a rational consumer to prefer the first bundle?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If the utility function (U)between food (F)and clothing (C)can be represented as U = 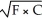 ,the marginal utility of food equals
,the marginal utility of food equals
A)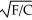 .
.
B)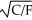 .
.
C) 1/2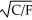 .
.
D) 1/2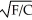 .
.
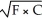 ,the marginal utility of food equals
,the marginal utility of food equalsA)
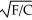 .
.B)
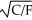 .
.C) 1/2
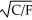 .
.D) 1/2
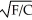 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If two bundles are on the same indifference curve,then
A) the consumer derives the same level of utility from each.
B) the consumer derives the same level of ordinal utility from each but not the same level of cardinal utility.
C) no comparison can be made between the two bundles since utility cannot really be measured.
D) B and C.
A) the consumer derives the same level of utility from each.
B) the consumer derives the same level of ordinal utility from each but not the same level of cardinal utility.
C) no comparison can be made between the two bundles since utility cannot really be measured.
D) B and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Explain why most indifference curves are convex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Assuming that good "x" is measured on the x-axis and good "y" is measured on the y-axis,if the utility for the two goods "x" and "y" can be measured as U = y,then it can be concluded that
A) "x" and "y" are perfect complements.
B) "x" is a "bad".
C) the indifference curves on the x,y graph are upward sloping.
D) the indifference curves on the x,y graph are horizontal.
A) "x" and "y" are perfect complements.
B) "x" is a "bad".
C) the indifference curves on the x,y graph are upward sloping.
D) the indifference curves on the x,y graph are horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Utility is the set of numerical values that
A) yields an absolute level of pleasure from a bundle of goods.
B) reflects the relative ranking of various bundles of goods.
C) describes how much more a consumer prefers one bundle to another.
D) yields a cardinal ranking of bundles.
A) yields an absolute level of pleasure from a bundle of goods.
B) reflects the relative ranking of various bundles of goods.
C) describes how much more a consumer prefers one bundle to another.
D) yields a cardinal ranking of bundles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If Fred's marginal rate of substitution of salad for pizza equals 5,then
A) he would give up 5 pizzas to get the next salad.
B) he would give up 5 salads to get the next pizza.
C) he will eat five times as much pizza as salad.
D) he will eat five times as much salad as pizza.
A) he would give up 5 pizzas to get the next salad.
B) he would give up 5 salads to get the next pizza.
C) he will eat five times as much pizza as salad.
D) he will eat five times as much salad as pizza.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Draw the indifference curves for nickels and dimes.Would they ever have a non-constant slope? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If two goods,"x" and "y",are perfect substitutes,then which of the following best represents the utility function for the two goods?
A) U = x + y
B) U = x ∗ y
C) U =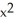 +
+ 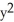
D) Any of the above.
A) U = x + y
B) U = x ∗ y
C) U =
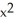 +
+ 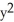
D) Any of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Assuming that good "x" is measured on the x-axis and good "y" is measured on the y-axis,if the utility for the two goods "x" and "y" can be measured as U = x,then it can be concluded that
A) "x" and "y" are perfect complements.
B) "y" is a "bad".
C) the indifference curves on the x,y graph are upward sloping.
D) the indifference curves on the x,y graph are vertical.
A) "x" and "y" are perfect complements.
B) "y" is a "bad".
C) the indifference curves on the x,y graph are upward sloping.
D) the indifference curves on the x,y graph are vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
People view alcohol and marijuana as perfect substitutes.This means that
A) individuals will consume either alcohol or marijuana, but not both, regardless of price.
B) as the price of alcohol decreases, marijuana use decreases.
C) the marginal utility for alcohol and marijuana is constant.
D) Both B and C.
A) individuals will consume either alcohol or marijuana, but not both, regardless of price.
B) as the price of alcohol decreases, marijuana use decreases.
C) the marginal utility for alcohol and marijuana is constant.
D) Both B and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Some people view cosmetic surgery (c)and facials (f)as perfect substitutes as measured by the utility function U(c,f)= 5c + 10f.What is the marginal utility of cosmetic surgery?
A) MU = 5.
B) MU = 10.
C) MU = 15.
D) None of the above.
A) MU = 5.
B) MU = 10.
C) MU = 15.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If Fred's marginal utility of pizza equals 10 and his marginal utility of salad equals 2,then
A) he would give up 5 pizzas to get the next salad.
B) he would give up 5 salads to get the next pizza.
C) he will eat five times as much pizza as salad.
D) he will eat five times as much salad as pizza.
A) he would give up 5 pizzas to get the next salad.
B) he would give up 5 salads to get the next pizza.
C) he will eat five times as much pizza as salad.
D) he will eat five times as much salad as pizza.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Clifford lives by the motto "Eat,drink and be merry today,for tomorrow doesn't matter." If today's consumption is measured on the horizontal axis and tomorrow's consumption is measured on the vertical axis,Clifford's indifference curves
A) are horizontal straight lines.
B) are vertical straight lines.
C) show decreasing utility as one moves upward.
D) cannot be determined from the information given.
A) are horizontal straight lines.
B) are vertical straight lines.
C) show decreasing utility as one moves upward.
D) cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the utility function (U)between food (F)and clothing (C)can be represented as U =  ,the marginal rate of substitution of clothing for food equals
,the marginal rate of substitution of clothing for food equals
A) -C/F.
B) -F/C.
C) -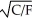 .
.
D) -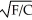 .
.
 ,the marginal rate of substitution of clothing for food equals
,the marginal rate of substitution of clothing for food equalsA) -C/F.
B) -F/C.
C) -
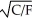 .
.D) -
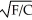 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the utility function (U)between food (F)and clothing (C)can be represented as U = 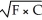 ,the marginal utility of food
,the marginal utility of food
A) is not positive.
B) does not diminish as food increases.
C) is not affected by the amount clothing.
D) increases as one obtains more clothing.
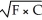 ,the marginal utility of food
,the marginal utility of foodA) is not positive.
B) does not diminish as food increases.
C) is not affected by the amount clothing.
D) increases as one obtains more clothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Draw the indifference curves for rock concerts and food for each of the following:
(a)a typical 17-year-old
(b)a typical 75-year-old
(a)a typical 17-year-old
(b)a typical 75-year-old

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Clifford lives by the motto "Eat drink and be merry today,for tomorrow doesn't matter." If today's consumption is represented by "x" and tomorrow's consumption is represented by "y",then which of the following best represents Clifford's utility function?
A) U = x - y
B) U = x/y
C) U = x
D) U = y
A) U = x - y
B) U = x/y
C) U = x
D) U = y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If Johnny likes homework (H)but hates exercise (E),which of the following might best represent his utility function for homework and exercise?
A) U = H + E
B) U = H/E
C) U =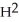 +
+ 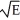
D) U =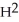 ×
× 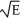
A) U = H + E
B) U = H/E
C) U =
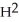 +
+ 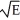
D) U =
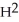 ×
× 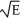

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Adrian's total utilities of two consumption bundles are 50 and 100.This implies that
A) the consumer prefers the first bundle.
B) the consumer prefers the second bundle.
C) the consumer likes the second bundle twice as much.
D) the consumer likes the first bundle twice as much.
A) the consumer prefers the first bundle.
B) the consumer prefers the second bundle.
C) the consumer likes the second bundle twice as much.
D) the consumer likes the first bundle twice as much.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If the utility for two goods "x" and "y" is measured as U = x + y,then it can be concluded that
A) "x" and "y" are perfect substitutes.
B) "x" and "y" are perfect complements.
C) "x" and "y" are both bads.
D) the indifference curves on the x,y graph will be upward sloping.
A) "x" and "y" are perfect substitutes.
B) "x" and "y" are perfect complements.
C) "x" and "y" are both bads.
D) the indifference curves on the x,y graph will be upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If both prices increases by 50%,
A) budget constraint will be unchanged.
B) slope of the budget constraint stay the same.
C) slope of the budget constraint will decrease.
D) budget constraint will shift outward in a parallel fashion.
A) budget constraint will be unchanged.
B) slope of the budget constraint stay the same.
C) slope of the budget constraint will decrease.
D) budget constraint will shift outward in a parallel fashion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the difference between ordinal and cardinal measurement?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Joe's income is $500,the price of food (F)is $2,and the price of shelter (S)is $100.Which of the following bundles is in Joe's opportunity set?
A) 50 units of food, 5 units of shelter
B) 200 units of food, 2 units of shelter
C) 100 units of food, 1 unit of shelter
D) 150 units of food, 3 units of shelter
A) 50 units of food, 5 units of shelter
B) 200 units of food, 2 units of shelter
C) 100 units of food, 1 unit of shelter
D) 150 units of food, 3 units of shelter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the consumer's income increases while the prices of both goods remain unchanged,what will happen to the budget line?
A) The budget line rotates inward from the intercept on the horizontal axis.
B) The budget line rotates outward from the intercept on the vertical axis.
C) The budget line shifts inward without a change in slope.
D) The budget line shifts outward without a change in slope.
A) The budget line rotates inward from the intercept on the horizontal axis.
B) The budget line rotates outward from the intercept on the vertical axis.
C) The budget line shifts inward without a change in slope.
D) The budget line shifts outward without a change in slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose Joe's utility for lobster (L)and soda (S)can be represented as U = L0.5 S0.5.Draw the indifference curve that yields a utility level of 9.Calculate the MUL,MUS,and MRS of L for S on that indifference curve when S = 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Joe's income is $500,the price of food (F)is $2 per unit,and the price of shelter (S)is $100.Which of the following represents his marginal rate of transformation of food for shelter?
A) -5
B) -50
C) -.02
D) None of the above.
A) -5
B) -50
C) -.02
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Betty consumes good x and good y.If the price of x = $3 and the price of y = $4,then
A) an extra unit of x costs 4/3 units of y.
B) an extra unit of y costs 4/3 units of x.
C) an extra unit of x costs 3/4 units of y.
D) Both B and C.
A) an extra unit of x costs 4/3 units of y.
B) an extra unit of y costs 4/3 units of x.
C) an extra unit of x costs 3/4 units of y.
D) Both B and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A consumer buys food (F)and shelter (S).If the consumer's income rises and there is no change in the prices of F or S,the marginal rate of transformation of F for S will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
D) change, but there is not enough information to know how.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
D) change, but there is not enough information to know how.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Individuals derive utility from picnics,p,and kayak trips,k.Assuming that an individual's utility is U(p,k)= k0.5p0.5 and income is $100,what is the marginal rate of substitution (MRS)between picnics and kayak trips?
A) MRS = 1.
B) MRS = -1.
C) MRS = -
D) There is no substitution because picnics and kayak trips are perfect complements.
A) MRS = 1.
B) MRS = -1.
C) MRS = -

D) There is no substitution because picnics and kayak trips are perfect complements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Lisa eats both pizzas and burritos.If the price of a pizza increases,Lisa's opportunity set
A) becomes larger.
B) becomes smaller.
C) is unchanged.
D) cannot be determined without more information.
A) becomes larger.
B) becomes smaller.
C) is unchanged.
D) cannot be determined without more information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the price of one good increases while the price of the other good and the consumer's income remain unchanged,what will happen to the budget line?
A) The budget line rotates inward from the intercept on the axis of the good that did not change in price.
B) The budget line rotates outward from the intercept on the axis of the good that did not change in price.
C) The budget line shifts inward without a change in slope.
D) The budget line shifts outward without a change in slope.
A) The budget line rotates inward from the intercept on the axis of the good that did not change in price.
B) The budget line rotates outward from the intercept on the axis of the good that did not change in price.
C) The budget line shifts inward without a change in slope.
D) The budget line shifts outward without a change in slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If the prices of both goods and income increase by the same percentage,what will happen to the budget line?
A) The budget line rotates inward from the intercept on the axis of the good that did not change in price.
B) The budget line rotates outward from the intercept on the axis of the good that did not change in price.
C) The budget line shifts outward without a change in slope.
D) Nothing.
A) The budget line rotates inward from the intercept on the axis of the good that did not change in price.
B) The budget line rotates outward from the intercept on the axis of the good that did not change in price.
C) The budget line shifts outward without a change in slope.
D) Nothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The marginal rate of transformation of y for x represents
A) the slope of the budget constraint.
B) the rate at which the consumer must give up y to get one more x.
C) -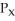 /
/ 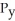 .
.
D) All of the above.
A) the slope of the budget constraint.
B) the rate at which the consumer must give up y to get one more x.
C) -
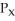 /
/ 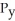 .
.D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Joe's income is $500,the price of food (F)is $2 per unit,and the price of shelter (S)is $100.Which of the following represents his budget constraint?
A) 500 = 2F + 100S
B) F = 250 - 50S
C) S = 5 - .02F
D) All of the above.
A) 500 = 2F + 100S
B) F = 250 - 50S
C) S = 5 - .02F
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Joe's budget constraint equals 500 = 2F + 100S,where $500 is Joe's income,$2 is the price of food (F)and $100 is the price of shelter (S).How much food can Joe buy if he buys one unit of shelter?
A) 2 units
B) 200 units
C) 250 units
D) 400 units
A) 2 units
B) 200 units
C) 250 units
D) 400 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The absolute value of the slope of an indifference curve equals the ratio of the marginal utilities of the two goods involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If the utility function (U)between bananas (B)and jam (J)can be represented as U = 3ln(B)+4ln(J)the marginal utility of jam equals
A) 4B.
B) 3B/J.
C) 4/J.
D) B/J.
A) 4B.
B) 3B/J.
C) 4/J.
D) B/J.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If the utility function (U)between bananas (B)and jam (J)can be represented as U(B,J)= 3ln(B)+4ln(J),what is the marginal rate of substitution (MRS)between bananas and jam?
A) 4B.
B) -3J/(4B).
C) 4/(3J).
D) 3B/J.
A) 4B.
B) -3J/(4B).
C) 4/(3J).
D) 3B/J.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Joe's income is $500,the price of food (F)is $2 per unit,and the price of shelter (S)is $100.Which of the following represents his budget constraint?
A) 500 = 100F + 2S
B) 500 = 2F + 100S
C) S = 500 - 2F
D) All of the above.
A) 500 = 100F + 2S
B) 500 = 2F + 100S
C) S = 500 - 2F
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If both prices decreases by 50%,
A) budget constraint will be unchanged.
B) slope of the budget constraint will increase.
C) slope of the budget constraint will decrease.
D) budget constraint will shift outward in a parallel fashion.
A) budget constraint will be unchanged.
B) slope of the budget constraint will increase.
C) slope of the budget constraint will decrease.
D) budget constraint will shift outward in a parallel fashion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
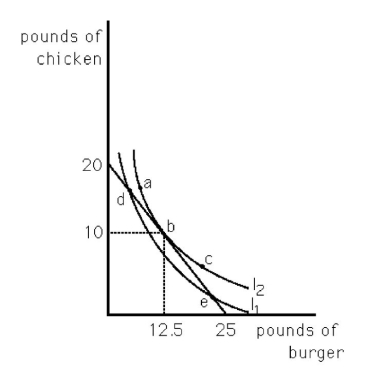
Max has allocated $100 toward meats for his barbecue.His budget line and an indifference map are shown in the above figure.Which bundle will Max choose?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
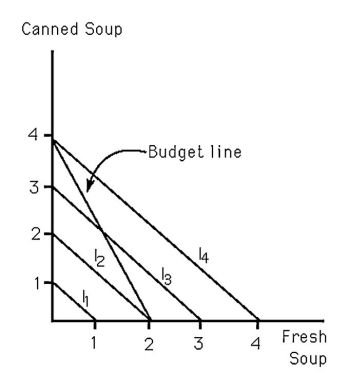
Keith is indifferent between canned soup and fresh soup.In the figure above,Keith's indifference curves are represented by I1,I2,I3,and I4 curves.Which of the following choices Keith cannot afford?
A) 3 canned soups and 2 fresh soups
B) 2 canned soups and 1 fresh soup
C) only 4 canned soups
D) only 2 fresh soups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
With respect to consuming food and shelter,two consumers face the same prices and both claim to be in equilibrium.We therefore know that
A) they both have the same marginal utility for food.
B) they both have the same marginal utility for shelter.
C) they both have the same MRS of food for shelter.
D) All of the above.
A) they both have the same marginal utility for food.
B) they both have the same marginal utility for shelter.
C) they both have the same MRS of food for shelter.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Economists assume consumers select a bundle of goods that maximizes their well-being subject to
A) their budget constraint.
B) their income.
C) relative prices.
D) their marginal rate of substitution.
A) their budget constraint.
B) their income.
C) relative prices.
D) their marginal rate of substitution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If a consumer's budget line for food (F)and shelter (S)is represented as F = 250 - 5S,we know that
A) the consumer's income is 250.
B) the price of shelter is 5.
C) the price of shelter is 5 times the price of food.
D) All of the above.
A) the consumer's income is 250.
B) the price of shelter is 5.
C) the price of shelter is 5 times the price of food.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Johnny has allocated $30 toward coffee and tea and feels that coffee and tea are perfect substitutes.Due to differences in caffeine levels,his MRS of tea for coffee equals 2.If coffee and tea sell for the same price,Johnny will
A) spend all $30 on tea.
B) spend all $30 on coffee.
C) spend $20 on coffee and $10 on tea.
D) be indifferent between any bundle of coffee and tea costing $30.
A) spend all $30 on tea.
B) spend all $30 on coffee.
C) spend $20 on coffee and $10 on tea.
D) be indifferent between any bundle of coffee and tea costing $30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67

Keith is indifferent between canned soup and fresh soup.In the figure above,Keith's indifference curves are represented by I1,I2,I3,and I4 curves.What is the marginal rate of transformation (MRT)of Keith's budget constraint?
A) MRT = -2
B) MRT = -1
C) MRT = -4
D) MRT = -0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The slope of the budget line represents the rate at which the consumer is willing to trade one good for another at any given bundle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Lisa has an income of $100.She spends all of her income on pizza and burritos.A pizza costs $10 and a burrito costs $5.However,the store where Lisa buys her burritos has a special deal.After you've bought 6 burritos,then you can buy each burrito for $2.50.Draw Lisa's opportunity set.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An optimum that occurs as a corner solution
A) includes only one good.
B) cannot be an equilibrium.
C) cannot exhaust the budget constraint.
D) includes the exact same amounts of each good.
A) includes only one good.
B) cannot be an equilibrium.
C) cannot exhaust the budget constraint.
D) includes the exact same amounts of each good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Assume the price of beer is $4,the price of pizza is $10 and the consumer's income is $250.Which consumption bundle will NOT be the consumer's choice?
A) 5 Beer, 5 Pizza
B) 0 Beer, 25 Pizza
C) 25 Beer, 15 Pizza
D) None of the bundle will be chosen.
A) 5 Beer, 5 Pizza
B) 0 Beer, 25 Pizza
C) 25 Beer, 15 Pizza
D) None of the bundle will be chosen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Explain the difference between the marginal rate of substitution and the marginal rate of transformation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Joe subscribes to an Internet provider that charges $2 per hour.Draw his budget line for Internet access on the horizontal axis and money spent on all other goods on the vertical axis assuming he has $100 per month to spend.Another company offers unlimited Internet access for a flat monthly fee of $20.Draw this budget line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose a taco costs $4 and a burrito costs $2.Moreover,this Mexican restaurant has a special deal.After you've bought 6 burritos,you can buy each extra burrito for $1.50.Assume that tacos are on the vertical axis and burritos on the horizontal axis.What is the marginal rate of transformation (MRT)when 8 burritos are purchased?
A) MRT = 0.375
B) MRT = 0.50
C) MRT = 2
D) MRT = 2.67
A) MRT = 0.375
B) MRT = 0.50
C) MRT = 2
D) MRT = 2.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Quotas,such as limiting the amount of residential water use during a drought,restricts an individual's preference set and
A) reduces utility because an individual cannot consume as much as they would without the quota.
B) increases utility because quotas restrict output and raise profits for the water company.
C) reduces utility because an individual is forced to substitute to other goods.
D) does not affect overall utility.
A) reduces utility because an individual cannot consume as much as they would without the quota.
B) increases utility because quotas restrict output and raise profits for the water company.
C) reduces utility because an individual is forced to substitute to other goods.
D) does not affect overall utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
By selecting a bundle where MRS = MRT,the consumer is
A) achieving a corner solution.
B) reaching the highest possible indifference curve she can afford.
C) not behaving in an optimal way.
D) All of the above.
A) achieving a corner solution.
B) reaching the highest possible indifference curve she can afford.
C) not behaving in an optimal way.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
By selecting a bundle where MRS = MRT,the consumer is saying
A) "I value my last unit of each good equally."
B) "I am willing to trade one good for the other at the same rate that I am required to do so."
C) "I will equate the amounts spent on all goods consumed."
D) All of the above.
A) "I value my last unit of each good equally."
B) "I am willing to trade one good for the other at the same rate that I am required to do so."
C) "I will equate the amounts spent on all goods consumed."
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The consumer is in equilibrium when
A) MRT = MRS.
B)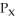 /
/ 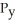 =
= 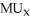 /
/ 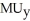 .
.
C) the budget line is tangent to the indifference curve at the bundle chosen.
D) All of the above.
A) MRT = MRS.
B)
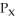 /
/ 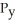 =
= 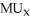 /
/ 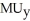 .
.C) the budget line is tangent to the indifference curve at the bundle chosen.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A consumer derives utility for "all other goods," g,and cigarettes,s.The price of "all other goods" equals $9 and the price of cigarettes is $10.Now suppose the government implements a $0.50 per-unit tax on cigarettes to encourage a decrease in smoking.How does the tax affect the marginal rate of transformation,MRT?
A) The MRT will decrease to -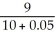 .
.
B) The MRT will increase to -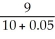 .
.
C) The MRT will increase to -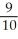 + 0.05.
+ 0.05.
D) The MRT will decrease to -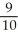 - 0.05.
- 0.05.
A) The MRT will decrease to -
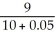 .
.B) The MRT will increase to -
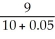 .
.C) The MRT will increase to -
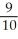 + 0.05.
+ 0.05.D) The MRT will decrease to -
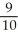 - 0.05.
- 0.05.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The intuition behind the budget constraint is that
A) more options are preferred to less.
B) money is the root of all happiness.
C) information is power.
D) scarcity is avoidable with prosperity.
A) more options are preferred to less.
B) money is the root of all happiness.
C) information is power.
D) scarcity is avoidable with prosperity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



